Politics Of Idaho on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the
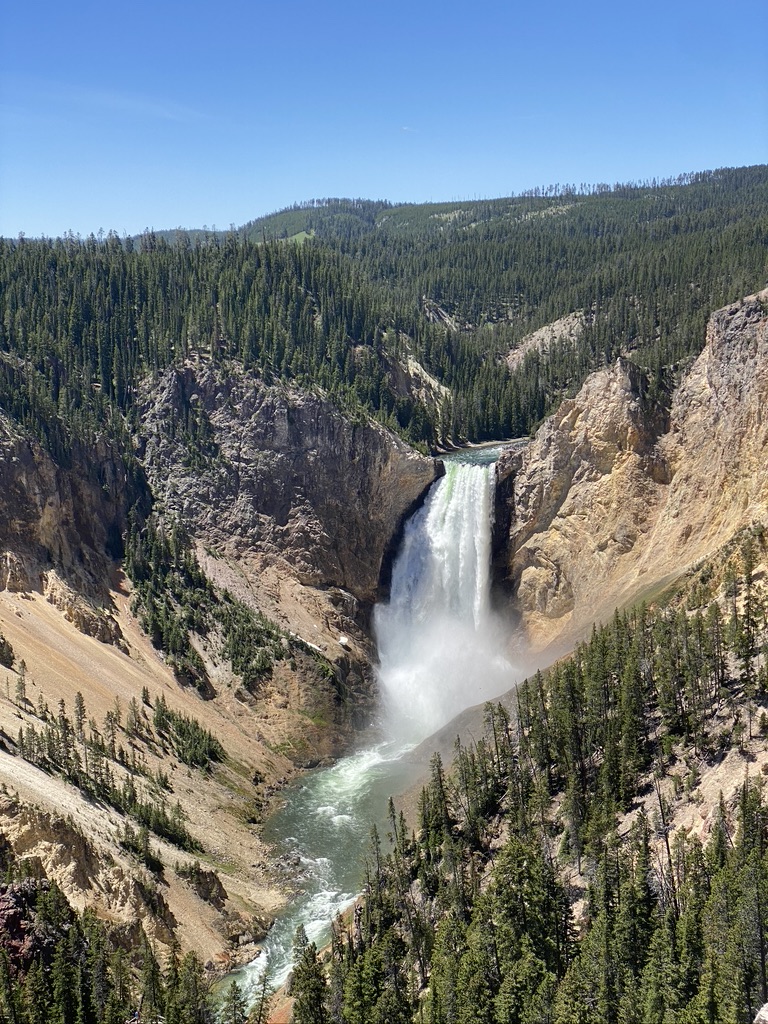 The vast majority of Idaho's population lives in the Snake River Plain, a valley running from across the entirety of southern Idaho from east to west. The valley contains the major cities of Boise,
The vast majority of Idaho's population lives in the Snake River Plain, a valley running from across the entirety of southern Idaho from east to west. The valley contains the major cities of Boise,
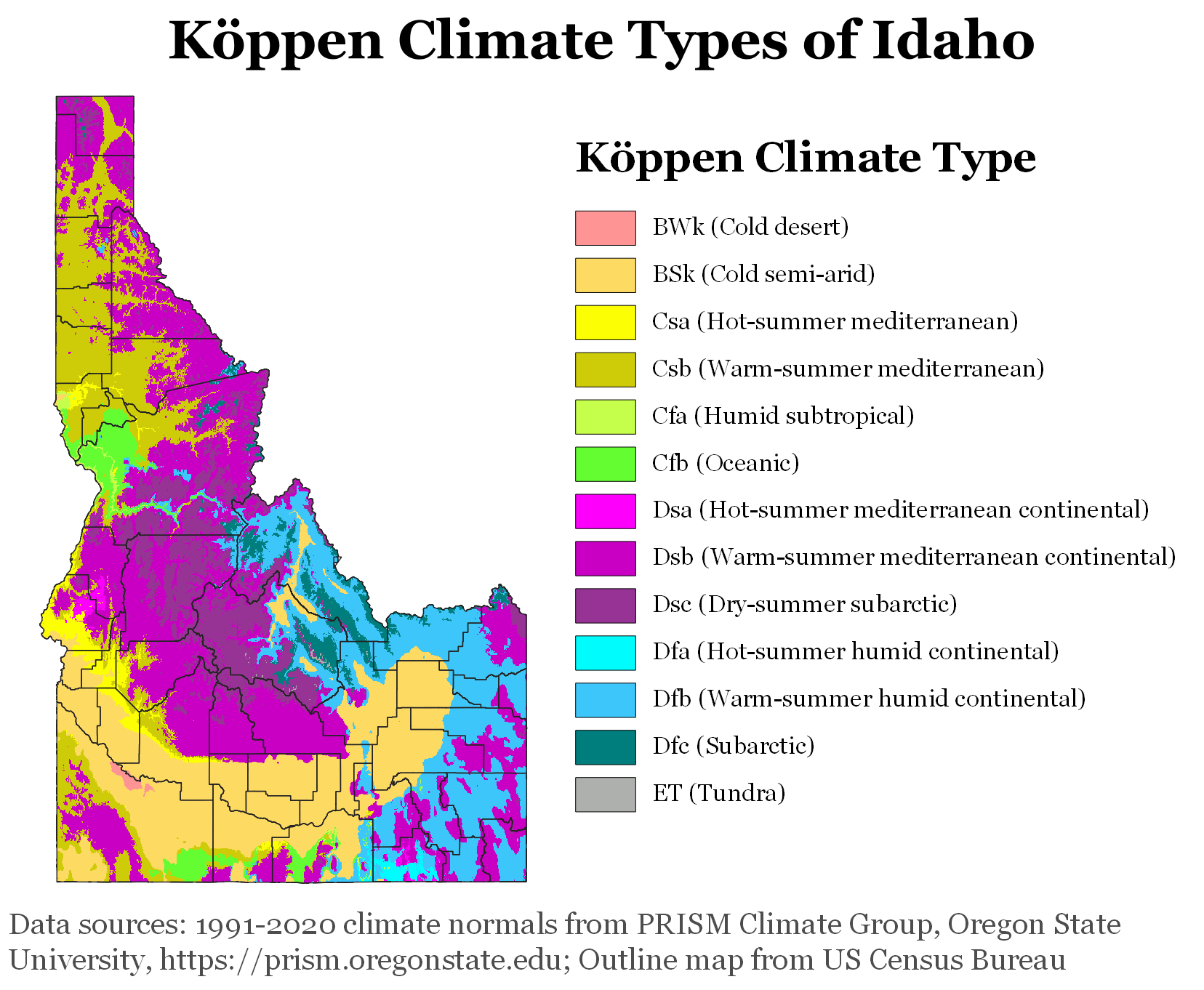 Idaho's climate varies widely. Although the state's western border is about from the Pacific Ocean, the maritime influence is still felt in Idaho; especially, in the winter when cloud cover, humidity, and precipitation are at their maximum extent. This influence has a moderating effect in the winter where temperatures are not as low as would otherwise be expected for a northern state with predominantly high elevations. In the panhandle, moist air masses from the coast are released as precipitation over the North Central Rockies forests, creating the
Idaho's climate varies widely. Although the state's western border is about from the Pacific Ocean, the maritime influence is still felt in Idaho; especially, in the winter when cloud cover, humidity, and precipitation are at their maximum extent. This influence has a moderating effect in the winter where temperatures are not as low as would otherwise be expected for a northern state with predominantly high elevations. In the panhandle, moist air masses from the coast are released as precipitation over the North Central Rockies forests, creating the




 The United States Census Bureau determined Idaho's population was 1,900,923 on July 1, 2021, a 21% increase since the
The United States Census Bureau determined Idaho's population was 1,900,923 on July 1, 2021, a 21% increase since the  According to the 2017
According to the 2017  ''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
 According to the
According to the
US ID AmericanFalls.jpg, American Falls Dam
Wheat harvest.jpg, Wheat harvest on the Palouse
 As of 2017, the primary energy source in Idaho was hydropower, and the energy companies had a total retail sales of 23,793,790 megawatt hours (MWh). As of 2017, Idaho had a regulated electricity market, with the Idaho Public Utilities Commission regulating the three major utilities of Avista Utilities, Idaho Power, and Rocky Mountain Power.
