Pyrazoles Synthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the
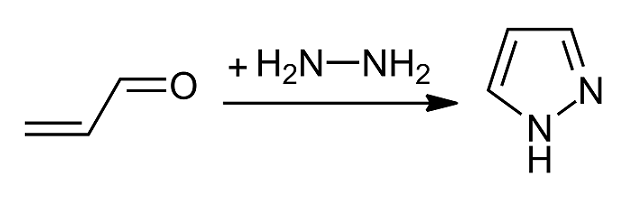 Substituted pyrazoles are prepared by condensation of 1,3-
Substituted pyrazoles are prepared by condensation of 1,3-


 In 1959, the first natural pyrazole, 1-pyrazolyl-alanine, was isolated from seeds of
In 1959, the first natural pyrazole, 1-pyrazolyl-alanine, was isolated from seeds of
formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwee ...
C3H3N2H. It is a heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different chemical element, elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis ...
characterized by a 5-membered ring of three carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms.
Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, ankyl ...
(celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol
Stanozolol (Abbreviation, abbrev. Stz), sold under many brand names, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It is used to treat hereditary angioedema. It was developed by American pharmaceuti ...
.
Preparation and reactions
Pyrazoles are synthesized by the reaction of α,β-unsaturatedaldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl grou ...
s with hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
and subsequent dehydrogenation
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At ...
:
: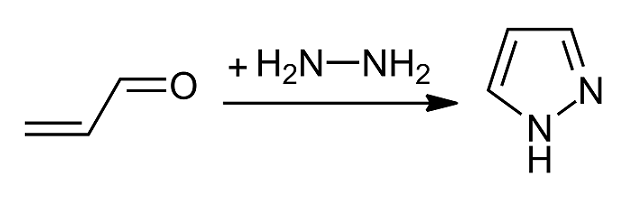 Substituted pyrazoles are prepared by condensation of 1,3-
Substituted pyrazoles are prepared by condensation of 1,3-diketone
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls ...
s with hydrazine ( Knorr-type reactions). For example, acetylacetone
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless liquid, classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer . These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are tre ...
and hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
gives 3,5-dimethylpyrazole:
:CH3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3 + N2H4 → (CH3)2C3HN2H + 2 H2O
History
The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German ChemistLudwig Knorr
Ludwig Knorr (2 December 1859 – 4 June 1921) was a German chemist. Together with Carl Paal, he discovered the Paal–Knorr synthesis, and the Knorr quinoline synthesis and Knorr pyrrole synthesis are also named after him. The synthesis in 18 ...
in 1883. In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann
Hans von Pechmann (1 April 1850 – 19 April 1902) was a German chemist, renowned for his discovery of diazomethane in 1894. Pechmann condensation and Pechmann pyrazole synthesis. He also first prepared 1,2-diketones (e.g., diacetyl), acetonedicarb ...
in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure ...
and diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost u ...
.
Conversion to scorpionates
Pyrazoles react withpotassium borohydride
Borohydride refers to the anion , which is also called tetrahydroborate, and its salts. Borohydride or hydroborate is also the term used for compounds containing , where ''n'' is an integer from 0 to 3, for example cyanoborohydride or cyanotrihydr ...
to form a class of ligands known as scorpionate. Pyrazole itself reacts with potassium borohydride
Borohydride refers to the anion , which is also called tetrahydroborate, and its salts. Borohydride or hydroborate is also the term used for compounds containing , where ''n'' is an integer from 0 to 3, for example cyanoborohydride or cyanotrihydr ...
at high temperatures (~200 °C) to form a tridentate ligand
A tridentate ligand (or terdentate ligand) is a ligand that has three atoms that can function as acceptor atoms in a coordination complex.
Well-known tridentate ligands include diethylenetriamine with three nitrogen donor atoms, and the iminodia ...
known as Tp ligand:
:3,5-Diphenyl-1''H''-pyrazole
3,5-Diphenyl-1''H''-pyrazole is produced when (''E'')-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one is reacted withhydrazine hydrate
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine h ...
in the presence of elemental sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
or sodium persulfate
Sodium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 S2 O8. It is the sodium salt of peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8, an oxidizing agent. It is a white solid that dissolves in water. It is almost non-hygroscopic and has good shelf-life ...
, or by using a hydrazone
Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure . They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the = functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes. ...
in which case an azine
Azines are a functional class of organic compounds with the connectivity RR'C=N-N=CRR'. These compounds are the product of the condensation of hydrazine with ketones and aldehydes, although in practice they are often made by alternative routes ...
is produced as a by-product.
:Occurrence and uses
 In 1959, the first natural pyrazole, 1-pyrazolyl-alanine, was isolated from seeds of
In 1959, the first natural pyrazole, 1-pyrazolyl-alanine, was isolated from seeds of watermelons
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 varieti ...
.
In medicine, derivatives of pyrazole are widely used, including celecoxib
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, ankyl ...
and similar COX-2 inhibitors
COX-2 inhibitors are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly targets cyclooxygenase-2, COX-2, an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity for COX-2 reduces the risk of peptic ulceration and i ...
, zaleplon
Zaleplon, sold under the brand names Sonata among others, is a sedative-hypnotic, used to treat insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class.
It is manufactured by King Pharmaceuticals and Gedeon Richter Plc. ...
, betazole
Betazole (also known as ametazole) is a histamine H2 receptor agonist. Betazole hydrochloride is known as gastramine and histalog.
It has been used as a gastric stimulant to test for maximal production of gastric secretion activity. The test ...
, and CDPPB.
The pyrazole ring is found within a variety of pesticides as fungicides, insecticides and herbicides, including fenpyroximate, fipronil
Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide that belongs to the phenylpyrazole chemical family. Fipronil disrupts the insect central nervous system by blocking the ligand-gated ion channel of the GABAA receptor and glutamate-gated chloride (GluCl ...
, tebufenpyrad
Tebufenpyrad is an insecticide and acaricide widely used in greenhouses. It is a white solid chemical with a slight aromatic smell. It is soluble in water and also in organic solvents.http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@ ...
and tolfenpyrad. Pyrazole moieties are listed among the highly used ring systems for small molecule drugs by the US FDATaylor, R. D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A. D. G. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 5845.
See also
*3,5-dimethylpyrazole
3,5-Dimethylpyrazole is an organic compound with the formula (CH3C)2CHN2H. It is one of several isomeric derivatives of pyrazole that contain two methyl substituents. The compound is unsymmetrical but the corresponding conjugate acid (pyrazolium ...
* Pyrazolidine, fully saturated analogue
*imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole Diazole refers ...
, structural analogue of pyrazole with two ''non''-adjacent nitrogen atoms.
*isoxazole
Isoxazole is an electron-rich azole with an oxygen atom next to the nitrogen. It is also the class of compounds containing this ring. Isoxazolyl is the univalent radical derived from isoxazole.
Occurrence
Isoxazole rings are found in some natural ...
, another analogue, the nitrogen atom in position 1 replaced by oxygen.
References
Further reading
{{Cite journal , author1=A. Schmidt , author2=A. Dreger , journal=Curr. Org. Chem. , date=2011 , volume=15 , issue=16 , pages=2897–2970 , title=Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Pyrazoles. Part 2. Reactions and N-Heterocyclic Carbenes of Pyrazole , doi=10.2174/138527211796378497 Aromatic bases Simple aromatic rings