Panay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the
 According to Maragtas, the
According to Maragtas, the
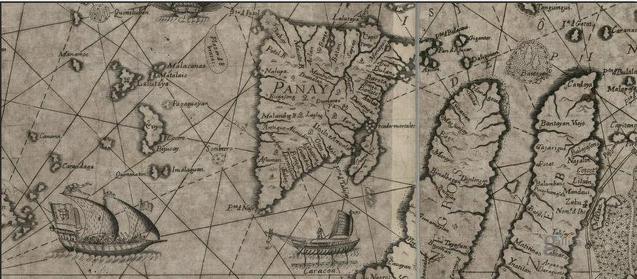 During the early part of the Spanish colonization of the Philippines, the Spanish Augustinian Friar Gaspar de San Agustín, O.S.A. described Panay as: ''"…very similar to that of Sicily in its triangular form, as well as in it fertility and abundance of provision. It is the most populated island after Manila and Mindanao, and one of the largest (with over a hundred leagues of coastline). In terms of fertility and abundance, it is the first.'' ��''It is very beautiful, very pleasant, and full of coconut palms… Near the river Alaguer'' (''Halaur''), ''which empties into the sea two leagues from the town of Dumangas…, in the ancient times, there was a trading center and a court of the most illustrious nobility in the whole island."'' Padre Francisco Colin (1592–1660), an early Jesuit missionary and Provincial of his Order in the Philippines also records in the chronicles of the Society of Jesus (published later in 1663 as ''Labor euangelica'') that Panay is the island which is most abundant and fertile.
The first Spanish settlement in Panay island and the second oldest Spanish settlement in the Philippines was established by the
During the early part of the Spanish colonization of the Philippines, the Spanish Augustinian Friar Gaspar de San Agustín, O.S.A. described Panay as: ''"…very similar to that of Sicily in its triangular form, as well as in it fertility and abundance of provision. It is the most populated island after Manila and Mindanao, and one of the largest (with over a hundred leagues of coastline). In terms of fertility and abundance, it is the first.'' ��''It is very beautiful, very pleasant, and full of coconut palms… Near the river Alaguer'' (''Halaur''), ''which empties into the sea two leagues from the town of Dumangas…, in the ancient times, there was a trading center and a court of the most illustrious nobility in the whole island."'' Padre Francisco Colin (1592–1660), an early Jesuit missionary and Provincial of his Order in the Philippines also records in the chronicles of the Society of Jesus (published later in 1663 as ''Labor euangelica'') that Panay is the island which is most abundant and fertile.
The first Spanish settlement in Panay island and the second oldest Spanish settlement in the Philippines was established by the  The island is the most fertile and well-provisioned of all the islands discovered, except the island of
The island is the most fertile and well-provisioned of all the islands discovered, except the island of
 In 1572, the island was organized into two provinces: jurisdictions of
In 1572, the island was organized into two provinces: jurisdictions of
 On April 16, 1942,
On April 16, 1942,
 Panay island is the sixth largest island in the Philippines by area, with a total land area of .
Panay island is the sixth largest island in the Philippines by area, with a total land area of .
 Panay Island's economy thrives due to the combined strengths and contributions of its four provinces. The diversity of industries, including agriculture, fishing, tourism, manufacturing, and natural resource utilization, sustains the island's robust economic growth and development. As a result, Panay Island has emerged as the fifth economic giant in the Philippines.
Iloilo, including Iloilo City, which serves as the economic center, plays a pivotal role in driving the island's economy. The province is a hub for various industries, including real estate, accommodation, medical centers, education, shopping centers, business centers, IT/BPO centers, and more. Its vibrant and multifaceted economy has positioned Iloilo as one of the most competitive provinces in the country.
Aklan, known for Boracay Island, serves as the tourism center of Panay Island. The world-famous tourist destination attracts a significant number of visitors, contributing to the province's tourism industry. Aklan's economy benefits from the influx of tourists and the diverse range of activities and services catering to their needs.
Capiz, dubbed the "Seafood Capital of the Philippines," takes advantage of its coastal areas and swampy lands, supporting a thriving fishing industry. The province's aquamarine resources, including prawns, milkfish, marlin, squid, oysters, shrimp, and seaweed, contribute significantly to its economic growth.
Antique's economy relies on fishing, with a rich fishing ground along its coastline. Additionally, the province's forest resources, such as bamboo, buri, bariw, nito, logs, and charcoal, contribute to the construction industry, furniture-making, and handicrafts. The natural beauty of Antique, including the presence of the rafflesia flower and protected forestland, further enhances its tourism potential.
Panay Island's economy thrives due to the combined strengths and contributions of its four provinces. The diversity of industries, including agriculture, fishing, tourism, manufacturing, and natural resource utilization, sustains the island's robust economic growth and development. As a result, Panay Island has emerged as the fifth economic giant in the Philippines.
Iloilo, including Iloilo City, which serves as the economic center, plays a pivotal role in driving the island's economy. The province is a hub for various industries, including real estate, accommodation, medical centers, education, shopping centers, business centers, IT/BPO centers, and more. Its vibrant and multifaceted economy has positioned Iloilo as one of the most competitive provinces in the country.
Aklan, known for Boracay Island, serves as the tourism center of Panay Island. The world-famous tourist destination attracts a significant number of visitors, contributing to the province's tourism industry. Aklan's economy benefits from the influx of tourists and the diverse range of activities and services catering to their needs.
Capiz, dubbed the "Seafood Capital of the Philippines," takes advantage of its coastal areas and swampy lands, supporting a thriving fishing industry. The province's aquamarine resources, including prawns, milkfish, marlin, squid, oysters, shrimp, and seaweed, contribute significantly to its economic growth.
Antique's economy relies on fishing, with a rich fishing ground along its coastline. Additionally, the province's forest resources, such as bamboo, buri, bariw, nito, logs, and charcoal, contribute to the construction industry, furniture-making, and handicrafts. The natural beauty of Antique, including the presence of the rafflesia flower and protected forestland, further enhances its tourism potential.
 All the provinces in Panay are interconnected by major inter-provincial roads. Iloilo City is served mostly by passenger jeepneys, white metered taxis and tricycles within the city limits. The primary transportation vehicle used within Roxas City, Kalibo, San Jose de Buenavista and other cities and municipalities in Panay is the tricycle. Travel between cities and municipalities is typically by jeepney, vans and Ceres operated buses. In March 2019, the Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board announced the opening of a new
All the provinces in Panay are interconnected by major inter-provincial roads. Iloilo City is served mostly by passenger jeepneys, white metered taxis and tricycles within the city limits. The primary transportation vehicle used within Roxas City, Kalibo, San Jose de Buenavista and other cities and municipalities in Panay is the tricycle. Travel between cities and municipalities is typically by jeepney, vans and Ceres operated buses. In March 2019, the Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board announced the opening of a new
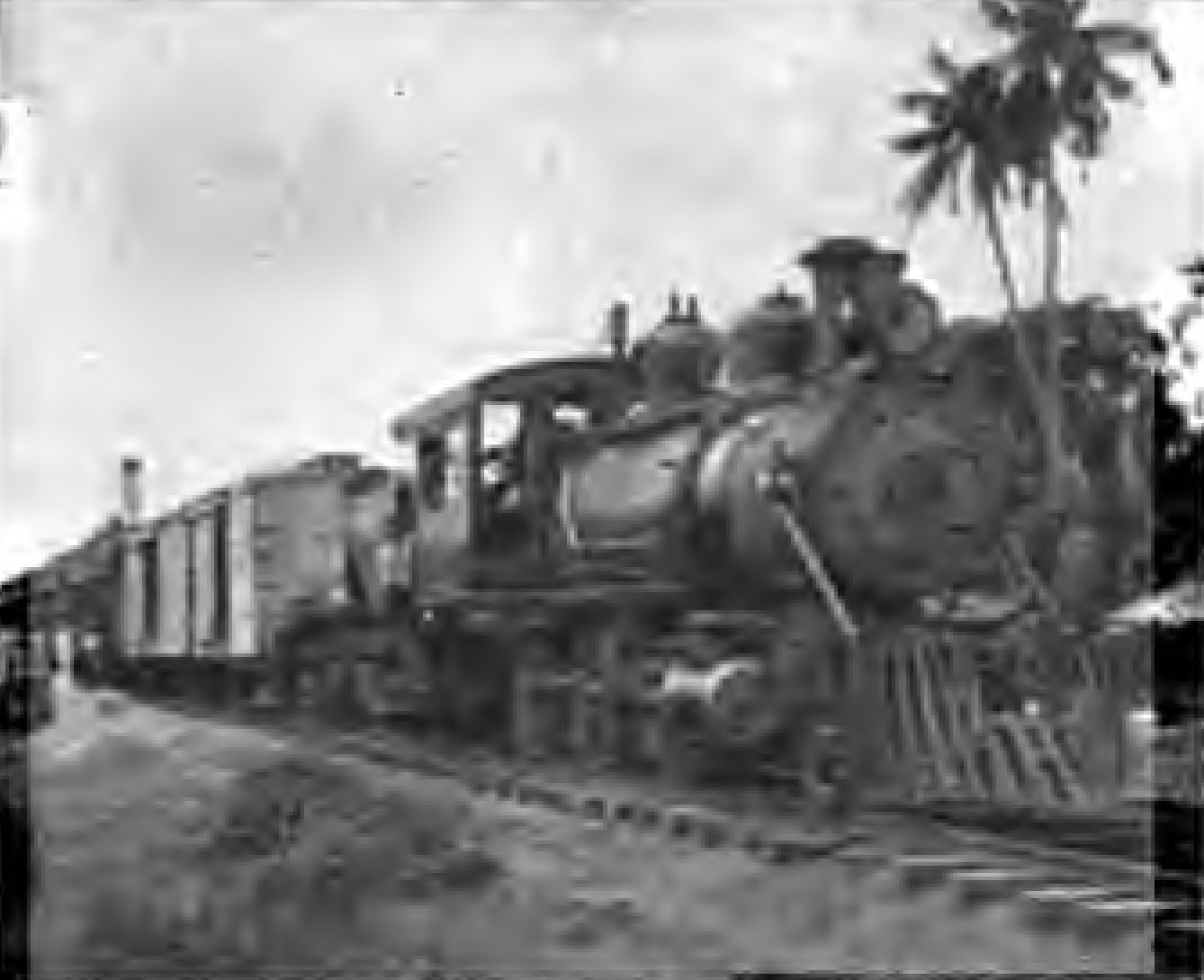 Proposals to re-connect again Iloilo-Roxas, Iloilo-Kalibo, Iloilo-Malay (Aklan) and Iloilo-San Jose (Antique) from the Iloilo City via rail was included in the revival of the currently defunct Panay Railways network which has a station in Santa Barbara town proper.
Proposals to re-connect again Iloilo-Roxas, Iloilo-Kalibo, Iloilo-Malay (Aklan) and Iloilo-San Jose (Antique) from the Iloilo City via rail was included in the revival of the currently defunct Panay Railways network which has a station in Santa Barbara town proper.
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, with a total land area of and a total population of 4,542,926, as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City of Iloilo
Iloilo City, officially the City of Iloilo ( hil, Siyudad/Dakbanwa sang Iloilo; fil, Lungsod ng Iloilo), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Western Visayas region of the Philippines on the island of Panay. It is the capital city of t ...
is its largest settlement with a total population of 457,626 inhabitants, as of 2020 census.
Panay is a triangular island, located in the western part of the Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Bisayan languages, Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three Island groups of the Philippines, principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao ...
. It is about across. It is divided into four provinces: Aklan, Antique
An antique ( la, antiquus; 'old', 'ancient') is an item perceived as having value because of its aesthetic or historical significance, and often defined as at least 100 years old (or some other limit), although the term is often used loosely ...
, Capiz, and Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the ...
, all in the Western Visayas
Western Visayas ( hil, Kabisay-an Nakatundan; tl, Kanlurang Kabisayaan or ''Kanlurang Visayas'') is an administrative region in the Philippines, numerically designated as Region VI. It consists of six provinces (Aklan, Antique, Capiz, Guimara ...
Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
. Just off the mid-southeastern coast lies the island-province of Guimaras. It is located southeast of the island of Mindoro
Mindoro is the seventh largest and eighth-most populous island in the Philippines. With a total land area of 10,571 km2 ( 4,082 sq.mi ) and has a population of 1,408,454 as of 2020 census. It is located off the southwestern coast of Luz ...
and northwest of Negros
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of . Negros is one of the many islands of the Visayas, in the central part of the country. The predominant inhabitants of the island region a ...
across the Guimaras Strait. To the north and northeast is the Sibuyan Sea, Jintotolo Channel
The Jintotolo Channel (or Jintotolo Strait) is the body of water that connects the Sibuyan Sea with the Visayan Sea. It is located between the Philippines, Philippine islands of Panay Island, Panay and Masbate Island, Masbate, and is an important s ...
and the island-provinces of Romblon and Masbate; to the west and southwest is the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
and the Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in ...
archipelago and to the south is Panay Gulf. Panay is the only main island in the Visayas whose provinces don't bear the name of their island.
Panay is bisected by the Central Panay Mountain Range
Central Panay Mountain Range is the longest and largest mountain range in the island of Panay and Western Visayas in the Philippines. With a total length of long north–south and width east–west. Mount Madja-as is the highest point with a ...
, its longest mountain chain. The island has many rivers, the longest being the Panay River
The Panay River (known as Pan-ay River) is the longest river on Panay Island in the Philippines, with a total length of approximately and a drainage basin area of . It drains almost the entire province of Capiz and northern portion of Iloilo prov ...
at a length of , followed by the Jalaur, Aklan, Sibalom
Sibalom, officially the Municipality of Sibalom, ( krj, Banwa kang Sibalom; hil, Banwa sang Sibalom; tl, Bayan ng Sibalom), is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population ...
, Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the ...
and Bugang
''Bugang'' is a Daoist ritual dance or walk, based upon the ''Yubu'' "Steps of Yu" tradition, in which a Taoist priest paces through a supernatural pattern, such as stars in the Big Dipper or numbers in the Loshu magic square. Texts from the (4 ...
rivers. Standing at about , the dormant Mount Madja-as
Mount Madja-as
is a large dormant volcano, is the highest peak in the island of Panay in the Philippines and second highest mountain in Visayas, after Mount Kanlaon in Negros. With an elevation of 6,946 feet (2,117 meters) above sea level, maki ...
(situated in Culasi, Antique
Culasi, officially the Municipality of Culasi ( krj, Banwa kang Culasi; hil, Banwa sang Culasi; tl, Bayan ng Culasi), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 44, ...
) is the highest point of the island, with Mount Nangtud
Mount Nangtud is the second highest peak on the island of Panay, in the Philippines and third highest mountain in the Visayas, after Mount Kanlaon and Mount Madja-as. With an elevation of above sea level, it is located in Jamindan, Capiz sharin ...
(located between Barbaza, Antique
Barbaza, officially the Municipality of Barbaza ( krj, Banwa kang Barbaza; hil, Banwa sang Barbaza; tl, Bayan ng Barbaza), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of ...
and Jamindan, Capiz
Jamindan, officially the Municipality of Jamindan ( Capiznon/ Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Jamindan''; Aklanon: ''Banwa it Jamindan''; krj, Banwa kang Jamindan; tl, Bayan ng Jamindan), is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Capiz, Philippi ...
) following next at .
Historically, the terms ''Bisaya'' or Visayan were first used to refer only to the people of this island, the Panayan or Hiligaynon people, and to their other settlements on the nearby islands, in the western portion of Negros Island and the smaller islands of Romblon and Guimaras. Panay also originally represented the entire Visayas region on the Philippine flag
The national flag of the Philippines ( tgl, Pambansang watawat ng Pilipinas; ilo, Nailian a bandera ti Filipinas; ceb, Nasudnong bandila ng Pilipinas; es, Bandera Nacional de Filipinas) is a horizontal List of flags by design#Bicolour, bicol ...
as one of the three stars, as it served as the center or mainland of the Visayas during the Philippine Revolution.
The island lent its name to several United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
vessels including , sunk in 1937 by the Japanese in the USS ''Panay'' incident.
History
Etymology
Before the 13th century, Panay was called ''Simsiman''. The community is located at the shores of the Ulian River and was linked by a creek. The creek provided salt to theAti people
The Ati are a Negrito ethnic group in the Visayas, the central portion of the Philippine archipelago. Their small numbers are principally concentrated in the islands of Boracay, Panay and Negros. They are genetically related to other Negrito et ...
as well as animals which lick the salt out of the salty water. Coming from the root word "''simsim''", "''simsimin''" means "''to lick something to eat or to drink''", thus the place was called ''Simsiman''.
The native Ati called the island ''Aninipay'' from words "''ani''" to harvest and "''nipay''", a hairy grass abundant in the whole Panay.
Precolonial era
No pre-Hispanic written accounts of Iloilo and Panay island exist today. Oral traditions, in the form of recited epics like the '' Hinilawod'', have survived to a small degree. A few recordings of these epic poems exist. The most notable are the works of noted Filipino anthropologistFelipe Jocano
Felipe Landa Jocano (February 5, 1930 – October 27, 2013) was a Filipino anthropologist, educator, and author known for his significant body of work within the field of Philippine Anthropology, and in particular for documenting and translatin ...
.
While no current archaeological evidence exists describing pre-Hispanic Panay, an original work by Pedro Alcantara Monteclaro published in 1907 called Maragtas
The ''Maragtas'' is a work by Pedro Alcantara Monteclaro titled (in English translation) ''History of Panay from the first inhabitants and the Bornean immigrants, from which they descended, to the arrival of the Spaniards''. The work is in mixed ...
details the alleged accounts of the founding of the various pre-Hispanic polities on Panay Island. The book is based on oral and written accounts available to the author at the time. The author made no claim for the historical accuracy of the accounts. Noted anthropologist and historian William Henry Scott initially concluded in his dissertation that it was a myth, but in a revised version admitted its credibility is debatable and concluded it was most likely based on real folk legends.
 According to Maragtas, the
According to Maragtas, the Confederation of Madja-as
The Confederation of Madya-as was a legendary pre-colonial supra-baranganic polity on the island of Panay in the Philippines. It was mentioned in Pedro Monteclaro's book titled Maragtas. It was supposedly created by Datu Sumakwel to exerci ...
was founded after ten datus fled Borneo and landed on Panay Island. The book then goes on to detail their subsequent purchase of the coastal lands in which they settled from the native Ati people.
An old manuscript ''Margitas'' of uncertain date (discovered by the anthropologist H. Otley Beyer
Henry Otley Beyer (July 13, 1883 – December 31, 1966) was an American anthropologist, who spent most of his adult life in the Philippines teaching Philippine indigenous culture. A.V.H. Hartendorp called Beyer the "Dean of Philippine ethnolo ...
) gives interesting details about the laws, government, social customs, and religious beliefs of the early Visayans, who settled Panay within the first half of the thirteenth century.G. Nye Steiger, H. Otley Beyer, Conrado Benitez, ''A History of the Orient'', Oxford: 1929, Ginn and Company, p. 122. The term ''Visayan
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, ...
'' was first applied only to them and to their settlements eastward in the island of Negros, and northward in the smaller islands, which now compose the province of Romblon. In fact, even at the early part of Spanish colonialization of the Philippines, the Spaniards used the term ''Visayan'' only for these areas. While the people of Cebu, Bohol, and Leyte were for a long time known only as Pintados. The name ''Visayan'' was later extended to them because, as several of the early writers state, their languages are closely allied to the Visayan dialect of Panay.
Gabriel Ribera, captain of the Spanish royal infantry in the Philippine Islands, also distinguished Panay from the rest of the Pintados Islands. In his report (dated 20 March 1579) regarding a campaign to pacify the natives living along the rivers of Mindanao (a mission he received from Dr. Francisco de Sande, Governor and Captain-General of the Archipelago), Ribera mentioned that his aim was to make the inhabitants of that island "''vassals of King Don Felipe… as are all the natives of the island of Panay, the Pintados Islands, and those of the island of Luzon…''"
During the early part of the colonial period in the Archipelago, the Spaniards led by Miguel López de Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as '' El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spaniard who, from the age of 26, lived and built a career in Mexico (then the Viceroyalty of New Spain) and, i ...
transferred their camp from Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 167 ...
to Panay in 1569. On 5 June 1569, Guido de Lavezaris, the royal treasurer in the Archipelago, wrote to Philip II reporting about the Portuguese attack to Cebu in the preceding autumn. A letter from another official, Andres de Mirandaola (dated three days later, 8 June), also described briefly this encounter with the Portuguese. The danger of another attack led the Spaniards to remove their camp from Cebu to Panay, which they considered a safer place. Legazpi himself, in his report to the Viceroy in New Spain (dated 1 July 1569), mentioned the same reason for the relocation of Spaniards to Panay.Cf. BLAIR, Emma Helen & ROBERTSON, James Alexander, eds. (1911). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1803. Volume 03 of 55 (1493–1803). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord BOURNE. Cleveland, Ohio: Arthur H. Clark Company. . OCLC 769945704. "Explorations by early navigators, descriptions of the islands and their peoples, their history and records of the catholic missions, as related in contemporaneous books and manuscripts, showing the political, economic, commercial and religious conditions of those islands from their earliest relations with European nations to the beginning of the nineteenth century.", pp. 15–16. It was in Panay that the conquest of Luzon was planned, and later launched on 8 May 1570.
The account of early Spanish explorers
 During the early part of the Spanish colonization of the Philippines, the Spanish Augustinian Friar Gaspar de San Agustín, O.S.A. described Panay as: ''"…very similar to that of Sicily in its triangular form, as well as in it fertility and abundance of provision. It is the most populated island after Manila and Mindanao, and one of the largest (with over a hundred leagues of coastline). In terms of fertility and abundance, it is the first.'' ��''It is very beautiful, very pleasant, and full of coconut palms… Near the river Alaguer'' (''Halaur''), ''which empties into the sea two leagues from the town of Dumangas…, in the ancient times, there was a trading center and a court of the most illustrious nobility in the whole island."'' Padre Francisco Colin (1592–1660), an early Jesuit missionary and Provincial of his Order in the Philippines also records in the chronicles of the Society of Jesus (published later in 1663 as ''Labor euangelica'') that Panay is the island which is most abundant and fertile.
The first Spanish settlement in Panay island and the second oldest Spanish settlement in the Philippines was established by the
During the early part of the Spanish colonization of the Philippines, the Spanish Augustinian Friar Gaspar de San Agustín, O.S.A. described Panay as: ''"…very similar to that of Sicily in its triangular form, as well as in it fertility and abundance of provision. It is the most populated island after Manila and Mindanao, and one of the largest (with over a hundred leagues of coastline). In terms of fertility and abundance, it is the first.'' ��''It is very beautiful, very pleasant, and full of coconut palms… Near the river Alaguer'' (''Halaur''), ''which empties into the sea two leagues from the town of Dumangas…, in the ancient times, there was a trading center and a court of the most illustrious nobility in the whole island."'' Padre Francisco Colin (1592–1660), an early Jesuit missionary and Provincial of his Order in the Philippines also records in the chronicles of the Society of Jesus (published later in 1663 as ''Labor euangelica'') that Panay is the island which is most abundant and fertile.
The first Spanish settlement in Panay island and the second oldest Spanish settlement in the Philippines was established by the Miguel López de Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as '' El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spaniard who, from the age of 26, lived and built a career in Mexico (then the Viceroyalty of New Spain) and, i ...
expedition in Panay, Capiz
Panay, officially the Municipality of Panay ( Capiznon/ Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Panay''; tl, Bayan ng Panay), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Capiz, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 48,890 people. ...
at the banks of the Panay River
The Panay River (known as Pan-ay River) is the longest river on Panay Island in the Philippines, with a total length of approximately and a drainage basin area of . It drains almost the entire province of Capiz and northern portion of Iloilo prov ...
in northern Panay, the name of which was extended to the whole Panay island. López de Legazpi transferred the capital there from Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 167 ...
since it had abundant provisions and was better protected from Portuguese attacks before the capital was once again transferred to Manila.
Miguel de Luarca, who was among the first Spanish settlers in the Island, made one of the earliest account about Panay and its people according to a Westerner's point of view. In June 1582, while he was in Arévalo (Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the ...
), he wrote in his ''Relación de las Yslas Filipinas'' the following observations:
 The island is the most fertile and well-provisioned of all the islands discovered, except the island of
The island is the most fertile and well-provisioned of all the islands discovered, except the island of Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
: for it is exceedingly fertile, and abounds in rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, swine, fowls, wax
Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low ...
, and honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
; it produces also a great quantity of cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
and abacá fiber.Miguel de Loarca, ''Relacion de las Yslas Filipinas'' (Arevalo: June 1582) in BLAIR, Emma Helen & ROBERTSON, James Alexander, eds. (1903). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1803. Volume 05 of 55 (1582–1583). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord BOURNE. Cleveland, Ohio: Arthur H. Clark Company. . OCLC 769945704. "Explorations by early navigators, descriptions of the islands and their peoples, their history and records of the catholic missions, as related in contemporaneous books and manuscripts, showing the political, economic, commercial and religious conditions of those islands from their earliest relations with European nations to the beginning of the nineteenth century.", p. 67.
''"The villages are very close together, and the people are peaceful and open to conversion. The land is healthful and well-provisioned, so that the Spaniards who are stricken in other islands go thither to recover their health."''
''"The natives are healthy and clean, and although the island of Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 167 ...
is also healthful and had a good climate, most of its inhabitants are always afflicted with the itch and buboes. In the island of Panay, the natives declare that no one of them had ever been afflicted with buboes until the people from Bohol
Bohol (), officially the Province of Bohol ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bohol; tl, Lalawigan ng Bohol), is an island province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas Regions of the Philippines, region, consisting of the island itself and 75 m ...
– who, as we said above, abandoned Bohol on account of the people of Maluco – came to settle in Panay, and gave the disease to some of the natives. For these reasons the governor, Don Gonzalo Ronquillo, founded the town of Arévalo, on the south side of this island; for the island runs north and south, and on that side live the majority of the people, and the villages are near this town, and the land here is more fertile."'' This probably explains why there are reference of presence of Pintados
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, ...
in the Island.
''"The island of Panay provides the city of Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
and other places with a large quantity of rice and meat…"''... ''"As the island contains great abundance of timber and provisions, it has almost continuously had a shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance a ...
on it, as is the case of the town of Arévalo, for galley
A galley is a type of ship that is propelled mainly by oars. The galley is characterized by its long, slender hull, shallow draft, and low freeboard (clearance between sea and gunwale). Virtually all types of galleys had sails that could be used ...
s and fragatas. Here the ship 'Visaya' was launched."''
Another Spanish chronicler in the early Spanish period, Dr. Antonio de Morga (Year 1609) is also responsible for recording other Visayan customs. Customs such as Visayans' affinity for singing among their warrior-castes as well as the playing of gongs and bells in naval battles.
''Their customary method of trading was by bartering one thing for another, such as food, cloth, cattle, fowls, lands, houses, fields, slaves, fishing-grounds, and palm-trees (both nipa and wild). Sometimes a price intervened, which was paid in gold, as agreed upon, or in metal bells brought from China. These bells they regard as precious jewels; they resemble large pans and are very sonorous. They play upon these at their feasts, and carry them to the war in their boats instead of drums and other instruments.''
''The early Dutch fleet commander Cornelis Matelieff de Jonge called at Panay in 1607. He mentions a town named "Oton" on the island where there were "18 Spanish soldiers with a number of other Spanish inhabitants so that there may be 40 whites in all". He explained that "a lot of rice and meat is produced there, with which they .e. the Spanishsupply Manila."''
According to Stephanie J. Mawson, using recruitment records found in Mexico, in addition to the 40 Caucasian Spaniards who then lived in Oton, there were an additional set of 66 Mexican soldiers of Mulatto, Mestizo or Native American descent sentried there during the year 1603. However, the Dutch visitor, Cornelis Matelieff de Jongedid, did not count them in since they were not pure whites like him.
Iloilo City in Panay was awarded by the Queen of Spain the title: "'' La Muy Leal y Noble Ciudad de Iloilo''" (The Most Loyal and Noble City) for being the most loyal and noble city in the Spanish Empire since it clung on to Spain amidst the Philippine revolution the last nation to revolt against Spain in the Spanish Empire.
Colonial rule (1565–1898)
 In 1572, the island was organized into two provinces: jurisdictions of
In 1572, the island was organized into two provinces: jurisdictions of Panay
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of and has a total population of 4,542,926 as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City o ...
(Capiz and Aklan) and Oton
Oton, officially the Municipality of Oton (; krj, Banwa kang Oton, hil, Banwa sang Oton, tgl, Bayan ng Oton), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Iloilo, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 98,509 p ...
(Iloilo and Antique).
In 1693, the town of Capiz, known as El Puerto de Capiz was finally created.
In 1716, Capiz was organized into a separate politico-military province with the transfer of the capital from the town of Panay, Under its jurisdiction were the neighboring islands of Campo, Romblon, Tablas, and Sibuyan.
In 1796, Panay island was divided into three provinces: Iloilo, Antique, and Capiz (which included Aklan and Romblon).
In 1853, The island now comprising Romblon province and Maestre de Campo was organized into separate politico-military “comandancia” administered from Capiz.
In 1898, The Spanish educated Panay Island and were replaced by the revolutionary forces, who were in turn overthrown by the American the following year.
