politics of Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous
 ''
''
 Africa is considered by most
Africa is considered by most
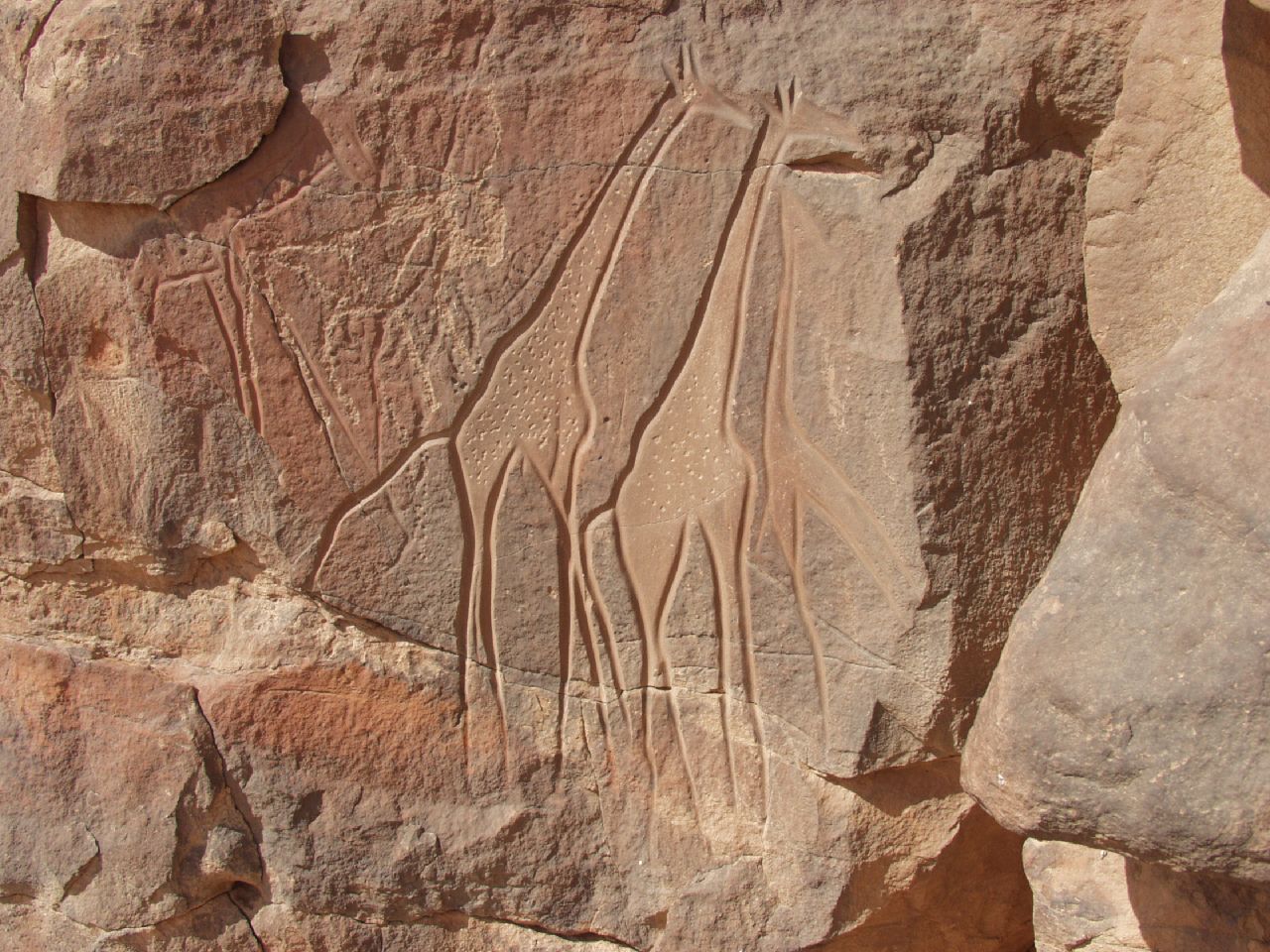 The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gatherer cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC, cattle were domesticated in North Africa. In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals, including the donkey and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to
The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gatherer cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC, cattle were domesticated in North Africa. In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals, including the donkey and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to
, SWI swissinfo.ch – the international service of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (SBC), 18 January 2007 In the
 At about 3300 BC, the historical record opens in Northern Africa with the rise of literacy in the
At about 3300 BC, the historical record opens in Northern Africa with the rise of literacy in the  Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean
Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean
 Pre-colonial Africa possessed perhaps as many as 10,000 different states and polities characterized by many different sorts of political organization and rule. These included small family groups of hunter-gatherers such as the
Pre-colonial Africa possessed perhaps as many as 10,000 different states and polities characterized by many different sorts of political organization and rule. These included small family groups of hunter-gatherers such as the  The
The

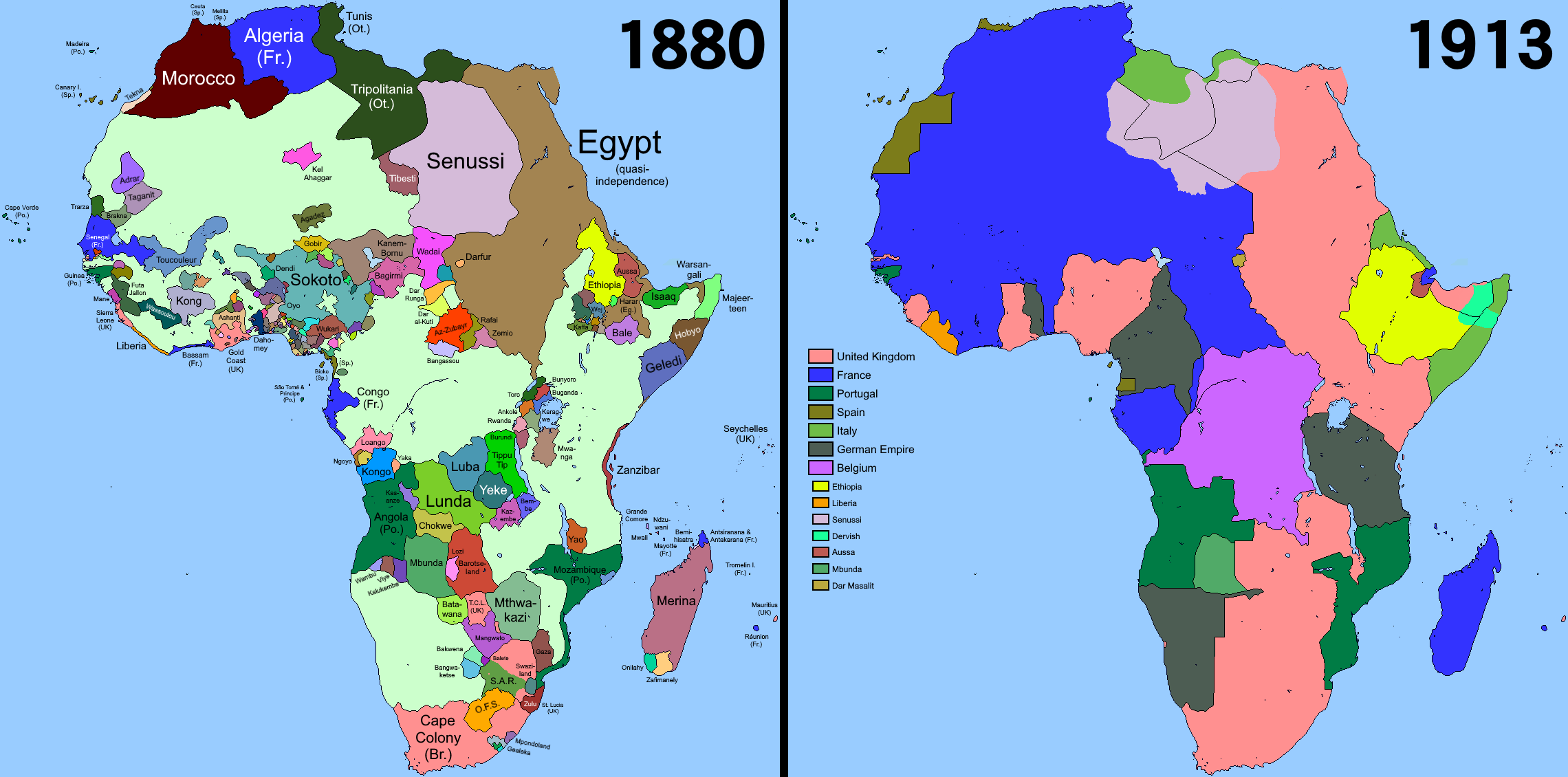
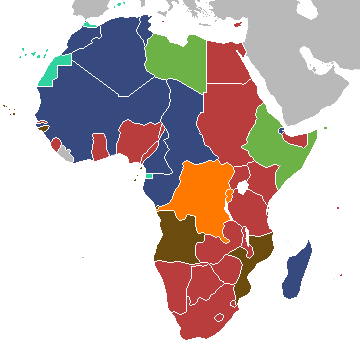 Imperial rule by Europeans would continue until after the conclusion of
Imperial rule by Europeans would continue until after the conclusion of
File:African nations order of independence 1950-1993.gif, An animated map shows the order of independence of African nations, 1950–2011
File:Africa’s wars and conflicts, 1980–96.svg, Africa's wars and conflicts, 1980–96
File:Political Map of Africa.svg, Political map of Africa in 2021
Various conflicts between various insurgent groups and governments continue. Since 2003 there has been an ongoing conflict in Darfur (Sudan) which peaked in intensity from 2003 to 2005 with notable spikes in violence in 2007 and 2013–15, killing around 300,000 people total. The
 Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest
Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest
African Studies Center
, University of Pennsylvania. Accessed June 2011. The record for the highest-ever recorded temperature, in
 Africa has over 3,000
Africa has over 3,000


 Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of
Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of
 The
The
 Although it has abundant
Although it has abundant
continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
, after Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
s, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism
Tribalism is the state of being organized by, or advocating for, tribes or tribal lifestyles. Human evolution has primarily occurred in small hunter-gatherer groups, as opposed to in larger and more recently settled agricultural societies or civ ...
, colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, neocolonialism
Neocolonialism is the continuation or reimposition of imperialist rule by a state (usually, a former colonial power) over another nominally independent state (usually, a former colony). Neocolonialism takes the form of economic imperialism, gl ...
, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context.
The continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
to the north, the Isthmus of Suez
The Isthmus of Suez is the land bridge"Suez Canal ...
and the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
to the northeast, the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
to the southeast and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the west. The continent includes Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and various archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
s. It contains 54 fully recognised sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
s, eight territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
and two ''de facto'' independent states with limited or no recognition. Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
is Africa's largest country by area, and Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
is its largest by population. African nations cooperate through the establishment of the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
, which is headquartered in Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
.
Africa straddles the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
and the prime meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great c ...
. It is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
to the southern temperate zones. The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, with a substantial portion and number of countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of the continent lies in the tropics, except for a large part of Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the r ...
, Algeria, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, the northern tip of Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, and the entire territories of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
, Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
, Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
, and Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
which in turn are located above the tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward ...
, in the northern temperate zone. In the other extreme of the continent, southern Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, southern Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
, great parts of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, the entire territories of Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
and Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
and the southern tips of Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
and Madagascar are located below the tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reac ...
, in the southern temperate zone.
Africa is highly biodiverse
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa also is heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water Water resources, resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water ...
and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) a ...
has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.Niang, I., O.C. Ruppel, M.A. Abdrabo, A. Essel, C. Lennard, J. Padgham, and P. Urquhart, 2014: Africa. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change arros, V.R., C.B. Field, D.J. Dokken et al. (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1199–1265. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/WGIIAR5-Chap22_FINAL.pdf
The history of Africa
The history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and — around 300–250,000 years ago—anatomically modern humans (''Homo sapiens''), in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of d ...
is long, complex, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. Africa, particularly Eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
, is widely accepted as the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ea ...
clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
(great ape
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the east ...
s). The earliest hominids
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the east ...
and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, including ''Sahelanthropus tchadensis
''Sahelanthropus tchadensis'' is an extinct species of the Homininae (African apes) dated to about , during the Miocene epoch. The species, and its genus ''Sahelanthropus'', was announced in 2002, based mainly on a partial cranium, nicknamed ''T ...
'', ''Australopithecus africanus
''Australopithecus africanus'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived between about 3.3 and 2.1 million years ago in the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of South Africa. The species has been recovered from Taung, Sterkfonte ...
'', ''A. afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not ta ...
'', ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'', ''H. habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly c ...
'' and '' H. ergaster''— the earliest ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' (modern human) remains, found in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
, date to circa 233,000, 259,000, and 300,000 years ago respectively, and ''Homo sapiens'' is believed to have originated in Africa around 350,000–260,000 years ago. Africa is also considered by anthropologists to be the most genetically diverse continent as a result of being the longest inhabited.
Early human civilizations, such as Ancient Egypt and Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
emerged in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. Following a subsequent long and complex history of civilizations, migration and trade, Africa hosts a large diversity of ethnicities
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, cultures
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
and languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
. The last 400 years have witnessed an increasing European influence on the continent. Starting in the 16th century, this was driven by trade, including the Trans-Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
, which created large African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were e ...
populations in the Americas. From the late 19th century
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 (Roman numerals, MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (Roman numerals, MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium.
