Pepys (ward) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no maritime experience, but he rose to be the Chief Secretary to the Admiralty under both King Charles II and King James II through patronage, diligence, and his talent for administration. His influence and reforms at the Admiralty were important in the early professionalisation of the Royal Navy.
The detailed private diary that Pepys kept from 1660 until 1669 was first published in the 19th century and is one of the most important primary sources for the English Restoration period. It provides a combination of personal revelation and eyewitness accounts of great events, such as the Great Plague of London, the Second Dutch War, and the
 Pepys was born in Salisbury Court,
Pepys was born in Salisbury Court,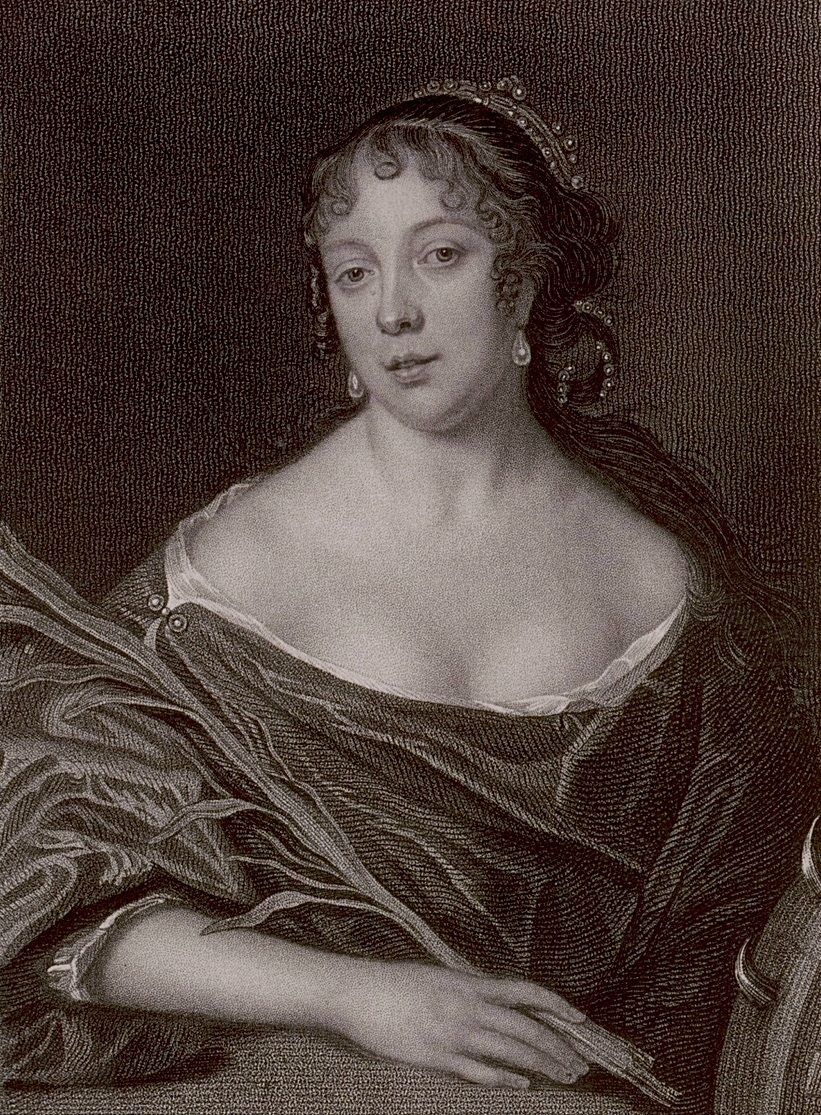  In 1650, he went to the University of Cambridge, having received two
In 1650, he went to the University of Cambridge, having received two
 On 1 January 1660 ("1 January 1659/1660" in contemporary terms), Pepys began to keep a diary. He recorded his daily life for almost ten years. This record of a decade of Pepys's life is more than a million words long and is often regarded as Britain's most celebrated diary. Pepys has been called the greatest diarist of all time due to his frankness in writing concerning his own weaknesses and the accuracy with which he records events of daily British life and major events in the 17th century. Pepys wrote about the contemporary court and theatre (including his amorous affairs with the actresses), his household, and major political and social occurrences. Historians have been using his diary to gain greater insight and understanding of life in London in the 17th century. Pepys wrote consistently on subjects such as personal finances, the time he got up in the morning, the weather, and what he ate. He wrote at length about his new watch which he was very proud of (and which had an alarm, a new accessory at the time), a country visitor who did not enjoy his time in London because he felt that it was too crowded, and his cat waking him up at one in the morning. Pepys's diary is one of a very few sources which provides such length in details of everyday life of an upper-middle-class man during the seventeenth century.
Aside from day-to-day activities, Pepys also commented on the significant and turbulent events of his nation. England was in disarray when he began writing his diary. Oliver Cromwell had died just a few years before, creating a period of civil unrest and a large power vacuum to be filled. Pepys had been a strong supporter of Cromwell, but he converted to the Royalist cause upon the Protector's death. He was on the ship that returned Charles II to England to take up his throne, and gave first-hand accounts of other significant events from the early years of
On 1 January 1660 ("1 January 1659/1660" in contemporary terms), Pepys began to keep a diary. He recorded his daily life for almost ten years. This record of a decade of Pepys's life is more than a million words long and is often regarded as Britain's most celebrated diary. Pepys has been called the greatest diarist of all time due to his frankness in writing concerning his own weaknesses and the accuracy with which he records events of daily British life and major events in the 17th century. Pepys wrote about the contemporary court and theatre (including his amorous affairs with the actresses), his household, and major political and social occurrences. Historians have been using his diary to gain greater insight and understanding of life in London in the 17th century. Pepys wrote consistently on subjects such as personal finances, the time he got up in the morning, the weather, and what he ate. He wrote at length about his new watch which he was very proud of (and which had an alarm, a new accessory at the time), a country visitor who did not enjoy his time in London because he felt that it was too crowded, and his cat waking him up at one in the morning. Pepys's diary is one of a very few sources which provides such length in details of everyday life of an upper-middle-class man during the seventeenth century.
Aside from day-to-day activities, Pepys also commented on the significant and turbulent events of his nation. England was in disarray when he began writing his diary. Oliver Cromwell had died just a few years before, creating a period of civil unrest and a large power vacuum to be filled. Pepys had been a strong supporter of Cromwell, but he converted to the Royalist cause upon the Protector's death. He was on the ship that returned Charles II to England to take up his throne, and gave first-hand accounts of other significant events from the early years of
 On the Navy Board, Pepys proved to be a more able and efficient worker than colleagues in higher positions. This often annoyed Pepys and provoked much harsh criticism in his diary. Among his colleagues were
On the Navy Board, Pepys proved to be a more able and efficient worker than colleagues in higher positions. This often annoyed Pepys and provoked much harsh criticism in his diary. Among his colleagues were
 In early 1665, the start of the Second Anglo-Dutch War placed great pressure on Pepys. His colleagues were either engaged elsewhere or incompetent, and Pepys had to conduct a great deal of business himself. He excelled under the pressure, which was extreme due to the complexity and under-funding of the Royal Navy. At the outset, he proposed a centralised approach to supplying the fleet. His idea was accepted, and he was made surveyor-general of
In early 1665, the start of the Second Anglo-Dutch War placed great pressure on Pepys. His colleagues were either engaged elsewhere or incompetent, and Pepys had to conduct a great deal of business himself. He excelled under the pressure, which was extreme due to the complexity and under-funding of the Royal Navy. At the outset, he proposed a centralised approach to supplying the fleet. His idea was accepted, and he was made surveyor-general of
