PT Barnum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phineas Taylor Barnum (; July 5, 1810 – April 7, 1891) was an American showman, businessman, and politician, remembered for promoting celebrated hoaxes and founding the
 In 1842 Barnum introduced his first major hoax: a creature with the body of a monkey and the tail of a fish known as the "Feejee" mermaid. He leased it from fellow museum owner
In 1842 Barnum introduced his first major hoax: a creature with the body of a monkey and the tail of a fish known as the "Feejee" mermaid. He leased it from fellow museum owner
 Barnum became aware of the popularity of Jenny Lind, the "Swedish Nightingale", during his European tour with Tom Thumb when her career was at its height in Europe. Barnum had never heard her and conceded to being unmusical himself,Rogers, Francis
Barnum became aware of the popularity of Jenny Lind, the "Swedish Nightingale", during his European tour with Tom Thumb when her career was at its height in Europe. Barnum had never heard her and conceded to being unmusical himself,Rogers, Francis
"Jenny Lind"
''The Musical Quarterly'', Vol. 32, No. 3 (July 1946), pp. 437–48 but he approached her to sing in America at $1,000 a night for 150 nights, all expenses paid by him. He was confident that he could make use of Lind's reputation for morality and philanthropy in his publicity. Lind demanded the fee in advance and Barnum agreed; this permitted her to raise a fund for charities, principally endowing schools for poor children in Sweden.Miller, Philip L
"Review: P. T. Barnum Presents Jenny Lind: The American Tour of the Swedish Nightingale"
''American Music'', Spring 1983, pp. 78–80 Barnum borrowed heavily on his mansion and his museum to raise the money to pay Lind but he was still short of funds; so he persuaded a Philadelphia minister that Lind would be a good influence on American morals, and the minister lent him the final $6,000. The contract also gave Lind the option of withdrawing from the tour after 60 or 100 performances, paying Barnum $50,000 if she did so. Lind and her small company sailed to America in September 1850, but she was a celebrity even before she arrived because of Barnum's months of preparations; close to 40,000 people greeted her at the docks and another 20,000 at her hotel. The press was also in attendance, and "Jenny Lind items" were available to buy. When she realized how much money Barnum stood to make from the tour, she insisted on a new agreement which he signed on September 3, 1850. This gave her the original fee plus the remainder of each concert's profits after Barnum's $5,500 management fee. She was determined to accumulate as much money as possible for her charities. The tour began with a concert at
The tour began with a concert at
"Reading Lind Mania: Print Culture and the Construction of Eighteenth-Century Audiences"
''Book History'', Vol. 1 (1998), pp. 94–106 The blatant commercialism of Barnum's ticket auctions distressed Lind, and she persuaded him to make a substantial number of tickets available at reduced prices."Jenny Lind's Progress in America", ''The Observer,'' October 6, 1850, p. 3 On the tour Barnum's publicity always preceded Lind's arrival and whipped up enthusiasm; he had up to 26 journalists on his payroll.Hambrick, Keith S
"P. T. Barnum Presents Jenny Lind – The American Tour of the Swedish Nightingale"
''Louisiana History: The Journal of the Louisiana Historical Association'', Vol. 22, No. 2 (Spring, 1981), pp. 208–09 After New York, the company toured the East Coast with continued success, and later went through the Southern states and Cuba. By early 1851, Lind had become uncomfortable with Barnum's relentless marketing of the tour, and she invoked a contractual right to sever her ties with him. They parted amicably, and she continued the tour for nearly a year under her own management. Lind gave 93 concerts in America for Barnum, earning her about $350,000, while Barnum netted at least $500,000 ().
 Barnum went on to create America's first aquarium and to expand the wax figure department of his museum. His "Seven Grand Salons" demonstrated the Seven Wonders of the World. The collections expanded to four buildings, and he published a "Guide Book to the Museum" which claimed 850,000 "curiosities". Late in 1860,
Barnum went on to create America's first aquarium and to expand the wax figure department of his museum. His "Seven Grand Salons" demonstrated the Seven Wonders of the World. The collections expanded to four buildings, and he published a "Guide Book to the Museum" which claimed 850,000 "curiosities". Late in 1860,
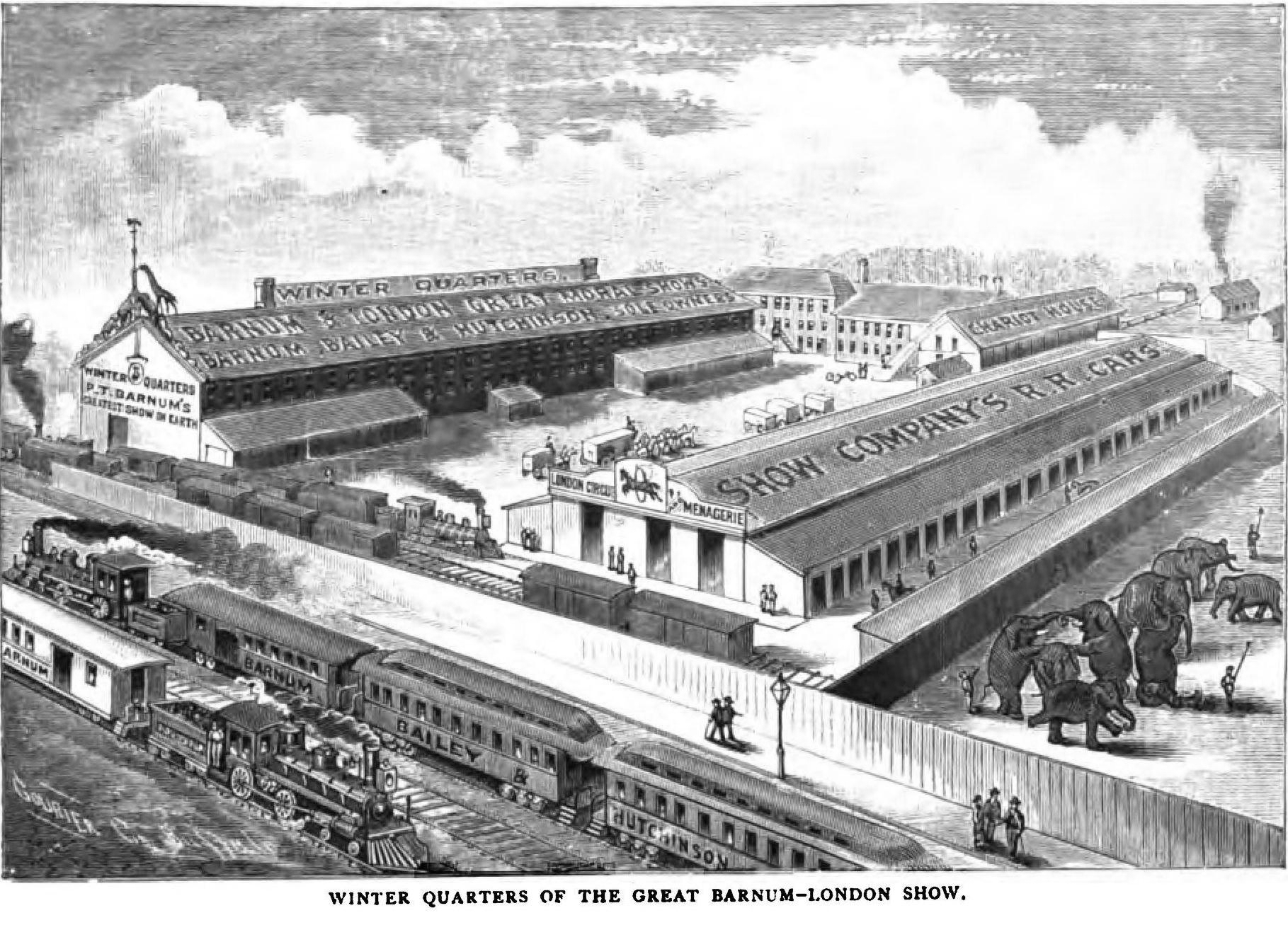
 Barnum did not enter the circus business until he was 60 years old. He established "P. T. Barnum's Grand Traveling Museum, Menagerie, Caravan &
Barnum did not enter the circus business until he was 60 years old. He established "P. T. Barnum's Grand Traveling Museum, Menagerie, Caravan &
 Barnum wrote several books, including ''Life of P. T. Barnum'' (1855), ''The Humbugs of the World'' (1865), ''Struggles and Triumphs'' (1869), ''Forest and jungle, or, Thrilling adventures in all quarters of the globe :'' and ''The Art of Money-Getting'' (1880).
Barnum was often referred to as the "Prince of Humbugs", and he saw nothing wrong in entertainers or vendors using hoaxes (or "humbug", as he termed it) in promotional material, as long as the public was getting value for money. However, he was contemptuous of those who made money through fraud, especially the spiritualist mediums popular in his day; he testified against noted "spirit photographer" William H. Mumler in his trial for fraud, and he exposed "the tricks of the trade" used by mediums to cheat the bereaved. In ''The Humbugs of the World'', he offered $500 (about $9,000 in 2021) to any medium who could prove power to communicate with the dead.
Barnum wrote several books, including ''Life of P. T. Barnum'' (1855), ''The Humbugs of the World'' (1865), ''Struggles and Triumphs'' (1869), ''Forest and jungle, or, Thrilling adventures in all quarters of the globe :'' and ''The Art of Money-Getting'' (1880).
Barnum was often referred to as the "Prince of Humbugs", and he saw nothing wrong in entertainers or vendors using hoaxes (or "humbug", as he termed it) in promotional material, as long as the public was getting value for money. However, he was contemptuous of those who made money through fraud, especially the spiritualist mediums popular in his day; he testified against noted "spirit photographer" William H. Mumler in his trial for fraud, and he exposed "the tricks of the trade" used by mediums to cheat the bereaved. In ''The Humbugs of the World'', he offered $500 (about $9,000 in 2021) to any medium who could prove power to communicate with the dead.
 Barnum enjoyed what he publicly dubbed "profitable philanthropy". "If by improving and beautifying our city Bridgeport, Connecticut, and adding to the pleasure and prosperity of my neighbors, ndI can do so at a profit, the incentive to 'good works' will be twice as strong as if it were otherwise." He was appointed to the board of trustees to
Barnum enjoyed what he publicly dubbed "profitable philanthropy". "If by improving and beautifying our city Bridgeport, Connecticut, and adding to the pleasure and prosperity of my neighbors, ndI can do so at a profit, the incentive to 'good works' will be twice as strong as if it were otherwise." He was appointed to the board of trustees to
* Betts, John Rickards. "P. T. Barnum and the Popularization of Natural History", ''Journal of the History of Ideas'' 20, no. 3 (1959): 353–368. * * Cook, James W. ''The Arts of Deception: Playing with Fraud in the Age of Barnum''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2001. . Relates Barnum's Fiji Mermaid and What Is It? exhibits to other popular arts of the nineteenth century, including magic shows and ''
The Barnum Museum
Phineas Taylor Barnum papers, 1818–1993
– A virtual reproduction of Barnum's American Museum; includes a collection of primary source materials ;Biographical information
at the ''Barnum Family Genealogy'' website *
P. T. Barnum at Ringling Brothers and Barnum and Bailey Circus
Entry on P. T. Barnum in the Concise Encyclopedia of Tufts History
* Full text of
The Life of Phineas T. Barnum
' by Joel Benton, from
Barnum's circus affiliation
P.T. Barnum – Ultrarunning Promoter (1874)
– An article about Barnum's handwriting & signature
* ttp://www.ptbarnum.org P. T. Barnum, the Shakespeare of Advertising
P. T. Barnum and Henry Bergh
Bergh was founder of the
Facebook Page
Bethel Historical Society, P. T. Barnum Monument, "P. T. Barnum – The Lost Legend" Documentary.
An 1890 recording of Barnum's voice
Marina Mansion
Tribute to Ringling Bros.and Barnum & Bailey Circus by brothers Charles Elias Disney & Daniel H. Disney
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Barnum, P. T. * 1810 births 1891 deaths American entertainment industry businesspeople 19th-century American memoirists Burials at Mountain Grove Cemetery, Bridgeport Connecticut Democrats Connecticut Republicans Mayors of Bridgeport, Connecticut Members of the Connecticut House of Representatives Businesspeople from Bridgeport, Connecticut People from Fairfield, Connecticut Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus Members of the Universalist Church of America 19th-century Christian universalists 19th-century American people 19th-century American politicians Circus owners American slave owners American abolitionists Christian abolitionists 19th-century American businesspeople Museum founders
Barnum & Bailey Circus
The Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus (also known as the Ringling Bros. Circus, Ringling Bros., the Barnum & Bailey Circus, Barnum & Bailey, or simply Ringling) is an American traveling circus company billed as The Greatest Show on Ear ...
(1871–2017) with James Anthony Bailey
James Anthony Bailey (July 4, 1847 – April 11, 1906), born James Anthony McGinnis, was an American owner and manager of several 19th-century circuses, including The Barnum and Bailey Greatest Show on Earth.
Early life
James Anthony McGinn ...
. He was also an author, publisher, and philanthropist, though he said of himself: "I am a showman by profession ... and all the gilding shall make nothing else of me." According to his critics, his personal aim was "to put money in his own coffers". He is widely credited with coining the adage " There's a sucker born every minute", although no evidence has been collected of him saying this.
Barnum became a small business owner in his early twenties and founded a weekly newspaper before moving to New York City in 1834. He embarked on an entertainment career, first with a variety troupe called "Barnum's Grand Scientific and Musical Theater", and soon after by purchasing Scudder's American Museum
Scudder's American Museum was a museum located in New York City from 1810 to 1841, when it was purchased by P.T. Barnum and transformed into the very successful Barnum's American Museum.
Before Scudder
The roots of the museum date back to 1791 ...
which he renamed after himself. He used the museum as a platform to promote hoaxes and human curiosities such as the Fiji mermaid and General Tom Thumb
Charles Sherwood Stratton (January 4, 1838 – July 15, 1883), better known by his stage name "General Tom Thumb", was an American dwarf who achieved great fame as a performer under circus pioneer P. T. Barnum.
Childhood and early life
Bo ...
. In 1850, he promoted the American tour of Swedish opera singer Jenny Lind, paying her an unprecedented $1,000 a night for 150 nights. He suffered economic reversals in the 1850s due to bad investments, as well as years of litigation and public humiliation, but he used a lecture tour as a temperance
Temperance may refer to:
Moderation
*Temperance movement, movement to reduce the amount of alcohol consumed
*Temperance (virtue), habitual moderation in the indulgence of a natural appetite or passion
Culture
*Temperance (group), Canadian danc ...
speaker to emerge from debt. His museum added America's first aquarium and expanded the wax-figure department.
Barnum served two terms in the Connecticut legislature in 1865 as a Republican for Fairfield, Connecticut. He spoke before the legislature concerning the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Thirteenth Amendment (Amendment XIII) to the United States Constitution abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. The amendment was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, by the House of Representative ...
which abolished slavery and involuntary servitude: "A human soul, 'that God has created and Christ died for,' is not to be trifled with. It may tenant the body of a Chinaman, a Turk, an Arab, or a Hottentot—it is still an immortal spirit". He was elected in 1875 as mayor of Bridgeport, Connecticut where he worked to improve the water supply, bring gas lighting to streets, and enforce liquor and prostitution laws. He was also instrumental in starting Bridgeport Hospital in 1878 and was its first president. Nevertheless, the circus business, begun when he was 60 years old, was the source of much of his enduring fame. He established "P. T. Barnum's Grand Traveling Museum, Menagerie, Caravan & Hippodrome" in 1870, a traveling circus, menagerie, and museum of "freaks" which adopted many names over the years.
Barnum was married to Charity Hallett from 1829 until her death in 1873, and they had four children. In 1874, a few months after his wife's death, he married Nancy Fish
Nancy Fish Barnum Callias D'Orengiani, Baroness (née Fish; 22 April 1850 – 23 June 1927) was an English socialite, daughter of a successful cotton miller and the second wife of P. T. Barnum, 40 years her senior. After the death of Barnum's ...
, his friend's daughter who was 40 years younger than P. T. Barnum. They were married until 1891 when Barnum died of a stroke at his home. He was buried in Mountain Grove Cemetery, Bridgeport, which he designed himself.
Early life
Barnum was born inBethel, Connecticut
Bethel () is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. Its population was 11,988 in 2022 according to World Population Review. The town includes the Bethel Census Designated Place.
Interstate 84 passes through Bethel, and it has ...
, the son of innkeeper, tailor, and store-keeper Philo Barnum (1778–1826) and his second wife Irene Taylor. His maternal grandfather Phineas Taylor was a Whig, legislator, landowner, justice of the peace, and lottery schemer who had a great influence on him.
Barnum had several businesses over the years, including a general store, a book auctioning trade, real estate speculation, and a statewide lottery network. He started a weekly newspaper in 1829 called ''The Herald of Freedom
''The Herald of Freedom'', established 1829, was a newspaper published by P. T. Barnum, based in Bethel, Connecticut. The newspaper was created in reaction against the religious oppression and militant Calvinism
Calvinism (also called th ...
'' in Danbury, Connecticut. His editorials against the elders of local churches led to libel suits and a prosecution which resulted in imprisonment for two months, but he became a champion of the liberal movement upon his release. He sold his store in 1834.
He began his career as a showman in 1835 when he was 25 with the purchase and exhibition of a blind and almost completely paralyzed slave woman named Joice Heth
Joice Heth (February 19, 1836)"Joice Heth", Hoaxes.org was an African-American woman who was exhibited by P.T. Barnum with the false claim that she was the 161-year-old nursing mammy of George Washington. Her exhibition under these claims, and ...
, whom an acquaintance was trumpeting around Philadelphia as George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
's former nurse and 161 years old. Slavery was already outlawed in New York, but he exploited a loophole which allowed him to lease her for a year for $1,000, borrowing $500 to complete the sale. Heth died in February 1836, at no more than 80 years old. Barnum had worked her for 10 to 12 hours a day, and he hosted a live autopsy of her body in a New York saloon where spectators paid 50 cents to see the dead woman cut up, as he revealed that she was likely half her purported age.
Showman
Barnum had a year of mixed success with his first variety troupe called "Barnum's Grand Scientific and Musical Theater", followed by the Panic of 1837 and three years of difficult circumstances. He purchasedScudder's American Museum
Scudder's American Museum was a museum located in New York City from 1810 to 1841, when it was purchased by P.T. Barnum and transformed into the very successful Barnum's American Museum.
Before Scudder
The roots of the museum date back to 1791 ...
in 1841, located at Broadway and Ann Street, New York City. He improved the attraction, upgrading the building and adding exhibits, then renamed it "Barnum's American Museum"; it became a popular showplace. He added a lighthouse lamp which attracted attention up and down Broadway and flags along the roof's edge that attracted attention in daytime, while giant paintings of animals between the upper windows drew attention from pedestrians. The roof was transformed to a strolling garden with a view of the city, where he launched hot-air balloon rides daily. A changing series of live acts and curiosities were added to the exhibits of stuffed animals, including albinos
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
, giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
*Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'gi ...
, little people, jugglers, magicians, exotic women, detailed models of cities and famous battles, and a menagerie of animals.
Fiji mermaid and Tom Thumb
 In 1842 Barnum introduced his first major hoax: a creature with the body of a monkey and the tail of a fish known as the "Feejee" mermaid. He leased it from fellow museum owner
In 1842 Barnum introduced his first major hoax: a creature with the body of a monkey and the tail of a fish known as the "Feejee" mermaid. He leased it from fellow museum owner Moses Kimball
Moses Kimball (October 24, 1809 – February 21, 1895) was a US politician and showman. Kimball was a close associate of P. T. Barnum, and public-spirited citizen of Boston, Massachusetts.
Biography
Kimball was descended from Richard and Urs ...
of Boston who became his friend, confidant, and collaborator. Barnum justified his hoaxes by saying that they were advertisements to draw attention to the museum. "I don't believe in duping the public", he said, "but I believe in first attracting and then pleasing them."
He followed the mermaid by exhibiting Charles Stratton, the little person called "General Tom Thumb
Charles Sherwood Stratton (January 4, 1838 – July 15, 1883), better known by his stage name "General Tom Thumb", was an American dwarf who achieved great fame as a performer under circus pioneer P. T. Barnum.
Childhood and early life
Bo ...
" ("the Smallest Person that ever Walked Alone") who was then four years old but was stated to be 11. With heavy coaching and natural talent, the boy was taught to imitate people from Hercules to Napoleon.
In 1843 Barnum hired the Native American dancer fu-Hum-Me, the first of many First Nations people whom he presented. During 1844–45 he toured with General Tom Thumb in Europe and met Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
, who was amused but saddened by the little man, and the event was a publicity coup. It opened the door to visits from royalty throughout Europe, including the Tsar of Russia
This is a list of all reigning monarchs in the history of Russia. It includes the princes of medieval Rus′ state (both centralised, known as Kievan Rus′ and feudal, when the political center moved northeast to Vladimir and finally to Mos ...
, and enabled Barnum to acquire dozens of new attractions, including automatons and other mechanical marvels. During this time he went on a spending spree and bought other museums, including artist Rembrandt Peale
Rembrandt Peale (February 22, 1778 – October 3, 1860) was an American artist and museum keeper. A prolific portrait painter, he was especially acclaimed for his likenesses of presidents George Washington and Thomas Jefferson. Peale's style w ...
's Museum in Philadelphia, the nation's first major museum. By late 1846, Barnum's Museum was drawing 400,000 visitors a year.
Jenny Lind
 Barnum became aware of the popularity of Jenny Lind, the "Swedish Nightingale", during his European tour with Tom Thumb when her career was at its height in Europe. Barnum had never heard her and conceded to being unmusical himself,Rogers, Francis
Barnum became aware of the popularity of Jenny Lind, the "Swedish Nightingale", during his European tour with Tom Thumb when her career was at its height in Europe. Barnum had never heard her and conceded to being unmusical himself,Rogers, Francis"Jenny Lind"
''The Musical Quarterly'', Vol. 32, No. 3 (July 1946), pp. 437–48 but he approached her to sing in America at $1,000 a night for 150 nights, all expenses paid by him. He was confident that he could make use of Lind's reputation for morality and philanthropy in his publicity. Lind demanded the fee in advance and Barnum agreed; this permitted her to raise a fund for charities, principally endowing schools for poor children in Sweden.Miller, Philip L
"Review: P. T. Barnum Presents Jenny Lind: The American Tour of the Swedish Nightingale"
''American Music'', Spring 1983, pp. 78–80 Barnum borrowed heavily on his mansion and his museum to raise the money to pay Lind but he was still short of funds; so he persuaded a Philadelphia minister that Lind would be a good influence on American morals, and the minister lent him the final $6,000. The contract also gave Lind the option of withdrawing from the tour after 60 or 100 performances, paying Barnum $50,000 if she did so. Lind and her small company sailed to America in September 1850, but she was a celebrity even before she arrived because of Barnum's months of preparations; close to 40,000 people greeted her at the docks and another 20,000 at her hotel. The press was also in attendance, and "Jenny Lind items" were available to buy. When she realized how much money Barnum stood to make from the tour, she insisted on a new agreement which he signed on September 3, 1850. This gave her the original fee plus the remainder of each concert's profits after Barnum's $5,500 management fee. She was determined to accumulate as much money as possible for her charities.
 The tour began with a concert at
The tour began with a concert at Castle Garden
Castle Clinton (also known as Fort Clinton and Castle Garden) is a circular sandstone fort within Battery Park at the southern end of Manhattan in New York City. Built from 1808 to 1811, it was the first American immigration station, predating ...
on September 11, 1850, and it was a major success, recouping Barnum four times his investment. Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
proclaimed, "She is enough to counterbalance, of herself, all the evil that the world is threatened with by the great convention of women. So God save Jenny Lind!" Tickets for some of her concerts were in such demand that Barnum sold them by auction, and public enthusiasm was so strong that the press coined the term "Lind mania".Linkon, Sherry Lee"Reading Lind Mania: Print Culture and the Construction of Eighteenth-Century Audiences"
''Book History'', Vol. 1 (1998), pp. 94–106 The blatant commercialism of Barnum's ticket auctions distressed Lind, and she persuaded him to make a substantial number of tickets available at reduced prices."Jenny Lind's Progress in America", ''The Observer,'' October 6, 1850, p. 3 On the tour Barnum's publicity always preceded Lind's arrival and whipped up enthusiasm; he had up to 26 journalists on his payroll.Hambrick, Keith S
"P. T. Barnum Presents Jenny Lind – The American Tour of the Swedish Nightingale"
''Louisiana History: The Journal of the Louisiana Historical Association'', Vol. 22, No. 2 (Spring, 1981), pp. 208–09 After New York, the company toured the East Coast with continued success, and later went through the Southern states and Cuba. By early 1851, Lind had become uncomfortable with Barnum's relentless marketing of the tour, and she invoked a contractual right to sever her ties with him. They parted amicably, and she continued the tour for nearly a year under her own management. Lind gave 93 concerts in America for Barnum, earning her about $350,000, while Barnum netted at least $500,000 ().
Diversified leisure-time activities
Barnum's next challenge was to change public attitudes about the theater which was widely seen as a so-called "den of evil". He wanted to position theaters as palaces of edification and delight, and as respectable middle-class entertainment. He built New York City's largest and most modern theater, naming it the "Moral Lecture Room." He hoped that this would avoid seedy connotations, attract a family crowd, and win the approval of the moral crusaders of New York City. He started the nation's first theatrical matinées to encourage families and to lessen the fear of crime. He opened with '' The Drunkard,'' a thinly disguised temperance lecture (he had become a teetotaler after returning from Europe). He followed that with melodramas, farces, and historical plays put on by highly regarded actors. He watered down Shakespearean plays and others such as ''Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U ...
'' to make them family entertainment.
He organized flower shows, beauty contests, dog shows, and poultry contests, but the most popular were baby contests such as the fattest baby or the handsomest twins. In 1853 he started the pictorial weekly newspaper ''Illustrated News''; he completed his autobiography a year later which sold more than a million copies over the course of numerous revisions. Mark Twain loved the book, but the ''British Examiner'' thought it "trashy" and "offensive" and wrote that it inspired "nothing but sensations of disgust" and "sincere pity for the wretched man who compiled it".
In the early 1850s Barnum began investing to develop East Bridgeport, Connecticut. He made substantial loans to the Jerome Clock Company to get it to move to his new industrial area, but the company went bankrupt by 1856, taking Barnum's wealth with it. This started four years of litigation and public humiliation. Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
proclaimed that Barnum's downfall showed "the gods visible again" and other critics celebrated Barnum's public dilemma. But Tom Thumb offered his services, as he was touring on his own, and the two undertook another European tour. Barnum also started a lecture tour, mostly as a temperance speaker. By 1860, he emerged from debt and built a mansion which he called "Lindencroft", and he resumed ownership of his museum.
 Barnum went on to create America's first aquarium and to expand the wax figure department of his museum. His "Seven Grand Salons" demonstrated the Seven Wonders of the World. The collections expanded to four buildings, and he published a "Guide Book to the Museum" which claimed 850,000 "curiosities". Late in 1860,
Barnum went on to create America's first aquarium and to expand the wax figure department of his museum. His "Seven Grand Salons" demonstrated the Seven Wonders of the World. The collections expanded to four buildings, and he published a "Guide Book to the Museum" which claimed 850,000 "curiosities". Late in 1860, Siamese Twins
Conjoined twins – sometimes popularly referred to as Siamese twins – are twins joined ''in utero''. A very rare phenomenon, the occurrence is estimated to range from 1 in 49,000 births to 1 in 189,000 births, with a somewhat higher incidence ...
Chang and Eng
Chang Bunker and Eng Bunker (May 11, 1811 – January 17, 1874) were Siamese-American conjoined twin brothers whose fame propelled the expression " Siamese twins" to become synonymous for conjoined twins in general. They were widely exhibited as ...
came out of retirement because they needed more money to send their numerous children to college. They had a touring career on their own and went to live on a North Carolina plantation with their families and slaves under the name of Bunker. They also appeared at Barnum's Museum for six weeks. Also in 1860, Barnum introduced "man-monkey" William Henry Johnson, a microcephalic
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
black little person who spoke a mysterious language created by Barnum. In 1862 he discovered giantess Anna Swan and Commodore Nutt, a new Tom Thumb with whom Barnum visited President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
at the White House. During the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, his museum drew large audiences seeking diversion from the conflict. He added pro-Unionist exhibits, lectures, and dramas, and he demonstrated commitment to the cause. He hired Pauline Cushman in 1864, an actress who had served as a spy for the Union, to lecture about her "thrilling adventures" behind Confederate lines. Barnum's Unionist sympathies incited a Confederate sympathizer to start a fire in 1864. Barnum's American Museum burned to the ground on July 13, 1865, from a fire of unknown origin. Barnum re-established it at another location in New York City, but this also was destroyed by fire in March 1868. The loss was too great the second time, and Barnum retired from the museum business.
Circus King

 Barnum did not enter the circus business until he was 60 years old. He established "P. T. Barnum's Grand Traveling Museum, Menagerie, Caravan &
Barnum did not enter the circus business until he was 60 years old. He established "P. T. Barnum's Grand Traveling Museum, Menagerie, Caravan & Hippodrome
The hippodrome ( el, ἱππόδρομος) was an ancient Greek stadium for horse racing and chariot racing. The name is derived from the Greek words ''hippos'' (ἵππος; "horse") and ''dromos'' (δρόμος; "course"). The term is used i ...
" in Delavan, Wisconsin
Delavan is a city in Walworth County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 8,505 at the 2020 census. It is located southwest of Milwaukee. The city is located partially within the Town of Delavan, but the two entities are politically i ...
, in 1870 with William Cameron Coup
William Cameron Coup (August 4, 1836 – March 4, 1895) was a Wisconsin businessman who partnered with P. T. Barnum and Dan Castello in 1870 to form the "P. T. Barnum's Museum, Menagerie and Circus". Previously Barnum had a museum at a fixed loc ...
; it was a traveling circus, menagerie, and museum of "freaks". It went through various names: "P. T. Barnum's Travelling World's Fair, Great Roman Hippodrome and Greatest Show on Earth", and "P. T. Barnum's Greatest Show on Earth, And The Great London Circus, Sanger's Royal British Menagerie and The Grand International Allied Shows United" after an 1881 merger with James Bailey and James L. Hutchinson, soon shortened to "Barnum & Bailey's". This entertainment phenomenon was the first circus to display three rings. The show's first primary attraction was Jumbo
Jumbo (about December 25, 1860 – September 15, 1885), also known as Jumbo the Elephant and Jumbo the Circus Elephant, was a 19th-century male African bush elephant born in Sudan. Jumbo was exported to Jardin des Plantes, a zoo in Paris, and t ...
, an African elephant that Barnum purchased in 1882 from the London Zoo. The Barnum and Bailey Circus still contained acts similar to his Traveling Menagerie, including acrobats, freak shows, and General Tom Thumb. Barnum persisted in growing the circus in spite of more fires, train disasters, and other setbacks, and he was aided by circus professionals who ran the daily operations. He and Bailey split up in 1885, but they came back together in 1888 with the "Barnum & Bailey Greatest Show On Earth", later "Barnum & Bailey Circus
The Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus (also known as the Ringling Bros. Circus, Ringling Bros., the Barnum & Bailey Circus, Barnum & Bailey, or simply Ringling) is an American traveling circus company billed as The Greatest Show on Ear ...
" which toured the world.
Barnum was one of the first circus owners to move his circus by train, on the suggestion of Bailey and other business partners, and probably the first to own his own train. Given the lack of paved highways in America at that time, this turned out to be a shrewd decision that vastly expanded Barnum's geographical reach. In this new industry, Barnum leaned more on the advice of his partners, most of whom were young enough to be his sons.
Barnum became known as the "Shakespeare of Advertising" due to his innovative and impressive ideas.
Author and debunker
 Barnum wrote several books, including ''Life of P. T. Barnum'' (1855), ''The Humbugs of the World'' (1865), ''Struggles and Triumphs'' (1869), ''Forest and jungle, or, Thrilling adventures in all quarters of the globe :'' and ''The Art of Money-Getting'' (1880).
Barnum was often referred to as the "Prince of Humbugs", and he saw nothing wrong in entertainers or vendors using hoaxes (or "humbug", as he termed it) in promotional material, as long as the public was getting value for money. However, he was contemptuous of those who made money through fraud, especially the spiritualist mediums popular in his day; he testified against noted "spirit photographer" William H. Mumler in his trial for fraud, and he exposed "the tricks of the trade" used by mediums to cheat the bereaved. In ''The Humbugs of the World'', he offered $500 (about $9,000 in 2021) to any medium who could prove power to communicate with the dead.
Barnum wrote several books, including ''Life of P. T. Barnum'' (1855), ''The Humbugs of the World'' (1865), ''Struggles and Triumphs'' (1869), ''Forest and jungle, or, Thrilling adventures in all quarters of the globe :'' and ''The Art of Money-Getting'' (1880).
Barnum was often referred to as the "Prince of Humbugs", and he saw nothing wrong in entertainers or vendors using hoaxes (or "humbug", as he termed it) in promotional material, as long as the public was getting value for money. However, he was contemptuous of those who made money through fraud, especially the spiritualist mediums popular in his day; he testified against noted "spirit photographer" William H. Mumler in his trial for fraud, and he exposed "the tricks of the trade" used by mediums to cheat the bereaved. In ''The Humbugs of the World'', he offered $500 (about $9,000 in 2021) to any medium who could prove power to communicate with the dead.
Role in politics
Barnum was significantly involved in politics. He mainly focused on race, slavery, and sectionalism in the period leading up to theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
. He opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
of 1854, which supported slavery, so he left the Democratic Party which endorsed slavery and became part of the new anti-slavery Republican Party.
Barnum claimed that "politics were always distasteful to me", yet he was elected to the Connecticut legislature in 1865 as Republican representative for Fairfield and served four terms. He hired spies to get insider information on the New York and New Haven Railroad lines and exposed a secret that would raise fares by 20 percent. He said during the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Thirteenth Amendment (Amendment XIII) to the United States Constitution abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. The amendment was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, by the House of Representative ...
: "A human soul, 'that God has created and Christ died for,' is not to be trifled with. It may tenant the body of a Chinaman, a Turk, an Arab or a Hottentot—it is still an immortal spirit." He also acknowledged that he had owned slaves when he lived in the South. "I whipped my slaves. I ought to have been whipped a thousand times for this myself. But then I was a Democrat—one of those ''nondescript'' Democrats, who are Northern men with Southern principles".
Barnum was elected for the next four sessions and succeeded Senator Orris S. Ferry. He was the legislative sponsor of a law enacted by the Connecticut General Assembly in 1879 which prohibited the use of "any drug, medicinal article or instrument for the purpose of preventing conception", and also made it a crime to act as an accessory to the use of contraception; this law remained in effect in Connecticut until it was overturned in 1965 by the U.S. Supreme Court in ''Griswold v. Connecticut
''Griswold v. Connecticut'', 381 U.S. 479 (1965), was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protects the liberty of married couples to buy and use contraceptives withou ...
''. He ran for Congress in 1867 and lost to his third cousin William Henry Barnum. In 1875, he worked as mayor of Bridgeport, Connecticut, to improve the water supply, bring gas lighting to streets, and enforce liquor and prostitution laws. He was instrumental in starting Bridgeport Hospital
Bridgeport Hospital is a not-for-profit general medical and surgical hospital in Bridgeport, Connecticut. It is a member of Yale New Haven Health System and affiliated with Yale School of Medicine. During 2018, Bridgeport Hospital received profes ...
, founded in 1878, and was its first president.
Profitable philanthropy
Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
prior to its founding, and he made several significant contributions to the fledgling institution, including a gift of $50,000 () in 1883 to establish a museum (later known as Barnum Museum of Natural History) and hall for the Department of Natural History. Tufts made Jumbo the elephant the school's mascot, and Tufts students are known as "Jumbos".
Personal life and death
On November 8, 1829, Barnum married Charity Hallett, and they had four children: Caroline Cornelia (1833–1911), Helen Maria (1840–1915), Frances Irena (1842–1844), and Pauline Taylor (1846–1877). His wife died on November 19, 1873, and he marriedNancy Fish
Nancy Fish Barnum Callias D'Orengiani, Baroness (née Fish; 22 April 1850 – 23 June 1927) was an English socialite, daughter of a successful cotton miller and the second wife of P. T. Barnum, 40 years her senior. After the death of Barnum's ...
, the daughter of his close friend John Fish, the following year; Nancy was 40 years younger than he was.
Barnum died from a stroke at home in 1891 aged 80. He is buried in Mountain Grove Cemetery, Bridgeport, Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
, a cemetery that he designed.
Legacy
Barnum built four mansions in Bridgeport, Connecticut:Iranistan
Iranistan was a Moorish Revival mansion in Bridgeport, Connecticut commissioned by P. T. Barnum in 1848. It was designed by Bohemian-American architect Leopold Eidlitz. At this "beautiful country seat"
, Lindencroft, Waldemere, and Marina. Iranistan was the most notable, a Moorish Revival
Moorish Revival or Neo-Moorish is one of the exotic revival architectural styles that were adopted by architects of Europe and the Americas in the wake of Romanticist Orientalism. It reached the height of its popularity after the mid-19th centu ...
architecture designed by Leopold Eidlitz
Leopold Eidlitz (March 10, 1823, Prague, Bohemia – March 22, 1908, New York City) was a prominent New York architect best known for his work on the New York State Capitol (Albany, New York, 1876–1881), as well as " Iranistan" (1848), P. T. B ...
with domes, spires, and lacy fretwork inspired by the Royal Pavilion
The Royal Pavilion, and surrounding gardens, also known as the Brighton Pavilion, is a Grade I listed former royal residence located in Brighton, England. Beginning in 1787, it was built in three stages as a seaside retreat for George, Princ ...
in Brighton, England. It was built in 1848 but it burned down in 1857. The Marina Mansion was demolished by the University of Bridgeport in 1964 in order to build their cafeteria.
At his death, critics praised Barnum for good works and called him an icon of American spirit and ingenuity. He asked the ''Evening Sun'' to print his obituary just prior to his death so that he might read it. On April 7, 1891, Barnum asked about the box-office receipts for the day; a few hours later, he was dead.
In 1893, a statue in his honor was placed by his former partners James Bailey, James A. Hutchinson, and W. W. Cole, at Seaside Park in Bridgeport. Barnum had donated the land for this park in 1865. His circus was sold to Ringling Brothers
The Ringling brothers (originally Rüngling) were seven American siblings who transformed their small touring company of performers into one of the largest circuses in the United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Four brothers ...
on July 8, 1907, for $400,000 (about $10.45 million in 2017 dollars). The Ringling Brothers and Barnum & Bailey circuses ran separately until they merged in 1919, forming the Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus.
The United States Mint issued a commemorative coin
Commemorative coins are coins issued to commemorate some particular event or issue with a distinct design with reference to the occasion on which they were issued. Many coins of this category serve as collectors items only, although some countries ...
in 1936 for Bridgeport's centennial celebration, with Barnum's portrait for the obverse. Cartoonist Walt Kelly
Walter Crawford Kelly Jr. (August 25, 1913 – October 18, 1973), commonly known as Walt Kelly, was an American animator and cartoonist, best known for the comic strip '' Pogo''. He began his animation career in 1936 at Walt Disney Studios, contr ...
grew up in Bridgeport and named a character in Barnum's honor in his '' Pogo'' comic strip. An annual six-week Barnum Festival was held for many years in Bridgeport as a tribute to Barnum. The Bethel Historical Society commissioned a life-sized sculpture to honor the 200th anniversary of his birth, created by local resident David Gesualdi and placed outside the public library. The statue was dedicated on September 26, 2010.
Barnum co-founded the Bridgeport & Port Jefferson Steamboat Company in 1883 with Charles E. Tooker, which continues to operate across the Long Island Sound between Port Jefferson, New York
Port Jefferson (informally known as "Port Jeff") is an incorporated village in the town of Brookhaven in Suffolk County, New York, on the North Shore of Long Island. Officially known as the Incorporated Village of Port Jefferson, the population ...
, and Bridgeport. The company owns and operates three vessels, one of which is named the M.V. ''PT Barnum''. The Barnum Museum
The Barnum Museum is a museum at 820 Main Street in Bridgeport, Connecticut, United States. It has an extensive collection related to P. T. Barnum and the history of Bridgeport, and is housed in a historic building on the National Register o ...
in Bridgeport houses many of Barnum's oddities and curiosities.
In popular culture
Films and television
* ''A Lady's Morals
''A Lady's Morals'' is a 1930 American pre-Code film offering a highly fictionalized account of opera singer Jenny Lind. The movie features Grace Moore as Lind, Reginald Denny as a lover, and Wallace Beery as P. T. Barnum. The film contains so ...
'' (1930) – played by Wallace Beery
Wallace Fitzgerald Beery (April 1, 1885 – April 15, 1949) was an American film and stage actor. He is best known for his portrayal of Bill in '' Min and Bill'' (1930) opposite Marie Dressler, as General Director Preysing in '' Grand Hotel'' ( ...
* '' Jenny Lind'' (1932) – played by André Berley
André Berley (13 January 1890 – 26 November 1936) was a French actor.
Berley was born André Edmond Obrecht in the 6th arrondissement of Paris.
Selected filmography
* ''The Passion of Joan of Arc'' (1928)
* '' Olimpia'' (1930)
* '' The ...
* ''The Mighty Barnum
''The Mighty Barnum'' is a 1934 film starring Wallace Beery as P.T. Barnum. The movie was written by Gene Fowler and Bess Meredyth, adapted from their play of the same name, and directed by Walter Lang. Beery had played Barnum four years earlie ...
'' (1934) – played again by Wallace Beery
* '' The Greatest Show on Earth'' (1952) – centers around a fictionalized version of the contemporary Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus, although Barnum is neither the subject of the film nor a character in it
* ''Jules Verne's Rocket to the Moon
''Jules Verne's Rocket to the Moon'' is a 1967 Eastman color British science fiction comedy film directed by Don Sharp and starring Burl Ives, Troy Donahue, Gert Fröbe and Terry-Thomas.
It was released in the US as ''Those Fantastic Flying Foo ...
'' (1967) – played by Burl Ives
Burl Icle Ivanhoe Ives (June 14, 1909 – April 14, 1995) was an American musician, actor, and author with a career that spanned more than six decades.
Ives began his career as an itinerant singer and guitarist, eventually launching his own rad ...
* ''Barnum!'' (1986) – played by Michael Crawford
Michael Patrick Smith, (born 19 January 1942), known professionally as Michael Crawford, is an English tenor, actor and comedian.
Crawford is best known for playing both the hapless Frank Spencer in the sitcom '' Some Mothers Do 'Ave 'Em'' a ...
; a filmed version of the Broadway musical (see below), filmed in London
* ''Barnum'' (1986) – played by Burt Lancaster; made-for-TV movie
* ''P. T. Barnum'' (1999) – played by Beau Bridges; made-for-TV movie
* ''Gangs of New York
''Gangs of New York'' is a 2002 American epic historical drama film directed by Martin Scorsese and written by Jay Cocks, Steven Zaillian and Kenneth Lonergan, based on Herbert Asbury's 1927 book '' The Gangs of New York''. The film stars Le ...
'' (2002) – played by Roger Ashton-Griffiths
Roger Ashton-Griffiths (born 19 January 1957) is an English character actor, screenwriter and film director. He is best known for his role as Mace Tyrell in the HBO fantasy series ''Game of Thrones''.
Life and career
Born in Hertfordshire, ...
* ''The Greatest Showman
''The Greatest Showman'' is a 2017 American biographical musical drama film directed by Michael Gracey in his directorial debut, written by Jenny Bicks and Bill Condon and starring Hugh Jackman, Zac Efron, Michelle Williams, Rebecca Ferguson, ...
'' (2017) – a musical loosely based around P. T. Barnum and his circus. Hugh Jackman
Hugh Michael Jackman (born 12 October 1968) is an Australian actor. Beginning in theatre and television, he landed his breakthrough role as James "Logan" Howlett / Wolverine in the 20th Century Fox ''X-Men'' film series (2000–2017), a role ...
plays Barnum and co-produced the film
* '' I Didn't See You There'' (2022) – a disabled filmmaker from P. T. Barnum's hometown Bethel, CT meditates on the ableist legacy of the freak show
Theater
* ''Barnum
Phineas Taylor Barnum (; July 5, 1810 – April 7, 1891) was an American showman, businessman, and politician, remembered for promoting celebrated hoaxes and founding the Barnum & Bailey Circus (1871–2017) with James Anthony Bailey. He wa ...
'' (1980) – Broadway musical based on Barnum's life, with Jim Dale
Jim Dale (born James Smith; 15 August 1935) is an English actor, composer, director, narrator, singer and songwriter. In the United Kingdom he is known as a pop singer of the 1950s who became a leading actor at the National Theatre. In Britis ...
in the title role
Books
* ''The Great and Only Barnum; the Tremendous, Stupendous Life of Showman P. T. Barnum''Music
* "U.S. Blues" – a song on the album '' From the Mars Hotel'' by the Grateful DeadPublications
* ''The Life of P. T. Barnum: Written by Himself''. Originally published New York: Redfield, 1855. Reprint: Champaign: University of Illinois Press, 2000. . * ''Struggles and Triumphs, or Forty Years' Recollections of P. T. Barnum''. Originally published 1869. Reprint: Whitefish, MT: Kessinger, 2003. (Part 1) and (Part 2). . * ''Art of Money Getting, or, Golden Rules for Making Money''. Originally published 1880. Reprint: Bedford, MA: Applewood, 1999. . * ''The Wild Beasts, Birds, and Reptiles of the World: The Story of Their Capture''. Pub. 1888, R. S. Peale & Company, Chicago. * ''Why I Am a Universalist''. Originally published 1890. Reprint: Kessinger Pub Co. .See also
*Barnum effect
The Barnum effect, also called the Forer effect or, less commonly, the Barnum–Forer effect, is a common psychological phenomenon whereby individuals give high accuracy ratings to descriptions of their personality that supposedly are tailored ...
* Barnum's Aquarial Gardens, Boston, Massachusetts (1862–1863)
* Cardiff Giant
* Carl Hagenbeck
* Colonel Routh Goshen
Routh Goshen, born Arthur James Caley (1824 – February 12, 1889) was most commonly known as Colonel Routh Goshen or the Arabian Giant or the Palestine Giant. He was billed as the tallest man in the world at 7 ft, 11 inches (2.41 ...
* Fedor Jeftichew
* Human zoo
Human zoos, also known as ethnological expositions, were public displays of people, usually in a so-called "natural" or "primitive" state. They were most prominent during the 19th and 20th centuries. These displays sometimes emphasized the sup ...
* Isaac W. Sprague
* Jenny Lind private railroad car
The Jenny Lind private railroad car is the first specifically outfitted private railway coach. It was used on Jenny Lind's Jenny Lind tour of America, 1850–52, singing tour of the United States.
History
The idea of a private railroad car c ...
* Lucia Zarate Lucia may refer to:
Arts and culture
* ''Lucía'', a 1968 Cuban film by Humberto Solás
* ''Lucia'' (film), a 2013 Kannada-language film
* '' Lucia & The Best Boys'', a Scottish indie rock band formerly known as ''LUCIA''
* "Lucia", a Swedish c ...
* Nellie Keeler
* '' The Greatest Show on Earth'', 1952 film
* Wild Men of Borneo
* Zip the Pinhead
References
Further reading
* Adams, Bluford. ''E Pluribus Barnum: The Great Showman and the Making of U.S. Popular Culture''. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1997. . * Alderson, William T., ed. ''Mermaids, Mummies, and Mastodons: The Emergence of the American Museum''. Washington, DC: American Association of Museums for the Baltimore City Life Museums, 1992. * Barnum, Patrick Warren. ''Barnum Genealogy: 650 Years of Family History''. Boston: Higginson Book Co., 2006. (hardcover), (softcover), * Benton, Joel. ''The Life of Phineas T. Barnum''* Betts, John Rickards. "P. T. Barnum and the Popularization of Natural History", ''Journal of the History of Ideas'' 20, no. 3 (1959): 353–368. * * Cook, James W. ''The Arts of Deception: Playing with Fraud in the Age of Barnum''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2001. . Relates Barnum's Fiji Mermaid and What Is It? exhibits to other popular arts of the nineteenth century, including magic shows and ''
trompe-l'œil
''Trompe-l'œil'' ( , ; ) is an artistic term for the highly realistic optical illusion of three-dimensional space and objects on a two-dimensional surface. ''Trompe l'oeil'', which is most often associated with painting, tricks the viewer into ...
'' paintings.
* Harding, Les. ''Elephant Story: Jumbo and P. T. Barnum Under the Big Top''. Jefferson, NC.: McFarland & Co., 2000. . (129 p.)
* Harris, Neil. ''Humbug: The Art of P. T. Barnum''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1973. .
*
*
* Reiss, Benjamin. ''The Showman and the Slave: Race, Death, and Memory in Barnum's America''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2001. . Focuses on Barnum's exhibition of Joice Heth
Joice Heth (February 19, 1836)"Joice Heth", Hoaxes.org was an African-American woman who was exhibited by P.T. Barnum with the false claim that she was the 161-year-old nursing mammy of George Washington. Her exhibition under these claims, and ...
.
* Saxon, Arthur H. ''P. T. Barnum: The Legend and the Man''. New York: Columbia University Press, 1995. .
* Uchill, Ida Libert. ''Howdy, Sucker! What P. T. Barnum Did in Colorado''. Denver: Pioneer Peddler Press, 2001.
* Jefferson, Margo. ''On Michael Jackson''. New York: Pantheon, 2006. . Critique of Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the "King of Pop", he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural figures of the 20th century. Over a ...
, including his obsession with P. T. Barnum and "Freaks."
* ''The Colossal P. T. Barnum Reader: Nothing Else Like It in the Universe''. Ed. by James W. Cook. Champaign, University of Illinois Press
The University of Illinois Press (UIP) is an American university press and is part of the University of Illinois system. Founded in 1918, the press publishes some 120 new books each year, plus 33 scholarly journals, and several electronic proje ...
, 2005. .
* Woolf, John. ''The Wonders: Lifting the Curtain on the Freak Show, Circus and Victorian Age'' (London: Michael O'Mara, 2019)
External links
;Digital collections * * * * ;Physical collectionsThe Barnum Museum
Phineas Taylor Barnum papers, 1818–1993
– A virtual reproduction of Barnum's American Museum; includes a collection of primary source materials ;Biographical information
at the ''Barnum Family Genealogy'' website *
P. T. Barnum at Ringling Brothers and Barnum and Bailey Circus
Entry on P. T. Barnum in the Concise Encyclopedia of Tufts History
* Full text of
The Life of Phineas T. Barnum
' by Joel Benton, from
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital libr ...
;Scholarship and analysis
Barnum's circus affiliation
P.T. Barnum – Ultrarunning Promoter (1874)
– An article about Barnum's handwriting & signature
* ttp://www.ptbarnum.org P. T. Barnum, the Shakespeare of Advertising
P. T. Barnum and Henry Bergh
Bergh was founder of the
American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to preventing animal cruelty. Based in New York City since its inception in 1866, the organization's mission is "to provide effective me ...
(ASPCA).
;Other links
Facebook Page
Bethel Historical Society, P. T. Barnum Monument, "P. T. Barnum – The Lost Legend" Documentary.
An 1890 recording of Barnum's voice
Marina Mansion
Tribute to Ringling Bros.and Barnum & Bailey Circus by brothers Charles Elias Disney & Daniel H. Disney
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Barnum, P. T. * 1810 births 1891 deaths American entertainment industry businesspeople 19th-century American memoirists Burials at Mountain Grove Cemetery, Bridgeport Connecticut Democrats Connecticut Republicans Mayors of Bridgeport, Connecticut Members of the Connecticut House of Representatives Businesspeople from Bridgeport, Connecticut People from Fairfield, Connecticut Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus Members of the Universalist Church of America 19th-century Christian universalists 19th-century American people 19th-century American politicians Circus owners American slave owners American abolitionists Christian abolitionists 19th-century American businesspeople Museum founders