The 19th century was characterized by vast social ...
to the early 20th century, European nations colonized almost all of Africa, reaching a point when only Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
were independent polities. Most present states in Africa emerged from a process of decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Etymology
 ''
''Afri
(singular ) was a Latin name for the inhabitants of Africa, referring in its widest sense to all the lands south of the Mediterranean ( Ancient Libya). Latin speakers at first used as an adjective, meaning "of Africa". As a substantive, it den ...
'' was a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
name used to refer to the inhabitants of then-known northern Africa to the west of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
river, and in its widest sense referred to all lands south of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
(Ancient Libya
The Latin name ''Libya'' (from Greek Λιβύη: ''Libyē'', which came from Berber: ''Libu'') referred to North Africa during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity. Berbers occupied the area for thousands of years before the recording of histor ...
). This name seems to have originally referred to a native Libyan tribe, an ancestor of modern Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
; see Terence
Publius Terentius Afer (; – ), better known in English as Terence (), was a Roman African playwright during the Roman Republic. His comedies were performed for the first time around 166–160 BC. Terentius Lucanus, a Roman senator, brought ...
for discussion. The name had usually been connected with the Phoenician word ' meaning "dust", but a 1981 hypothesis has asserted that it stems from the Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
word ''ifri'' (plural ''ifran'') meaning "cave", in reference to cave dwellers. The same word may be found in the name of the Banu Ifran
The Banu Ifran ( ar, بنو يفرن, ''Banu Yafran'') or Ifranids, were a Zenata Berber tribe prominent in the history of pre-Islamic and early Islamic North Africa. In the 8th century, they established a kingdom in the central Maghreb, with ...
from Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province o ...
, a Berber tribe originally from Yafran
Yafran ( Berber: ⵢⴼⵔⴰⵏ ''Ifran'', ar, يفرن, links=https://www.temehu.com/Cities_sites/Yefren.htm ', it, Iefren), also spelled ''Jefren'', ''Yefren'', ''Yifran'', ''Yifrin'' or ''Ifrane'', is a city in northwestern Libya, in the J ...
(also known as ''Ifrane'') in northwestern Libya, as well as the city of Ifrane
Ifrane ( Berber: ⵉⴼⵔⴰⵏ; ar, إفران) is a city in the Middle Atlas region of northern Morocco (population 14,659 as of November 2014). The capital of Ifrane Province in the region of Fès-Meknès, Ifrane is located at an elevation of ...
in Morocco.
Under Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
rule, Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
became the capital of the province it then named ''Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
'', following its defeat of the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
in the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
in 146 BC, which also included the coastal part of modern Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
. The Latin suffix '' -ica'' can sometimes be used to denote a land (e.g., in '' Celtica'' from '' Celtae'', as used by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
). The later Muslim region of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
, following its conquest of the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire's '' Exarchatus Africae'', also preserved a form of the name.
According to the Romans, Africa lies to the west of Egypt, while "Asia" was used to refer to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
and lands to the east. A definite line was drawn between the two continents by the geographer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
(85–165 AD), indicating Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
along the Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great c ...
and making the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
the boundary between Asia and Africa. As Europeans came to understand the real extent of the continent, the idea of "Africa" expanded with their knowledge.
Other etymological hypotheses have been postulated for the ancient name "Africa":
* The 1st-century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly d ...
(''Ant. 1.15'') asserted that it was named for Epher Epher*Ephera'im, Effrain* ( ''ʿĒp̄er'') was a grandson of Abraham, according to Gen. 25:4, whose descendants, Jewish historian Flavius Josephus claimed, had invaded Libya. Josephus also claimed that Epher's name was the etymological root of the ...
, grandson of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
according to Gen. 25:4, whose descendants, he claimed, had invaded Libya.
* Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
in his 7th-century ''Etymologiae
''Etymologiae'' (Latin for "The Etymologies"), also known as the ''Origines'' ("Origins") and usually abbreviated ''Orig.'', is an etymological encyclopedia compiled by Isidore of Seville (c. 560–636) towards the end of his life. Isidore was ...
'' XIV.5.2. suggests "Africa comes from the Latin ''aprica'', meaning "sunny".
* Massey, in 1881, stated that Africa is derived from the Egyptian ''af-rui-ka'', meaning "to turn toward the opening of the Ka." The Ka is the energetic double of every person and the "opening of the Ka" refers to a womb or birthplace. Africa would be, for the Egyptians, "the birthplace."
* Michèle Fruyt in 1976 proposed linking the Latin word with ''africus'' "south wind", which would be of Umbrian origin and mean originally "rainy wind".
* Robert R. Stieglitz of Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's ...
in 1984 proposed: "The name Africa, derived from the Latin *Aphir-ic-a, is cognate to Hebrew Ophir
Ophir (; ) is a port or region mentioned in the Bible, famous for its wealth. King Solomon received a shipment from Ophir every three years (1 Kings 10:22) which consisted of gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes, and peacocks.
Biblica ...
rich'"
* Ibn Khallikan
Aḥmad bin Muḥammad bin Ibrāhīm bin Abū Bakr ibn Khallikān) ( ar, أحمد بن محمد بن إبراهيم بن أبي بكر ابن خلكان; 1211 – 1282), better known as Ibn Khallikān, was a 13th century Shafi'i Islamic scholar w ...
and some other historians claim that the name of Africa came from a Himyarite
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) ( fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerit ...
king called Afrikin ibn Kais ibn Saifi also called "Afrikus son of Abraham" who subdued Ifriqiya.
* Arabic ''afrīqā'' (feminine noun) and ''ifrīqiyā'', now usually pronounced ''afrīqiyā'' (feminine) 'Africa', from ''‘afara'' �� = ''‘ain'', not ''’alif'''to be dusty' from ''‘afar'' 'dust, powder' and ''‘afir'' 'dried, dried up by the sun, withered' and ''‘affara'' 'to dry in the sun on hot sand' or 'to sprinkle with dust'.
* Possibly Phoenician ''faraqa'' in the sense of 'colony, separation'.
History
Prehistory
 Africa is considered by most
Africa is considered by most paleoanthropologists
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship ...
to be the oldest inhabited territory on Earth, with the Human species originating from the continent. During the mid-20th century, anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and v ...
discovered many fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s and evidence of human occupation perhaps as early as 7 million years ago (BP=before present). Fossil remains of several species of early apelike humans thought to have evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
into modern man, such as ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not ...
'' radiometrically dated
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares t ...
to approximately 3.9–3.0 million years BP, ''Paranthropus boisei
''Paranthropus boisei'' is a species of australopithecine from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.5 to 1.15 million years ago. The holotype specimen, OH 5, was discovered by palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey in 1959, and described by h ...
'' (c. 2.3–1.4 million years BP) and ''Homo ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into ''Homo erectus, H. erectus'' is an ongoin ...
'' (c. 1.9 million–600,000 years BP) have been discovered.
After the evolution of ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' approximately 350,000 to 260,000 years BP in Africa, the continent was mainly populated by groups of hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s. These first modern humans left Africa and populated the rest of the globe
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve purposes similar to maps, but unlike maps, they do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A model globe ...
during the Out of Africa II
In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the ...
migration dated to approximately 50,000 years BP, exiting the continent either across Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (Arabic: , , ) is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
Name
The strait derives its name from the dangers attendin ...
over the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
, the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
in Morocco, or the Isthmus of Suez
The Isthmus of Suez is the land bridge"Suez Canal ...
in Egypt.
Other migrations of modern humans within the African continent have been dated to that time, with evidence of early human settlement found in Southern Africa, Southeast Africa, North Africa, and the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
.
Emergence of civilization
The size of the Sahara has historically been extremely variable, with its area rapidly fluctuating and at times disappearing depending on global climatic conditions. At the end of theIce age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
s, estimated to have been around 10,500 BC, the Sahara had again become a green fertile valley, and its African populations returned from the interior and coastal highlands in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, with rock art paintings depicting a fertile Sahara and large populations discovered in Tassili n'Ajjer
Tassili n'Ajjer ( Berber: ''Tassili n Ajjer'', ar, طاسيلي ناجر; "Plateau of rivers") is a national park in the Sahara desert, located on a vast plateau in southeastern Algeria. Having one of the most important groupings of prehistoric ...
dating back perhaps 10 millennia. However, the warming and drying climate meant that by 5000 BC, the Sahara region was becoming increasingly dry and hostile. Around 3500 BC, due to a tilt in the earth's orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
, the Sahara experienced a period of rapid desertification. The population trekked out of the Sahara region towards the Nile Valley below the Second Cataract
The Cataracts of the Nile are shallow lengths (or whitewater rapids) of the Nile river, between Khartoum and Aswan, where the surface of the water is broken by many small boulders and stones jutting out of the river bed, as well as many rocky ...
where they made permanent or semi-permanent settlements. A major climatic recession occurred, lessening the heavy and persistent rains in Central and Eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
. Since this time, dry conditions have prevailed in Eastern Africa and, increasingly during the last 200 years, in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.
 The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gatherer cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC, cattle were domesticated in North Africa. In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals, including the donkey and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to
The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gatherer cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC, cattle were domesticated in North Africa. In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals, including the donkey and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
.
Between 10,000 and 9,000 BC, pottery was independently invented in the region of Mali in the savannah of West Africa. Simon Bradley, ''A Swiss-led team of archaeologists has discovered pieces of the oldest African pottery in central Mali, dating back to at least 9,400BC'', SWI swissinfo.ch – the international service of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (SBC), 18 January 2007 In the
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
s and savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
hs of the Sahara and Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
in Northern West Africa, people possibly ancestral to modern Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. T ...
and Mandé cultures started to collect wild millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
, around 8000 to 6000 BC. Later, gourd
Gourds include the fruits of some flowering plant species in the family Cucurbitaceae, particularly ''Cucurbita'' and ''Lagenaria''. The term refers to a number of species and subspecies, many with hard shells, and some without. One of the earli ...
s, watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 varieti ...
s, castor bean
''Ricinus communis'', the castor bean or castor oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus, ''Ricinus'', and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of ...
s, and cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
were also collected. Sorghum was first domesticated in Eastern Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
around 4000 BC, in one of the earliest instances of agriculture in human history. Its cultivation would gradually spread across Africa, before spreading to India around 2000 BC.

Sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
was first domesticated in the . They also started making pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and por ...
and built stone settlements (e.g., Tichitt
Tichit or Tichitt ( ber, Ticit, ar, تيشيت) is a partly abandoned village at the foot of the Tagant Plateau in central southern Mauritania that is known for its vernacular architecture. The main agriculture in Tichit is date farming, and the ...
, Oualata
, settlement_type = Communes of Mauritania, Commune and town
, image_skyline = Oualata 03.jpg
, imagesize = 300px
, image_caption = View of the town looking in a southeas ...
). Fishing, using bone-tipped harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, seal hunting, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the t ...
s, became a major activity in the numerous streams and lakes formed from the increased rains. In West Africa, the wet phase ushered in an expanding rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
and wooded savanna from Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
to Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
. Between 9,000 and 5,000 BC, Niger–Congo speakers domesticated the oil palm
''Elaeis'' () is a genus of palms containing two species, called oil palms. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil. The African oil palm ''Elaeis guineensis'' (the species name ''guineensis'' referring to its co ...
and raffia palm
Raffia palms (''Raphia'') are a genus of about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species (''R. taedigera'') also occurring in Central and South America. ''R. taedigera'' is the sour ...
. Black-eyed pea
The black-eyed pea or black-eyed bean is a legume grown around the world for its medium-sized, edible bean. It is a subspecies of the cowpea, an Old World plant domesticated in Africa, and is sometimes simply called a cowpea.
The common commer ...
s and voandzeia
''Vigna'' is a genus of plants in the legume family, Fabaceae, with a pantropical distribution.Aitawade, M. M., et al. (2012)Section ''Ceratotropis'' of subgenus ''Ceratotropis'' of ''Vigna'' (Leguminosae–Papilionoideae) in India with a new ...
(African groundnuts), were domesticated, followed by okra
Okra or Okro (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in many English-speaking countries as ladies' fingers or ochro, is a flowering plant in the mallow family. It has edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with su ...
and kola nut
The term kola nut usually refers to the seeds of certain species of plant of the genus ''Cola'', placed formerly in the cocoa family Sterculiaceae and now usually subsumed in the mallow family Malvaceae (as subfamily Sterculioideae). These cola ...
s. Since most of the plants grew in the forest, the Niger–Congo speakers invented polished stone axes for clearing forest.
Around 4000 BC, the Saharan climate started to become drier at an exceedingly fast pace.O'Brien, Patrick K. ed. (2005) ''Oxford Atlas of World History''. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 22–23. This climate change caused lakes and rivers to shrink significantly and caused increasing desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
. This, in turn, decreased the amount of land conducive to settlements and encouraged migrations of farming communities to the more tropical climate of West Africa. During the first millennium BC, a reduction in wild grain populations related to changing climate conditions facilitated the expansion of farming communities and the rapid adoption of rice cultivation around the Niger River.
By the first millennium BC, ironworking
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
had been introduced in Northern Africa. Around that time it also became established in parts of sub-Saharan Africa, either through independent invention there or diffusion from the northBreunig, Peter. 2014. Nok: African Sculpture in Archaeological Context: p. 21. and vanished under unknown circumstances around 500 AD, having lasted approximately 2,000 years,Fagg, Bernard. 1969. Recent work in west Africa: New light on the Nok culture. World Archaeology 1(1): 41–50. and by 500 BC, metalworking began to become commonplace in West Africa. Ironworking
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
was fully established by roughly 500 BC in many areas of East and West Africa, although other regions didn't begin ironworking until the early centuries AD. Copper objects from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, North Africa, Nubia, and Ethiopia dating from around 500 BC have been excavated in West Africa, suggesting that Trans-Saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade requires travel across the Sahara between sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa. While existing from prehistoric times, the peak of trade extended from the 8th century until the early 17th century.
The Sahara once had a very d ...
networks had been established by this date.
Early civilizations
Pharaonic
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ...
civilization of Ancient Egypt. One of the world's earliest and longest-lasting civilizations, the Egyptian state continued, with varying levels of influence over other areas, until 343 BC. Egyptian influence reached deep into modern-day Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
and Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
, and, according to Martin Bernal, as far north as Crete.
An independent centre of civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Ci ...
with trading links to Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
was established by Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns from Tyre on the north-west African coast at Carthage.
European exploration of Africa
The geography of North Africa has been reasonably well known among Europeans since classical antiquity in Greco-Roman geography. Northwest Africa (the Maghreb) was known as either ''Libya'' or ''Africa'', while Egypt was considered part of Asia. ...
began with Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. In 332 BC, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
was welcomed as a liberator in Persian-occupied Egypt. He founded Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
after his death.
 Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean
Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, the area was integrated economically and culturally into the Roman system. Roman settlement occurred in modern Tunisia and elsewhere along the coast. The first Roman emperor native to North Africa was Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
, born in Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by other names
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent fil ...
in present-day Libya—his mother was Italian Roman and his father was Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
.
Christianity spread across these areas at an early date, from Judaea via Egypt and beyond the borders of the Roman world into Nubia; by AD 340 at the latest, it had become the state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular state, secular, is not n ...
of the Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
. Syro-Greek missionaries, who arrived by way of the Red Sea, were responsible for this theological development.
In the early 7th century, the newly formed Arabian Islamic Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
expanded into Egypt, and then into North Africa. In a short while, the local Berber elite had been integrated into Muslim Arab tribes. When the Umayyad capital Damascus fell in the 8th century, the Islamic centre of the Mediterranean shifted from Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
to Qayrawan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( ar, ٱلْقَيْرَوَان, al-Qayrawān , aeb, script=Latn, Qeirwān ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by t ...
in North Africa. Islamic North Africa had become diverse, and a hub for mystics, scholars, jurists, and philosophers. During the above-mentioned period, Islam spread to sub-Saharan Africa, mainly through trade routes and migration.
In West Africa, Dhar Tichitt
Dhar Tichitt is a Neolithic archaeological site located in the southwestern region of the Sahara Desert, in Mauritania. It is one of several settlement locations along the sandstone cliffs in the area. Dhar Tichitt, Dhar Walata, Dhar Néma, an ...
and Oualata
, settlement_type = Communes of Mauritania, Commune and town
, image_skyline = Oualata 03.jpg
, imagesize = 300px
, image_caption = View of the town looking in a southeas ...
in present-day Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
figure prominently among the early urban centers, dated to 2,000 BC. About 500 stone settlements litter the region in the former savannah of the Sahara. Its inhabitants fished and grew millet. It has been found by Augustin Holl that the Soninke of the Mandé peoples
The Mandé peoples are ethnic groups who are speakers of Mande languages. Various Mandé speaking ethnic groups are found particularly toward the west of West Africa. The Mandé Speaking languages are divided into two primary groups: East Mandé ...
were likely responsible for constructing such settlements. Around 300 BC the region became more desiccated and the settlements began to decline, most likely relocating to Koumbi Saleh
Koumbi Saleh, sometimes Kumbi Saleh is the site of a ruined medieval town in south east Mauritania that may have been the capital of the Ghana Empire.
From the ninth century, Arab authors mention the Ghana Empire in connection with the trans-Saha ...
. Architectural evidence and the comparison of pottery styles suggest that Dhar Tichitt was related to the subsequent Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, ...
. Djenné-Djenno
Djenné-Djenno (also Jenne-Jeno; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali. Literally translated to "ancient Djenné", it is the original site of both Djenné and Mali and is considered to be among ...
(in present-day Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
) was settled around 300 BC, and the town grew to house a sizable Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
population, as evidenced by crowded cemeteries. Living structures were made of sun-dried mud. By 250 BC Djenné-Djenno
Djenné-Djenno (also Jenne-Jeno; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali. Literally translated to "ancient Djenné", it is the original site of both Djenné and Mali and is considered to be among ...
had become a large, thriving market town.
Farther south, in central Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, around 1,500 BC, the Nok culture
The Nok culture (or Nok civilization) is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham village of Nok in Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria ...
developed on the Jos Plateau
The Jos Plateau is a plateau located near the centre of Nigeria. The plateau has given its name to the Plateau State in which it is found and is named for the state's capital, Jos. The plateau is home to people of diverse cultures and languages ...
. It was a highly centralized community. The Nok people produced lifelike representations in terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based ceramic glaze, unglazed or glazed ceramic where the pottery firing, fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, a ...
, including human heads and human figures, elephants, and other animals. By 500 BC, and possibly earlier, they were smelting iron. By 200 AD the Nok culture had vanished. and vanished under unknown circumstances around 500 AD, having lasted approximately 2,000 years. Based on stylistic similarities with the Nok terracottas, the bronze figurines of the Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
kingdom of Ife and those of the Bini kingdom of Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
are suggested to be continuations of the traditions of the earlier Nok culture.
Ninth to eighteenth centuries
San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, ...
of southern Africa; larger, more structured groups such as the family clan groupings of the Bantu-speaking
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The tot ...
peoples
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, ...
of central, southern, and eastern Africa; heavily structured clan groups in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
; the large Sahelian kingdoms
The Sahelian kingdoms were a series of centralized kingdoms or empires that were centered on the Sahel, the area of grasslands south of the Sahara, from the 8th century to the 19th. The wealth of the states came from controlling the trade routes ...
; and autonomous city-states and kingdoms such as those of the Akan Akan may refer to:
People and languages
*Akan people, an ethnic group in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire
*Akan language, a language spoken by the Akan people
*Kwa languages, a language group which includes Akan
*Central Tano languages, a language group w ...
; Edo, Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
, and Igbo people
The Igbo people ( , ; also spelled Ibo" and formerly also ''Iboe'', ''Ebo'', ''Eboe'',
*
*
* ''Eboans'', ''Heebo'';
natively ) are an ethnic group in Nigeria. They are primarily found in Abia, Anambra, Ebonyi, Enugu, and Imo States. A ...
in West Africa; and the Swahili coastal trading towns of Southeast Africa.
By the ninth century AD, a string of dynastic states, including the earliest Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
* ...
states, stretched across the sub-Saharan savannah from the western regions to central Sudan. The most powerful of these states were Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, Gao
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
, and the Kanem-Bornu Empire. Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
declined in the eleventh century, but was succeeded by the Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ...
which consolidated much of western Sudan in the thirteenth century. Kanem accepted Islam in the eleventh century.
In the forested regions of the West African coast, independent kingdoms grew with little influence from the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
north. The Kingdom of Nri
The Kingdom of Nri () was a medieval polity located in what is now Nigeria. The kingdom existed as a sphere of religious and political influence over a third of Igboland, and was administered by a priest-king called an ''Eze Nri''. The ''Eze Nri ...
was established around the ninth century and was one of the first. It is also one of the oldest kingdoms in present-day Nigeria and was ruled by the Eze Nri
The following is a list of rulers of Nri. The title of the ruler of Nri is ''Eze Nri''. He held religious and political authority over the Kingdom of Nri.
The Nri culture is believed to stretch back to at least the 13th century, with a traditiona ...
. The Nri kingdom is famous for its elaborate bronzes, found at the town of Igbo-Ukwu
Igbo-Ukwu (English: ''Great Igbo'') is a town in the Nigerian state of Anambra in the south-central part of the country. The town comprises three quarters namely Obiuno, Ngo, and Ihite (an agglomeration of 4 quarters) with several villages within ...
. The bronzes have been dated from as far back as the ninth century.
The Kingdom of Ife, historically the first of these Yoruba city-states or kingdoms, established government under a priestly oba ('king' or 'ruler' in the Yoruba language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. '; Ajami script, Ajami: ) is a language spoken in West Africa, primarily in South West (Nigeria), Southwestern Middle Belt, and Central Nigeria. It is spoken by the Ethnic group, ethnic Yoruba people. The number of Yoruba speake ...
), called the ''Ooni of Ife''. Ife was noted as a major religious and cultural centre in West Africa, and for its unique naturalistic tradition of bronze sculpture. The Ife model of government was adapted at the Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba empire of West Africa made up of parts of present-day eastern Benin and western Nigeria (including Southwest zone and the western half of Northcentral zone). It grew to become the largest Yoruba language, ...
, where its obas or kings, called the ''Alaafins of Oyo'', once controlled a large number of other Yoruba and non-Yoruba city-states and kingdoms; the Fon ''Kingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
'' was one of the non-Yoruba domains under Oyo control.
 The
The Almoravids
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
were a Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
dynasty from the Sahara that spread over a wide area of northwestern Africa and the Iberian peninsula during the eleventh century. The Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of th ...
and Banu Ma'qil
The Banu Ma'qil ( ar, بنو معقل) was an Arab nomadic tribe that originated in South Arabia. The tribe emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa with the Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym tribes in the 11th century. They mainly settled in and ...
were a collection of Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
tribes from the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
who migrated westwards via Egypt between the eleventh and thirteenth centuries. Their migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
resulted in the fusion of the Arabs and Berbers, where the locals were Arabized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
, and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
culture absorbed elements of the local culture, under the unifying framework of Islam.
Following the breakup of Mali, a local leader named Sonni Ali
Sunni Ali, also known as Si Ali, Sunni Ali Ber (Ber meaning "the Great"), was born in Ali Kolon. He reigned from about 1464 to 1492. Sunni Ali was the first king of the Songhai Empire, located in Africa and the 15th ruler of the Sunni dynasty. ...
(1464–1492) founded the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
in the region of middle Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesSudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
and took control of the trans-Saharan trade. Sonni Ali seized Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
in 1468 and Jenne in 1473, building his regime on trade revenues and the cooperation of Muslim merchants. His successor Askia Mohammad I
Askia Muhammad I (b. 1443 – d. 1538), born Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al-Turi or Muhammad Ture, was the first ruler of the Askia dynasty of the Songhai Empire, reigning from 1493 to 1528. He is also known as Askia the Great, and his name in modern ...
(1493–1528) made Islam the official religion, built mosques, and brought to Gao Muslim scholars, including al-Maghili (d.1504), the founder of an important tradition of Sudanic African Muslim scholarship.Lapidus, Ira M. (1988) ''A History of Islamic Societies'', Cambridge. By the eleventh century, some Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
* ...
states – such as Kano
Kano may refer to:
Places
*Kano State, a state in Northern Nigeria
* Kano (city), a city in Nigeria, and the capital of Kano State
**Kingdom of Kano, a Hausa kingdom between the 10th and 14th centuries
**Sultanate of Kano, a Hausa kingdom between ...
, jigawa, Katsina
Katsina, likely from "Tamashek" eaning son or bloodor mazza enwith "inna" otheris a Local Government Area and the capital city of Katsina State, in northern Nigeria.
, and Gobir
Gobir (Demonym: ''Gobirawa'') was a city-state in what is now Nigeria. Founded by the Hausa in the 11th century, Gobir was one of the seven original kingdoms of Hausaland, and continued under Hausa rule for nearly 700 years. Its capital was the ci ...
– had developed into walled towns engaging in trade, servicing caravans, and the manufacture of goods. Until the fifteenth century, these small states were on the periphery of the major Sudanic empires of the era, paying tribute to Songhai to the west and Kanem-Borno to the east.
Height of the slave trade
Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
had long been practiced in Africa. Between the 15th and the 19th centuries, the Atlantic slave trade took an estimated 7–12 million slaves to the New World. In addition, more than 1 million Europeans were captured by Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
and sold as slaves in North Africa between the 16th and 19th centuries.
In West Africa, the decline of the Atlantic slave trade in the 1820s caused dramatic economic shifts in local polities. The gradual decline of slave-trading, prompted by a lack of demand for slaves in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
, increasing anti-slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
legislation in Europe and America, and the British Royal Navy's increasing presence off the West African coast, obliged African states to adopt new economies. Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron
The West Africa Squadron, also known as the Preventative Squadron, was a squadron of the British Royal Navy whose goal was to suppress the Atlantic slave trade by patrolling the coast of West Africa. Formed in 1808 after the British Parliame ...
seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard.
Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers. The largest powers of West Africa (the Asante Confederacy
The Asante Empire ( Asante Twi: ), today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana as well as parts of ...
, the Kingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, and the Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba empire of West Africa made up of parts of present-day eastern Benin and western Nigeria (including Southwest zone and the western half of Northcentral zone). It grew to become the largest Yoruba language, ...
) adopted different ways of adapting to the shift. Asante and Dahomey concentrated on the development of "legitimate commerce" in the form of palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from ...
, cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
, timber and gold, forming the bedrock of West Africa's modern export trade. The Oyo Empire, unable to adapt, collapsed into civil wars.
Colonialism

Independence struggles
 Imperial rule by Europeans would continue until after the conclusion of
Imperial rule by Europeans would continue until after the conclusion of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, when almost all remaining colonial territories gradually obtained formal independence. Independence movements in Africa gained momentum following World War II, which left the major European powers weakened. In 1951, Libya, a former Italian colony, gained independence. In 1956, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
won their independence from France. Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
followed suit the next year (March 1957), becoming the first of the sub-Saharan colonies to be granted independence. Most of the rest of the continent became independent over the next decade.
Portugal's overseas presence in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
(most notably in Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, Cape Verde, Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
and São Tomé and Príncipe) lasted from the 16th century to 1975, after the Estado Novo regime was overthrown in a military coup in Lisbon. Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of S ...
unilaterally declared independence from the United Kingdom in 1965, under the white minority government of Ian Smith
Ian Douglas Smith (8 April 1919 – 20 November 2007) was a Rhodesian politician, farmer, and fighter pilot who served as Prime Minister of Rhodesia (known as Southern Rhodesia until October 1964 and now known as Zimbabwe) from 1964 to ...
, but was not internationally recognized as an independent state (as Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
) until 1980, when black nationalists gained power after a bitter guerrilla war. Although South Africa was one of the first African countries to gain independence, the state remained under the control of the country's white minority through a system of racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
known as apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
until 1994.
Post-colonial Africa
Today, Africa contains 54 sovereign countries, most of which have borders that were drawn during the era of European colonialism. Since independence, African states have frequently been hampered by instability, corruption, violence, and authoritarianism. The vast majority of African states are republics that operate under some form of thepresidential system
A presidential system, or single executive system, is a form of government in which a head of government, typically with the title of president, leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch in systems that use separati ...
of rule. However, few of them have been able to sustain democratic governments on a permanent basis—per the criteria laid out by Lührmann et al. (2018), only Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
and Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
have been consistently democratic for the entirety of their post-colonial history. Most African countries have experienced several coups or periods of military dictatorship
A military dictatorship is a dictatorship in which the military exerts complete or substantial control over political authority, and the dictator is often a high-ranked military officer.
The reverse situation is to have civilian control of the m ...
. Between 1990 and 2018, though, the continent as a whole has trended towards more democratic governance.
Upon independence an overwhelming majority of Africans lived in extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
. The continent suffered from the lack of infrastructural or industrial development under colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
rule, along with political instability. With limited financial resources or access to global markets, relatively stable countries such as Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
still experienced only very slow economic development. Only a handful of African countries succeeded in obtaining rapid economic growth prior to 1990. Exceptions include Libya and Equatorial Guinea, both of which possess large oil reserves.
Instability throughout the continent after decolonization resulted primarily from marginalization of ethnic groups, and corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
. In pursuit of personal political gain, many leaders deliberately promoted ethnic conflicts, some of which had originated during the colonial period, such as from the grouping of multiple unrelated ethnic groups into a single colony, the splitting of a distinct ethnic group between multiple colonies, or existing conflicts being exacerbated by colonial rule (for instance, the preferential treatment given to ethnic Hutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the prin ...
s over Tutsi
The Tutsi (), or Abatutsi (), are an ethnic group of the African Great Lakes region. They are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group and the second largest of three main ethnic groups in Rwanda and Burundi (the other two being the largest Bantu ethnic grou ...
s in Rwanda during German and Belgian rule).
Faced with increasingly frequent and severe violence, military rule was widely accepted by the population of many countries as means to maintain order, and during the 1970s and 1980s a majority of African countries were controlled by military dictatorships
A military dictatorship is a dictatorship in which the military exerts complete or substantial control over political authority, and the dictator is often a high-ranked military officer.
The reverse situation is to have civilian control of the m ...
. Territorial disputes between nations and rebellions by groups seeking independence were also common in independent African states. The most devastating of these was the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Nigerian–Biafran War or the Biafran War, was a civil war fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence f ...
, fought between government forces and an Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a ...
separatist republic, which resulted in a famine that killed 1-2 million people. Two civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
s in Sudan, the first The First may refer to:
* ''The First'' (album), the first Japanese studio album by South Korean boy group Shinee
* ''The First'' (musical), a musical with a book by critic Joel Siegel
* The First (TV channel), an American conservative opinion ne ...
lasting from 1955 to 1972 and the second
''The Second'' is the second studio album by Canadian-American rock band Steppenwolf, released in October 1968 on ABC Dunhill Records. The album contains one of Steppenwolf's most famous songs, " Magic Carpet Ride". The background of the orig ...
from 1983 to 2005 collectively killed around 3 million. Both were fought primarily on ethnic and religious lines.
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
conflicts between the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
also contributed to instability. Both the Soviet Union and the United States offered considerable incentives to African political and military leaders who aligned themselves with the superpowers' foreign policy. As an example, during the Angolan Civil War
The Angolan Civil War ( pt, Guerra Civil Angolana) was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war immediately began after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. The war was ...
, the Soviet and Cuban aligned MPLA
The People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola ( pt, Movimento Popular de Libertação de Angola, abbr. MPLA), for some years called the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola – Labour Party (), is an Angolan left-wing, social d ...
and the American aligned UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola ( pt, União Nacional para a Independência Total de Angola, abbr. UNITA) is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought alongside the Popular Movement for ...
received the vast majority of their military and political support from these countries. Many African countries became highly dependent on foreign aid. The sudden loss of both Soviet and American aid at the end of the Cold War and fall of the USSR
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
resulted in severe economic and political turmoil in the countries most dependent on foreign support.
There was a major famine in Ethiopia between 1983 and 1985, killing up to 1.2 million people, which most historians
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the stu ...
attribute primarily to the forced relocation of farmworkers and seizure of grain by communist Derg
The Derg (also spelled Dergue; , ), officially the Provisional Military Administrative Council (PMAC), was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia, then including present-day Eritrea, from 1974 to 1987, when the military leadership formally " c ...
government, further exacerbated by the civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. In 1994 a genocide in Rwanda
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed Hutu ...
resulted in up to 800,000 deaths, added to a severe refugee crisis and fueled the rise of militia groups in neighboring countries. This contributed to the outbreak of the first
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
Congo Wars, which were the most devastating military conflicts in modern Africa, with up to 5.5 million deaths, making it by far the deadliest conflict in modern African history and one of the costliest wars in human history.
File:Political Map of Africa.svg, Political map of Africa in 2021
Boko Haram Insurgency
The Boko Haram insurgency began in July 2009, when the militant Islamist and jihadist rebel group Boko Haram started an armed rebellion against the government of Nigeria. The conflict is taking place within the context of long-standing iss ...
primarily within Nigeria (with considerable fighting in Niger, Chad, and Cameroon as well) has killed around 350,000 people since 2009. Most African conflicts have been reduced to low-intensity conflicts as of 2022. However, the Tigray War
The Tigray War; ; . was an armed conflict that lasted from 3 November 2020 to 3 November 2022. The war was primarily fought in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia between the Ethiopian federal government and Eritrea on one side, and the Tigray Peop ...
which began in 2020 has killed an estimated 300,000-500,000 people, primarily due to famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
Overall though, violence across Africa has greatly declined in the 21st century, with the end of civil wars in Angola, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, and Algerian Civil War, Algeria in 2002, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
in 2003, and Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
and Burundi
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili language, Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French language, French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley at the ...
in 2005. The Second Congo War, which involved 9 countries and several insurgent groups, ended in 2003. This decline in violence coincided with many countries abandoning communist-style command economies and opening up for market reforms, which over the course of the 1990s and 2000s promoted the establishment of permanent, peaceful trade between neighboring countries (see Capitalist peace The capitalist peace, or capitalist peace theory, or commercial peace, posits that market openness contributes to more peaceful behavior among states, and that developed market-oriented economies are less likely to engage in conflict with one anot ...
).
Improved stability and economic reforms have led to a great increase in foreign investment into many African nations, mainly from China, which further spurred economic growth. Between 2000 and 2014, annual GDP growth in Sub-Saharan Africa averaged 5.02%, doubling its total GDP from $811 Billion to $1.63 Trillion (Constant 2015 USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
). North Africa experienced comparable growth rates. A significant part of this growth can also be attributed to the facilitated diffusion of information technologies and specifically the mobile telephone. While several individuals countries have maintained high growth rates, since 2014 overall growth has considerably slowed, primarily as a result of falling commodity prices, continued lack of industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
, and epidemics of Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
and COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
Geology, geography, ecology and environment
 Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest
Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the field of geology, a landmass is a defined section of continental ...
of the Earth. Separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, it is joined to Asia at its northeast extremity by the Isthmus of Suez
The Isthmus of Suez is the land bridge"Suez Canal ...
(transected by the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
), wide. (Geopolitically
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
, Egypt's Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a l ...
east of the Suez Canal is often considered part of Africa, as well.)
The coastline is long, and the absence of deep indentations of the shore is illustrated by the fact that Europe, which covers only – about a third of the surface of Africa – has a coastline of . From the most northerly point, Ras ben Sakka
Ras ben Sakka (Arabic for "Cape Ben Sakka"), the tip of Cape Angela in northern Tunisia, is the northernmost point of the African continent.
It is located from Bizerte and to the northeast of Ichkeul Lake World Heritage Site.
It is located ...
in Tunisia (37°21' N), to the most southerly point, Cape Agulhas
Cape Agulhas (; pt, Cabo das Agulhas , "Cape of the Needles") is a rocky headland in Western Cape, South Africa.
It is the geographic southern tip of the African continent and the beginning of the dividing line between the Atlantic and Indian ...
in South Africa (34°51'15" S), is a distance of approximately . Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
, 17°33'22" W, the westernmost point, is a distance of approximately to Ras Hafun
Ras Hafun ( so, Ras Xaafuun, ar, رأس حـافـون, it, Capo Hafun), also known as Cape Hafun, is a promontory in the northeastern Bari region of Somalia. Jutting out into the Guardafui Channel, it constitutes the easternmost point in Afri ...
, 51°27'52" E, the most easterly projection that neighbours Cape Guardafui
Cape Guardafui ( so, Gees Gardafuul, or Raas Caseyr, or Ras Asir, it, Capo Guardafui) is a headland in the autonomous Puntland region in Somalia. Coextensive with Puntland's Gardafuul administrative province, it forms the geographical apex of th ...
, the tip of the Horn of Africa.(1998) ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary (Index)'', Merriam-Webster, pp. 10–11.
Africa's largest country is Algeria, and its smallest country is Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
, an archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
off the east coast.Hoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A–Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publications. p. 11. The smallest nation on the continental mainland is The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
.
African plate
Climate
The climate of Africa ranges fromtropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
to subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
on its highest peaks. Its northern half is primarily desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
, or arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
, while its central and southern areas contain both savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
plains and dense jungle
A jungle is land covered with dense forest and tangled vegetation, usually in tropical climates. Application of the term has varied greatly during the past recent century.
Etymology
The word ''jungle'' originates from the Sanskrit word ''jaṅ ...
(rainforest) regions. In between, there is a convergence, where vegetation patterns such as sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
and steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
dominate. Africa is the hottest continent on Earth and 60% of the entire land surface consists of drylands and deserts."Africa: Environmental Atlas, 06/17/08.", University of Pennsylvania. Accessed June 2011.
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
in 1922 (), was discredited in 2013. (The 136 °F (57.8 °C), claimed by 'Aziziya, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, on 13 September 1922, has been officially deemed invalid by the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internati ...
.)
Ecology and biodiversity
 Africa has over 3,000
Africa has over 3,000 protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
s, with 198 marine protected areas, 50 biosphere reserves, and 80 wetlands reserves. Significant habitat destruction, increases in human population and poaching are reducing Africa's biological diversity and arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the ...
. Human encroachment, civil unrest and the introduction of non-native species threaten biodiversity in Africa. This has been exacerbated by administrative problems, inadequate personnel and funding problems.
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
is affecting Africa at twice the world rate, according to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on th ...
). According to the University of Pennsylvania African Studies Center, 31% of Africa's pasture lands and 19% of its forests and woodlands are classified as degraded, and Africa is losing over four million hectares of forest per year, which is twice the average deforestation rate for the rest of the world. Some sources claim that approximately 90% of the original, virgin forests in West Africa have been destroyed. Over 90% of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
's original forests have been destroyed since the arrival of humans 2000 years ago. About 65% of Africa's agricultural land suffers from soil degradation
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land t ...
.
Environmental issues
Water
Climate change

Fauna
 Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of
Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of wild animal
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted fo ...
populations and diversity, with wild populations of large carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other sof ...
s (such as lions, hyena
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek , ), are feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the clas ...
s, and cheetahs) and herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s (such as buffalo, elephants, camels, and giraffes) ranging freely on primarily open non-private plains. It is also home to a variety of "jungle" animals including snakes and primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
s and aquatic life
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The tw ...
such as crocodiles and amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s. In addition, Africa has the largest number of megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna.
Politics
African Union
 The
The African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
(AU) is a continental union
A continental union is a regional organization which facilitates pan-continental integration. Continental unions vary from collaborative intergovernmental organizations, to supranational politico- economic unions. Continental unions are a relativ ...
consisting of 55 member states
A member state is a state that is a member of an international organization or of a federation or confederation.
Since the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) include some members that are not sovereign states ...
. The union was formed, with Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
, Ethiopia, as its headquarters, on 26 June 2001. The union was officially established on 9 July 2002 as a successor to the Organisation of African Unity
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; french: Organisation de l'unité africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments. One of the main heads for OAU's ...
(OAU). In July 2004, the African Union's Pan-African Parliament
The Pan-African Parliament (PAP), also known as the African Parliament, is the legislative body of the African Union. It held its inaugural session in March 2004. The Parliament exercises oversight, and has advisory and consultative powers, ha ...
(PAP) was relocated to Midrand
Midrand is a former municipality in central Gauteng, South Africa. It is situated in-between Centurion and Sandton and now forms part of the City of Johannesburg Metropolitan Municipality.
History
Midrand was established as a municipality in 198 ...
, in South Africa, but the African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights
The African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights (ACHPR) is a quasi-judicial body tasked with promoting and protecting human rights and collective (peoples') rights throughout the African continent as well as interpreting the African Charter ...
remained in Addis Ababa.
The African Union, not to be confused with the AU Commission, is formed by the Constitutive Act of the African Union
The Constitutive Act of the African Union sets out the codified framework under which the African Union is to conduct itself. It was signed on 11 July 2000 at Lomé, Togo. It entered into force after two thirds of the 53 signatory states ratifi ...
, which aims to transform the African Economic Community
The African Economic Community (AEC) is an organization of African Union states establishing grounds for mutual economic development among the majority of African states. The stated goals of the organization include the creation of free trade ...
, a federated commonwealth, into a state under established international conventions. The African Union has a parliamentary government, known as the African Union Government, consisting of legislative, judicial and executive organs. It is led by the African Union President and Head of State, who is also the President of the Pan-African Parliament
The Pan-African Parliament (PAP), also known as the African Parliament, is the legislative body of the African Union. It held its inaugural session in March 2004. The Parliament exercises oversight, and has advisory and consultative powers, ha ...
. A person becomes AU President by being elected to the PAP, and subsequently gaining majority support in the PAP. The powers and authority of the President of the African Parliament derive from the Constitutive Act and the Protocol of the Pan-African Parliament, as well as the inheritance of presidential authority stipulated by African treaties and by international treaties, including those subordinating the Secretary General of the OAU
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; french: Organisation de l'unité africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments. One of the main heads for OAU's ...
Secretariat (AU Commission) to the PAP. The government of the AU consists of all-union, regional, state, and municipal authorities, as well as hundreds of institutions, that together manage the day-to-day affairs of the institution.
Extensive human rights abuses still occur in several parts of Africa, often under the oversight of the state. Most of such violations occur for political reasons, often as a side effect of civil war. Countries where major human rights violations have been reported in recent times include the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
, and Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
.
Boundary conflicts
Economy
natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
s, Africa remains the world's poorest and least-developed continent (other than Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
), the result of a variety of causes that may include corrupt governments that have often committed serious human rights violations
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
, failed central planning
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, part ...
, high levels of illiteracy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, huma ...
, low self-esteem, lack of access to foreign capital, legacies of colonialism, the slave
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
trade, and the Cold War, and frequent tribal and military conflict (ranging from guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
to genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
). Its total nominal GDP remains behind that of the United States, China, Japan, Germany, the United Kingdom, India and France. According to the United Nations' Human Development Report in 2003, the bottom 24 ranked nations (151st to 175th) were all African.
Poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
, illiteracy, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
and inadequate water supply and sanitation, as well as poor health, affect a large proportion of the people who reside in the African continent. In August 2008, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
announced revised global poverty estimates based on a new international poverty line of $1.25 per day (versus the previous measure of $1.00). 81% of the Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
population was living on less than $2.50 (PPP) per day in 2005, compared with 86% for India.
Sub-Saharan Africa is the least successful region of the world in reducing poverty ($1.25 per day); some 50% of the population living in poverty in 1981 (200 million people), a figure that rose to 58% in 1996 before dropping to 50% in 2005 (380 million people). The average poor person in sub-Saharan Africa is estimated to live on only 70 cents per day, and was poorer in 2003 than in 1973, indicating increasing poverty in some areas. Some of it is attributed to unsuccessful economic liberalization programmes spearheaded by foreign companies and governments, but other studies have cited bad domestic government policies more than external factors.
Africa is now at risk of being in debt once again, particularly in Sub-Saharan African countries. The last debt crisis
A crisis ( : crises; : critical) is either any event or period that will (or might) lead to an unstable and dangerous situation affecting an individual, group, or all of society. Crises are negative changes in the human or environmental affair ...
in 2005 was resolved with help from the heavily indebted poor countries scheme (HIPC). The HIPC resulted in some positive and negative effects on the economy in Africa. About ten years after the 2005 debt crisis in Sub-Saharan Africa was resolved, Zambia fell back into debt. A small reason was due to the fall in copper prices in 2011, but the bigger reason was that a large amount of the money Zambia borrowed was wasted or pocketed by the elite.
From 1995 to 2005, Africa's rate of economic growth increased, averaging 5% in 2005. Some countries experienced still higher growth rates, notably Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
and Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
, all of which had recently begun extracting their petroleum reserves or had expanded their oil extraction
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil dri ...
capacity.
In a recently published analysis based on World Values Survey
The World Values Survey (WVS) is a global research project that explores people's values and beliefs, how they change over time, and what social and political impact they have. Since 1981 a worldwide network of social scientists have conducted r ...
data, the Austrian political scientist Arno Tausch
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a sou ...
maintained that several African countries, most notably Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, perform quite well on scales of mass support for democracy and the market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
.
Tausch's global value comparison based on the World Values Survey
The World Values Survey (WVS) is a global research project that explores people's values and beliefs, how they change over time, and what social and political impact they have. Since 1981 a worldwide network of social scientists have conducted r ...
derived the following factor analytical scales: 1. The non-violent and law-abiding society 2. Democracy movement 3. Climate of personal non-violence 4. Trust in institutions 5. Happiness, good health 6. No redistributive religious fundamentalism 7. Accepting the market 8. Feminism 9. Involvement in politics 10. Optimism and engagement 11. No welfare mentality, acceptancy of the Calvinist work ethics. The spread in the performance of African countries with complete data, Tausch concluded "is really amazing". While one should be especially hopeful about the development of future democracy and the market economy in Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, the article suggests pessimistic tendencies for Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and especially for Africa's leading economy, South Africa. High Human Inequality
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, an ...
, as measured by the UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
's Human Development Report
The Human Development Report (HDR) is an annual Human Development Index report published by the Human Development Report Office of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
The first HDR was launched in 1990 by the Pakistani economist ...
's Index of Human Inequality
Index (or its plural form indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on a Halo megastru ...
, further impairs the development of human security Human security is a paradigm for understanding global vulnerabilities whose proponents challenges the traditional notion of national security through military security by arguing that the proper referent for security should be at the human rather t ...
. Tausch also maintains that the certain recent optimism, corresponding to economic and human rights data, emerging from Africa, is reflected in the development of a civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere.
The continent is believed to hold 90% of the world's
, ''Migration Information Source''. August 2008 A Harvard University study led by professor
 While Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs, the majority of the people respect African religions or parts of them. However, in formal surveys or census, most people will identify with major religions that came from outside the continent, mainly through colonisation. There are several reasons for this, the main one being the colonial idea that African religious beliefs and practices are not good enough. Religious beliefs and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are often a sensitive topic for governments with mixed religious populations. According to the ''World Book Encyclopedia'', Islam in Africa, Islam and Christianity in Africa, Christianity are the two largest religions in Africa. According to Encyclopædia Britannica, 45% of the population are Christians, 40% are Muslims, and 10% follow Traditional African religions, traditional religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Buddhist, Confucianist, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, or Judaism in Africa, Jewish. There is also a minority of people in Africa who are Irreligion in Africa, irreligious.
While Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs, the majority of the people respect African religions or parts of them. However, in formal surveys or census, most people will identify with major religions that came from outside the continent, mainly through colonisation. There are several reasons for this, the main one being the colonial idea that African religious beliefs and practices are not good enough. Religious beliefs and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are often a sensitive topic for governments with mixed religious populations. According to the ''World Book Encyclopedia'', Islam in Africa, Islam and Christianity in Africa, Christianity are the two largest religions in Africa. According to Encyclopædia Britannica, 45% of the population are Christians, 40% are Muslims, and 10% follow Traditional African religions, traditional religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Buddhist, Confucianist, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, or Judaism in Africa, Jewish. There is also a minority of people in Africa who are Irreligion in Africa, irreligious.
 * The Afroasiatic languages, ''Afroasiatic'' languages are a language family of about 240 languages and 285 million people widespread throughout the Horn of Africa, North Africa, the
* The Afroasiatic languages, ''Afroasiatic'' languages are a language family of about 240 languages and 285 million people widespread throughout the Horn of Africa, North Africa, the
 More than 85% of individuals in Africa use traditional medicine as an alternative to often expensive allopathic medical health care and costly pharmaceutical products. The Organisation of African Unity, Organization of African Unity (OAU) Heads of State and Government declared the 2000s decade as the African Decade on African traditional medicine in an effort to promote The WHO African Region's adopted resolution for institutionalizing traditional medicine in health care systems across the continent. Public policy makers in the region are challenged with consideration of the importance of traditional/indigenous health systems and whether their coexistence with the modern medical and health sub-sector would improve the equitability and accessibility of health care distribution, the health status of populations, and the social-economic development of nations within sub-Saharan Africa.
HIV/AIDS in Africa, AIDS in post-colonial Africa is a prevalent issue. Although the continent is home to about 15.2 percent of the world's population, more than two-thirds of the total infected worldwide – some 35 million people – were Africans, of whom 15 million have already died.
More than 85% of individuals in Africa use traditional medicine as an alternative to often expensive allopathic medical health care and costly pharmaceutical products. The Organisation of African Unity, Organization of African Unity (OAU) Heads of State and Government declared the 2000s decade as the African Decade on African traditional medicine in an effort to promote The WHO African Region's adopted resolution for institutionalizing traditional medicine in health care systems across the continent. Public policy makers in the region are challenged with consideration of the importance of traditional/indigenous health systems and whether their coexistence with the modern medical and health sub-sector would improve the equitability and accessibility of health care distribution, the health status of populations, and the social-economic development of nations within sub-Saharan Africa.
HIV/AIDS in Africa, AIDS in post-colonial Africa is a prevalent issue. Although the continent is home to about 15.2 percent of the world's population, more than two-thirds of the total infected worldwide – some 35 million people – were Africans, of whom 15 million have already died.
 Some aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practised in recent years as a result of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. For example, African customs were discouraged, and African languages were prohibited in mission schools. Leopold II of Belgium attempted to "civilize" Africans by discouraging polygamy and witchcraft.
Obidoh Freeborn posits that colonialism is one element that has created the character of modern African art. According to authors Douglas Fraser and Herbert M. Cole, "The precipitous alterations in the power structure wrought by colonialism were quickly followed by drastic iconographic changes in the art." Fraser and Cole assert that, in Igboland, some art objects "lack the vigor and careful craftsmanship of the earlier art objects that served traditional functions. Author Chika Okeke-Agulu states that "the racist infrastructure of British imperial enterprise forced upon the political and cultural guardians of empire a denial and suppression of an emergent sovereign Africa and modernist art." Editors F. Abiola Irele and Simon Gikandi comment that the current identity of African literature had its genesis in the "traumatic encounter between Africa and Europe." On the other hand, Mhoze Chikowero believes that Africans deployed music, dance, spirituality, and other performative cultures to (re)assert themselves as active agents and indigenous intellectuals, to unmake their colonial marginalization and reshape their own destinies."
There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalue African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of West African Vodun, Vodou and other forms of spirituality.
Some aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practised in recent years as a result of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. For example, African customs were discouraged, and African languages were prohibited in mission schools. Leopold II of Belgium attempted to "civilize" Africans by discouraging polygamy and witchcraft.
Obidoh Freeborn posits that colonialism is one element that has created the character of modern African art. According to authors Douglas Fraser and Herbert M. Cole, "The precipitous alterations in the power structure wrought by colonialism were quickly followed by drastic iconographic changes in the art." Fraser and Cole assert that, in Igboland, some art objects "lack the vigor and careful craftsmanship of the earlier art objects that served traditional functions. Author Chika Okeke-Agulu states that "the racist infrastructure of British imperial enterprise forced upon the political and cultural guardians of empire a denial and suppression of an emergent sovereign Africa and modernist art." Editors F. Abiola Irele and Simon Gikandi comment that the current identity of African literature had its genesis in the "traumatic encounter between Africa and Europe." On the other hand, Mhoze Chikowero believes that Africans deployed music, dance, spirituality, and other performative cultures to (re)assert themselves as active agents and indigenous intellectuals, to unmake their colonial marginalization and reshape their own destinies."
There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalue African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of West African Vodun, Vodou and other forms of spirituality.


 Fifty-four African countries have Association football, football teams in the Confederation of African Football. Egypt has won the African Cup seven times, and a record-making three times in a row. Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, Ghana, and Algeria have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so.
The top clubs in each African football league play the CAF Champions League, while lower-ranked clubs compete in CAF Confederation Cup.
In recent years, the continent has made major progress in terms of state-of-the-art basketball facilities which have been built in cites as diverse as Cairo, Dakar, Johannesburg, Kigali, Luanda and Rades. The number of African basketball players who drafted into the National Basketball Association, NBA has experienced major growth in the 2010s.
Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa national cricket team, South Africa and Zimbabwe national cricket team, Zimbabwe have Test cricket, Test status, while Kenya national cricket team, Kenya is the leading non-test team and previously had One Day International, One-Day International cricket (ODI) status (from President's Cup 1997-98, 10 October 1997, until 2014 Cricket World Cup Qualifier#Super Six, 30 January 2014). The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia national cricket team, Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup.
Fifty-four African countries have Association football, football teams in the Confederation of African Football. Egypt has won the African Cup seven times, and a record-making three times in a row. Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, Ghana, and Algeria have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so.
The top clubs in each African football league play the CAF Champions League, while lower-ranked clubs compete in CAF Confederation Cup.
In recent years, the continent has made major progress in terms of state-of-the-art basketball facilities which have been built in cites as diverse as Cairo, Dakar, Johannesburg, Kigali, Luanda and Rades. The number of African basketball players who drafted into the National Basketball Association, NBA has experienced major growth in the 2010s.
Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa national cricket team, South Africa and Zimbabwe national cricket team, Zimbabwe have Test cricket, Test status, while Kenya national cricket team, Kenya is the leading non-test team and previously had One Day International, One-Day International cricket (ODI) status (from President's Cup 1997-98, 10 October 1997, until 2014 Cricket World Cup Qualifier#Super Six, 30 January 2014). The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia national cricket team, Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup.
territory, with flag ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by area, Area
(km2) ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by population, Population{{cite web, url=https://www.census.gov\/cgi-bin/ipc/idbrank.pl, title=IDB: Countries Ranked by Population, date=28 November 1999, url-status=bot: unknown, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/19991128111024/http://www.census.gov/cgi-bin/ipc/idbrank.pl, archive-date=28 November 1999 ! Year ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by population density, Density
(per km2) ! Capital ! Language, Name(s) in official language(s) ! ISO 3166-1 alpha-3, ISO 3166-1 , - style="background:#eee;" , colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", North Africa , - , style="text-align:center" , , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Algeria
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Algeria
,
Santa Cruz de Tenerife , Canarias , IC , - , style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ceuta , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ceuta , , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Western Sahara
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Western Sahara
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Comoros
, Comoros
, style="text-align:right;", 2,170
, style="text-align:right;", 752,438
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 347
, Moroni, Comoros, Moroni
, Komori/Comores/جزر القمر (Juzur al-Qumur)
, COM
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Comoros
, Comoros
, style="text-align:right;", 2,170
, style="text-align:right;", 752,438
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 347
, Moroni, Comoros, Moroni
, Komori/Comores/جزر القمر (Juzur al-Qumur)
, COM
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Djibouti
, Djibouti
, style="text-align:right;", 23,000
, style="text-align:right;", 828,324
, style="text-align:right;", 2015
, style="text-align:right;", 22
, Djibouti (city), Djibouti
, Yibuuti/جيبوتي (Jībūtī)/Djibouti/Jabuuti
, DJI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Eritrea
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Eritrea
, Eritrea
, style="text-align:right;", 121,320
, style="text-align:right;", 5,647,168
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 47
, Asmara
, Eritrea
, ERI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ethiopia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ethiopia
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Djibouti
, Djibouti
, style="text-align:right;", 23,000
, style="text-align:right;", 828,324
, style="text-align:right;", 2015
, style="text-align:right;", 22
, Djibouti (city), Djibouti
, Yibuuti/جيبوتي (Jībūtī)/Djibouti/Jabuuti
, DJI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Eritrea
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Eritrea
, Eritrea
, style="text-align:right;", 121,320
, style="text-align:right;", 5,647,168
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 47
, Asmara
, Eritrea
, ERI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ethiopia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ethiopia
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Madagascar
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Madagascar
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mozambique
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mozambique
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Somalia
, Somalia
, style="text-align:right;", 637,657
, style="text-align:right;", 9,832,017
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 15
, Mogadishu
, 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖 (Soomaaliya) /الصومال (aṣ-Ṣūmāl)
, SOM
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Somalia
, Somalia
, style="text-align:right;", 637,657
, style="text-align:right;", 9,832,017
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 15
, Mogadishu
, 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖 (Soomaaliya) /الصومال (aṣ-Ṣūmāl)
, SOM
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Somaliland
, Somaliland
, style="text-align:right;", 176,120
, style="text-align:right;", 5,708,180
, style="text-align:right;", 2021
, style="text-align:right;", 25
, Hargeisa
, Soomaaliland/صوماليلاند (Ṣūmālīlānd)
,
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Somaliland
, Somaliland
, style="text-align:right;", 176,120
, style="text-align:right;", 5,708,180
, style="text-align:right;", 2021
, style="text-align:right;", 25
, Hargeisa
, Soomaaliland/صوماليلاند (Ṣūmālīlānd)
,
, -
, style="text-align:center" ,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, South Sudan
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, South Sudan
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Sudan
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Sudan
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Angola
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Angola
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Equatorial Guinea
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Equatorial Guinea
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, São Tomé and Príncipe
, São Tomé and Príncipe
, style="text-align:right;", 1,001
, style="text-align:right;", 212,679
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 212
, São Tomé
, São Tomé e Príncipe
, STP
, - style="background:#eee;"
, colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", Southern Africa
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Botswana
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Botswana
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, São Tomé and Príncipe
, São Tomé and Príncipe
, style="text-align:right;", 1,001
, style="text-align:right;", 212,679
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 212
, São Tomé
, São Tomé e Príncipe
, STP
, - style="background:#eee;"
, colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", Southern Africa
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Botswana
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Botswana
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Cape Verde
, Cape Verde
, style="text-align:right;", 4,033
, style="text-align:right;", 429,474
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 107
, Praia
, Cabo Verde/Kabu Verdi
, CPV
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, The Gambia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, The Gambia
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Cape Verde
, Cape Verde
, style="text-align:right;", 4,033
, style="text-align:right;", 429,474
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 107
, Praia
, Cabo Verde/Kabu Verdi
, CPV
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, The Gambia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, The Gambia
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Guinea
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Guinea
,  , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mauritania
,
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mauritania
,
African & Middle Eastern Reading Room
from the United States Library of Congress
Africa South of the Sahara
from Stanford University
The Index on Africa
from ''The Norwegian Council for Africa''
Aluka
Digital library of scholarly resources from and about Africa
Africa Interactive Map
from the United States Army Africa History
African Kingdoms
The Story of Africa
from BBC World Service *{{Cite EB1911, wstitle= Africa , volume= 1 , pages = 320–358 , short= 1
Africa Policy Information Center (APIC)
Hungarian military forces in Africa
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131103230525/http://www.scribd.com/doc/161017303/Hungarian-military-forces-in-Africa-%E2%80%93-past-and-future-Recovering-lost-knowledge-exploiting-cultural-anthropology-resources-creating-a-comprehensive , date=3 November 2013 News media
allAfrica.com
current news, events and statistics
''Focus on Africa''
magazine from BBC World Service {{Africa topics {{Africa {{Navboxes , title = Articles related to Africa , list = {{African Trade Agreements {{Continents of the world {{Regions of the world {{Authority control Africa, Continents Regions
cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, pr ...
, 90% of its platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platinu ...
, 50% of its gold, 98% of its chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
, 70% of its tantalite
The mineral group tantalite Fe,_manganese.html"_;"title="iron.html"_;"title="iron">Fe,_manganese">Mn)Tantalum">Ta2oxygen.html" ;"title="manganese">Mn)Tantalum.html" ;"title="iron">Fe,_manganese.html" ;"title="iron.html" ;"title="iron">Fe, manga ...
, 64% of its manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
and one-third of its uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
. The Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
(DRC) has 70% of the world's coltan
Coltan (short for columbite–tantalites and known industrially as tantalite) is a dull black metallic ore from which the elements niobium and tantalum are extracted. The niobium-dominant mineral in coltan is columbite (after niobium's original A ...
, a mineral used in the production of tantalum capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounded ...
s for electronic devices such as cell phones. The DRC also has more than 30% of the world's diamond reserves. Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
is the world's largest exporter of bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
. As the growth in Africa has been driven mainly by services and not manufacturing or agriculture, it has been growth without jobs and without reduction in poverty levels. In fact, the food security crisis of 2008 which took place on the heels of the global financial crisis pushed 100 million people into food insecurity.
In recent years, the People's Republic of China has built increasingly stronger ties with African nations and is Africa's largest trading partner. In 2007, Chinese companies invested a total of US$1 billion in Africa.Malia Politzer, "China and Africa: Stronger Economic Ties Mean More Migration", ''Migration Information Source''. August 2008 A Harvard University study led by professor
Calestous Juma
Calestous Juma (9 June 1953 – 15 December 2017) was a Kenyan scientist and academia, specializing in sustainable development. He was named one of the most influential 100 Africans in 2012, 2013 and 2014 by the ''New African'' magazine. He w ...
showed that Africa could feed itself by making the transition from importer to self-sufficiency. "African agriculture is at the crossroads; we have come to the end of a century of policies that favoured Africa's export of raw materials and importation of food. Africa is starting to focus on agricultural innovation as its new engine for regional trade and prosperity."
Demographics
Africa's population has rapidly increased over the last 40 years, and is consequently relatively young. In some African states, more than half the population is under 25 years of age. The total number of people in Africa increased from 229 million in 1950 to 630 million in 1990. As of , the population of Africa is estimated at billion . Africa's total population surpassing other continents is fairly recent; African population surpassed Europe in the 1990s, while the Americas was overtaken sometime around the year 2000; Africa's rapid population growth is expected to overtake the only two nations currently larger than its population, at roughly the same time – India and China's 1.4 billion people each will swap ranking around the year 2022. This increase in number of babies born in Africa compared to the rest of the world is expected to reach approximately 37% in the year 2050, an increase of 21% since 1990 alone. Speakers ofBantu languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The t ...
(part of the Niger–Congo family) are the majority in southern, central and southeast Africa. The Bantu-speaking peoples from the Sahel progressively expanded over most of Sub-Saharan Africa. But there are also several Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-sp ...
groups in South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
and East Africa, the mixed Swahili people
The Swahili people ( sw, WaSwahili) comprise mainly Bantu, Afro-Arab and Comorian ethnic groups inhabiting the Swahili coast, an area encompassing the Zanzibar archipelago and mainland Tanzania's seaboard, littoral Kenya, northern Mozambique, ...
on the Swahili Coast, and a few remaining indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Khoisan (" San" or "Bushmen") and Pygmy peoples
In anthropology, pygmy peoples are ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. The term pygmyism is used to describe the phenotype of endemic short stature (as opposed to disproportionate dwarfism occurring in isolated cases in a po ...
in southern and central Africa, respectively. Bantu-speaking Africans also predominate in Gabon and Equatorial Guinea, and are found in parts of southern Cameroon. In the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal de ...
of Southern Africa, the distinct people known as the Bushmen (also "San", closely related to, but distinct from "Khoikhoi, Hottentots") have long been present. The San are physically distinct from other Africans and are the indigenous people of southern Africa. Pygmies are the pre-Bantu indigenous peoples of central Africa.
The peoples of West Africa primarily speak Niger–Congo languages, belonging mostly to its non-Bantu branches, though some Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. T ...
and Afro-Asiatic speaking groups are also found. The Niger–Congo-speaking Yoruba language, Yoruba, Igbo language, Igbo, Fulani, Akan language, Akan and Wolof people, Wolof ethnic groups are the largest and most influential. In the central Sahara, Mandinka people, Mandinka or Mande languages, Mande groups are most significant. Chadic-speaking groups, including the Hausa language, Hausa, are found in more northerly parts of the region nearest to the Sahara, and Nilo-Saharan communities, such as the Songhai people, Songhai, Kanuri people, Kanuri and Zarma people, Zarma, are found in the eastern parts of West Africa bordering Central Africa.
The peoples of North Africa consist of three main indigenous groups: Berbers in the northwest, Egyptians in the northeast, and Nilo-Saharan-speaking peoples in the east. The Arabs who arrived in the 7th century AD introduced the Arabic language and Islam to North Africa. The Semitic Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns (who founded Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
) and Hyksos, the Indo-Iranian Alans, the Indo- European Ancient Greece, Greeks, Romans, and Vandals settled in North Africa as well. Significant Berber communities remain within Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
and Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
in the 21st century, while, to a lesser extent, Berber speakers are also present in some regions of Tunisia and Libya. The Berber-speaking Tuareg people, Tuareg and other often-nomadic peoples are the principal inhabitants of the Saharan interior of North Africa. In Mauritania, there is a small but near-extinct Berber community in the north and Niger–Congo-speaking peoples in the south, though in both regions Arabic and Arab culture predominates. In Sudan, although Arabic and Arab culture predominate, it is mostly inhabited by groups that originally spoke Nilo-Saharan, such as the Nubians, Fur, Masalit and Zaghawa, who, over the centuries, have variously intermixed with migrants from the Arabian peninsula. Small communities of Afro-Asiatic-speaking Beja nomads can also be found in Egypt and Sudan.
In the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, some Ethiopian and Eritrean groups (like the Amhara people, Amhara and Tigrayans, collectively known as Habesha people, Habesha) speak languages from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic language family, while the Oromo people, Oromo and Somalis, Somali speak languages from the Cushitic branch of Afro-Asiatic.
Prior to the decolonization movements of the post-World War II era, Ethnic groups in Europe, Europeans were represented in every part of Africa. Decolonization during the 1960s and 1970s often resulted in the mass emigration of white settlers – especially from Algeria and Morocco (1.6 million ''pieds-noirs'' in North Africa), Kenya, Congo, Rhodesia, Mozambique and Angola. Between 1975 and 1977, over a million colonials returned to Portugal alone. Nevertheless, White Africans of European ancestry, white Africans remain an important minority in many African states, particularly Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
, Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, Réunion, and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
. The country with the largest white African population is South Africa. Dutch people, Dutch and British diaspora in Africa, British diasporas represent the largest communities of European ancestry on the continent today.
European colonization also brought sizable groups of Asian people, Asians, particularly from the Indian subcontinent, to British colonies. Large Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin, Indian communities are found in South Africa, and smaller ones are present in Kenya, Tanzania, and some other southern and southeast African countries. The large Indians in Uganda, Indian community in Uganda was expulsion of Asians from Uganda, expelled by the dictator Idi Amin in 1972, though many have since returned. The islands in the Indian Ocean are also populated primarily by people of Asian origin, often mixed with Africans and Europeans. The Malagasy people of Madagascar are an Austronesian people, but those along the coast are generally mixed with Bantu, Arab, Indian and European origins. Malay and Indian ancestries are also important components in the group of people known in South Africa as Cape Coloureds (people with origins in two or more races and continents). During the 20th century, small but economically important communities of Demographics of Lebanon#The Lebanese Diaspora, Lebanese and Overseas Chinese, Chinese have also developed in the larger coastal cities of West Africa, West and East Africa, respectively.
Religion
 While Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs, the majority of the people respect African religions or parts of them. However, in formal surveys or census, most people will identify with major religions that came from outside the continent, mainly through colonisation. There are several reasons for this, the main one being the colonial idea that African religious beliefs and practices are not good enough. Religious beliefs and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are often a sensitive topic for governments with mixed religious populations. According to the ''World Book Encyclopedia'', Islam in Africa, Islam and Christianity in Africa, Christianity are the two largest religions in Africa. According to Encyclopædia Britannica, 45% of the population are Christians, 40% are Muslims, and 10% follow Traditional African religions, traditional religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Buddhist, Confucianist, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, or Judaism in Africa, Jewish. There is also a minority of people in Africa who are Irreligion in Africa, irreligious.
While Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs, the majority of the people respect African religions or parts of them. However, in formal surveys or census, most people will identify with major religions that came from outside the continent, mainly through colonisation. There are several reasons for this, the main one being the colonial idea that African religious beliefs and practices are not good enough. Religious beliefs and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are often a sensitive topic for governments with mixed religious populations. According to the ''World Book Encyclopedia'', Islam in Africa, Islam and Christianity in Africa, Christianity are the two largest religions in Africa. According to Encyclopædia Britannica, 45% of the population are Christians, 40% are Muslims, and 10% follow Traditional African religions, traditional religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Buddhist, Confucianist, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, or Judaism in Africa, Jewish. There is also a minority of people in Africa who are Irreligion in Africa, irreligious.
Languages
By most estimates, well over a thousand languages (UNESCO has estimated around two thousand) are spoken in Africa. Most are of African origin, though some are of European or Asian origin. Africa is the most Multilingualism, multilingual continent in the world, and it is not rare for individuals to fluently speak not only multiple African languages, but one or more European ones as well. There are four major language family, language families indigenous to Africa:Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, and Southwest Asia.
* The Nilo-Saharan languages, ''Nilo-Saharan'' language family consists of more than a hundred languages spoken by 30 million people. Nilo-Saharan languages are spoken by ethnic groups in Chad, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, Uganda, and northern Tanzania.
* The Niger–Congo languages, ''Niger-Congo'' language family covers much of Sub-Saharan Africa. In terms of number of languages, it is the largest language family in Africa and perhaps one of the largest in the world.
* The Khoisan languages, ''Khoisan'' languages number about fifty and are spoken in Southern Africa by approximately 400,000 people. Many of the Khoisan languages are endangered language, endangered. The Khoikhoi, Khoi and Bushmen, San peoples are considered the original inhabitants of this part of Africa.
Following the end of colonialism, nearly all African countries adopted official languages that originated outside the continent, although several countries also granted legal recognition to indigenous languages (such as Swahili language, Swahili, Yoruba language, Yoruba, Igbo language, Igbo and Hausa language, Hausa). In numerous countries, English and French (''see African French'') are used for communication in the public sphere such as government, commerce, education and the media. Arabic, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Afrikaans and Spanish are examples of languages that trace their origin to outside of Africa, and that are used by millions of Africans today, both in the public and private spheres. Italian is spoken by some in former Italian Colonial Empire, Italian colonies in Africa. German is spoken in Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, as it was a former German protectorate.
Health
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
alone accounted for an estimated 69 percent of all people living with HIV and 70 percent of all AIDS deaths in 2011. In the countries of sub-Saharan Africa most affected, AIDS has raised death rates and lowered life expectancy among adults between the ages of 20 and 49 by about twenty years. Furthermore, the life expectancy in many parts of Africa is declining, largely as a result of the HIV/AIDS epidemic with life-expectancy in some countries reaching as low as thirty-four years.
Culture
 Some aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practised in recent years as a result of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. For example, African customs were discouraged, and African languages were prohibited in mission schools. Leopold II of Belgium attempted to "civilize" Africans by discouraging polygamy and witchcraft.
Obidoh Freeborn posits that colonialism is one element that has created the character of modern African art. According to authors Douglas Fraser and Herbert M. Cole, "The precipitous alterations in the power structure wrought by colonialism were quickly followed by drastic iconographic changes in the art." Fraser and Cole assert that, in Igboland, some art objects "lack the vigor and careful craftsmanship of the earlier art objects that served traditional functions. Author Chika Okeke-Agulu states that "the racist infrastructure of British imperial enterprise forced upon the political and cultural guardians of empire a denial and suppression of an emergent sovereign Africa and modernist art." Editors F. Abiola Irele and Simon Gikandi comment that the current identity of African literature had its genesis in the "traumatic encounter between Africa and Europe." On the other hand, Mhoze Chikowero believes that Africans deployed music, dance, spirituality, and other performative cultures to (re)assert themselves as active agents and indigenous intellectuals, to unmake their colonial marginalization and reshape their own destinies."
There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalue African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of West African Vodun, Vodou and other forms of spirituality.
Some aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practised in recent years as a result of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. For example, African customs were discouraged, and African languages were prohibited in mission schools. Leopold II of Belgium attempted to "civilize" Africans by discouraging polygamy and witchcraft.
Obidoh Freeborn posits that colonialism is one element that has created the character of modern African art. According to authors Douglas Fraser and Herbert M. Cole, "The precipitous alterations in the power structure wrought by colonialism were quickly followed by drastic iconographic changes in the art." Fraser and Cole assert that, in Igboland, some art objects "lack the vigor and careful craftsmanship of the earlier art objects that served traditional functions. Author Chika Okeke-Agulu states that "the racist infrastructure of British imperial enterprise forced upon the political and cultural guardians of empire a denial and suppression of an emergent sovereign Africa and modernist art." Editors F. Abiola Irele and Simon Gikandi comment that the current identity of African literature had its genesis in the "traumatic encounter between Africa and Europe." On the other hand, Mhoze Chikowero believes that Africans deployed music, dance, spirituality, and other performative cultures to (re)assert themselves as active agents and indigenous intellectuals, to unmake their colonial marginalization and reshape their own destinies."
There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalue African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of West African Vodun, Vodou and other forms of spirituality.
Visual art

Architecture
Cinema
Music

Dance
Sports
 Fifty-four African countries have Association football, football teams in the Confederation of African Football. Egypt has won the African Cup seven times, and a record-making three times in a row. Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, Ghana, and Algeria have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so.
The top clubs in each African football league play the CAF Champions League, while lower-ranked clubs compete in CAF Confederation Cup.
In recent years, the continent has made major progress in terms of state-of-the-art basketball facilities which have been built in cites as diverse as Cairo, Dakar, Johannesburg, Kigali, Luanda and Rades. The number of African basketball players who drafted into the National Basketball Association, NBA has experienced major growth in the 2010s.
Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa national cricket team, South Africa and Zimbabwe national cricket team, Zimbabwe have Test cricket, Test status, while Kenya national cricket team, Kenya is the leading non-test team and previously had One Day International, One-Day International cricket (ODI) status (from President's Cup 1997-98, 10 October 1997, until 2014 Cricket World Cup Qualifier#Super Six, 30 January 2014). The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia national cricket team, Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup.
Fifty-four African countries have Association football, football teams in the Confederation of African Football. Egypt has won the African Cup seven times, and a record-making three times in a row. Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, Ghana, and Algeria have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so.
The top clubs in each African football league play the CAF Champions League, while lower-ranked clubs compete in CAF Confederation Cup.
In recent years, the continent has made major progress in terms of state-of-the-art basketball facilities which have been built in cites as diverse as Cairo, Dakar, Johannesburg, Kigali, Luanda and Rades. The number of African basketball players who drafted into the National Basketball Association, NBA has experienced major growth in the 2010s.
Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa national cricket team, South Africa and Zimbabwe national cricket team, Zimbabwe have Test cricket, Test status, while Kenya national cricket team, Kenya is the leading non-test team and previously had One Day International, One-Day International cricket (ODI) status (from President's Cup 1997-98, 10 October 1997, until 2014 Cricket World Cup Qualifier#Super Six, 30 January 2014). The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia national cricket team, Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup. Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
in northern Africa has also hosted the 2002 Morocco Cup, but the national team has never qualified for a major tournament.
Rugby union, Rugby is popular in several southern African nations. Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
both have appeared on multiple occasions at the Rugby World Cup, while South Africa is the joint-most successful national team (alongside New Zealand) at the Rugby World Cup, having won the tournament on 3 occasions, in 1995, 2007, and 2019.
Territories and regions
The countries in this table are categorized according to the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, scheme for geographic subregions used by the United Nations, and data included are per sources in cross-referenced articles. Where they differ, provisos are clearly indicated. {, class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto; border:1px solid #aaa;" , - style="background:#ececec;" ! class="unsortable" style="width:20px" , Coat of arms, Arms ! class="unsortable" style="width:20px" , Flag ! Name of region andterritory, with flag ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by area, Area
(km2) ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by population, Population{{cite web, url=https://www.census.gov\/cgi-bin/ipc/idbrank.pl, title=IDB: Countries Ranked by Population, date=28 November 1999, url-status=bot: unknown, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/19991128111024/http://www.census.gov/cgi-bin/ipc/idbrank.pl, archive-date=28 November 1999 ! Year ! data-sort-type="number" , List of countries and dependencies by population density, Density
(per km2) ! Capital ! Language, Name(s) in official language(s) ! ISO 3166-1 alpha-3, ISO 3166-1 , - style="background:#eee;" , colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", North Africa , - , style="text-align:center" ,
Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, style="text-align:right;", 2,381,740
, style="text-align:right;", 46,731,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 17.7
, Algiers
, الجزائر (al-Jazāʾir) / Algérie
, DZA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Canary Islands
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Canary Islands
, Canary Islands (Spain)
, style="text-align:right;", 7,492
, style="text-align:right;", 2,154,905
, style="text-align:right;", 2017
, style="text-align:right;", 226
, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria,Santa Cruz de Tenerife , Canarias , IC , - , style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ceuta , style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ceuta ,
Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
(Spain)
, style="text-align:right;", 20
, style="text-align:right;", 85,107
, style="text-align:right;", 2017
, style="text-align:right;", 3,575
, —
, Ceuta/Sebta/سَبْتَة (Sabtah)
, EA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Egypt
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Egypt
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,001,450
, style="text-align:right;", 107,800,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 102
, Cairo
, مِصر (Miṣr)
, EGY
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Libya
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Libya
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,759,540
, style="text-align:right;", 6,310,434
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 4
, Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli
, ليبيا (Lībiyā)
, LBY
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Madeira
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Madeira
, Madeira (Portugal)
, style="text-align:right;", 797
, style="text-align:right;", 245,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2001
, style="text-align:right;", 307
, Funchal
, Madeira
, PRT-30
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Melilla
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Melilla
, Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
(Spain)
, style="text-align:right;", 12
, style="text-align:right;", 85,116
, style="text-align:right;", 2017
, style="text-align:right;", 5,534
, —
, Melilla/Mlilt/مليلية
, EA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Morocco
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Morocco
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
, style="text-align:right;", 446,550
, style="text-align:right;", 35,740,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2017
, style="text-align:right;", 78
, Rabat
, المغرب (al-maḡrib)/ⵍⵎⵖⵔⵉⴱ (lmeɣrib)/Maroc
, MAR
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Tunisia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Tunisia
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, style="text-align:right;", 163,610
, style="text-align:right;", 10,486,339
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 64
, Tunis
, تونس (Tūnis)/Tunest/Tunisie
, TUN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the r ...
The territory of Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the r ...
is claimed by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
. The SADR is recognized as a sovereign state by the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
. Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
claims the entirety of the country as its Southern Provinces. Morocco administers 4/5 of the territory while the SADR controls 1/5. Morocco's annexation of this territory has not been recognized internationally.
, style="text-align:right;", 266,000
, style="text-align:right;", 405,210
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 2
, El Aaiún
, الصحراء الغربية (aṣ-Ṣaḥrā' al-Gharbiyyah)/Taneẓroft Tutrimt/Sáhara Occidental
, ESH
, - style="background:#eee;"
, colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", East Africa
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Burundi
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Burundi
, Burundi
, style="text-align:right;", 27,830
, style="text-align:right;", 8,988,091
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 323
, Gitega
, Uburundi/Burundi/Burundi
, BDI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,127,127
, style="text-align:right;", 113,800,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 92.7
, Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
, ኢትዮጵያ (Ītyōṗṗyā)/Itiyoophiyaa/ኢትዮጵያ/Itoophiyaa/Itoobiya/ኢትዮጵያ
, ETH
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, French Southern and Antarctic Lands
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, French Southern and Antarctic Lands
, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, French Southern Territories (France)
, style="text-align:right;", 439,781
, style="text-align:right;", 100
, style="text-align:right;", 2019
, style="text-align:right;", —
, Saint-Pierre, Réunion, Saint Pierre
, Terres australes et antarctiques françaises
, FRA-TF
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Kenya
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Kenya
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, style="text-align:right;", 582,650
, style="text-align:right;", 39,002,772
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 66
, Nairobi
, Kenya
, KEN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, style="text-align:right;", 587,040
, style="text-align:right;", 20,653,556
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 35
, Antananarivo
, Madagasikara/Madagascar
, MDG
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Malawi
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Malawi
, Malawi
, style="text-align:right;", 118,480
, style="text-align:right;", 14,268,711
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 120
, Lilongwe
, Malaŵi/Malaŵi
, MWI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Mauritius
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mauritius
, Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
, style="text-align:right;", 2,040
, style="text-align:right;", 1,284,264
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 630
, Port Louis
, Maurice/Moris
, MUS
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Mayotte
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mayotte, local
, Mayotte (France)
, style="text-align:right;", 374
, style="text-align:right;", 223,765
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 490
, Mamoudzou
, Mayotte/Maore/Maiôty
, MYT
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, style="text-align:right;", 801,590
, style="text-align:right;", 21,669,278
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 27
, Maputo
, Moçambique/Mozambiki/Msumbiji/Muzambhiki
, MOZ
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Réunion
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Réunion
, Réunion (France)
, style="text-align:right;", 2,512
, style="text-align:right;", 743,981
, style="text-align:right;", 2002
, style="text-align:right;", 296
, Saint-Denis, Réunion, Saint Denis
, La Réunion
, FRA-RE
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Rwanda
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Rwanda
, Rwanda
, style="text-align:right;", 26,338
, style="text-align:right;", 10,473,282
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 398
, Kigali
, Rwanda
, RWA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Seychelles
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Seychelles
, Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
, style="text-align:right;", 455
, style="text-align:right;", 87,476
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 192
, Victoria, Seychelles, Victoria
, Seychelles/Sesel
, SYC
, -
, style="text-align:center" , South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, style="text-align:right;", 619,745
, style="text-align:right;", 8,260,490
, style="text-align:right;", 2008
, style="text-align:right;", 13
, Juba
, South Sudan
, SSD
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,861,484
, style="text-align:right;", 30,894,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2008
, style="text-align:right;", 17
, Khartoum
, Sudan/السودان (as-Sūdān)
, SDN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Tanzania
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Tanzania
, Tanzania
, style="text-align:right;", 945,087
, style="text-align:right;", 61,800,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 47.5
, Dodoma
, Tanzania/Tanzania
, TZA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Uganda
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Uganda
, Uganda
, style="text-align:right;", 236,040
, style="text-align:right;", 32,369,558
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 137
, Kampala
, Uganda/Yuganda
, UGA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Zambia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Zambia
, Zambia
, style="text-align:right;", 752,614
, style="text-align:right;", 11,862,740
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 16
, Lusaka
, Zambia
, ZMB
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Zimbabwe
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Zimbabwe
, Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
, style="text-align:right;", 390,580
, style="text-align:right;", 11,392,629
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 29
, Harare
, Zimbabwe
, ZWE
, -
, colspan="10" style="background:#eee; text-align:center;", Central Africa
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,246,700
, style="text-align:right;", 12,799,293
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 10
, Luanda
, Angola
, AGO
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Cameroon
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Cameroon
, Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
, style="text-align:right;", 475,440
, style="text-align:right;", 18,879,301
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 40
, Yaoundé
, Cameroun/Kamerun
, CMR
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Central African Republic
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Central African Republic
, Central African Republic
, style="text-align:right;", 622,984
, style="text-align:right;", 4,511,488
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 7
, Bangui
, Ködörösêse tî Bêafrîka/République centrafricaine
, CAF
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Chad
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Chad
, Chad
, style="text-align:right;", 1,284,000
, style="text-align:right;", 10,329,208
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 8
, N'Djamena
, تشاد (Tšād)/Tchad
, TCD
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Republic of the Congo
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Republic of the Congo
, Republic of the Congo
, style="text-align:right;", 342,000
, style="text-align:right;", 4,012,809
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 12
, Brazzaville
, Congo/Kôngo/Kongó
, COG
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Democratic Republic of the Congo
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Democratic Republic of the Congo
, Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, style="text-align:right;", 2,345,410
, style="text-align:right;", 108,400,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 46.3
, Kinshasa
, République démocratique du Congo
, COD
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
, style="text-align:right;", 28,051
, style="text-align:right;", 633,441
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 23
, Malabo
, Guinea Ecuatorial/Guinée Équatoriale/Guiné Equatorial
, GNQ
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Gabon
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Gabon
, Gabon
, style="text-align:right;", 267,667
, style="text-align:right;", 1,514,993
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 6
, Libreville
, gabonaise
, GAB
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
, style="text-align:right;", 600,370
, style="text-align:right;", 1,990,876
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 3
, Gaborone
, Botswana/Botswana
, BWA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Eswatini
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Eswatini
, Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
, style="text-align:right;", 17,363
, style="text-align:right;", 1,123,913
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 65
, Mbabane
, eSwatini/Eswatini
, SWZ
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Lesotho
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Lesotho
, Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
, style="text-align:right;", 30,355
, style="text-align:right;", 2,130,819
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 70
, Maseru
, Lesotho/Lesotho
, LSO
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Namibia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Namibia
, Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, style="text-align:right;", 825,418
, style="text-align:right;", 2,108,665
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 3
, Windhoek
, Namibia
, NAM
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, South Africa
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, South Africa
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,219,912
, style="text-align:right;", 60,800,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 42.4
, Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria
, yaseNingizimu Afrika/yoMzantsi-Afrika/Suid-Afrika/Afrika-Borwa/Aforika Borwa/Afrika Borwa/Afrika Dzonga/yeNingizimu Afrika/Afurika Tshipembe/yeSewula Afrika
, ZAF
, - style="background:#eee;"
, colspan="10" style="text-align:center;", West Africa
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Benin
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Benin
, Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
, style="text-align:right;", 112,620
, style="text-align:right;", 8,791,832
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 78
, Porto-Novo
, Bénin
, BEN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Burkina Faso
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Burkina Faso
, Burkina Faso
, style="text-align:right;", 274,200
, style="text-align:right;", 15,746,232
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 57
, Ouagadougou
, Burkina Faso
, BFA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
, style="text-align:right;", 11,300
, style="text-align:right;", 1,782,893
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 158
, Banjul
, The Gambia
, GMB
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ghana
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ghana
, Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, style="text-align:right;", 239,460
, style="text-align:right;", 23,832,495
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 100
, Accra
, Ghana
, GHA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, style="text-align:right;", 245,857
, style="text-align:right;", 10,057,975
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 41
, Conakry
, Guinée
, GIN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Guinea-Bissau
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Guinea-Bissau
, Guinea-Bissau
, style="text-align:right;", 36,120
, style="text-align:right;", 1,533,964
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 43
, Bissau
, Guiné-Bissau
, GNB
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Ivory Coast
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Ivory Coast
, Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
, style="text-align:right;", 322,460
, style="text-align:right;", 20,617,068
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 64
, Abidjan,Yamoussoukro is the official capital of Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
, while Abidjan is the ''de facto'' seat. Yamoussoukro
, Côte d'Ivoire
, CIV
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Liberia
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Liberia
, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
, style="text-align:right;", 111,370
, style="text-align:right;", 3,441,790
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 31
, Monrovia
, Liberia
, LBR
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Mali
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Mali
, Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,240,000
, style="text-align:right;", 12,666,987
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 10
, Bamako
, Mali
, MLI
, -
, style="text-align:center" , Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, style="text-align:right;", 1,030,700
, style="text-align:right;", 3,129,486
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 3
, Nouakchott
, موريتانيا (Mūrītānyā)
, MRT
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Niger
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Niger
, Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesNigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, style="text-align:right;", 923,768
, style="text-align:right;", 225,100,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 218
, Abuja
, Nigeria
, NGA
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, United Kingdom
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
, style="text-align:right;", 420
, style="text-align:right;", 7,728
, style="text-align:right;", 2012
, style="text-align:right;", 13
, Jamestown, Saint Helena, Jamestown
, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
, SHN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Senegal
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Senegal
, Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, style="text-align:right;", 196,190
, style="text-align:right;", 13,711,597
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 70
, Dakar
, Sénégal
, SEN
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Sierra Leone
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Sierra Leone
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, style="text-align:right;", 71,740
, style="text-align:right;", 6,440,053
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 90
, Freetown
, Sierra Leone
, SLE
, -
, style="text-align:center" , {{Coat of arms, text=none, Togo
, style="text-align:center" , {{flagicon, Togo
, Togo
, style="text-align:right;", 56,785
, style="text-align:right;", 6,019,877
, style="text-align:right;", 2009
, style="text-align:right;", 106
, Lomé
, togolaise
, TGO
, - style="font-weight:bold; background:#eee;"
, colspan="3" , Africa Total
, style="text-align:right;", 30,368,609
, style="text-align:right;", 1,400,000,000
, style="text-align:right;", 2022
, style="text-align:right;", 33
! colspan="3",
See also
{{Portal, Africa * Index of Africa-related articles * African historiography * Outline of AfricaReferences
{{reflistSources
* {{Cite book, last=Malone, first=Jacqui, url= , title=Steppin' on the Blues: the Visible Rhythms of African American Dance, date=1996, publisher=University of Illinois Press, oclc=891842452 * {{Cite book, last=Welsh-Asante, first=Kariamu, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WrbrTfSO3fwC, title=African Dance, date=2009, publisher=Infobase Publishing, isbn=978-1-4381-2427-8, language=en * {{cite book , last1=Shillington , first1=Kevin , title=History of Africa , date=2005 , publisher=Palgrave Macmillan , isbn=978-0-333-59957-0Further reading
{{see also, Africa Bibliography {{refbegin * {{cite book, last=Asante, first=Molefi, author-link=Molefi Asante, title=The History of Africa, publisher=Routledge, location=US, date=2007, isbn=978-0-415-77139-9 * {{cite book, last=Clark, first=J. Desmond, author-link=J. Desmond Clark, title=The Prehistory of Africa, publisher=Thames and Hudson, location=London, date=1970, isbn=978-0-500-02069-2 * {{cite book, last=Crowder, first=Michael, title=The Story of Nigeria, publisher=Faber, location=London, date=1978, isbn=978-0-571-04947-9 * {{cite book, last=Davidson, first=Basil, author-link=Basil Davidson, title=The African Past: Chronicles from Antiquity to Modern Times, publisher=Penguin, location=Harmondsworth, date=1966, oclc=2016817 * {{cite book, last=Gordon, first=April A., first2=Donald L., last2=Gordon, title=Understanding Contemporary Africa, publisher=Lynne Rienner Publishers, location=Boulder, date=1996, isbn=978-1-55587-547-3 * {{cite book, last=Khapoya, first=Vincent B., title=The African experience: an introduction, publisher=Prentice Hall, location=Upper Saddle River, NJ, date=1998, isbn=978-0-13-745852-3, url=https://archive.org/details/africanexperienc00khap * Moore, Clark D., and Ann Dunbar (1968). ''Africa Yesterday and Today'', in series, ''The George School Readings on Developing Lands''. New York: Praeger Publishers. * V. S. Naipaul, Naipaul, V.S. ''The Masque of Africa: Glimpses of African Belief''. Picador, 2010. {{ISBN, 978-0-330-47205-0 * {{cite journal, last1=Wade, first1=Lizzie, title=Drones and satellites spot lost civilizations in unlikely places, journal=Science, doi=10.1126/science.aaa7864, year=2015, doi-access=free {{refendExternal links
{{Sister project links, n=Africa, voy=Africa General information * {{curlie, Regional/AfricaAfrican & Middle Eastern Reading Room
from the United States Library of Congress
Africa South of the Sahara
from Stanford University
The Index on Africa
from ''The Norwegian Council for Africa''
Aluka
Digital library of scholarly resources from and about Africa
Africa Interactive Map
from the United States Army Africa History
African Kingdoms
The Story of Africa
from BBC World Service *{{Cite EB1911, wstitle= Africa , volume= 1 , pages = 320–358 , short= 1
Africa Policy Information Center (APIC)
Hungarian military forces in Africa
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131103230525/http://www.scribd.com/doc/161017303/Hungarian-military-forces-in-Africa-%E2%80%93-past-and-future-Recovering-lost-knowledge-exploiting-cultural-anthropology-resources-creating-a-comprehensive , date=3 November 2013 News media
allAfrica.com
current news, events and statistics
''Focus on Africa''
magazine from BBC World Service {{Africa topics {{Africa {{Navboxes , title = Articles related to Africa , list = {{African Trade Agreements {{Continents of the world {{Regions of the world {{Authority control Africa, Continents Regions