|
Ballads
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads derive from the medieval French ''chanson balladée'' or '' ballade'', which were originally "dance songs". Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and song of Britain and Ireland from the Late Middle Ages until the 19th century. They were widely used across Europe, and later in Australia, North Africa, North America and South America. Ballads are often 13 lines with an ABABBCBC form, consisting of couplets (two lines) of rhymed verse, each of 14 syllables. Another common form is ABAB or ABCB repeated, in alternating eight and six syllable lines. Many ballads were written and sold as single sheet broadsides. The form was often used by poets and composers from the 18th century onwards to produce lyrical ballads. In the later 19th century, the term took on the meaning of a slow form of popular love song and is often used for any love song, particularly the sentimental ballad of pop or r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentimental Ballad
A sentimental ballad is an emotional style of music that often deals with romantic and intimate relationships, and to a lesser extent, loneliness, death, war, drug abuse, politics and religion, usually in a poignant but solemn manner.J. M. Curtis, ''Rock Eras: Interpretations of Music and Society, 1954-1984'' (Popular Press, 1987), p. 236. Ballads are generally melodic enough to get the listener's attention. Sentimental ballads are found in most music genres, such as pop, R&B, soul, country, folk, rock and electronic music. Usually slow in tempo, ballads tend to have a lush musical arrangement which emphasizes the song's melody and harmonies. Characteristically, ballads use acoustic instruments such as guitars, pianos, saxophones, and sometimes an orchestral set. Many modern mainstream ballads tend to feature synthesizers, drum machines and even, to some extent, a dance rhythm. Sentimental ballads had their origins in the early Tin Pan Alley music industry o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
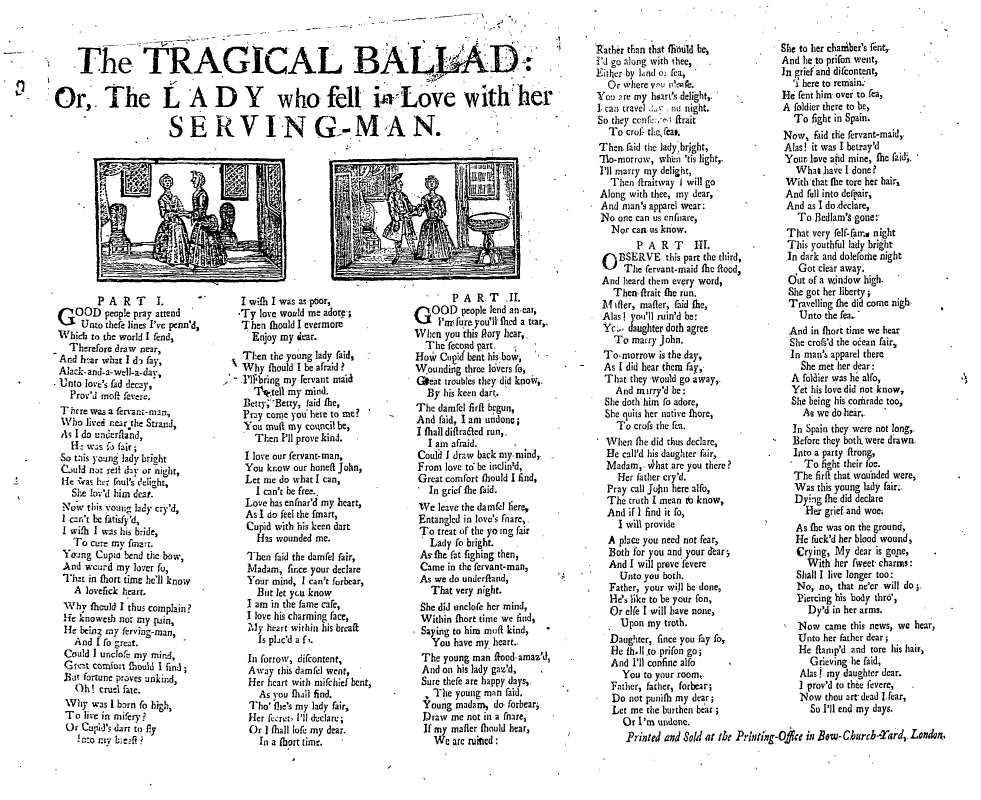
Broadside (music)
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Thomas And Fair Annet
Lord Thomas and Fair Annet (), also known as Lord Thomas and Fair Eleanor, is an English folk ballad. Synopsis Lord Thomas (or Sweet Willie) is in love with Fair Annet, or Annie, or Elinor, but she has little property. He asks for advice. His father, mother, and brother (or some of them) advise that he should marry the nut-brown maid with a rich dowry. His mother promises to curse him if he marries Annet and bless him if he marries the nut-brown maid. His sister warns her that her dowry may be lost and then he will be stuck with nothing but a hideous bride. Nevertheless, he takes his mother's advice. Fair Annet dresses as splendidly as she can and goes to the wedding. The nut-brown maid is so jealous that she stabs Annet to death. Lord Thomas stabs both the nut-brown maid and himself to death. A rose grows from Fair Annet's grave, a brier from Lord Thomas's, and they grow together. Texts The oldest known text, entitled "A tragical Story of Lord Thomas and Fair Ellinor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judas (ballad)
