|
Sahelanthropus Tchadensis
''Sahelanthropus tchadensis'' is an extinct species of the Homininae (African apes) dated to about , during the Miocene epoch. The species, and its genus ''Sahelanthropus'', was announced in 2002, based mainly on a partial cranium, nicknamed ''Toumaï'', discovered in northern Chad. ''Sahelanthropus tchadensis'' lived close to the time of the chimpanzee–human divergence, possibly related to ''Orrorin'', a species of Homininae that lived about one million years later. It may have been ancestral to both humans and chimpanzees (which would place it in the tribe Hominini), or alternatively an early member of the tribe Gorillini. In 2020, the femur was analyzed, and it was found that ''Sahelanthropus'' was not bipedal, casting some doubt on its position as a human ancestor, but this was refuted in 2022. Taxonomy Discovery Funded by the Mission Paléoanthropologique Franco–Tchadienne, Ahounta Djimdoumalbaye, Fanoné Gongdibé, Mahamat Adoum, and Alain Beauvilain identified the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messinian
The Messinian is in the geologic timescale the last age or uppermost stage of the Miocene. It spans the time between 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma and 5.333 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). It follows the Tortonian and is followed by the Zanclean, the first age of the Pliocene. The Messinian overlaps the Turolian European Land Mammal Mega Zone (more precisely MN 12 and 13) and the Pontian Central European Paratethys Stage. It also overlaps the late Huayquerian and early Montehermosan South American Land Mammal Ages, and falls inside the more extensive Hemphillian North American Land Mammal Age. During the Messinian, around 6 million years ago, the Messinian salinity crisis took place, which brought about repeated desiccations of the Mediterranean Sea. Definition The Messinian was introduced by Swiss stratigrapher Karl Mayer-Eymar in 1867. Its name comes from the Italian city of Messina on Sicily, where the Messinian evaporite deposit is of the same age. The base of the Messinia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
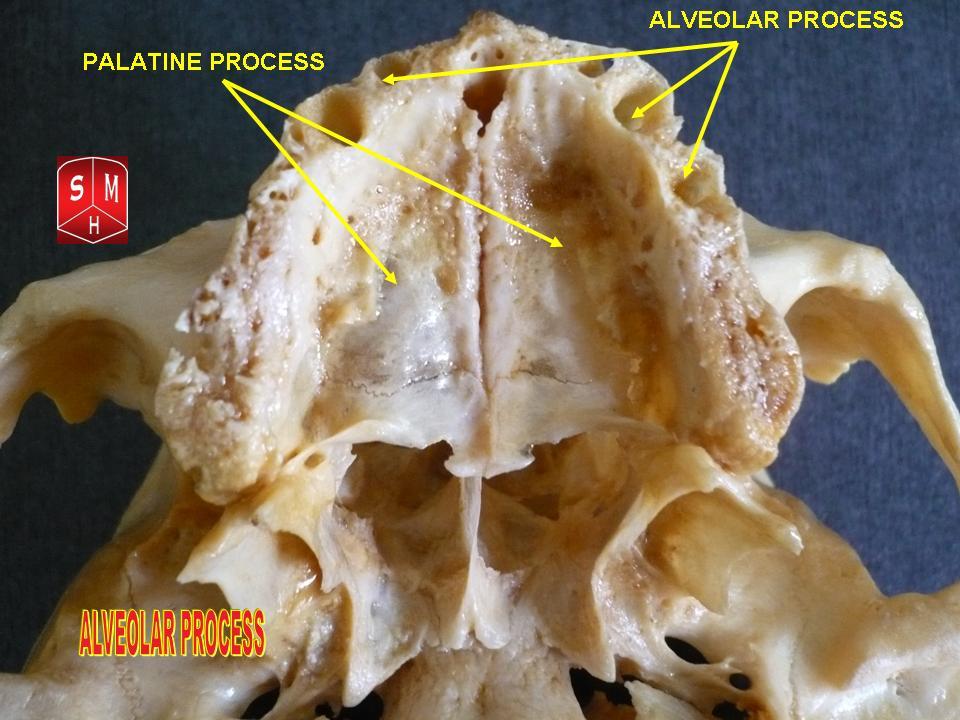
Tooth Socket
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idriss Déby
Idriss Déby Itno ' (18 June 1952 – 20 April 2021) was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the president of Chad from 1990 until his death in 2021. Déby was a member of the Bidayat clan of the Zaghawa ethnic group. A high-ranking commander of President Hissène Habré's military during the 1980s, Déby played important roles in the Toyota War which led to Chad's victory during the Libyan-Chadian conflict. He was later purged by Habré after being suspected of plotting a coup, and was forced into exile in Libya. He took power by leading a coup d'état against Habré in December 1990. Despite introducing a multi-party system in 1992 after several decades of one-party rule under his predecessors, throughout his presidency, his Patriotic Salvation Movement was the dominant party. Déby won presidential elections in 1996 and 2001, and after term limits were eliminated he won again in 2006, 2011, 2016, and 2021. During the Second Congo War, Déby briefly or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daza Language
Daza (also known as Dazaga) is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Daza people inhabiting northern Chad. The Daza are also known as the Gouran (Gorane) in Chad. Dazaga is spoken by around 380,000 people, primarily in the Djurab Desert region and the Borkou region, locally called Haya or Faya-Largeau northern-central Chad, the capital of the Dazaga people. Dazaga is spoken in the Tibesti Mountains of Chad (330,000 speakers), in eastern Niger near N'guigmi and to the north (50,000 speakers). It is also spoken to a smaller extent in Libya and in Sudan, where there is a community of 3,000 speakers in the city of Omdurman. There's also a small diaspora community working in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The two primary dialects of the Dazaga language are Daza and Kara, but there are several other mutually intelligible dialects, including Kaga, Kanobo, Taruge and Azza. It is closely related to the Tedaga language, spoken by the Teda, the other out of the two Toubou people groups, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably ''Homo erectus'' and '' Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of ''Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus ''Paranthropus'', is probably sister to '' Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. ''Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed '' Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Ape
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the eastern and western gorilla); '' Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only modern humans remain. Several revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''"hominid"'' to vary over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans, apes, and their ancestors were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''" hominin"'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (''Pan''). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Bahrelghazali
''Australopithecus bahrelghazali'' is an extinct species of australopithecine discovered in 1995 at Koro Toro, Bahr el Gazel, Chad, existing around 3.5 million years ago in the Pliocene. It is the first and only australopithecine known from Central Africa, and demonstrates that this group was widely distributed across Africa as opposed to being restricted to East and southern Africa as previously thought. The validity of ''A. bahrelghazali'' has not been widely accepted, in favour of classifying the specimens as ''A. afarensis'', a better known Pliocene australopithecine from East Africa, because of the anatomical similarity and the fact that ''A. bahrelghazali'' is known only from 3 partial jawbones and an isolated premolar. The specimens inhabited a lakeside grassland environment with sparse tree cover, possibly similar to the modern Okavango Delta, and similarly predominantly ate C4 savanna foods—such as grasses, sedges, storage organs, or rhizomes—and to a lesser deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. The Sahel part of Africa includes – from west to east – parts of northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, the extreme south of Algeria, Niger, the extreme north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia. Historically, the western part of the Sahel was sometimes known as the Sudan region (''bilād as-sūdān'' "lands of the Sudan"). This belt was located between the Sahara and the coastal areas of West Africa. There are frequent shortages of food and water due to the dry ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype Specimen
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |