Parnitha Satellite Map-blank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mount Parnitha ( ell, Πάρνηθα, ,
official site. The name of the mountain dates back to
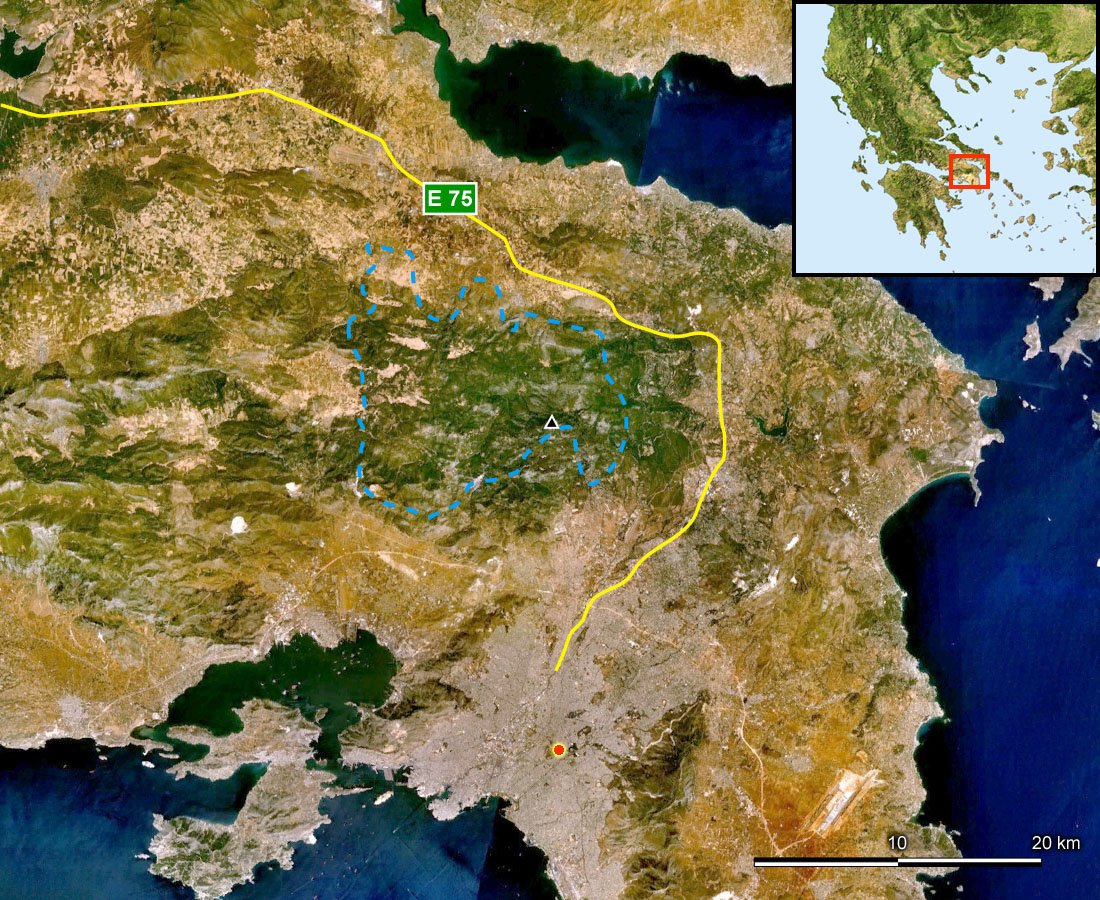 Towns surrounding the mountain include
Towns surrounding the mountain include
 Parnitha has several places of archaeological interest. In antiquity, several fortresses had been built on the mountain, for the defense of the peninsula of
Parnitha has several places of archaeological interest. In antiquity, several fortresses had been built on the mountain, for the defense of the peninsula of  Parnitha has also natural monuments. The cave of Panas is on the west slopes of the mountain at a height of 750 meters. It was a worship site in antiquity. Near the cave there is the steep gorge of Gouras and the gorge of Keladonas river. A beautiful site of the mountain is Beletsi Lake, on the east slopes of the mountain, near
Parnitha has also natural monuments. The cave of Panas is on the west slopes of the mountain at a height of 750 meters. It was a worship site in antiquity. Near the cave there is the steep gorge of Gouras and the gorge of Keladonas river. A beautiful site of the mountain is Beletsi Lake, on the east slopes of the mountain, near