Idaho imports most of the energy it consumes. Imports account for more than 80% of energy consumption, including all of Idaho's natural gas and petroleum supplies and more than half of its electricity. Of the electricity consumed in Idaho in 2005, 48% came from hydroelectricity, 42% was generated by burning coal and 9% was generated by burning natural gas. The remainder came from other renewable sources, such as wind.
The state's river basins allow hydroelectric power plants to provide 556,000 MWh, which amounts to about three-fourths of Idaho's electricity generated in the state. Washington State provides most of the natural gas used in Idaho through one of the two major pipeline systems supplying the state. Although the state relies on out-of-state sources for its entire natural gas supply, it uses natural gas-fired plants to generate 127,000 MWh, or about ten percent of its output. Coal-fired generation and the state's small array of wind turbines supplies the remainder of the state's electricity output. The state produces 739,000 MWh but still needs to import half of its electricity from out-of-state to meet demand.
In addition, Idaho also has the 6th fastest growing population in the United States with the population expected to increase by 31% from 2008 to 2030. This projected increase in population will contribute to a 42% increase in demand by 2030, further straining Idaho's finite hydroelectric resources.
Idaho has an upper-boundary estimate of development potential to generate 44,320 GWh/year from 18,076 MW of wind power, and 7,467,000 GWh/year from solar power using 2,061,000 MW of photovoltaics (PV), including 3,224 MW of rooftop photovoltaics, and 1,267,000 MW of
As of 2017, the primary energy source in Idaho was hydropower, and the energy companies had a total retail sales of 23,793,790 megawatt hours (MWh). As of 2017, Idaho had a regulated electricity market, with the Idaho Public Utilities Commission regulating the three major utilities of Avista Utilities, Idaho Power, and Rocky Mountain Power.
Idaho imports most of the energy it consumes. Imports account for more than 80% of energy consumption, including all of Idaho's natural gas and petroleum supplies and more than half of its electricity. Of the electricity consumed in Idaho in 2005, 48% came from hydroelectricity, 42% was generated by burning coal and 9% was generated by burning natural gas. The remainder came from other renewable sources, such as wind.
The state's river basins allow hydroelectric power plants to provide 556,000 MWh, which amounts to about three-fourths of Idaho's electricity generated in the state. Washington State provides most of the natural gas used in Idaho through one of the two major pipeline systems supplying the state. Although the state relies on out-of-state sources for its entire natural gas supply, it uses natural gas-fired plants to generate 127,000 MWh, or about ten percent of its output. Coal-fired generation and the state's small array of wind turbines supplies the remainder of the state's electricity output. The state produces 739,000 MWh but still needs to import half of its electricity from out-of-state to meet demand.
In addition, Idaho also has the 6th fastest growing population in the United States with the population expected to increase by 31% from 2008 to 2030. This projected increase in population will contribute to a 42% increase in demand by 2030, further straining Idaho's finite hydroelectric resources.
Idaho has an upper-boundary estimate of development potential to generate 44,320 GWh/year from 18,076 MW of wind power, and 7,467,000 GWh/year from solar power using 2,061,000 MW of photovoltaics (PV), including 3,224 MW of rooftop photovoltaics, and 1,267,000 MW of

 Major federal aid highways in Idaho:
Major federal aid highways in Idaho:

 Idaho's legislature is part-time. Because of this, Idaho's legislators are considered "citizen legislators", meaning their position as a legislator is not their main occupation. However, the session may be extended if necessary, and often is.
Terms for both the
Idaho's legislature is part-time. Because of this, Idaho's legislators are considered "citizen legislators", meaning their position as a legislator is not their main occupation. However, the session may be extended if necessary, and often is.
Terms for both the
 After the Civil War, many Midwestern and Southern Democrats moved to the
After the Civil War, many Midwestern and Southern Democrats moved to the
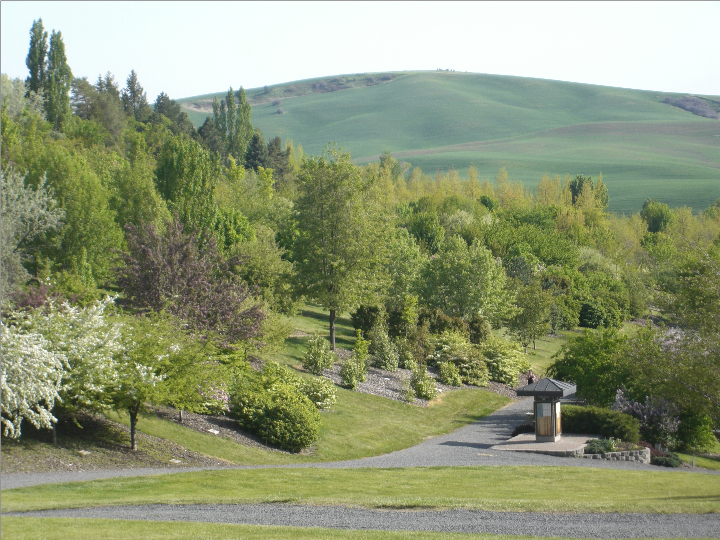

 The Idaho State Board of Education oversees three comprehensive universities. The University of Idaho in Moscow was the first university in the state (founded in 1889). It opened its doors in 1892 and is the land-grant institution and primary research university of the state. Idaho State University in Pocatello opened in 1901 as the Academy of Idaho, attained four-year status in 1947 and university status in 1963. Boise State University is the most recent school to attain university status in Idaho. The school opened in 1932 as Boise Junior College and became Boise State University in 1974. Lewis-Clark State College in Lewiston is the only public, non-university four-year college in Idaho. It opened as a normal school in 1893.
Idaho has four regional community colleges: North Idaho College in Coeur d'Alene; College of Southern Idaho in Twin Falls; College of Western Idaho in
The Idaho State Board of Education oversees three comprehensive universities. The University of Idaho in Moscow was the first university in the state (founded in 1889). It opened its doors in 1892 and is the land-grant institution and primary research university of the state. Idaho State University in Pocatello opened in 1901 as the Academy of Idaho, attained four-year status in 1947 and university status in 1963. Boise State University is the most recent school to attain university status in Idaho. The school opened in 1932 as Boise Junior College and became Boise State University in 1974. Lewis-Clark State College in Lewiston is the only public, non-university four-year college in Idaho. It opened as a normal school in 1893.
Idaho has four regional community colleges: North Idaho College in Coeur d'Alene; College of Southern Idaho in Twin Falls; College of Western Idaho in
Idaho State Guide, from the Library of Congress
* * . * . * . * —Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Idaho state agencies. * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * {{coord, 45, -115, dim:500000_region:US-ID_type:adm1st, name=State of Idaho, display=title 1890 establishments in the United States States and territories established in 1890 States of the United States U.S. states with multiple time zones Western United States Contiguous United States
Canada–United States border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Can ...
with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington and Oregon to the west. The state's capital and largest city is Boise. With an area of , Idaho is the 14th largest state by land area, but with a population of approximately 1.8 million, it ranks as the 13th least populous and the 7th least densely populated of the 50 U.S. states.
For thousands of years, and prior to European colonization, Idaho has been inhabited by native peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
. In the early 19th century, Idaho was considered part of the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
, an area of dispute between the U.S. and the British Empire. It officially became U.S. territory with the signing of the Oregon Treaty of 1846, but a separate Idaho Territory
The Territory of Idaho was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1863, until July 3, 1890, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as Idaho.
History
1860s
The territory w ...
was not organized until 1863, instead being included for periods in Oregon Territory and Washington Territory. Idaho was eventually admitted to the Union on July 3, 1890, becoming the 43rd state
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
.
Forming part of the Pacific Northwest (and the associated Cascadia bioregion), Idaho is divided into several distinct geographic and climatic regions. The state's north, the relatively isolated Idaho Panhandle
The Idaho Panhandle—locally known as North Idaho—is a salient region of the U.S. state of Idaho encompassing the state's 10 northernmost counties: Benewah, Bonner, Boundary, Clearwater, Idaho, Kootenai, Latah, Lewis, Nez Perce, and Shosh ...
, is closely linked with Eastern Washington, with which it shares the Pacific Time Zone
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00) ...
—the rest of the state uses the Mountain Time Zone. The state's south includes the Snake River Plain
image:Snake River view near Twin Falls, Idaho.jpg, The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges, gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho
The Snake River Plain is a geology, geologic feature ...
(which has most of the population and agricultural land), and the southeast incorporates part of the Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California ...
. Idaho is quite mountainous, and contains several stretches of the Rocky Mountains. The United States Forest Service holds about 38% of Idaho's land, the highest proportion of any state.
Industries significant for the state economy include manufacturing, agriculture, mining, forestry, and tourism. A number of science and technology firms are either headquartered in Idaho or have factories there, and the state also contains the Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. While the laboratory does other research, historically it has been involved with nu ...
, which is the country's largest Department of Energy facility. Idaho's agricultural sector supplies many products, but the state is best known for its potato crop, which comprises around one-third of the nationwide yield. The official state nickname is the "Gem State", a figurative expression which references Idaho's natural beauty.
Etymology
The name's origin remains a mystery. In the early 1860s, when the U.S. Congress was considering organizing a new territory in the Rocky Mountains, the name "Idaho" was suggested byGeorge M. Willing
George Maurice "Doc" Willing, Jr. (c. 1829March 12 or 13, 1874) was an American physician, prospector, and political lobbyist. He is known for his time as an unelected delegate to the United States Congress for Jefferson Territory and as the per ...
, a politician posing as an unrecognized delegate from the unofficial Jefferson Territory. Willing claimed that the name was derived from a Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easter ...
term meaning "the sun comes from the mountains" or "gem of the mountains", but it was revealed later that there was no such term and Willing claimed that he had been inspired to coin the name when he met a little girl named ''Ida''. Since the name appeared to be fabricated, the U.S. Congress ultimately decided to name the area Colorado Territory instead when it was created in February 1861, but by the time this decision was made, the town of Idaho Springs, Colorado had already been named after Willing's proposal.
The same year Congress created Colorado Territory, a county called Idaho County
Idaho County is a county in the U.S. state of Idaho, and the largest by area in the state. As of the 2020 census, the population was 16,541. The county seat is Grangeville. Previous county seats of the area were Florence
Florence ( ; it ...
was created in eastern Washington Territory. The county was named after a steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
named ''Idaho'', which was launched on the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
in 1860. It is unclear whether the steamship was named before or after Willing's claim was revealed. Regardless, part of Washington Territory, including Idaho County, was used to create Idaho Territory
The Territory of Idaho was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1863, until July 3, 1890, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as Idaho.
History
1860s
The territory w ...
in 1863. Idaho Territory would later change its boundaries to the area that became the U.S. state.
History
Humans may have been present in the Idaho area as long as 14,500 years ago. Excavations atWilson Butte Cave
Wilson Butte Cave is located on the Snake River plain in Jerome County northeast of Twin Falls and southeast of Shoshone, Idaho. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places as an archeological site, it is maintained by the Bureau of La ...
near Twin Falls in 1959 revealed evidence of human activity, including arrowheads, that rank among the oldest dated artifacts in North America. American Indian peoples predominant in the area included the Nez Percé in the north and the Northern and Western Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easter ...
in the south.
A Late Upper Paleolithic site was identified at Cooper's Ferry in western Idaho near the town of Cottonwood by archaeologists in 2019. Based on evidence found at the site, first people lived in this area 15,300 to 16,600 years ago, predating the Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
land bridge by about a thousand years. The discoverers emphasized that they possess similarities with tools and artifacts discovered in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
that date from 16,000 to 13,000 years ago. The discovery also showed that the first people might not have come to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
by land, as previously theorized. On the contrary, they probably came through the water, using a Pacific coastal route.
An early presence of French-Canadian trappers is visible in names and toponyms: ''Nez Percé, Cœur d'Alène, Boisé, Payette''. Some of these names appeared prior to the Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
and Astorian expeditions ,which included significant numbers of French and Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives ...
guides recruited for their familiarity with the terrain.
Idaho, as part of the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
, was claimed by both the United States and Great Britain until the United States gained undisputed jurisdiction in 1846. From 1843 to 1849, present-day Idaho was under the de facto jurisdiction of the Provisional Government of Oregon. When Oregon became a state in 1849, what is now Idaho was situated in what remained of the original Oregon Territory, designated as the Washington Territory.
Between 1849 and the creation of the Idaho Territory
The Territory of Idaho was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1863, until July 3, 1890, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as Idaho.
History
1860s
The territory w ...
in 1863, parts of present-day Idaho were included in the Oregon, Washington, and Dakota Territories. The new Idaho territory included present-day Idaho, Montana, and most of Wyoming. The Lewis and Clark expedition crossed Idaho in 1805 on the way to the Pacific, and in 1806, on the return trip, largely following the Clearwater River in both directions. The first non-indigenous settlement was Kullyspell House, established on the shore of Lake Pend Oreille in 1809 by David Thompson of the North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
for fur trading. In 1812 Donald Mackenzie, working for the Pacific Fur Company at the time, established a post on the lower Clearwater River near present-day Lewiston. This post, known as "MacKenzie's Post" or "Clearwater", operated until the Pacific Fur Company was bought out by the North West Company in 1813, after which the post was abandoned. The first organized non-indigenous communities within the present borders of Idaho were established in 1860. The first permanent, substantial incorporated community was Lewiston, in 1861.
Idaho achieved statehood in 1890, following a difficult start as a territory, including the chaotic transfer of the territorial capital from Lewiston to Boise, disenfranchisement of Mormon polygamists upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court in 1890, and a federal attempt to split the territory between Washington Territory, which gained statehood in 1889, a year before Idaho, and the state of Nevada which had been a state since 1864, .
Idaho was one of the hardest hit of the Pacific Northwest states during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. Prices plummeted for Idaho's major crops: in 1932 a bushel of potatoes brought only ten cents compared to $1.51 in 1919, while Idaho farmers saw their annual income of $686 in 1929 drop to $250 by 1932.
In recent years, Idaho has expanded its commercial base as a tourism and agricultural state to include science and technology industries. Science and technology have become the largest single economic center (over 25% of the state's total revenue) within the state and are greater than agriculture, forestry and mining combined.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Idaho enacted statewide crisis standards of care as COVID-19 patients overwhelmed hospitals. The state had one of the lowest vaccination rates in the country as of mid-October 2021.
Geography
Idaho borders six U.S. states and one Canadian province. The states of Washington and Oregon are to the west, Nevada and Utah are to the south, and Montana and Wyoming are to the east. Idaho also shares a short border with the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. The landscape is rugged, with some of the largest unspoiled natural areas in the United States. For example, at 2.3 million acres (930,000 ha), the Frank Church-River of No Return Wilderness Area is the largest contiguous area of protected wilderness in the continental United States. Idaho is a Rocky Mountain state with abundant natural resources and scenic areas. The state has snow-capped mountain ranges, rapids, vast lakes and steep canyons. The waters of theSnake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
run through Hells Canyon
Hells Canyon is a canyon in the Western United States, located along the border of eastern Oregon, a small section of eastern Washington and western Idaho. It is part of the Hells Canyon National Recreation Area which is also located i ...
, the deepest gorge in the United States. Shoshone Falls falls down cliffs from a height greater than Niagara Falls.
By far, the most important river in Idaho is the Snake River, a major tributary of the Columbia River. The Snake River flows out from Yellowstone in northwestern Wyoming through the Snake River Plain
image:Snake River view near Twin Falls, Idaho.jpg, The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges, gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho
The Snake River Plain is a geology, geologic feature ...
in southern Idaho before turning north, leaving the state at Lewiston before joining the Columbia in Kennewick. Other major rivers are the Clark Fork/ Pend Oreille River, the Spokane River, and, many major tributaries of the Snake River, including the Clearwater River, the Salmon River, the Boise River
The Boise River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. , accessed May 3, 2011 tributary of the Snake River in the Northwestern United States. It drains a rugged portion of the Sawtooth Range in sou ...
, and the Payette River. The Salmon River empties into the Snake in Hells Canyon and forms the southern boundary of Nez Perce County on its north shore, of which Lewiston is the county seat. The Port of Lewiston, at the confluence of the Clearwater and the Snake Rivers is the farthest inland seaport on the West Coast at 465 river miles from the Pacific at Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is a port city and the seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1811, Astoria is the oldest city in the state and was the first permanent American settlement west of the Rocky Mountains. The county is the northwest corne ...
.
 The vast majority of Idaho's population lives in the Snake River Plain, a valley running from across the entirety of southern Idaho from east to west. The valley contains the major cities of Boise,
The vast majority of Idaho's population lives in the Snake River Plain, a valley running from across the entirety of southern Idaho from east to west. The valley contains the major cities of Boise, Meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
, Nampa
The Namibia Press Agency (NAMPA) is the national news agency of the Namibia, Republic of Namibia. It was founded in 1987 under the name Namibia Press Association as a SWAPO partisan press agency, and resuscitated after Namibian War of Independence ...
, Caldwell
Caldwell may refer to:
People
* Caldwell (surname)
* Caldwell (given name)
* Caldwell First Nation, a federally recognized Indian band in southern Ontario, Canada
Places
Great Britain
* Caldwell, Derbyshire, a hamlet
* Caldwell, East ...
, Twin Falls, Idaho Falls, and Pocatello. The plain served as an easy pass through the Rocky Mountains for westward-bound settlers on the Oregon Trail, and many settlers chose to settle the area rather than risking the treacherous route through the Blue Mountains and the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
to the west. The western region of the plain is known as the Treasure Valley, bound between the Owyhee Mountains to the southwest and the Boise Mountains to the northeast. The central region of the Snake River Plain is known as the Magic Valley.
Idaho's highest point is Borah Peak, , in the Lost River Range north of Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airport ...
. Idaho's lowest point, , is in Lewiston, where the Clearwater River joins the Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
and continues into Washington. The Sawtooth Range is often considered Idaho's most famous mountain range. Other mountain ranges in Idaho include the Bitterroot Range, the White Cloud Mountains
The White Cloud Mountains are part of the Rocky Mountains of the western United States, located in central Idaho, southeast of Stanley in Custer County. The range is located within the Sawtooth National Recreation Area (SNRA) and partially ...
, the Lost River Range, the Clearwater Mountains, and the Salmon River Mountains
The Salmon River Mountains are a major mountain range covering most of the central part of the U.S. state of Idaho. The range is over long and its boundaries are usually defined by the Salmon River and its large tributary forks. Part of the centr ...
.
Salmon-Challis National Forest is located in the east central sections of the state, with Salmon National Forest to the north and Challis National Forest to the south. The forest is in an area known as the Idaho Cobalt Belt, which consists of a long geological formation of sedimentary rock that contains some of the largest cobalt deposits in the U.S.
Idaho has two time zones, with the dividing line approximately midway between Canada and Nevada. Southern Idaho, including the Boise metropolitan area
The Boise–Nampa, Idaho Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) (commonly known as the Boise Metropolitan Area or the Treasure Valley) is an area that encompasses Ada, Boise, Canyon, Gem, and Owyhee counties in southwestern Idaho, anchored by the c ...
, Idaho Falls, Pocatello, and Twin Falls, are in the Mountain Time Zone. A legislative error ( §264) theoretically placed this region in the Central Time Zone, but this was corrected with a 2007 amendment. Areas north of the Salmon River, including Coeur d'Alene, Moscow, Lewiston, and Sandpoint
Sandpoint ( Kutenai language: kamanqukuⱡ) is the largest city in, and the county seat of, Bonner County, Idaho. Its population was 8,639 at the 2020 census.
Sandpoint's major economic contributors include forest products, light manufacturing, ...
, are in the Pacific Time Zone
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00) ...
, which contains less than a quarter of the state's population and land area.
Climate
 Idaho's climate varies widely. Although the state's western border is about from the Pacific Ocean, the maritime influence is still felt in Idaho; especially, in the winter when cloud cover, humidity, and precipitation are at their maximum extent. This influence has a moderating effect in the winter where temperatures are not as low as would otherwise be expected for a northern state with predominantly high elevations. In the panhandle, moist air masses from the coast are released as precipitation over the North Central Rockies forests, creating the
Idaho's climate varies widely. Although the state's western border is about from the Pacific Ocean, the maritime influence is still felt in Idaho; especially, in the winter when cloud cover, humidity, and precipitation are at their maximum extent. This influence has a moderating effect in the winter where temperatures are not as low as would otherwise be expected for a northern state with predominantly high elevations. In the panhandle, moist air masses from the coast are released as precipitation over the North Central Rockies forests, creating the North American inland temperate rainforest
The North American inland temperate rainforest is a 7 million hectare disjunct temperate rainforest spreading over parts of British Columbia in Canada as well as Washington, Idaho and Montana on the US side. Its patches are located on the windward ...
. The maritime influence is least prominent in the state's eastern part where the precipitation patterns are often reversed, with wetter summers and drier winters, and seasonal temperature differences are more extreme, showing a more semi-arid continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
.
Idaho can be hot, although extended periods over are rare, except for the lowest point in elevation, Lewiston, which correspondingly sees little snow. Hot summer days are tempered by the low relative humidity and cooler evenings during summer months since, for most of the state, the highest diurnal difference in temperature is often in the summer. Winters can be cold, although extended periods of bitter cold weather below zero are unusual. Idaho's all-time highest temperature of was recorded at Orofino on July 28, 1934; the all-time lowest temperature of was recorded at Island Park Dam on January 18, 1943.
Lakes and rivers


Protected areas
As of 2018:National parks, reserves, monuments and historic sites
* Salmon-Challis National Forest * California National Historic Trail *City of Rocks National Reserve
The City of Rocks National Reserve, also known as the Silent City of Rocks, is a United States National Reserve and state park in south-central Idaho, approximately north of the border with Utah. It is widely known for its enormous granite ro ...
* Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve
* Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument
* Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail
* Minidoka National Historic Site
* Nez Perce National Historical Park
* Oregon National Historic Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kan ...
* Yellowstone National Park
* Pacific Northwest National Scenic Trail
The Pacific Northwest Trail (PNT) is a 1200-mile hiking trail running from the Continental Divide in Montana to the Pacific Ocean on Washington's Olympic Coast. Along the way, the PNT crosses three national parks, seven national forests, and two ...
National recreation areas
National wildlife refuges and Wilderness Areas
National conservation areas
*Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area
The Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area has one of the densest populations of nesting raptors. The National Conservation Area (NCA) is located south of Boise, Idaho along of the Snake River, and is managed by the B ...

State parks

Demographics
Population
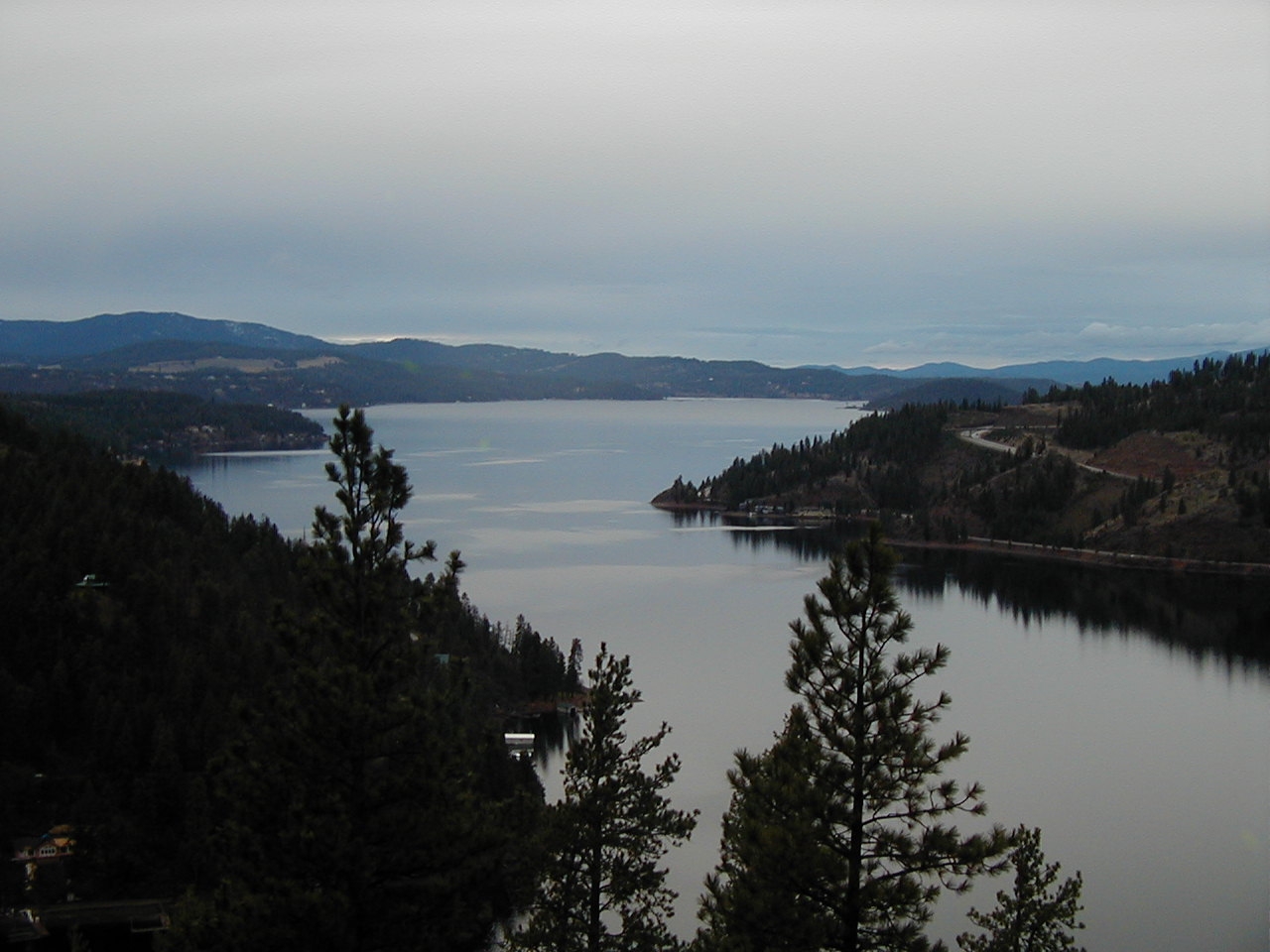
 The United States Census Bureau determined Idaho's population was 1,900,923 on July 1, 2021, a 21% increase since the
The United States Census Bureau determined Idaho's population was 1,900,923 on July 1, 2021, a 21% increase since the 2010 U.S. census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
.
Idaho had an estimated population of 1,754,208 in 2018, which was an increase of 37,265, from the prior year and an increase of 186,626, or 11.91%, since 2010. This included a natural increase since the last census of 58,884 (111,131 births minus 52,247 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 75,795 people into the state. There are large numbers of Americans of English and German ancestry in Idaho. Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 14,522 people, and migration within the country produced a net increase of 61,273 people.
This made Idaho the ninth fastest-growing state after Utah (+14.37%), Texas (+14.14%), Florida (+13.29%), Colorado (+13.25%), North Dakota (+13.01%), Nevada (+12.36%), Arizona (+12.20%) and Washington. From 2017 to 2018, Idaho grew the second-fastest, surpassed only by Nevada.
Nampa, about west of downtown Boise, became the state's second largest city in the late 1990s, passing Pocatello and Idaho Falls. Nampa's population was under 29,000 in 1990 and grew to over 81,000 by 2010. Located between Nampa and Boise, Meridian also experienced high growth, from fewer than 10,000 residents in 1990 to more than 75,000 in 2010 and is now Idaho's third largest city. Growth of 5% or more over the same period has also been observed in Caldwell
Caldwell may refer to:
People
* Caldwell (surname)
* Caldwell (given name)
* Caldwell First Nation, a federally recognized Indian band in southern Ontario, Canada
Places
Great Britain
* Caldwell, Derbyshire, a hamlet
* Caldwell, East ...
, Coeur d'Alene, Post Falls, and Twin Falls.
From 1990 to 2010, Idaho's population increased by over 560,000 (55%). The Boise metropolitan area
The Boise–Nampa, Idaho Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) (commonly known as the Boise Metropolitan Area or the Treasure Valley) is an area that encompasses Ada, Boise, Canyon, Gem, and Owyhee counties in southwestern Idaho, anchored by the c ...
(officially known as the Boise City-Nampa, ID Metropolitan Statistical Area) is Idaho's largest metropolitan area. Other metropolitan areas in order of size are Coeur d'Alene, Idaho Falls, Pocatello and Lewiston.
The table below shows the ethnic composition of Idaho's population as of 2016.
 According to the 2017
According to the 2017 American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is a demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educati ...
, 12.2% of Idaho's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
(10.6%), Puerto Rican (0.2%), Cuban (0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (1.3%). The five largest ancestry groups were: German (17.5%), English (16.4%), Irish (9.3%), American (8.1%), and Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
(3.2%).
;;Birth data
Religion
 According to the
According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
on Religion & Public Life, the self-identified religious affiliations of Idahoans over the age of 18 in 2008 and 2014 were:
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives, the largest denominations by number of members in 2010 were The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 409,265; the Catholic Church with 123,400; the non-denominational Evangelical Protestant with 62,637; and the Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
with 22,183.
Language
English is the state's predominant language. Minority languages include Spanish and various Native American languages.Economy
As of 2016, the state's total employment was 562,282, and the total employer establishments were 45,826. Gross state product for 2015 was $64.9 billion, and the per capita income based on 2015 GDP and 2015 population estimates was $39,100. Important industries in Idaho are food processing, lumber and wood products, machinery, chemical products, paper products, electronics manufacturing, silver and other mining, and tourism. The world's largest factory for barrel cheese, the raw product for processed cheese, is in Gooding, Idaho. It has a capacity of 120,000 metric tons per year of barrel cheese and belongs to the Glanbia group.Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
has operated a large plant in Boise since the 1970s, which is devoted primarily to LaserJet printers production.
Idaho has a state gambling lottery, which contributed $333.5 million in payments to all Idaho public schools
Public school may refer to:
*State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
*Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England and ...
and Idaho higher education from 1990 to 2006.
Taxation
Tax is collected by the Idaho State Tax Commission. The state personal income tax ranges from 1.6% to 7.8% in eight income brackets. Idahoans may apply for state tax credits for taxes paid to other states, as well as for donations to Idaho state educational entities and some nonprofit youth and rehabilitation facilities. The statesales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
is 6% with a very limited, selective local option up to 6.5%. Sales tax applies to the sale, rental or lease of tangible personal property and some services. Food is taxed, but prescription drug
A prescription drug (also prescription medication or prescription medicine) is a pharmaceutical drug that legally requires a medical prescription to be dispensed. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs can be obtained without a prescription. The rea ...
s are not. Hotel, motel, and campground
A campsite, also known as a campground or camping pitch, is a place used for camping, overnight stay in an outdoor area. In British English, a ''campsite'' is an area, usually divided into a number of pitches, where people can camp overnight u ...
accommodations are taxed at a higher rate (7% to 11%). Some jurisdictions impose local option sales tax.
The sales tax was introduced at 3% in 1965, easily approved by voters, where it remained at 3% until 1983.
Energy
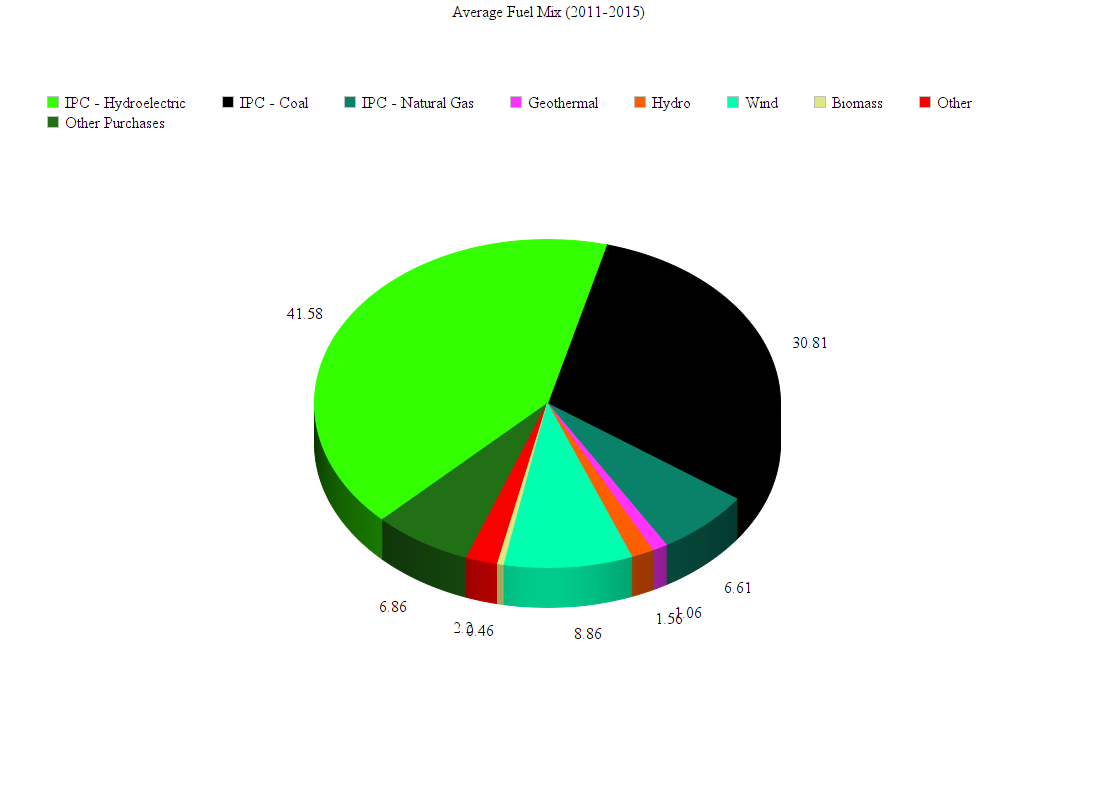
 As of 2017, the primary energy source in Idaho was hydropower, and the energy companies had a total retail sales of 23,793,790 megawatt hours (MWh). As of 2017, Idaho had a regulated electricity market, with the Idaho Public Utilities Commission regulating the three major utilities of Avista Utilities, Idaho Power, and Rocky Mountain Power.
Idaho imports most of the energy it consumes. Imports account for more than 80% of energy consumption, including all of Idaho's natural gas and petroleum supplies and more than half of its electricity. Of the electricity consumed in Idaho in 2005, 48% came from hydroelectricity, 42% was generated by burning coal and 9% was generated by burning natural gas. The remainder came from other renewable sources, such as wind.
The state's river basins allow hydroelectric power plants to provide 556,000 MWh, which amounts to about three-fourths of Idaho's electricity generated in the state. Washington State provides most of the natural gas used in Idaho through one of the two major pipeline systems supplying the state. Although the state relies on out-of-state sources for its entire natural gas supply, it uses natural gas-fired plants to generate 127,000 MWh, or about ten percent of its output. Coal-fired generation and the state's small array of wind turbines supplies the remainder of the state's electricity output. The state produces 739,000 MWh but still needs to import half of its electricity from out-of-state to meet demand.
In addition, Idaho also has the 6th fastest growing population in the United States with the population expected to increase by 31% from 2008 to 2030. This projected increase in population will contribute to a 42% increase in demand by 2030, further straining Idaho's finite hydroelectric resources.
Idaho has an upper-boundary estimate of development potential to generate 44,320 GWh/year from 18,076 MW of wind power, and 7,467,000 GWh/year from solar power using 2,061,000 MW of photovoltaics (PV), including 3,224 MW of rooftop photovoltaics, and 1,267,000 MW of
As of 2017, the primary energy source in Idaho was hydropower, and the energy companies had a total retail sales of 23,793,790 megawatt hours (MWh). As of 2017, Idaho had a regulated electricity market, with the Idaho Public Utilities Commission regulating the three major utilities of Avista Utilities, Idaho Power, and Rocky Mountain Power.
Idaho imports most of the energy it consumes. Imports account for more than 80% of energy consumption, including all of Idaho's natural gas and petroleum supplies and more than half of its electricity. Of the electricity consumed in Idaho in 2005, 48% came from hydroelectricity, 42% was generated by burning coal and 9% was generated by burning natural gas. The remainder came from other renewable sources, such as wind.
The state's river basins allow hydroelectric power plants to provide 556,000 MWh, which amounts to about three-fourths of Idaho's electricity generated in the state. Washington State provides most of the natural gas used in Idaho through one of the two major pipeline systems supplying the state. Although the state relies on out-of-state sources for its entire natural gas supply, it uses natural gas-fired plants to generate 127,000 MWh, or about ten percent of its output. Coal-fired generation and the state's small array of wind turbines supplies the remainder of the state's electricity output. The state produces 739,000 MWh but still needs to import half of its electricity from out-of-state to meet demand.
In addition, Idaho also has the 6th fastest growing population in the United States with the population expected to increase by 31% from 2008 to 2030. This projected increase in population will contribute to a 42% increase in demand by 2030, further straining Idaho's finite hydroelectric resources.
Idaho has an upper-boundary estimate of development potential to generate 44,320 GWh/year from 18,076 MW of wind power, and 7,467,000 GWh/year from solar power using 2,061,000 MW of photovoltaics (PV), including 3,224 MW of rooftop photovoltaics, and 1,267,000 MW of concentrated solar power
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated when ...
. Idaho had 973 MW of installed wind power as of 2020.
Transportation
The Idaho Transportation Department is thegovernment agency
A government or state agency, sometimes an appointed commission, is a permanent or semi-permanent organization in the machinery of government that is responsible for the oversight and administration of specific functions, such as an administrati ...
responsible for Idaho's transportation infrastructure, including operations and maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
, as well as planning for future needs. The agency is also responsible for overseeing the disbursement of federal, state, and grant funding for the transportation programs of the state.
Highways
Airports
Major airports include the Boise Airport which serves the southwest region of Idaho and the Spokane International Airport (in Spokane, Washington) which serves northern Idaho. Other airports with scheduled service are the Pullman-Moscow Regional Airport serving the Palouse; the Lewiston-Nez Perce County Airport, serving the Lewis-Clark Valley and north central and west central Idaho; TheMagic Valley Regional Airport
Magic Valley Regional Airport , also known as Joslin Field, is a public use airport located four nautical miles (7 km) south of the central business district of Twin Falls, Idaho. The airport is owned by the City and County of Twin Fa ...
in Twin Falls; the Idaho Falls Regional Airport; and the Pocatello Regional Airport.
Railroads
Idaho is served by three transcontinental railroads. The Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) connects theIdaho Panhandle
The Idaho Panhandle—locally known as North Idaho—is a salient region of the U.S. state of Idaho encompassing the state's 10 northernmost counties: Benewah, Bonner, Boundary, Clearwater, Idaho, Kootenai, Latah, Lewis, Nez Perce, and Shosh ...
with Seattle, Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, and Spokane to the west, and Minneapolis and Chicago to the east. The BNSF travels through Kootenai, Bonner Bonner may refer to:
People
* Bonner (name)
Places
;United States
* Bonner Springs, Kansas
* Bonner County, Idaho
* Bonners Ferry, Idaho
* Bonner-West Riverside, Montana
* Bonner, Nebraska
;Australia
* Bonner, Australian Capital Territory, subur ...
, and Boundary counties. The Union Pacific Railroad crosses North Idaho, entering from Canada through Boundary and Bonner Bonner may refer to:
People
* Bonner (name)
Places
;United States
* Bonner Springs, Kansas
* Bonner County, Idaho
* Bonners Ferry, Idaho
* Bonner-West Riverside, Montana
* Bonner, Nebraska
;Australia
* Bonner, Australian Capital Territory, subur ...
, and proceeding to Spokane. Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadi ...
uses Union Pacific Railroad tracks in North Idaho, carrying products from Alberta to Spokane and Portland, Oregon. Amtrak's Empire Builder crosses northern Idaho, with its only stop being in Sandpoint
Sandpoint ( Kutenai language: kamanqukuⱡ) is the largest city in, and the county seat of, Bonner County, Idaho. Its population was 8,639 at the 2020 census.
Sandpoint's major economic contributors include forest products, light manufacturing, ...
. Montana Rail Link
Montana Rail Link is a privately held Class II railroad in the United States. It operates on trackage originally built by the Northern Pacific Railway and leased from its successor BNSF. MRL is a unit of The Washington Companies and is he ...
also operates between Billings, Montana, and Sandpoint, Idaho.
The Union Pacific Railroad also crosses southern Idaho traveling between Portland, Oregon, Green River, Wyoming, and Ogden, Utah
Ogden is a city in and the county seat of Weber County, Utah, United States, approximately east of the Great Salt Lake and north of Salt Lake City. The population was 87,321 in 2020, according to the US Census Bureau, making it Utah's eighth ...
, and serves Boise, Nampa
The Namibia Press Agency (NAMPA) is the national news agency of the Namibia, Republic of Namibia. It was founded in 1987 under the name Namibia Press Association as a SWAPO partisan press agency, and resuscitated after Namibian War of Independence ...
, Twin Falls, and Pocatello.
Ports
The Port of Lewiston is the farthest inland Pacific port on the west coast. A series of dams and locks on the Snake River and Columbia River facilitate barge travel from Lewiston to Portland, where goods are loaded on ocean-going vessels.Law and government

State constitution
The constitution of Idaho is roughly modeled on the national constitution, with several additions. The constitution defines the form and functions of the state government, and may be amended through plebiscite. The state constitution presently requires the state government to maintain abalanced budget
A balanced budget (particularly that of a government) is a budget in which revenues are equal to expenditures. Thus, neither a budget deficit nor a budget surplus exists (the accounts "balance"). More generally, it is a budget that has no budge ...
.
Idaho Code and Statutes
All of Idaho's state laws are contained in the Idaho Code and Statutes. The code is amended through the legislature with the approval of the governor. Idaho still operates under its original (1889) state constitution.State government
The constitution of Idaho provides for three branches of government: the executive, legislative and judicial branches. Idaho has abicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
legislature, elected from 35 legislative districts, each represented by one senator and two representatives.
Since 1946, statewide elected constitutional officers have been elected to four-year terms. They include: Governor, Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
, Secretary of State, Idaho state controller (Auditor before 1994), Treasurer, Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
, and Superintendent of Public Instruction.
Last contested in 1966, Inspector of Mines was an originally elected constitutional office. Afterward it was an appointed position and ultimately done away with entirely in 1974.
Idaho's government has an alcohol monopoly; the Idaho State Liquor Division.
Executive branch
The governor of Idaho serves a four-year term, and is elected during what is nationally referred to as midterm elections. As such, the governor is not elected in the same election year as the president of the United States. The current governor is Republican Brad Little, who was elected in 2018.Legislative branch
 Idaho's legislature is part-time. Because of this, Idaho's legislators are considered "citizen legislators", meaning their position as a legislator is not their main occupation. However, the session may be extended if necessary, and often is.
Terms for both the
Idaho's legislature is part-time. Because of this, Idaho's legislators are considered "citizen legislators", meaning their position as a legislator is not their main occupation. However, the session may be extended if necessary, and often is.
Terms for both the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and House of Representatives are two years. Legislative elections occur every even numbered year.
The Idaho Legislature has been continuously controlled by the Republican Party since the late 1950s, although Democratic legislators are routinely elected from Boise, Pocatello, Blaine County and the northern Panhandle.
Judicial branch
The highest court in Idaho is the Idaho Supreme Court. There is also an intermediate appellate court, the Idaho Court of Appeals, which hears cases assigned to it from the Supreme Court. The state's District Courts serve seven judicial districts.Politics
Idaho Territory
The Territory of Idaho was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1863, until July 3, 1890, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as Idaho.
History
1860s
The territory w ...
. As a result, the early territorial legislatures were solidly Democrat-controlled. In contrast, most of the territorial governors were appointed by Republican presidents and were Republicans. This led to sometimes-bitter clashes between the two parties, including a range war with the Democrats backing the sheepherders and the Republicans the cattlemen, which ended in the "Diamondfield" Jack Davis murder trial. In the 1880s, Republicans became more prominent in local politics.
In 1864, Clinton DeWitt Smith removed the territorial seal and the state constitution from a locked safe, and took them to Boise. This effectively moved the capital from where they were stored (Lewiston, Idaho
Lewiston is a city and the county seat of Nez Perce County, Idaho, United States, in the state's north central region. It is the second-largest city in the northern Idaho region, behind Coeur d'Alene, and ninth-largest in the state. Lewiston is ...
) to the current capital, Boise.
Since statehood, the Republican Party has usually been the dominant party in Idaho. At one time, Idaho had two Democratic parties, one being the mainstream and the other called the Anti-Mormon Democrats, lasting into the early 20th century. In the 1890s and early 1900s, the Populist Party enjoyed prominence, while the Democratic Party maintained a brief dominance in the 1930s during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. Since World WarII, most statewide-elected officials have been Republicans, though the Democrats did hold the majority in the House (by one seat) in 1958 and the governorship from 1971 to 1995.
Idaho Congressional delegations have also been generally Republican since statehood. Several Idaho Democrats have had electoral success in the U.S. House of Representatives over the years, but the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
delegation has been a Republican stronghold for decades. Several Idaho Republicans, including current Senators Mike Crapo and Jim Risch, have won reelection to the Senate, but only Frank Church
Frank Forrester Church III (July 25, 1924 – April 7, 1984) was an Americans, American politician and lawyer. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as a United States Senate, United States senator from Idah ...
has won reelection as a Democrat. Church's 1974
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; f ...
victory was the last win for his party for either Senate seat, and Walt Minnick's 2008 victory in the 1st congressional district was the last Democratic win in any congressional race.
In modern times, Idaho has been a reliably Republican state in presidential politics. It has not supported a Democrat for president since 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
. Even in that election, Lyndon Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
defeated Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for presiden ...
in the state by fewer than two percentage points, compared to a landslide nationally. In 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 6 ...
, Republican George W. Bush carried Idaho by a margin of 38 percentage points and with 68.4% of the vote, winning in 43 of 44 counties. Only Blaine County, which contains the Sun Valley Sun Valley may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sun Valley, New South Wales
* Sun Valley, Queensland, a suburb of Gladstone
United States
* Valley of the Sun, a region that covers the Phoenix metropolitan area
*Sun Valley, Arizona
* Sun Valley, Los A ...
ski resort, supported John Kerry, who owns a home in the area. In 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
Barack Obama's 36.1 percent showing was the best for a Democratic presidential candidate in Idaho since 1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
. However, Republican margins were narrower in 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: 1992 Los Angeles riots, Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the Police brutality, police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment buildi ...
and 1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
.
In the 2006 elections, Republicans, led by gubernatorial candidate Butch Otter, won all the state's constitutional offices and retained both of the state's seats in the House. However, Democrats picked up several seats in the Idaho Legislature, notably in the Boise area.
Republicans lost one of the House seats in 2008 to Minnick, but Republican Jim Risch retained Larry Craig's Senate seat for the GOP by a comfortable margin. Minnick lost his seat in the 2010 election to Republican State Rep. Raul Labrador.
In a 2020 study, Idaho was ranked as the 18th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Education
K–12
As of January 2020, the State of Idaho contains 105 school districts and 62 charter schools. The school districts range in enrollment from two to 39,507 students. Idaho school districts are governed by elected school boards, which are elected in November of odd-numbered years, except for the Boise School District, whose elections are held in September.Colleges and universities


 The Idaho State Board of Education oversees three comprehensive universities. The University of Idaho in Moscow was the first university in the state (founded in 1889). It opened its doors in 1892 and is the land-grant institution and primary research university of the state. Idaho State University in Pocatello opened in 1901 as the Academy of Idaho, attained four-year status in 1947 and university status in 1963. Boise State University is the most recent school to attain university status in Idaho. The school opened in 1932 as Boise Junior College and became Boise State University in 1974. Lewis-Clark State College in Lewiston is the only public, non-university four-year college in Idaho. It opened as a normal school in 1893.
Idaho has four regional community colleges: North Idaho College in Coeur d'Alene; College of Southern Idaho in Twin Falls; College of Western Idaho in
The Idaho State Board of Education oversees three comprehensive universities. The University of Idaho in Moscow was the first university in the state (founded in 1889). It opened its doors in 1892 and is the land-grant institution and primary research university of the state. Idaho State University in Pocatello opened in 1901 as the Academy of Idaho, attained four-year status in 1947 and university status in 1963. Boise State University is the most recent school to attain university status in Idaho. The school opened in 1932 as Boise Junior College and became Boise State University in 1974. Lewis-Clark State College in Lewiston is the only public, non-university four-year college in Idaho. It opened as a normal school in 1893.
Idaho has four regional community colleges: North Idaho College in Coeur d'Alene; College of Southern Idaho in Twin Falls; College of Western Idaho in Nampa
The Namibia Press Agency (NAMPA) is the national news agency of the Namibia, Republic of Namibia. It was founded in 1987 under the name Namibia Press Association as a SWAPO partisan press agency, and resuscitated after Namibian War of Independence ...
, which opened in 2009, College of Eastern Idaho in Idaho Falls, which transitioned from a technical college in 2017.
Private institutions in Idaho are Boise Bible College, affiliated with congregations of the Christian churches and churches of Christ; Brigham Young University-Idaho
Brigham may refer to:
Places
* Brigham, Cumbria, England
* Brigham, East Riding of Yorkshire, England
* Brigham City, Utah, USA
* Brigham, Wisconsin, USA
* Brigham, Quebec, Canada
People
* Brigham (surname), including a list of people with the ...
in Rexburg, which is affiliated with The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and a sister college to Brigham Young University; The College of Idaho in Caldwell
Caldwell may refer to:
People
* Caldwell (surname)
* Caldwell (given name)
* Caldwell First Nation, a federally recognized Indian band in southern Ontario, Canada
Places
Great Britain
* Caldwell, Derbyshire, a hamlet
* Caldwell, East ...
, which still maintains a loose affiliation with the Presbyterian Church; Northwest Nazarene University in Nampa
The Namibia Press Agency (NAMPA) is the national news agency of the Namibia, Republic of Namibia. It was founded in 1987 under the name Namibia Press Association as a SWAPO partisan press agency, and resuscitated after Namibian War of Independence ...
; and New Saint Andrews College
New Saint Andrews College is a private classical Christian college in Moscow, Idaho. It was founded in 1994 by Christ Church, and modeled in part on the curriculum of Harvard College of the seventeenth century. The college offers no undergradu ...
in Moscow, of reformed Christian theological background. McCall College
McCall College (McC) is an American private college located in McCall, Idaho. It primarily serves Valley County, Adams County and Idaho County. McCall also serves as a destination college for students from the Pacific Northwest.
Mission
Prov ...
is a non-affiliated two-year private college in McCall
McCall is a Gaelic surname, of Irish and Scottish origin.
Notable people with this surname include:
* Andy McCall (footballer, born 1911) (1911–1979), Scottish footballer and manager
*Andy McCall (footballer, born 1925) (1925–2014), Scottish f ...
, which was founded in 2011 and later opened in 2013.
Sports
Central Idaho is home to one of North America's oldest ski resorts,Sun Valley Sun Valley may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sun Valley, New South Wales
* Sun Valley, Queensland, a suburb of Gladstone
United States
* Valley of the Sun, a region that covers the Phoenix metropolitan area
*Sun Valley, Arizona
* Sun Valley, Los A ...
, where the world's first chairlift was installed in 1936. Other noted outdoor sites include Hells Canyon
Hells Canyon is a canyon in the Western United States, located along the border of eastern Oregon, a small section of eastern Washington and western Idaho. It is part of the Hells Canyon National Recreation Area which is also located i ...
, the Salmon River, and its embarkation point of Riggins.
The Boise Open
The Albertsons Boise Open presented by Chevron is a professional golf tournament in Idaho on the Korn Ferry Tour, played annually at Hillcrest Country Club in Boise. Held in mid-September for its first 23 years, the new September playoff schedule ...
professional golf tournament has been played at Hillcrest Country Club since 1990 as part of the Korn Ferry Tour. The Open has been part of the Korn Ferry Tour Finals since 2016.
High school sports are overseen by the Idaho High School Activities Association (IHSAA).
In 2016, Meridian's Michael Slagowski ran 800 meters in 1:48.70. That is one of the 35 fastest 800-meter times ever run by a high school boy in the United States. Weeks later, he would become only the ninth high school boy to complete a mile in under four minutes, running 3:59.53.
In popular culture
The 1985 film '' Pale Rider'' was primarily filmed in the Boulder Mountains and the Sawtooth National Recreation Area in central Idaho, just north ofSun Valley Sun Valley may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sun Valley, New South Wales
* Sun Valley, Queensland, a suburb of Gladstone
United States
* Valley of the Sun, a region that covers the Phoenix metropolitan area
*Sun Valley, Arizona
* Sun Valley, Los A ...
. River Phoenix and Keanu Reeves
Keanu Charles Reeves ( ; born September 2, 1964) is a Canadian actor. Born in Beirut and raised in Toronto, Reeves began acting in theatre productions and in television films before making his feature film debut in '' Youngblood'' (1986). ...
starred in the 1991 movie '' My Own Private Idaho'', portions of which take place in Idaho. The 2004 cult film
A cult film or cult movie, also commonly referred to as a cult classic, is a film that has acquired a cult following. Cult films are known for their dedicated, passionate fanbase which forms an elaborate subculture, members of which engage ...
'' Napoleon Dynamite'' takes place in Preston, Idaho; the film's director, Jared Hess, attended Preston High School.
See also
*Index of Idaho-related articles
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of Idaho.
0–9
* .id.us – Internet second-level domain for the state of Idaho
* 43rd state to join the United States of America
* North American ice storm of Jan ...
* Outline of Idaho
References
External links
* .Idaho State Guide, from the Library of Congress
* * . * . * . * —Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Idaho state agencies. * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * {{coord, 45, -115, dim:500000_region:US-ID_type:adm1st, name=State of Idaho, display=title 1890 establishments in the United States States and territories established in 1890 States of the United States U.S. states with multiple time zones Western United States Contiguous United States