psoriasis vulgaris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious
 Psoriasis vulgaris (also known as chronic stationary psoriasis or plaque-like psoriasis) is the most common form and affects 85–90% of people with psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis typically appears as raised areas of
Psoriasis vulgaris (also known as chronic stationary psoriasis or plaque-like psoriasis) is the most common form and affects 85–90% of people with psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis typically appears as raised areas of
Image:Psoriasis2010a.JPG, Plaques of psoriasis
Image:Psoriasis.jpg, A person's arm covered with plaque psoriasis
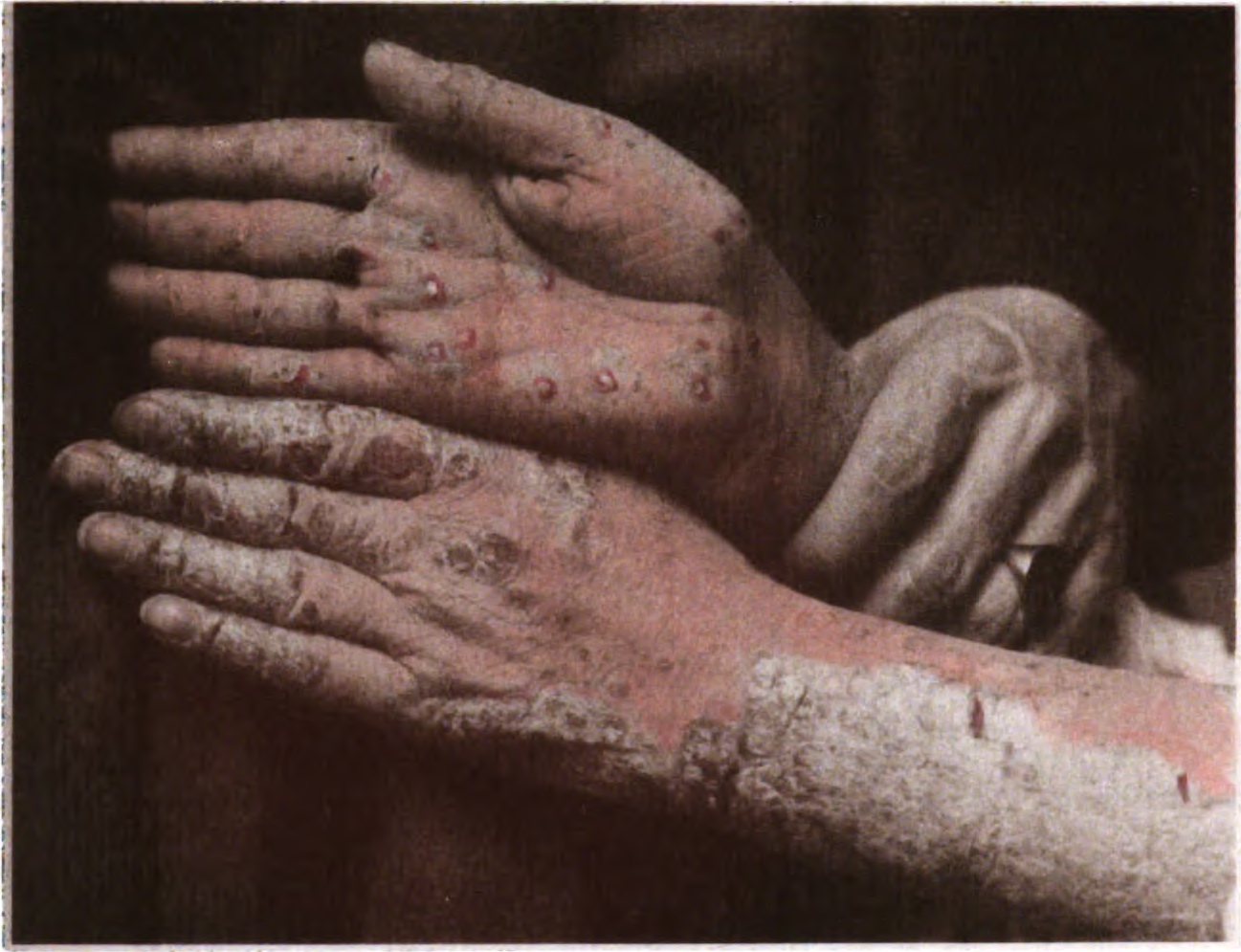
File:Psoriasis of the palms.jpg, Psoriasis of the palms


 Psoriasis can affect the nails and produces a variety of changes in the appearance of fingers and toenails. Nail psoriasis occurs in 40–45% of people with psoriasis affecting the skin, and has a lifetime incidence of 80–90% in those with psoriatic arthritis. These changes include pitting of the nails (pinhead-sized depressions in the nail is seen in 70% with nail psoriasis), whitening of the nail, small areas of bleeding from capillaries under the nail, yellow-reddish discoloration of the nails known as the oil drop or salmon spots, dryness, thickening of the skin under the nail (subungual hyperkeratosis), loosening and separation of the nail (
Psoriasis can affect the nails and produces a variety of changes in the appearance of fingers and toenails. Nail psoriasis occurs in 40–45% of people with psoriasis affecting the skin, and has a lifetime incidence of 80–90% in those with psoriatic arthritis. These changes include pitting of the nails (pinhead-sized depressions in the nail is seen in 70% with nail psoriasis), whitening of the nail, small areas of bleeding from capillaries under the nail, yellow-reddish discoloration of the nails known as the oil drop or salmon spots, dryness, thickening of the skin under the nail (subungual hyperkeratosis), loosening and separation of the nail (
 A
A
There have been few studies of the efficacy of anti-TNF medications for psoriasis in children. One randomized control study suggested that 12 weeks of etanercept treatment reduced the extent of psoriasis in children with no lasting adverse effects. Two medications that target T cells are
autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
, pink, or purple, dry, itch
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant ...
y, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon
The Koebner phenomenon or Köbner phenomenon (, ), also called the Koebner response or the isomorphic response, attributed to Heinrich Köbner, is the appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a ...
.
The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types. Fingernails
A nail is a claw-like plate found at the tip of the fingers and toes on most primates. Nails correspond to the claws found in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called alpha-keratin, which is a polymer. ...
and toenails are affected in most people with psoriasis at some point in time. This may include pits in the nails or changes in nail color.
Psoriasis is generally thought to be a genetic disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
that is triggered by environmental factors. If one twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
has psoriasis, the other twin is three times more likely to be affected if the twins are identical
Two things are identical if they are the same, see Identity (philosophy).
Identical may also refer to:
* ''Identical'' (Hopkins novel), a 2008 young adult novel by Ellen Hopkins
* ''Identical'' (Turow novel), a 2013 legal drama novel by Scott T ...
than if they are nonidentical. This suggests that genetic factors predispose to psoriasis. Symptoms often worsen during winter and with certain medications, such as beta blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart ...
or NSAIDs. Infections and psychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Exces ...
can also play a role. The underlying mechanism involves the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
reacting to skin cell
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
s. Diagnosis is typically based on the signs and symptoms.
There is no known cure for psoriasis, but various treatments can help control the symptoms. These treatments include steroid creams, vitamin D3 cream, ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, immunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
s, such as methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, and biologic therapies targeting specific immunologic pathways. About 75% of skin involvement improves with creams alone. The disease affects 2–4% of the population. Men and women are affected with equal frequency. The disease may begin at any age, but typically starts in adulthood. Psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. Thi ...
, lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlar ...
s, cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
, Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension ...
, and depression. Psoriatic arthritis affects up to 30% of individuals with psoriasis.
The word "psoriasis" is from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
ψωρίασις, meaning "itching condition" or "being itchy" from ''psora
''Psora'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Psoraceae. Members of the genus are commonly called fishscale lichens. Lichens in the genus ''Psora'' are known to have a squamulose thallus and anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also call ...
'', "itch", and '' -iasis'', "action, condition".
Signs and symptoms
Plaque psoriasis
inflamed
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecu ...
skin covered with silvery-white, scaly skin. These areas are called plaques and are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and back.
Other forms
Additional types of psoriasis comprise about 10% of cases. They include pustular, inverse, napkin, guttate, oral, and seborrheic-like forms.Pustular psoriasis

Pustular psoriasis The term pustular psoriasis is used for a heterogeneous group of diseases that share pustular skin characteristics.
Signs and symptoms
Characteristics may vary according to the subtype of pustular psoriasis. For example, it can be localized, comm ...
appears as raised bumps filled with noninfectious pus (pustules
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this sy ...
). The skin under and surrounding the pustules is red and tender. Pustular psoriasis can either be localized or more widespread throughout the body. Two types of localized pustular psoriasis include psoriasis pustulosa palmoplantaris and acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau; both forms are localized to the hands and feet.
Inverse psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis or flexural psoriasis is a form of psoriasis that selectively, and often exclusively, involves the folds, recesses, and flexor surfaces such as the ears, axillae, groin folds, inframammary folds, navel, intergluteal cleft, penis, ...
(also known as flexural psoriasis) appears as smooth, inflamed patches of skin. The patches frequently affect skin fold
Skin folds or skinfolds are areas of skin that are naturally folded. Many skin folds are distinct, heritable anatomical features, and may be used for identification of animal species, while others are non-specific and may be produced either by ind ...
s, particularly around the genitals
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
(between the thigh and groin), the armpit
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorl ...
s, in the skin folds of an overweight abdomen (known as panniculus
Panniculus, often incorrectly referred to as pannus, is a medical term describing a dense layer of fatty tissue, consisting of excess subcutaneous fat within the lower abdominal region. Panniculi can form after rapid weight loss, as seen with st ...
), between the buttocks in the intergluteal cleft, and under the breasts
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secret ...
in the inframammary fold
In human anatomy, the inframammary fold (IMF), inframammary crease or inframammary line is the natural lower boundary of the breast, the place where the breast and the chest meet. The choice of the term depends on the prominence of the feature. It ...
. Heat, trauma, and infection are thought to play a role in the development of this atypical form of psoriasis.
Napkin psoriasis
Napkin psoriasis is a subtype of psoriasis common in infants characterized by red papules with silver scale in the diaper area that may extend to the torso or limbs. Napkin psoriasis is often misdiagnosed as napkin dermatitis (diaper rash).Guttate psoriasis

Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis (also known as eruptive psoriasis) is a type of psoriasis that presents as small (0.5–1.5 cm in diameter) lesions over the upper trunk and proximal extremities; it is found frequently in young adults.
The term " guttate" i ...
is characterized by numerous small, scaly, red or pink, droplet-like lesions (papules). These numerous spots of psoriasis appear over large areas of the body, primarily the trunk, but also the limbs and scalp. Guttate psoriasis is often triggered by a streptococcal
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell divisio ...
infection, typically streptococcal pharyngitis
Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as streptococcal sore throat (strep throat), is pharyngitis (an infection of the pharynx, the back of the throat) caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a gram-positive, group A streptococcus. Common symptom ...
.
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Psoriatic erythroderma
Psoriatic erythroderma represents a form of psoriasis that affects all body sites, including the face, hands, feet, nails, trunk, and extremities.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ...
(erythrodermic psoriasis) involves widespread inflammation and exfoliation of the skin over most of the body surface, often involving greater than 90% of the body surface area. It may be accompanied by severe dryness, itching, swelling, and pain. It can develop from any type of psoriasis. It is often the result of an exacerbation of unstable plaque psoriasis, particularly following the abrupt withdrawal of systemic glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s. This form of psoriasis can be fatal as the extreme inflammation and exfoliation disrupt the body's ability to regulate temperature and perform barrier functions.
Mouth
Psoriasis in the mouth is very rare, in contrast tolichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, fla ...
, another common papulosquamous disorder that commonly involves both the skin and mouth. When psoriasis involves the oral mucosa (the lining of the mouth), it may be asymptomatic, but it may appear as white or grey-yellow plaques. Fissured tongue
Fissured tongue is a benign condition characterized by deep grooves (fissures) in the dorsum of the tongue. Although these grooves may look unsettling, the condition is usually painless. Some individuals may complain of an associated burning sens ...
is the most common finding in those with oral psoriasis and has been reported to occur in 6.5–20% of people with psoriasis affecting the skin. The microscopic appearance of oral mucosa affected by geographic tongue
Geographic tongue, also known by several other terms, is a condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue, usually on the dorsal surface. It is a common condition, affecting approximately 2–3% of the general population. It is characterized by a ...
(migratory stomatitis) is very similar to the appearance of psoriasis. However, modern studies have failed to demonstrate any link between the two conditions.
Seborrheic-like psoriasis
Seborrheic-like psoriasis
Seborrheic-like psoriasis is a skin condition characterized by psoriasis with an overlapping seborrheic dermatitis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. ...
is a common form of psoriasis with clinical aspects of psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the ...
, and it may be difficult to distinguish from the latter. This form of psoriasis typically manifests as red plaques with greasy scales in areas of higher sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
production such as the scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
Structure
The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:
* S: The ski ...
, forehead
In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. The bottom of the fore ...
, skin folds next to the nose, the skin surrounding the mouth, skin on the chest above the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
, and in skin folds
Skin folds or skinfolds are areas of skin that are naturally folded. Many skin folds are distinct, heritable anatomical features, and may be used for identification of animal species, while others are non-specific and may be produced either by ind ...
.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. Thi ...
is a form of chronic inflammatory arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
that has a highly variable clinical presentation and frequently occurs in association with skin and nail psoriasis. It typically involves painful inflammation of the joints and surrounding connective tissue, and can occur in any joint, but most commonly affects the joints of the fingers and toes. This can result in a sausage-shaped swelling of the fingers and toes known as dactylitis
Dactylitis or sausage digit is inflammation of an entire digit (a finger or toe), and can be painful.
The word dactyl comes from the Greek word "daktylos" meaning "finger". In its medical term, it refers to both the fingers and the toes.
Associa ...
. Psoriatic arthritis can also affect the hips, knees, spine (spondylitis
Spondylitis is an inflammation of the vertebrae. It is a form of spondylopathy. In many cases, spondylitis involves one or more vertebral joints, as well, which itself is called spondylarthritis.
__TOC__
Types
Pott disease is a tuberculous di ...
), and sacroiliac joint
The sacroiliac joint or SI joint (SIJ) is the joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis, which are connected by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side. The ...
(sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis is inflammation within the sacroiliac joint. It is a feature of spondyloarthropathies, such as axial spondyloarthritis (including ankylosing spondylitis), psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis or arthritis related to inflammatory bo ...
). About 30% of individuals with psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis. Skin manifestations of psoriasis tend to occur before arthritic manifestations in about 75% of cases.
Nail changes

onycholysis
Onycholysis is a common medical condition characterized by the painless detachment of the nail from the nail bed, usually starting at the tip and/or sides. On the hands, it occurs particularly on the ring finger but can occur on any of the fingern ...
), and crumbling of the nail.
Medical signs
In addition to the appearance and distribution of the rash, specificmedical sign
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s may be used by medical practitioners to assist with diagnosis. These may include Auspitz's sign (pinpoint bleeding when scale is removed), Koebner phenomenon
The Koebner phenomenon or Köbner phenomenon (, ), also called the Koebner response or the isomorphic response, attributed to Heinrich Köbner, is the appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a ...