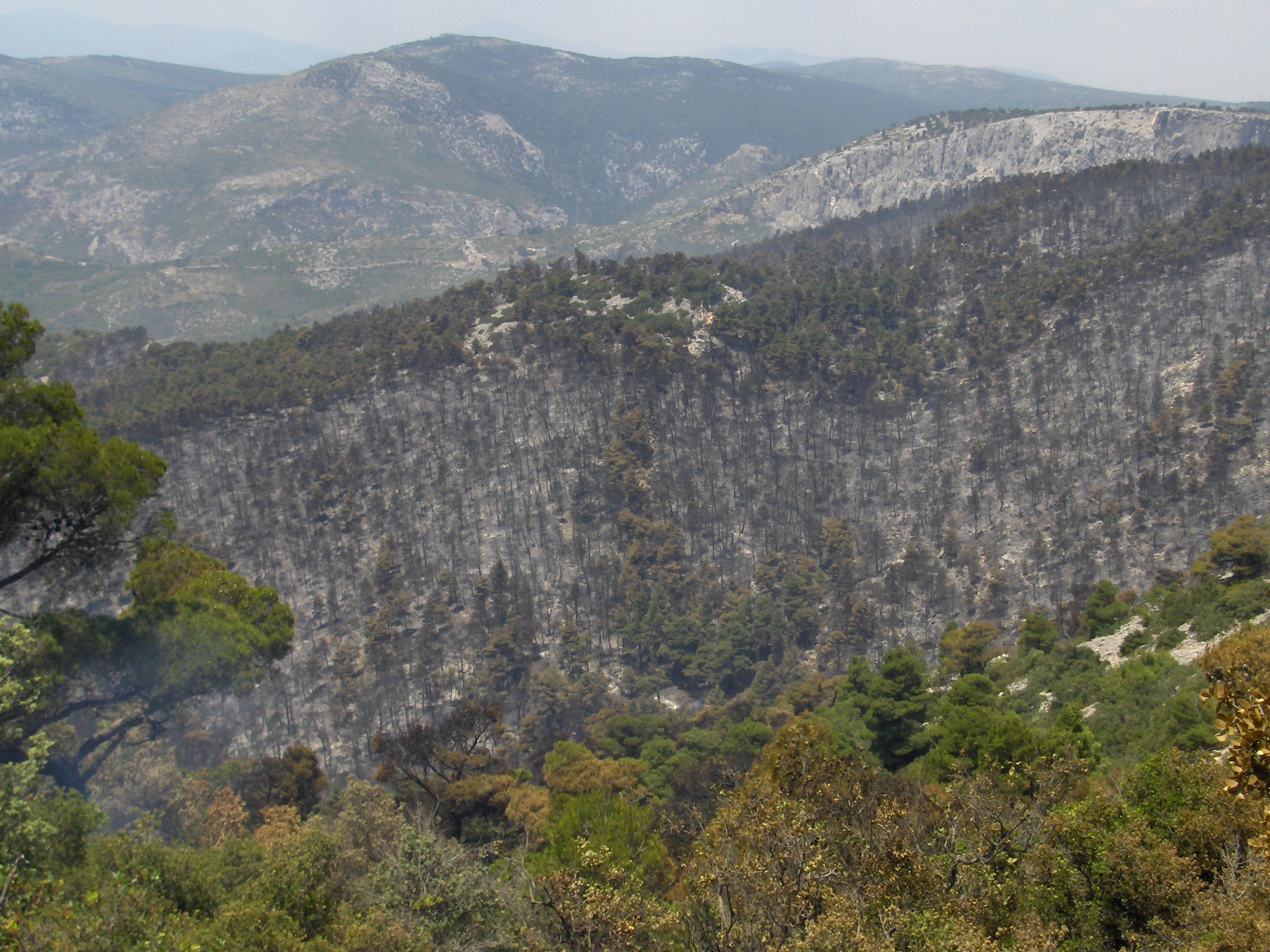

 Parnitha suffered extensive damage from a
Parnitha suffered extensive damage from a
Official website of the Parnitha National Park
Accurate Forecasts in Parnitha
Official website of the shelter Mpafi
{{authority control Landforms of Attica Mountain ranges of Greece National parks of Greece Tourist attractions in Attica Landforms of West Attica Landforms of East Attica Natura 2000 in Greece
Katharevousa
Katharevousa ( el, Καθαρεύουσα, , literally "purifying anguage) is a conservative form of the Modern Greek language conceived in the late 18th century as both a literary language and a compromise between Ancient Greek and the contempor ...
and grc, Πάρνης ''Parnis''/''Parnes''; sometimes Parnetha) is a densely forested mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and ...
range north of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, the highest on the peninsula of Attica
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean Se ...