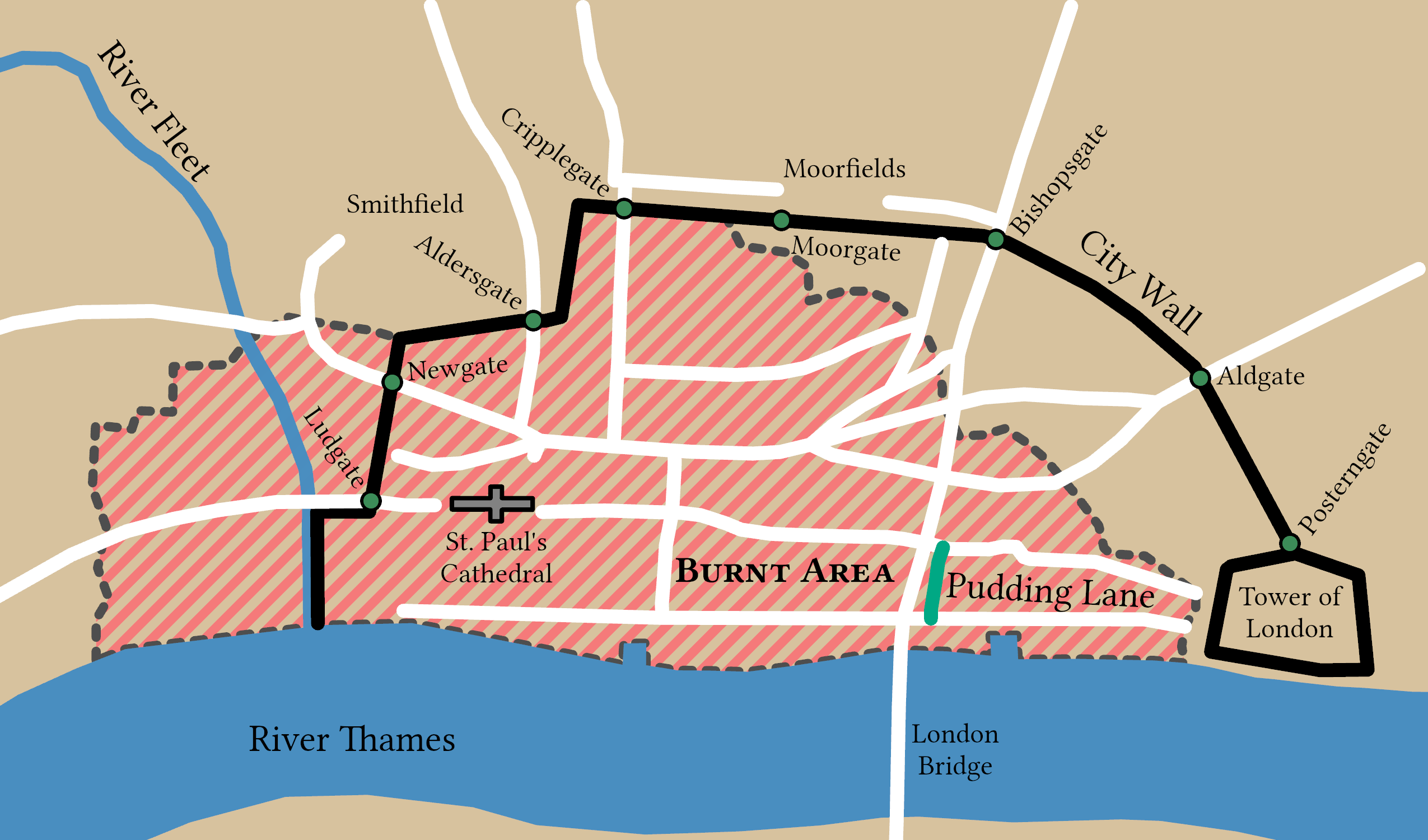 In the early hours of 2 September 1666, Pepys was awakened by Jane the maid, his servant, who had spotted a fire in the Billingsgate area. He decided that the fire was not particularly serious and returned to bed. Shortly after waking, his servant returned and reported that 300 houses had been destroyed and that
In the early hours of 2 September 1666, Pepys was awakened by Jane the maid, his servant, who had spotted a fire in the Billingsgate area. He decided that the fire was not particularly serious and returned to bed. Shortly after waking, his servant returned and reported that 300 houses had been destroyed and that 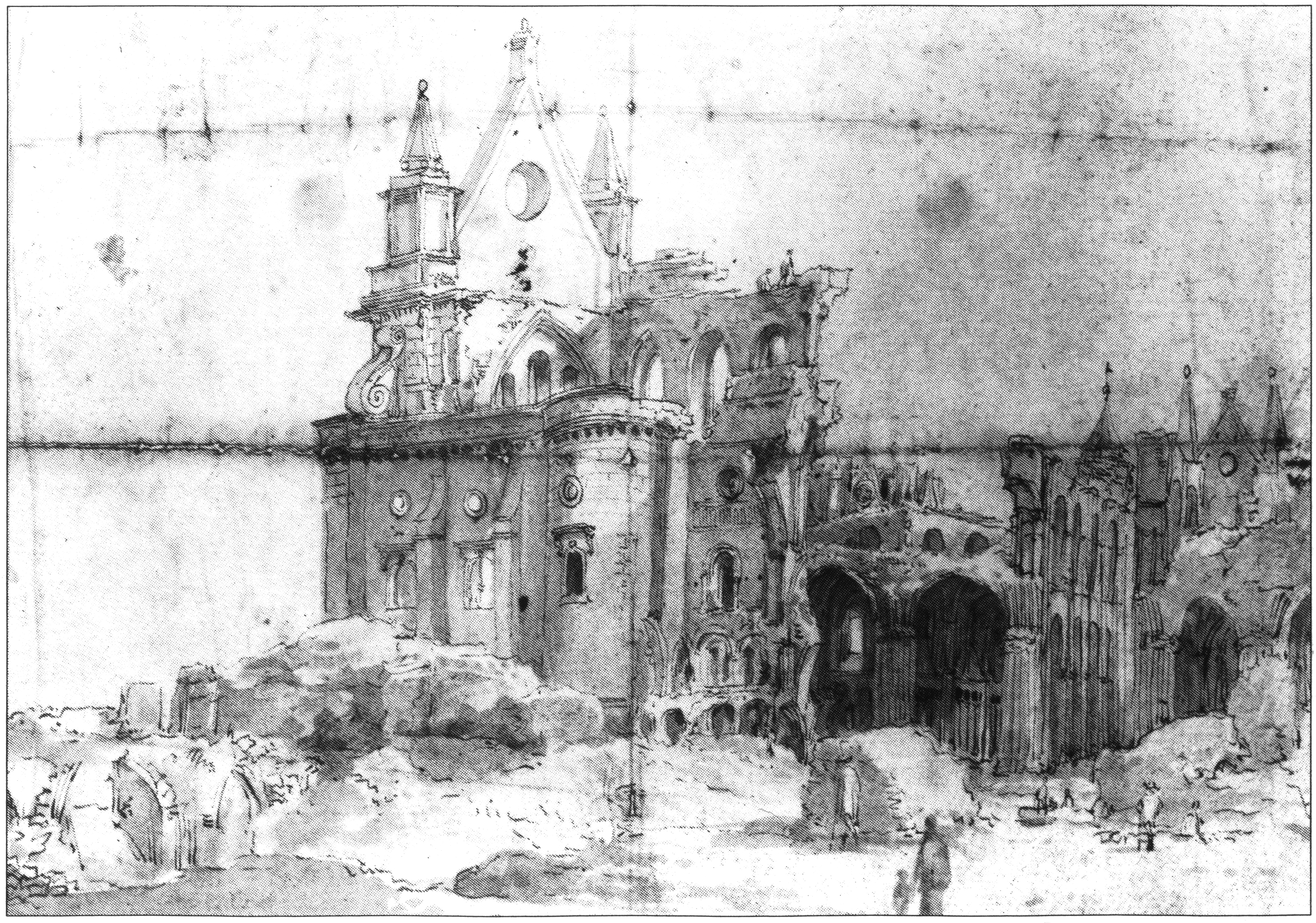 A cart arrived at 4 a.m. on 3 September and Pepys spent much of the day arranging the removal of his possessions. Many of his valuables, including his diary, were sent to a friend from the Navy Office at Bethnal Green. At night, he "fed upon the remains of yesterday's dinner, having no fire nor dishes, nor any opportunity of dressing any thing." The next day, Pepys continued to arrange the removal of his possessions. By then, he believed that Seething Lane was in grave danger, so he suggested calling men from Deptford to help pull down houses and defend the king's property. He described the chaos in the city and his curious attempt at saving his own goods:
Pepys had taken to sleeping on his office floor; on Wednesday, 5 September, he was awakened by his wife at 2 a.m. She told him that the fire had almost reached
A cart arrived at 4 a.m. on 3 September and Pepys spent much of the day arranging the removal of his possessions. Many of his valuables, including his diary, were sent to a friend from the Navy Office at Bethnal Green. At night, he "fed upon the remains of yesterday's dinner, having no fire nor dishes, nor any opportunity of dressing any thing." The next day, Pepys continued to arrange the removal of his possessions. By then, he believed that Seething Lane was in grave danger, so he suggested calling men from Deptford to help pull down houses and defend the king's property. He described the chaos in the city and his curious attempt at saving his own goods:
Pepys had taken to sleeping on his office floor; on Wednesday, 5 September, he was awakened by his wife at 2 a.m. She told him that the fire had almost reached
 The diary gives a detailed account of Pepys's personal life. He was fond of wine, plays, and the company of other people. He also spent time evaluating his fortune and his place in the world. He was always curious and often acted on that curiosity, as he acted upon almost all his impulses. Periodically, he would resolve to devote more time to hard work instead of leisure. For example, in his entry for New Year's Eve, 1661, he writes: "I have newly taken a solemn oath about abstaining from plays and wine…" The following months reveal his lapses to the reader; by 17 February, it is recorded, "Here I drank wine upon necessity, being ill for the want of it."
Pepys was one of the most important civil servants of his age, and was also a widely cultivated man, taking an interest in books, music, the theatre and science. Aside from English, he was fluent in French and read many texts in Latin. His favourite author was Virgil. He was passionately interested in music; he composed, sang, and played for pleasure, and even arranged music lessons for his servants. He played the
The diary gives a detailed account of Pepys's personal life. He was fond of wine, plays, and the company of other people. He also spent time evaluating his fortune and his place in the world. He was always curious and often acted on that curiosity, as he acted upon almost all his impulses. Periodically, he would resolve to devote more time to hard work instead of leisure. For example, in his entry for New Year's Eve, 1661, he writes: "I have newly taken a solemn oath about abstaining from plays and wine…" The following months reveal his lapses to the reader; by 17 February, it is recorded, "Here I drank wine upon necessity, being ill for the want of it."
Pepys was one of the most important civil servants of his age, and was also a widely cultivated man, taking an interest in books, music, the theatre and science. Aside from English, he was fluent in French and read many texts in Latin. His favourite author was Virgil. He was passionately interested in music; he composed, sang, and played for pleasure, and even arranged music lessons for his servants. He played the
 Pepys's health suffered from the long hours that he worked throughout the period of the diary. Specifically, he believed that his eyesight had been affected by his work. He reluctantly concluded in his last entry, dated 31 May 1669, that he should completely stop writing for the sake of his eyes, and only dictate to his clerks from then on, which meant that he could no longer keep his diary.
Pepys and his wife took a holiday to France and the Low Countries in June–October 1669; on their return, Elisabeth fell ill and died on 10 November 1669. Pepys erected a monument to her in the church of St Olave's, Hart Street, London. Pepys never remarried, but he did have a long-term housekeeper named Mary Skinner who was assumed by many of his contemporaries to be his mistress and sometimes referred to as Mrs. Pepys. In his will, he left her an annuity of £200 and many of his possessions.
Pepys's health suffered from the long hours that he worked throughout the period of the diary. Specifically, he believed that his eyesight had been affected by his work. He reluctantly concluded in his last entry, dated 31 May 1669, that he should completely stop writing for the sake of his eyes, and only dictate to his clerks from then on, which meant that he could no longer keep his diary.
Pepys and his wife took a holiday to France and the Low Countries in June–October 1669; on their return, Elisabeth fell ill and died on 10 November 1669. Pepys erected a monument to her in the church of St Olave's, Hart Street, London. Pepys never remarried, but he did have a long-term housekeeper named Mary Skinner who was assumed by many of his contemporaries to be his mistress and sometimes referred to as Mrs. Pepys. In his will, he left her an annuity of £200 and many of his possessions.
 Though he had resigned from the Tangier committee in 1679, in 1683 he was sent to Tangier to assist Lord Dartmouth with the evacuation and abandonment of the English colony. After six months' service, he travelled back through Spain accompanied by the naval engineer Edmund Dummer, returning to England after a particularly rough passage on 30 March 1684. In June 1684, once more in favour, he was appointed King's Secretary for the affairs of the Admiralty, a post that he retained after the death of Charles II (February 1685) and the accession of
Though he had resigned from the Tangier committee in 1679, in 1683 he was sent to Tangier to assist Lord Dartmouth with the evacuation and abandonment of the English colony. After six months' service, he travelled back through Spain accompanied by the naval engineer Edmund Dummer, returning to England after a particularly rough passage on 30 March 1684. In June 1684, once more in favour, he was appointed King's Secretary for the affairs of the Admiralty, a post that he retained after the death of Charles II (February 1685) and the accession of
 He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1665 and served as its President from 1 December 1684 to 30 November 1686. Isaac Newton's '' Principia Mathematica'' was published during this period, and its title page bears Pepys's name. There is a probability problem called the " Newton–Pepys problem" that arose out of correspondence between Newton and Pepys about whether one is more likely to roll at least one six with six dice or at least two sixes with twelve dice. It has only recently been noted that the gambling advice which Newton gave Pepys was correct, while the logical argument with which Newton accompanied it was unsound.
He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1665 and served as its President from 1 December 1684 to 30 November 1686. Isaac Newton's '' Principia Mathematica'' was published during this period, and its title page bears Pepys's name. There is a probability problem called the " Newton–Pepys problem" that arose out of correspondence between Newton and Pepys about whether one is more likely to roll at least one six with six dice or at least two sixes with twelve dice. It has only recently been noted that the gambling advice which Newton gave Pepys was correct, while the logical argument with which Newton accompanied it was unsound.

 Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his large collection of books, manuscripts, and prints. At his death, there were more than 3,000 volumes, including the diary, all carefully catalogued and indexed; they form one of the most important surviving 17th-century private libraries. The most important items in the Library are the six original bound manuscripts of Pepys's diary, but there are other remarkable holdings, including:
*
Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his large collection of books, manuscripts, and prints. At his death, there were more than 3,000 volumes, including the diary, all carefully catalogued and indexed; they form one of the most important surviving 17th-century private libraries. The most important items in the Library are the six original bound manuscripts of Pepys's diary, but there are other remarkable holdings, including:
*
 Motivated by the publication of John Evelyn's Diary in 1818, Lord Granville deciphered a few pages.
Motivated by the publication of John Evelyn's Diary in 1818, Lord Granville deciphered a few pages. ' s Best of British Blogs. In 2021, Gyford noted the existence of the Samuel Pepys Twitter account; set up in 2008, the account similarly serialises Pepys' diary each day.
 Several detailed studies of Pepys's life are available. Arthur Bryant published his three-volume study in 1933–1938, long before the definitive edition of the diary, but, thanks to Bryant's lively style, it is still of interest. In 1974 Richard Ollard produced a new biography that drew on Latham's and Matthew's work on the text, benefiting from the author's deep knowledge of Restoration politics. Other biographies include: ''Samuel Pepys: A Life'', by Stephen Coote (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 2000) and, ''Samuel Pepys and His World'', by Geoffrey Trease (London: Thames and Hudson, 1972).
The most recent general study is by
Several detailed studies of Pepys's life are available. Arthur Bryant published his three-volume study in 1933–1938, long before the definitive edition of the diary, but, thanks to Bryant's lively style, it is still of interest. In 1974 Richard Ollard produced a new biography that drew on Latham's and Matthew's work on the text, benefiting from the author's deep knowledge of Restoration politics. Other biographies include: ''Samuel Pepys: A Life'', by Stephen Coote (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 2000) and, ''Samuel Pepys and His World'', by Geoffrey Trease (London: Thames and Hudson, 1972).
The most recent general study is by
Samuel Pepys's diary
which provides a daily entry from the diary, detailed background articles, plus annotations from readers.
Duncan Grey's pages on Pepys
;Other sites
Pepys library
online at Magdalene College, Cambridge, including an essay by Robert Latham
Magdalene College Libraries' Blog
including the Pepys Library
Pepys Ballad Archive
The Samuel Pepys Club
Internet Movies Database: list of actors who have portrayed Pepys in visual media
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pepys, Samuel 1633 births 1703 deaths 17th-century Royal Navy personnel English diarists English civil servants Fellows of the Royal Society Presidents of the Royal Society English book and manuscript collectors Honourable Artillery Company Alumni of Magdalene College, Cambridge People educated at St Paul's School, London People from the City of London English Anglicans English bibliophiles Christ's Hospital staff Prisoners in the Tower of London 17th-century English writers 17th-century English male writers Members of Trinity House English MPs 1661–1679 English MPs 1679 English MPs 1685–1687 People in English Tangier
Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through central London from Sunday 2 September to Thursday 6 September 1666, gutting the medieval City of London inside the old Roman city wall, while also extending past the ...
.
Early life
 Pepys was born in Salisbury Court,
Pepys was born in Salisbury Court, Fleet Street
Fleet Street is a major street mostly in the City of London. It runs west to east from Temple Bar at the boundary with the City of Westminster to Ludgate Circus at the site of the London Wall and the River Fleet from which the street was na ...
, London, on 23 February 1633, the son of John Pepys (1601–1680), a tailor, and Margaret Pepys (''née'' Kite; died 1667), daughter of a Whitechapel butcher. His great uncle Talbot Pepys was Recorder and briefly Member of Parliament (MP) for Cambridge in 1625. His father's first cousin Sir Richard Pepys was elected MP for Sudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario (official name; the city continues to be known simply as Sudbury for most purposes)
** Sudbury (electoral district), one of the city's federal e ...
in 1640, appointed Baron of the Exchequer
The Barons of the Exchequer, or ''barones scaccarii'', were the judges of the English court known as the Exchequer of Pleas. The Barons consisted of a Chief Baron of the Exchequer and several puisne (''inferior'') barons. When Robert Shute was a ...
on 30 May 1654, and appointed Lord Chief Justice of Ireland on 25 September 1655.
Pepys was the fifth of eleven children, but child mortality was high and he was soon the oldest survivor. He was baptised at St Bride's Church
St Bride's Church is a church in the City of London, England. The building's most recent incarnation was designed by Sir Christopher Wren in 1672 in Fleet Street in the City of London, though Wren's original building was largely gutted by fire d ...
on 3 March 1633. Pepys did not spend all of his infancy in London; for a while, he was sent to live with nurse Goody
Goody, Goodies, or Goody's may refer to:
Brands
* Goody (brand), a brand of hair styling products owned by ACON Investments, LLC.
* Goody's Powder, a pain reliever sold primarily in the southern United States
* Goody's (restaurant), a fast food ...
Lawrence at Kingsland Kingsland may refer to:
Places
;Barbados
* Kingsland, Barbados (in Christ Church, Barbados Parish)
;Canada
* Kingsland, Calgary, Alberta, a neighborhood
;Australia
* proposed alternative name for the Northern Territory in 1912
;New Zealand
* Kings ...
, just north of the city. In about 1644, Pepys attended Huntingdon Grammar School
Huntingdon is a market town in the Huntingdonshire district in Cambridgeshire, England. The town was given its town charter by King John in 1205. It was the county town of the historic county of Huntingdonshire. Oliver Cromwell was born there ...
before being educated at St Paul's School, London, c. 1646–1650. He attended the execution of Charles I in 1649.
 In 1650, he went to the University of Cambridge, having received two
In 1650, he went to the University of Cambridge, having received two exhibition
An exhibition, in the most general sense, is an organized presentation and display of a selection of items. In practice, exhibitions usually occur within a cultural or educational setting such as a museum, art gallery, park, library, exhibition ...
s from St Paul's School (perhaps owing to the influence of George Downing, who was chairman of the judges and for whom he later worked at the Exchequer) and a grant from the Mercers' Company. In October, he was admitted as a sizar to Magdalene College; he moved there in March 1651 and took his Bachelor of Arts degree in 1654.
Later in 1654 or early in 1655, he entered the household of one of his father's cousins, Sir Edward Montagu, who was later created the 1st Earl of Sandwich.
When he was 22, Pepys married fourteen-year-old Elisabeth de St Michel, a descendant of French Huguenot immigrants, first in a religious ceremony on 10 October 1655 and later in a civil ceremony on 1 December 1655 at St Margaret's, Westminster.
Illness
From a young age, Pepys suffered frombladder stones
A bladder stone is a stone found in the urinary bladder.
Signs and symptoms
Bladder stones are small mineral deposits that can form in the bladder. In most cases bladder stones develop when the urine becomes very concentrated or when one is d ...
in his urinary tract—a condition from which his mother and brother John also later suffered. He was almost never without pain, as well as other symptoms, including "blood in the urine" ( haematuria). By the time of his marriage, the condition was very severe.
In 1657 Pepys decided to undergo surgery; not an easy option, as the operation was known to be especially painful and hazardous. Nevertheless, Pepys consulted surgeon Thomas Hollier and, on 26 March 1658, the operation took place in a bedroom in the house of Pepys's cousin Jane Turner. Pepys's stone was successfully removed and he resolved to hold a celebration on every anniversary of the operation, which he did for several years. However, there were long-term effects from the operation. The incision on his bladder broke open again late in his life. The procedure may have left him sterile, though there is no direct evidence for this, as he was childless before the operation. In mid-1658 Pepys moved to Axe Yard, near the modern Downing Street. He worked as a teller in the Exchequer under George Downing.
Diary
 On 1 January 1660 ("1 January 1659/1660" in contemporary terms), Pepys began to keep a diary. He recorded his daily life for almost ten years. This record of a decade of Pepys's life is more than a million words long and is often regarded as Britain's most celebrated diary. Pepys has been called the greatest diarist of all time due to his frankness in writing concerning his own weaknesses and the accuracy with which he records events of daily British life and major events in the 17th century. Pepys wrote about the contemporary court and theatre (including his amorous affairs with the actresses), his household, and major political and social occurrences. Historians have been using his diary to gain greater insight and understanding of life in London in the 17th century. Pepys wrote consistently on subjects such as personal finances, the time he got up in the morning, the weather, and what he ate. He wrote at length about his new watch which he was very proud of (and which had an alarm, a new accessory at the time), a country visitor who did not enjoy his time in London because he felt that it was too crowded, and his cat waking him up at one in the morning. Pepys's diary is one of a very few sources which provides such length in details of everyday life of an upper-middle-class man during the seventeenth century.