Aklan (Akean) became an independent province through '' Republic Act No. 1414'' signed by Philippine President Ramon Magsaysay on April 25, 1956, separating Aklan from Capiz. The original towns were Altavas
Altavas, officially the Municipality of Altavas (Aklanon language, Aklanon: ''Banwa it Altavas''; Hiligaynon language, Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Altavas''; tl, Bayan ng Altavas), is a 4th class municipality of the Philippines, municipality in the ...
, Balete, Batan, Banga
Banga may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Banga'' (album), a 2012 album by Patti Smith
* A song by Ali Shaheed Muhammad from the 2004 album '' Shaheedullah and Stereotypes''
* The name of Pontius Pilate's dog in Mikhail Bulgakov's novel ' ...
, Buruanga, Ibajay, Kalibo, Lezo, Libacao
Libacao, officially the Municipality of Libacao ( Aklanon: ''Banwa it Libacao''; Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Libacao''; tl, Bayan ng Libacao), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a ...
, Madalag
Madalag, officially the Municipality of Madalag ( Aklanon: ''Banwa it Madalag''; Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Madalag''; tl, Bayan ng Madalag), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. It is Aklan's largest municipality b ...
, Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, Makato
Makato, officially the Municipality of Makato ( Aklanon: ''Banwa it Makato''; Hiligaynon: ''Banwa sang Makato''; tl, Bayan ng Makato), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a pop ...
, Malinao, Nabas, New Washington, Numancia, and Tangalan, then all part of the province of Capiz. The province was inaugurated on November 8, 1956. Jose Raz Menez was appointed the first governor of Aklan by President Magsaysay and he served until December 30, 1959. In 1960, Godofredo P. Ramos became the first elected governor but upon resigning to run for Congress he was succeeded by the vice governor, Virgilio S. Patricio. In 1964, José B. Legaspi succeeded Patricio and he held office for two consecutive terms from 1964 to 1971.
World War II
 On April 16, 1942,
On April 16, 1942, Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
forces landed at San Jose de Buenavista, Capiz City (now the city of Roxas), and Iloilo City during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
in order to secure Panay and the rest of Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Bisayan languages, Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three Island groups of the Philippines, principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao ...
. Guerrilla forces under Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Macario Peralta Jr.
Macario Peralta Jr. (July 30, 1913 – January 7, 1975) was a Filipino soldier, lawyer, senator and Secretary of National Defense.
Early life
Born in Manila on July 30, 1913 of Ilocano-Pangasinan descent, Peralta grew up in Tarlac. He finished ...
later liberated most of the island and eventually captured the city of Capiz on December 20, 1944. Peralta's forces therefore achieved the liberation from Japanese occupation of all of Capiz Province before Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
forces landed at Iloilo City on March 18, 1945, and mopped up the remaining Japanese forces in the island.
Geography
 Panay island is the sixth largest island in the Philippines by area, with a total land area of .
Panay island is the sixth largest island in the Philippines by area, with a total land area of . Mount Madja-as
Mount Madja-as
is a large dormant volcano, is the highest peak in the island of Panay in the Philippines and second highest mountain in Visayas, after Mount Kanlaon in Negros. With an elevation of 6,946 feet (2,117 meters) above sea level, maki ...
is the highest point in Panay with an elevation of above sea level, located in town of Culasi
Culasi, officially the Municipality of Culasi ( krj, Banwa kang Culasi; hil, Banwa sang Culasi; tl, Bayan ng Culasi), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 44, ...
in the northern province of Antique. Central Panay Mountain Range
Central Panay Mountain Range is the longest and largest mountain range in the island of Panay and Western Visayas in the Philippines. With a total length of long north–south and width east–west. Mount Madja-as is the highest point with a ...
is the longest and largest mountain range in the island with a total length of north-south. Panay River
The Panay River (known as Pan-ay River) is the longest river on Panay Island in the Philippines, with a total length of approximately and a drainage basin area of . It drains almost the entire province of Capiz and northern portion of Iloilo prov ...
is the longest river in the island with a total length of located in the province of Capiz.
Boracay Island
Boracay (; often locally shortened to Bora) is a resort island in the Western Visayas region of the Philippines, located off the northwest coast of Panay. It has a total land area of , under the jurisdiction of three barangays in Malay, Aklan ...
, a popular tourist destination known for its long white sand shore, is located off the northwest tip of Panay Island. It is part of Aklan province under the jurisdiction of the municipality of Malay.
Topography
The highest mountain isMount Madja-as
Mount Madja-as
is a large dormant volcano, is the highest peak in the island of Panay in the Philippines and second highest mountain in Visayas, after Mount Kanlaon in Negros. With an elevation of 6,946 feet (2,117 meters) above sea level, maki ...
, at .
Rivers
Major rivers in Panay include: *Jalaur River
The Jalaur River, also known as Jalaud River, is the second longest river on Panay island in the Philippines, with a total length of and the second largest by drainage basin after Panay River in Capiz. The Jalaur has a drainage area of . Its sou ...
* Iloilo River
The Iloilo River is an estuary river located in the province of Iloilo, in Western Visayas, Philippines. The river starts in Oton, Iloilo, Oton at the Batiano estuary, then traverses through the Iloilo City districts of Lapuz, Iloilo City, Lapuz, ...
* Batiano River
* Aklan River
The Aklan River is the longest river in the province of Aklan, Philippines, and third-longest river on Panay island (after the Panay River in Capiz and Jalaur River in Iloilo). Its drainage basin is the third largest in Panay. The river source is ...
* Sibalom River
The Sibalom River is the longest river in the province of Antique in Panay island Philippines. With a total length of and a drainage basin covering , it is the largest river system in Antique and fourth longest in Panay after the Panay River, J ...
* Tipulu-an River
The Tipulu-an River is a tributary of the Sibalom River located in Antique
An antique ( la, antiquus; 'old', 'ancient') is an item perceived as having value because of its aesthetic or historical significance, and often defined as at least ...
* Mao-it River
The Mao-it River is a tributary of the Sibalom River located in Antique province in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, ...
* Bugang River
The Bugang River is a river situated in the northwest of Panay island in the Philippines. It is located in municipality of Pandan, Antique which is noted for its distinction as the "Cleanest Inland Body of Water" in the country.