, with an elevation of 1,413 m, and a summit known as Karavola (Καραβόλα). Much of the mountain is designated a national park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
, and is a protected habitat for wildfowl
The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on ...
, first created in 1961. The summit is located 18 km north of Acharnes
Acharnes ( el, Αχαρνές, , before 1915: Μενίδι Menidi, ) is a northwestern suburb of Athens, Attica, Greece. With 106,943 inhabitants (2011 census), it is the most populous municipality in East Attica. It is part of the Athens Urban ar ...
and about 30 km north of Athens city center, while the mountain covers approximately 250 km² of land. Other peaks include Mavrovouni (Μαυροβούνι), Ornio (1,350 m), Area (1,160 m), Avgo or Avgho (1,150 m), and Xerovouni (Ξεροβούνι, meaning "dry mountain": 1,120 m). It also has two shelters Mpafi
The Bafi Refuge (also spelt Mpafi) belongs to the Greek Mountaineering Club, E.O.S. Athens founded in 1928 in the Mount Parnitha National Park, at an altitude of 1160m, roughly 2.5 km from Mont Parness, inside the national park
A nat ...
and Flampouri.Parnitha National parkofficial site. The name of the mountain dates back to
ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
, when it was under the ancient deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and ear ...
s of Acharnae
Acharnae or Acharnai (; grc, Ἀχαρναί) was a ''deme'' of ancient Athens. It was part of the phyle Oineis.
Acharnae, according to Thucydides, was the largest deme in Attica. In the fourth century BCE, 22 of the 500 members of the At ...
and Decelea
Decelea ( grc, Δεκέλεια, ), ''Dekéleia''), was a deme and ancient village in northern Attica serving as a trade route connecting Euboea with Athens, Greece. It was situated near the entrance of the eastern pass across Mount Parnes, which ...
.
Geography
 Towns surrounding the mountain include
Towns surrounding the mountain include Aspropyrgos
Aspropyrgos ( el, Ασπρόπυργος) is a suburb of Athens, and a municipality in the West Attica regional unit, Attica, Greece. The municipality had a population of 30,251 at the 2011 census. It has an area of 101.983 km2.
Etymology
The na ...
, Fyli
Fyli ( el, Φυλή, , meaning "tribe") is a town and a municipality in the northwestern part of Attica, Greece. It lies in the northeastern corner of the West Attica regional unit, and is a suburb of Athens. The seat of the municipality is the to ...
, Acharnes, Varymbombi
Varympompi or Varibobi ( el, Βαρυμπόμπη) is a suburb of Athens in the municipality of Acharnes, East Attica, Greece.
Geography
Varympompi is situated at the foot of the forested Parnitha mountains, 3 km east of Thrakomakedones, 4 km wes ...
, Thrakomakedones
Thrakomakedones (Greek: Θρακομακεδόνες from Thrace and Macedonia), is a town in the regional unit East Attica, in Attica region, Greece. It is a northern suburb of Athens. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the muni ...
, Dekeleia, Avlona and Agios Stefanos as well as the settlement of Agios Merkourios
''Agios'' ( el, Άγιος), plural ''Agioi'' (), transcribes masculine gender Greek words meaning 'sacred' or ' saint' (for example Agios Dimitrios, Agioi Anargyroi). It is frequently shortened in colloquial language to ''Ai'' (for example Ai ...
. The highway GR-1 ( E75) surrounds the northern and eastern part of the mountain along with the Cephissus river, while the Attiki Odos
Attiki Odos ( el, Αττική Οδός) is a privately owned toll motorway system in Greece. The Attiki Odos motorways form the outer beltways of the Athens, Greater Athens metropolitan area. The total length of the motorways is . The Attiki Odos ...
motorway (GR-6) runs to its south. The mountain offers panoramic views of the mountains northeast of Parnitha, Penteli
Penteli ( el, Πεντέλη) is a village and a municipality in the North Athens regional unit, Attica, Greece. It belongs to the Athens rural area. It takes its name from Mount Pentelicus.
Municipality
The municipality Penteli was formed at the ...
to the east, the Hymettus
Hymettus (), also Hymettos (; el, Υμηττός, translit=Ymittós, pronounced ), is a mountain range in the Athens area of Attica, East Central Greece. It is also colloquially known as ''Trellós'' (crazy) or ''Trellóvouno'' (crazy mountain) ...
to the southeast, the Aigaleo
Aigaleo or Egaleo ( el, Αιγάλεω ) is a suburban municipality in the western part of Athens, belonging to the West Athens regional administrative unit. It takes its name from Mount Aigaleo. Its population was 69,946 at the 2011 census.
Ge ...
to the south and another to the west; from its summit, one can also see the Thriasian Plain
The Thriasio Plain ( el, Θριάσιο Πεδίο, translit=Thriasio Pedio) is a plain in western Attica, immediately to the west of Athens, in Greece. It is bounded by Mount Egaleo to the east, Mount Parnitha to the north, Mount Pateras to th ...
, the Saronic Gulf
The Saronic Gulf (Greek: Σαρωνικός κόλπος, ''Saronikós kólpos'') or Gulf of Aegina in Greece is formed between the peninsulas of Attica and Argolis and forms part of the Aegean Sea. It defines the eastern side of the isthmus of Co ...
including the islands of Salamina, Aigina
Aegina (; el, Αίγινα, ''Aígina'' ; grc, Αἴγῑνα) is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina, the mother of the hero Aeacus, who was born on the island and b ...
and the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
, the South Euboean Gulf
The South Euboean Gulf ( el, Νότιος Ευβοϊκός Κόλπος, ''Notios Evvoïkos Kolpos'') is a gulf in Central Greece, between the island of Euboea and the Greek mainland (Boeotia and Attica). With a total length of approximately 50&n ...
s and island of Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest poin ...
, and most of central and northern Greater Athens. The view during clear days can extend to northern Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its lar ...
and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
.
Climate
Parnitha mountain has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate with frequent snowfalls in winter and pleasant temperatures in summer. The mountain is significantly wetter than areas of east and southern Attica. The mountain was also affected by several major blizzards, including two in 2005 and 2006, stranding cars and closing roads, as well as the cable car.Ecology
Forests ofAleppo Pine
''Pinus halepensis'', commonly known as the Aleppo pine, also known as the Jerusalem pine, is a pine native to the Mediterranean region.
Description
''Pinus halepensis'' is a small to medium-sized tree, tall, with a trunk diameter up to , exce ...
cover all slopes beneath 1,000 m altitude, and are often threatened by forest fires, such as happened in 2005 and 2007. Above 1,000 m it is covered principally in Greek Fir
''Abies cephalonica'' or Greek fir is a fir native to the mountains of Greece, primarily in the Peloponnesos and the island of Kefallonia, intergrading with the closely related Bulgarian fir further north in the Pindus mountains of northern Gre ...
, grasses and shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees ...
bery, and beneath 300 m mainly farmlands and suburban housing to the east. About 1,000 species of plants can be found on the mountain, including crocus
''Crocus'' (; plural: crocuses or croci) is a genus of seasonal flowering plants in the family Iridaceae (iris family) comprising about 100 species of perennials growing from corms. They are low growing plants, whose flower stems remain undergro ...
and tulips
Tulips (''Tulipa'') are a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes (having bulbs as storage organs). The flowers are usually large, showy and brightly coloured, generally red, pink, yellow, or white (usually in warm ...
, and the mountain also provides a native habitat to its red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
(''Cervus elaphus''), which were known in ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
. After the traumatic fire in 2007 (''see below''), they are even scarcer. Several large mines lie to the northwest, and the ore from them was shipped to a nearby factory in industrial areas.
Historical monuments and places of interest
 Parnitha has several places of archaeological interest. In antiquity, several fortresses had been built on the mountain, for the defense of the peninsula of
Parnitha has several places of archaeological interest. In antiquity, several fortresses had been built on the mountain, for the defense of the peninsula of Attica
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean Se ...
and more specifically Classical Athens
The city of Athens ( grc, Ἀθῆναι, ''Athênai'' .tʰɛ̂ː.nai̯ Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' or, more commonly and in singular, Αθήνα, ''Athina'' .'θi.na during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) wa ...
against the Boeotians
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its lar ...
and others enemies from the north. Today some fortresses are kept in good condition such as the Phyle
''Phyle'' ( gr, φυλή, phulē, "tribe, clan"; pl. ''phylai'', φυλαί; derived from ancient Greek φύεσθαι "to descend, to originate") is an ancient Greek term for tribe or clan. Members of the same ''phyle'' were known as ''symphylet ...
fortress, at a height of 687 meters in the west of Parnitha. Other notable fortresses are the Panakton, in the area of Dervenochoria
Dervenochoria ( el, Δερβενοχώρια) is a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Tanagra, of which it is a municipal unit. In 2011 its population was 1,869. The municip ...
and Eleutherae
Eleutherae ( grc, Ἐλευθεραί) is a city in the northern part of Attica, bordering the territory of Boeotia. One of the best preserved fortresses of Ancient Greece stands now on the spot of an Ancient Eleutherae castle, dated between 37 ...
fortress near Mount Cithaeron
Cithaeron or Kithairon (Κιθαιρών, -ῶνος) is a mountain and mountain range about sixteen kilometres (ten miles) long in Central Greece. The range is the physical boundary between Boeotia in the north and Attica in the south. It is mai ...
. Dekeleia was also an important fortress on the site of modern-day former royal palace in Tatoi
Tatoi ( el, Τατόι, ) was the summer palace and estate of the former Greek royal family. The area is a densely wooded southeast-facing slope of Mount Parnitha, and its ancient and current official name is Dekeleia. It is located from t ...
, and the fort of Limiko was situated deep inside the mountain, just north of its peak.
A notable monument of later periods is the Monastery of Kleiston. It is a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
monastery dated from 13th century. It is mentioned by Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV ( la, Innocentius IV; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universitie ...
in 1209 with the name Monastery of Kyras. Southeast of Parnitha, in a dense forest, is Tatoi Palace
Tatoi ( el, Τατόι, ) was the summer palace and estate of the former Greek royal family. The area is a densely wooded southeast-facing slope of Mount Parnitha, and its ancient and current official name is Dekeleia. It is located from t ...
. It was the palace of the Greek royal family and it was built in 19th century. Today it is abandoned.
Afidnes
Afidnes ( el, Αφίδνες, or Ἀφίδναι, from the Middle Ages until 1919: Κιούρκα - ''Kiourka'') is a small town in East Attica, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Oropos, of which it is ...
, and it is important place for migratory birds.
Modern facilities
A casino, the Mont Parnes Casino, is located near the top of the mountain and is served by a suspended cable car. Two shelters are also on Parnitha, the most known of which isMpafi
The Bafi Refuge (also spelt Mpafi) belongs to the Greek Mountaineering Club, E.O.S. Athens founded in 1928 in the Mount Parnitha National Park, at an altitude of 1160m, roughly 2.5 km from Mont Parness, inside the national park
A nat ...
. A series of trails are found around the mountain as well as forest roads, and also on the mountain is Athens' second transmitter, broadcasting radio and television since the mid-1950s, across the range of television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
channels from ERT, ANT1
Antenna, better known as ANT1, is a television network airing in Greece. The alternate spelling is wordplay in Greek; ''ena'' (ένα) is the Greek number ''1'' (one), thus ''ANT1'' is pronounced the same as ''Antenna'' (Αντέννα). It laun ...
, Mega
Mega or MEGA may refer to:
Science
* mega-, a metric prefix denoting 106
* Mega (number), a certain very large integer in Steinhaus–Moser notation
* "mega-" a prefix meaning "large" that is used in taxonomy
* Gravity assist, for ''Moon-Eart ...
, Alter
Alter may refer to:
* Alter (name), people named Alter
* Alter (automobile)
* Alter (crater), a lunar crater
* Alter Channel, a Greek TV channel
* Archbishop Alter High School, a Roman Catholic high school in Kettering, Ohio
* ALTER, a comman ...
and more, to satellite, including Super Sport, Seven X and Filmnet
FilmNet was the name used for several premium television channels in Europe during the 1980s, 1990s and 2000s. It was launched on 9 March 1985, broadcasting with a focus on Scandinavia, the Netherlands and the northern part of Belgium (Flanders). ...
, and a multitude of radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
including ERA Radio
The Hellenic Radio ( el, Ελληνική Ραδιοφωνία; or ERA) is the main public radio broadcaster in Greece. Founded in 1987 as a subsidiary of public broadcaster Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation (ERT), it broadcasts four domestic ra ...
, Klik FM, ANT1 Radio, Ciao FM, Rhythmos, Super Sport FM, Top FM
A spinning top, or simply a top, is a toy with a squat body and a sharp point at the bottom, designed to be spun on its vertical axis, balancing on the tip due to the gyroscopic effect.
Once set in motion, a top will usually wobble for a fe ...
and others. The supporting road connection was paved in the mid-20th century.
2007 wildfire


wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
on Thursday, 28 June 2007 around the morning and noon hours, continuing for several days and burning approximately 56 km² of land; one of the worst recorded wildfires in the prefecture after that of Penteli
Penteli ( el, Πεντέλη) is a village and a municipality in the North Athens regional unit, Attica, Greece. It belongs to the Athens rural area. It takes its name from Mount Pentelicus.
Municipality
The municipality Penteli was formed at the ...
. The magnitude of the devastation was unforeseen. A smaller fire had, however, taken place in the 1960s.
The fire consumed dozens of acres of forest across two prefectures. Firefighters, helicopters, and planes were brought into action across the mountain area and its edges fighting the enormous blaze, which took days to contain. It spread rapidly with the help of intense winds, and intensified into the northwestern edges of Greater Athens, including both Ano Liosia
Ano Liosia ( el, Άνω Λιόσια) is a suburb and a former municipality in the northern part of the Athens agglomeration, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Fyli, of which it is the seat and a munici ...
and towns and villages such as Fyli
Fyli ( el, Φυλή, , meaning "tribe") is a town and a municipality in the northwestern part of Attica, Greece. It lies in the northeastern corner of the West Attica regional unit, and is a suburb of Athens. The seat of the municipality is the to ...
, near Thrakomakedones
Thrakomakedones (Greek: Θρακομακεδόνες from Thrace and Macedonia), is a town in the regional unit East Attica, in Attica region, Greece. It is a northern suburb of Athens. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the muni ...
, Pyli
Pyli ( el, Πύλη) is a municipality in the Trikala regional unit, Greece. Situated 18 km west of Trikala, right at the bottom of two mountains Itamos, and Koziakas, which mark the beginning of the Pindos mountainline, Pyli marks the entra ...
and both Skoura and Schimatari
Schimatari ( el, Σχηματάρι) is a town and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Tanagra, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area ...
north of the mountain. From Athens, inhabitants could see the mountainside burning throughout the night. In Schimatari in Boeotia, it ruined several acres of forest and businesses. The fire claimed 80% of the rare Greek Fir and Aleppo Pine forest, 150 animals of the red deer population (an endangered species), birds, and other rare animals. The remains of the green firs and pines are scattered around its edges. The smoke from the massive destruction formed a line that traveled east over Attica, southern Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest poin ...
, Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic ...
, to the edge of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, approximately 350 km away.
On June 30, the fire was mostly contained and warnings of new fires were reduced, as only a few fires were slowly burning sporadically in separate parts of the mountain. The main blaze was completely put out on July 1. At the edges of the burnt parts, several fires slowly continued to burn in sections after June 30, with a slow expansion.
Scientists estimate that the area's recovery time may be as long as a century. They predict the effect of the loss will only begin to be felt in the coming years; the air may become a little stale and the already known problems of air pollution and smog in Athens may reappear and intensify. Temperatures could also rise and flooding may become a problem for several years. The Ministry of Environment is currently considering a conclusive reforestation program, while many citizens marched on the streets of Athens to express their disapproval of the handling of the situation. More recently, reforestation has been underway, and the government will be receiving tens of thousands of trees to be planted around the mountains, most of them from outside the country, albeit at a small scale thus far.
Investigations are still underway as to the fire's cause. One scenario suggests a transformer belonging to a major power line exploded due to overuse and overheating by the 47C heatwave, some days before the fire. Another holds that this was one of the many arson attacks that have claimed forested land in Greece over recent decades to illegally clear formerly-protected land for expanded real estate.
See also
*List of mountains in Greece
A list of mountains in Greece:
See also
* Mount Kythnos
*Movri
*Omplos
* Pantokrator (Corfu)
*Skollis
External linksMaps of mountains in Greeceby Geopsis
{{List of mountains in Europe
Greece
*
Mountains
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ...
* National parks in Greece
Greece is characterized by an extremely fragmented, rugged landscape hosting a great diversity of ecosystems and an outstanding biodiversity. Almost 5% of its extensive coastline consists of ecologically sensitive wetlands. Two thirds of the total ...
References
Further reading
* : ''Parnes. In: Der Kleine'' (''Parnitha''), Pauly 1972.External links
Official website of the Parnitha National Park
Accurate Forecasts in Parnitha
Official website of the shelter Mpafi
{{authority control Landforms of Attica Mountain ranges of Greece National parks of Greece Tourist attractions in Attica Landforms of West Attica Landforms of East Attica Natura 2000 in Greece