Aside from day-to-day activities, Pepys also commented on the significant and turbulent events of his nation. England was in disarray when he began writing his diary. Oliver Cromwell had died just a few years before, creating a period of civil unrest and a large power vacuum to be filled. Pepys had been a strong supporter of Cromwell, but he converted to the Royalist cause upon the Protector's death. He was on the ship that returned Charles II to England to take up his throne, and gave first-hand accounts of other significant events from the early years of
On 1 January 1660 ("1 January 1659/1660" in contemporary terms), Pepys began to keep a diary. He recorded his daily life for almost ten years. This record of a decade of Pepys's life is more than a million words long and is often regarded as Britain's most celebrated diary. Pepys has been called the greatest diarist of all time due to his frankness in writing concerning his own weaknesses and the accuracy with which he records events of daily British life and major events in the 17th century. Pepys wrote about the contemporary court and theatre (including his amorous affairs with the actresses), his household, and major political and social occurrences. Historians have been using his diary to gain greater insight and understanding of life in London in the 17th century. Pepys wrote consistently on subjects such as personal finances, the time he got up in the morning, the weather, and what he ate. He wrote at length about his new watch which he was very proud of (and which had an alarm, a new accessory at the time), a country visitor who did not enjoy his time in London because he felt that it was too crowded, and his cat waking him up at one in the morning. Pepys's diary is one of a very few sources which provides such length in details of everyday life of an upper-middle-class man during the seventeenth century.
Aside from day-to-day activities, Pepys also commented on the significant and turbulent events of his nation. England was in disarray when he began writing his diary. Oliver Cromwell had died just a few years before, creating a period of civil unrest and a large power vacuum to be filled. Pepys had been a strong supporter of Cromwell, but he converted to the Royalist cause upon the Protector's death. He was on the ship that returned Charles II to England to take up his throne, and gave first-hand accounts of other significant events from the early years of the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
, such as the coronation of Charles II, the Great Plague, the Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through central London from Sunday 2 September to Thursday 6 September 1666, gutting the medieval City of London inside the old Roman city wall, while also extending past the ...
and the Anglo–Dutch Wars.
Pepys did not plan on his contemporaries ever seeing his diary, which is evident from the fact that he wrote in shorthand and sometimes in a "code" of various Spanish, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, and Italian words (especially when describing his illicit affairs). However, Pepys often juxtaposed profanities in his native English amidst his "code" of foreign words, a practice which would reveal the details to any casual reader. He did intend future generations to see the diary, as evidenced by its inclusion in his library and its catalogue before his death along with the shorthand guide he used and the elaborate planning by which he ensured his library survived intact after his death.
The women whom he pursued, his friends, and his dealings are all laid out. His diary reveals his jealousies, insecurities, trivial concerns, and his fractious relationship with his wife. It has been an important account of London in the 1660s. The juxtaposition of his commentary on politics and national events, alongside the very personal, can be seen from the beginning. His opening paragraphs, written in January 1660, begin:
The entries from the first few months were filled with news of General George Monck's march on London. In April and May of that year, he was encountering problems with his wife, and he accompanied Montagu's fleet to the Netherlands to bring Charles II back from exile. Montagu was made Earl of Sandwich on 18 June, and Pepys secured the position of Clerk of the Acts to the Navy Board on 13 July. As secretary to the board, Pepys was entitled to a £350 annual salary plus the various gratuities and benefits that came with the job—including bribes. He rejected an offer of £1,000 for the position from a rival and soon afterwards moved to official accommodation in Seething Lane in the City of London.
Pepys stopped writing his diary in 1669. His eyesight began to trouble him and he feared that writing in dim light was damaging his eyes. He did imply in his last entries that he might have others write his diary for him, but doing so would result in a loss of privacy and it seems that he never went through with those plans. In the end, Pepys lived another 34 years without going blind, but he never took to writing his diary again.
However, Pepys dictated a journal for two months in 1669–70 as a record of his dealings with the Commissioners of Accounts at that period. He also kept a diary for a few months in 1683 when he was sent to Tangier, Morocco as the most senior civil servant in the navy, during the English evacuation. The diary mostly covers work-related matters.
Public life
 On the Navy Board, Pepys proved to be a more able and efficient worker than colleagues in higher positions. This often annoyed Pepys and provoked much harsh criticism in his diary. Among his colleagues were
On the Navy Board, Pepys proved to be a more able and efficient worker than colleagues in higher positions. This often annoyed Pepys and provoked much harsh criticism in his diary. Among his colleagues were Admiral Sir William Penn
Sir William Penn (23 April 1621 – 16 September 1670) was an English admiral and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1660 to 1670. He was the father of William Penn, founder of the Province of Pennsylvania (today, Commonwealth of Pe ...
, Sir George Carteret, Sir John Mennes
Vice Admiral Sir John Mennes (with variant spellings, 1 March 1599 – 18 February 1671) was an English naval officer, who went on to be Comptroller of the Navy. He was also considered a wit. His comic and satirical verses, written in correspond ...
and Sir William Batten
Sir William Batten (1601 to 5 October 1667) was an English naval officer and administrator from Somerset, who began his career as a merchant seaman, served as second-in-command of the Parliamentarian navy during the First English Civil War, th ...
.
Pepys learned arithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers— addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th ...
from a private tutor and used models of ships to make up for his lack of first-hand nautical experience, and ultimately came to play a significant role in the board's activities. In September 1660, he was made a Justice of the Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
; on 15 February 1662, Pepys was admitted as a Younger Brother of Trinity House; and on 30 April, he received the freedom of Portsmouth. Through Sandwich, he was involved in the administration of the short-lived English colony at Tangier. He joined the Tangier committee in August 1662 when the colony was first founded and became its treasurer in 1665. In 1663, he independently negotiated a £3,000 contract for Norwegian masts, demonstrating the freedom of action that his superior abilities allowed. He was appointed to a commission of the royal fishery on 8 April 1664.
Pepys's job required him to meet many people to dispense money and make contracts. He often laments how he "lost his labour" having gone to some appointment at a coffee house or tavern, only to discover that the person whom he was seeking was not there. These occasions were a constant source of frustration to Pepys.
Major events
Pepys's diary provides a first-hand account of the Restoration, and includes detailed accounts of several major events of the 1660s, along with the lesser knowndiary of John Evelyn
The ''Diary'' of John Evelyn (31 October 1620 – 27 February 1706), a gentlemanly Royalist and ''virtuoso'' of the seventeenth century, was first published in 1818 (2nd edition, 1819) under the title ''Memoirs Illustrative of the Life and Writing ...
. In particular, it is an invaluable source for the study of the Second Anglo-Dutch War of 1665–7, the Great Plague of 1665, and the Great Fire of London in 1666. In relation to the Plague and Fire, C. S. Knighton has written: "From its reporting of these two disasters to the metropolis in which he thrived, Pepys's diary has become a national monument." Robert Latham, editor of the definitive edition of the diary, remarks concerning the Plague and Fire: "His descriptions of both—agonisingly vivid—achieve their effect by being something more than superlative reporting; they are written with compassion. As always with Pepys it is people, not literary effects, that matter."
Second Anglo-Dutch War
 In early 1665, the start of the Second Anglo-Dutch War placed great pressure on Pepys. His colleagues were either engaged elsewhere or incompetent, and Pepys had to conduct a great deal of business himself. He excelled under the pressure, which was extreme due to the complexity and under-funding of the Royal Navy. At the outset, he proposed a centralised approach to supplying the fleet. His idea was accepted, and he was made surveyor-general of
In early 1665, the start of the Second Anglo-Dutch War placed great pressure on Pepys. His colleagues were either engaged elsewhere or incompetent, and Pepys had to conduct a great deal of business himself. He excelled under the pressure, which was extreme due to the complexity and under-funding of the Royal Navy. At the outset, he proposed a centralised approach to supplying the fleet. His idea was accepted, and he was made surveyor-general of victualling
A victualler is traditionally a person who supplies food, beverages and other provisions for the crew of a vessel at sea.
There are a number of other more particular uses of the term, such as:
* The official supplier of food to the Royal Navy in ...
in October 1665. The position brought a further £300 a year.
Pepys wrote about the Second Anglo-Dutch War: "In all things, in wisdom, courage, force and success, the Dutch have the best of us and do end the war with victory on their side". And King Charles II said: "Don't fight the Dutch, imitate them".
In 1667, with the war lost, Pepys helped to discharge the navy. The Dutch had defeated England on open water and now began to threaten English soil itself. In June 1667, they conducted their Raid on the Medway, broke the defensive chain at Gillingham, and towed away the , one of the Royal Navy's most important ships. As he had done during the Fire and the Plague, Pepys again removed his wife and his gold from London.
The Dutch raid was a major concern in itself, but Pepys was personally placed under a different kind of pressure: the Navy Board and his role as Clerk of the Acts came under scrutiny from the public and from Parliament. The war ended in August and, on 17 October, the House of Commons created a committee of "miscarriages". On 20 October, a list was demanded from Pepys of ships and commanders at the time of the division of the fleet in 1666. However, these demands were actually quite desirable for him, as tactical and strategic mistakes were not the responsibility of the Navy Board.
The Board did face some allegations regarding the Medway raid, but they could exploit the criticism already attracted by commissioner of Chatham Peter Pett to deflect criticism from themselves. The committee accepted this tactic when they reported in February 1668. The Board was, however, criticised for its use of tickets to pay seamen. These tickets could only be exchanged for cash at the Navy's treasury in London. Pepys made a long speech at the bar of the Commons on 5 March 1668 defending this practice. It was, in the words of C. S. Knighton, a "virtuoso performance".
The commission was followed by an investigation led by a more powerful authority, the commissioners of accounts. They met at Brooke House, Holborn and spent two years scrutinising how the war had been financed. In 1669, Pepys had to prepare detailed answers to the committee's eight "Observations" on the Navy Board's conduct. In 1670, he was forced to defend his own role. A seaman's ticket with Pepys's name on it was produced as incontrovertible evidence of his corrupt dealings but, thanks to the intervention of the king, Pepys emerged from the sustained investigation relatively unscathed.
Great Plague
Outbreaks of plague were not unusual events in London; major epidemics had occurred in 1592, 1603, 1625 and 1636. Furthermore, Pepys was not among the group of people who were most at risk. He did not live in cramped housing, he did not routinely mix with the poor, and he was not required to keep his family in London in the event of a crisis. It was not until June 1665 that the unusual seriousness of the plague became apparent, so Pepys's activities in the first five months of 1665 were not significantly affected by it.Claire Tomalin
Claire Tomalin (née Delavenay; born 20 June 1933) is an English journalist and biographer, known for her biographies of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Samuel Pepys, Jane Austen and Mary Wollstonecraft.
Early life
Tomalin was born Claire Del ...
wrote that 1665 was, to Pepys, one of the happiest years of his life. He worked very hard that year, and the outcome was that he quadrupled his fortune. In his annual summary on 31 December, he wrote, "I have never lived so merrily (besides that I never got so much) as I have done this plague time".
Nonetheless, Pepys was certainly concerned about the plague. On 16 August he wrote:
He also chewed tobacco as a protection against infection, and worried that wig-makers
A wig is a head or hair accessory made from human hair, animal hair, or synthetic fiber. The word wig is short for periwig, which makes its earliest known appearance in the English language in William Shakespeare's ''The Two Gentlemen of Verona ...
might be using hair from the corpses as a raw material. Furthermore, it was Pepys who suggested that the Navy Office should evacuate to Greenwich, although he did offer to remain in town himself. He later took great pride in his stoicism. Meanwhile, Elisabeth Pepys was sent to Woolwich. She did not return to Seething Lane until January 1666, and was shocked by the sight of St Olave's churchyard, where 300 people had been buried.
Great Fire of London
 In the early hours of 2 September 1666, Pepys was awakened by Jane the maid, his servant, who had spotted a fire in the Billingsgate area. He decided that the fire was not particularly serious and returned to bed. Shortly after waking, his servant returned and reported that 300 houses had been destroyed and that
In the early hours of 2 September 1666, Pepys was awakened by Jane the maid, his servant, who had spotted a fire in the Billingsgate area. He decided that the fire was not particularly serious and returned to bed. Shortly after waking, his servant returned and reported that 300 houses had been destroyed and that London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It r ...
was threatened. Pepys went to the Tower of London to get a better view. Without returning home, he took a boat and observed the fire for over an hour. In his diary, Pepys recorded his observations as follows:
The wind was driving the fire westward, so he ordered the boat to go to Whitehall and became the first person to inform the king of the fire. According to his entry of 2 September 1666, Pepys recommended to the king that homes be pulled down in the path of the fire in order to stem its progress. Accepting this advice, the king told him to go to Lord Mayor Thomas Bloodworth
Sir Thomas Bloodworth, born Blidward, also spelt Bludworth (baptised 13 February 1620 – 12 May 1682) was an English merchant and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1660 to 1679. He was Lord Mayor of London from October 1665 to ...
and tell him to start pulling down houses. Pepys took a coach back as far as St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Grad ...
before setting off on foot through the burning city. He found the Lord Mayor, who said, "Lord! what can I do? I am spent: people will not obey me. I have been pulling down houses; but the fire overtakes us faster than we can do it." At noon, he returned home and "had an extraordinary good dinner, and as merry, as at this time we could be", before returning to watch the fire in the city once more. Later, he returned to Whitehall, then met his wife in St James's Park. In the evening, they watched the fire from the safety of Bankside. Pepys writes that "it made me weep to see it". Returning home, Pepys met his clerk Tom Hayter who had lost everything. Hearing news that the fire was advancing, he started to pack up his possessions by moonlight.
 A cart arrived at 4 a.m. on 3 September and Pepys spent much of the day arranging the removal of his possessions. Many of his valuables, including his diary, were sent to a friend from the Navy Office at Bethnal Green. At night, he "fed upon the remains of yesterday's dinner, having no fire nor dishes, nor any opportunity of dressing any thing." The next day, Pepys continued to arrange the removal of his possessions. By then, he believed that Seething Lane was in grave danger, so he suggested calling men from Deptford to help pull down houses and defend the king's property. He described the chaos in the city and his curious attempt at saving his own goods:
Pepys had taken to sleeping on his office floor; on Wednesday, 5 September, he was awakened by his wife at 2 a.m. She told him that the fire had almost reached
A cart arrived at 4 a.m. on 3 September and Pepys spent much of the day arranging the removal of his possessions. Many of his valuables, including his diary, were sent to a friend from the Navy Office at Bethnal Green. At night, he "fed upon the remains of yesterday's dinner, having no fire nor dishes, nor any opportunity of dressing any thing." The next day, Pepys continued to arrange the removal of his possessions. By then, he believed that Seething Lane was in grave danger, so he suggested calling men from Deptford to help pull down houses and defend the king's property. He described the chaos in the city and his curious attempt at saving his own goods:
Pepys had taken to sleeping on his office floor; on Wednesday, 5 September, he was awakened by his wife at 2 a.m. She told him that the fire had almost reached All Hallows-by-the-Tower
All Hallows-by-the-Tower, at one time dedicated jointly to All Hallows (All Saints) and the Virgin Mary and sometimes known as All Hallows Barking, is an ancient Anglican church on Byward Street in the City of London, overlooking the Tower o ...
and that it was at the foot of Seething Lane. He decided to send her and his gold—about £2,350—to Woolwich. In the following days, Pepys witnessed looting, disorder, and disruption. On 7 September, he went to Paul's Wharf and saw the ruins of St Paul's Cathedral, of his old school, of his father's house, and of the house in which he had had his stone removed. Despite all this destruction, Pepys's house, office, and diary were saved.
Personal life
 The diary gives a detailed account of Pepys's personal life. He was fond of wine, plays, and the company of other people. He also spent time evaluating his fortune and his place in the world. He was always curious and often acted on that curiosity, as he acted upon almost all his impulses. Periodically, he would resolve to devote more time to hard work instead of leisure. For example, in his entry for New Year's Eve, 1661, he writes: "I have newly taken a solemn oath about abstaining from plays and wine…" The following months reveal his lapses to the reader; by 17 February, it is recorded, "Here I drank wine upon necessity, being ill for the want of it."
Pepys was one of the most important civil servants of his age, and was also a widely cultivated man, taking an interest in books, music, the theatre and science. Aside from English, he was fluent in French and read many texts in Latin. His favourite author was Virgil. He was passionately interested in music; he composed, sang, and played for pleasure, and even arranged music lessons for his servants. He played the
The diary gives a detailed account of Pepys's personal life. He was fond of wine, plays, and the company of other people. He also spent time evaluating his fortune and his place in the world. He was always curious and often acted on that curiosity, as he acted upon almost all his impulses. Periodically, he would resolve to devote more time to hard work instead of leisure. For example, in his entry for New Year's Eve, 1661, he writes: "I have newly taken a solemn oath about abstaining from plays and wine…" The following months reveal his lapses to the reader; by 17 February, it is recorded, "Here I drank wine upon necessity, being ill for the want of it."
Pepys was one of the most important civil servants of his age, and was also a widely cultivated man, taking an interest in books, music, the theatre and science. Aside from English, he was fluent in French and read many texts in Latin. His favourite author was Virgil. He was passionately interested in music; he composed, sang, and played for pleasure, and even arranged music lessons for his servants. He played the lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lute" can ref ...
, viol, violin, flageolet
The flageolet is a woodwind instrument and a member of the fipple flute family which includes recorders and tin whistles. Its invention was erroneously ascribed to the 16th-century Sieur Juvigny in 1581. There are two basic forms of the instrume ...
, recorder and spinet to varying degrees of proficiency. He was also a keen singer, performing at home, in coffee houses, and even in Westminster Abbey. He and his wife took flageolet lessons from master Thomas Greeting
Thomas Greeting (fl. 1675) was an English musician.
Greeting published in 1675 ''The Pleasant Companion, or new Lessons and Instructions for the Flagelet''. Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and ...
. He also taught his wife to sing and paid for dancing lessons for her (although these stopped when he became jealous of the dancing master).
Pepys was an investor in the Company of Royal Adventurers Trading to Africa, which held the Royal monopoly on trading along the west coast of Africa in gold, silver, ivory and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
.
Sexual relations
Propriety did not prevent him from engaging in a number of extramarital liaisons with various women that were chronicled in his diary, often in some detail when relating the intimate details. The most dramatic of these encounters was with Deborah Willet, a young woman engaged as acompanion
Companion may refer to:
Relationships Currently
* Any of several interpersonal relationships such as friend or acquaintance
* A domestic partner, akin to a spouse
* Sober companion, an addiction treatment coach
* Companion (caregiving), a caregive ...
for Elisabeth Pepys. On 25 October 1668, Pepys was surprised by his wife as he embraced Deb Willet; he writes that his wife "coming up suddenly, did find me imbracing the girl con '' ith' my hand sub ''nder Nder may refer to:
* Alioune Mbaye Nder (born 1969), Senegalese singer
*N'Der
N'Der (also spelled Nder or Ndeer) is a small town on the western shore of the Lac de Guiers, in northern Senegal. It was the third and last capital of Waalo until the a ...
' su '' er' coats; and endeed I was with my main '' and' in her cunny. I was at a wonderful loss upon it and the girl also...." Following this event, he was characteristically filled with remorse, but (equally characteristically) continued to pursue Willet after she had been dismissed from the Pepys household. Pepys also had a habit of fondling the breasts of his maid Mary Mercer while she dressed him in the morning.
Pepys may also have dallied with a leading actress of the Restoration period, Mary Knep. "Mrs Knep was the wife of a Smithfield horsedealer, and the mistress of Pepys"—or at least "she granted him a share of her favours". Scholars disagree on the full extent of the Pepys/Knep relationship, but much of later generations' knowledge of Knep comes from the diary. Pepys first met Knep on 6 December 1665. He described her as "pretty enough, but the most excellent, mad-humoured thing, and sings the noblest that I ever heard in my life." He called her husband "an ill, melancholy, jealous-looking fellow" and suspected him of abusing his wife. Knep provided Pepys with backstage access and was a conduit for theatrical and social gossip. When they wrote notes to each other, Pepys signed himself "Dapper Dickey", while Knep was " Barbry Allen" (a popular song that was an item in her musical repertory).
Pepys's reference to purchasing the pornographic book ''L'Escole des Filles
''L'Escole des Filles, ou la Philosophie des dames'' (), known in English as ''The School of Venus'', is an early work of erotica in French. Published anonymously in 1655, later editions sometimes ascribe it to M chelMillilot and Jean L'Ange.
...
'' appears to be the first English reference to pornography. He writes in his diary that it was a "mighty lewd book," and burned it after reading it.
Text of the diary
The diary was written in one of the many standard forms of shorthand used in Pepys's time, in this case called tachygraphy and devised by Thomas Shelton. It is clear from its content that it was written as a purely personal record of his life and not for publication, yet there are indications that Pepys took steps to preserve the bound manuscripts of his diary. He wrote it out in fair copy from rough notes, and he also had the loose pages bound into six volumes, catalogued them in his library with all his other books, and is likely to have suspected that eventually someone would find them interesting.Simplified Pepys family tree
This tree summarizes, in a more compact form and with a few additional details, trees published elsewhere in a box-like form.Latham & Matthews (1970–83), Vol. X – Companion. It is meant to help the reader of the ''Diary'' and also integrates some biographical informations found in the same sources. * William Pepys of Cottenham (Cambs.) (? – 1519) ** Thomas Pepys *** Richard Pepys (? – ''c.'' 1571) **** William Pepys of Norwich, ''draper'' (1561 – ''c.'' 1639) ***** Richard Pepys of London, ''upholsterer'' (? – 1679) ** John Pepys of South Creak (Norf.) (? – 1542) *** Thomas Pepys (? – 1569) **** Jerome Pepys (1548–1634) ***** John Pepys of Ashtead (Surrey), ''man of business to Chief JusticeEdward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sa ...
'' (1576–1652) +(1610)+ Anne Walpole
****** Edward Pepys of Broomsthorpe (Norf.), ''lawyer'' (1617–1663) + Elizabeth Walpole
****** Elizabeth Pepys + Thomas Dyke
****** Jane Pepys (“Madam Turner”) (1623–1686) +(1650)+ John Turner, ''Yorkshire lawyer'' (1631–1689)
******* Charles Turner + Margaret Cholmley
******* Theophila Turner (“The”) (1652–1702) +(1673)+ Sir Arthur Harris, 1st Baronet, of Stowford, ''M.P. for Okehampton'' (''c.'' 1650 – 1686)
******* William Turner + Mary Foulis
******* Elizabeth Turner (“Betty”) + William Hooker
** William Pepys of Cottenham (Cambs.)
*** John Pepys of Cottenham and Impington (Cambs.) (? – 1589) (1) + ? ? (2) + Edith Talbot (? – 1583)
**** John Pepys 1 (? – 1604) + Elizabeth Bendish of Essex
***** Sir Richard Pepys, ''M.P. for Sudbury and Lord Chief Justice of Ireland'' (1589–1659) (1) +(1620)+ Judith Cutte (2) + Mary Gosnold
****** Richard Pepys of Ashen (Essex), ''lawyer'' (? – 1664)
****** Samuel Pepys of Dublin, ''clergyman''
****** Elizabeth Pepys + Thomas Strudwick, ''confectioner''
****** Judith Pepys (? – 1664) + Benjamin Scott, ''pewterer'' (? – 1664)
**** Thomas Pepys (“the Black”) 1 (? – 1606) + Mary Day
***** Robert Pepys of Brampton (Hunts.), ''bailiff at Hinchingbrooke'' (? – 1661) + Anne, widow Trice
***** Thomas Pepys of St Alphage (1595–1676) + Mary Syvret hiveret''
****** Thomas Pepys (“the turner”), ''trader with the W. Indies'' +(1664)+ Elizabeth Howes
****** Charles Pepys (“the joiner”), ''Master-Joiner with the Chatham yard'' (''c.'' 1632 – ''c.'' 1701) +(1662)+ Joan, widow Smith
****** Mary Pepys (? – 1667) +(1662)+ Samuel de Santhune, ''weaver of Huguenot origin''
***** Jane Pepys (? – 1666) + John Perkin of Parson Drove (Cambs.)
****** Jane Perkin
****** Frank Perkin, ''miller and fiddler''
***** Mary Pepys (1597 – ?) + Robert Holcroft
****** John Holcroft
***** Edith Pepys (“Aunt Bell”) (1599–1665) + John Bell
***** John Pepys, ''tailor in Salisbury Court'' (1601–1680) +(1626)+ Margaret Kite, ''washmaid'' (? – 1667)
****** Mary Pepys (1627–1640)
****** Paulina Pepys (1628–1632)
****** Esther Pepys (1630–1631)
****** John Pepys (1632–1640)
****** SAMUEL PEPYS, ''diarist, naval administrator, and M.P. for Castle Rising and Harwich'' (1633–1703) +(1655)+ Élisabeth de Saint-Michel, ''born from an Anglo-French wedding, of Angevin gentry by her father'' (1640–1669)
****** Thomas Pepys (“Tom”), ''tailor against his will'' (1634–1664)
******* Elizabeth Taylor, ''an illegitimate daughter with his maid Margeret''
****** Sarah Pepys (1635–1641)
****** Jacob Pepys (1637–1637)
****** Robert Pepys (1638–1638)
****** Paulina Pepys (“Pall”) (1640–1689) +(1668)+ John Jackson, ''farmer in Ellington (Hunts.)'' (? – 1680)
******* Samuel Jackson (1669 – ?)
******* John Jackson, ''secretary and heir to SP'' (1673–1724) + Anne Edgeley
******** John Jackson (? – 1780)
******** ''1 other son and 2 daughters''
******** Anne Jackson + Brabazon Hallows
******** Paulina Jackson + Admiral R. Collins
******** Frances Jackson (1722–1769) +(1747)+ John Cockerell of Bishops Hull (Somer.) (1714–1767)
********* John Cockerell
********* Charles Cockerell
********* Samuel Pepys Cockerell, ''architect'' (1754–1827)
********** Charles Robert Cockerell
Charles Robert Cockerell (27 April 1788 – 17 September 1863) was an English architect, archaeologist, and writer. He studied architecture under Robert Smirke. He went on an extended Grand Tour lasting seven years, mainly spent in Greece. H ...
, ''architect'' (1788–1863) +(1828)+ Anna Rennie (1803–1872)
*********** Frederick Pepys Cockerell, ''architect'' (1833–1878) +(1867)+ Mary Mulock
************ ''6 children''
*********** ''9 other children''
******* ''2 other children dead in infancy''
****** John Pepys, ''naval administrator, unmarr.'' (1642–1677)
**** Thomas Pepys (“the Red”) 1 of Hatcham Barnes (Surrey) (? – 1615) + Kezia ?
***** Thomas Pepys (“the Executor”), ''lawyer'' (1611–1675) (1) +(1654)+ Anne Cope (2) +(1660)+ Ursula Stapleton (? – ''c.'' 1693)
****** ''1 son and 1 daughter by the second wedding''
***** Elizabeth Pepys +(1633)+ Percival Angier, ''business man'' (? – 1665)
**** Elizabeth Pepys 1 +(1593)+ Henry Alcock
***** ''issue''
**** Apollo Pepys 1 (1576–1645)
**** Paulina Pepys 2 (1581–1638) +(1618)+ Sidney Montagu (? – 1644)
***** Elizabeth Montagu (1620 – ?) +(1638)+ Sir Gilbert Pickering, 1st Baronet, ''Lord Chamberlain to Oliver and Richard Cromwell'' (1613–1668)
****** Elizabeth Pickering +(1668)+ John Creed, ''secretary to Edward Montagu and SP's principal rival'' (? – 1701)
******* ''11 children''
****** ''11 other children''
***** Henry Montagu (1622–1625)
***** Edward Montagu, 1st Earl of Sandwich (“My Lord”) (1625–1672) +(1642)+ Jemima Crew (“My Lady”) (1625–1674)
****** Jemima Montagu (“Lady Jem”) (1646–1671) +(1665)+ Philip Carteret, ''commissioned lieutenant in the Navy'' (1643–1672)
******* George Carteret, 1st Baron Carteret, (1667–1695) + Lady Grace Granville (1654–1744)
******** John Carteret, 2nd Earl Granville, ''Prime Minister to George II'' (1690–1763) + Lady Frances Worsley
******* ''2 other sons''
****** Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of Sandwich (“Ned”) (1648–1688) +(1668)+ Lady Anne Boyle (? – 1671)
******* ''descent of the Earls of Sandwich''
****** Paulina Montagu (1649–1669)
****** Sidney Montagu, later Wortley-Montagu (1650–1727) + ? ?, ''Yorkshire heiress''
******* ''issue''
****** Anne Montagu (1653–1729) (1) +(1671)+ Richard Edgcumbe (1640–1688) (2) + Christopher Montagu
****** Oliver Montagu (1655–1693)
****** John Montagu, ''Dean of Durham'' (1655–1729)
****** Charles Montagu (1658–1721) (1) + Elizabeth Forester (2) + Sarah Rogers
******* ''issue by both weddings''
****** Catherine Montagu (1661–1757) (1) + Nicholas Bacon, ''M.P. for Ipswich'' (1622–1687) (2) + Balthazar Gardeman, ''clergyman''
****** James Montagu (1664 – ?)
**** Talbot Pepys 2 of Impington (Cambs.), ''Recorder and M.P. for Cambridge, remarried 3 times'' (1583–1666) + Beatrice Castell
***** Roger Pepys
Roger Pepys (3 May 1617 – 4 October 1688) was an English lawyer and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1661 to 1678. He is chiefly remembered as Samuel Pepys's "Cousin Roger". He and his children appear regularly in Samuel's great ...
of Impington (Cambs.), ''Recorder and M.P. for Cambridge'' (1617–1688) (1) + Anne Banks (2) +(''c.'' 1646)+ Barbara Bacon (? – 1657) (3) + Parnell Duke (4) +(1669)+ Esther, widow Dickenson (“the good-humoured fat widow”)
****** Talbot Pepys 2 (1647–1681)
****** Barbara Pepys (“Bab”) 2 (1649–1689) +(1674)+ Dr Thomas Gale, ''High Master of St Paul's School and Dean of York'' (1635–1702)
******* Charles Gale
******* Thomas Gale
******* Elizabeth Gale
******* Roger Gale
Sir Roger James Gale (born 20th August 1943) is a British politician who has served as the member of Parliament (MP) for North Thanet since 1983. He had a career in journalism and broadcasting from 1964, around the same time as he joined the C ...
, ''antiquary'' (1672–1744)
******* Samuel Gale, ''antiquary'' (1682–1754)
****** Elizabeth Pepys (“Betty”) 2 (1651–1716) +(1680)+ Charles Long, ''fellow of Caius College and rector of Risby (Suff.)''
****** John Pepys 3
***** Dr John Pepys, ''fellow of Trinity Hall and lawyer'' (1618–1692) + Catherine, widow Hobson
***** Dr Thomas Pepys, ''physician, poorly appreciated by SP, unmarr.''
***** Paulina Pepys + Hammond Claxton of Booton (Norf.)
After the diary
 Pepys's health suffered from the long hours that he worked throughout the period of the diary. Specifically, he believed that his eyesight had been affected by his work. He reluctantly concluded in his last entry, dated 31 May 1669, that he should completely stop writing for the sake of his eyes, and only dictate to his clerks from then on, which meant that he could no longer keep his diary.
Pepys and his wife took a holiday to France and the Low Countries in June–October 1669; on their return, Elisabeth fell ill and died on 10 November 1669. Pepys erected a monument to her in the church of St Olave's, Hart Street, London. Pepys never remarried, but he did have a long-term housekeeper named Mary Skinner who was assumed by many of his contemporaries to be his mistress and sometimes referred to as Mrs. Pepys. In his will, he left her an annuity of £200 and many of his possessions.
Pepys's health suffered from the long hours that he worked throughout the period of the diary. Specifically, he believed that his eyesight had been affected by his work. He reluctantly concluded in his last entry, dated 31 May 1669, that he should completely stop writing for the sake of his eyes, and only dictate to his clerks from then on, which meant that he could no longer keep his diary.
Pepys and his wife took a holiday to France and the Low Countries in June–October 1669; on their return, Elisabeth fell ill and died on 10 November 1669. Pepys erected a monument to her in the church of St Olave's, Hart Street, London. Pepys never remarried, but he did have a long-term housekeeper named Mary Skinner who was assumed by many of his contemporaries to be his mistress and sometimes referred to as Mrs. Pepys. In his will, he left her an annuity of £200 and many of his possessions.
Member of Parliament and Secretary of the Admiralty
In 1672 he became an Elder Brother of Trinity House and served in this capacity until 1689; he was Master of Trinity House in 1676–1677 and again in 1685–1686. In 1673 he was promoted to Secretary of the Admiralty Commission and elected MP forCastle Rising
Castle Rising is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. The village is situated some north-east of the town of King's Lynn and west of the city of Norwich. The River Babingley skirts the north of the village separating C ...
in Norfolk.
In 1673 he was involved with the establishment of the Royal Mathematical School at Christ's Hospital, which was to train 40 boys annually in navigation, for the benefit of the Royal Navy and the English Merchant Navy. In 1675 he was appointed a Governor of Christ's Hospital and for many years he took a close interest in its affairs. Among his papers are two detailed memoranda on the administration of the school. In 1699, after the successful conclusion of a seven-year campaign to get the master of the Mathematical School replaced by a man who knew more about the sea, he was rewarded for his service as a Governor by being made a Freeman of the City of London. He also served as Master (without ever having been a Freeman or Liveryman) of the Clothworkers' Company (1677-8).
At the beginning of 1679 Pepys was elected MP for Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on- ...
in Charles II's third parliament which formed part of the Cavalier Parliament. He was elected along with Sir Anthony Deane
Sir Anthony Deane FRS (16331721) was a 17th-century mayor of Harwich, naval architect, Master Shipwright and commercial shipbuilder, and Member of Parliament.
Early life
Deane was baptised at Stow-on-the-Wold, Gloucestershire, on 3 December 163 ...
, a Harwich alderman and leading naval architect, to whom Pepys had been patron since 1662. By May of that year, they were under attack from their political enemies. Pepys resigned as Secretary of the Admiralty. They were imprisoned in the Tower of London on suspicion of treasonable correspondence with France, specifically leaking naval intelligence. The charges are believed to have been fabricated under the direction of Anthony Ashley-Cooper, 1st Earl of Shaftesbury. Pepys was accused, among other things, of being a secret member of the Catholic Church in England. Pepys and Deane were released in July, but proceedings against them were not dropped until June 1680.
 Though he had resigned from the Tangier committee in 1679, in 1683 he was sent to Tangier to assist Lord Dartmouth with the evacuation and abandonment of the English colony. After six months' service, he travelled back through Spain accompanied by the naval engineer Edmund Dummer, returning to England after a particularly rough passage on 30 March 1684. In June 1684, once more in favour, he was appointed King's Secretary for the affairs of the Admiralty, a post that he retained after the death of Charles II (February 1685) and the accession of
Though he had resigned from the Tangier committee in 1679, in 1683 he was sent to Tangier to assist Lord Dartmouth with the evacuation and abandonment of the English colony. After six months' service, he travelled back through Spain accompanied by the naval engineer Edmund Dummer, returning to England after a particularly rough passage on 30 March 1684. In June 1684, once more in favour, he was appointed King's Secretary for the affairs of the Admiralty, a post that he retained after the death of Charles II (February 1685) and the accession of James II James II may refer to:
* James II of Avesnes (died c. 1205), knight of the Fourth Crusade
* James II of Majorca (died 1311), Lord of Montpellier
* James II of Aragon (1267–1327), King of Sicily
* James II, Count of La Marche (1370–1438), King C ...
. The phantom Pepys Island, alleged to be near South Georgia
South Georgia ( es, Isla San Pedro) is an island in the South Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It lies around east of the Falkland Islands. Stretching in the east� ...
, was named after him in 1684, having been first "discovered" during his tenure at the Admiralty.
From 1685 to 1688, he was active not only as Secretary of the Admiralty, but also as MP for Harwich. He had been elected MP for Sandwich, but this election was contested and he immediately withdrew to Harwich. When James fled the country at the end of 1688, Pepys's career also came to an end. In January 1689, he was defeated in the parliamentary election at Harwich; in February, one week after the accession of William III William III or William the Third may refer to:
Kings
* William III of Sicily (c. 1186–c. 1198)
* William III of England and Ireland or William III of Orange or William II of Scotland (1650–1702)
* William III of the Netherlands and Luxembourg ...
and Mary II
Mary II (30 April 166228 December 1694) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, co-reigning with her husband, William III & II, from 1689 until her death in 1694.
Mary was the eldest daughter of James, Duke of York, and his first wife ...
, he resigned his secretaryship.
Royal Society
 He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1665 and served as its President from 1 December 1684 to 30 November 1686. Isaac Newton's '' Principia Mathematica'' was published during this period, and its title page bears Pepys's name. There is a probability problem called the " Newton–Pepys problem" that arose out of correspondence between Newton and Pepys about whether one is more likely to roll at least one six with six dice or at least two sixes with twelve dice. It has only recently been noted that the gambling advice which Newton gave Pepys was correct, while the logical argument with which Newton accompanied it was unsound.
He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1665 and served as its President from 1 December 1684 to 30 November 1686. Isaac Newton's '' Principia Mathematica'' was published during this period, and its title page bears Pepys's name. There is a probability problem called the " Newton–Pepys problem" that arose out of correspondence between Newton and Pepys about whether one is more likely to roll at least one six with six dice or at least two sixes with twelve dice. It has only recently been noted that the gambling advice which Newton gave Pepys was correct, while the logical argument with which Newton accompanied it was unsound.
Retirement and death
He was imprisoned on suspicion of Jacobitism from May to July 1689 and again in June 1690, but no charges were ever successfully brought against him. After his release, he retired from public life at age 57. He moved out of London ten years later (1701) to a house in Clapham owned by his friend William Hewer, who had begun his career working for Pepys in the admiralty. Clapham was in the country at the time; it is now part of inner London. Pepys lived there until his death on 26 May 1703. He had no children and bequeathed his estate to his unmarried nephew John Jackson. Pepys had disinherited his nephew Samuel Jackson for marrying contrary to his wishes. When John Jackson died in 1724, Pepys's estate reverted to Anne, daughter of Archdeacon Samuel Edgeley, niece of Will Hewer and sister of Hewer Edgeley, nephew and godson of Pepys's old Admiralty employee and friend Will Hewer. Hewer was also childless and left his immense estate to his nephew Hewer Edgeley (consisting mostly of the Clapham property, as well as lands in Clapham, London, Westminster and Norfolk) on condition that the nephew (and godson) would adopt the surname Hewer. So Will Hewer's heir became Hewer Edgeley-Hewer, and he adopted the old Will Hewer home in Clapham as his residence. That is how the Edgeley family acquired the estates of both Samuel Pepys and Will Hewer, sister Anne inheriting Pepys's estate, and brother Hewer inheriting that of Will Hewer. On the death of Hewer Edgeley-Hewer in 1728, the old Hewer estate went to Edgeley-Hewer's widow Elizabeth, who left the estate to Levett Blackborne, the son of Abraham Blackborne, merchant of Clapham, and other family members, who later sold it off in lots. Lincoln's Inn barrister Levett Blackborne also later acted as attorney in legal scuffles for the heirs who had inherited the Pepys estate. Pepys's formerprotégé
Mentorship is the influence, guidance, or direction given by a mentor. A mentor is someone who teaches or gives help and advice to a less experienced and often younger person. In an organizational setting, a mentor influences the personal and p ...
and friend Hewer acted as the executor of Pepys's estate.
Pepys was buried along with his wife in St Olave's Church, Hart Street
St Olave's Church, Hart Street, is a Church of England church in the City of London, located on the corner of Hart Street and Seething Lane near Fenchurch Street railway station.
John Betjeman described St Olave's as "a country church in the wo ...
in London.
Pepys Library

 Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his large collection of books, manuscripts, and prints. At his death, there were more than 3,000 volumes, including the diary, all carefully catalogued and indexed; they form one of the most important surviving 17th-century private libraries. The most important items in the Library are the six original bound manuscripts of Pepys's diary, but there are other remarkable holdings, including:
*
Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his large collection of books, manuscripts, and prints. At his death, there were more than 3,000 volumes, including the diary, all carefully catalogued and indexed; they form one of the most important surviving 17th-century private libraries. The most important items in the Library are the six original bound manuscripts of Pepys's diary, but there are other remarkable holdings, including:
* Incunabula
In the history of printing, an incunable or incunabulum (plural incunables or incunabula, respectively), is a book, pamphlet, or broadside that was printed in the earliest stages of printing in Europe, up to the year 1500. Incunabula were pro ...
by William Caxton, Wynkyn de Worde, and Richard Pynson
* Sixty medieval manuscripts
* The ''Pepys Manuscript
The Pepys Manuscript is a late fifteenth-century English choirbook, in the library of Magdalene College, Cambridge, MS Pepys 1236. Along with the Ritson Manuscript it is much less elaborate than the Eton, Lambeth and Caius Choirbooks; it cont ...
'', a late-15th-century English choirbook
* Naval records such as two of the ' Anthony Rolls', illustrating the Royal Navy's ships c. 1546, including the '' Mary Rose''
* Sir Francis Drake's personal almanac
* Over 1,800 printed ballads, one of the finest collections in existence.
Pepys made detailed provisions in his will for the preservation of his book collection. His nephew and heir John Jackson died in 1723, when it was transferred intact to Magdalene College, Cambridge, where it can be seen in the Pepys Library
The Pepys Library of Magdalene College, Cambridge, is the personal library collected by Samuel Pepys which he bequeathed to the college following his death in 1703.
Background
Samuel Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his ...
. The bequest included all the original bookcases and his elaborate instructions that placement of the books "be strictly reviewed and, where found requiring it, more nicely adjusted".
The Ephemera Society emblem uses Pepys' portrait and characterizes him as “the first general ephemerist.” Two large albums of ephemera saved by Pepys are in his library.
Publication history of the diary
 Motivated by the publication of John Evelyn's Diary in 1818, Lord Granville deciphered a few pages.
Motivated by the publication of John Evelyn's Diary in 1818, Lord Granville deciphered a few pages. John Smith
John Smith is a common personal name. It is also commonly used as a placeholder name and pseudonym, and is sometimes used in the United States and the United Kingdom as a term for an average person. It may refer to:
People
:''In chronological ...
(later the Rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
of St Mary the Virgin in Baldock) was then engaged to transcribe the diaries into plain English. He laboured at this task for three years, from 1819 to 1822, unaware until nearly finished that a key to the shorthand system was stored in Pepys's library a few shelves above the diary volumes. Others had apparently succeeded in reading the diary earlier, perhaps knowing about the key, because a work of 1812 quotes from a passage of it. Smith's transcription, which is also kept in the Pepys Library, was the basis for the first published edition of the diary, edited by Lord Braybrooke, released in two volumes in 1825.
A second transcription, done with the benefit of the key, but often less accurately, was completed in 1875 by Mynors Bright
Mynors Bright (1818–1883) was an English academic, president of Magdalene College, Cambridge, from 1853 to 1873. He was the decipherer of the diary of Samuel Pepys.
Life
Mynors Bright was the son of the physician John Bright, and of Eliza his wi ...
and published in 1875–1879. This added about a third to the previously published text, but still left only about 80% of the diary in print. Henry B. Wheatley
Henry Benjamin Wheatley FSA (1838–30 April 1917) was a British author, editor, and indexer. His '' London Past and Present'' was described as his most important work and "the standard dictionary of London".
Life
He was a posthumous son of ...
, drawing on both his predecessors, produced a new edition in 1893–1899, revised in 1926, with extensive notes and an index.
All of these editions omitted passages (chiefly about Pepys's sexual adventures) which the editors thought too obscene ever to be printed. Wheatley, in the preface to his edition noted, "a few passages which cannot possibly be printed. It may be thought by some that these omissions are due to an unnecessary squeamishness, but it is not really so, and readers are therefore asked to have faith in the judgement of the editor."
The complete, unexpurgated, and definitive edition, edited and transcribed by Robert Latham and William Matthews, was published by Bell & Hyman, London, and the University of California Press, Berkeley, in nine volumes, along with separate Companion and Index volumes, over the years 1970–1983. Various single-volume abridgements of this text are also available.
The Introduction in volume I provides a scholarly but readable account of "The Diarist", "The Diary" ("The Manuscript", "The Shorthand", and "The Text"), "History of Previous Editions", "The Diary as Literature", and "The Diary as History". The Companion provides a long series of detailed essays about Pepys and his world.
The first unabridged recording of the diary as an audiobook was published in 2015 by ''Naxos AudioBooks''.
On 1 January 2003 Phil Gyford started a weblog, pepysdiary.com, that serialised the diary one day each evening together with annotations from public and experts alike. In December 2003 the blog won the best specialist blog award in '' The Guardian''Adaptations
In 1958 the BBC produced a serial called ''Samuel Pepys!'', in which Peter Sallis played the title role. In 2003 a television film '' The Private Life of Samuel Pepys'' aired onBBC2
BBC Two is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It covers a wide range of subject matter, with a remit "to broadcast programmes of depth and substance" in contrast to the more mainstream an ...
. Steve Coogan
Stephen John Coogan (; born 14 October 1965) is an English actor, comedian, producer and screenwriter. He is most known for creating original characters such as Alan Partridge, a socially inept and politically incorrect media personality, which ...
played Pepys. The 2004 film '' Stage Beauty'' concerns London theatre in the 17th century and is based on Jeffrey Hatcher's play ''Compleat Female Stage Beauty'', which in turn was inspired by a reference in Pepys's diary to the actor Edward Kynaston, who played female roles in the days when women were forbidden to appear on stage. Pepys is a character in the film and is portrayed as an ardent devotee of the theatre. Hugh Bonneville plays Pepys. Daniel Mays portrays Pepys in ''The Great Fire'', a 2014 BBC television miniseries. Pepys has also been portrayed in various other film and television productions, played by diverse actors including Mervyn Johns, Michael Palin, Michael Graham Cox and Philip Jackson.
BBC Radio 4 has broadcast serialised radio dramatisations of the diary. In the 1990s it was performed as a ''Classic Serial'' starring Bill Nighy, and in the 2010s it was serialised as part of the '' Woman's Hour'' radio magazine programme. One audiobook edition of Pepys's diary selections is narrated by Kenneth Branagh. A fictionalised Pepys narrates the second chapter of Harry Turtledove's science fiction novel '' A Different Flesh'' (serialised 1985–1988, book form 1988). This chapter is entitled "And So to Bed" and written in the form of entries from the Pepys diary. The entries detail Pepys's encounter with American ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' specimens (imported to London as beasts of burden) and his formation of the "transformational theory of life", thus causing evolutionary theory to gain a foothold in scientific thought in the 17th century rather than the 19th. Deborah Swift's 2017 novel ''Pleasing Mr Pepys'' is described as a "re-imagining of the events in Samuel Pepys's Diary".
Biographical studies
 Several detailed studies of Pepys's life are available. Arthur Bryant published his three-volume study in 1933–1938, long before the definitive edition of the diary, but, thanks to Bryant's lively style, it is still of interest. In 1974 Richard Ollard produced a new biography that drew on Latham's and Matthew's work on the text, benefiting from the author's deep knowledge of Restoration politics. Other biographies include: ''Samuel Pepys: A Life'', by Stephen Coote (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 2000) and, ''Samuel Pepys and His World'', by Geoffrey Trease (London: Thames and Hudson, 1972).
The most recent general study is by
Several detailed studies of Pepys's life are available. Arthur Bryant published his three-volume study in 1933–1938, long before the definitive edition of the diary, but, thanks to Bryant's lively style, it is still of interest. In 1974 Richard Ollard produced a new biography that drew on Latham's and Matthew's work on the text, benefiting from the author's deep knowledge of Restoration politics. Other biographies include: ''Samuel Pepys: A Life'', by Stephen Coote (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 2000) and, ''Samuel Pepys and His World'', by Geoffrey Trease (London: Thames and Hudson, 1972).
The most recent general study is by Claire Tomalin
Claire Tomalin (née Delavenay; born 20 June 1933) is an English journalist and biographer, known for her biographies of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Samuel Pepys, Jane Austen and Mary Wollstonecraft.
Early life
Tomalin was born Claire Del ...
, which won the 2002 Whitbread Book of the Year award, the judges calling it a "rich, thoughtful and deeply satisfying" account that unearths "a wealth of material about the uncharted life of Samuel Pepys".
See also
* John Evelyn – contemporary diarist * Rota Club * Samuel Pepys ClubNotes
References
Bibliography
Cited secondary sources
* * * * (spring) * * * * * * * * * * * Andrew Godsell "Samuel Pepys: A Man and His Diary" in "Legends of British History" 2008 * *Editions of letters and other publications by Pepys
* * Pepys, Samuel (1995) Robert Latham ed. '' Samuel Pepys and the Second Dutch War. Pepys's Navy White Book and Brooke House Papers ''Aldershot: Scholar Press for the Navy Records Society ublications, Vol 133 * * *The Diary
* Volume I. Introduction and 1660. * Volume II. 1661. * Volume III. 1662. * Volume IV. 1663. * Volume V. 1664. * Volume VI. 1665. * Volume VII. 1666. * Volume VIII. 1667. * Volume IX. 1668–9. * Volume X. Companion. * Volume XI. Index.Further reading
* * . Includes an extensive specialist annotated bibliography. US edition published in New York, 2005. * . A detailed account of the Popish Plot and Pepys's involvement in it, 1679–1680. * Loveman, Kate (2022). "Women and the History of Samuel Pepys's Diary". ''The Historical Journal.'' * *External links
;Works online * * * * ;Portals about Pepys * Phil Gyford'Samuel Pepys's diary
which provides a daily entry from the diary, detailed background articles, plus annotations from readers.
Duncan Grey's pages on Pepys
;Other sites
Pepys library
online at Magdalene College, Cambridge, including an essay by Robert Latham
Magdalene College Libraries' Blog
including the Pepys Library
Pepys Ballad Archive
The Samuel Pepys Club
Internet Movies Database: list of actors who have portrayed Pepys in visual media
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pepys, Samuel 1633 births 1703 deaths 17th-century Royal Navy personnel English diarists English civil servants Fellows of the Royal Society Presidents of the Royal Society English book and manuscript collectors Honourable Artillery Company Alumni of Magdalene College, Cambridge People educated at St Paul's School, London People from the City of London English Anglicans English bibliophiles Christ's Hospital staff Prisoners in the Tower of London 17th-century English writers 17th-century English male writers Members of Trinity House English MPs 1661–1679 English MPs 1679 English MPs 1685–1687 People in English Tangier
Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ...
17th-century diarists
18th-century diarists