"Judas", Child ballad 23, dates to at least the 13th century and is one of the oldest surviving English ballads. It is numbered as 23 in Francis Child's collection.Bertrand Harris Bronson -''The Ballad as Song'' 1969 Page 97 "First, then, for the materials, taking the Child ballads as our convenient base. ... Whereas the earliest text among Child's ballads, the "Judas," goes back to the mid-thirteenth century, no tune specifically attached in the record by title or ... Synopsis Christ gives Judas 30 pieces of silver to buy food for the Apostles An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...; on his way to the market, Judas is waylaid by his sister, who lulls him to sleep and steals the money. Unwilling to confess his loss, Judas sells Christ to the Romans for the same amou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional ( memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller Thriller may refer to: * Thriller (genre), a broad genre of literature, film and television ** Thriller film, a film genre under the general thriller genre Comics * ''Thriller'' (DC Comics), a comic book series published 1983–84 by DC Comics i ..., novel, etc.). Narratives can be presented through a sequence of written or spoken words, through still or moving images, or through any combination of these. The word derives from the Latin verb ''narrare'' (to tell), which is derived from the adjective ''gnarus'' (knowing or skilled). Narration (i.e., the process of presenting a narrative) is a rhetorical modes, rhetorical mode of discourse, broadly defined (and paralleling argumentation, description, and exposition (narrative), exposition), is one of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballade (forme Fixe)
The ''ballade'' (; ; not to be confused with the ballad) is a form of medieval and Renaissance French poetry as well as the corresponding musical chanson form. It was one of the three '' formes fixes'' (the other two were the rondeau and the virelai) and one of the verse forms in France most commonly set to music between the late 13th and the 15th centuries. The formes fixes were standard forms in French-texted song of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. The ballade is usually in three stanzas, each ending with a refrain (a repeated segment of text and music). The ballade as a verse form typically consists of three eight-line stanzas, each with a consistent metre and a particular rhyme scheme. The last line in the stanza is a refrain. The stanzas are often followed by a four-line concluding stanza (an '' envoi'') usually addressed to a prince. The rhyme scheme is therefore usually , where the capital "C" is a refrain. The many different rhyming words that are needed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanzas
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme and metrical schemes, but they are not required to have either. There are many different forms of stanzas. Some stanzaic forms are simple, such as four-line quatrains. Other forms are more complex, such as the Spenserian stanza. Fixed verse poems, such as sestinas, can be defined by the number and form of their stanzas. The stanza has also been known by terms such as ''batch'', ''fit'', and ''stave''. The term ''stanza'' has a similar meaning to ''strophe'', though ''strophe'' sometimes refers to an irregular set of lines, as opposed to regular, rhymed stanzas. Even though the term "stanza" is taken from Italian, in the Italian language the word "strofa" is more commonly used. In music, groups of lines are typically referred to as '' verses''. The stanza in poetry is analogous with the paragrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iamb (foot)
An iamb () or iambus is a metrical foot used in various types of poetry Poetry (derived from the Greek '' poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings .... Originally the term referred to one of the feet of the quantitative meter of classical Greek prosody: a short syllable followed by a long syllable (as in () "beautiful (f.)"). This terminology was adopted in the description of accentual-syllabic verse in English, where it refers to a foot comprising an unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable (as in ''abóve''). Thus a Latin word like , because of its short-long rhythm, is considered by Latin scholars to be an iamb, but because it has a stress on the first syllable, in modern linguistics it is considered to be a trochee. Etymology Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrameter
In poetry, a tetrameter is a line of four metrical feet. The particular foot can vary, as follows: * ''Anapestic tetrameter:'' ** "And the ''sheen'' of their ''spears'' was like ''stars'' on the ''sea''" (Lord Byron, "The Destruction of Sennacherib") ** "Twas the ''night'' before ''Christ''mas when ''all'' through the ''house''" (" A Visit from St. Nicholas") * ''Iambic tetrameter:'' ** "Be''cause'' I ''could'' not ''stop'' for ''Death''" (Emily Dickinson, eponymous lyric) * ''Trochaic tetrameter:'' ** "''Pet''er, ''Pet''er, ''pump''kin-''eat''er" ( English nursery rhyme) * '' Dactylic tetrameter:'' ** ''Pic''ture your ''self'' in a ''boat'' on a ''riv''er with ..(The Beatles, "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds") * '' Spondaic tetrameter:'' ** ''Long sounds move slow'' * '' Pyrrhic tetrameter'' (with spondees white breast" and "dim sea": ** And the ''white breast'' of the ''dim sea'' * '' Amphibracic tetrameter:'' ** And, ''speak''ing of ''birds'', there's the ''Russ''ian Pa''loo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimeter
In poetry, a trimeter (Greek for "three measure") is a metre of three metrical feet per line. Examples: : When here // the spring // we see, : Fresh green // upon // the tree. See also * Anapaest An anapaest (; also spelled anapæst or anapest, also called antidactylus) is a metrical foot used in formal poetry. In classical quantitative meters it consists of two short syllables followed by a long one; in accentual stress meters it consis ... * Dactyl * Tristich * Triadic-line poetry References Types of verses {{Poetry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Consonance
Consonance is a stylistic literary device identified by the repetition of identical or similar consonants in neighboring words whose vowel sounds are different (e.g. coming home, hot foot). Consonance may be regarded as the counterpart to the vowel-sound repetition known as assonance. Alliteration is a special case of consonance where the repeated consonant sound is at the stressed syllable, as in "few flocked to the fight" or "around the rugged rock the ragged rascal ran". Alliteration is usually distinguished from other types of consonance in poetic analysis, and has different uses and effects. Another special case of consonance is sibilance, the use of several |
Common Metre
Common metre or common measure—abbreviated as C. M. or CM—is a poetic metre consisting of four lines that alternate between iambic tetrameter (four metrical feet per line) and iambic trimeter (three metrical feet per line), with each foot consisting of an unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable. The metre is denoted by the syllable count of each line, i.e. 8.6.8.6, 86.86, or 86 86, depending on style, or by its shorthand abbreviation "CM". Common metre has been used for ballads such as " Tam Lin" and hymns such as " Amazing Grace" and the Christmas carol " O Little Town of Bethlehem". The upshot of this commonality is that lyrics of one song can be sung to the tune of another; for example, " Advance Australia Fair", " House of the Rising Sun", Pokémon Theme and "Amazing Grace" can have their lyrics set to the tune of any of the others. Historically, lyrics were not always wedded to tunes and would therefore be sung to any fitting melody; "Amazing Grace", for inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |