Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American
airline
An airline is a company that provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for codeshare agreements, in which ...
that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas
flag carrier of the United States for much of the 20th century. It was the first airline to fly worldwide and pioneered numerous innovations of the modern airline industry such as
jumbo jets, and
computerized reservation systems.
Until its dissolution in 1991, Pan Am "epitomized the luxury and glamour of intercontinental travel",
and it remains a cultural icon of the 20th century, identified by its blue globe logo ("The Blue Meatball"), the use of the word "
Clipper" in its aircraft names and
call signs, and the white uniform caps of its pilots.
Founded in 1927 by two former
U.S. Army Air Corps majors, Pan Am began as a scheduled airmail and passenger service flying between
Key West, Florida, and
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. , Cuba. Under the leadership of American entrepreneur
Juan Trippe
Juan Terry Trippe (June 27, 1899 – April 3, 1981) was an American commercial aviation pioneer, entrepreneur and the founder of Pan American World Airways, one of the iconic airlines of the 20th century. He was involved in the introduction of t ...
, in the 1930s the airline purchased a fleet of
flying boats
A flying boat is a type of fixed-winged aircraft, fixed-winged seaplane with a hull (watercraft), hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in that a flying boat's fuselage is purpose-designed for floatation and contains a ...
and focused its route network on Central and South America, gradually adding
transatlantic
Transatlantic, Trans-Atlantic or TransAtlantic may refer to:
Film
* Transatlantic Pictures, a film production company from 1948 to 1950
* Transatlantic Enterprises, an American production company in the late 1970s
* ''Transatlantic'' (1931 film ...
and
transpacific destinations.
By the mid-20th century, Pan Am enjoyed a near monopoly on international routes.
It led the aircraft industry into the
Jet Age
The Jet Age is a period in the history of aviation defined by the advent of aircraft powered by jet turbine engines, and by the social change this brought about.
Jet airliners were able to fly much higher, faster, and farther than older pis ...
by acquiring new jetliners such as the
Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first flew on December ...
and
Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, ...
. Pan Am's modern fleet allowed it to fly larger numbers of passengers, at a longer range, and with fewer stops than rivals. Its primary hub and flagship terminal was the
Worldport at
John F. Kennedy International Airport in
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
.
During its peak between the late 1950s and early 1970s, Pan Am was world-renowned for its advanced fleet, highly trained staff, and amenities. In 1970, it flew 11 million passengers to 86 countries, with destinations in every continent save Antarctica. In an era dominated by
flag carriers that were wholly or majority-owned by governments, it became the unofficial national carrier of the United States. Pan Am was a founding member of the
International Air Transport Association
The International Air Transport Association (IATA ) is a trade association of the world's airlines founded in 1945. IATA has been described as a cartel since, in addition to setting technical standards for airlines, IATA also organized tar ...
(IATA), the global airline industry association.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, Pan Am began facing a series of challenges both internal and external, along with rising competition from the deregulation of the airline industry in 1978. After several attempts at financial restructuring and rebranding throughout the 1980s, Pan Am gradually sold off its assets before declaring bankruptcy in 1991. By the time it ceased operations, the airline's trademark was the second most recognized worldwide, and its loss was felt among travelers and many Americans as signifying the end of the golden age of air travel. Its brand, iconography, and contributions to the industry remain well known in the 21st century. The airline's name and imagery were purchased in 1998 by railroad holding company Guilford Transportation Industries, which changed its name to
Pan Am Systems and adopted Pan Am's logo.
History
Formation

Pan American Airways, Incorporated (PAA) was founded as a
shell company on March 14, 1927, by
United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical ri ...
officers
Henry "Hap" Arnold,
Carl Spaatz and John Jouett out of concern for the growing influence of the German-owned
Colombian air carrier
SCADTA, in
Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. Operating in Colombia since 1920, SCADTA lobbied hard for landing rights in the
Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone ( es, Zona del Canal de Panamá), also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the terr ...
, ostensibly to survey air routes for a connection to the United States, which the Air Corps viewed as a precursor to a possible German aerial threat to the canal. In the spring of 1927, the
United States Post Office
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
requested bids on a contract to deliver mail from
Key West, Florida to
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. , Cuba before 19 October 1927. Arnold and Spaatz drew up the
prospectus for Pan American after they learned that SCADTA hired a company in
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
to obtain air mail contracts from the
US government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
.
Also competing for the contract,
Juan Trippe
Juan Terry Trippe (June 27, 1899 – April 3, 1981) was an American commercial aviation pioneer, entrepreneur and the founder of Pan American World Airways, one of the iconic airlines of the 20th century. He was involved in the introduction of t ...
formed the Aviation Corporation of the Americas (ACA) on June 2, 1927, with $250,000 in startup capital and the backing of powerful and politically connected financiers including
Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney and
W. Averell Harriman
William Averell Harriman (November 15, 1891July 26, 1986), better known as Averell Harriman, was an American Democratic politician, businessman, and diplomat. The son of railroad baron E. H. Harriman, he served as Secretary of Commerce un ...
. Their operation had the all-important landing rights for
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. , having acquired American International Airways, a small airline established in 1926 by John K. Montgomery and Richard B. Bevier as a
seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tec ...
service from Key West to Havana. A third company, Atlantic, Gulf, and Caribbean Airways, was established on October 11, 1927, by New York City
investment bank
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing is ...
er Richard Hoyt to bid for the contract.
The Postal Service awarded Pan American Airways the
US mail
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
delivery contract to Cuba, at the end of the bidding process, but Pan American lacked any aircraft to perform the job and did not have landing rights in Cuba.
Just days before the 19 October deadline, the three companies decided to form a partnership. ACA chartered a
Fairchild FC-2 floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, ...
from a small
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
carrier, West Indian Aerial Express, allowing Pan Am to operate the first flight to Havana on 19 October 1927. The three companies formally merged on June 23, 1928. Richard Hoyt was named as president of the new Aviation Corporation of the Americas, but Trippe and his partners held 40% of the
equity and Whitney was made president. Trippe became operational head of Pan American Airways, the new company's principal operating subsidiary.
The US government approved the original Pan Am's mail delivery contract with little objection, out of fears that SCADTA would have no competition in bidding for routes between Latin America and the United States. The government further helped Pan Am by insulating it from its US competitors, seeing the airline as the "chosen instrument" for US-based international air routes. The airline expanded internationally, benefiting from a virtual monopoly on foreign routes.
Trippe and his associates planned to extend Pan Am's network through all of
Central and South America. During the late 1920s and early 1930s, Pan Am purchased a number of ailing or defunct airlines in Central and South America and negotiated with postal officials to win most of the government's
airmail contracts to the region. In September 1929 Trippe toured Latin America with
Charles Lindbergh
Charles Augustus Lindbergh (February 4, 1902 – August 26, 1974) was an American aviator, military officer, author, inventor, and activist. On May 20–21, 1927, Lindbergh made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance o ...
to negotiate landing rights in a number of countries, including
Barranquilla on SCADTA's home turf of Colombia, as well as
Maracaibo
)
, motto = "''Muy noble y leal''"(English: "Very noble and loyal")
, anthem =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_alt = ...
and
Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the ...
in
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
. By the end of the year, Pan Am offered flights along the west coast of South America to Peru. Following government favors for the denial of mail contracts to their competition, a forced merger was created with
New York, Rio, and Buenos Aires Line, giving a seaplane route along the east coast of South America to
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the Capital city, capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata ...
, Argentina, and westbound to
Santiago, Chile
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, whose ...
.
Its Brazilian subsidiary
NYRBA do Brasil was later renamed as
Panair do Brasil. Pan Am also partnered with the
Grace Shipping Company in 1929 to form
Pan American-Grace Airways
Pan American-Grace Airways, also known as Panagra, and dubbed "The World's Friendliest Airline" was an airline formed as a joint venture between Pan American World Airways and Grace Shipping Company. On September 13, 1928, a small single-engine ...
, better known as Panagra, to gain a foothold to destinations in South America.
[ In the same year, Pan Am acquired a controlling stake in ]Mexicana de Aviación
Compañía Mexicana de Aviación, S.A. de C.V. (usually shortened to Mexicana de Aviación or simply Mexicana) was Mexico's oldest airline and one of the oldest continuously single-branded airlines (after KLM, Avianca and QANTAS). It was ...
and took over Mexicana's Ford Trimotor route between Brownsville, Texas and Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
, extending this service to the Yucatan Peninsula to connect with Pan Am's Caribbean route network.holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
, the Aviation Corporation of the Americas, was one of the most sought after stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company ...
s on the New York Curb Exchange in 1929, and flurries of speculation surrounded each of its new route awards. In April 1929 Trippe and his associates reached an agreement with United Aircraft and Transport Corporation (UATC) to segregate Pan Am operations to the south of the Mexico – United States border, in exchange for UATC taking a large shareholder stake (UATC was the parent company of what are now Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
, Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military avi ...
, and United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois. ). The Aviation Corporation of the Americas changed its name to ''Pan American Airways Corporation'' in 1931.
Clipper era

 Pan Am started its South American routes with Consolidated Commodore and
Pan Am started its South American routes with Consolidated Commodore and Sikorsky S-38
The Sikorsky S-38 was an American twin-engined ten-seat sesquiplane amphibious aircraft. It was Sikorsky's first widely produced amphibious flying boat, serving successfully for Pan American Airways and the United States military.
Design an ...
flying boats. The S-40, larger than the eight-passenger S-38, began flying for Pan Am in 1931. Carrying the nicknames ''American Clipper'', ''Southern Clipper'', and ''Caribbean Clipper'', they were the first of the series of 28 ''Clipper''s that symbolized Pan Am between 1931 and 1946. During this time, Pan Am operated Clipper services to Latin America from the International Pan American Airport at Dinner Key in Miami, Florida
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at th ...
.
In 1937 Pan Am turned to Britain and France to begin seaplane service between the United States and Europe. Pan Am reached an agreement with both countries to offer service from Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 cen ...
, to Europe via Bermuda
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, ...
and the Azores
)
, motto=
( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem=( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
using the S-42s. A joint service from Port Washington, New York, to Bermuda began in June 1937, with Pan Am using Sikorskys and Imperial Airways
Imperial Airways was the early British commercial long-range airline, operating from 1924 to 1939 and principally serving the British Empire routes to Union of South Africa, South Africa, British India, India, Australia and the Far East, inclu ...
using the C class flying boat RMA ''Cavalier''.Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
from Port Washington, via Shediac, New Brunswick. The next day Pan Am ''Clipper III'' left Botwood for Foynes in County Limerick
"Remember Limerick"
, image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Limerick.svg
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Republic of Ireland, Ireland
, subdivision_type1 = Provinces of Ireland, Province
, subd ...
, Ireland. The same day, a Short Empire C-Class flying boat, the ''Caledonia'', left Foynes for Botwood, and landed July 6, 1937, reaching Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
on July 8 and New York on July 9.
Trippe decided to start a service from San Francisco to Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the islan ...
and on to Hong Kong and Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
following steamship routes. After negotiating traffic rights in 1934 to land at Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the ...
, Midway Island
Midway Atoll (colloquial: Midway Islands; haw, Kauihelani, translation=the backbone of heaven; haw, Pihemanu, translation=the loud din of birds, label=none) is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the Unit ...
, Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the Sida fallax, kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, sou ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic ce ...
, and Subic Bay
Subic Bay is a bay on the west coast of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, about northwest of Manila Bay. An extension of the South China Sea, its shores were formerly the site of a major United States Navy facility, U.S. Naval Base Sub ...
(Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
), Pan Am shipped $500,000 worth of aeronautical equipment and construction crews westward in March 1935 using the S.S. ''North Haven'', a 15,000-ton merchant ship chartered for the purpose of provisioning each island that the clippers would stop at on their 4- to 5-day flight. Pan Am ran its first survey flight to Honolulu in April 1935 with a Sikorsky S-42 flying boat. Construction crews, including Bill Mullahey
William Justin Mullahey (1909 – April 15, 1981) was an American airline executive who was a long-time employee of Pan American Airways, helping the company expand its presence across the Pacific. He also played a large role in developing tour ...
who would later oversee Pan Am's Pacific operations, cleared coral from lagoons, constructed hotels, and installed the radio navigation equipment necessary for the clippers to island hop from Hawaii to Asia. The airline won the contract for a San Francisco–Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ent ...
mail route later that year and operated its first commercial flight carrying mail and express (no passengers) in a Martin M-130 from Alameda to Manila amid media fanfare on November 22, 1935. The five-leg, flight arrived in Manila on November 29 and returned to San Francisco on December 6, cutting the time between the two cities by the fastest scheduled steamship by over two weeks. (Both the United States and Philippine Islands issued special stamps for the two flights.) The first passenger flight left Alameda on October 21, 1936.Collier Trophy
The Robert J. Collier Trophy is an annual aviation award administered by the U.S. National Aeronautic Association (NAA), presented to those who have made "the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to im ...
, on behalf of PAA from President Franklin D. Roosevelt for the company's "establishment of the transpacific airline and the successful execution of extended overwater navigation and the regular operations thereof."

 Pan Am also used Boeing 314 flying boats for the Pacific route: in China, passengers could connect to domestic flights on the Pan Am-operated China National Aviation Corporation (CNAC) network, co-owned with the
Pan Am also used Boeing 314 flying boats for the Pacific route: in China, passengers could connect to domestic flights on the Pan Am-operated China National Aviation Corporation (CNAC) network, co-owned with the Chinese government
The Government of the People's Republic of China () is an authoritarian political system in the People's Republic of China under the exclusive political leadership of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It consists of legislative, executive, mi ...
. Pan Am flew to Singapore for the first time in 1941, starting a semi-monthly service which reduced San Francisco–Singapore travel times from 25 days to six days.
Six large, long-range Boeing 314 flying boats were delivered to Pan Am in early 1939. On March 30, 1939, the ''Yankee Clipper'', piloted by Harold E. Gray
Harold E. Gray (April 15, 1906 – December 23, 1972) was an American pilot and executive for Pan American World Airways who served as CEO from 1968 to 1969.
Early life
Gray was born on April 15, 1906, in Guttenberg, Iowa. He attended the Univer ...
, made the first-ever trans-Atlantic passenger flight. The first leg of the flight, Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
to Horta
Horta may refer to:
People
* Horta (surname), a list of people
Places
* Horta, Africa, an ancient city and former bishopric in Africa Proconsularis, now in Tunisia and a Latin Catholic titular see
* Horta, Azores, Portugal, a municipality an ...
, took 17 hours and 32 minutes and covered . The second leg from Horta to Pan Am's newly built airport in Lisbon took 7 hours and 7 minutes and covered . The Boeing 314 also enabled the start of scheduled weekly contract Foreign Air Mail (F.A.M. 18) service and later passenger flights from New York (Port Washington, L.I.) to both France and Britain. The Southern route to France was inaugurated for airmail on May 20, 1939, by the ''Yankee Clipper'' piloted by Arthur E. LaPorte flying via Horta, Azores, and Lisbon, Portugal to Marseilles. Passenger service over the route was added on June 28, 1939, by the ''Dixie Clipper'' piloted by R.O.D. Sullivan. The Eastbound trip departed every Wednesday at Noon and arrived at Marseilles on Friday at 3 pm GCT with return service leaving Marseilles on Sunday at 8 am and arriving at Port Washington on Tuesday at 7 am. The Northern transatlantic route to Britain was inaugurated for Air Mail service on June 24, 1939, by the ''Yankee Clipper'' piloted by Harold Gray flying via Shediac (New Brunswick), Botwood (Newfoundland), and Foynes (Ireland) to Southampton
Southampton () is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire, S ...
. Passenger service was added on the Northern route on July 8, 1939, by the ''Yankee Clipper''. Eastbound flights left on Saturday at 7:30 am and arrived at Southampton on Sunday at 1 pm GCT. Westbound service departed Southampton on Wednesday at Noon and arrived at Port Washington on Thursday at 3 pm. After the outbreak of World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, the terminus became Foynes until the service ceased for the winter on October 5 while transatlantic service to Lisbon via the Azores continued into 1941. During World War II, Pan Am flew over worldwide in support of military operations.[
The "Clippers" — the name hearkened back to the 19th century fast-sailing ]clipper
A clipper was a type of mid-19th-century merchant sailing vessel, designed for speed. Clippers were generally narrow for their length, small by later 19th century standards, could carry limited bulk freight, and had a large total sail area. "Cl ...
s — were the only American passenger aircraft of the time capable of intercontinental travel. To compete with ocean liners, the airline offered first-class seats on such flights, and the style of flight crews became more formal. Instead of being leather-jacketed, silk-scarved airmail pilots, the crews of the "Clippers" wore naval-style uniforms and adopted a set procession when boarding the aircraft. In 1940 Pan Am and TWA both received and began using the Boeing 307 Stratoliner
The Boeing Model 307 Stratoliner (or Strato-Clipper in Pan American service, or C-75 in USAAF service) is an American stressed-skin four-engine low-wing tailwheel monoplane airliner derived from the B-17 Flying Fortress bomber, which entered c ...
, the first pressurize
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transp ...
d airliner to enter service. The Boeing 307's airline service was short-lived, as all were commandeered for military service when the United States entered World War II.
During World War II most Clippers were pressed into military service. A new Pan Am subsidiary pioneered an air military-supply route across the Atlantic from Brazil to West Africa. The onward flight to Sudan and Egypt tracked an existing British civil air route. In January 1942, the '' Pacific Clipper'' completed the first circumnavigation of the globe by a commercial airliner. Another first occurred in January 1943, when Franklin D. Roosevelt became the first US president
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
to fly abroad, in the ''Dixie Clipper''. During this period ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vario ...
'' creator Gene Roddenberry
Eugene Wesley Roddenberry Sr. (August 19, 1921 – October 24, 1991) was an American television screenwriter, producer, and creator of ''Star Trek: The Original Series'', its sequel spin-off series '' Star Trek: The Animated Series,'' and '' S ...
was a Clipper pilot; he was aboard the ''Clipper Eclipse'' when it crashed in Syria on June 19, 1947.
Post-war expansion and modernization
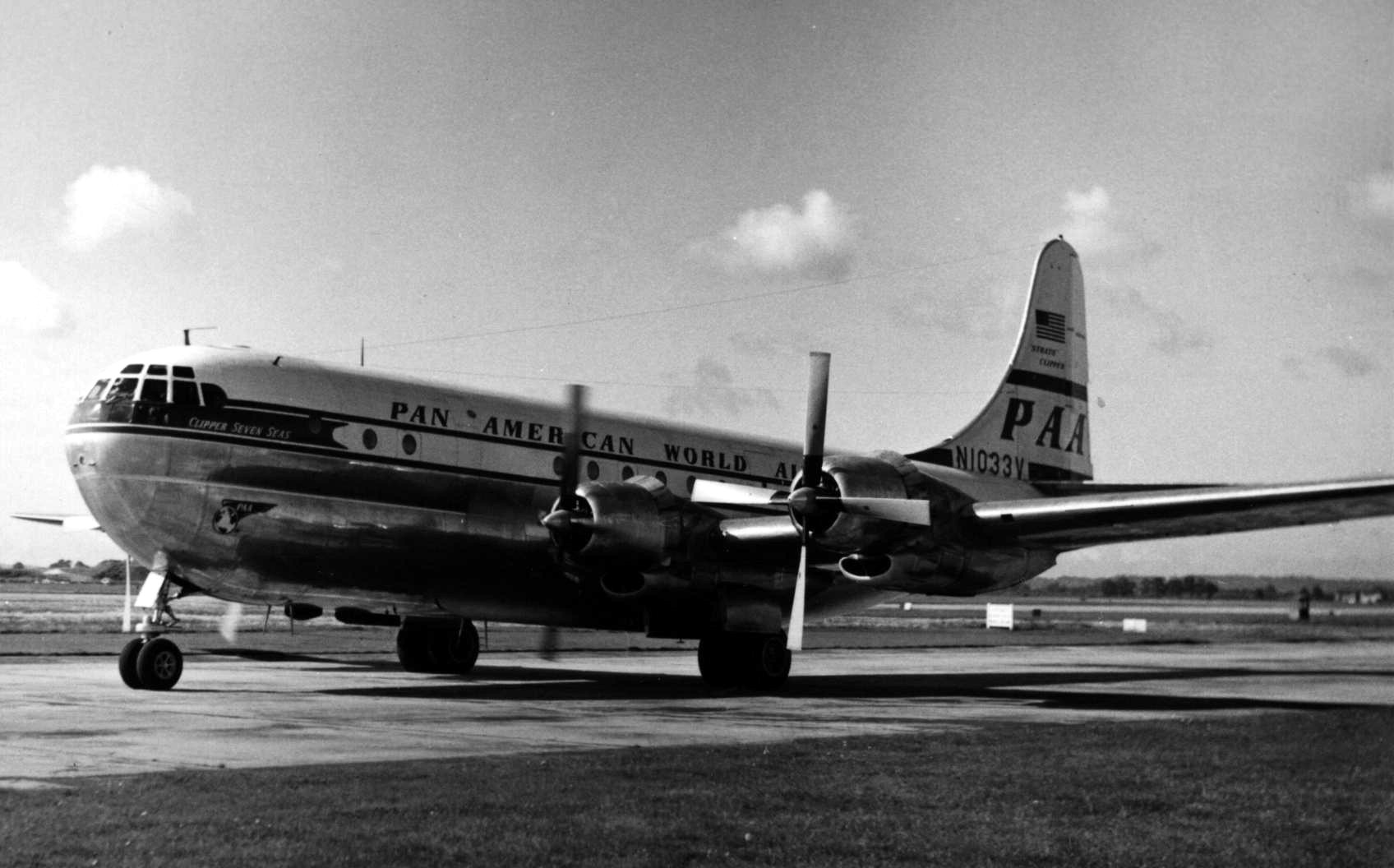
 The growing importance of air transport in the post-war era meant that Pan Am would no longer enjoy the official patronage it had been afforded in pre-war days to prevent the emergence of any meaningful competition, both at home and abroad.
The growing importance of air transport in the post-war era meant that Pan Am would no longer enjoy the official patronage it had been afforded in pre-war days to prevent the emergence of any meaningful competition, both at home and abroad.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2)'', p. 48, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]
Although Pan Am continued to use its political influence to lobby for protection of its position as America's primary international airline, it encountered increasing competition – first from American Export Airlines
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
across the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
to Europe, and subsequently from others including TWA to Europe, Braniff to South America, United to Hawaii and Northwest Orient
Northwest Airlines Corp. (NWA) was a major American airline founded in 1926 and absorbed into Delta Air Lines, Inc. by a merger. The merger, approved on October 29, 2008, made Delta the largest airline in the world until the American Airlines- ...
to East Asia, as well as five potential rivals to Mexico. This changed situation resulted from the new post-war approach the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) took toward the promotion of competition between major US carriers on key domestic and international scheduled routes compared with pre-war US aviation policy.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – South American problems)'', p. 50, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]

American Overseas Airlines
American Overseas Airlines (AOA) was an airline that operated between the United States and Europe between 1945 and 1950. It was headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City.
History
American Export Airlines (AEA), commonly known as Am E ...
(AOA) was the first airline to begin regular landplane flights across the Atlantic, on October 24, 1945. In January 1946 Pan Am scheduled seven DC-4s a week east from LaGuardia Airport
LaGuardia Airport is a civil airport in East Elmhurst, Queens, New York City. Covering , the facility was established in 1929 and began operating as a public airport in 1939. It is named after former New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia ...
, five to London ( Hurn Airport) and two to Lisbon. Time to Hurn was 17 hours 40 minutes including stops or 20 hours 45 minutes to Lisbon. A Boeing 314 flying boat flew LaGuardia to Lisbon once every two weeks in 29 hours 30 minutes; flying boat flights ended shortly thereafter.[The 1/46 Air Traffic Guide shows the B314 to Lisbon, but a B314 book says PA's last transatlantic B314 was in December 1945.]
TWA's transatlantic challenge – the impending introduction of its faster, pressurized Lockheed Constellation
The Lockheed Constellation ("Connie") is a propeller-driven, four-engined airliner built by Lockheed Corporation starting in 1943. The Constellation series was the first pressurized-cabin civil airliner series to go into widespread use. Its pre ...
s – resulted in Pan Am ordering its own Constellation fleet at $750,000 apiece. Pan Am began transatlantic Constellation flights on January 14, 1946, beating TWA by three weeks.Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
and Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of t ...
took 22 hours 45 minutes.Curtiss C-46
The Curtiss C-46 Commando is a twin-engine transport aircraft derived from the Curtiss CW-20 pressurised high-altitude airliner design. Early press reports used the name "Condor III" but the Commando name was in use by early 1942 in company pub ...
s for a freight network that eventually extended to Buenos Aires.[Pan American Airways System Timetable](_blank)
(pdf) January 1, 1958 The Stratocruisers' double-deck fuselage with sleeping berths and a lower-deck lounge helped it compete with its rival. "Super Stratocruisers" with more fuel appeared on Pan Am's transatlantic routes in November 1954, making nonstop eastward and one-stop westward schedules more reliably.
In June 1947 Pan Am started the first scheduled round-the-world airline flight. In September the weekly DC-4 was scheduled to leave San Francisco at 2200 Thursday as Flight 1, stopping at Honolulu, Midway, Wake
Wake or The Wake may refer to:
Culture
*Wake (ceremony), a ritual which takes place during some funeral ceremonies
*Wakes week, an English holiday tradition
* Parish Wake, another name of the Welsh ', the fairs held on the local parish's patron s ...
, Guam, Manila, Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estimated populatio ...
and arriving in Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comm ...
on Monday at 1245, where it met Flight 2, a Constellation that had left New York at 2330 Friday. The DC-4 returned to San Francisco as Flight 2; the Constellation left Calcutta 1330 Tuesday, stopped at Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former ...
, Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
, London, Shannon, Gander, and arrived LaGuardia Thursday at 1455. A few months later PA 3 took over the Manila route while PA 1 shifted to Tokyo and Shanghai. All Pan Am round-the-world flights included at least one change of plane until Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first flew on December ...
s took over in 1960. PA 1 became daily in 1962–63, making different en-route stops on different days of the week; in January 1963 it left San Francisco at 0900 daily and was scheduled into New York 56 hr 10 min later. Los Angeles replaced San Francisco in 1968; when Boeing 747s finished replacing 707s in 1971 all stops except Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the Capital city, capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is th ...
and Karachi were served daily in each direction. For a year or so in 1975–76 Pan Am finally completed the round-the-world trip, New York to New York.
In January 1950 Pan American Airways Corporation officially became Pan American World Airways, Inc. (The airline had begun calling itself ''Pan American World Airways'' in 1943.)[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – New name, new aircraft)'', p. 50, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011] In September 1950 Pan Am completed the $17.45 million purchase of American Overseas Airlines
American Overseas Airlines (AOA) was an airline that operated between the United States and Europe between 1945 and 1950. It was headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City.
History
American Export Airlines (AEA), commonly known as Am E ...
from American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passenge ...
.tourist
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism ...
class ''Rainbow'' service between New York and London on May 1, 1952, to complement the all- first ''President'' Stratocruiser service.DC-6B
The Douglas DC-6 is a piston-powered airliner and cargo aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company from 1946 to 1958. Originally intended as a military transport near the end of World War II, it was reworked after the war to compete with ...
s began replacing DC-4s on Pan Am's internal German routes.[''BEA in Berlin''](_blank)
, ''Flight International'', August 10, 1972, p. 180[''Aeroplane – Pan Am and the IGS'', Vol. 116, No. 2972, pp. 4, 8, Temple Press, London, October 2, 1968]
Pan Am introduced the Douglas DC-7C "Seven Seas" on transatlantic routes in summer 1956. In January 1958 the DC-7C nonstop took 10 hours 45 minutes Idlewild to London, enabling Pan Am to hold its own against TWA's Super Constellations and Starliners. In 1957 Pan Am started DC-7C flights direct from the West Coast of the United States to London and Paris with a fuel stop in Canada or Greenland. The introduction of the faster Bristol Britannia turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. ...
by British Overseas Airways Corporation
British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) was the United Kingdom, British state-owned airline created in 1939 by the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. It continued operating overseas services throughout World War II. ...
(BOAC) between New York and London from December 19, 1957, ended Pan Am's competitive leadership there.
Jet age
 Pan Am considered purchasing the world's first jetliner, the British
Pan Am considered purchasing the world's first jetliner, the British De Havilland Comet
The de Havilland DH.106 Comet was the world's first commercial jet airliner. Developed and manufactured by de Havilland in the United Kingdom, the Comet 1 prototype first flew in 1949. It featured an aerodynamically clean design with four ...
, but instead waited to become Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first flew on December ...
launch customer in 1955 with an order for 20. It also purchased 25 Douglas DC-8
The Douglas DC-8 (sometimes McDonnell Douglas DC-8) is a long-range narrow-body airliner built by the American Douglas Aircraft Company.
After losing the May 1954 US Air Force tanker competition to the Boeing KC-135, Douglas announced in Jul ...
, which could seat six across. The 707 was originally to be 144 inches (3.66 m) wide with five-abreast seating but Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
widened their design to match the DC-8. The combined order value was $269 million.
Pan Am's first scheduled jet flight was from New York Idlewild to Paris Le Bourget
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Sin ...
, stopping at Gander to refuel, on October 26, 1958. The Boeing 707-121 ''Clipper America'' N711PA carried 111 passengers.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – Leading the way)'', p. 50, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]
320 "Intercontinental" series Boeing 707s delivered in 1959–60, and the Douglas DC-8 in March 1960, enabled non-stop transatlantic crossings with a viable payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
in both directions.
Widebody era
 Pan Am was a
Pan Am was a Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, ...
launch customer, placing a $525 million order for 25 in April 1966.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – A falling star)'', p. 51, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]
On January 15, 1970 First Lady Pat Nixon christened Pan Am Boeing 747 ''Clipper Young America'' at Washington Dulles and during the next few days, Pan Am flew 747s to major airports in the United States where the public could tour them.
Pan Am's inaugural 747 service on the evening of January 21, 1970, was delayed for several hours by engine failure affecting the scheduled ''Clipper Young America''. ''Clipper Victor'' was substituted for the flight from New York John F. Kennedy to London Heathrow. While on the tarmac at Heathrow, two students from Aston University
Aston University (abbreviated as ''Aston''. for post-nominals) is a public university, public Research university, research university situated in the city centre of Birmingham, England. Aston began as the Birmingham Municipal Technical School ...
boarded the aircraft undetected and distributed rag mags in the passenger accommodation as a publicity stunt.
Pan Am carried 11 million passengers over 20 billion miles (32 billion km) in 1970, the year it introduced widebodied airline travel.
Supersonic plans
Pan Am was one of the first three airlines to sign options for the Aérospatiale-BAC Concorde, but like other airlines that took out options – with the exception of BOAC and Air France
Air France (; formally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. It is a subsidiary of the Air France–KLM Group and a founding member of the SkyTeam global airl ...
– it did not purchase the supersonic jet. Pan Am was the first US airline to sign for the Boeing 2707, the American supersonic transport
A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupo ...
(SST) project, with 15 delivery positions reserved; these aircraft never saw service after Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
voted against additional funding in 1971.
Computerized reservations, Pan Am Building and Worldport
 Pan Am commissioned IBM to build PANAMAC, a large computer that booked airline and hotel reservations, which was installed in 1964. It also held large amounts of information about cities, countries, airports, aircraft, hotels, and restaurants.
The computer occupied the fourth floor of the Pan Am Building, which was the largest commercial office building in the world for some time.
The airline also built Worldport, a terminal building at John F. Kennedy Airport in New York. It was distinguished by its elliptical, four-acre (16,000 m2) roof, suspended far from the outside columns of the terminal below by 32 sets of steel posts and cables. The terminal was designed to allow passengers to board and disembark via stairs without getting wet by parking the nose of the aircraft under the overhang. The introduction of the jetbridge made this feature obsolete. Pan Am built a gilded training building in the style of
Pan Am commissioned IBM to build PANAMAC, a large computer that booked airline and hotel reservations, which was installed in 1964. It also held large amounts of information about cities, countries, airports, aircraft, hotels, and restaurants.
The computer occupied the fourth floor of the Pan Am Building, which was the largest commercial office building in the world for some time.
The airline also built Worldport, a terminal building at John F. Kennedy Airport in New York. It was distinguished by its elliptical, four-acre (16,000 m2) roof, suspended far from the outside columns of the terminal below by 32 sets of steel posts and cables. The terminal was designed to allow passengers to board and disembark via stairs without getting wet by parking the nose of the aircraft under the overhang. The introduction of the jetbridge made this feature obsolete. Pan Am built a gilded training building in the style of Edward Durell Stone
Edward Durell Stone (March 9, 1902 – August 6, 1978) was an American architect known for the formal, highly decorative buildings he designed in the 1950s and 1960s. His works include the Museum of Modern Art, in New York City, the Museo de ...
designed by Steward-Skinner Architects in Miami.

Peak
At its peak in the late 1960s and early 1970s, Pan Am advertised under the slogan, the "World's Most Experienced Airline". It carried 6.7 million passengers in 1966, and by 1968, its 150 jets flew to 86 countries on every continent except for Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
over a scheduled route network of 81,410 unduplicated miles (131,000 km). During that period the airline was profitable and its cash reserves totaled $1 billion.helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribut ...
shuttle between New York's John F. Kennedy, LaGuardia and Newark airports and Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan (also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York) is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with ...
, operated by New York Airways. Aside from the DC-8, the Boeing 707 and 747, the Pan Am jet fleet included Boeing 720Bs and 727
727 may refer to:
* Boeing 727, an airliner
* AD 727, a year
* 727 BC, a year
* 727 (number), a number
* "727", a song by The Box Tops from the album '' Cry Like a Baby''
* '' 7/27'', a 2016 album by Fifth Harmony
* Area code 727, for telephon ...
s (the first aircraft to sport ''Pan Am'' – rather than ''Pan American'' – titlesBoeing 737
The Boeing 737 is a narrow-body aircraft produced by Boeing at its Renton Factory in Washington.
Developed to supplement the Boeing 727 on short and thin routes, the twinjet retains the 707 fuselage width and six abreast seating with two ...
s and 747SPs (which could fly nonstop New York to Tokyo), Lockheed L-1011 Tristars, McDonnell-Douglas DC-10s, and Airbus A300
The Airbus A300 is a wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Airbus.
In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in the United Kingdom, France, and West Germany signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a large airliner.
West ...
s and A310s. Pan Am owned the InterContinental Hotel chain and had a financial interest in the Falcon Jet Corporation, which held marketing rights to the Dassault Falcon 20
The Dassault Falcon 20 is a French business jet developed and manufactured by Dassault Aviation. The first business jet developed by the firm, it became the first of a family of business jets to be produced under the same name; of these, both ...
business jet
A business jet, private jet, or bizjet is a jet aircraft designed for transporting small groups of people. Business jets may be adapted for other roles, such as the evacuation of casualties or express parcel deliveries, and some are used by pu ...
in North America. The airline was involved in creating a missile-tracking range in the South Atlantic and operating a nuclear-engine testing laboratory in Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
. In addition, Pan Am participated in several notable humanitarian flights.
At its height Pan Am was well regarded for its modern fleet and experienced crews: cabin staff were multilingual and usually college graduates, hired from around the world, frequently with nursing training. Pan Am's onboard service and cuisine, inspired by Maxim's de Paris, were delivered "with a personal flair that has rarely been equaled."
Internal German Services (IGS) and other operations
 From 1950 until 1990 Pan Am operated a comprehensive network of high-frequency, short-haul scheduled services between
From 1950 until 1990 Pan Am operated a comprehensive network of high-frequency, short-haul scheduled services between West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
and West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under m ...
, first with Douglas DC-4
The Douglas DC-4 is an American four-engined (piston), propeller-driven airliner developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company. Military versions of the plane, the C-54 and R5D, served during World War II, in the Berlin Airlift and into the 1960 ...
s, then with DC-6Bs (from 1954) and Boeing 727
The Boeing 727 is an American narrow-body airliner that was developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
After the heavy 707 quad-jet was introduced in 1958, Boeing addressed the demand for shorter flight lengths from smaller airp ...
s (from 1966).[''Cold War Times''](_blank)
, Vol. 9, No. 1, p. 7, February 2009Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
at the end of World War II which prohibited Germany from having its own airlines and restricted the provision of commercial air services from and to Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
to air transport providers headquartered in these four countries. Rising Cold War tensions between the Soviet Union and the three Western powers resulted in unilateral Soviet withdrawal from the quadripartite Allied Control Commission in 1948, culminating in the division of Germany the following year. These events, together with Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
insistence on a very narrow interpretation of the post-war agreement on the Western powers' access rights to Berlin, meant that until the end of the Cold War air transport in West Berlin continued to be confined to the carriers of the remaining Allied Control Commission powers, with aircraft required to fly across hostile East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
territory through three wide air corridors at a maximum altitude of .[the cruising altitude of propliners employed on the Berlin Airlift]Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. These flights carried American service personnel for R&R leaves in Hong Kong, Tokyo, and other Asian cities.
Passenger traffic (1951–1989)
In August 1953 PAA scheduled passenger flights to 106 airports; in May 1968 to 122 airports; in November 1978 to 65 airports (plus a few freight-only airports); in November 1985 to 98 airports; in November 1991 to 46 airports (plus 14 more with only "Pan Am Express" prop flights).
Downturn

Fallout from 1973 oil crisis
Pan Am had invested in a large fleet of Boeing 747s expecting that air travel would continue to increase. It did not, as the introduction of many wide-bodies by Pan Am and its competitors coincided with an economic slowdown. Reduced air travel after the 1973 oil crisis made the overcapacity problem worse. Pan Am was vulnerable, with its high overheads as a result of a large decentralized infrastructure. High fuel prices and its many older, less fuel-efficient narrow-bodied airplanes increased the airline's operating costs. Federal route awards to other airlines, such as the Transpacific Route Case, further reduced the number of passengers Pan Am carried and its profit margins. On September 23, 1974, a group of Pan Am employees published an advertisement in ''
On September 23, 1974, a group of Pan Am employees published an advertisement in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' to register their disagreement over federal policies which they felt were harming the financial viability of their employer. The ad cited discrepancies in airport landing fees, such as Pan Am paying $4,200 to land a plane in Sydney, while the Australian carrier, Qantas
Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the List of airlines by foundation date, world's third-oldest airline sti ...
, paid only $178 to land a jet in Los Angeles. The ad also contended that the United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the executive branch of the Federal government of the Uni ...
was paying foreign airlines five times as much to carry US mail in comparison to Pan Am. Finally, the ad questioned why the Export-Import Bank of the United States loaned money to Japan, France, and Saudi Arabia at 6% interest while Pan Am paid 12%.
By the mid-1970s Pan Am had racked up $364 million of accumulated losses over a 10-year period, and its debts approached $1 billion. This threatened the airline with bankruptcy. Former American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passenge ...
vice president of operations, William T. Seawell, who had replaced Najeeb Halaby as Pan Am president in 1972, began implementing a turnaround strategy: trimming the network by 25%, slashing the 40,000-strong workforce by 30% and cutting wages, introducing stringent economies and rescheduling debt, and reducing the size of the fleet. These measures aided by the use of tax-loss credits enabled Pan Am to avert financial collapse and return to profitability in 1977.
Attempts to build a US domestic network
Since the 1930s Juan Trippe had coveted domestic routes for Pan Am. Through the late 1950s and early 1960s, and in the mid-1970s, there were talks of merging the airline with a domestic operator such as American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passenge ...
, Eastern Air Lines
Eastern Air Lines, also colloquially known as Eastern, was a major United States airline from 1926 to 1991. Before its dissolution, it was headquartered at Miami International Airport in an unincorporated area of Miami-Dade County, Florida.
Ea ...
, Trans World Airlines
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with F ...
or United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois. .Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
). The last time Pan Am was permitted to merge with another airline prior to the deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a r ...
of the US airline industry was in 1950, when it took over American Overseas Airlines from American Airlines.
National Airlines takeover
To acquire domestic routes, Pan Am, under president Seawell, set its eyes on National Airlines. Pan Am wound up in a bidding war with Frank Lorenzo's Texas International that boosted National's stock price, but Pan Am was granted permission to buy National in 1980 in what was described as the "Coup of the Decade." The acquisition of National Airlines for $437 million further burdened Pan Am's balance sheet, already under strain after financing the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, ...
s ordered in the mid-1960s. This acquisition did little to improve Pan Am's competitive position in relation to nimbler, lower-cost competitors in a deregulated industry, as National's north–south route structure provided insufficient feed at Pan Am's transatlantic and transpacific gateways in New York and Los Angeles. The airlines had incompatible fleets (apart from the Boeing 727
The Boeing 727 is an American narrow-body airliner that was developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
After the heavy 707 quad-jet was introduced in 1958, Boeing addressed the demand for shorter flight lengths from smaller airp ...
) and corporate cultures (partly as a result of National being perceived by some Pan Am employees as mainly a regional "backwoods" carrier with few trunk routes), and the integration was poorly handled by Pan Am management who presided over an increase in labor costs as a result of harmonizing National's pay scales with Pan Am's. Although revenues increased by 62% from 1979 to 1980, fuel costs from the merger increased by 157% during a weak economic climate. Further "miscellaneous expenses" increased by 74%.

Disposal of non-core assets and operational cutbacks
As 1980 progressed and the airline's financial situation worsened, Seawell began selling Pan Am's non-core assets. The first asset to be sold off was the airline's 50% interest in Falcon Jet Corporation in August. Later in November, Pan Am sold the Pan Am Building to the Metropolitan Life Insurance Company for $400 million. In September 1981 Pan Am sold off its InterContinental hotels chain. Before this transaction closed, Seawell was replaced by C. Edward Acker, Air Florida's founder and ex-president as well as a former Braniff International executive. The combined sale value of the InterContinental chain and the Falcon Jet Corp stake was $500 million.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – National acquisition)'', p. 52, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]
Acker followed up the asset disposal program he had inherited from his predecessor with operational cutbacks. Most prominent among these was the discontinuation of the round-the world service from October 31, 1982, when Pan Am ceased flying between Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders wi ...
, Bangkok and Hong Kong due to the sector's unprofitability. To provide additional seating capacity for its 1983 spring/summer season, the airline also acquired three passenger Boeing 747-200Bs from Flying Tigers
The First American Volunteer Group (AVG) of the Republic of China Air Force, nicknamed the Flying Tigers, was formed to help oppose the Japanese invasion of China. Operating in 1941–1942, it was composed of pilots from the United States ...
, who took four of Pan Am's 747-100 freighters in return.
Fleet restructuring
Despite Pan Am's precarious financial situation, in summer 1984 Acker went ahead with an order for new Airbus models in wide body and narrow-bodied aircraft, becoming the second American company to order Airbus aircraft, after Eastern Air Lines. These advanced aircraft, economically and operationally superior to the 747s and 727s Pan Am operated at the time, were intended to make the airline more competitive. In 1985 new A310-221s began replacing 727s on the Internal German Services (IGS) and A300s flew in the Caribbean networks later the same year while from early 1986 additional new longer range A310-222s replaced some of the 747s on the slimmed-down transatlantic network following ETOPS
ETOPS () is an acronym for ''Extended-range Twin-engine Operations Performance Standards''—a special part of flight rules for one-engine-inoperative flight conditions. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) coined the acronym for ...
certification (approval by the Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
(FAA) of transoceanic flying with twin-engined aircraft). The first A310 ETOPS transatlantic route was New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
to Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at ...
to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
followed shortly after that. Pan Am's decision not to take delivery of the A320s and to sell its delivery positions to Braniff meant that the majority of its short-haul US domestic and European feeder routes, and most of its IGS services, continued to be flown with obsolete 727s until the airline's demise. This put it at a disadvantage against rivals operating state-of-the-art aircraft with greater passenger appeal.
Sale of Pacific division
Given the airline's dire state, in April 1985, Acker sold Pan Am's entire Pacific Division, which consisted of 25% of its entire route system and their major hub at Tokyo Narita International Airport
Narita International Airport ( ja, 成田国際空港, Narita Kokusai Kūkō) , also known as Tokyo-Narita, formerly and originally known as , is one of two international airports serving the Greater Tokyo Area, the other one being Haneda Airport ...
to United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois. for $750 million. This sale also enabled Pan Am to address fleet incompatibility issues related to the earlier acquisition of National Airlines as it included Pan Am's Pratt & Whitney JT9D-powered 747SPs, its Rolls-Royce RB211
The Rolls-Royce RB211 is a British family of high-bypass turbofan engines made by Rolls-Royce. The engines are capable of generating of thrust. The RB211 engine was the first production three-spool engine, and turned Rolls-Royce from a sign ...
-powered L-1011-500s and the General Electric CF6-powered DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas.
The DC-10 was intended to succeed the Douglas DC-8, DC-8 for long-Range (aeronautics), range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; i ...
s inherited from National, which were transferred to United along with the Pacific routes.Transport Workers Union of America
Transport Workers Union of America (TWU) is a United States labor union that was founded in 1934 by subway workers in New York City, then expanded to represent transit employees in other cities, primarily in the eastern U.S. This article discu ...
.
Establishment of local feeder networks
In the early 1980s, Pan Am contracted several regional airlines ( Air Atlanta, Colgan Air
Colgan Air was an American certificated regional airline subsidiary of Pinnacle Airlines Corp. The headquarters of Colgan Air were located in Memphis, Tennessee.
Colgan Air operated for Continental Express/United Express, and US Airways Express ...
, Emerald Air, Empire Airlines, Presidential Airways and Republic Airlines) to operate feeder flights under the ''Pan Am Express
Pan Am Express was a brand name for a code sharing passenger feed service operated by other airlines on behalf of Pan American World Airways ( Pan Am). It was founded in the early 1980s, and lasted until the demise of Pan Am in 1991.
History
...
'' branding.
The acquisition of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Ma ...
-based commuter airline Ransome Airlines for $65 million (which was finalized in 1987) was meant to address the issue of providing additional feed for Pan Am's mainline services at its hubs in New York, Los Angeles and Miami in the United States, and Berlin in Germany.
US East coast shuttle
In an attempt to gain a presence on the busy Washington–New York–Boston commuter air corridor, the Ransome Ransome may refer to:
* Ransome, Queensland, Australia, a suburb of Brisbane
* 6440 Ransome, an asteroid
* Ransome Airlines, a regional airline in the United States
* Ransome (surname)
* Ransome Gillett Holdridge (1836–1899), an early San Francisc ...
acquisition was accompanied by the $100 million purchase of New York Air
New York Air was a low-cost U.S. airline owned by Texas Air Corporation and based at Hangar 5 at LaGuardia Airport in Flushing, Queens, New York. It ceased operations on February 1, 1987, in a merger with Continental Airlines.
New York Ai ...
's shuttle service between Boston, New York, and Washington, D.C. This parallel move was intended to enable Pan Am to provide a high-frequency service for high- yield business travelers in direct competition with the long-established, successful Eastern Air Lines Shuttle
Eastern Air Lines Shuttle (or Eastern Air Shuttle) was the brand name of Eastern's air shuttle that began on April 30, 1961. The shuttle originally flew between New York City, Boston, Washington, D.C. and Newark. The shuttle became part of ...
operation. The renamed Pan Am Shuttle began operating out of LaGuardia Airport's refurbished historic Marine Air Terminal
The Marine Air Terminal (also known as Terminal A) is an airport terminal located at LaGuardia Airport in Queens, New York City. Its main building, designed in the Art Deco style by William Delano of the firm Delano & Aldrich, opened in 1940. Th ...
in October 1986. However, it did not address the pressing issue of Pan Am's continuing lack of a strong domestic feeder network.
Financial, operational and reputational setbacks
In 1987, Towers Financial Corporation, led by its CEO Steven Hoffenberg and his consultant Jeffrey Epstein
Jeffrey Edward Epstein ( ; January 20, 1953August 10, 2019) was an American sex offender and financier. Epstein, who was born and raised in Brooklyn, New York City, began his professional life by teaching at the Dalton School in Manhattan, de ...
, unsuccessfully tried to take over Pan Am in a corporate raid with Towers Financial as their raiding vessel. Their bid failed.Thomas G. Plaskett
Thomas George Plaskett (December 24, 1943June 24, 2021) was an American business executive. He served as CEO of Continental Airlines, Pan American World Airways, and Greyhound Lines. He was instrumental in establishing AAdvantage.
Early life and ...
, a former American Airlines and Continental executive, replaced Acker as president in January 1988 (joining Pan Am from the latter).Pan Am flight 103
Pan Am Flight 103 was a regularly scheduled Pan American World Airways, Pan Am transatlantic flight from Frankfurt to Detroit via a stopover in London and another in New York City. The transatlantic leg of the route was operated by ''Clipper M ...
above Lockerbie, Scotland, resulted in 270 fatalities. Faced with a $300 million lawsuit filed by more than 100 families of the victims, the airline subpoena
A subpoena (; also subpœna, supenna or subpena) or witness summons is a writ issued by a government agency, most often a court, to compel testimony by a witness or production of evidence under a penalty for failure. There are two common types of ...
ed records of six US government agencies, including the CIA, the Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA; ) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating drug trafficking and distribution within th ...
, and the State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nat ...
. Though the records suggested that the US government was aware of warnings of a bombing and failed to pass the information to the airline, the families claimed Pan Am was attempting to shift the blame.
Also, in December 1988 the FAA fined Pan Am for 19 security failures, out of the 236 that were detected amongst 29 airlines.
Failed bid for Northwest Airlines
In June 1989 Plaskett presented Northwest Airlines
Northwest Airlines Corp. (NWA) was a major American airline founded in 1926 and absorbed into Delta Air Lines, Inc. by a merger. The merger, approved on October 29, 2008, made Delta the largest airline in the world until the American Airline ...
with a $2.7 billion takeover bid that was backed by Bankers Trust, Morgan Guaranty Trust, Citicorp and Prudential-Bache
Prudential Securities, also formerly known as Prudential Securities Incorporated (PSI), was the financial services arm of the insurer, Prudential Financial. In 2003, Prudential Securities was merged into Wachovia Securities, a division of Wachovi ...
. The proposed merger was Pan Am's final attempt to create a strong domestic network to provide sufficient feed for the two remaining mainline hubs at New York JFK and Miami. It was also intended to help the airline regain its status as a global airline by re-establishing a sizable transpacific presence. The merger was expected to result in annual savings of $240 million. However, billionaire financier Al Checchi
Alfred Attilio Checchi (born June 6, 1948) is an American businessman who was a candidate for Governor of California in the 1998 gubernatorial election, losing to fellow Democrat Gray Davis in the June 1998 primary. Checchi finished in second ...
outbid Pan Am by presenting Northwest's directors with a superior proposal.
Fallout from 1990–91 Persian Gulf War
The first Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
triggered by the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait was an operation conducted by Iraq on 2 August 1990, whereby it invaded the neighboring State of Kuwait, consequently resulting in a seven-month-long Iraqi military occupation of the country. The invasion and Ira ...
on August 2, 1990, caused fuel prices to rise, which severely depressed global economic activity. This in turn caused a sharp contraction of worldwide air travel demand, plunging once profitable operations, including Pan Am's prime transatlantic routes, into steep losses. These unforeseen events constituted a further major blow to Pan Am, which was still reeling from the 1988 Lockerbie disaster. To shore up its finances, Pan Am sold most of its routes serving London Heathrow – arguably Pan Am's most important international destination – to United Airlines. This left Pan Am with only two daily London flights, serving Detroit and Miami, which used Gatwick as their London terminal from the start of the 1990/91 winter timetable. Further asset disposals included Pan Am's sale of its IGS routes to Berlin to Lufthansa
Deutsche Lufthansa AG (), commonly shortened to Lufthansa, is the flag carrier of Germany. When combined with its subsidiaries, it is the second- largest airline in Europe in terms of passengers carried. Lufthansa is one of the five founding ...
for $150 million, which became effective at the same time and brought the total value of asset disposals to $1.2 billion.
Bankruptcy
 Pan Am was forced to file for bankruptcy protection on January 8, 1991.
Pan Am was forced to file for bankruptcy protection on January 8, 1991.Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline, along wi ...
purchased the remaining profitable assets of Pan Am, including its remaining European routes (except one from Miami to Paris), and Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its ...
mini hub, the Shuttle
The original meaning of the word shuttle is the device used in weaving to carry the weft. By reference to the continual to-and-fro motion associated with that, the term was then applied in transportation and then in other spheres. Thus the word ma ...
operation, 45 jets, and the Pan Am Worldport at John F. Kennedy Airport, for $416 million. Delta also injected $100 million becoming a 45 percent owner of a reorganized but smaller Pan Am serving the Caribbean, Central and South America from a main hub in Miami. The airline's creditors would hold the other 55 percent.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – Down ... but not quite out)'', p. 52, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011][''Comment''](_blank)
, ''Flight International'', December 18–24, 1991, p. 3
The Boston–New York LaGuardia– Washington National ''Pan Am Shuttle'' service was taken over by Delta in September 1991. Two months later Delta assumed all of Pan Am's remaining transatlantic traffic rights, except Miami to Paris and London.Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for ...
's and the traveling public's confidence in the viability of the reorganized Pan Am. Pan Am's senior executives outlined a projected shortfall of between $100 million and possibly $200 million, with the airline requiring a $25 million installment just to fly through the following week. On the evening of December 3, Pan Am's Creditors Committee advised US Bankruptcy Judge Cornelius Blackshear that it was close to convincing an airline (TWA) to invest $15 million to keep Pan Am operating. A deal with TWA owner
Pan Am's senior executives outlined a projected shortfall of between $100 million and possibly $200 million, with the airline requiring a $25 million installment just to fly through the following week. On the evening of December 3, Pan Am's Creditors Committee advised US Bankruptcy Judge Cornelius Blackshear that it was close to convincing an airline (TWA) to invest $15 million to keep Pan Am operating. A deal with TWA owner Carl Icahn
Carl Celian Icahn (; born February 16, 1936) is an American financier. He is the founder and controlling shareholder of Icahn Enterprises, a public company and diversified conglomerate holding company based in Sunny Isles Beach. Icahn takes l ...
could not be struck. Pan Am opened for business at 9:00 am and within the hour, Ray was forced to withdraw Pan Am's plan of reorganization and execute an immediate shutdown plan for Pan Am.
Pan Am ceased operations on December 4, 1991,Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden ...
.[Salpukas, Agis.]
Its Cash Depleted, Pan Am Shuts
." ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''. Thursday December 5, 1991. Retrieved August 28, 2009. As a result, some 7,500 Pan Am employees lost their jobs, thousands of whom had worked in the New York City area and were preparing to move to the Miami area to work at Pan Am's new headquarters near Miami International Airport
Miami International Airport , also known as MIA and historically as Wilcox Field, is the primary airport serving the greater Miami metropolitan area with over 1,000 daily flights to 167 domestic and international destinations, including most co ...
. Economists predicted that 9,000 jobs in the Miami area, including jobs at companies not connected to Pan Am that were dependent on the airline's presence, would be lost after it folded.Bridgetown, Barbados
Bridgetown (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The Ci ...
at 2 pm ( EST) for Miami under the command of Captain Mark Pyle flying ''Clipper Goodwill'', a Boeing 727-200 (N368PA).Eastern Air Lines
Eastern Air Lines, also colloquially known as Eastern, was a major United States airline from 1926 to 1991. Before its dissolution, it was headquartered at Miami International Airport in an unincorporated area of Miami-Dade County, Florida.
Ea ...
and Midway Airlines. After serving only two months as Pan Am's CEO, Ray was replaced by Peter McHugh to supervise the sale of Pan Am's remaining assets by Pan Am's Creditor's Committee. Pan Am's last remaining hub (at Miami International Airport) was split during the following years between United Airlines and American Airlines. TWA's Carl Icahn purchased Pan Am Express at a court ordered bankruptcy auction for $13 million, renaming it Trans World Express. The Pan Am brand was sold to Charles Cobb, CEO of Cobb Partners and former United States Ambassador to the
After serving only two months as Pan Am's CEO, Ray was replaced by Peter McHugh to supervise the sale of Pan Am's remaining assets by Pan Am's Creditor's Committee. Pan Am's last remaining hub (at Miami International Airport) was split during the following years between United Airlines and American Airlines. TWA's Carl Icahn purchased Pan Am Express at a court ordered bankruptcy auction for $13 million, renaming it Trans World Express. The Pan Am brand was sold to Charles Cobb, CEO of Cobb Partners and former United States Ambassador to the Republic of Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its sur ...
under President George H.W. Bush and Under Secretary of the US Department of Commerce under President Reagan. Cobb, along with Hanna-Frost partners invested in a new Pan American World Airways headed by veteran airline executive Martin R. Shugrue, Jr, a former Pan Am executive with 20 years of experience at the original carrier.
In his book, ''Pan Am: An Aviation Legend'', Barnaby Conrad III
Barnaby Conrad III (born 1952) is an American author, artist, and editor.
Early years
Conrad was born in San Francisco in 1952, the son of author Barnaby Conrad, Jr and architect Dale (Cowgill) Crichton. His father was an amateur bullfighter, a ...
contends that the collapse of the original Pan Am was a combination of corporate mismanagement, government indifference to protecting its prime international carrier, and flawed regulatory policy. He cites an observation made by former Pan Am Vice President for External Affairs, Stanley Gewirtz:
Under the terms of bankruptcy, the airline's International Flight Academy in Miami was permitted to remain open. It was established as an independent training organization beginning in 1992 under its current name, Pan Am International Flight Academy. The company began operating by using the flight simulation and type rating training center of the defunct Pan Am. In 2006, American Capital Strategies invested $58 million into the academy. Owned by the parent of Japanese airline All Nippon Airways
, also known as ANA (''Ē-enu-ē'') or is an airline in Japan. Its headquarters are located in Shiodome City Center in the Shiodome area of Minato ward of Tokyo. It operates services to both domestic and international destinations and had m ...
as of October 2014, Pan Am International Flight Academy is the only surviving division of Pan American World Airways.
Reuse of name
Aside from the aforementioned flight academy, the Pan Am brand has been resurrected six times since 1991, but the reincarnations were related to the original Pan Am in name only.
Airlines
Pan American World Airways trademarks and some assets were purchased by Eclipse Holdings, Inc. at an auction by the US Bankruptcy Court on December 2–3, 1993. The scheduled airline rights were sold to Pan American Airways on December 20–29, 1993 by Eclipse Holdings, which was to retain the Pan Am charter rights and operate through its subsidiary, Pan Am Charters, Inc., now Airways Corporation.[''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2 – Down ... but not quite out)'', p. 53, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011]
The first reincarnation of the original Pan Am operated from 1996 to 1998, with a focus on low-cost, long-distance flights between the United States and the Caribbean with the IATA airline designator ''PN''. The second was unrelated to the first and was a small regional carrier based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, that operated between 1998 and 2004. It found its niche in operating usually at smaller airports near major ones, such as Pease International (Portsmouth), and Gary Municipal Airport in
The second was unrelated to the first and was a small regional carrier based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, that operated between 1998 and 2004. It found its niche in operating usually at smaller airports near major ones, such as Pease International (Portsmouth), and Gary Municipal Airport in Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
. It used the IATA code ''PA'', and the ICAO
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international ...
code ''PAA''.Pan Am Dominicana
PAWA Dominicana (legally ''Pan Am World Airways Dominicana'') was the international flag carrier of the Dominican Republic. It was created as a subsidiary airline for Pan American Airways. This airline had scheduled flights between Santo Domingo ...
.
Railways
 In 1998, Guilford Transportation Industries purchased Pan American World Airways and all related naming rights and intellectual properties.
In 1998, Guilford Transportation Industries purchased Pan American World Airways and all related naming rights and intellectual properties.
Record-setting flights
At the outbreak of the war in the Pacific in December 1941, the '' Pacific Clipper'' was en route to New Zealand from San Francisco. Rather than risk flying back to Honolulu and being shot down by Japanese fighters, it was directed to fly west to New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. Starting on December 8, 1941, at Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
, New Zealand, the ''Pacific Clipper'' covered over 31,500 miles (50,694 km) via such exotic locales as Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of East Java and the second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. Located on the northeastern border of Java island, on the Mad ...
, Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
, Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
and Leopoldville. The ''Pacific Clipper'' landed at Pan American's LaGuardia Field
LaGuardia Airport is a civil airport in East Elmhurst, Queens, New York City. Covering , the facility was established in 1929 and began operating as a public airport in 1939. It is named after former New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia. ...
seaplane base at 7:12 on the morning of January 6, 1942, completing the first commercial plane flight to circumnavigate the world.North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
and the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
with stops in London Heathrow, Cape Town Airport and Auckland Airport. 747SP-21 ''Clipper New Horizons'' was the former ''Liberty Bell'', making the plane the only one to go around the globe over the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can al ...
and the poles. The flight made it in 54 hours, 7 minutes, and 12 seconds, creating seven new world records certified by the FAI. Captain Walter H. Mullikin, who commanded this flight, also commanded the Liberty Bell Express flight.
Corporate affairs
For much of its history the corporate headquarters were the Pan Am Building in Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
.
When Juan Trippe
Juan Terry Trippe (June 27, 1899 – April 3, 1981) was an American commercial aviation pioneer, entrepreneur and the founder of Pan American World Airways, one of the iconic airlines of the 20th century. He was involved in the introduction of t ...
had the company offices relocated to New York City, he rented space in a building on 42nd Street. This facility was across from the Grand Central Terminal
Grand Central Terminal (GCT; also referred to as Grand Central Station or simply as Grand Central) is a commuter rail terminal located at 42nd Street and Park Avenue in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Grand Central is the southern termi ...
. From a period in the 1930s until 1963, the airline headquarters were in the Chrysler Building
The Chrysler Building is an Art Deco skyscraper on the East Side of Manhattan in New York City, at the intersection of 42nd Street and Lexington Avenue in Midtown Manhattan. At , it is the tallest brick building in the world with a steel f ...
,[Clausen, p]
137
. on 135 East 42nd Street, also in Midtown Manhattan.
In September 1960 Trippe and developer Erwin Wolfson Erwin may refer to:
People Given name
* Erwin Chargaff (1905–2002), Austrian biochemist
* Erwin Dold (1919–2012), German concentration camp commandant in World War 2
* Erwin Hauer (1926–2017), Austrian-born American sculptor
* Egon Erwin Kis ...
signed a $115,500,000 lease agreement for the airline to occupy worth of space for the headquarters, totaling about 15 floors, and a new main ticket office at the intersection of 45th Street and Vanderbilt Avenue. At the time, the 30-year lease in the Chrysler Building was nearing the end of its life. The new lease was scheduled for 25 years.[
]
In popular culture
Pan Am held a lofty position in the popular culture of the Cold War era. One of the most famous images in which a Pan Am plane formed a backdrop was the Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developm ...
' February 7, 1964 arrival at John F. Kennedy Airport aboard a Pan Am Boeing 707-321, ''Clipper Defiance''.
From 1964 to 1968 con artist
A confidence trick is an attempt to defraud a person or group after first gaining their trust. Confidence tricks exploit victims using their credulity, naïveté, compassion, vanity, confidence, irresponsibility, and greed. Researchers ha ...
Frank Abagnale, Jr., claims to have masqueraded as a Pan Am pilot while still a minor, dead-heading to many destinations in the cockpit jump seat. He also claims to have used Pan Am's preferred hotels, paid the bills with bogus checks, and later cashed fake payroll checks in Pan Am's name. Abagnale and his co-author Stan Redding documented this era in the memoir '' Catch Me if You Can'', which became a film in 2002
The year 2002 in film involved some significant events.
Highest-grossing films
The top 10 films released in 2002 by worldwide gross are as follows:
2002 was the first year to see three films cross the eight-hundred-million-dollar mileston ...
. Abagnale called Pan Am the " Ritz-Carlton of airlines", and noted that the days of luxury in airline travel were over. In 2021 however, research by journalist Alan C. Logan proved that Frank Abagnale's claims were for the most part fabrications. He had in reality spent most of his late teenage years in prison, and had only written a handful of false Pan Am checks that were rapidly detected as false, and landed him back in prison.
In August 1964 Pan Am accepted the reservation of Gerhard Pistor, a journalist from Vienna, Austria, as the first passenger for future flights to the Moon. He paid a deposit of 500 Austrian Schillings (roughly US$20 at the time). About 93,000 people followed on the Pan Am waiting list, called "First Moon Flights Club
The First Moon Flights Club was a marketing campaign of American airline Pan Am that ran between 1968 and 1971. Self-described as a space tourism program, it was essentially a "waiting list" of people interested in taking commercial flights to the ...
". Pan Am expected the flight to depart about 2000.
A fictional Pan Am "Space Clipper",spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
called the ''Orion III'', had a prominent role in Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick (; July 26, 1928 – March 7, 1999) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and photographer. Widely considered one of the greatest filmmakers of all time, his films, almost all of which are adaptations of nove ...
's 1968 film '' 2001: A Space Odyssey'' and was featured prominently in one of the movie's posters. Plastic models of the 2001 Pan Am Space Clipper were sold by both the Aurora Company and Airfix at the time of the film's release in 1968. A satire of the movie by '' Mad'' magazine in 1968 showed Pan Am female flight attendant
A flight attendant, also known as steward/stewardess or air host/air hostess, is a member of the aircrew aboard commercial flights, many business jets and some government aircraft. Collectively called cabin crew, flight attendants are pri ...
s in "Actionwear by Monsanto" outfits as they joked about the problems their passengers faced while vomiting in zero gravity. The film's sequel, '' 2010'', also featured Pan Am in a background television commercial in the home of David Bowman's widow with the slogan, "At Pan Am, the sky is no longer the limit."
The airline appeared in other movies, notably in several James Bond
The ''James Bond'' series focuses on a fictional Secret Intelligence Service, British Secret Service agent created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short-story collections. Since Fleming's death in 19 ...
films. The company's Boeing 707s were featured in '' Dr. No'' (1962) and '' From Russia with Love'' (1963), while a Pan Am 747 and the Worldport appeared in the 1973 film '' Live and Let Die''.
A term used in popular psychology is "Pan American (or Pan Am) Smile." Named after the smile stewardesses gave to passengers in the airline's television commercials. It consists of a perfunctory mouth movement without the activity of facial muscles around the eyes that characterizes a genuine smile.
The 1982 film ''Blade Runner
''Blade Runner'' is a 1982 science fiction film directed by Ridley Scott, and written by Hampton Fancher and David Peoples. Starring Harrison Ford, Rutger Hauer, Sean Young, and Edward James Olmos, it is an adaptation of Philip K. Dick ...
'' contains several prominent shots of advertisements for Pan Am. The 2017 sequel, '' Blade Runner 2049'' also shows a Pan Am sign in an establishing shot.
 In 2011, ABC announced a new television series based on the lives of a 1960s Pan Am flight crew. The series, titled '' Pan Am'', began airing in September 2011. It was canceled in May 2012.
In 2020, Funko Games released a ''Pan Am'' board game, in which players play as airlines in competition with Pan Am.
In 2011, ABC announced a new television series based on the lives of a 1960s Pan Am flight crew. The series, titled '' Pan Am'', began airing in September 2011. It was canceled in May 2012.
In 2020, Funko Games released a ''Pan Am'' board game, in which players play as airlines in competition with Pan Am.
Flight crews
 Critical to Pan Am's success as an airline was the proficiency of its flight crews, who were rigorously trained in long-distance flight, seaplane anchorage and berthing operations, over-water navigation, radio procedure, aircraft repair, and marine tides. During the day, use of the compass while judging drift from sea currents was normal procedure; at night, all flight crews were trained to use
Critical to Pan Am's success as an airline was the proficiency of its flight crews, who were rigorously trained in long-distance flight, seaplane anchorage and berthing operations, over-water navigation, radio procedure, aircraft repair, and marine tides. During the day, use of the compass while judging drift from sea currents was normal procedure; at night, all flight crews were trained to use celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface ...
. In bad weather, pilots used dead reckoning and timed turns, making successful landings at fogged-in harbors by landing out to sea, then taxiing the plane into port. Many pilots had merchant marine certifications and radio licenses as well as pilot certificates.
A Pan Am flight captain would normally begin his career years earlier as a radio operator
A radio operator (also, formerly, wireless operator in British and Commonwealth English) is a person who is responsible for the operations of a radio system. The profession of radio operator has become largely obsolete with the automation of ra ...
or even mechanic, steadily gaining his licenses and working his way up the flight crew roster to navigator, second officer, and first officer. Before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
it was not unusual for a captain to make engine repairs at remote locations.[Masland, William M., ''Through the Back Doors of the World in a Ship That Had Wings'', Vantage Press (1984)]
Pan Am's mechanics and support staff were similarly trained. Newly hired applicants were frequently paired with experienced flight mechanics in several areas of the company until they had achieved proficiency in all aircraft types. Emphasis was placed on learning to maintain and overhaul aircraft in harsh seaborne environments when faced with logistical difficulties, as might be expected in a small foreign port without an aviation infrastructure or even an adequate road network. Many crews supported repair operations by flying in spare parts to planes stranded overseas, in some cases performing repairs themselves.
Acquisitions and divestments
* 1927: Pan American Airways, Atlantic, Gulf, and Caribbean Airways, and Aviation Corporation of the Americas founded.
* 1928: All three precursor firms merge into Aviation Corporation of the Americas, with Pan American Airways as its brand.
* 1928: 50% interest of Peruvian Airways acquired by Pan American.
* 1929: Mexicana of Mexico acquired by Pan Am.
* 1929: Pan American-Grace Airways
Pan American-Grace Airways, also known as Panagra, and dubbed "The World's Friendliest Airline" was an airline formed as a joint venture between Pan American World Airways and Grace Shipping Company. On September 13, 1928, a small single-engine ...
(PANAGRA), operating on the west coast of South America, formed as a 50–50 joint venture with W. R. Grace and Company.
* 1930: New York, Rio, and Buenos Aires Line (NYRBA) acquired, allowing Pan Am to operate along the east coast of South America. NYRBA's Brazilian subsidiary is renamed Panair do Brasil.
* 1931: Majority control of SCADTA of Colombia acquired in secret.
* 1931: Pacific Alaska Airways formed.
* 1931: Boston-Maine Airways begins contract operations.
* 1932: Aerovias Centrales, S.A. formed.
* 1932: Cubana of Cuba acquired.
* 1932: Uraba, Medellin and Central Airways acquired.
* 1933: China National Aviation Corporation (CNAC) acquired.
* 1933: Servicios Aviacion de Guatemala acquired.
* 1933: Panama Airways acquired.
* 1937: CNAC merged with China Airways
The China National Aviation Corporation () was a Chinese airline which was nationalized after the Chinese Communist Party took control in 1949, and merged into the People's Aviation Company of China () in 1952. It was a major airline under the R ...
.
* 1940: Minority holders of SCADTA bought-out.
* 1940: Aerovías de Guatemala formed.
* 1940: 40% of Aeronaves de Mexico acquired.
* 1941: SCADTA merged into SACO to form Avianca, owned by the Colombian government.
* 1943: Aerovías Venezolanas, S.A. (AVENSA) of Venezuela founded as a joint venture.
* 1943: 45% interest of Bahamas Airways acquired.
* 1944: Cuban investors acquire 56% of Cubana through a stock float.
* 1945: SAHSA was founded, being owned 40% of Pan Am, 40% of the Honduran Government, and 20% from private carriers.
* 1946: InterContinental, a chain of hotels, founded.
* 1946: Brazilian investors bought 4% of Panair do Brasil, with Pan Am's share decreased to 48%.
* 1949: Pan Am acquires a stake in Middle East Airlines
Middle East Airlines – Air Liban S.A.L. ( ar, طيران الشرق الأوسط ـ الخطوط الجوية اللبنانية ''Ṭayyarān al-Sharq al-Awsaṭ – al-Khuṭūṭ al-jawiyyah al-lubnāniyyah''), more commonly known as Middle ...
(MEA), as well as a management contract.
* 1949: Pan Am's 20% stake in CNAC acquired by Chinese Nationalists, with assets split variously between the Nationalists and the People's Republic of China.
* 1950: American Overseas Airlines
American Overseas Airlines (AOA) was an airline that operated between the United States and Europe between 1945 and 1950. It was headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City.
History
American Export Airlines (AEA), commonly known as Am E ...
(AOA) acquired from American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passenge ...
.
* 1954: Pan Am receives a contract to operate Patrick Air Force Base.
* 1954: Cuban government acquires Pan Am's remaining stake in Cubana.
* 1955: Pan Am's 49% stake in MEA is sold to British Overseas Airways Corporation
British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) was the United Kingdom, British state-owned airline created in 1939 by the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. It continued operating overseas services throughout World War II. ...
(BOAC).
* 1959: Mexican government acquires Pan Am's stake in Mexicana and Aeronaves de México (later renamed Aeroméxico).
* 1961: Brazilian investors acquires all the Pan Am's share in Panair do Brasil.
* 1967: PANAGRA sold to Braniff International Airways.
* 1970: Pan Am's 40% stake in SAHSA acquired by Transportes Aéreos Nacionales (TAN).
* 1976: AVENSA stake divested to Venezuelan government.
* 1980: National Airlines acquired.
* 1981: Pan Am Building sold to MetLife.
* 1981: InterContinental sold to Grand Metropolitan.
* 1986: Pacific Division sold to United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois. .
* 1988: Pan Am's queue for 50 A320 sold to Braniff Inc.
Braniff Airways, Inc., operated as Braniff International Airways from 1948 until 1965, and then Braniff International from 1965 until air operations ceased, was an airline in the United States that once flew air carrier operations from 1928 un ...
* 1989: Pan Am World Services (PAWS) sold to Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls International is an American
Irish-domiciled multinational conglomerate headquartered in Cork, Ireland, that produces fire, HVAC, and security equipment for buildings. As of mid-2019, it employed 105,000 people in around 2,0 ...
.
* 1990: London–Heathrow
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others be ...
-based routes sold to United Airlines.
* 1990: Internal German Services Division sold to Lufthansa
Deutsche Lufthansa AG (), commonly shortened to Lufthansa, is the flag carrier of Germany. When combined with its subsidiaries, it is the second- largest airline in Europe in terms of passengers carried. Lufthansa is one of the five founding ...
.
* 1991: Atlantic Division, Pan Am Shuttle, and New York City Worldport sold to Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline, along wi ...
.
Accidents and incidents
Fleet
Fleet in 1990
The following were aircraft operated Pan Am and Pan Am Express in March 1990, a year and a half before the airline's collapse:
Fleet history
All the aircraft ever operated by Pan Am:
Destinations
See also
* Avensa
*Pan Am Air Bridge ( Chalk's International Airlines sold its seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tec ...
operations to a group of investors who operated Chalk's under the ''Bridge'' name with Pan Am logos)
* Pan American Airways (1996–1998)
*Pan American Airways (1998–2004)
Pan American Airways (also known as Pan Am III) was a United States airline that operated scheduled services in the eastern US, as well as charters for tour operators and services to the Dominican RepublicFlight International 12–18 April 2005 ...
* Boston-Maine Airways (operated Pan Am Clipper Connection from 2004 to February 2008)
* Pan Am Railways
* Pan Am Systems
* ''Pan Am'' (TV series)
* Pan Am International Flight Academy – Only surviving division of Pan American World Airways
* Pan American Airways Guided Missile Range Division
Notes and citations
;Notes
;Citations
Sources
*
*
*
* Clausen, Meredith
Meredith L. Clausen (born 1942) is an American architectural historian, and professor in the School of Art and the Department of Architecture at the University of Washington in Seattle, Washington, USA.[MIT Press
The MIT Press is a university press affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts (United States). It was established in 1962.
History
The MIT Press traces its origins back to 1926 when MIT publ ...]
, 2005. , 9780262033244.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
''Aviation News'' online
Further reading
*
''Aviation News'' online
*
''Kelsey Publishing Group'' online
External links
Pan Am Brands
Pan Am Historical Foundation
Pan American World Airways, Inc. Records
– University of Miami, Special Collections
The Pan Am Museum Foundation, Inc.
everythingPanAm.com
– a virtual Pan Am museum
PanAmAir.org
– a site working to preserve the memories of Pan Am
*
Old photographs of Pan Am aircraft and advertisements
{{Authority control
Defunct airlines of the United States
Airlines established in 1927
Airlines disestablished in 1991
History of Key West, Florida
Landmarks in Key West, Florida
Collier Trophy recipients
American companies established in 1927
American companies disestablished in 1991
Defunct seaplane operators
 Pan American Airways, Incorporated (PAA) was founded as a shell company on March 14, 1927, by
Pan American Airways, Incorporated (PAA) was founded as a shell company on March 14, 1927, by 

 Pan Am started its South American routes with Consolidated Commodore and
Pan Am started its South American routes with Consolidated Commodore and 
 Pan Am also used Boeing 314 flying boats for the Pacific route: in China, passengers could connect to domestic flights on the Pan Am-operated China National Aviation Corporation (CNAC) network, co-owned with the
Pan Am also used Boeing 314 flying boats for the Pacific route: in China, passengers could connect to domestic flights on the Pan Am-operated China National Aviation Corporation (CNAC) network, co-owned with the 
 The growing importance of air transport in the post-war era meant that Pan Am would no longer enjoy the official patronage it had been afforded in pre-war days to prevent the emergence of any meaningful competition, both at home and abroad.''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2)'', p. 48, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011
Although Pan Am continued to use its political influence to lobby for protection of its position as America's primary international airline, it encountered increasing competition – first from
The growing importance of air transport in the post-war era meant that Pan Am would no longer enjoy the official patronage it had been afforded in pre-war days to prevent the emergence of any meaningful competition, both at home and abroad.''Aviation News (Pan American Airways: Part 2)'', p. 48, Key Publishing, Stamford, November 2011
Although Pan Am continued to use its political influence to lobby for protection of its position as America's primary international airline, it encountered increasing competition – first from 
 Pan Am considered purchasing the world's first jetliner, the British
Pan Am considered purchasing the world's first jetliner, the British  Pan Am was a
Pan Am was a  Pan Am commissioned IBM to build PANAMAC, a large computer that booked airline and hotel reservations, which was installed in 1964. It also held large amounts of information about cities, countries, airports, aircraft, hotels, and restaurants.
The computer occupied the fourth floor of the Pan Am Building, which was the largest commercial office building in the world for some time.
The airline also built Worldport, a terminal building at John F. Kennedy Airport in New York. It was distinguished by its elliptical, four-acre (16,000 m2) roof, suspended far from the outside columns of the terminal below by 32 sets of steel posts and cables. The terminal was designed to allow passengers to board and disembark via stairs without getting wet by parking the nose of the aircraft under the overhang. The introduction of the jetbridge made this feature obsolete. Pan Am built a gilded training building in the style of
Pan Am commissioned IBM to build PANAMAC, a large computer that booked airline and hotel reservations, which was installed in 1964. It also held large amounts of information about cities, countries, airports, aircraft, hotels, and restaurants.
The computer occupied the fourth floor of the Pan Am Building, which was the largest commercial office building in the world for some time.
The airline also built Worldport, a terminal building at John F. Kennedy Airport in New York. It was distinguished by its elliptical, four-acre (16,000 m2) roof, suspended far from the outside columns of the terminal below by 32 sets of steel posts and cables. The terminal was designed to allow passengers to board and disembark via stairs without getting wet by parking the nose of the aircraft under the overhang. The introduction of the jetbridge made this feature obsolete. Pan Am built a gilded training building in the style of 
 From 1950 until 1990 Pan Am operated a comprehensive network of high-frequency, short-haul scheduled services between
From 1950 until 1990 Pan Am operated a comprehensive network of high-frequency, short-haul scheduled services between 
 On September 23, 1974, a group of Pan Am employees published an advertisement in ''
On September 23, 1974, a group of Pan Am employees published an advertisement in ''
 Pan Am was forced to file for bankruptcy protection on January 8, 1991.
Pan Am was forced to file for bankruptcy protection on January 8, 1991.  Pan Am's senior executives outlined a projected shortfall of between $100 million and possibly $200 million, with the airline requiring a $25 million installment just to fly through the following week. On the evening of December 3, Pan Am's Creditors Committee advised US Bankruptcy Judge Cornelius Blackshear that it was close to convincing an airline (TWA) to invest $15 million to keep Pan Am operating. A deal with TWA owner
Pan Am's senior executives outlined a projected shortfall of between $100 million and possibly $200 million, with the airline requiring a $25 million installment just to fly through the following week. On the evening of December 3, Pan Am's Creditors Committee advised US Bankruptcy Judge Cornelius Blackshear that it was close to convincing an airline (TWA) to invest $15 million to keep Pan Am operating. A deal with TWA owner  After serving only two months as Pan Am's CEO, Ray was replaced by Peter McHugh to supervise the sale of Pan Am's remaining assets by Pan Am's Creditor's Committee. Pan Am's last remaining hub (at Miami International Airport) was split during the following years between United Airlines and American Airlines. TWA's Carl Icahn purchased Pan Am Express at a court ordered bankruptcy auction for $13 million, renaming it Trans World Express. The Pan Am brand was sold to Charles Cobb, CEO of Cobb Partners and former United States Ambassador to the
After serving only two months as Pan Am's CEO, Ray was replaced by Peter McHugh to supervise the sale of Pan Am's remaining assets by Pan Am's Creditor's Committee. Pan Am's last remaining hub (at Miami International Airport) was split during the following years between United Airlines and American Airlines. TWA's Carl Icahn purchased Pan Am Express at a court ordered bankruptcy auction for $13 million, renaming it Trans World Express. The Pan Am brand was sold to Charles Cobb, CEO of Cobb Partners and former United States Ambassador to the  The second was unrelated to the first and was a small regional carrier based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, that operated between 1998 and 2004. It found its niche in operating usually at smaller airports near major ones, such as Pease International (Portsmouth), and Gary Municipal Airport in
The second was unrelated to the first and was a small regional carrier based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, that operated between 1998 and 2004. It found its niche in operating usually at smaller airports near major ones, such as Pease International (Portsmouth), and Gary Municipal Airport in  In 1998, Guilford Transportation Industries purchased Pan American World Airways and all related naming rights and intellectual properties. The railway was later operated as Pan Am Railways. In 2022, the company was acquired by CSX Corporation.
In 1998, Guilford Transportation Industries purchased Pan American World Airways and all related naming rights and intellectual properties. The railway was later operated as Pan Am Railways. In 2022, the company was acquired by CSX Corporation.
 In 2011, ABC announced a new television series based on the lives of a 1960s Pan Am flight crew. The series, titled '' Pan Am'', began airing in September 2011. It was canceled in May 2012.
In 2020, Funko Games released a ''Pan Am'' board game, in which players play as airlines in competition with Pan Am.
In 2011, ABC announced a new television series based on the lives of a 1960s Pan Am flight crew. The series, titled '' Pan Am'', began airing in September 2011. It was canceled in May 2012.
In 2020, Funko Games released a ''Pan Am'' board game, in which players play as airlines in competition with Pan Am.
 Critical to Pan Am's success as an airline was the proficiency of its flight crews, who were rigorously trained in long-distance flight, seaplane anchorage and berthing operations, over-water navigation, radio procedure, aircraft repair, and marine tides. During the day, use of the compass while judging drift from sea currents was normal procedure; at night, all flight crews were trained to use
Critical to Pan Am's success as an airline was the proficiency of its flight crews, who were rigorously trained in long-distance flight, seaplane anchorage and berthing operations, over-water navigation, radio procedure, aircraft repair, and marine tides. During the day, use of the compass while judging drift from sea currents was normal procedure; at night, all flight crews were trained to use