Topography
The Bu ...
Demographics
Panay is the mostethnically
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
and linguistically
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
diverse major island in the Visayas, being native to four non-indigenous ethnolinguistic groups ( Hiligaynon/Ilonggo, Karay-a, Capiznon
Capiznon or Capiceño () is an Austronesian regional language spoken in Western Visayas in the Philippines. Capiznon is concentrated in the province of Capiz in the northeast of Panay Island. It is a member of the Bisayan language family and th ...
, Aklanon), and two indigenous groups
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
(Suludnon
The Suludnon, also known as the Panay-Bukidnon, Pan-ayanon, or Tumandok, are a culturally indigenous Visayan group of people who reside in the Capiz-Lambunao mountainous area and the Antique-Iloilo mountain area of Panay in the Visayan islands o ...
, Ati
Ati or ATI may refer to:
* Ati people, a Negrito ethnic group in the Philippines
**Ati language (Philippines), the language spoken by this people group
** Ati-Atihan festival, an annual celebration held in the Philippines
*Ati language (China), a ...
) or minorities. However, the ethnic and linguistic boundaries within the island do not correspond to its administrative
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal
** Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an administrative officer, administ ...
divisions. Only the province of Antique
An antique ( la, antiquus; 'old', 'ancient') is an item perceived as having value because of its aesthetic or historical significance, and often defined as at least 100 years old (or some other limit), although the term is often used loosely ...
is monolingual, which only speaks Kinaray-a as its primary language. The ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' of the island is Hiligaynon, native to Iloilo City
Iloilo City, officially the City of Iloilo ( hil, Siyudad/Dakbanwa sang Iloilo; fil, Lungsod ng Iloilo), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Western Visayas region of the Philippines on the island of Panay. It is the capital city of t ...
and the northeastern coastal strip lining the province of Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the ...
. For local administrative, educational, and commercial purposes, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Tagalog are also widely used.
Economy
 Panay Island's economy thrives due to the combined strengths and contributions of its four provinces. The diversity of industries, including agriculture, fishing, tourism, manufacturing, and natural resource utilization, sustains the island's robust economic growth and development. As a result, Panay Island has emerged as the fifth economic giant in the Philippines.
Iloilo, including Iloilo City, which serves as the economic center, plays a pivotal role in driving the island's economy. The province is a hub for various industries, including real estate, accommodation, medical centers, education, shopping centers, business centers, IT/BPO centers, and more. Its vibrant and multifaceted economy has positioned Iloilo as one of the most competitive provinces in the country.
Aklan, known for Boracay Island, serves as the tourism center of Panay Island. The world-famous tourist destination attracts a significant number of visitors, contributing to the province's tourism industry. Aklan's economy benefits from the influx of tourists and the diverse range of activities and services catering to their needs.
Capiz, dubbed the "Seafood Capital of the Philippines," takes advantage of its coastal areas and swampy lands, supporting a thriving fishing industry. The province's aquamarine resources, including prawns, milkfish, marlin, squid, oysters, shrimp, and seaweed, contribute significantly to its economic growth.
Antique's economy relies on fishing, with a rich fishing ground along its coastline. Additionally, the province's forest resources, such as bamboo, buri, bariw, nito, logs, and charcoal, contribute to the construction industry, furniture-making, and handicrafts. The natural beauty of Antique, including the presence of the rafflesia flower and protected forestland, further enhances its tourism potential.
Panay Island's economy thrives due to the combined strengths and contributions of its four provinces. The diversity of industries, including agriculture, fishing, tourism, manufacturing, and natural resource utilization, sustains the island's robust economic growth and development. As a result, Panay Island has emerged as the fifth economic giant in the Philippines.
Iloilo, including Iloilo City, which serves as the economic center, plays a pivotal role in driving the island's economy. The province is a hub for various industries, including real estate, accommodation, medical centers, education, shopping centers, business centers, IT/BPO centers, and more. Its vibrant and multifaceted economy has positioned Iloilo as one of the most competitive provinces in the country.
Aklan, known for Boracay Island, serves as the tourism center of Panay Island. The world-famous tourist destination attracts a significant number of visitors, contributing to the province's tourism industry. Aklan's economy benefits from the influx of tourists and the diverse range of activities and services catering to their needs.
Capiz, dubbed the "Seafood Capital of the Philippines," takes advantage of its coastal areas and swampy lands, supporting a thriving fishing industry. The province's aquamarine resources, including prawns, milkfish, marlin, squid, oysters, shrimp, and seaweed, contribute significantly to its economic growth.
Antique's economy relies on fishing, with a rich fishing ground along its coastline. Additionally, the province's forest resources, such as bamboo, buri, bariw, nito, logs, and charcoal, contribute to the construction industry, furniture-making, and handicrafts. The natural beauty of Antique, including the presence of the rafflesia flower and protected forestland, further enhances its tourism potential.
Administrative divisions
The island is covered by 4 provinces, 1highly urbanized city
A city ( fil, lungsod/siyudad) is one of the units of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities ( fil, nakakartang lungsod), whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own ...
, 2 component cities, 92 municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
(93 municipalities if the associated islands of Caluya are included), and 3,291 barangay
A barangay (; abbreviated as Brgy. or Bgy.), historically referred to as barrio (abbreviated as Bo.), is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district, or ward. In metropolitan ...
s, all under the jurisdiction of the Western Visayas
Western Visayas ( hil, Kabisay-an Nakatundan; tl, Kanlurang Kabisayaan or ''Kanlurang Visayas'') is an administrative region in the Philippines, numerically designated as Region VI. It consists of six provinces (Aklan, Antique, Capiz, Guimara ...
region.
Transportation
Road
 All the provinces in Panay are interconnected by major inter-provincial roads. Iloilo City is served mostly by passenger jeepneys, white metered taxis and tricycles within the city limits. The primary transportation vehicle used within Roxas City, Kalibo, San Jose de Buenavista and other cities and municipalities in Panay is the tricycle. Travel between cities and municipalities is typically by jeepney, vans and Ceres operated buses. In March 2019, the Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board announced the opening of a new
All the provinces in Panay are interconnected by major inter-provincial roads. Iloilo City is served mostly by passenger jeepneys, white metered taxis and tricycles within the city limits. The primary transportation vehicle used within Roxas City, Kalibo, San Jose de Buenavista and other cities and municipalities in Panay is the tricycle. Travel between cities and municipalities is typically by jeepney, vans and Ceres operated buses. In March 2019, the Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board announced the opening of a new Premium Point-to-Point Bus Service
The Premium Point-to-Point (P2P) Bus Service, formerly known as ''Express Connect'', is an express bus service in the Philippines administered by the Department of Transportation and operated by private bus companies in partnership with the Land ...
in Iloilo City with express bus services to the airports in Cabatuan, Kalibo and Boracay (Caticlan).
Iloilo is one of the few cities in the Philippines that recently initiated to adopt the mini-bus-like type modern PUJ or modern Jeepneys in contrast to the President Rodrigo Duterte's administration to phase out the old dilapidated jeepneys as the mode of mass public transportation in the Philippines.
The Iloilo-Capiz-Aklan Expressway (ICAEx) is also being proposed, which might reduce travel time between provinces in Panay. It will connect Iloilo City and Malay, Aklan through Passi City, Roxas City and Kalibo, Aklan.
Airports
Panay Island is now served by five airports. TheIloilo International Airport
Iloilo International Airport ( hil, Pangkalibutan nga Hulugpaan sang Iloilo, fil, Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Iloilo; ), also known as Iloilo Airport, and as Cabatuan Airport, after the municipality of Cabatuan, Iloilo where it is located, is the ...
, located in Cabatuan, Iloilo
Cabatuan, officially the Municipality of Cabatuan ( hil, Banwa sang Cabatuan, tgl, Bayan ng Cabatuan), is a 2nd class municipality of the Philippines, municipality in the Philippine Province, province of Iloilo, Philippines. According to the 20 ...
, serves the general area of Iloilo-Guimaras Metropolitan as well the whole province of Iloilo, and is also considered to be the primary gateway into the region. The Kalibo International Airport
Kalibo International Airport ( Aklanon: ''Paeoparang Pangkalibutan it Kalibo'', hil, Pangkalibutan nga Hulugpaan sang Kalibo, fil, Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Kalibo; ) is an international airport that serves the general area of Kalibo, the capita ...
is one of the two airports serving Boracay, the other being Godofredo P. Ramos Airport
Godofredo P. Ramos Airport ( Aklanon: ''Paeoparan it Godofredo P. Ramos'', Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Godofredo P. Ramos'', fil, Paliparang Godofredo P. Ramos) , also known as Caticlan Airport and recently, Boracay Airport by its developer ...
(also known as Caticlan Airport) in the municipality of Malay. The Roxas Airport
Roxas Airport ( Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Roxas'', Tagalog: ''Paliparan ng Roxas'') is a domestic airport serving the general area of Roxas City and the province of Capiz, in the Philippines. The airport is currently classified as a Class 1 ...
is a domestic airport serving the general area of Roxas City and the province of Capiz. The Evelio Javier Airport
Evelio B. Javier Airport (Kinaray-a: ''Hurugpaan kang Evelio B. Javier'', Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Evelio B. Javier'', Filipino: ''Paliparang Evelio B. Javier'') , also known as San Jose Airport, and officially as Antique Airport is the only ...
(Antique Airport) is the only airport serving the province of Antique located in San Jose. The other, Semirara Airport in Caluya is a municipal airport.
International
*Iloilo International Airport
Iloilo International Airport ( hil, Pangkalibutan nga Hulugpaan sang Iloilo, fil, Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Iloilo; ), also known as Iloilo Airport, and as Cabatuan Airport, after the municipality of Cabatuan, Iloilo where it is located, is the ...
* Kalibo International Airport
Kalibo International Airport ( Aklanon: ''Paeoparang Pangkalibutan it Kalibo'', hil, Pangkalibutan nga Hulugpaan sang Kalibo, fil, Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Kalibo; ) is an international airport that serves the general area of Kalibo, the capita ...
Domestic
*Godofredo P. Ramos Airport
Godofredo P. Ramos Airport ( Aklanon: ''Paeoparan it Godofredo P. Ramos'', Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Godofredo P. Ramos'', fil, Paliparang Godofredo P. Ramos) , also known as Caticlan Airport and recently, Boracay Airport by its developer ...
(Caticlan Airport)
* Roxas Airport
Roxas Airport ( Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Roxas'', Tagalog: ''Paliparan ng Roxas'') is a domestic airport serving the general area of Roxas City and the province of Capiz, in the Philippines. The airport is currently classified as a Class 1 ...
* Evelio Javier Airport
Evelio B. Javier Airport (Kinaray-a: ''Hurugpaan kang Evelio B. Javier'', Hiligaynon: ''Hulugpaan sang Evelio B. Javier'', Filipino: ''Paliparang Evelio B. Javier'') , also known as San Jose Airport, and officially as Antique Airport is the only ...
(Antique Airport)
Rail
 Proposals to re-connect again Iloilo-Roxas, Iloilo-Kalibo, Iloilo-Malay (Aklan) and Iloilo-San Jose (Antique) from the Iloilo City via rail was included in the revival of the currently defunct Panay Railways network which has a station in Santa Barbara town proper.
Proposals to re-connect again Iloilo-Roxas, Iloilo-Kalibo, Iloilo-Malay (Aklan) and Iloilo-San Jose (Antique) from the Iloilo City via rail was included in the revival of the currently defunct Panay Railways network which has a station in Santa Barbara town proper.
See also
*Macario Peralta, Jr.
Macario Peralta Jr. (July 30, 1913 – January 7, 1975) was a Filipino soldier, lawyer, senator and Secretary of National Defense.
Early life
Born in Manila on July 30, 1913 of Ilocano- Pangasinan descent, Peralta grew up in Tarlac. He finished ...
* Panay Railways
* Church of Panay
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Landforms of the Sulu Sea Islands of Aklan Islands of Antique (province) Islands of Capiz Islands of Iloilo