Poly Depletion Effect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Polysilicon depletion effect is the phenomenon in which unwanted variation of threshold voltage of the
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
devices using polysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produce ...
as gate material is observed, leading to unpredicted behavior of the electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical ...
. Because of this variation High-k Dielectric Metal Gates (HKMG) were introduced to solve the issue.
Polycrystalline silicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produ ...
, also called polysilicon, is a material consisting of small silicon crystals. The latter differs from mocrystalline silicon used for semiconductor electronics and solar cells
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physics, physical and Chemical substance, chemical phenomenon.amorphous silicon, used for thin film devices and solar cells.
 ''Vgs'' = Gate Voltage
''Vgs'' = Gate Voltage
''Vth'' = Threshold Voltage
n+ = Highly doped N region In ''figure 1(a) of'' an '' nMOS'' transistor it is observed that the free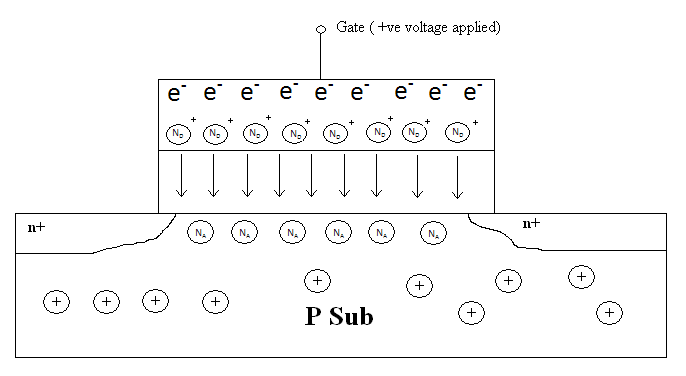 In an NMOS with n+ Polysilicon gate, the poly depletion effect aids in the channel formation by the combined effect of the ''(+)ve'' field of donor ions (ND) and the externally applied ''(+)ve'' field at gate terminal. Basically the accumulation of the ''(+)ve'' charged Donor ions (ND) on the polysilicon enhances the Formation of the inversion channel and when ' an inversion layer is formed, which can be seen in the figure 1(b) where the inversion channel is formed of acceptor ions (NA) (
In an NMOS with n+ Polysilicon gate, the poly depletion effect aids in the channel formation by the combined effect of the ''(+)ve'' field of donor ions (ND) and the externally applied ''(+)ve'' field at gate terminal. Basically the accumulation of the ''(+)ve'' charged Donor ions (ND) on the polysilicon enhances the Formation of the inversion channel and when ' an inversion layer is formed, which can be seen in the figure 1(b) where the inversion channel is formed of acceptor ions (NA) (
Reduction of Polysilicon Gate Depletion Effect in NMOS
*
Fabrication of microprocessor by intel
Gate material choice
The gate contact may be ofpolysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produce ...
or metal, previously polysilicon was chosen over metal because the interfacing between polysilicon and gate oxide ( SiO2) was favorable. But the conductivity of the poly-silicon layer is very low and because of this low conductivity, the charge accumulation is low, leading to a delay in channel formation and thus unwanted delays in circuits. The poly layer is doped with N-type or P-type impurity to make it behave like a perfect conductor and reduce the delay.
Doped polysilicon gate disadvantages
 ''Vgs'' = Gate Voltage
''Vgs'' = Gate Voltage''Vth'' = Threshold Voltage
n+ = Highly doped N region In ''figure 1(a) of'' an '' nMOS'' transistor it is observed that the free
majority carriers
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and electron hole, holes. Th ...
are scattered throughout the structure because of the absence of an external electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ...
. When a positive field is applied on the gate, the scattered carriers arrange themselves like ''figure 1(b)'', the electrons move closer toward the gate terminal but due to the open circuit configuration they don't start to flow. As a result of the separation of charges a depletion region is formed on the polysilicon-oxide interface, which has a direct effect on the channel formation in MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
s.
 In an NMOS with n+ Polysilicon gate, the poly depletion effect aids in the channel formation by the combined effect of the ''(+)ve'' field of donor ions (ND) and the externally applied ''(+)ve'' field at gate terminal. Basically the accumulation of the ''(+)ve'' charged Donor ions (ND) on the polysilicon enhances the Formation of the inversion channel and when ' an inversion layer is formed, which can be seen in the figure 1(b) where the inversion channel is formed of acceptor ions (NA) (
In an NMOS with n+ Polysilicon gate, the poly depletion effect aids in the channel formation by the combined effect of the ''(+)ve'' field of donor ions (ND) and the externally applied ''(+)ve'' field at gate terminal. Basically the accumulation of the ''(+)ve'' charged Donor ions (ND) on the polysilicon enhances the Formation of the inversion channel and when ' an inversion layer is formed, which can be seen in the figure 1(b) where the inversion channel is formed of acceptor ions (NA) (minority carriers
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is used ...
). Polysilicon depletion can vary laterally across a transistor depending on the fabrication process, which can lead to significant transistor variability in certain transistor dimensions.
Metal gates re-introduced
For the above reason as the devices go down on the scaling (32-28nm nodes) poly gates are being replaced by metal gates. The following technology is known as High-k Dielectric Metal Gate (HKMG) integration. In 2011Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
has released a press-kit regarding their fabrication procedures of different nodes, which showed the use of Metal gate technology.
Doped polysilicon was preferred earlier as gate material in MOS devices. Polysilicons were used as their work function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" m ...
matched with the Si substrate (which results in the low threshold voltage of MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
). Metal gates were re-introduced at the time when SiO2 dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
s are being replaced by high-k dielectrics like Hafnium oxide
Hafnium(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also known as hafnium dioxide or hafnia, this colourless solid is one of the most common and stable compounds of hafnium. It is an electrical insulator with a band gap of 5.3~5.7 eV. H ...
as gate oxide in the mainstream CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
technology. Also at the interface with gate dielectric, Polysilicon forms an SiOx layer. Moreover, there remains a high probability for Fermi level pinning to occur. So the effect with doped poly is an undesired reduction of threshold voltage that wasn't taken into account during circuit simulation. In order to avoid this kind of variation in vth of the MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
, at present metal gate is preferred over Polysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produce ...
.
See also
Reduction of Polysilicon Gate Depletion Effect in NMOS
*
Drain-induced barrier lowering
Drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) is a short-channel effect in MOSFETs referring originally to a reduction of threshold voltage of the transistor at higher drain voltages.
In a classic planar field-effect transistor with a long channel, the bo ...
* Gate materialFabrication of microprocessor by intel
References
{{Reflist Transistors Semiconductor devices Semiconductor technology MOSFETs