Pachycephalosaurids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a
 Most pachycephalosaurid remains are not complete, usually consisting of portions of the frontoparietal bone that forms the distinctive dome. This can make
Most pachycephalosaurid remains are not complete, usually consisting of portions of the frontoparietal bone that forms the distinctive dome. This can make
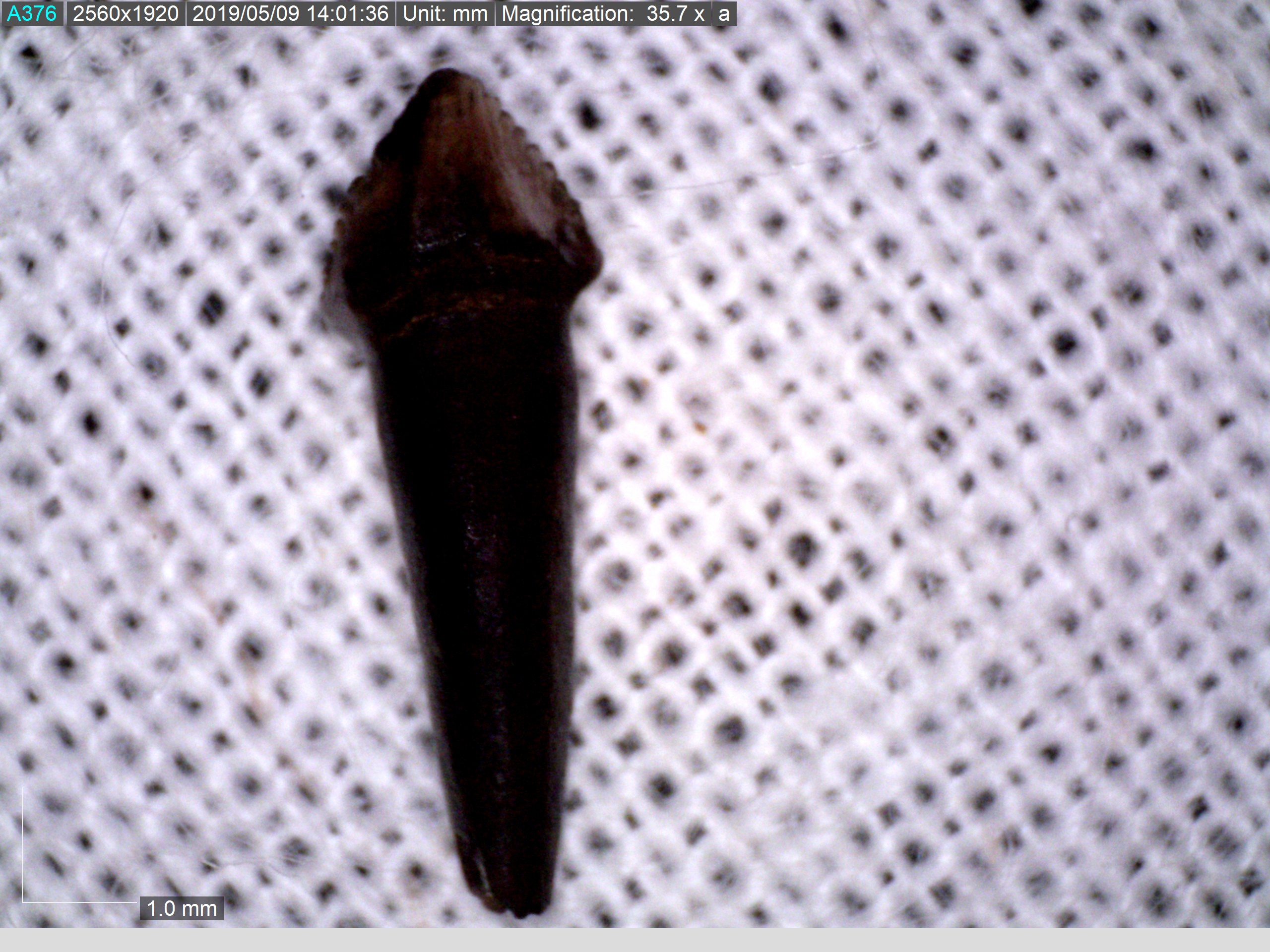 The Pachycephalosauria was first named as a
The Pachycephalosauria was first named as a
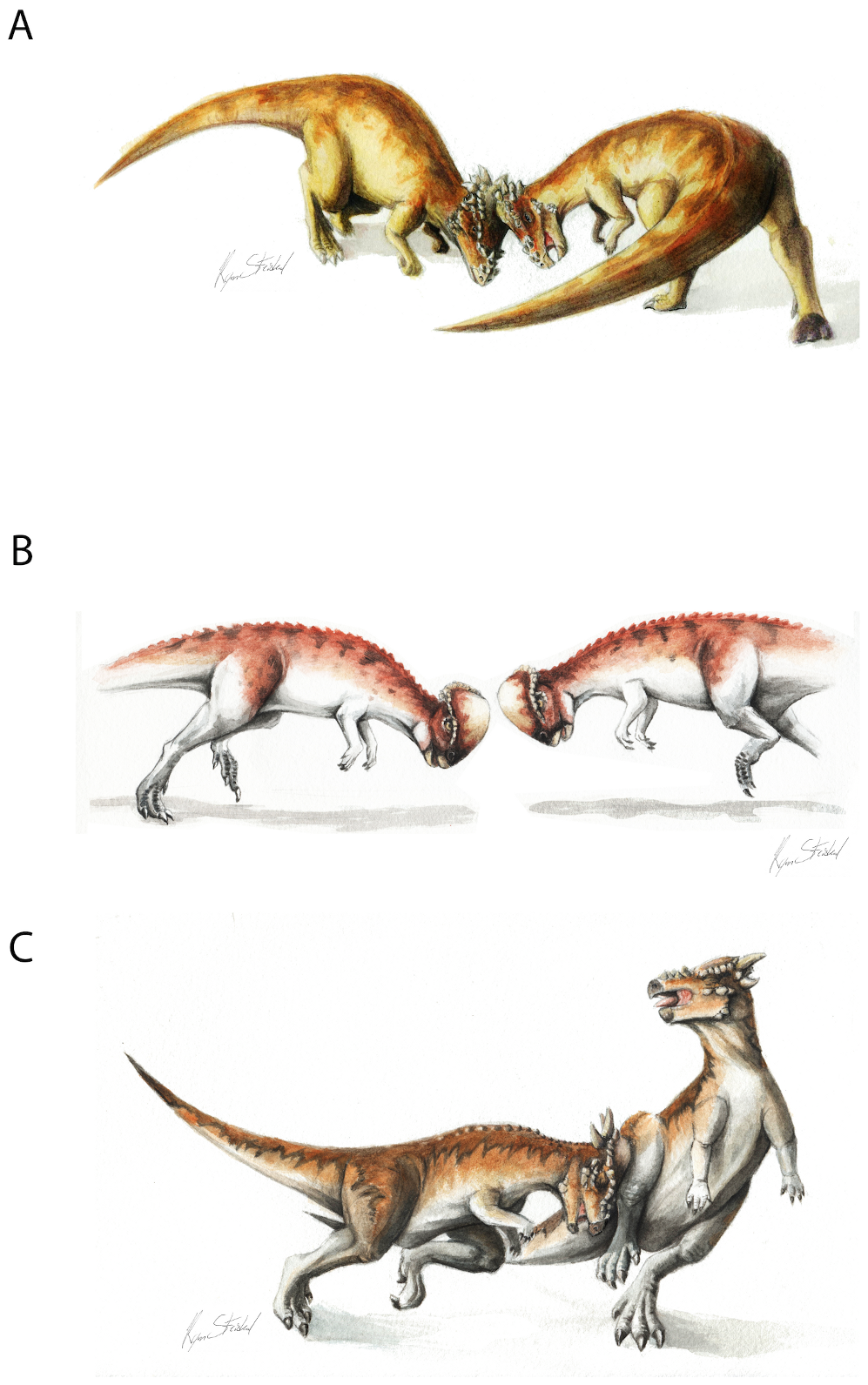 The adaptive significance of the skull dome has been heavily debated. The popular hypothesis among the general public that the skull was used in head-butting, as sort of a dinosaurian battering ram, was first proposed by . This view was popularized in the 1956 science fiction story " A Gun for Dinosaur" by
The adaptive significance of the skull dome has been heavily debated. The popular hypothesis among the general public that the skull was used in head-butting, as sort of a dinosaurian battering ram, was first proposed by . This view was popularized in the 1956 science fiction story " A Gun for Dinosaur" by  A histological study conducted by argued against the battering ram hypothesis. They argued that the dome was "an ephemeral ontogenetic stage", the spongy bone structure could not sustain the blows of combat, and the radial pattern was simply an effect of rapid growth. Later biomechanical analyses by and concluded, however, that the domes could withstand combat stresses. argued that the growth patterns discussed by Goodwin and Horner are not inconsistent with head-butting behavior.
instead argued that the dome functioned for species recognition. There is evidence that the dome had some form of external covering, and it is reasonable to consider the dome may have been brightly covered, or subject to change color seasonally. Due to the nature of the fossil record, however, it cannot be observed whether or not color played a role in dome function.
argued that species recognition is an unlikely evolutionary cause for the dome, because dome forms are not notably different between species. Because of this general similarity, several genera of Pachycephalosauridae have sometimes been incorrectly lumped together. This is unlike the case in ceratopsians and
A histological study conducted by argued against the battering ram hypothesis. They argued that the dome was "an ephemeral ontogenetic stage", the spongy bone structure could not sustain the blows of combat, and the radial pattern was simply an effect of rapid growth. Later biomechanical analyses by and concluded, however, that the domes could withstand combat stresses. argued that the growth patterns discussed by Goodwin and Horner are not inconsistent with head-butting behavior.
instead argued that the dome functioned for species recognition. There is evidence that the dome had some form of external covering, and it is reasonable to consider the dome may have been brightly covered, or subject to change color seasonally. Due to the nature of the fossil record, however, it cannot be observed whether or not color played a role in dome function.
argued that species recognition is an unlikely evolutionary cause for the dome, because dome forms are not notably different between species. Because of this general similarity, several genera of Pachycephalosauridae have sometimes been incorrectly lumped together. This is unlike the case in ceratopsians and
 Histological examination reveals that pachycephalosaurid domes are composed of a unique form of fibrolamellar bone which contains fibroblasts that play a critical role in wound healing, and are capable of rapidly depositing bone during remodeling. Peterson ''et al.'' (2013) concluded that, taken together, the frequency of lesion distribution and the bone structure of frontoparietal domes lend strong support to the hypothesis that pachycephalosaurids used their unique cranial structures for
Histological examination reveals that pachycephalosaurid domes are composed of a unique form of fibrolamellar bone which contains fibroblasts that play a critical role in wound healing, and are capable of rapidly depositing bone during remodeling. Peterson ''et al.'' (2013) concluded that, taken together, the frequency of lesion distribution and the bone structure of frontoparietal domes lend strong support to the hypothesis that pachycephalosaurids used their unique cranial structures for
 The Asian and North American species of pachycephalosaurs lived in markedly different environments. Asian specimens are normally more intact, indicating they were not transported far from their place of death before fossilization. They likely lived in a large desert region in central Asia with a hot and
The Asian and North American species of pachycephalosaurs lived in markedly different environments. Asian specimens are normally more intact, indicating they were not transported far from their place of death before fossilization. They likely lived in a large desert region in central Asia with a hot and
clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
of ornithischian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s. Along with Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period, dating between about 85.8 and 65.5 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, all of them being found in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/ omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found.
Candidates for the earliest known pachycephalosaur include ''Ferganocephale adenticulatum'' from Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations co ...
Period strata of Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
and ''Stenopelix valdensis'' from Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
strata of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, although R.M. Sullivan has doubted that either of these species are pachycephalosaurs. /sup> The oldest known pachycephalosaur is currently ''Sinocephale bexelli
''Sinocephale'' (meaning "Chinese head") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur that lived in Inner Mongolia, China during the Cretaceous period. The only species, ''Sinocephale bexelli'', was originally named as a species of the genus ''Trood ...
'' from the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. In 2017, a phylogenetic analysis conducted by Han and colleagues identified ''Stenopelix'' as a member of the Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
.
Description
Pachycephalosaurs were bipedalornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
ns characterized by their thickened skulls. They had a bulky torso with an expanded gut cavity and broad hips, short forelimbs, long legs, a short, thick neck, and a heavy tail. Large orbits and a large optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
point to pachycephalosaurs having good vision, and uncharacteristically large olfactory lobes
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a grey matter, neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of odor, smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitof ...
indicate that they had a good sense of smell relative to other dinosaurs. They were fairly small dinosaurs, with most falling in the range of 2–3 meters (6.6-9.8 feet) in length and the largest, ''Pachycephalosaurus wyomingensis
''Pachycephalosaurus'' (; meaning "thick-headed lizard", from Greek ''pachys-/'' "thick", ''kephale/'' "head" and ''sauros/'' "lizard") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaurs. The type species, ''P. wyomingensis'', is the only known species, ...
,'' estimated to measure 4.5 meters (14.8 feet) long and weigh 450 kilograms (990 pounds). The characteristic skull of pachycephalosaurs is a result of the fusion and thickening
A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their t ...
of the frontals and parietals, accompanied by the closing of the supratemporal fenestra
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
. In some species this takes the form of a raised dome; in others, the skull is flat or wedge-shaped. While the flat-headed pachycephalosaurs are traditionally regarded as distinct species or even families, they may represent juveniles of dome-headed adults. /sup> /sup> All display highly ornamented jugals, squamosals, and postorbitals in the form of blunt horns and nodes. Many species are only known from skull fragments, and a complete pachycephalosaur skeleton is yet to be found.
Classification
 Most pachycephalosaurid remains are not complete, usually consisting of portions of the frontoparietal bone that forms the distinctive dome. This can make
Most pachycephalosaurid remains are not complete, usually consisting of portions of the frontoparietal bone that forms the distinctive dome. This can make taxonomic
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
identification a difficult task, as the classification of genera and species within ''Pachycephalosauria'' relies almost entirely on cranial characteristics. Consequently, improper species have historically been appointed to the clade. For instance, '' Majungatholus'', once thought to be a pachycephalosaur, is now recognized as a specimen of the abelisaurid theropod '' Majungasaurus'', and ''Yaverlandia
''Yaverlandia'' (meaning "of Yaverland Point/Yaverland Battery") is a genus of maniraptoran dinosaur. Known from a partial fossil skull (MIWG 1530) found in Lower Cretaceous strata of the Wessex Formation ( Upper Silty Bed; Vectis Formation) on t ...
'', another dinosaur initially described as a pachycephalosaurid, has also recently been reclassified as a coelurosaur
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyrann ...
(Naish in ). Further complicating matters are the diverse interpretations of ontogenetic
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the st ...
and sexual features in pachycephalosaurs.
A 2009 paper proposed that ''Dracorex'' and ''Stygimoloch'' were just early growth stages of ''Pachycephalosaurus'', rather than distinct genera.
A 2020 reworking of Cerapoda
Cerapoda ("ceratopsians" and "ornithopods") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia, that includes pachycephalosaurs, ceratopsians and ornithopods
Classification
Cerapoda is divided into two groups: Ornithopoda ("bird-foot") and Margin ...
by Dieudonné ''et al.'' recovered the animals traditionally considered 'heterodontosaurids
Heterodontosauridae is a family of ornithischian dinosaurs that were likely among the most basal (primitive) members of the group. Their phylogenetic placement is uncertain but they are most commonly found to be primitive, outside of the group ...
' as a basal grouping within Pachycephalosauria, paraphyletic with respect to the traditional, dome-headed pachycephalosaurs.
Taxonomy
 The Pachycephalosauria was first named as a
The Pachycephalosauria was first named as a suborder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
of the order Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
by . They included within it only one family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
, the Pachycephalosauridae. Later researchers, such as Michael Benton, have ranked it as an infraorder of a suborder Cerapoda
Cerapoda ("ceratopsians" and "ornithopods") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia, that includes pachycephalosaurs, ceratopsians and ornithopods
Classification
Cerapoda is divided into two groups: Ornithopoda ("bird-foot") and Margin ...
, which unites the ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
ns and ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous world ...
s. In 2006, Robert Sullivan published a re-evaluation of pachycephalosaur taxonomy. Sullivan considered attempts by Maryańska and Osmólska to restrict the definition of Pachycephalosauria redundant with their Pachycephalosauridae, since they were diagnosed by the same anatomical characters. Sullivan also rejected attempts by , in his phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
studies, to re-define Pachycephalosauridae to include only "dome-skulled" species (including ''Stegoceras'' and ''Pachycephalosaurus''), while leaving more "basal" species outside that family in Pachycephalosauria. Therefore, Sullivan's use of Pachycephalosauridae is equivalent to Sereno and Benton's use of Pachycephalosauria.
Sullivan diagnosed the Pachycephalosauridae-based only on characters of the skull, with the defining character being a dome-shaped frontoparietal skull bone. According to Sullivan, the absence of this feature in some species assumed to be primitive led to the split in classification between domed and non-domed pachycephalosaurs; however, discovery of more advanced and possibly juvenile pachycephalosaurs with flat skulls (such as ''Dracorex hogwartsia'') show this distinction to be incorrect. Sullivan also pointed out that the original diagnosis of Pachycephalosauridae centered around "flat to dome-like" skulls, so the flat-headed forms should be included in the family. In a paper published in 2003, Thomas E. Williamson
Thomas may refer to:
People
* List of people with given name Thomas
* Thomas (name)
* Thomas (surname)
* Saint Thomas (disambiguation)
* Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church
* Thomas the Ap ...
and Thomas D. Carr discovered a clade of the Pachycephalosauridae that was a sister taxa to the genus '' Stegoceras'', made up of "all other dome-headed pachycephalosaurians; this was referred to as Pachycephalosaurinae
Phylogeny
The cladogram presented here follows an analysis by . Cladogram after . Below is a cladogram from .Paleobiology
Feeding
The small size of most pachycephalosaur species and lack of skeletal adaptation indicates that they were not climbers and primarily ate food close to the ground. Mallon et al. (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of Laramidia, during the Late Cretaceous and concluded that pachycephalosaurids were generally restricted to feeding on vegetation at, or below, the height of 1 meter. They exhibitheterodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology.
In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals where teeth are differentiated into different forms. For example, ...
y, having different tooth morphology between the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
ry teeth and maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
ry teeth. Front teeth are small and peg-like with an ovular cross section and were most likely used for grabbing food. In some species, the last premaxillary tooth was enlarged and canine-like. Back teeth are small and triangular with denticles on the front and back of the crown, used for mouth processing. In species in which the dentary has been found, mandibular teeth are similar in size and shape to those in the upper jaw. Wear patterns on the teeth vary by species, indicating a range of food preferences which could include seeds, stems, leaves, fruits, and possibly insects. A very wide rib cage and large gut cavity extending all the way to the base of the tail suggests the use of fermentation to digest food.
Head-butting behavior
 The adaptive significance of the skull dome has been heavily debated. The popular hypothesis among the general public that the skull was used in head-butting, as sort of a dinosaurian battering ram, was first proposed by . This view was popularized in the 1956 science fiction story " A Gun for Dinosaur" by
The adaptive significance of the skull dome has been heavily debated. The popular hypothesis among the general public that the skull was used in head-butting, as sort of a dinosaurian battering ram, was first proposed by . This view was popularized in the 1956 science fiction story " A Gun for Dinosaur" by L. Sprague de Camp
Lyon Sprague de Camp (; November 27, 1907 – November 6, 2000) was an American writer of science fiction, fantasy and non-fiction. In a career spanning 60 years, he wrote over 100 books, including novels and works of non-fiction, including biog ...
. Many paleontologists have since argued for the head-butting hypothesis, including and . In this hypothesis, pachycephalosaurs rammed each other head-on, as do modern-day bighorn sheep
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subspec ...
and musk oxen.
Anatomical evidence for combative behavior includes vertebral articulations providing spinal rigidity, and the shape of the back indicating strong neck musculature. It has been suggested that a pachycephalosaur could make its head, neck, and body horizontally straight, in order to transmit stress during ramming. However, in no known dinosaur could the head, neck, and body be oriented in such a position. Instead, the cervical and anterior dorsal vertebrae of pachycephalosaurs show that the neck was carried in an "S"- or "U"-shaped curve.
Also, the rounded shape of the skull would lessen the contacted surface area during head-butting, resulting in glancing blows. Other possibilities include flank-butting, defense against predators, or both. The relatively wide build of pachycephalosaurs (which would protect vital internal organs from harm during flank-butting) and the squamosal horns of the '' Stygimoloch'' (which would have been used to great effect during flank-butting) add credence to the flank-butting hypothesis.
 A histological study conducted by argued against the battering ram hypothesis. They argued that the dome was "an ephemeral ontogenetic stage", the spongy bone structure could not sustain the blows of combat, and the radial pattern was simply an effect of rapid growth. Later biomechanical analyses by and concluded, however, that the domes could withstand combat stresses. argued that the growth patterns discussed by Goodwin and Horner are not inconsistent with head-butting behavior.
instead argued that the dome functioned for species recognition. There is evidence that the dome had some form of external covering, and it is reasonable to consider the dome may have been brightly covered, or subject to change color seasonally. Due to the nature of the fossil record, however, it cannot be observed whether or not color played a role in dome function.
argued that species recognition is an unlikely evolutionary cause for the dome, because dome forms are not notably different between species. Because of this general similarity, several genera of Pachycephalosauridae have sometimes been incorrectly lumped together. This is unlike the case in ceratopsians and
A histological study conducted by argued against the battering ram hypothesis. They argued that the dome was "an ephemeral ontogenetic stage", the spongy bone structure could not sustain the blows of combat, and the radial pattern was simply an effect of rapid growth. Later biomechanical analyses by and concluded, however, that the domes could withstand combat stresses. argued that the growth patterns discussed by Goodwin and Horner are not inconsistent with head-butting behavior.
instead argued that the dome functioned for species recognition. There is evidence that the dome had some form of external covering, and it is reasonable to consider the dome may have been brightly covered, or subject to change color seasonally. Due to the nature of the fossil record, however, it cannot be observed whether or not color played a role in dome function.
argued that species recognition is an unlikely evolutionary cause for the dome, because dome forms are not notably different between species. Because of this general similarity, several genera of Pachycephalosauridae have sometimes been incorrectly lumped together. This is unlike the case in ceratopsians and hadrosaur
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includ ...
ids, which had much more distinct cranial ornamentation. Longrich ''et al.'' argued that instead the dome had a mechanical function, such as combat, one which was important enough to justify the resource investment.
Dome paleopathology
studied cranial pathologies among the Pachycephalosauridae and found that 22% of all domes examined had lesions that are consistent with osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone resulting from penetrating trauma, or trauma to the tissue overlying the skull leading to an infection of the bone tissue. This high rate of pathology lends more support to the hypothesis that pachycephalosaurid domes were employed in intra-specific combat. The frequency of trauma was comparable across the different genera in thisfamily
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
, despite the fact that these genera vary with respect to the size and architecture of their domes, and fact that they existed during varying geologic periods. These findings were in stark contrast with the results from analysis of the relatively flat-headed pachycephalosaurids, where there was an absence of pathology. This would support the hypothesis that these individuals represent either females or juveniles, where intra-specific combat behavior is not expected.
 Histological examination reveals that pachycephalosaurid domes are composed of a unique form of fibrolamellar bone which contains fibroblasts that play a critical role in wound healing, and are capable of rapidly depositing bone during remodeling. Peterson ''et al.'' (2013) concluded that, taken together, the frequency of lesion distribution and the bone structure of frontoparietal domes lend strong support to the hypothesis that pachycephalosaurids used their unique cranial structures for
Histological examination reveals that pachycephalosaurid domes are composed of a unique form of fibrolamellar bone which contains fibroblasts that play a critical role in wound healing, and are capable of rapidly depositing bone during remodeling. Peterson ''et al.'' (2013) concluded that, taken together, the frequency of lesion distribution and the bone structure of frontoparietal domes lend strong support to the hypothesis that pachycephalosaurids used their unique cranial structures for agonistic behavior
Agonistic behaviour is any social behaviour related to fighting. The term has broader meaning than aggressive behaviour because it includes threats, displays, retreats, placation, and conciliation. The term "agonistic behaviour" was first implemen ...
.
Paleoecology
 The Asian and North American species of pachycephalosaurs lived in markedly different environments. Asian specimens are normally more intact, indicating they were not transported far from their place of death before fossilization. They likely lived in a large desert region in central Asia with a hot and
The Asian and North American species of pachycephalosaurs lived in markedly different environments. Asian specimens are normally more intact, indicating they were not transported far from their place of death before fossilization. They likely lived in a large desert region in central Asia with a hot and arid climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
. North American specimens are typically found in rocks that were formed by erosion from the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
. Specimens are far less intact; usually only skull caps are recovered, and those found regularly exhibit surface exfoliation and other signs that they were transported long distances by water before fossilization. It is assumed that they lived in the mountains in a temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
and were carried by erosion after death to their final resting place.
Distribution
Pachycephalosaurs lived exclusively inLaurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
, being found in western North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and central Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. Pachycephalosaurs originated in Asia and had two major dispersal events, resulting in the two separate waves of pachycephalosaur evolution observed in Asia. The first, occurring before the late Santonian
The Santonian is an age in the geologic timescale or a chronostratigraphic stage. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 86.3 ± 0.7 mya (million years ago) and 83.6 ± 0.7 mya. The ...
or early Campanian, involved a migration from Asia to North America, most likely by way of the Bering Land Bridge. This migration was by a common ancestor of '' Stygimoloch'', '' Stegoceras'', '' Tylocephale'', '' Prenocephale,'' and ''Pachycephalosaurus
''Pachycephalosaurus'' (; meaning "thick-headed lizard", from Greek ''pachys-/'' "thick", ''kephale/'' "head" and ''sauros/'' "lizard") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaurs. The type species, ''P. wyomingensis'', is the only known species, ...
''. The second event occurred before the middle Campanian, and involved a migration back into Asia from North America by a common ancestor of '' Prenocephale'' and '' Tylocephale''. Two species originally reported to be pachycephalosaurs discovered outside this range, ''Yaverlandia bitholus
''Yaverlandia'' (meaning "of Yaverland Point/Yaverland Battery") is a genus of maniraptoran dinosaur. Known from a partial fossil skull (MIWG 1530) found in Lower Cretaceous strata of the Wessex Formation ( Upper Silty Bed; Vectis Formation) on t ...
'' of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and '' Majungatholus atopus'' of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, have recently been shown to actually be theropods.
See also
* Timeline of pachycephalosaur researchNotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* byJack Horner Jack Horner may refer to:
*''Little Jack Horner'', a nursery rhyme
People
* Jack Horner (baseball) (1863–1910), American professional baseball player
*Jack Horner (journalist) (1912–2005), Gordon John Horner, Minnesota sportscaster
* Jack B. H ...
on shape-shifting dinosaur skulls and dinosaur misclassification
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131376
Marginocephalians
Turonian first appearances
Maastrichtian extinctions
Taxa named by Teresa Maryańska
Taxa named by Halszka Osmólska