(psoriatic skin lesions induced by trauma to the skin), and itching
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasan ...
and pain localized to papules and plaques.
Causes
The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but many theories exist.Genetics
Around one-third of people with psoriasis report afamily history
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their Lineage (anthropology), lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family a ...
of the disease, and researchers have identified genetic loci associated with the condition. Identical twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
studies suggest a 70% chance of a twin developing psoriasis if the other twin has the disorder. The risk is around 20% for nonidentical twins. These findings suggest both a genetic susceptibility and an environmental response in developing psoriasis.
Psoriasis has a strong hereditary component, and many genes are associated with it, but how those genes work together is unclear. Most of the identified genes relate to the immune system, particularly the major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are calle ...
(MHC) and T cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell re ...
. Genetic studies are valuable due to their ability to identify molecular mechanisms and pathways for further study and potential medication targets.
Classic genome-wide linkage analysis
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separ ...
has identified nine loci on different chromosomes associated with psoriasis. They are called psoriasis susceptibility 1 through 9 ('' PSORS1'' through ''PSORS9''). Within those loci are genes on pathways that lead to inflammation. Certain variations (mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
s) of those genes are commonly found in psoriasis. Genome-wide association scans have identified other genes that are altered to characteristic variants in psoriasis. Some of these genes express inflammatory signal proteins, which affect cells in the immune system that are also involved in psoriasis. Some of these genes are also involved in other autoimmune diseases.
The major determinant is ''PSORS1'', which probably accounts for 35–50% of psoriasis heritability. It controls genes that affect the immune system or encode skin proteins that are overabundant with psoriasis. ''PSORS1'' is located on chromosome 6
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total ...
in the MHC, which controls important immune functions. Three genes in the ''PSORS1'' locus have a strong association with psoriasis vulgaris: ''HLA-C'' variant ''HLA-Cw6'', which encodes an MHC class I protein; ''CCHCR1
Coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1, also known as CCHCR1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCHCR1'' gene.
Gene
The Human CCHCR1 gene is located at 6p21.33. It is also known as Coiled-Coil Alphahelical Rod Protein 1, C6orf18 ...
'', variant WWC, which encodes a coiled coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which 2–7
alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. (Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological fun ...
protein overexpressed in psoriatic epidermis; and '' CDSN'', variant allele 5, which encodes corneodesmosin
Corneodesmosin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDSN'' gene.
This gene encodes a protein found in corneodesmosomes, which localize to the human epidermis and other cornified squamous epithelia. During maturation of the cornified lay ...
, a protein expressed in the granular and cornified layer
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. The human stratum corneum comprises several levels of flattened corneocytes that are divided into two layers: the ''stratum ...
s of the epidermis and upregulated in psoriasis.
Two major immune system genes under investigation are interleukin-12 subunit beta (''IL12B'') on chromosome 5q, which expresses interleukin-12B; and ''IL23R
The interleukin-23 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. It is encoded in human by the ''IL23R'' gene. In complex with the interleukin-12 receptor β1 subunit ( IL-12Rβ1), it is activated by the cytokine interleukin 23 (IL-23). The ''IL23R'' mR ...
'' on chromosome 1p, which expresses the interleukin-23 receptor, and is involved in T cell differentiation. Interleukin-23 receptor and ''IL12B'' have both been strongly linked with psoriasis. T cells are involved in the inflammatory process that leads to psoriasis. These genes are on the pathway that upregulate tumor necrosis factor-α and nuclear factor κB, two genes involved in inflammation. The first gene directly linked to psoriasis was identified as the ''CARD14
Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 14, also known as D-containing MAGUK protein 2 (Carma 2), is a protein in the CARD-CC protein family that in humans is encoded by the ''CARD14'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene bel ...
''gene located in the ''PSORS2'' locus. A rare mutation in the gene encoding for the ''CARD14
Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 14, also known as D-containing MAGUK protein 2 (Carma 2), is a protein in the CARD-CC protein family that in humans is encoded by the ''CARD14'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene bel ...
''-regulated protein plus an environmental trigger was enough to cause plaque psoriasis (the most common form of psoriasis).
Lifestyle
Conditions reported as worsening the disease include chronic infections, stress, and changes in season andclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
. Others factors that might worsen the condition include hot water, scratching psoriasis skin lesions, skin dryness
Xeroderma, xerosis or xerosis cutis, or simply dry skin, is a skin condition characterized by excessively dry skin.
The medical term ''xeroderma'', meaning "dry skin", derives from modern Latin, ''xero-'' 'dry' + Greek ''derma'' 'skin'.
In most ...
, excessive alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
, and obesity. The effects of stopping cigarette smoking or alcohol misuse have yet to be studied as of 2019.
HIV
The rate of psoriasis inhuman immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the ...
-positive (HIV) individuals is comparable to that of HIV-negative individuals, but psoriasis tends to be more severe in people infected with HIV. A much higher rate of psoriatic arthritis occurs in HIV-positive individuals with psoriasis than in those without the infection. The immune response in those infected with HIV is typically characterized by cellular signals from Th2 subset of CD4+ helper T cells, whereas the immune response in psoriasis vulgaris is characterized by a pattern of cellular signals typical of Th1 subset of CD4+ helper T cells and Th17 helper T cells. The diminished CD4+-T cell presence is thought to cause an overactivation of CD8+-T cells, which are responsible for the exacerbation of psoriasis in HIV-positive people. Psoriasis in those with HIV/AIDS is often severe and may be untreatable with conventional therapy. In those with long-term, well-controlled psoriasis, new HIV infection can trigger a severe flare-up of psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis.
Microbes
Psoriasis has been described as occurring afterstrep throat
Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as streptococcal sore throat (strep throat), is pharyngitis (an infection of the pharynx, the back of the throat) caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a gram-positive, group A streptococcus. Common symptom ...
, and may be worsened by skin or gut colonization with ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive ...
'', ''Malassezia
''Malassezia'' (formerly known as ''Pityrosporum'') is a genus of fungi. It is the sole genus in family Malasseziaceae, which is the only family in order Malasseziales, itself the single member of class Malasseziomycetes. ''Malassezia'' species ...
'' spp., and ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is us ...
''. Guttate psoriasis often affects children and adolescents and can be triggered by a recent group A streptococcal infection
Group A streptococcal infections are a number of infections with ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a group A streptococcus (GAS). ''S. pyogenes'' is a species of beta-hemolytic gram-positive bacteria that is responsible for a wide range of infections tha ...
(tonsillitis or pharyngitis).
Medications
Drug-induced psoriasis may occur withbeta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart ...
s, lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
, antimalarial medication
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young c ...
s, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s, terbinafine
Terbinafine, sold under the brand name Lamisil among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat pityriasis versicolor, fungal nail infections, and ringworm including jock itch and athlete's foot. It is either taken by mouth or applied to ...
, calcium channel blockers
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
, captopril
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure. Captopril was the first oral ACE inh ...
, glyburide
Glibenclamide, also known as glyburide, is an antidiabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is recommended that it be taken together with diet and exercise. It may be used with other antidiabetic medication. It is not recommended f ...
, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF or GCSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF 3), is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.
Functional ...
, interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related ...
s, interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten the ...
s, lipid-lowering medications, and paradoxically TNF inhibitor
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ...
s such as infliximab
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spon ...
or adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativ ...
. Withdrawal of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
s (topical steroid cream) can aggravate psoriasis due to the rebound effect
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the emergence or re-emergence of symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage. In the case of re ...
.
Pathophysiology
Psoriasis is characterized by an abnormally excessive and rapid growth of the epidermal layer of the skin. Abnormal production of skin cells (especially duringwound repair
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue.
In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier agains ...
) and an overabundance of skin cells result from the sequence of pathological events in psoriasis. The sequence of pathological events in psoriasis is thought to start with an initiation phase in which an event (skin trauma, infection, or drugs) leads to activation of the immune system and then the maintenance phase consisting of chronic progression of the disease. Skin cells are replaced every 3–5 days in psoriasis rather than the usual 28–30 days. These changes are believed to stem from the premature maturation of keratinocytes
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells.
Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referred ...
induced by an inflammatory cascade in the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
involving dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s, macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, and T cells (three subtypes of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s). These immune cells move from the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
to the epidermis and secrete inflammatory chemical signals (cytokines) such as interleukin-36γ, tumor necrosis factor-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, interleukin-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin" ...
, interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene.
In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth ...
, and interleukin-22
Interleukin-22 (IL-22) is protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL22'' gene.
Structure
IL-22 is an α-helical cytokine. IL-22 binds to a heterodimeric cell surface receptor composed of IL-10R2 and IL-22R1 subunits. IL-22R is expressed o ...
. These secreted inflammatory signals are believed to stimulate keratinocytes to proliferate. One hypothesis is that psoriasis involves a defect in regulatory T cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosup ...
s, and in the regulatory cytokine interleukin-10
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti- inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 ...
. The inflammatory cytokines found in psoriatic nails and joints (in the case of psoriatic arthritis) are similar to those of psoriatic skin lesions, suggesting a common inflammatory mechanism.
Gene mutations of proteins involved in the skin's ability to function as a barrier have been identified as markers of susceptibility for the development of psoriasis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) released from dying cells acts as an inflammatory stimulus in psoriasis and stimulates the receptors on certain dendritic cells, which in turn produce the cytokine interferon-α. In response to these chemical messages from dendritic cells and T cells, keratinocytes also secrete cytokines such as interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α, which signal downstream inflammatory cells to arrive and stimulate additional inflammation.
Dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s bridge the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
and adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
. They are increased in psoriatic lesions and induce the proliferation of T cells and type 1 helper T cells (Th1). Targeted immunotherapy, as well as psoralen
Psoralen (also called psoralene) is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins. It is structurally related to coumarin by the addition of a fused furan ring, and may be considered a ...
and ultraviolet A
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
(PUVA
PUVA (psoralen and UVA) is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, vitiligo, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizing effe ...
) therapy, can reduce the number of dendritic cells and favors a Th2 cell cytokine secretion pattern over a Th1/Th17 cell cytokine profile. Psoriatic T cells move from the dermis into the epidermis and secrete interferon-γ and interleukin-17
Interleukin 17 family (IL17 family) is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identifie ...
. Interleukin-23 is known to induce the production of interleukin-17 and interleukin-22. Interleukin-22 works in combination with interleukin-17 to induce keratinocytes to secrete neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
-attracting cytokines.
Diagnosis
 A
A diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
of psoriasis is usually based on the appearance of the skin. Skin characteristics typical for psoriasis are scaly, erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not assoc ...
tous plaques, papules, or patches of skin that may be painful and itch. No special blood tests or diagnostic procedures are usually required to make the diagnosis.
The differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
of psoriasis includes dermatological conditions similar in appearance such as discoid eczema, seborrheic eczema, pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea is a type of skin rash. Classically, it begins with a single red and slightly scaly area known as a "herald patch". This is then followed, days to weeks later, by an eruption of many smaller scaly spots; pinkish with a red edge i ...
(may be confused with guttate psoriasis), nail fungus
Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Toenails or fingernails may be affected, ...
(may be confused with nail psoriasis) or cutaneous T cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T ...
(50% of individuals with this cancer are initially misdiagnosed
A medical error is a preventable adverse effect of care ("iatrogenesis"), whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, i ...
with psoriasis). Dermatologic manifestations of systemic illnesses such as the rash of secondary syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and ...
may also be confused with psoriasis.
If the clinical diagnosis is uncertain, a skin biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
or scraping may be performed to rule out other disorders and to confirm the diagnosis. Skin from a biopsy shows clubbed epidermal projections that interdigitate with dermis on microscopy. Epidermal thickening is another characteristic histologic finding of psoriasis lesions. The stratum granulosum
The stratum granulosum (or granular layer) is a thin layer of cells in the epidermis lying above the stratum spinosum and below the stratum corneum (stratum lucidum on the soles and palms).James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005) ''A ...
layer of the epidermis is often missing or significantly decreased in psoriatic lesions; the skin cells from the most superficial layer of skin are also abnormal as they never fully mature. Unlike their mature counterparts, these superficial cells keep their nuclei. Inflammatory infiltrates can typically be seen on microscopy when examining skin tissue or joint tissue affected by psoriasis. Epidermal skin tissue affected by psoriatic inflammation often has many CD8+ T cells, while a predominance of CD4+ T cells makes up the inflammatory infiltrates of the dermal layer of skin and the joints.
Classification
Morphological
Psoriasis is classified as apapulosquamous disorder
A papulosquamous disorder is a condition which presents with both papules and scales, or both scaly papules and plaques.
Examples include psoriasis, lichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that aff ...
and is most commonly subdivided into different categories based on histological characteristics. Variants include plaque, pustular, guttate, and flexural psoriasis. Each form has a dedicated ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, ...
code. Psoriasis can also be classified into nonpustular and pustular
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
types.
Pathogenetic
Another classification scheme considers genetic and demographic factors. Type 1 has a positive family history, starts before the age of 40, and is associated with thehuman leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
, ''HLA-Cw6''. Conversely, type 2 does not show a family history, presents after age 40, and is not associated with ''HLA-Cw6''. Type 1 accounts for about 75% of persons with psoriasis.
The classification of psoriasis as an autoimmune disease has sparked considerable debate. Researchers have proposed differing descriptions of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis; some authors have classified them as autoimmune diseases while others have classified them as distinct from autoimmune diseases and referred to them as immune-mediated inflammatory diseases
An immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) is any of a group of conditions or diseases that lack a definitive etiology, but which are characterized by common inflammatory pathways leading to inflammation, and which may result from, or be trigg ...
.
Severity
No consensus exists about how to classify the severity of psoriasis. Mild psoriasis has been defined as a percentage of body surface area (BSA)≤10, aPsoriasis Area and Severity Index
Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) is the most widely used tool for the measurement of severity of psoriasis. PASI combines the assessment of the severity of lesions and the area affected into a single score in the range 0 (no disease) to ...
(PASI) score ≤10, and a Dermatology Life Quality Index
The Dermatology life Quality Index (DLQI) is a ten-question questionnaire used to measure the impact of skin disease on the quality of life of an affected person. It is designed for people aged 16 years and above.
History
The DLQI was created b ...
(DLQI) score ≤10. Moderate to severe psoriasis was defined by the same group as BSA >10 or PASI score >10 and a DLQI score >10.
The DLQI is a 10-question tool used to measure the impact of several dermatologic diseases on daily functioning. The DLQI score ranges from 0 (minimal impairment) to 30 (maximal impairment) and is calculated with each answer being assigned 0–3 points with higher scores indicating greater social or occupational impairment.
The PASI is the most widely used measurement tool for psoriasis. It assesses the severity of lesions and the area affected and combines these two factors into a single score from 0 (no disease) to 72 (maximal disease). Nevertheless, the PASI can be too unwieldy to use outside of research settings, which has led to attempts to simplify the index for clinical use.
Management
While no cure is available for psoriasis, many treatment options exist. Topical agents are typically used for mild disease, phototherapy for moderate disease, and systemic agents for severe disease. There is no evidence to support the effectiveness of conventional topical and systemic drugs, biological therapy, or phototherapy for acute guttate psoriasis or an acute guttate flare of chronic psoriasis.Topical agents
Topical corticosteroid preparations are the most effective agents when used continuously for eight weeks;retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
Retinoids have many important functions throughout t ...
s and coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoriasi ...
were found to be of limited benefit and may be no better than placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
. Greater benefit has been observed with very potent corticosteroids when compared to potent corticosteroids.
Vitamin D analogue The active natural hormonal form of vitamin D is 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D). This molecule and other naturally occurring forms of vitamin D, including its precursors and metabolites, have been modified to synthesize pharmaceuticals with p ...
s such as paricalcitol
Paricalcitol (chemically it is 19-nor-1,25-(OH)2-vitamin D2. Marketed by Abbott Laboratories under the trade name Zemplar) is a drug used for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (excessive secretion of parathyroid horm ...
are superior to placebo. Combination therapy with vitamin D and a corticosteroid are superior to either treatment alone and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
is superior to coal tar for chronic plaque psoriasis.
For psoriasis of the scalp, a 2016 review found dual therapy (vitamin D analogues and topical corticosteroids) or corticosteroid monotherapy to be more effective and safer than topical vitamin D analogues alone. Due to their similar safety profiles and minimal benefit of dual therapy over monotherapy, corticosteroid monotherapy appears to be an acceptable treatment for short-term treatment.
Moisturizers and emollients such as mineral oil
Mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils.
The name 'mineral oil' by itself is imprecise, ...
, petroleum jelly
Petroleum jelly, petrolatum, white petrolatum, soft paraffin, or multi-hydrocarbon, CAS number 8009-03-8, is a semi-solid mixture of hydrocarbons (with carbon numbers mainly higher than 25), originally promoted as a topical ointment for its h ...
, calcipotriol
Calcipotriol, also known as calcipotriene, is a synthetic derivative of calcitriol, a form of vitamin D. It is used in the treatment of psoriasis. It is safe for long-term application in psoriatic skin conditions.
It was patented in 1985 and a ...
, and decubal (an oil-in-water emollient) were found to increase the clearance of psoriatic plaques. Some emollients have been shown to be even more effective at clearing psoriatic plaques when combined with phototherapy. Certain emollients, though, have no impact on psoriasis plaque clearance or may even decrease the clearance achieved with phototherapy, e.g. the emollient salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substance ...
is structurally similar to para-aminobenzoic acid
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as ''para''-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the ''para'' position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA i ...
, commonly found in sunscreen, and is known to interfere with phototherapy in psoriasis. Coconut oil
frameless , right , alt = A cracked coconut and a bottle of coconut oil
Coconut oil (or coconut butter) is an edible oil derived from the wick, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat; in warmer climates duri ...
, when used as an emollient in psoriasis, has been found to decrease plaque clearance with phototherapy. Medicated creams and ointments applied directly to psoriatic plaques can help reduce inflammation, remove built-up scale, reduce skin turnover, and clear affected skin of plaques. Ointment and creams containing coal tar, dithranol
Dithranol ( INN) or anthralin (USAN and former BAN) is a hydroxyanthrone, anthracene derivative, medicine applied to the skin of people with psoriasis.
It is available as creams, ointment or pastes in 0.1 to 2% strengths (Drithocreme, Dithrocream, ...
, corticosteroids (i.e. desoximetasone), fluocinonide
Fluocinonide (sold under various brand names) is a potent glucocorticoid used topically as an anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of skin disorders such as eczema and seborrhoeic dermatitis. It relieves itching, redness, dryness, crustin ...
, vitamin D3 analogues (for example, calcipotriol), and retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
Retinoids have many important functions throughout t ...
s are routinely used. (The use of the finger tip unit In medicine, a finger tip unit (FTU) is defined as the amount of ointment, cream or other semi-solid dosage form expressed from a tube with a 5 mm diameter nozzle, applied from the distal skin-crease to the tip of the index finger of an adult.F ...
may be helpful in guiding how much topical treatment to use.)
Vitamin D analogues may be useful with steroids; steroids alone have a higher rate of side effects. Vitamin D analogues may allow less steroids to be used.
Another topical therapy used to treat psoriasis is a form of balneotherapy
Balneotherapy ( la, balneum "bath") is a method of treating diseases by bathing, a traditional medicine technique usually practiced at spas. Since ancient times, humans have used hot springs, public baths and thermal medicine for therapeutic eff ...
, which involves daily baths in the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
. This is usually done for four weeks with the benefit attributed to sun exposure and specifically UVB
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
light. This is cost-effective and it has been propagated as an effective way to treat psoriasis without medication. Decreases of PASI scores greater than 75% and remission for several months have commonly been observed. Side effects may be mild such as itchiness, folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
A ...
, sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is ho ...
, poikiloderma
Poikiloderma is a skin condition that consists of areas of hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, telangiectasias and atrophy.
Poikiloderma of Civatte is most frequently seen on the chest or the neck, characterized by red colored pigment on the skin ...
, and a theoretical risk of nonmelanoma cancer or melanoma has been suggested. Some studies indicate no increased risk of melanoma in the long term. Data are inconclusive with respect to nonmelanoma skin cancer risk, but support the idea that the therapy is associated with an increased risk of benign forms of sun-induced skin damage such as, but not limited to, actinic elastosis
Actinic elastosis, also known as solar elastosis, is an accumulation of abnormal elastin (elastic tissue) in the dermis of the skin, or in the conjunctiva of the eye, which occurs as a result of the cumulative effects of prolonged and excessive s ...
or liver spots. Dead Sea balneotherapy is also effective for psoriatic arthritis. Tentative evidence indicates that balneophototherapy, a combination of salt bathes and exposure to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
B-light (UVB), in chronic plaque psoriasis is better than UVB alone.
UV phototherapy
Phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is intentional daily exposure to direct sunlight or similar-intensity artificial light in order to treat medical disorders, especially seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and circadi ...
in the form of sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
has long been used for psoriasis. UVB wavelengths of 311–313 nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
s are most effective, and special lamps have been developed for this application. The exposure time should be controlled to avoid overexposure and burning of the skin. The UVB lamps should have a timer that turns off the lamp when the time ends. The amount of light used is determined by a person's skin type. Increased rates of cancer from treatment appear to be small. Narrowband UVB therapy
PUVA (psoralen and UVA) is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, vitiligo, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizing effe ...
has been demonstrated to have similar efficacy to psoralen and ultraviolet A phototherapy
PUVA (psoralen and UVA) is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, vitiligo, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizing eff ...
(PUVA). A 2013 meta-analysis found no difference in efficacy between NB-UVB and PUVA in the treatment of psoriasis, but NB-UVB is usually more convenient.
One of the problems with clinical phototherapy is the difficulty many people have gaining access to a facility. Indoor tanning resources are almost ubiquitous today and could be considered as a means for people to get UV exposure when dermatologist-provided phototherapy is not available. Indoor tanning is already used by many people as a treatment for psoriasis; one indoor facility reported that 50% of its clients were using the center for psoriasis treatment; another reported 36% were doing the same thing. However, a concern with the use of commercial tanning is that tanning beds that primarily emit UVA might not effectively treat psoriasis. One study found that plaque psoriasis is responsive to erythemogenic doses of either UVA or UVB, as exposure to either can cause dissipation of psoriatic plaques. It does require more energy to reach erythemogenic dosing with UVA.
UV light therapies all have risks; tanning beds are no exception, being listed by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
as carcinogens. Exposure to UV light is known to increase the risks of melanoma and squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas; younger people with psoriasis, particularly those under age 35, are at increased risk from melanoma from UV light treatment. A review of studies recommends that people who are susceptible to skin cancers exercise caution when using UV light therapy as a treatment.
A major mechanism of NB-UVB is the induction of DNA damage in the form of pyrimidine dimer
Pyrimidine dimers are molecular lesions formed from thymine or cytosine bases in DNA via photochemical reactions, commonly associated with direct DNA damage. Ultraviolet light (UV; particularly UVB) induces the formation of covalent linkages betwe ...
s. This type of phototherapy is useful in the treatment of psoriasis because the formation of these dimers interferes with the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subs ...
and stops it. The interruption of the cell cycle induced by NB-UVB opposes the characteristic rapid division of skin cells seen in psoriasis. The activity of many types of immune cells found in the skin is also effectively suppressed by NB-UVB phototherapy treatments. The most common short-term side effect of this form of phototherapy is redness of the skin; less common side effects of NB-UVB phototherapy are itching and blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled wi ...
ing of the treated skin, irritation of the eyes in the form of conjunctival inflammation or inflammation of the cornea, or cold sores
Herpes labialis, commonly known as cold sores or fever blisters, is a type of infection by the herpes simplex virus that affects primarily the lip. Symptoms typically include a burning pain followed by small blisters or sores. The first attack ...
due to reactivation of the herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
in the skin surrounding the lips. Eye protection is usually given during phototherapy treatments.
PUVA combines the oral or topical administration of psoralen with exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) light. The mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targe ...
of PUVA is unknown, but probably involves activation of psoralen by UVA light, which inhibits the abnormally rapid production of the cells in psoriatic skin. There are multiple mechanisms of action associated with PUVA, including effects on the skin's immune system. PUVA is associated with nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, burning, and itching. Long-term treatment is associated with squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
(but not with melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
). A combination therapy for moderate to severe psoriasis using PUVA plus acitretin
Acitretin (trade names Soriatane and Neotigason) is a second-generation retinoid. It is taken orally, and is typically used for psoriasis.
Acitretin is an oral retinoid used in the treatment of severe resistant psoriasis. Because of the potentia ...
resulted in benefit, but acitretin use has been associated with birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
s and liver damage
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the sig ...
.
Systemic agents
Psoriasis resistant to topical treatment andphototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is intentional daily exposure to direct sunlight or similar-intensity artificial light in order to treat medical disorders, especially seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and circadi ...
may be treated with systemic therapies including medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
s by mouth or injectable treatments. People undergoing systemic treatment must have regular blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
and liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
to check for medication toxicities. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
must be avoided for most of these treatments. The majority of people experience a recurrence of psoriasis after systemic treatment is discontinued.
Non-biologic systemic treatments frequently used for psoriasis include methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, ciclosporin
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is a natural product. It is taken orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, ...
, hydroxycarbamide
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, essential thrombocythemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, and cervical cancer. In sickle-cell disease it increases fetal hemoglobin and d ...
, fumarate
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297.
The salts and esters are known as f ...
s such as dimethyl fumarate
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) is the methyl ester of fumaric acid and is named after the earth smoke plant (''Fumaria officinalis''). Dimethyl fumarate combined with three other fumaric acid esters (FAEs) is solely licensed in Germany as an oral thera ...
, and retinoids
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
Retinoids have many important functions throughout ...
. Methotrexate and ciclosporin are medications that suppress the immune system; retinoids are synthetic forms of vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably bet ...
. These agents are also regarded as first-line treatments for psoriatic erythroderma. Oral corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
s should not be used, for they can severely flare psoriasis upon their discontinuation.
Biologics
A biopharmaceutical, also known as a biological medical product, or biologic, is any pharmaceutical drug product manufactured in, extracted from, or semisynthesized from biological sources. Different from totally synthesized pharmaceuticals, th ...
are manufactured proteins that interrupt the immune process involved in psoriasis. Unlike generalized immunosuppressive medical therapies such as methotrexate, biologics target specific aspects of the immune system contributing to psoriasis. These medications are generally well-tolerated, and limited long-term outcome data have demonstrated biologics to be safe for long-term use in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. However, due to their immunosuppressive actions, biologics have been associated with a small increase in the risk for infection.
Guidelines regard biologics as third-line treatment for plaque psoriasis following inadequate response to topical treatment, phototherapy, and non-biologic systemic treatments. The safety of biologics during pregnancy has not been assessed. European guidelines recommend avoiding biologics if a pregnancy is planned; anti-TNF therapies such as infliximab are not recommended for use in chronic carriers of the hepatitis B virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
Disease
Despite there bein ...
or individuals infected with HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
.
Several monoclonal antibodies target cytokines, the molecules that cells use to send inflammatory signals to each other. TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
is one of the main executor inflammatory cytokines. Four monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ca ...
(MAbs) (infliximab
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spon ...
, adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativ ...
, golimumab
Golimumab is a human monoclonal antibody which is used as an immunosuppressive medication and sold under the brand name Simponi. Golimumab targets tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), a pro-inflammatory molecule and hence is a TNF inhibitor. ...
, and certolizumab pegol
Certolizumab pegol, sold under the brand name Cimzia, is a biologic medication for the treatment of Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. It is a fragment of a monoclonal antibody specific to tumor ...
) and one recombinant TNF-α decoy receptor A decoy receptor is a receptor that is able to recognize and bind specific growth factors or cytokines efficiently, but is not structurally able to signal or activate the intended receptor complex. It acts as an inhibitor, binding a ligand and keepi ...
, etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. It h ...
, have been developed to inhibit TNF-α signaling. Additional monoclonal antibodies, such as ixekizumab
Ixekizumab, sold under the brand name Taltz, is an injectable medication for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Chemically, it is a form of a humanized monoclonal antibody. The substance acts by binding interleukin 17A and neutralizing it, re ...
, have been developed against pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit the inflammatory pathway at a different point than the anti-TNF-α antibodies. IL-12 and IL-23 share a common domain, p40, which is the target of the FDA-approved ustekinumab
Ustekinumab, sold under the brand name Stelara is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, for the treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, targeting both IL-12 and ...
. In 2017 the US FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
approved guselkumab
Guselkumab, sold under the brand name Tremfya, is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-23 used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Medical uses
Guselkumab is indicated to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, and psoriatic arthri ...
for plaque psoriasis.Novel Drug Approvals for 2017There have been few studies of the efficacy of anti-TNF medications for psoriasis in children. One randomized control study suggested that 12 weeks of etanercept treatment reduced the extent of psoriasis in children with no lasting adverse effects. Two medications that target T cells are
efalizumab
Efalizumab (trade name Raptiva, Genentech, Merck Serono) is a formerly available medication designed to treat autoimmune diseases, originally marketed to treat psoriasis. As implied by the suffix ''-zumab'', it is a recombinant humanized monoclon ...
and alefacept
Alefacept is a genetically engineered immunosuppressive drug. It was sold under the brand name Amevive in Canada, the United States, Israel, Switzerland and Australia. In 2011, the manufacturers made a decision to cease promotion, manufacturing, d ...
. Efalizumab is a monoclonal antibody that specifically targets the CD11a
Integrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide), also known as ITGAL, is a protein that in human is encoded by ''ITGAL'' gene. CD11a functions in the immune system. It is involved in cellular a ...
subunit of LFA-1 Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) is an integrin found on lymphocytes and other leukocytes. LFA-1 plays a key role in emigration, which is the process by which leukocytes leave the bloodstream to enter the tissues. LFA-1 also mediates ...
. It also blocks the adhesion molecules on the endothelial
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
cells that line blood vessels, which attract T cells. Efalizumab was voluntarily withdrawn from the European market in February 2009, and from the U.S. market in June 2009, by the manufacturer due to the medication's association with cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare and often fatal viral disease characterized by progressive damage (''-pathy'') or inflammation of the white matter (''leuko-'') of the brain (''-encephalo-'') at multiple locations (''mu ...
. Alefacept also blocks the molecules that dendritic cells use to communicate with T cells and even causes natural killer cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and repres ...
s to kill T cells as a way of controlling inflammation. Apremilast
Apremilast, sold under the brand name Otezla among others, is a medication for the treatment of certain types of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. It may also be useful for other immune system-related inflammatory diseases. The drug acts as a se ...
may also be used.
Individuals with psoriasis may develop neutralizing antibodies
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralization renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic.
Neutralizing antibod ...
against monoclonal antibodies. Neutralization occurs when an antidrug antibody prevents a monoclonal antibody such as infliximab from binding antigen in a laboratory test. Specifically, neutralization occurs when the anti-drug antibody binds to infliximab's antigen binding site instead of TNF-α. When infliximab no longer binds tumor necrosis factor alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, it no longer decreases inflammation, and psoriasis may worsen. Neutralizing antibodies have not been reported against etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. It h ...
, a biologic medication that is a fusion protein composed of two TNF-α receptors. The lack of neutralizing antibodies against etanercept is probably secondary to the innate presence of the TNF-α receptor, and the development of immune tolerance
Immune tolerance, or immunological tolerance, or immunotolerance, is a state of unresponsiveness of the immune system to substances or tissue that would otherwise have the capacity to elicit an immune response in a given organism. It is induced by ...
.
A 2021 meta-analysis found that ixekizumab, secukinumab
Secukinumab, sold under the brand name Cosentyx, is a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. It binds to the protein interleukin (IL)-17A and is marketed by Novartis ...
, brodalumab
Brodalumab, sold under the brand name Siliq in the US and Kyntheum in the EU, is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
In February 2017, it received US FDA approval to treat moderate to severe plaque ps ...
, guselkumab
Guselkumab, sold under the brand name Tremfya, is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-23 used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Medical uses
Guselkumab is indicated to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, and psoriatic arthri ...
, certolizumab, and ustekinumab were the most effective biologics for treating psoriasis. In general, anti-IL17, anti-IL12/23, anti-IL23, and anti-TNF alpha biologics were found to be more effective than traditional systemic treatments. The immunologic pathways of psoriasis involve Th9, Th17
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg different ...
, Th1 lymphocytes, and IL-22. The aforementioned biologic agents hinder different aspects of these pathways.
Another treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis is fumaric acid esters (FAE) which may be similar in effectiveness to methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
.
It has been theorized that antistreptococcal medications may improve guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis; however, the limited studies do not show that antibiotics are effective.
Surgery
Limited evidence suggests removal of the tonsils may benefit people with chronic plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and palmoplantar pustulosis.Diet
Uncontrolled studies have suggested that individuals with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis may benefit from a diet supplemented withfish oil
Fish oil is oil derived from the tissues of oily fish. Fish oils contain the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), precursors of certain eicosanoids that are known to reduce inflammation in the body a ...
rich in eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-c ...
(EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. In physiological literature, it is given the name 22:6(n-3). It can be synthesized from alpha-lino ...
(DHA). A low-calorie diet appears to reduce the severity of psoriasis. Diet recommendations include consumption of cold water fish (preferably wild fish, not farmed) such as salmon, herring, and mackerel; extra virgin olive oil; legumes; vegetables; fruits; and whole grains; and avoid consumption of alcohol, red meat, and dairy products (due to their saturated fat). The effect of consumption of caffeine (including coffee, black tea, mate, and dark chocolate) remains to be determined.
Many patients report improvements after consuming less tobacco, caffeine, sugar, nightshades
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and orna ...
(tomatoes, eggplant, peppers, paprika and white potatoes) and taking probiotics and oral Vitamin D.
There is a higher rate of celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barl ...
among people with psoriasis. When adopting a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
, disease severity generally decreases in people with celiac disease and those with anti-gliadin antibodies
Anti-gliadin antibodies are produced in response to gliadin, a prolamin found in wheat. In bread wheat it is encoded by three different alleles, AA, BB, and DD. These alleles can produce slightly different gliadins, which can cause the body to pro ...
.
Prognosis
Most people with psoriasis experience nothing more than mild skin lesions that can be treated effectively with topical therapies. Psoriasis is known to hurt the quality of life of both the affected person and the individual's family members. Depending on the severity and location of outbreaks, individuals may experience significant physical discomfort and some disability. Itching and pain can interfere with basic functions, such as self-care and sleep. Participation in sporting activities, certain occupations, and caring for family members can become difficult activities for those with plaques located on their hands and feet. Plaques on the scalp can be particularly embarrassing, as flaky plaque in the hair can be mistaken fordandruff
Dandruff is a skin condition that mainly affects the scalp. Symptoms include flaking and sometimes mild itchiness. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. A more severe form of the condition, which includes inflammation of the skin, ...
.
Individuals with psoriasis may feel self-conscious about their appearance and have a poor self-image that stems from fear of public rejection and psychosexual concerns. Psoriasis has been associated with low self-esteem and depression is more common among those with the condition. People with psoriasis often feel prejudiced against due to the commonly held incorrect belief that psoriasis is contagious. Psychological distress can lead to significant depression and social isolation
Social isolation is a state of complete or near-complete lack of contact between an individual and society. It differs from loneliness, which reflects temporary and involuntary lack of contact with other humans in the world. Social isolation c ...
; a high rate of thoughts about suicide has been associated with psoriasis. Many tools exist to measure the quality of life of people with psoriasis and other dermatological disorders. Clinical research has indicated individuals often experience a diminished quality of life. Children with psoriasis may encounter bullying
Bullying is the use of force, coercion, hurtful teasing or threat, to abuse, aggressively dominate or intimidate. The behavior is often repeated and habitual. One essential prerequisite is the perception (by the bully or by others) of an imba ...
.
Several conditions are associated with psoriasis. These occur more frequently in older people. Nearly half of individuals with psoriasis over the age of 65 have at least three comorbidities
In medicine, comorbidity - from Latin morbus ("sickness"), co ("together"), -ity (as if - several sicknesses together) - is the presence of one or more additional conditions often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary c ...
(concurrent conditions), and two-thirds have at least two comorbidities.
Cardiovascular disease
Psoriasis has been associated withobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
and several other cardiovascular and metabolic disturbances. The number of new cases per year of diabetes is 27% higher in people affected by psoriasis than in those without the condition. Severe psoriasis may be even more strongly associated with the development of diabetes than mild psoriasis. Younger people with psoriasis may also be at increased risk for developing diabetes. Individuals with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis have a slightly higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks when compared to the general population. Cardiovascular disease risk appeared to be correlated with the severity of psoriasis and its duration. There is no strong evidence to suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of death from cardiovascular events. Methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
may provide a degree of protection for the heart.
The odds of having hypertension are 1.58 times higher in people with psoriasis than those without the condition; these odds are even higher with severe cases of psoriasis. A similar association was noted in people who have psoriatic arthritis—the odds of having hypertension were found to be 2.07 times greater when compared to odds of the general population. The link between psoriasis and hypertension is not currently understood. Mechanisms hypothesized to be involved in this relationship include the following: dysregulation of the renin–angiotensin system
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.
When renal blood flow is reduced, juxt ...
, elevated levels of endothelin 1
Endothelin 1 (ET-1), also known as preproendothelin-1 (PPET1), is a potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. The protein encoded by this gene ''EDN1'' is proteolytically processed to release endothelin 1. Endotheli ...
in the blood, and increased oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily Detoxification, detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances ...
. The number of new cases of the heart rhythm abnormality atrial fibrillation is 1.31 times higher in people with mild psoriasis and 1.63 times higher in people with severe psoriasis. There may be a slightly increased risk of stroke associated with psoriasis, especially in severe cases. Treating high levels of cholesterol with statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low- ...
s has been associated with decreased psoriasis severity, as measured by PASI score, and has also been associated with improvements in other cardiovascular disease risk factors such as markers of inflammation. These cardioprotective effects are attributed to ability of statins to improve blood lipid profile and because of their anti-inflammatory effects. Statin use in those with psoriasis and hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids (fats, cholesterol, or triglycerides) or lipoproteins in the blood. citing: and The term ''hyperlipidemia'' refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbre ...
was associated with decreased levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin- ...
and TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
as well as decreased activity of the immune protein LFA-1 Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) is an integrin found on lymphocytes and other leukocytes. LFA-1 plays a key role in emigration, which is the process by which leukocytes leave the bloodstream to enter the tissues. LFA-1 also mediates ...
. Compared to individuals without psoriasis, those affected by psoriasis are more likely to satisfy the criteria for metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndrome ...
.
Other diseases
The rates ofCrohn disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension ...
and ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and a ...
are increased when compared with the general population, by a factor of 3.8 and 7.5 respectively. People with psoriasis also have a higher risk of celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barl ...
. Few studies have evaluated the association of multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
with psoriasis, and the relationship has been questioned. Psoriasis has been associated with a 16% increase in overall relative risk for non-skin cancer, thought to be attributed to systemic therapy, particularly methotrexate. People treated with long term systemic therapy for psoriasis have a 52% increased risk cancers of the lung and bronchus, a 205% increase in the risk of developing cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract, a 31% increase in the risk of developing cancers of the urinary tract, a 90% increase in the risk of developing liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
, and a 46% increase in the risk of developing pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of t ...
. The risk for development of non-melanoma skin cancers is also increased. Psoriasis increases the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
Squamous-cell skin cancer, also known as cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), is one of the main types of skin cancer along with basal cell cancer and melanoma. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but can also form an ulcer. O ...
by 431% and increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raise ...
by 100%. There is no increased risk of melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
associated with psoriasis. People with psoriasis have a higher risk of developing cancer.
Epidemiology
Psoriasis is estimated to affect 2–4% of the population of the western world. The rate of psoriasis varies according to age, region and ethnicity; a combination of environmental and genetic factors is thought to be responsible for these differences. It can occur at any age, although it most commonly appears for the first time between the ages of 15 and 25 years. Approximately one third of people with psoriasis report being diagnosed before age 20. Psoriasis affects bothsex
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones (ova, oft ...
es equally.
Psoriasis affects about 6.7million Americans and occurs more frequently in adults.
Psoriasis is about five times more common in people of European descent than in people of Asian descent.
People with inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine a ...
such as Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis are at an increased risk of developing psoriasis. Psoriasis is more common in countries farther from the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
. Persons of white European ancestry are more likely to have psoriasis and the condition is relatively uncommon in African Americans and extremely uncommon in Native Americans.
History
Scholars believe psoriasis to have been included among the various skin conditions called ''tzaraath
''Tzaraath'' (Hebrew צָרַעַת ''ṣāraʿaṯ''), variously transcribed into English and frequently mistranslated as leprosy, describes various ritually unclean disfigurative conditions of the skin, hair of the beard and head, clothing mad ...
'' (translated as leprosy) in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
, a condition imposed as a punishment for slander. The person was deemed "impure" (see ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
tumah and taharah
In Jewish law, ''ṭumah'' (, ) and ''ṭaharah'' (, ) are the state of being ritually "impure" and "pure", respectively. The Hebrew noun ''ṭum'ah'', meaning "impurity", describes a state of ritual impurity. A person or object which contracts ' ...
) during their affected phase and is ultimately treated by the kohen
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally b ...
. However, it is more likely that this confusion arose from the use of the same Greek term for both conditions. The Greeks used the term lepra (λεπρα) for scaly skin conditions. They used the term psora to describe itchy skin conditions. It became known as ''Willan's lepra'' in the late 18th century when English dermatologist
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
s Robert Willan
__NOTOC__
Robert Willan (12 November 1757, near Sedbergh, Yorkshire – 7 April 1812, in Madeira) was an English physician and the founder of dermatology as a medical specialty.
Life
Willan was educated at Sedbergh School, and received his M ...
and Thomas Bateman differentiated it from other skin diseases. Leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damag ...
, they said, is distinguished by the regular, circular form of patches, while psoriasis is always irregular. Willan identified two categories: ''leprosa graecorum'' and ''psora leprosa''.
Psoriasis is thought to have first been described in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
by Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus ( 25 BC 50 AD) was a Roman encyclopaedist, known for his extant medical work, ''De Medicina'', which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The ''De Medicina'' is a primary source on d ...
. The British dermatologist Thomas Bateman
Thomas Bateman (8 November 1821 (baptised) – 28 August 1861) was an English antiquary and barrow-digger.
Biography
Thomas Bateman was born in Rowsley, Derbyshire, England, the son of the amateur archaeologist William Bateman. After the death ...
described a possible link between psoriasis and arthritic symptoms in 1813.
The history of psoriasis is littered with treatments of dubious effectiveness and high toxicity. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Fowler's solution Fowler's solution is a solution containing 1% potassium arsenite (KAsO2), and was once prescribed as a remedy or a tonic. Thomas Fowler (1736–1801) of Stafford, England, proposed the solution in 1786 as a substitute for a patent medicine, "tast ...
, which contains a poisonous
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
and carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
compound, was used by dermatologists as a treatment for psoriasis. Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
was also used for psoriasis treatment during this time period. Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, and phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ...
were also commonly used treatments for psoriasis during this era when it was incorrectly believed that psoriasis was an infectious disease. Coal tars were widely used with ultraviolet light irradiation as a topical treatment approach in the early 1900s. During the same time period, psoriatic arthritis cases were treated with intravenously administered gold preparations in the same manner as rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
.
Society and culture
The International Federation of Psoriasis Associations (IFPA) is the global umbrella organization for national and regional psoriasis associations and also gathers the leading experts in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis research for scientific conferences every three years. The Psoriasis International Network, a program of the Fondation René Touraine, gathers dermatologists,rheumatologist
Rheumatology (Greek ''ῥεῦμα'', ''rheûma'', flowing current) is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatolog ...
s and other caregivers involved in the management of psoriasis. Non-profit organizations like the National Psoriasis Foundation in the United States, the Psoriasis Association in the United Kingdom, and Psoriasis Australia offer advocacy and education about psoriasis in their respective countries.
Cost
The annual cost for treating psoriasis in the United States is estimated as high as $32.5billion, including $12.2billion in direct costs. Pharmacy costs are the main source of direct expense, with biologic therapy the most prevalent. These costs increase significantly when co-morbid conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, lung disease and psychiatric disorders are factored in. Expenses linked to co-morbidities are estimated at an additional $23,000 per person per year.Research
The role ofinsulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cell (biology), cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood gluco ...
in the pathogenesis of psoriasis is under investigation. Preliminary research has suggested that antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
s such as polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of ...
s may have beneficial effects on the inflammation characteristic of psoriasis.
Many novel medications being researched during the 2010s target the Th17
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg different ...
/ IL-23 axis, particularly IL-23p19 inhibitors, as IL-23p19 is present in increased concentrations in psoriasis skin lesions while contributing less to protection against opportunistic infections. Other cytokines such as IL-17 and IL-22 also have been targets for inhibition as they play important roles in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Another avenue of research has focused on the use of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors to treat psoriasis. Oral agents being investigated during the 2010s as alternatives to medications administered by injection include Janus kinase inhibitor
A Janus kinase inhibitor, also known as JAK inhibitor or jakinib, is a type of immune modulating medication, which inhibits the activity of one or more of the Janus kinase family of enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, TYK2), thereby interfering with the JA ...
s, protein kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and t ...
inhibitors, mitogen-activated protein kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to ...
inhibitors, and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, all of which have proven effective in various phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. These agents have potentially severe side-effects due to their immunosuppressive mechanisms.
References
Further reading
* * *External links
* * {{Authority control Autoimmune diseases Cutaneous conditions Psoriasis Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate