|
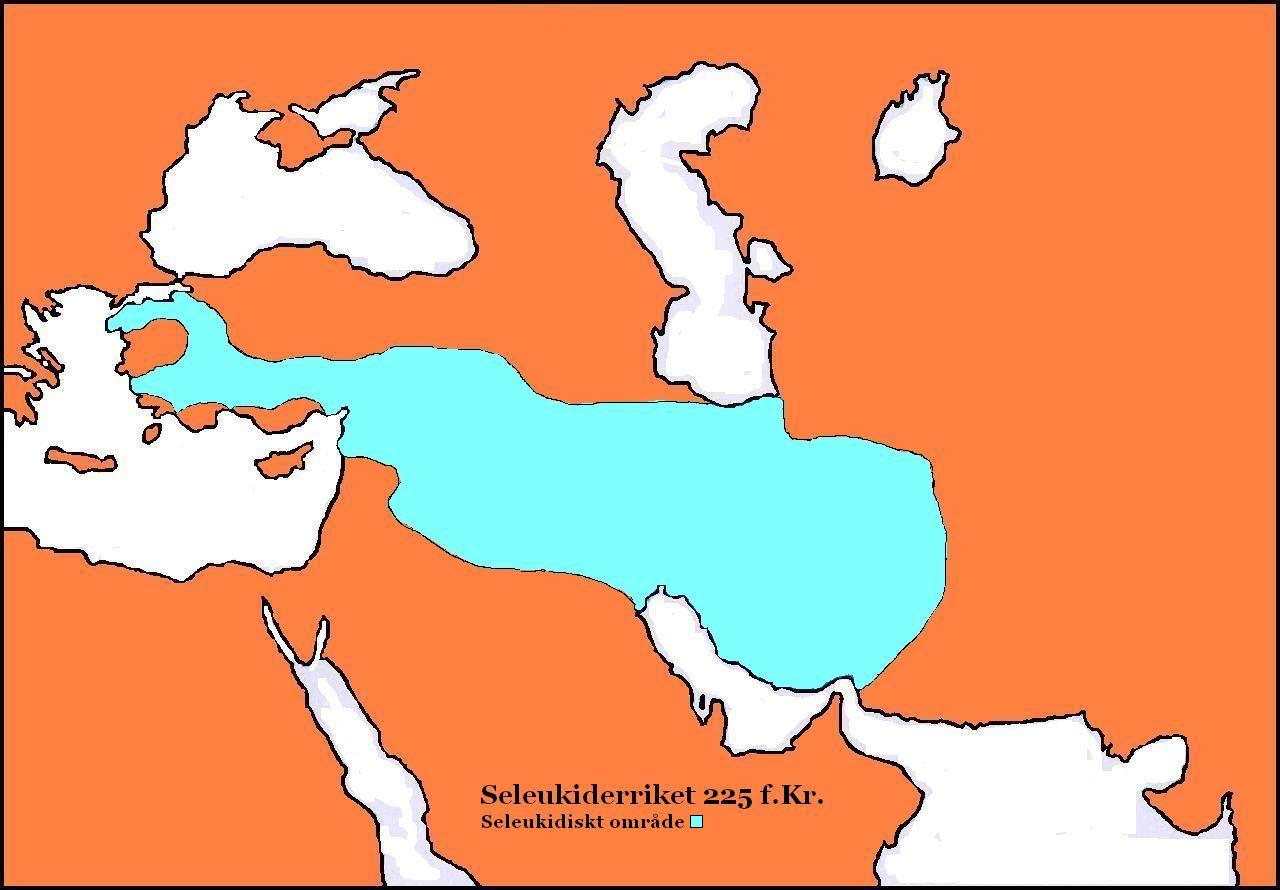
Roman–Seleucid War
The Seleucid War (192–188 BC), also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea and Asia Minor. The war was the consequence of a "cold war" between both powers, which had started in 196 BC. In this period, the Romans and the Seleucids attempted to settle spheres of influence by forging alliances with the small Greek city-states. The fighting ended with a clear Roman victory. In the Treaty of Apamea, the Seleucids were forced to give up Asia Minor, which fell to Roman allies. As a main result of the war, the Roman Republic gained hegemony over the Greek city-states and Asia Minor and became the only remaining major power around the Mediterranean Sea. Prelude Antiochus III the Great, the Seleucid king, first became involved with Greece when he signed an alliance with King Philip V of Macedon in 203 BC.Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Wars
The Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League (which is often considered to be the final stage of the final Macedonian war). The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, while the war with Macedonia was the second, and both of these wars effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination. Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geographic proximity to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatians (people)
The Galatians ( grc, Γαλάται, Galátai}; la, Galatae, Galati, Gallograeci; el, Γαλάτες, translit=Galátes, lit=Gauls) were a Celtic people dwelling in Galatia, a region of central Anatolia surrounding present-day Ankara, during the Hellenistic period. They spoke the Galatian language, which was closely related to Gaulish, a contemporary Celtic language spoken in Gaul. The Galatians were descended from Celts who had invaded Greece in the 3rd century BC. The original settlers of Galatia came through Thrace under the leadership of Leogarios and Leonnorios c. 278 BC. They consisted mainly of three gaulish tribes, the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii, but there were also other minor tribes. In 25 BC, Galatia became a province of the Roman Empire, with Ankara (''Ancyra'') as its capital. In the 1st century AD, many Galatians were Christianized by Paul the Apostle's missionary activities. The '' Epistle to the Galatians'' by Paul the Apostle is addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Asiaticus
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (properly Asiagenes; 3rd century BC – after 183 BC) was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius Cornelius Scipio and the younger brother of Scipio Africanus. He was elected Roman consul, consul in 190 BC, and later that year led (with his brother) the Roman forces to victory at the Battle of Magnesia. Although his career may be eclipsed by the shadow of his elder brother, Lucius' life is noteworthy in several respects. Family background Lucius belonged to the Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician ''gens'' Cornelia gens, Cornelia, one of the most important gentes of the Republic, which counted more consulships than any other. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius, the consul of 218 who died against the Punics, Carthaginians at the Battle of the Upper Baetis in 211, and Pomponia, the daughter of Manius Pomponius Matho, consul in 233. Lucius als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Aemilius Regillus
Lucius Aemilius Regillus (fl. c. 190 – 189 BC) was a Roman admiral and praetor during the war with Antiochus III of Syria. Born to Marcus Aemilius Regillus, much of Lucius Regillus's early life and military career is unknown before being appointed commander of Roman naval forces in the Aegean Sea in 190 BC. That same year, supported by a flotilla from Rhodes, Regillus defeated a Syrian fleet commanded by former Carthaginian General Hannibal (his first, and subsequently last naval battle) at the Battle of Eurymedon and, after defeating a second Syrian fleet at the Battle of Myonessus secured the Aegean Sea under the control of Rome and its Rhodian and Pergamene allies. Upon his return to Rome in 189 BC, Regillus had a temple built in honor of the ''lares permarini Largo di Torre Argentina is a square in Rome, Italy, with four Roman Republican temples and the remains of Pompey's Theatre. It is in the ancient Campus Martius. The name of the square comes from the ''Torre Argenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariarathes IV Of Cappadocia
Ariarathes IV, surnamed ''Eusebes'', "the Pious", ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Εὐσεβής, Ariaráthēs Eusebḗs), was the king of Cappadocia in 220–163 BC. Early life Ariarathes IV was the son of the king of Cappadocia Ariarathes III and his Macedonian Greek wife Stratonice. He was a child at his accession, and reigned for about 57 years. He married his cousin Antiochis, the daughter of Antiochus III the Great, king of Syria, and Laodice III, and, in consequence of this alliance, assisted Antiochus in his war against the Romans. After the defeat of Antiochus by the Romans in 190 BC, Ariarathes sued for peace in 188, which he obtained on favourable terms, as his daughter, Stratonice, was about that time betrothed to Eumenes II, king of Pergamum, whom she later married, and became an ally of the Romans. In 183–179 , he assisted Eumenes in his war against Pharnaces, king of Pontus. Polybius mentions that a Roman embassy was sent to Ariarathes after the death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amynander Of Athamania
Amynander ( grc-gre, Ἀμύνανδρος, ''Amynandros'', in Polybios also ''Amynas'') was king of the Athamanes in south Epirus, following his predecessor Theodorus of Athamania. He was a brother-in-law of the Illyrian king Scerdilaidas and first appears in history as a mediator between Philip V of Macedon and the Aetolians. When the Romans were about to wage war on Philip, they sent ambassadors to Amynander to inform him of their intention. On the commencement of the war, he came to the camp of the Romans and promised them assistance: the task of bringing over the Aetolians to an alliance with the Romans was assigned to him. In 198 BC Amynander took the towns of Phoca and Gomphi, and ravaged Thessaly. He was present at the conference between Flamininus and Philip, and during the short truce was sent by the former to Rome. He was again present at the conference held with Philip after the battle of Cynoscephalae. On the conclusion of peace, he was allowed to retain all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyxenidas
Polyxenidas ( grc, Πολυξενίδας) the Rhodian, was a general and admiral who was exiled from his native country and entered the service of Antiochus III the Great. He is first mentioned in 209 BC, when he commanded a body of Cretan mercenaries for Antiochus during the Battle of Mount Labus. But in 192 BC, when the Syrian king had determined upon war with Rome, and crossed over into Greece to commence it, Polyxenidas obtained the chief command of his fleet. After co-operating with Menippus in the reduction of Chalcis, he was sent back to Asia to assemble additional forces during the winter. We do not hear anything of his operations in the ensuing campaign, 191 BC, but when Antiochus, after his defeat at the Battle of Thermopylae (191 BC), withdrew to Asia, Polyxenidas was again appointed to command the king's main fleet on the Ionian coast. Having learnt that the praetor Gaius Livius Salinator had arrived at Delos with the Roman fleet, he strongly urged upon the king the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
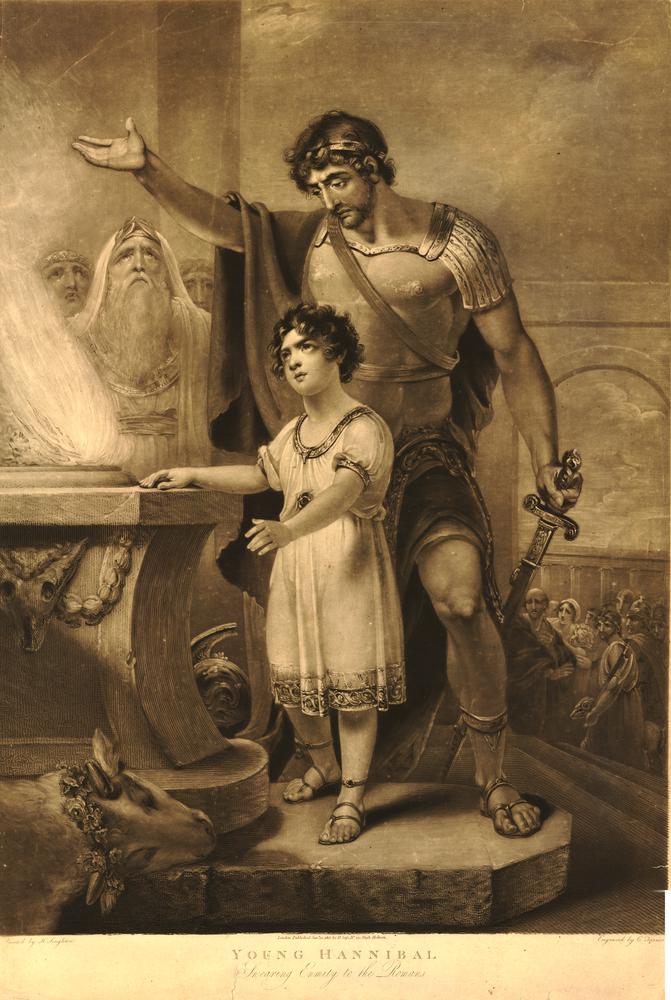
Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago and Hasdrubal; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome". In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto, Spain), an ally of Rome, in Hispania, sparking the Second Pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (ancient Kingdom)
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the ''sarissa'' pike, PhilipII d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergina Sun - Golden Larnax
Vergina ( el, Βεργίνα, ''Vergína'' ) is a small town in northern Greece, part of Veria municipality in Imathia, Central Macedonia. Vergina was established in 1922 in the aftermath of the Population exchange between Greece and Turkey, population exchanges after the Treaty of Lausanne and was a separate Municipalities and communities of Greece, municipality until 2011, when it was merged with Veroia under the Kallikratis Plan. Vergina is best known as the site of ancient Aegae (Macedonia), Aigai (Αἰγαί, ''Aigaí'', Latinisation of names, Latinized: ''Aegae''), the first capital of Macedon. In 336 BC Philip II of Macedon, Philip II was assassinated in Aigai's theatre and his son, Alexander the Great, was proclaimed king. In 1977, the burial sites of several kings of Macedon were uncovered, including the tomb of Philip II which had not been disturbed or looted, unlike so many of the other tombs there. The ancient town was also the site of an extensive royal palace. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Pergamon
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστεία των Ατταλιδών, translit=Dynasteía ton Attalidón). The kingdom was a rump state that was created from the territory ruled by Lysimachus, a general of Alexander the Great. Philetaerus, one of Lysimachus' lieutenants, rebelled and took the city of Pergamon and its environs with him; Lysimachus died soon after in 281 BC. The new kingdom was initially in a vassal-like relationship of nominal fealty to the Seleucid Empire, but exercised considerable autonomy and soon became entirely independent. It was a monarchy ruled by Philetaerus's extended family and their descendants. It lasted around 150 years before being eventually absorbed by the Roman Republic during the period from 133–129 BC. History Philetaerus was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |