Old Continent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Europe is a large
 In classical
In classical
The prevalent definition of Europe as a geographical term has been in use since the mid-19th century.
Europe is taken to be bounded by large bodies of water to the north, west and south; Europe's limits to the east and north-east are usually taken to be the  Islands are generally grouped with the nearest continental landmass, hence
Islands are generally grouped with the nearest continental landmass, hence
 The first recorded usage of ''Eurṓpē'' as a geographic term is in the
The first recorded usage of ''Eurṓpē'' as a geographic term is in the

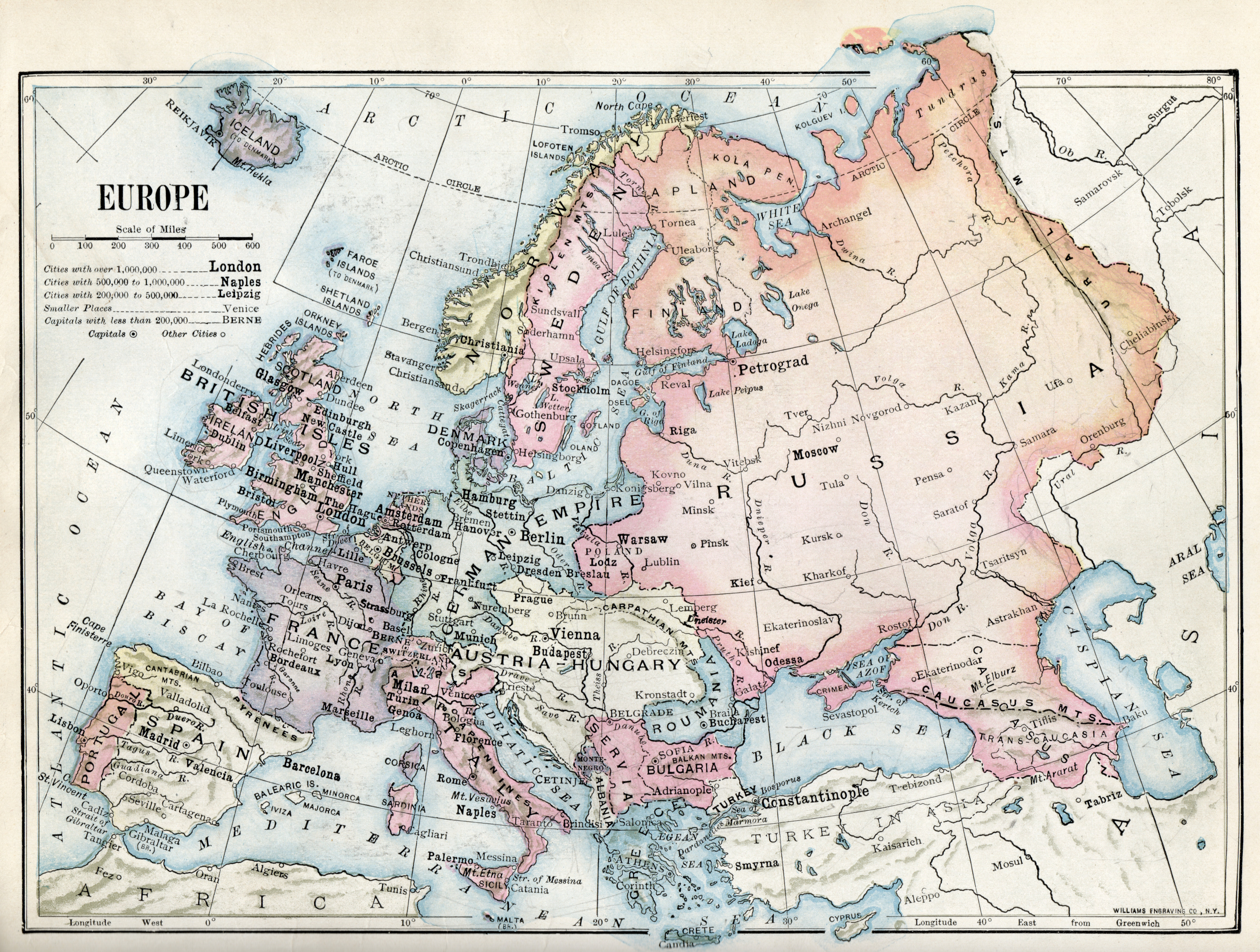 The question of defining a precise eastern boundary of Europe arises in the Early Modern period, as the eastern extension of
The question of defining a precise eastern boundary of Europe arises in the Early Modern period, as the eastern extension of
 During the 2.5 million years of the
During the 2.5 million years of the
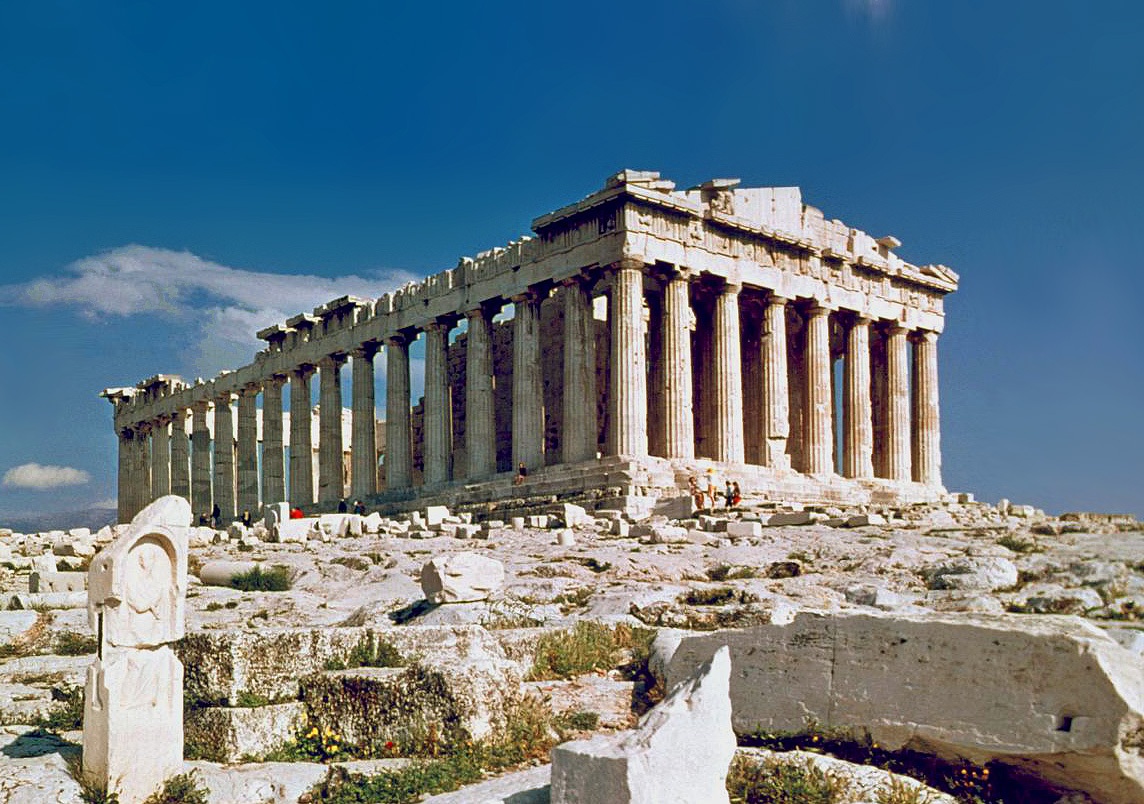 Ancient Greece was the founding culture of Western civilisation. Western democratic and rationalist culture are often attributed to Ancient Greece. The Greek city-state, the
Ancient Greece was the founding culture of Western civilisation. Western democratic and rationalist culture are often attributed to Ancient Greece. The Greek city-state, the 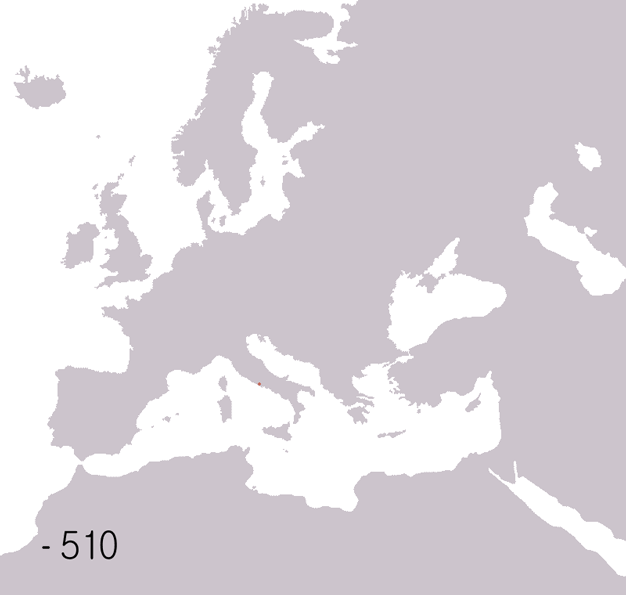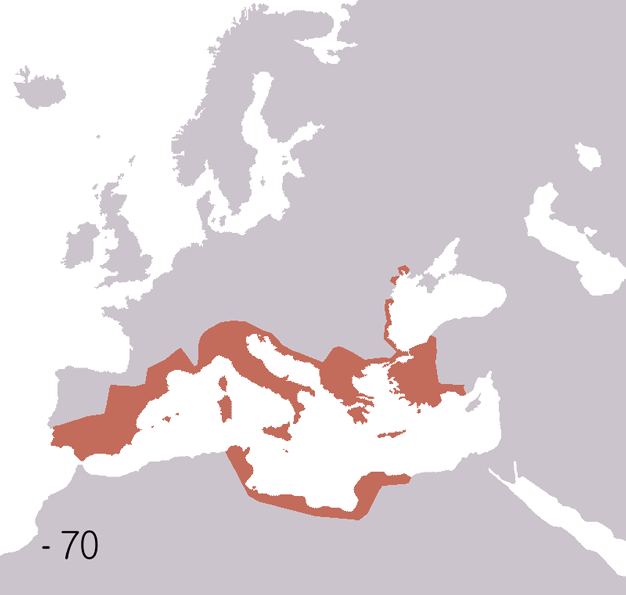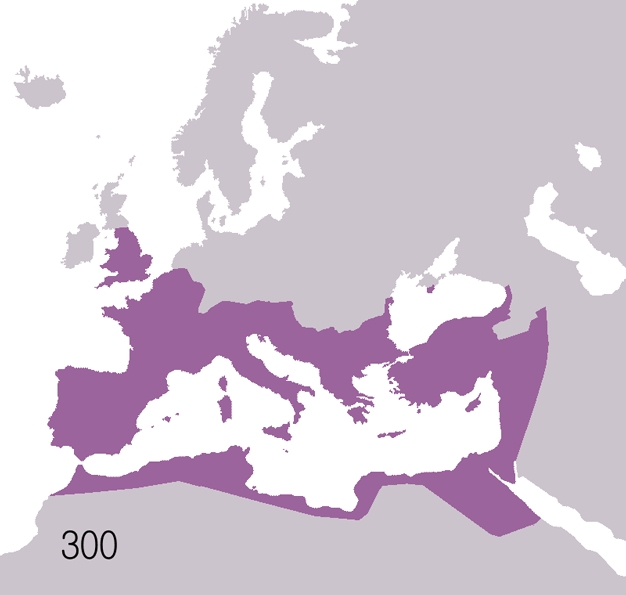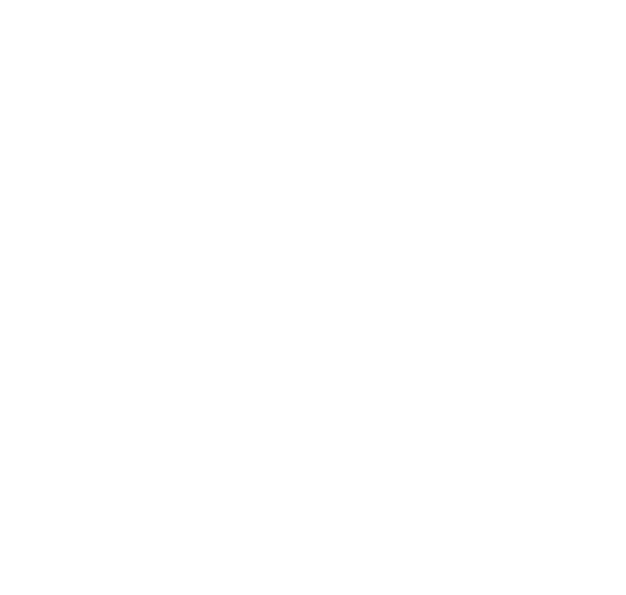 Greece was followed by
Greece was followed by
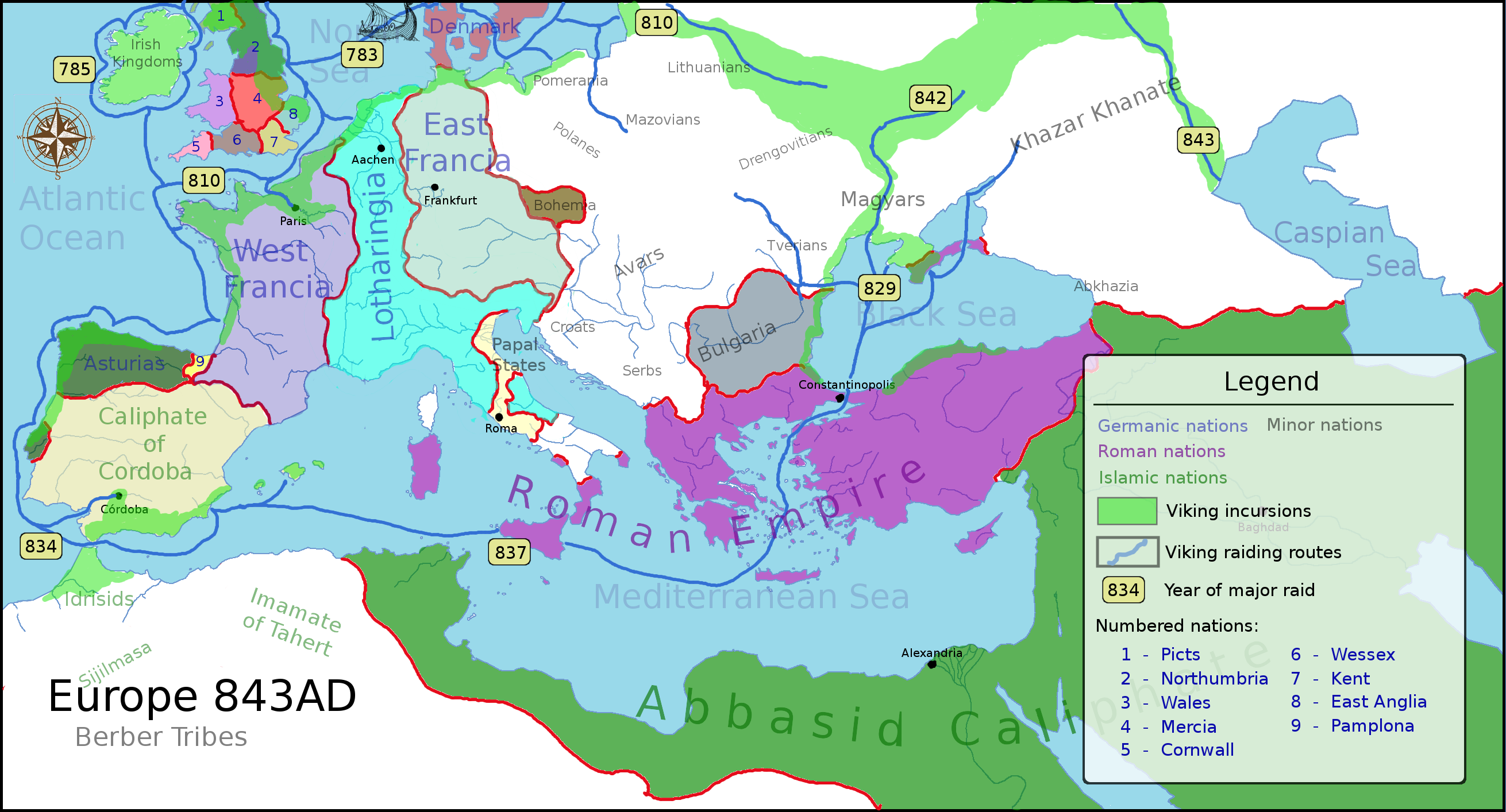 During the Dark Ages, the
During the Dark Ages, the
 The period between the year 1000 and 1250 is known as the High Middle Ages, followed by the Late Middle Ages until c. 1500.
During the High Middle Ages the population of Europe experienced significant growth, culminating in the Renaissance of the 12th century. Economic growth, together with the lack of safety on the mainland trading routes, made possible the development of major commercial routes along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Baltic Seas. The growing wealth and independence acquired by some coastal cities gave the Maritime Republics a leading role in the European scene.
The Middle Ages on the mainland were dominated by the two upper echelons of the social structure: the nobility and the clergy. Feudalism developed in
The period between the year 1000 and 1250 is known as the High Middle Ages, followed by the Late Middle Ages until c. 1500.
During the High Middle Ages the population of Europe experienced significant growth, culminating in the Renaissance of the 12th century. Economic growth, together with the lack of safety on the mainland trading routes, made possible the development of major commercial routes along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Baltic Seas. The growing wealth and independence acquired by some coastal cities gave the Maritime Republics a leading role in the European scene.
The Middle Ages on the mainland were dominated by the two upper echelons of the social structure: the nobility and the clergy. Feudalism developed in  The Papacy reached the height of its power during the High Middle Ages. An East-West Schism in 1054 split the former Roman Empire religiously, with the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Catholic Church in the former Western Roman Empire. In 1095 Pope Urban II called for a Crusades, crusade against Muslims occupying Jerusalem and the Holy Land.National Geographic, 192. In Europe itself, the Church organised the Inquisition against heretics. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Reconquista concluded with the Granada War#Last stand at Granada, fall of Granada in 1492, ending over seven centuries of Islamic rule in the south-western peninsula.National Geographic, 199.
In the east, a resurgent Byzantine Empire recaptured Crete and Cyprus from the Muslims, and reconquered the Balkans. Constantinople was the largest and wealthiest city in Europe from the 9th to the 12th centuries, with a population of approximately 400,000. The Empire was weakened following the defeat at Battle of Manzikert, Manzikert, and was weakened considerably by the Siege of Constantinople (1204), sack of Constantinople in 1204, during the Fourth Crusade. Although it would recover Constantinople in 1261, Byzantine Empire, Byzantium Fall of Constantinople, fell in 1453 when Fall of Constantinople, Constantinople was taken by the Ottoman Empire.National Geographic, 211.
The Papacy reached the height of its power during the High Middle Ages. An East-West Schism in 1054 split the former Roman Empire religiously, with the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Catholic Church in the former Western Roman Empire. In 1095 Pope Urban II called for a Crusades, crusade against Muslims occupying Jerusalem and the Holy Land.National Geographic, 192. In Europe itself, the Church organised the Inquisition against heretics. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Reconquista concluded with the Granada War#Last stand at Granada, fall of Granada in 1492, ending over seven centuries of Islamic rule in the south-western peninsula.National Geographic, 199.
In the east, a resurgent Byzantine Empire recaptured Crete and Cyprus from the Muslims, and reconquered the Balkans. Constantinople was the largest and wealthiest city in Europe from the 9th to the 12th centuries, with a population of approximately 400,000. The Empire was weakened following the defeat at Battle of Manzikert, Manzikert, and was weakened considerably by the Siege of Constantinople (1204), sack of Constantinople in 1204, during the Fourth Crusade. Although it would recover Constantinople in 1261, Byzantine Empire, Byzantium Fall of Constantinople, fell in 1453 when Fall of Constantinople, Constantinople was taken by the Ottoman Empire.National Geographic, 211.
 In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Cuman-Kipchak Confederation, Cuman-Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic peoples, Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north, and temporarily halted the expansion of the Rus' state to the south and east. Like many other parts of
In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Cuman-Kipchak Confederation, Cuman-Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic peoples, Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north, and temporarily halted the expansion of the Rus' state to the south and east. Like many other parts of
 The Renaissance was a period of cultural change originating in Florence, and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The rise of a Renaissance humanism, new humanism was accompanied by the recovery of forgotten Classical Greece, classical Greek and Arabic knowledge from Monasticism, monastic libraries, often translated from Arabic into Latin language, Latin. The Renaissance spread across Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries: it saw the flowering of
The Renaissance was a period of cultural change originating in Florence, and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The rise of a Renaissance humanism, new humanism was accompanied by the recovery of forgotten Classical Greece, classical Greek and Arabic knowledge from Monasticism, monastic libraries, often translated from Arabic into Latin language, Latin. The Renaissance spread across Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries: it saw the flowering of 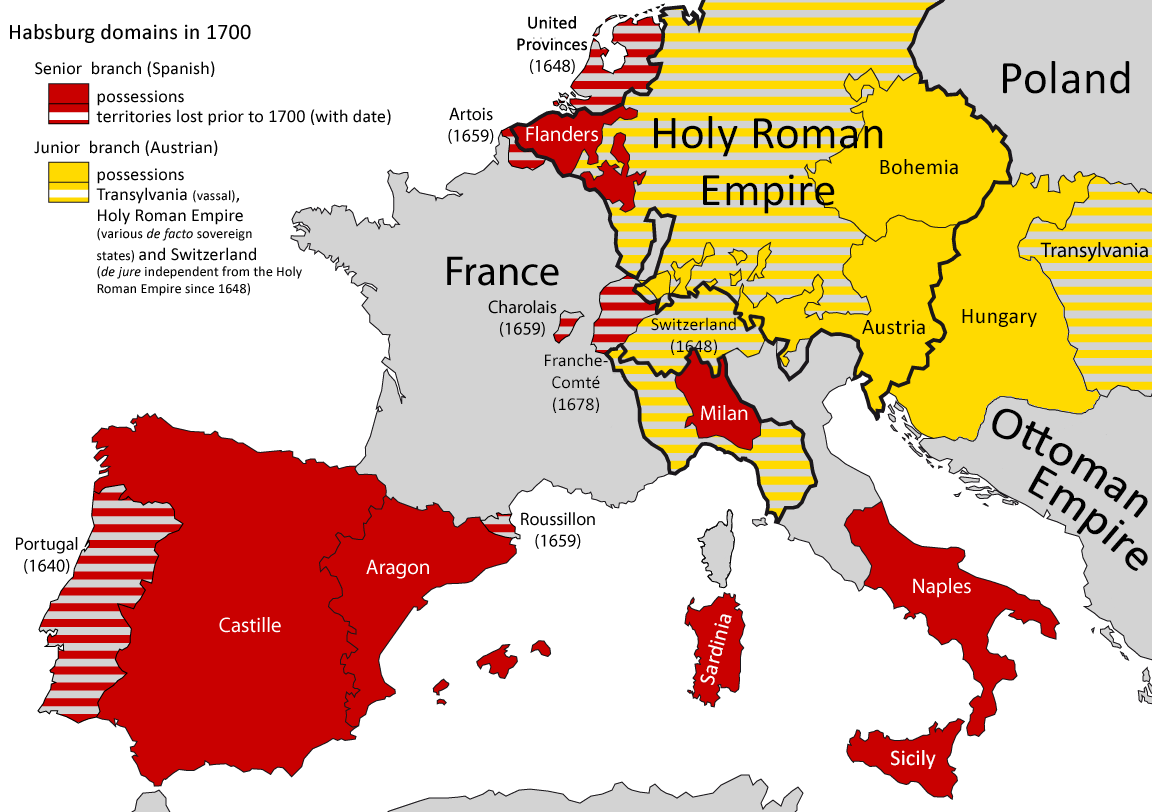 The Church's power was further weakened by the Protestant reformation, Protestant Reformation in 1517 when German theologian Martin Luther nailed his ''Ninety-five Theses'' criticising the selling of indulgences to the church door. He was subsequently excommunicated in the papal bull ''Exsurge Domine'' in 1520 and his followers were condemned in the 1521 Diet of Worms, which divided German princes between Protestant and Roman Catholic faiths.National Geographic, 256–257. European wars of religion, Religious fighting and warfare spread with Protestantism. The plunder of the empires of the Americas allowed Spain to finance Spanish Inquisition, religious persecution in Europe for over a century. The Thirty Years War (1618–1648) crippled the Holy Roman Empire and devastated much of Early Modern history of Germany, Germany, killing between 25 and 40 percent of its population. In the aftermath of the Peace of Westphalia, France rose to predominance within Europe.National Geographic, 269. The defeat of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the historic end of Ottoman wars in Europe, Ottoman expansion into Europe.
The 17th century in central and parts of eastern Europe was a period of general The General Crisis, decline; the region experienced more than 150 famines in a 200-year period between 1501 and 1700. From the Union of Krewo (1385) east-central Europe was dominated by the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The hegemony of the vast Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had ended with the devastation brought by the Second Northern War (Swedish Deluge, Deluge) and subsequent conflicts; the state itself was Partitions of Poland, partitioned and ceased to exist at the end of the 18th century.
From the 15th to 18th centuries, when the disintegrating khanates of the Golden Horde were conquered by Russia, Crimean Tatars, Tatars from the Crimean Khanate frequently Crimean-Nogai raids into East Slavic lands, raided Eastern Slavic lands to Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, capture slaves. Further east, the Nogai Horde and Kazakh Khanate frequently raided the Slavic-speaking areas of contemporary Russia and Ukraine for hundreds of years, until the Russian expansion and conquest of most of northern Eurasia (i.e. Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Siberia).
The Renaissance and the New Monarchs marked the start of an Age of Discovery, a period of exploration, invention and scientific development. Among the great figures of the Western scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries were Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Isaac Newton. According to Peter Barrett, "It is widely accepted that 'modern science' arose in the Europe of the 17th century (towards the end of the Renaissance), introducing a new understanding of the natural world."Peter Barrett (2004),
The Church's power was further weakened by the Protestant reformation, Protestant Reformation in 1517 when German theologian Martin Luther nailed his ''Ninety-five Theses'' criticising the selling of indulgences to the church door. He was subsequently excommunicated in the papal bull ''Exsurge Domine'' in 1520 and his followers were condemned in the 1521 Diet of Worms, which divided German princes between Protestant and Roman Catholic faiths.National Geographic, 256–257. European wars of religion, Religious fighting and warfare spread with Protestantism. The plunder of the empires of the Americas allowed Spain to finance Spanish Inquisition, religious persecution in Europe for over a century. The Thirty Years War (1618–1648) crippled the Holy Roman Empire and devastated much of Early Modern history of Germany, Germany, killing between 25 and 40 percent of its population. In the aftermath of the Peace of Westphalia, France rose to predominance within Europe.National Geographic, 269. The defeat of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the historic end of Ottoman wars in Europe, Ottoman expansion into Europe.
The 17th century in central and parts of eastern Europe was a period of general The General Crisis, decline; the region experienced more than 150 famines in a 200-year period between 1501 and 1700. From the Union of Krewo (1385) east-central Europe was dominated by the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The hegemony of the vast Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had ended with the devastation brought by the Second Northern War (Swedish Deluge, Deluge) and subsequent conflicts; the state itself was Partitions of Poland, partitioned and ceased to exist at the end of the 18th century.
From the 15th to 18th centuries, when the disintegrating khanates of the Golden Horde were conquered by Russia, Crimean Tatars, Tatars from the Crimean Khanate frequently Crimean-Nogai raids into East Slavic lands, raided Eastern Slavic lands to Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, capture slaves. Further east, the Nogai Horde and Kazakh Khanate frequently raided the Slavic-speaking areas of contemporary Russia and Ukraine for hundreds of years, until the Russian expansion and conquest of most of northern Eurasia (i.e. Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Siberia).
The Renaissance and the New Monarchs marked the start of an Age of Discovery, a period of exploration, invention and scientific development. Among the great figures of the Western scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries were Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Isaac Newton. According to Peter Barrett, "It is widely accepted that 'modern science' arose in the Europe of the 17th century (towards the end of the Renaissance), introducing a new understanding of the natural world."Peter Barrett (2004),
Science and Theology Since Copernicus: The Search for Understanding
'', pp. 14–18, Continuum International Publishing Group,
 The Seven Years' War brought to an end the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), "Old System" of alliances in Europe. Consequently, when the American Revolutionary War turned into a global war between 1778 and 1783, Britain found itself opposed by a strong coalition of European powers, and lacking any substantial ally.
The Age of Enlightenment was a powerful intellectual movement during the 18th century promoting scientific and reason-based thoughts.National Geographic, 255. Discontent with the aristocracy and clergy's monopoly on political power in France resulted in the French Revolution, and the establishment of the French First Republic, First Republic as a result of which the monarchy and many of the nobility perished during the initial Reign of Terror, reign of terror. Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and established the First French Empire that, during the
The Seven Years' War brought to an end the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), "Old System" of alliances in Europe. Consequently, when the American Revolutionary War turned into a global war between 1778 and 1783, Britain found itself opposed by a strong coalition of European powers, and lacking any substantial ally.
The Age of Enlightenment was a powerful intellectual movement during the 18th century promoting scientific and reason-based thoughts.National Geographic, 255. Discontent with the aristocracy and clergy's monopoly on political power in France resulted in the French Revolution, and the establishment of the French First Republic, First Republic as a result of which the monarchy and many of the nobility perished during the initial Reign of Terror, reign of terror. Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and established the First French Empire that, during the  The
The
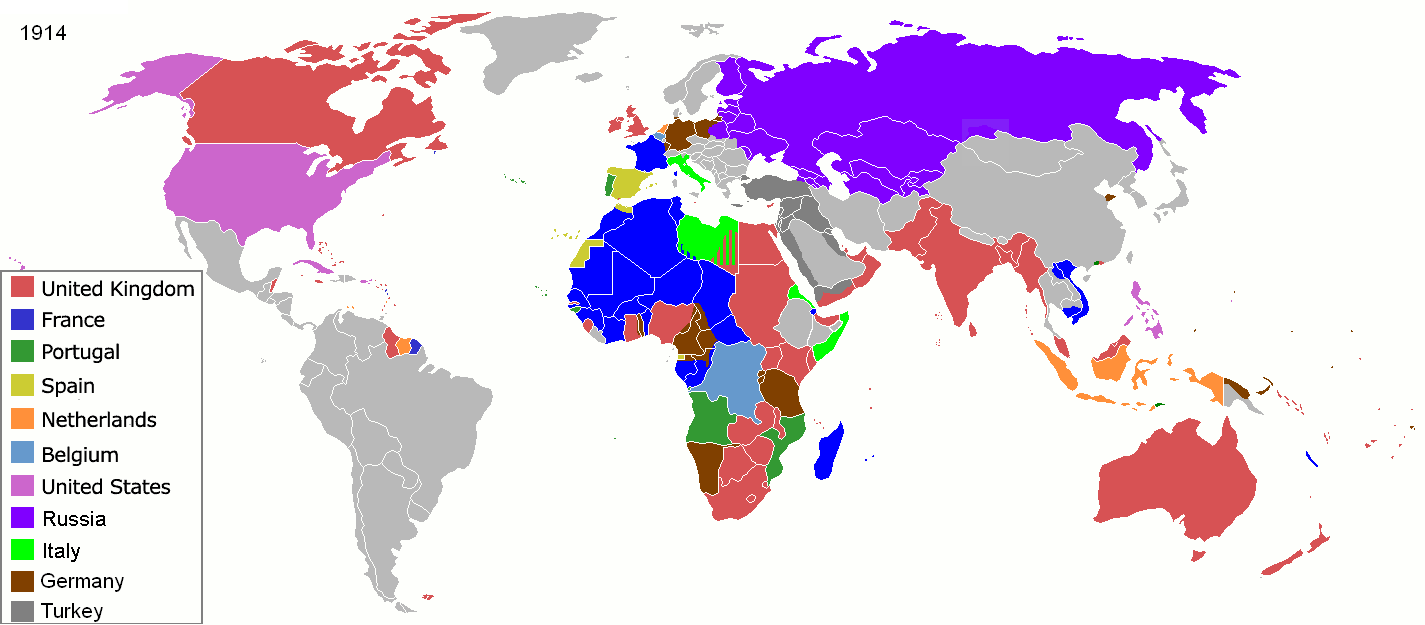 Two world wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Yugoslav nationalism, Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip.National Geographic, 407. Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (French Third Republic, France,
Two world wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Yugoslav nationalism, Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip.National Geographic, 407. Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (French Third Republic, France,  Russia was plunged into the Russian Revolution, which threw down the Russian Empire, Tsarist monarchy and replaced it with the communist
Russia was plunged into the Russian Revolution, which threw down the Russian Empire, Tsarist monarchy and replaced it with the communist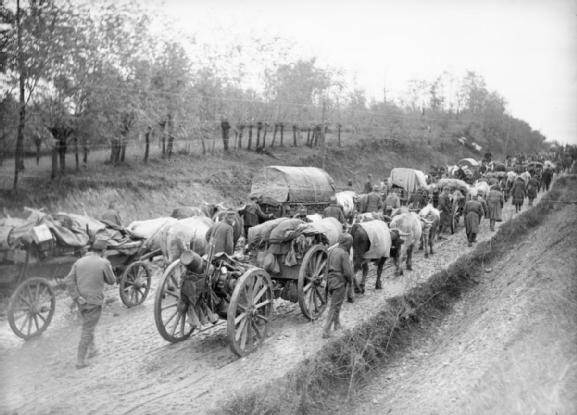  The social revolutions sweeping through Russia also affected other European nations following The Great War: in 1919, with the Weimar Republic in Germany and the First Austrian Republic; in 1922, with Benito Mussolini, Mussolini's one-party Fascism, fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy and in Atatürk's Turkey, Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet and state secularism.
Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This, and the Wall Street Crash of 1929, brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis, social instability and the threat of communism, Fascism, fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler in power of what became Nazi Germany.''National Geographic'', 438.
In 1933, Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards his goal of building Greater Germany. Germany re-expanded and took back the Saarland and Rhineland in 1935 and 1936. In 1938, Austria became a part of Germany following the Anschluss. Later that year, following the Munich Agreement signed by Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Italy, Germany annexed the Sudetenland, which was a part of Czechoslovakia inhabited by ethnic Germans, and in early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic. At the time, the United Kingdom and France preferred a policy of appeasement.
With tensions mounting between Germany and Second Polish Republic, Poland over the future of Gdańsk, Danzig, the Germans turned to the Soviets and signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which allowed the Soviets to invade the Baltic states and parts of Poland and Romania. Germany Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 3 September, opening the European Theatre of World War II, European Theatre of the Second World War.National Geographic, 465. The Soviet invasion of Poland started on 17 September and Poland fell soon thereafter. On 24 September, the Soviet Union attacked the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states (1940), Baltic countries and, on 30 November, Finland, the latter of which was followed by the devastating Winter War for the Red Army. The British hoped to land at Battles of Narvik, Narvik and send troops to aid Finland, but their primary objective in the landing was to encircle Germany and cut the Germans off from Scandinavian resources. Around the same time, Germany moved troops into Denmark. The Phoney War continued.
In May 1940, Germany Battle of France, attacked France through the Low Countries. France capitulated in June 1940. By August, Germany had begun a Battle of Britain, bombing offensive against the United Kingdom but failed to convince the Britons to give up.''National Geographic'', 510. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa.''National Geographic'', 532. On 7 December 1941 Empire of Japan, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire, and other Allies of World War II, allied forces.''National Geographic'', 511.''National Geographic'', 519.
After the staggering Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback. The Battle of Kursk, which involved the largest Battle of Prokhorovka, tank battle in history, was the last major German offensive on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. In June 1944, British and American forces invaded France in the Normandy landings, D-Day landings, opening a new front against Germany. Berlin finally Battle of Berlin, fell in 1945, ending the Second World War in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with World War II casualties, 60 million dead across the world.''National Geographic'', 439. More than 40 million people in Europe had died as a result of the Second World War, including between 11 and 17 million people who perished during the Holocaust. The Soviet Union World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, lost around 27 million people (mostly civilians) during the war, about half of all Second World War casualties. By the end of the Second World War, Europe had more than 40 million refugees. Several World War II evacuation and expulsion, post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe displaced a total of about 20 million people.
The First World War, and especially the Second World War, diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After the Second World War the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an "
The social revolutions sweeping through Russia also affected other European nations following The Great War: in 1919, with the Weimar Republic in Germany and the First Austrian Republic; in 1922, with Benito Mussolini, Mussolini's one-party Fascism, fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy and in Atatürk's Turkey, Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet and state secularism.
Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This, and the Wall Street Crash of 1929, brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis, social instability and the threat of communism, Fascism, fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler in power of what became Nazi Germany.''National Geographic'', 438.
In 1933, Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards his goal of building Greater Germany. Germany re-expanded and took back the Saarland and Rhineland in 1935 and 1936. In 1938, Austria became a part of Germany following the Anschluss. Later that year, following the Munich Agreement signed by Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Italy, Germany annexed the Sudetenland, which was a part of Czechoslovakia inhabited by ethnic Germans, and in early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic. At the time, the United Kingdom and France preferred a policy of appeasement.
With tensions mounting between Germany and Second Polish Republic, Poland over the future of Gdańsk, Danzig, the Germans turned to the Soviets and signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which allowed the Soviets to invade the Baltic states and parts of Poland and Romania. Germany Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 3 September, opening the European Theatre of World War II, European Theatre of the Second World War.National Geographic, 465. The Soviet invasion of Poland started on 17 September and Poland fell soon thereafter. On 24 September, the Soviet Union attacked the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states (1940), Baltic countries and, on 30 November, Finland, the latter of which was followed by the devastating Winter War for the Red Army. The British hoped to land at Battles of Narvik, Narvik and send troops to aid Finland, but their primary objective in the landing was to encircle Germany and cut the Germans off from Scandinavian resources. Around the same time, Germany moved troops into Denmark. The Phoney War continued.
In May 1940, Germany Battle of France, attacked France through the Low Countries. France capitulated in June 1940. By August, Germany had begun a Battle of Britain, bombing offensive against the United Kingdom but failed to convince the Britons to give up.''National Geographic'', 510. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa.''National Geographic'', 532. On 7 December 1941 Empire of Japan, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire, and other Allies of World War II, allied forces.''National Geographic'', 511.''National Geographic'', 519.
After the staggering Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback. The Battle of Kursk, which involved the largest Battle of Prokhorovka, tank battle in history, was the last major German offensive on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. In June 1944, British and American forces invaded France in the Normandy landings, D-Day landings, opening a new front against Germany. Berlin finally Battle of Berlin, fell in 1945, ending the Second World War in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with World War II casualties, 60 million dead across the world.''National Geographic'', 439. More than 40 million people in Europe had died as a result of the Second World War, including between 11 and 17 million people who perished during the Holocaust. The Soviet Union World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, lost around 27 million people (mostly civilians) during the war, about half of all Second World War casualties. By the end of the Second World War, Europe had more than 40 million refugees. Several World War II evacuation and expulsion, post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe displaced a total of about 20 million people.
The First World War, and especially the Second World War, diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After the Second World War the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an " In the 1980s the glasnost, reforms of Mikhail Gorbachev and the Solidarity (Polish trade union), Solidarity movement in Poland weakened the previously rigid communist system. The opening of the
In the 1980s the glasnost, reforms of Mikhail Gorbachev and the Solidarity (Polish trade union), Solidarity movement in Poland weakened the previously rigid communist system. The opening of the
 Europe lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being subjected to prevailing westerlies. The climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore, the average temperature throughout the year of Aveiro, Portugal, Aveiro is , while it is only in New York City which is almost on the same latitude, bordering the same ocean. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in far south-eastern Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average around higher than those in Calgary and they are almost higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk.
The large water masses of the
Europe lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being subjected to prevailing westerlies. The climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore, the average temperature throughout the year of Aveiro, Portugal, Aveiro is , while it is only in New York City which is almost on the same latitude, bordering the same ocean. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in far south-eastern Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average around higher than those in Calgary and they are almost higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk.
The large water masses of the  It is notable how the average temperatures for the coldest month, as well as the annual average temperatures, drop from the west to the east. For instance, Edinburgh is warmer than Belgrade during the coldest month of the year, although Belgrade is around 10° of latitude farther south.
It is notable how the average temperatures for the coldest month, as well as the annual average temperatures, drop from the west to the east. For instance, Edinburgh is warmer than Belgrade during the coldest month of the year, although Belgrade is around 10° of latitude farther south.
 The geological history of Europe traces back to the formation of the Baltic Shield (Fennoscandia) and the Sarmatian craton, both around 2.25 billion years ago, followed by the Volgo–Uralia shield, the three together leading to the East European craton (≈ Baltica) which became a part of the supercontinent Columbia (supercontinent), Columbia. Around 1.1 billion years ago, Baltica and Arctica (as part of the Laurentia block) became joined to Rodinia, later resplitting around 550 million years ago to reform as Baltica. Around 440 million years ago Euramerica was formed from Baltica and Laurentia; a further joining with Gondwana then leading to the formation of Pangea. Around 190 million years ago, Gondwana and Laurasia split apart due to the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. Finally and very soon afterwards, Laurasia itself split up again, into Laurentia (North America) and the Eurasian continent. The land connection between the two persisted for a considerable time, via Greenland, leading to interchange of animal species. From around 50 million years ago, rising and falling sea levels have determined the actual shape of Europe and its connections with continents such as Asia. Europe's present shape dates to the late Tertiary period about five million years ago.
The geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary. Europe's most significant feature is the dichotomy between highland and mountainous Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern plain ranging from Ireland in the west to the
The geological history of Europe traces back to the formation of the Baltic Shield (Fennoscandia) and the Sarmatian craton, both around 2.25 billion years ago, followed by the Volgo–Uralia shield, the three together leading to the East European craton (≈ Baltica) which became a part of the supercontinent Columbia (supercontinent), Columbia. Around 1.1 billion years ago, Baltica and Arctica (as part of the Laurentia block) became joined to Rodinia, later resplitting around 550 million years ago to reform as Baltica. Around 440 million years ago Euramerica was formed from Baltica and Laurentia; a further joining with Gondwana then leading to the formation of Pangea. Around 190 million years ago, Gondwana and Laurasia split apart due to the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. Finally and very soon afterwards, Laurasia itself split up again, into Laurentia (North America) and the Eurasian continent. The land connection between the two persisted for a considerable time, via Greenland, leading to interchange of animal species. From around 50 million years ago, rising and falling sea levels have determined the actual shape of Europe and its connections with continents such as Asia. Europe's present shape dates to the late Tertiary period about five million years ago.
The geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary. Europe's most significant feature is the dichotomy between highland and mountainous Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern plain ranging from Ireland in the west to the
 Having lived side by side with agricultural peoples for millennia, Europe's animals and plants have been profoundly affected by the presence and activities of man. With the exception of Fennoscandia and northern Russia, few areas of untouched wilderness are currently found in Europe, except for various national parks.
The main natural vegetation cover in Europe is mixed forest. The conditions for growth are very favourable. In the north, the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift warm the continent. Southern Europe could be described as having a warm, but mild climate. There are frequent summer droughts in this region. Mountain ridges also affect the conditions. Some of these (Alps, Pyrenees) are oriented east–west and allow the wind to carry large masses of water from the ocean in the interior. Others are oriented south–north (Scandinavian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, Dinarides, Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, Apennine Mountains, Apennines) and because the rain falls primarily on the side of mountains that is oriented towards the sea, forests grow well on this side, while on the other side, the conditions are much less favourable. Few corners of mainland Europe have not been grazed by livestock at some point in time, and the cutting down of the preagricultural forest habitat caused disruption to the original plant and animal ecosystems.
Having lived side by side with agricultural peoples for millennia, Europe's animals and plants have been profoundly affected by the presence and activities of man. With the exception of Fennoscandia and northern Russia, few areas of untouched wilderness are currently found in Europe, except for various national parks.
The main natural vegetation cover in Europe is mixed forest. The conditions for growth are very favourable. In the north, the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift warm the continent. Southern Europe could be described as having a warm, but mild climate. There are frequent summer droughts in this region. Mountain ridges also affect the conditions. Some of these (Alps, Pyrenees) are oriented east–west and allow the wind to carry large masses of water from the ocean in the interior. Others are oriented south–north (Scandinavian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, Dinarides, Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, Apennine Mountains, Apennines) and because the rain falls primarily on the side of mountains that is oriented towards the sea, forests grow well on this side, while on the other side, the conditions are much less favourable. Few corners of mainland Europe have not been grazed by livestock at some point in time, and the cutting down of the preagricultural forest habitat caused disruption to the original plant and animal ecosystems.
 Possibly 80 to 90 percent of Europe was once covered by forest. It stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Although over half of Europe's original forests disappeared through the centuries of deforestation, Europe still has over one quarter of its land area as forest, such as the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest, broadleaf and mixed forests, taiga of Scandinavia and Russia, mixed rainforests of the Caucasus and the Cork oak forests in the western Mediterranean. During recent times, deforestation has been slowed and many trees have been planted. However, in many cases monoculture plantations of Pinophyta, conifers have replaced the original mixed natural forest, because these grow quicker. The plantations now cover vast areas of land, but offer poorer habitats for many European forest dwelling species which require a mixture of tree species and diverse forest structure. The amount of natural forest in Western Europe is just 2–3% or less, while in its Western Russia its 5–10%. The European country with the List of countries by forest area, smallest percentage of forested area is
Possibly 80 to 90 percent of Europe was once covered by forest. It stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Although over half of Europe's original forests disappeared through the centuries of deforestation, Europe still has over one quarter of its land area as forest, such as the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest, broadleaf and mixed forests, taiga of Scandinavia and Russia, mixed rainforests of the Caucasus and the Cork oak forests in the western Mediterranean. During recent times, deforestation has been slowed and many trees have been planted. However, in many cases monoculture plantations of Pinophyta, conifers have replaced the original mixed natural forest, because these grow quicker. The plantations now cover vast areas of land, but offer poorer habitats for many European forest dwelling species which require a mixture of tree species and diverse forest structure. The amount of natural forest in Western Europe is just 2–3% or less, while in its Western Russia its 5–10%. The European country with the List of countries by forest area, smallest percentage of forested area is
 Glaciation during the Quaternary glaciation, most recent ice age and the presence of man affected the distribution of Fauna of Europe, European fauna. As for the animals, in many parts of Europe most large animals and top predator species have been hunted to extinction. The woolly mammoth was extinct before the end of the Neolithic period. Today wolf, wolves (carnivores) and bears (omnivores) are endangered. Once they were found in most parts of Europe. However, deforestation and hunting caused these animals to withdraw further and further. By the
Glaciation during the Quaternary glaciation, most recent ice age and the presence of man affected the distribution of Fauna of Europe, European fauna. As for the animals, in many parts of Europe most large animals and top predator species have been hunted to extinction. The woolly mammoth was extinct before the end of the Neolithic period. Today wolf, wolves (carnivores) and bears (omnivores) are endangered. Once they were found in most parts of Europe. However, deforestation and hunting caused these animals to withdraw further and further. By the  European wild cat, foxes (especially the red fox), jackal and different species of martens, hedgehogs, different species of reptiles (like snakes such as vipers and grass snakes) and amphibians, different birds (owls, hawks and other birds of prey).
Important European herbivores are snails, larvae, fish, different birds and mammals, like rodents, deer and roe deer, boars and living in the mountains, marmots, steinbocks, chamois among others. A number of insects, such as the small tortoiseshell butterfly, add to the biodiversity.
The extinction of the Cretan Dwarf Hippopotamus, dwarf hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on the islands of the Mediterranean.
Sea creatures are also an important part of European flora and fauna. The sea flora is mainly phytoplankton. Important animals that live in European seas are zooplankton, molluscs, echinoderms, different crustaceans, squids and octopuses, fish, dolphins and whales.
Biodiversity is protected in Europe through the Council of Europe's Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats, Bern Convention, which has also been signed by the European Community as well as non-European states.
European wild cat, foxes (especially the red fox), jackal and different species of martens, hedgehogs, different species of reptiles (like snakes such as vipers and grass snakes) and amphibians, different birds (owls, hawks and other birds of prey).
Important European herbivores are snails, larvae, fish, different birds and mammals, like rodents, deer and roe deer, boars and living in the mountains, marmots, steinbocks, chamois among others. A number of insects, such as the small tortoiseshell butterfly, add to the biodiversity.
The extinction of the Cretan Dwarf Hippopotamus, dwarf hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on the islands of the Mediterranean.
Sea creatures are also an important part of European flora and fauna. The sea flora is mainly phytoplankton. Important animals that live in European seas are zooplankton, molluscs, echinoderms, different crustaceans, squids and octopuses, fish, dolphins and whales.
Biodiversity is protected in Europe through the Council of Europe's Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats, Bern Convention, which has also been signed by the European Community as well as non-European states.
 As a continent, the economy of Europe is currently the largest on Earth and it is the richest region as measured by assets under management with over $32.7 trillion compared to North America's $27.1 trillion in 2008. In 2009 Europe remained the wealthiest region. Its $37.1 trillion in assets under management represented one-third of the world's wealth. It was one of several regions where wealth surpassed its precrisis year-end peak. As with other continents, Europe has a large variation of wealth among its countries. The richer states tend to be in the Western Europe, West, followed by Central Europeans, while some of the Eastern Europe economies are still emerging from the collapse of the Soviet Union and the breakup of Yugoslavia.
The model of the Blue Banana was designed as an economic geographic representation of the respective economic power of the regions, which was further developed into the Golden Banana or Blue Star. The trade between East and West, as well as towards Asia, which had been disrupted for a long time by the two world wars, new borders and the Cold War, increased sharply after 1989. In addition, there is new impetus from the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative across the Suez Canal towards Africa and Asia.
The European Union, a political entity composed of 27 European states, comprises the List of countries by GDP (nominal), largest single economic area in the world. Nineteen EU Eurozone, countries share the
As a continent, the economy of Europe is currently the largest on Earth and it is the richest region as measured by assets under management with over $32.7 trillion compared to North America's $27.1 trillion in 2008. In 2009 Europe remained the wealthiest region. Its $37.1 trillion in assets under management represented one-third of the world's wealth. It was one of several regions where wealth surpassed its precrisis year-end peak. As with other continents, Europe has a large variation of wealth among its countries. The richer states tend to be in the Western Europe, West, followed by Central Europeans, while some of the Eastern Europe economies are still emerging from the collapse of the Soviet Union and the breakup of Yugoslavia.
The model of the Blue Banana was designed as an economic geographic representation of the respective economic power of the regions, which was further developed into the Golden Banana or Blue Star. The trade between East and West, as well as towards Asia, which had been disrupted for a long time by the two world wars, new borders and the Cold War, increased sharply after 1989. In addition, there is new impetus from the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative across the Suez Canal towards Africa and Asia.
The European Union, a political entity composed of 27 European states, comprises the List of countries by GDP (nominal), largest single economic area in the world. Nineteen EU Eurozone, countries share the

 After the Second World War the economy of the UK was in a state of ruin, and continued to suffer relative economic decline in the following decades. Italy was also in a poor economic condition but regained a high level of growth by the 1950s. West Germany Wirtschaftswunder, recovered quickly and had doubled production from pre-war levels by the 1950s. France also staged a remarkable comeback enjoying rapid growth and modernisation; later on Spain, under the leadership of Francisco Franco, Franco, also recovered and the nation recorded huge unprecedented economic growth beginning in the 1960s in what is called the Spanish miracle. The majority of Central and Eastern European states came under the control of the
After the Second World War the economy of the UK was in a state of ruin, and continued to suffer relative economic decline in the following decades. Italy was also in a poor economic condition but regained a high level of growth by the 1950s. West Germany Wirtschaftswunder, recovered quickly and had doubled production from pre-war levels by the 1950s. France also staged a remarkable comeback enjoying rapid growth and modernisation; later on Spain, under the leadership of Francisco Franco, Franco, also recovered and the nation recorded huge unprecedented economic growth beginning in the 1960s in what is called the Spanish miracle. The majority of Central and Eastern European states came under the control of the
Appendix B: The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
The states which retained a free-market system were given a large amount of aid by the United States under the Marshall Plan. The western states moved to link their economies together, providing the basis for the EU and increasing cross border trade. This helped them to enjoy rapidly improving economies, while those states in COMECON were struggling in a large part due to the cost of the With the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe in 1991, the post-socialist states began free market reforms.
After East Germany, East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, the economy of West Germany struggled as it had to support and largely rebuild the infrastructure of East Germany.
By the millennium change, the EU dominated the economy of Europe, comprising the five largest European economies of the time: Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. In 1999, 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone replacing their former national currencies by the common euro. The three who chose to remain outside the Eurozone were the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Sweden. The European Union is now the largest economy in the world.
Figures released by Eurostat in 2009 confirmed that the Eurozone had gone into Late 2000s recession in Europe, recession in 2008. It impacted much of the region. In 2010, fears of a European sovereign-debt crisis, sovereign debt crisis developed concerning some countries in Europe, especially Greece, Ireland, Spain and Portugal. As a result, measures were taken, especially for Greece, by the leading countries of the Eurozone. The European Union, EU-27 unemployment rate was 10.3% in 2012. For those aged 15–24 it was 22.4%.Unemployment statistics
With the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe in 1991, the post-socialist states began free market reforms.
After East Germany, East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, the economy of West Germany struggled as it had to support and largely rebuild the infrastructure of East Germany.
By the millennium change, the EU dominated the economy of Europe, comprising the five largest European economies of the time: Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. In 1999, 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone replacing their former national currencies by the common euro. The three who chose to remain outside the Eurozone were the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Sweden. The European Union is now the largest economy in the world.
Figures released by Eurostat in 2009 confirmed that the Eurozone had gone into Late 2000s recession in Europe, recession in 2008. It impacted much of the region. In 2010, fears of a European sovereign-debt crisis, sovereign debt crisis developed concerning some countries in Europe, especially Greece, Ireland, Spain and Portugal. As a result, measures were taken, especially for Greece, by the leading countries of the Eurozone. The European Union, EU-27 unemployment rate was 10.3% in 2012. For those aged 15–24 it was 22.4%.Unemployment statistics
. Eurostat. April 2012.
 In 2017, the population of Europe was estimated to be 742 million according to , which is slightly more than one-ninth of the world's population.
A century ago, Europe had nearly a quarter of the world population, world's population.World Population Growth, 1950–2050
In 2017, the population of Europe was estimated to be 742 million according to , which is slightly more than one-ninth of the world's population.
A century ago, Europe had nearly a quarter of the world population, world's population.World Population Growth, 1950–2050
Population Reference Bureau. The population of Europe has grown in the past century, but in other areas of the world (in particular Africa and Asia) the population has grown far more quickly. Among the continents, Europe has a relatively high population density, second only to Asia. Most of Europe is in a mode of sub-replacement fertility, which means that each new(-born) generation is being less populous than the older. The most densely populated country in Europe (and in the world) is the microstate of Monaco.
 Europe is home to the highest number of migrants of all global regions at 70.6 million people, the International Organisation for Migration, IOM's report said. In 2005, the EU had an overall net gain from immigration of 1.8 million people. This accounted for almost 85% of Europe's total population growth. In 2008, 696,000 persons were given citizenship of an EU27 member state, a decrease from 707,000 the previous year. In 2017, approximately 825,000 persons acquired Citizenship of the European Union, citizenship of an EU28 member state. 2.4 million immigrants from non-EU countries entered the EU in 2017.
Early modern emigration from Europe began with Spanish and Portuguese settlers in the 16th century, and French and English settlers in the 17th century. But numbers remained relatively small until waves of mass emigration in the 19th century, when millions of poor families left Europe.
Today, European diaspora, large populations of European descent are found on every continent. European ancestry predominates in North America and to a lesser degree in South America (particularly in Uruguay, Argentina, Chile and Brazil, while most of the other Latin American countries also have a considerable White Latin American, population of European origins). Australia and New Zealand have large European-derived populations. Africa has no countries with European-derived majorities (or with the exception of Cape Verde and probably São Tomé and Príncipe, depending on context), but there are significant minorities, such as the White South Africans in South Africa. In Asia, European-derived populations, (specifically Russians), predominate in
Europe is home to the highest number of migrants of all global regions at 70.6 million people, the International Organisation for Migration, IOM's report said. In 2005, the EU had an overall net gain from immigration of 1.8 million people. This accounted for almost 85% of Europe's total population growth. In 2008, 696,000 persons were given citizenship of an EU27 member state, a decrease from 707,000 the previous year. In 2017, approximately 825,000 persons acquired Citizenship of the European Union, citizenship of an EU28 member state. 2.4 million immigrants from non-EU countries entered the EU in 2017.
Early modern emigration from Europe began with Spanish and Portuguese settlers in the 16th century, and French and English settlers in the 17th century. But numbers remained relatively small until waves of mass emigration in the 19th century, when millions of poor families left Europe.
Today, European diaspora, large populations of European descent are found on every continent. European ancestry predominates in North America and to a lesser degree in South America (particularly in Uruguay, Argentina, Chile and Brazil, while most of the other Latin American countries also have a considerable White Latin American, population of European origins). Australia and New Zealand have large European-derived populations. Africa has no countries with European-derived majorities (or with the exception of Cape Verde and probably São Tomé and Príncipe, depending on context), but there are significant minorities, such as the White South Africans in South Africa. In Asia, European-derived populations, (specifically Russians), predominate in
 Europe has about 225 indigenous languages, mostly falling within three Indo-European languages, Indo-European language groups: the Romance languages, derived from the Latin language, Latin of the
Europe has about 225 indigenous languages, mostly falling within three Indo-European languages, Indo-European language groups: the Romance languages, derived from the Latin language, Latin of the
, accessed 8 December 2014.Thomas E. Woods and Antonio Canizares, 2012, "How the Catholic Church Built Western Civilization," Reprint edn., Washington, DC: Regnery History, , se
accessed 8 December 2014. p. 1: "Western civilization owes far more to Catholic Church than most people – Catholic included – often realize. The Church in fact built Western civilization."
/ref> and for at least a millennium and a half, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture, even though the religion was inherited from the
 "Europe" as a cultural concept is substantially derived from the shared heritage of
"Europe" as a cultural concept is substantially derived from the shared heritage of
Europe and the Faith
, Chapter I This shared cultural heritage is combined by overlapping indigenous national cultures and folklores, roughly divided into Slavic Europe, Slavic, Romance-speaking Europe, Latin (Romance) and Germanic Europe, Germanic, but with several components not part of either of these group (notably Greek culture, Greek, Basque culture, Basque and Celtic Europe, Celtic). Historically, special examples with overlapping cultures are Strasbourg with Latin (Romance) and Germanic or Trieste with Latin, Slavic and Germanic roots. Cultural contacts and mixtures shape a large part of the regional cultures of Europe. Europe is often described as "maximum cultural diversity with minimal geographical distances". Different cultural events are organized in Europe, with the aim of bringing different cultures closer together and raising awareness of their importance, such as the European Capital of Culture, the European Region of Gastronomy, the European Youth Capital and the European Capital of Sport.
Council of Europe
European Union
The Columbia Gazetteer of the World Online
Columbia University Press
"Introducing Europe"
fro
Lonely Planet
Travel Guides and Information Historical Maps
Borders in Europe 3000BC to the present
Geacron Historical atlas
Online history of Europe in 21 maps
{{Authority control Europe, Continents
peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
conventionally considered a continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to pol ...
. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia (also Afroeurasia, Eurafrasia or the Old World) is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Its mainland is the largest and most populou ...
with both Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
to the north, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the west, the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, the Ural River
The Ural (russian: Урал, ), known before 1775 as Yaik (russian: Яик, ba, Яйыҡ, translit=Yayıq, ; kk, Жайық, translit=Jaiyq, ), is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia ...
, the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
, the Greater Caucasus
The Greater Caucasus ( az, Böyük Qafqaz, Бөјүк Гафгаз, بيوک قافقاز; ka, დიდი კავკასიონი, ''Didi K’avk’asioni''; russian: Большой Кавказ, ''Bolshoy Kavkaz'', sometimes translat ...
, the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles."
Europe covers about , or 2% of Earth's surface (6.8% of land area), making it the second-smallest continent (using the seven-continent model). Politically, Europe is divided into about fifty sovereign states, of which Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
is the largest
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (or ...
and most populous, spanning 39% of the continent and comprising 15% of its population. Europe had a total population of about million (about 10% of the world population
In demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently living. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded 8 billion in November 2022. It took over 200,000 years of human prehistory and history for the ...
) in . The European climate
Europe is generally characterized by a temperate climate. Most of Western Europe has an Oceanic climate, in the Köppen climate classification, featuring cool to warm summers and cool winters with frequent overcast skies. Southern Europe has a d ...
is largely affected by warm Atlantic currents that temper winters and summers on much of the continent, even at latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s along which the climate in Asia and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
is severe. Further from the sea, seasonal differences are more noticeable than close to the coast.
European culture is the root of Western civilisation
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
, which traces its lineage back to ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
. The fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
in 476 AD and the subsequent Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
marked the end of Europe's ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
, and the beginning of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
, exploration, art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
led to the modern era
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
. Since the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, started by Portugal and Spain, Europe played a predominant role in global affairs. Between the 16th and 20th centuries, European powers colonised at various times the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, almost all of Africa and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
, and the majority of Asia.
The Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, the subsequent French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
and the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
shaped the continent culturally, politically and economically from the end of the 17th century until the first half of the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, which began in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
at the end of the 18th century, gave rise to radical economic, cultural and social change in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
and eventually the wider world. Both world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
s took place for the most part in Europe, contributing to a decline in Western European dominance in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and the United States took prominence.National Geographic, 534. During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, Europe was divided along the Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. The term symbolizes the efforts by the Soviet Union (USSR) to block itself and its s ...
between NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in the West and the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
in the East, until the Revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Natio ...
, Fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall (german: Mauerfall) on 9 November 1989, during the Peaceful Revolution, was a pivotal event in world history which marked the destruction of the Berlin Wall and the figurative Iron Curtain and one of the series of eve ...
and the Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
.
In 1949, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
was founded with the idea of unifying Europe to achieve common goals and prevent future wars. Further European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic integration, economic, political, legal, social integration, social, and cultural Regional integration, integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integrat ...
by some states led to the formation of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU), a separate political entity that lies between a confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
and a federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. The EU originated in Western Europe but has been expanding eastward since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991. The currency of most countries of the European Union, the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
, is the most commonly used among Europeans; and the EU's Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
abolishes border and immigration controls between most of its member states, and some non-member states. There exists a political movement favouring the evolution of the European Union into a single federation encompassing much of the continent.
Name
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliff ...
( grc, Εὐρώπη, ) was a Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n princess. One view is that her name derives from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
elements () 'wide, broad', and (, , ) 'eye, face, countenance', hence their composite would mean 'wide-gazing' or 'broad of aspect'. ''Broad'' has been an epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, di ...
of Earth herself in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European religion
Proto-Indo-European mythology is the body of myths and deities associated with the Proto-Indo-Europeans, the hypothetical speakers of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language. Although the mythological motifs are not directly attested � ...
and the poetry devoted to it. An alternative view is that of Robert Beekes
Robert Stephen Paul Beekes (; 2 September 1937 – 21 September 2017) was a Dutch linguist who was emeritus professor of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University and an author of many monographs on the Proto-Indo-European lan ...
, who has argued in favour of a Pre-Indo-European origin for the name, explaining that a derivation from would yield a different toponym than Europa. Beekes has located toponyms related to that of Europa in the territory of ancient Greece, and localities such as that of Europos in ancient Macedonia
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
.
There have been attempts to connect to a Semitic term for ''west'', this being either Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
meaning 'to go down, set' (said of the sun) or Phoenician 'evening, west', which is at the origin of Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
and Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
. Martin Litchfield West
Martin Litchfield West, (23 September 1937 – 13 July 2015) was a British philologist and classical scholar. In recognition of his contribution to scholarship, he was awarded the Order of Merit in 2014.
West wrote on ancient Greek music, Gree ...
stated that "phonologically, the match between Europa's name and any form of the Semitic word is very poor", while Beekes considers a connection to Semitic languages improbable.
Most major world languages use words derived from or ''Europa'' to refer to the continent. Chinese, for example, uses the word , which is an abbreviation of the transliterated name ( means "continent"); a similar Chinese-derived term is also sometimes used in Japanese such as in the Japanese name of the European Union, , despite the katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji). The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
being more commonly used. In some Turkic languages, the originally Persian name ('land of the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
') is used casually in referring to much of Europe, besides official names such as or .
Definition
Contemporary definition
Clickable map of Europe, showing one of the most commonly used continental boundaries
Key: blue: states which straddle the border between Europe and Asia; green: countries not geographically in Europe, but closely associated with the continent
Key: blue: states which straddle the border between Europe and Asia; green: countries not geographically in Europe, but closely associated with the continent
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, the Ural River
The Ural (russian: Урал, ), known before 1775 as Yaik (russian: Яик, ba, Яйыҡ, translit=Yayıq, ; kk, Жайық, translit=Jaiyq, ), is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia ...
, and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
; to the south-east, the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
, the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, and the waterways connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea.
 Islands are generally grouped with the nearest continental landmass, hence
Islands are generally grouped with the nearest continental landmass, hence Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
is considered to be part of Europe, while the nearby island of Greenland is usually assigned to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, although politically belonging to Denmark. Nevertheless, there are some exceptions based on sociopolitical and cultural differences. Cyprus is closest to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
(or Asia Minor), but is considered part of Europe politically and it is a member state of the EU. Malta was considered an island of North-western Africa for centuries, but now it is considered to be part of Europe as well.
"Europe", as used specifically in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
, may also refer to Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
exclusively.
The term "continent" usually implies the physical geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, h ...
of a large land mass completely or almost completely surrounded by water at its borders. Prior to the adoption of the current convention that includes mountain divides, the border between Europe and Asia had been redefined several times since its first conception in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, but always as a series of rivers, seas and straits that were believed to extend an unknown distance east and north from the Mediterranean Sea without the inclusion of any mountain ranges. Cartographer Herman Moll
Herman Moll (mid-17th century – 22 September 1732) was a London cartographer, engraver, and publisher.
Origin and early life
While Moll's exact place and date of birth are unknown, he was probably born in the mid-seventeenth century in G ...
suggested in 1715 Europe was bounded by a series of partly-joined waterways directed towards the Turkish straits, and the Irtysh River
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'erj ...
draining into the upper part of the Ob River
}
The Ob ( rus, Обь, p=opʲ: Ob') is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia; and together with Irtysh forms the world's List of rivers by length, seventh-longest river system, at . It forms at the confluence of the Biya (river), Biya ...
and the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
. In contrast, the present eastern boundary of Europe partially adheres to the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, which is somewhat arbitrary and inconsistent compared to any clear-cut definition of the term "continent".
The current division of Eurasia into two continents now reflects East-West cultural, linguistic and ethnic differences which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. The geographic border between Europe and Asia does not follow any state boundaries and now only follows a few bodies of water. Turkey is generally considered a transcontinental country
This is a list of countries with territory that straddles more than one continent, known as transcontinental states or intercontinental states.
Contiguous transcontinental countries are states that have one continuous or immediately-adjacent ...
divided entirely by water, while Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
are only partly divided by waterways. France, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
are also transcontinental (or more properly, intercontinental, when oceans or large seas are involved) in that their main land areas are in Europe while pockets of their territories are located on other continents
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
separated from Europe by large bodies of water. Spain, for example, has territories south of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
—namely, Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
—which are parts of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and share a border with Morocco. According to the current convention, Georgia and Azerbaijan are transcontinental countries where waterways have been completely replaced by mountains as the divide between continents.
History of the concept
Early history
 The first recorded usage of ''Eurṓpē'' as a geographic term is in the
The first recorded usage of ''Eurṓpē'' as a geographic term is in the Homeric Hymn
The ''Homeric Hymns'' () are a collection of thirty-three anonymous ancient Greek hymns celebrating individual gods. The hymns are "Homeric" in the sense that they employ the same epic meter—dactylic hexameter—as the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', ...
to Delian Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, in reference to the western shore of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
. As a name for a part of the known world, it is first used in the 6th century BCE by Anaximander
Anaximander (; grc-gre, Ἀναξίμανδρος ''Anaximandros''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 403. a city of Ionia (in moder ...
and Hecataeus. Anaximander placed the boundary between Asia and Europe along the Phasis River (the modern Rioni River
The Rioni ( ka, რიონი, ; , ) is the main river of western Georgia. It originates in the Caucasus Mountains, in the region of Racha and flows west to the Black Sea, entering it north of the city of Poti (near ancient Phasis). The city o ...
on the territory of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
) in the Caucasus, a convention still followed by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
in the 5th century BCE. Herodotus mentioned that the world had been divided by unknown persons into three parts, Europe, Asia and Libya (Africa), with the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
and the Phasis forming their boundaries—though he also states that some considered the River Don, rather than the Phasis, as the boundary between Europe and Asia. Europe's eastern frontier was defined in the 1st century by geographer Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
at the River Don. The ''Book of Jubilees
The Book of Jubilees, sometimes called Lesser Genesis (Leptogenesis), is an ancient Jewish religious work of 50 chapters (1,341 verses), considered canonical by the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as well as Beta Israel (Ethiopian Jews), where it is ...
'' described the continents as the lands given by Noah
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ኖህ, ''Noḥ''; ar, نُوح '; grc, Νῶε ''Nôe'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5– ...
to his three sons; Europe was defined as stretching from the Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
at the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
, separating it from Northwest Africa
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, to the Don, separating it from Asia.
The convention received by the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and surviving into modern usage is that of the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
used by Roman-era authors such as Posidonius
Posidonius (; grc-gre, wikt:Ποσειδώνιος, Ποσειδώνιος , "of Poseidon") "of Apamea (Syria), Apameia" (ὁ Ἀπαμεύς) or "of Rhodes" (ὁ Ῥόδιος) (), was a Greeks, Greek politician, astronomer, astrologer, geog ...
, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, who took the Tanais (the modern Don River) as the boundary.
The Roman Empire did not attach a strong identity to the concept of continental divisions. However, following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
, the culture that developed in its place, linked to Latin and the Catholic church, began to associate itself with the concept of "Europe". The term "Europe" is first used for a cultural sphere in the Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the State church of the Roman Emp ...
of the 9th century. From that time, the term designated the sphere of influence of the Western Church
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic C ...
, as opposed to both the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
churches and to the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
.
A cultural definition of Europe as the lands of Latin Christendom
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
coalesced in the 8th century, signifying the new cultural condominium created through the confluence of Germanic traditions and Christian-Latin culture, defined partly in contrast with Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, and limited to northern Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, the British Isles, France, Christianised western Germany, the Alpine regions and northern and central Italy. The concept is one of the lasting legacies of the Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the State church of the Roman Emp ...
: ''Europa'' often figures in the letters of Charlemagne's court scholar, Alcuin
Alcuin of York (; la, Flaccus Albinus Alcuinus; 735 – 19 May 804) – also called Ealhwine, Alhwin, or Alchoin – was a scholar, clergyman, poet, and teacher from York, Northumbria. He was born around 735 and became the student o ...
. The transition of Europe to being a cultural term as well as a geographic one led to the borders of Europe being affected by cultural considerations in the East, especially relating to areas under Byzantine, Ottoman, and Russian influence. Such questions were affected by the positive connotations associated with the term Europe by its users. Such cultural considerations were not applied to the Americas, despite their conquest and settlement by European states. Instead, the concept of "Western civilization" emerged as a way of grouping together Europe and these colonies.
Modern definitions
 The question of defining a precise eastern boundary of Europe arises in the Early Modern period, as the eastern extension of
The question of defining a precise eastern boundary of Europe arises in the Early Modern period, as the eastern extension of Muscovy Muscovy is an alternative name for the Grand Duchy of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
* Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata'') and Domes ...
began to include North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographical terms and is coextensive with the Asian part of Russia, and consists of three Russian regions east of the Ural Mountains: ...
. Throughout the Middle Ages and into the 18th century, the traditional division of the landmass of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
into two continents, Europe and Asia, followed Ptolemy, with the boundary following the Turkish Straits, the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, the Kerch Strait
The Kerch Strait, uk, Керченська протока, crh, Keriç boğazı, ady, Хы ТӀуалэ is a strait in Eastern Europe. It connects the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov, separating the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea in the west from ...
, the Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
and the Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
(ancient Tanais
Tanais ( el, Τάναϊς ''Tánaïs''; russian: Танаис) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in the Don River (Russia), Don river delta, called the Maeotian Swamp, Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana ...
). But maps produced during the 16th to 18th centuries tended to differ in how to continue the boundary beyond the Don bend at Kalach-na-Donu
Kalach-na-Donu (russian: Кала́ч-на-Дону́), or Kalach-on-the-Don, is a town and the administrative center of Kalachyovsky District in Volgograd Oblast, Russia, located on the Don River, west of Volgograd, the administrative center of ...
(where it is closest to the Volga, now joined with it by the Volga–Don Canal
Lenin Volga–Don Shipping Canal (Russian:Волго-Донской судоходный канал имени, ''В. И. Ленина, Volga-Donskoy soudokhodniy kanal imeni V. I. Lenina'', abbreviated ВДСК, ''VDSK'') is a ship canal in Rus ...
), into territory not described in any detail by the ancient geographers.
Around 1715, Herman Moll
Herman Moll (mid-17th century – 22 September 1732) was a London cartographer, engraver, and publisher.
Origin and early life
While Moll's exact place and date of birth are unknown, he was probably born in the mid-seventeenth century in G ...
produced a map showing the northern part of the Ob River
}
The Ob ( rus, Обь, p=opʲ: Ob') is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia; and together with Irtysh forms the world's List of rivers by length, seventh-longest river system, at . It forms at the confluence of the Biya (river), Biya ...
and the Irtysh River
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'erj ...
, a major tributary of the Ob, as components of a series of partly-joined waterways taking the boundary between Europe and Asia from the Turkish Straits, and the Don River all the way to the Arctic Ocean. In 1721, he produced a more up to date map that was easier to read. However, his proposal to adhere to major rivers as the line of demarcation was never taken up by other geographers who were beginning to move away from the idea of water boundaries as the only legitimate divides between Europe and Asia.
Four years later, in 1725, Philip Johan von Strahlenberg
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
was the first to depart from the classical Don boundary. He drew a new line along the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
, following the Volga north until the Samara Bend
The Samara Bend (''Samarskaya Luka''; ) is a large hairpin bend of the middle Volga River to the east where it meets the Samara River. It is situated in the Samara region of Russia.
As the Volga enters its middle course it reaches the Zhiguli M ...
, along Obshchy Syrt Obshchy Syrt (russian: Общий Сырт) is a highland ridge, or plateau (''syrt''), in the European part of Russia. It starts north of Orenburg as a branch of the Ural Mountains and runs in a southwesterly direction to the east bank of the Volga ...
(the drainage divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a singl ...
between the Volga and Ural River
The Ural (russian: Урал, ), known before 1775 as Yaik (russian: Яик, ba, Яйыҡ, translit=Yayıq, ; kk, Жайық, translit=Jaiyq, ), is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia ...
s), then north and east along the latter waterway to its source in the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. At this point he proposed that mountain ranges could be included as boundaries between continents as alternatives to nearby waterways. Accordingly, he drew the new boundary north along Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
rather than the nearby and parallel running Ob and Irtysh rivers. This was endorsed by the Russian Empire and introduced the convention that would eventually become commonly accepted. However, this did not come without criticism. Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his ...
, writing in 1760 about Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
's efforts to make Russia more European, ignored the whole boundary question with his claim that neither Russia, Scandinavia, northern Germany, nor Poland were fully part of Europe. Since then, many modern analytical geographers like Halford Mackinder
Sir Halford John Mackinder (15 February 1861 – 6 March 1947) was an English geographer, academic and politician, who is regarded as one of the founding fathers of both geopolitics and geostrategy. He was the first Principal of University Ext ...
have declared that they see little validity in the Ural Mountains as a boundary between continents.
The mapmakers continued to differ on the boundary between the lower Don and Samara well into the 19th century. The 1745 atlas published by the Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
has the boundary follow the Don beyond Kalach as far as Serafimovich before cutting north towards Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies o ...
, while other 18th- to 19th-century mapmakers such as John Cary
John Cary (c. 1754 – 1835) was an English cartographer.
Life
Cary served his apprenticeship as an engraver in London, before setting up his own business in the Strand in 1783. He soon gained a reputation for his maps and globes, his atla ...
followed Strahlenberg's prescription. To the south, the Kuma–Manych Depression
The Kuma–Manych depression ( rus, Кумо–Манычская впадина, Kumo–Manychskaya vpadina), is a geological depression in southwestern Russia that separates the Russian Plain to the north from Ciscaucasia to the south. It is ...
was identified circa 1773 by a German naturalist, Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810.
Life and work
Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son ...
, as a valley that once connected the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, and subsequently was proposed as a natural boundary between continents.
By the mid-19th century, there were three main conventions, one following the Don, the Volga–Don Canal
Lenin Volga–Don Shipping Canal (Russian:Волго-Донской судоходный канал имени, ''В. И. Ленина, Volga-Donskoy soudokhodniy kanal imeni V. I. Lenina'', abbreviated ВДСК, ''VDSK'') is a ship canal in Rus ...
and the Volga, the other following the Kuma–Manych Depression to the Caspian and then the Ural River, and the third abandoning the Don altogether, following the Greater Caucasus watershed
The Greater Caucasus ( az, Böyük Qafqaz, Бөјүк Гафгаз, بيوک قافقاز; ka, დიდი კავკასიონი, ''Didi K’avk’asioni''; russian: Большой Кавказ, ''Bolshoy Kavkaz'', sometimes translat ...
to the Caspian. The question was still treated as a "controversy" in geographical literature of the 1860s, with Douglas Freshfield
Douglas William Freshfield (27 April 1845 – 9 February 1934) was a British lawyer, mountaineer and author, who edited the ''Alpine Journal ''from 1872 to 1880. He was an active member of the Royal Geographical Society and the Alpine Club (UK), ...
advocating the Caucasus crest boundary as the "best possible", citing support from various "modern geographers".
In Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, the boundary along the Kuma–Manych Depression was the most commonly used as early as 1906. In 1958, the Soviet Geographical Society formally recommended that the boundary between the Europe and Asia be drawn in textbooks from Baydaratskaya Bay
Baydaratskaya Bay or Baydarata Bay (russian: Байдарацкая губа, Baydaratskaya guba, Tundra Nenets language, Tundra Nenets: Пэдарита, ''Pėdarita'') is a gulf in Russia, located in the southern part of the Kara Sea between t ...
, on the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. ...
, along the eastern foot of Ural Mountains, then following the Ural River
The Ural (russian: Урал, ), known before 1775 as Yaik (russian: Яик, ba, Яйыҡ, translit=Yayıq, ; kk, Жайық, translit=Jaiyq, ), is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia ...
until the Mugodzhar Hills
Mugodzhar Hills ( kk, Мұғалжар тауы, ''Mūğaljar tauy''; russian: Мугоджары, Мугоджарский хребет) or Mugodzhar RangeEmba River
The Emba ( kk, Ембі ''Embı'' or ''Jem'', russian: Эмба) in west Kazakhstan rises in the Mugodzhar Hills and flows into the Caspian Sea. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .
; and Kuma–Manych Depression, thus placing the Caucasus entirely in Asia and the Urals entirely in Europe. However, most geographers in the Soviet Union favoured the boundary along the Caucasus crest, and this became the common convention in the later 20th century, although the Kuma–Manych boundary remained in use in some 20th-century maps.
Some view separation of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
into Asia and Europe as a residue of Eurocentrism
Eurocentrism (also Eurocentricity or Western-centrism)
is a worldview that is centered on Western civilization or a biased view that favors it over non-Western civilizations. The exact scope of Eurocentrism varies from the entire Western worl ...
: "In physical, cultural and historical diversity, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
are comparable to the entire European landmass, not to a single European country. .."
History
Prehistory
 During the 2.5 million years of the
During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
, numerous cold phases called glacials
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate bet ...
(Quaternary ice age
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
), or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in Europe and North America, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
s which lasted about 10,000–15,000 years. The last cold episode of the last glacial period ended about 10,000 years ago. Earth is currently in an interglacial period of the Quaternary, called the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
.
''Homo erectus georgicus
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million y ...
'', which lived roughly 1.8 million years ago in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, is the earliest hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The t ...
to have been discovered in Europe. Other
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
hominin remains, dating back roughly 1 million years, have been discovered in Atapuerca, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. Neanderthal man
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
(named after the Neandertal valley in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
) appeared in Europe 150,000 years ago (115,000 years ago it is found already in the territory of present-day Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
) and disappeared from the fossil record about 40,000 years ago, with their final refuge being the Iberian Peninsula. The Neanderthals were supplanted by modern humans (Cro-Magnons
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They ...
), who appeared in Europe around 43,000 to 40,000 years ago.National Geographic, 21. Homo sapiens arrived in Europe around 54,000 years ago, some 10,000 years earlier than previously thought. The earliest sites in Europe dated 48,000 years ago are Riparo Mochi
The Balzi Rossi caves (Ligurian: ''baussi rossi'' "red rocks") in Ventimiglia ''comune'', Liguria, Italy, is one of the most important archaeological sites of the early Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the ...
(Italy), Geissenklösterle
Geissenklösterle () is an archaeological site of significance for the central European Upper Paleolithic, located near the town of Blaubeuren in the Swabian Jura in Baden-Württemberg, southern Germany. First explored in 1963, the cave contains t ...
(Germany) and Isturitz
Isturits (; also ''Isturitz'') is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in south-western France.
It is located in the former province of Lower Navarre (''Arberoa'').European Neolithic
The European Neolithic is the period when Neolithic (New Stone Age) technology was present in Europe, roughly between 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) and c.2000–1700 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age ...
period—marked by the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock, increased numbers of settlements and the widespread use of pottery—began around 7000 BCE in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, probably influenced by earlier farming practices in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
and the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
. It spread from the Balkans along the valleys of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
(Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
), and along the Mediterranean coast
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the eas ...
( Cardial culture). Between 4500 and 3000 BCE, these central European neolithic cultures developed further to the west and the north, transmitting newly acquired skills in producing copper artifacts. In Western Europe the Neolithic period was characterised not by large agricultural settlements but by field monuments, such as causewayed enclosure
A causewayed enclosure is a type of large prehistoric earthwork common to the early Neolithic in Europe. It is an enclosure marked out by ditches and banks, with a number of causeways crossing the ditches. More than 100 examples are recorded in ...
s, burial mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
s and megalithic tomb
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
s. The Corded Ware
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a va ...
cultural horizon flourished at the transition from the Neolithic to the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
. During this period giant megalithic
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
monuments, such as the Megalithic Temples of Malta
The Megalithic Temples of Malta ( mt, It-Tempji Megalitiċi ta' Malta) are several prehistoric temples, some of which are UNESCO World Heritage Sites, built during three distinct periods approximately between 3600 BC and 2500 BC on the island coun ...
and Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
, were constructed throughout Western and Southern Europe.
The modern native populations of Europe largely descend from three distinct lineages: Mesolithic hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s, a derivative of the Cro-Magnon population of Europe, Neolithic farmers who migrated from Anatolia during the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, and Yamnaya
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
pastoralists
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal ...
who expanded into Europe in the context of the Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
. The European Bronze Age
The European Bronze Age is characterized by bronze artifacts and the use of bronze implements. The regional Bronze Age succeeds the Neolithic and Copper Age and is followed by the Iron Age. It starts with the Aegean Bronze Age in 3200 BC
(succ ...
began c. 3200 BCE in Greece with the Minoan civilisation
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
on Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
, the first advanced civilisation in Europe. The Minoans were followed by the Myceneans
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
, who collapsed suddenly around 1200 BCE, ushering the European Iron Age
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods,The Junior Encyclopædia Britannica: A reference library of general knowledge. (1897). Chicago: E.G. Melvin. (seriously? 1897 "Junior" ...
. Iron Age colonisation by the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
and Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
gave rise to early Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
cities. Early Iron Age Italy
The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when species of ''Homo'' colonized the Italian territory for the first time, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Italy.
Paleolithic
In prehistoric times ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
from around the 8th century BCE gradually gave rise to historical Classical antiquity, whose beginning is sometimes dated to 776 BCE, the year of the first Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
.
Classical antiquity
 Ancient Greece was the founding culture of Western civilisation. Western democratic and rationalist culture are often attributed to Ancient Greece. The Greek city-state, the
Ancient Greece was the founding culture of Western civilisation. Western democratic and rationalist culture are often attributed to Ancient Greece. The Greek city-state, the polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
, was the fundamental political unit of classical Greece. In 508 BCE, Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; grc-gre, Κλεισθένης), or Clisthenes (c. 570c. 508 BC), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishm ...
instituted the world's first democratic system of government in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
. The Greek political ideals were rediscovered in the late 18th century by European philosophers and idealists. Greece also generated many cultural contributions: in philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humani ...
and rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification".Lacey, A.R. (1996), ''A Dictionary of Philosophy' ...
under Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
and Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
; in history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
with Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
and Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientifi ...
; in dramatic and narrative verse, starting with the epic poems of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
;National Geographic, 76. in drama with Sophocles
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or co ...
and Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful e ...
, in medicine with Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
and Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
; and in science with Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samos, Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionians, Ionian Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher and the eponymou ...
, Euclid
Euclid (; grc-gre, Wikt:Εὐκλείδης, Εὐκλείδης; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the ''Euclid's Elements, Elements'' trea ...
and Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
. In the course of the 5th century BCE, several of the Greek city states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
would ultimately check the Achaemenid Persian advance in Europe through the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
, considered a pivotal moment in world history, as the 50 years of peace that followed are known as Golden Age of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is a coastal city in the Mediterranean and is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest c ...
, the seminal period of ancient Greece that laid many of the foundations of Western civilisation.
 Greece was followed by
Greece was followed by Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, which left its mark on law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
, politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
, language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
and many more key aspects in western civilisation. By 200 BCE, Rome had conquered Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
and over the following two centuries it conquered Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
and Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania ...
(Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
), the North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
n coast, much of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
(France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
) and Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
(England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
).
Expanding from their base in central Italy beginning in the third century BCE, the Romans gradually expanded to eventually rule the entire Mediterranean Basin and Western Europe by the turn of the millennium. The Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
ended in 27 BCE, when Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
proclaimed the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. The two centuries that followed are known as the ''pax romana
The Pax Romana (Latin for 'Roman peace') is a roughly 200-year-long timespan of Roman history which is periodization, identified as a period and as a golden age (metaphor), golden age of increased as well as sustained Imperial cult of ancient Rome ...
'', a period of unprecedented peace, prosperity and political stability in most of Europe. The empire continued to expand under emperors such as Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatoria ...
and Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
, who spent time on the Empire's northern border fighting Germanic, Pictish
Pictish is the extinct language, extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited num ...
and Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
tribes.National Geographic, 123. Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
was legalised
Legalization is the process of removing a legal prohibition against something which is currently not legal.
Legalization is a process often applied to what are regarded, by those working towards legalization, as victimless crimes, of which one ...
by Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
in 313 CE after three centuries of Persecution of early Christians in the Roman Empire, imperial persecution. Constantine also permanently moved the capital of the empire from Rome to the city of Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
(modern-day Istanbul) which was renamed Constantinople in his honour in 330 CE. Christianity became the sole official religion of the empire in 380 CE and in 391–392 CE, the emperor Theodosius I, Theodosius outlawed pagan religions. This is sometimes considered to mark the end of antiquity; alternatively antiquity is considered to end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
in 476 CE; the closure of the pagan Platonic Academy, Platonic Academy of Athens in 529 CE; or the rise of Islam in the early 7th century CE. During most of its existence, the Byzantine Empire was one of the most powerful economic, cultural, and military forces in Europe.
Early Middle Ages
During the decline of the Roman Empire, Europe entered a long period of change arising from what historians call the "Age of Migrations". There were numerous invasions and migrations amongst the Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Goths, Vandals, Huns,Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, Angles, Saxons, Slavs, Pannonian Avars, Avars, Bulgars and, later on, the Vikings, Pechenegs, Cumans and Magyars. Renaissance thinkers such as Petrarch would later refer to this as the "Dark Ages".
Isolated monastic communities were the only places to safeguard and compile written knowledge accumulated previously; apart from this very few written records survive and much literature, philosophy, mathematics and other thinking from the classical period disappeared from Western Europe, though they were preserved in the east, in the Byzantine Empire.
While the Roman empire in the west continued to decline, Roman traditions and the Roman state remained strong in the predominantly Greek-speaking Eastern Roman Empire, also known as the Byzantine Empire. During most of its existence, the Byzantine Empire was the most powerful economic, cultural and military force in Europe. Emperor Justinian I presided over Constantinople's first golden age: he established a Code of Justinian, legal code that forms the basis of many modern legal systems, funded the construction of the Hagia Sophia and brought the Christian church under state control.National Geographic, 135.
From the 7th century onwards, as the Byzantines and neighbouring Sasanids, Sasanid Persians were severely weakened due to the protracted, centuries-lasting and frequent Byzantine–Sasanian wars, the Muslim Arabs began to make inroads into historically Roman territory, taking the Levant and North Africa and making inroads into Asia Minor. In the mid-7th century, following the Muslim conquest of Persia, Islam penetrated into the Caucasus region. Over the next centuries Muslim forces took Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Cyprus, Malta, Emirate of Crete, Crete, Emirate of Sicily, Sicily and history of Islam in southern Italy, parts of southern Italy. Between 711 and 720, most of the lands of the Visigothic Kingdom of Iberian Peninsula, Iberia was brought under Muslim rule—save for small areas in the north-west (Asturias) and largely Basque people, Basque regions in the Pyrenees. This territory, under the Arabic name Al-Andalus, became part of the expanding Umayyad Caliphate. The unsuccessful Siege of Constantinople (717–718), second siege of Constantinople (717) weakened the Umayyad, Umayyad dynasty and reduced their prestige. The Umayyads were then defeated by the Francia, Frankish leader Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours, Battle of Poitiers in 732, which ended their northward advance. In the remote regions of north-western Iberia and the middle Pyrenees the power of the Muslims in the south was scarcely felt. It was here that the foundations of the Christian kingdoms of Kingdom of Asturias, Asturias, Kingdom of Leon, Leon and Kingdom of Galicia, Galicia were laid and from where the reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula would start. However, no coordinated attempt would be made to drive the Moors out. The Christian kingdoms were mainly focussed on their own internal power struggles. As a result, the Reconquista took the greater part of eight hundred years, in which period a long list of Alfonsos, Sanchos, Ordoños, Ramiros, Fernandos and Bermudos would be fighting their Christian rivals as much as the Muslim invaders.
 During the Dark Ages, the
During the Dark Ages, the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
fell under the control of various tribes. The Germanic and Slav tribes established their domains over Western and Eastern Europe, respectively.National Geographic, 143–145. Eventually the Frankish tribes were united under Clovis I.National Geographic, 162. Charlemagne, a Frankish king of the Carolingian dynasty who had conquered most of Western Europe, was anointed "Holy Roman Emperor" by the Pope in 800. This led in 962 to the founding of the Holy Roman Empire, which eventually became centred in the German principalities of central Europe.National Geographic, 166.
East Central Europe saw the creation of the first Slavic states and the adoption of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
(. The powerful West Slavs, West Slavic state of Great Moravia spread its territory all the way south to the Balkans, reaching its largest territorial extent under Svatopluk I of Moravia, Svatopluk I and causing a series of armed conflicts with East Francia. Further south, the first South Slavs, South Slavic states emerged in the late 7th and 8th century and adopted Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
: the First Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia (early medieval), Serbian Principality (later Kingdom of Serbia (medieval), Kingdom and Serbian Empire, Empire) and the Duchy of Croatia (later Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Kingdom of Croatia). To the East, Kievan Rus' expanded from its capital in Kiev to become the largest state in Europe by the 10th century. In 988, Vladimir the Great adopted Russian Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity as the religion of state. Further East, Volga Bulgaria became an Islamic state in the 10th century, but was eventually absorbed into Russia several centuries later.
High and Late Middle Ages
 The period between the year 1000 and 1250 is known as the High Middle Ages, followed by the Late Middle Ages until c. 1500.
During the High Middle Ages the population of Europe experienced significant growth, culminating in the Renaissance of the 12th century. Economic growth, together with the lack of safety on the mainland trading routes, made possible the development of major commercial routes along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Baltic Seas. The growing wealth and independence acquired by some coastal cities gave the Maritime Republics a leading role in the European scene.
The Middle Ages on the mainland were dominated by the two upper echelons of the social structure: the nobility and the clergy. Feudalism developed in
The period between the year 1000 and 1250 is known as the High Middle Ages, followed by the Late Middle Ages until c. 1500.
During the High Middle Ages the population of Europe experienced significant growth, culminating in the Renaissance of the 12th century. Economic growth, together with the lack of safety on the mainland trading routes, made possible the development of major commercial routes along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Baltic Seas. The growing wealth and independence acquired by some coastal cities gave the Maritime Republics a leading role in the European scene.
The Middle Ages on the mainland were dominated by the two upper echelons of the social structure: the nobility and the clergy. Feudalism developed in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
in the Early Middle Ages, and soon spread throughout Europe.National Geographic, 158. A struggle for influence between the nobility and the monarchy in England led to the writing of the ''Magna Carta'' and the establishment of a parliament.National Geographic, 186. The primary source of culture in this period came from the Roman Catholic Church. Through monasteries and cathedral schools, the Church was responsible for education in much of Europe.
 The Papacy reached the height of its power during the High Middle Ages. An East-West Schism in 1054 split the former Roman Empire religiously, with the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Catholic Church in the former Western Roman Empire. In 1095 Pope Urban II called for a Crusades, crusade against Muslims occupying Jerusalem and the Holy Land.National Geographic, 192. In Europe itself, the Church organised the Inquisition against heretics. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Reconquista concluded with the Granada War#Last stand at Granada, fall of Granada in 1492, ending over seven centuries of Islamic rule in the south-western peninsula.National Geographic, 199.
In the east, a resurgent Byzantine Empire recaptured Crete and Cyprus from the Muslims, and reconquered the Balkans. Constantinople was the largest and wealthiest city in Europe from the 9th to the 12th centuries, with a population of approximately 400,000. The Empire was weakened following the defeat at Battle of Manzikert, Manzikert, and was weakened considerably by the Siege of Constantinople (1204), sack of Constantinople in 1204, during the Fourth Crusade. Although it would recover Constantinople in 1261, Byzantine Empire, Byzantium Fall of Constantinople, fell in 1453 when Fall of Constantinople, Constantinople was taken by the Ottoman Empire.National Geographic, 211.
The Papacy reached the height of its power during the High Middle Ages. An East-West Schism in 1054 split the former Roman Empire religiously, with the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Catholic Church in the former Western Roman Empire. In 1095 Pope Urban II called for a Crusades, crusade against Muslims occupying Jerusalem and the Holy Land.National Geographic, 192. In Europe itself, the Church organised the Inquisition against heretics. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Reconquista concluded with the Granada War#Last stand at Granada, fall of Granada in 1492, ending over seven centuries of Islamic rule in the south-western peninsula.National Geographic, 199.
In the east, a resurgent Byzantine Empire recaptured Crete and Cyprus from the Muslims, and reconquered the Balkans. Constantinople was the largest and wealthiest city in Europe from the 9th to the 12th centuries, with a population of approximately 400,000. The Empire was weakened following the defeat at Battle of Manzikert, Manzikert, and was weakened considerably by the Siege of Constantinople (1204), sack of Constantinople in 1204, during the Fourth Crusade. Although it would recover Constantinople in 1261, Byzantine Empire, Byzantium Fall of Constantinople, fell in 1453 when Fall of Constantinople, Constantinople was taken by the Ottoman Empire.National Geographic, 211.
 In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Cuman-Kipchak Confederation, Cuman-Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic peoples, Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north, and temporarily halted the expansion of the Rus' state to the south and east. Like many other parts of
In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Cuman-Kipchak Confederation, Cuman-Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic peoples, Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north, and temporarily halted the expansion of the Rus' state to the south and east. Like many other parts of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
, these territories were Mongol invasion of Rus, overrun by the Mongols. The invaders, who became known as Tatars, were mostly Turkic-speaking peoples under Mongol suzerainty. They established the state of the Golden Horde with headquarters in Crimea, which later adopted Islam as a religion, and ruled over modern-day southern and central Russia for more than three centuries. After the collapse of Mongol dominions, the first Romanian states (principalities) emerged in the 14th century: Moldavia and Walachia. Previously, these territories were under the successive control of Pechenegs and Cumans. From the 12th to the 15th centuries, the Grand Duchy of Moscow grew from a small principality under Mongol rule to the largest state in Europe, overthrowing the Mongols in 1480, and eventually becoming the Tsardom of Russia. The state was consolidated under Ivan III the Great and Ivan the Terrible, steadily expanding to the east and south over the next centuries.
The Great Famine of 1315–1317 was the first Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, crisis that would strike Europe in the late Middle Ages. The period between 1348 and 1420 witnessed the heaviest loss. The population of France in the Middle Ages, France was reduced by half. Medieval Britain was afflicted by 95 famines, and France suffered the effects of 75 or more in the same period. Europe was devastated in the mid-14th century by the Black Death, one of the most deadly pandemics in human history which killed an estimated 25 million people in Europe alone—a third of the Medieval demography, European population at the time.
The plague had a devastating effect on Europe's social structure; it induced people to live for the moment as illustrated by Giovanni Boccaccio in ''The Decameron'' (1353). It was a serious blow to the Roman Catholic Church and led to increased persecution of Jews, beggars and lepers.National Geographic, 223. The plague is thought to have returned every generation with varying virulence and mortalities until the 18th century. During this period, more than 100 plague List of epidemics, epidemics swept across Europe.
Early modern period
 The Renaissance was a period of cultural change originating in Florence, and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The rise of a Renaissance humanism, new humanism was accompanied by the recovery of forgotten Classical Greece, classical Greek and Arabic knowledge from Monasticism, monastic libraries, often translated from Arabic into Latin language, Latin. The Renaissance spread across Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries: it saw the flowering of
The Renaissance was a period of cultural change originating in Florence, and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The rise of a Renaissance humanism, new humanism was accompanied by the recovery of forgotten Classical Greece, classical Greek and Arabic knowledge from Monasticism, monastic libraries, often translated from Arabic into Latin language, Latin. The Renaissance spread across Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries: it saw the flowering of art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, music and the History of science in the Renaissance, sciences, under the joint patronage of Royal family, royalty, the nobility, the Roman Catholic Church and an emerging merchant class.National Geographic, 254. Patrons in Italy, including the Medici family of Florentine bankers and the Popes in Rome, funded prolific quattrocento and cinquecento artists such as Raphael, Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci.National Geographic, 292.
Political intrigue within the Church in the mid-14th century caused the Western Schism. During this forty-year period, two popes—one in Avignon and one in Rome—claimed rulership over the Church. Although the schism was eventually healed in 1417, the papacy's spiritual authority had suffered greatly.National Geographic, 193. In the 15th century, Europe started to extend itself beyond its geographic frontiers. Spain and Portugal, the greatest naval powers of the time, took the lead in exploring the world.National Geographic, 296. Exploration reached the Southern Hemisphere in the Atlantic and the Southern tip of Africa. Christopher Columbus reached the New World in 1492, and Vasco da Gama opened the ocean route to the Orient, East linking the Atlantic and Indian Oceans in 1498. The Portuguese-born explorer Ferdinand Magellan reached Asia westward across the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans in a Spanish expedition, resulting in the first Timeline of Magellan's circumnavigation, circumnavigation of the globe, completed by the Spaniard Juan Sebastián Elcano (1519–1522). Soon after, the Spanish and Portuguese began establishing large global empires in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, Asia, Africa and Oceania.National Geographic, 338. France, the Netherlands and England soon followed in building large colonial empires with vast holdings in Africa, the Americas and Asia. In 1588, a Spanish armada failed to invade England. A year later English Armada, England tried unsuccessfully to invade Spain, allowing Philip II of Spain to maintain his dominant war capacity in Europe. This English disaster also allowed the Spanish fleet to retain its capability to wage war for the next decades. However, two more Spanish armadas failed to invade England (2nd Spanish Armada and 3rd Spanish Armada).
 The Church's power was further weakened by the Protestant reformation, Protestant Reformation in 1517 when German theologian Martin Luther nailed his ''Ninety-five Theses'' criticising the selling of indulgences to the church door. He was subsequently excommunicated in the papal bull ''Exsurge Domine'' in 1520 and his followers were condemned in the 1521 Diet of Worms, which divided German princes between Protestant and Roman Catholic faiths.National Geographic, 256–257. European wars of religion, Religious fighting and warfare spread with Protestantism. The plunder of the empires of the Americas allowed Spain to finance Spanish Inquisition, religious persecution in Europe for over a century. The Thirty Years War (1618–1648) crippled the Holy Roman Empire and devastated much of Early Modern history of Germany, Germany, killing between 25 and 40 percent of its population. In the aftermath of the Peace of Westphalia, France rose to predominance within Europe.National Geographic, 269. The defeat of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the historic end of Ottoman wars in Europe, Ottoman expansion into Europe.
The 17th century in central and parts of eastern Europe was a period of general The General Crisis, decline; the region experienced more than 150 famines in a 200-year period between 1501 and 1700. From the Union of Krewo (1385) east-central Europe was dominated by the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The hegemony of the vast Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had ended with the devastation brought by the Second Northern War (Swedish Deluge, Deluge) and subsequent conflicts; the state itself was Partitions of Poland, partitioned and ceased to exist at the end of the 18th century.
From the 15th to 18th centuries, when the disintegrating khanates of the Golden Horde were conquered by Russia, Crimean Tatars, Tatars from the Crimean Khanate frequently Crimean-Nogai raids into East Slavic lands, raided Eastern Slavic lands to Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, capture slaves. Further east, the Nogai Horde and Kazakh Khanate frequently raided the Slavic-speaking areas of contemporary Russia and Ukraine for hundreds of years, until the Russian expansion and conquest of most of northern Eurasia (i.e. Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Siberia).
The Renaissance and the New Monarchs marked the start of an Age of Discovery, a period of exploration, invention and scientific development. Among the great figures of the Western scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries were Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Isaac Newton. According to Peter Barrett, "It is widely accepted that 'modern science' arose in the Europe of the 17th century (towards the end of the Renaissance), introducing a new understanding of the natural world."Peter Barrett (2004),
The Church's power was further weakened by the Protestant reformation, Protestant Reformation in 1517 when German theologian Martin Luther nailed his ''Ninety-five Theses'' criticising the selling of indulgences to the church door. He was subsequently excommunicated in the papal bull ''Exsurge Domine'' in 1520 and his followers were condemned in the 1521 Diet of Worms, which divided German princes between Protestant and Roman Catholic faiths.National Geographic, 256–257. European wars of religion, Religious fighting and warfare spread with Protestantism. The plunder of the empires of the Americas allowed Spain to finance Spanish Inquisition, religious persecution in Europe for over a century. The Thirty Years War (1618–1648) crippled the Holy Roman Empire and devastated much of Early Modern history of Germany, Germany, killing between 25 and 40 percent of its population. In the aftermath of the Peace of Westphalia, France rose to predominance within Europe.National Geographic, 269. The defeat of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the historic end of Ottoman wars in Europe, Ottoman expansion into Europe.
The 17th century in central and parts of eastern Europe was a period of general The General Crisis, decline; the region experienced more than 150 famines in a 200-year period between 1501 and 1700. From the Union of Krewo (1385) east-central Europe was dominated by the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The hegemony of the vast Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had ended with the devastation brought by the Second Northern War (Swedish Deluge, Deluge) and subsequent conflicts; the state itself was Partitions of Poland, partitioned and ceased to exist at the end of the 18th century.
From the 15th to 18th centuries, when the disintegrating khanates of the Golden Horde were conquered by Russia, Crimean Tatars, Tatars from the Crimean Khanate frequently Crimean-Nogai raids into East Slavic lands, raided Eastern Slavic lands to Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, capture slaves. Further east, the Nogai Horde and Kazakh Khanate frequently raided the Slavic-speaking areas of contemporary Russia and Ukraine for hundreds of years, until the Russian expansion and conquest of most of northern Eurasia (i.e. Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Siberia).
The Renaissance and the New Monarchs marked the start of an Age of Discovery, a period of exploration, invention and scientific development. Among the great figures of the Western scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries were Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Isaac Newton. According to Peter Barrett, "It is widely accepted that 'modern science' arose in the Europe of the 17th century (towards the end of the Renaissance), introducing a new understanding of the natural world."Peter Barrett (2004), Science and Theology Since Copernicus: The Search for Understanding
'', pp. 14–18, Continuum International Publishing Group,
18th and 19th centuries
 The Seven Years' War brought to an end the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), "Old System" of alliances in Europe. Consequently, when the American Revolutionary War turned into a global war between 1778 and 1783, Britain found itself opposed by a strong coalition of European powers, and lacking any substantial ally.
The Age of Enlightenment was a powerful intellectual movement during the 18th century promoting scientific and reason-based thoughts.National Geographic, 255. Discontent with the aristocracy and clergy's monopoly on political power in France resulted in the French Revolution, and the establishment of the French First Republic, First Republic as a result of which the monarchy and many of the nobility perished during the initial Reign of Terror, reign of terror. Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and established the First French Empire that, during the
The Seven Years' War brought to an end the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), "Old System" of alliances in Europe. Consequently, when the American Revolutionary War turned into a global war between 1778 and 1783, Britain found itself opposed by a strong coalition of European powers, and lacking any substantial ally.
The Age of Enlightenment was a powerful intellectual movement during the 18th century promoting scientific and reason-based thoughts.National Geographic, 255. Discontent with the aristocracy and clergy's monopoly on political power in France resulted in the French Revolution, and the establishment of the French First Republic, First Republic as a result of which the monarchy and many of the nobility perished during the initial Reign of Terror, reign of terror. Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and established the First French Empire that, during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, grew to encompass large parts of Europe before collapsing in 1815 with the Battle of Waterloo.National Geographic, 360. Napoleonic Empire, Napoleonic rule resulted in the further dissemination of the ideals of the French Revolution, including that of the nation state, as well as the widespread adoption of the French models of centralised government, administration, Napoleonic code, law and Education in France, education.National Geographic, 350. The Congress of Vienna, convened after Napoleon's downfall, established a new balance of power (international relations), balance of power in Europe centred on the five "Great Powers": the UK, France, Prussia, Austrian Empire, Austria and Russia.National Geographic, 367. This balance would remain in place until the Revolutions of 1848, during which liberal uprisings affected all of Europe except for Russia and the UK. These revolutions were eventually put down by conservative elements and few reforms resulted.National Geographic, 371–373. The year 1859 saw the unification of Romania, as a nation state, from smaller principalities. In 1867, the Austro-Hungarian empire was Ausgleich, formed; 1871 saw the unifications of both Italian unification, Italy and Unification of Germany, Germany as nation-states from smaller principalities.
In parallel, the Eastern Question grew more complex ever since the Ottoman defeat in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774). As the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire seemed imminent, the Great Powers struggled to safeguard their strategic and commercial interests in the Ottoman domains. The Russian Empire stood to benefit from the decline, whereas the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Empire and United Kingdom, Britain perceived the preservation of the Ottoman Empire to be in their best interests. Meanwhile, the Serbian revolution (1804) and Greek War of Independence (1821) marked the beginning of the end of Ottoman rule in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, which ended with the Balkan Wars in 1912–1913. Formal recognition of the ''de facto'' independent principalities of Montenegro, Principality of Serbia, Serbia and Romania ensued at the Congress of Berlin in 1878.
 The
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
started in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
in the last part of the 18th century and spread throughout Europe. The invention and implementation of new technologies resulted in rapid urban growth, mass employment and the rise of a new working class. Reforms in social and economic spheres followed, including the Factory Acts, first laws on child labour, the legalisation of trade unions, and the abolitionism in the United Kingdom, abolition of slavery. In Britain, the Public Health Act of 1875 was passed, which significantly improved living conditions in many British cities. Europe's population increased from about 100 million in 1700 to 400 million by 1900. The last major famine recorded in Western Europe, the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of Ireland, caused death and mass emigration of millions of Irish people. In the 19th century, 70 million people left Europe in migrations to various European colonies abroad and to the United States. Demographic growth meant that, by 1900, Europe's share of the world's population was 25%.
20th century to the present
 Two world wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Yugoslav nationalism, Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip.National Geographic, 407. Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (French Third Republic, France,
Two world wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Yugoslav nationalism, Yugoslav nationalist Gavrilo Princip.National Geographic, 407. Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (French Third Republic, France, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Serbia, Portugal, Russian Empire, Russia, the United Kingdom, and later Italy, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, Romania, and the United States) and the Central Powers (Austria-Hungary, German Empire, Germany, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire). The war left more than 16 million civilians and military dead.''National Geographic'', 440. Over 60 million European soldiers were mobilised from 1914 to 1918.
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
,National Geographic, 480. leading also to the independence of many former Governorate (Russia), Russian governorates, such as Finland, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, as new European countries. Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire collapsed and broke up into separate nations, and many other nations had their borders redrawn. The Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended the First World War in 1919, was harsh towards Germany, upon whom it placed full responsibility for the war and imposed heavy sanctions.''National Geographic'', 443. Excess deaths in Russia over the course of the First World War and the Russian Civil War (including the postwar Russian famine of 1921, famine) amounted to a combined total of 18 million. In 1932–1933, under Stalin's leadership, confiscations of grain by the Soviet authorities contributed to the Soviet famine of 1932-1933, second Soviet famine which caused millions of deaths; surviving kulaks were persecuted and many sent to Gulags to do Unfree labour, forced labour. Stalin was also responsible for the Great Purge of 1937–38 in which the NKVD executed 681,692 people; millions of people were population transfer in the Soviet Union, deported and exiled to remote areas of the Soviet Union.
 The social revolutions sweeping through Russia also affected other European nations following The Great War: in 1919, with the Weimar Republic in Germany and the First Austrian Republic; in 1922, with Benito Mussolini, Mussolini's one-party Fascism, fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy and in Atatürk's Turkey, Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet and state secularism.
Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This, and the Wall Street Crash of 1929, brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis, social instability and the threat of communism, Fascism, fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler in power of what became Nazi Germany.''National Geographic'', 438.
In 1933, Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards his goal of building Greater Germany. Germany re-expanded and took back the Saarland and Rhineland in 1935 and 1936. In 1938, Austria became a part of Germany following the Anschluss. Later that year, following the Munich Agreement signed by Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Italy, Germany annexed the Sudetenland, which was a part of Czechoslovakia inhabited by ethnic Germans, and in early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic. At the time, the United Kingdom and France preferred a policy of appeasement.
With tensions mounting between Germany and Second Polish Republic, Poland over the future of Gdańsk, Danzig, the Germans turned to the Soviets and signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which allowed the Soviets to invade the Baltic states and parts of Poland and Romania. Germany Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 3 September, opening the European Theatre of World War II, European Theatre of the Second World War.National Geographic, 465. The Soviet invasion of Poland started on 17 September and Poland fell soon thereafter. On 24 September, the Soviet Union attacked the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states (1940), Baltic countries and, on 30 November, Finland, the latter of which was followed by the devastating Winter War for the Red Army. The British hoped to land at Battles of Narvik, Narvik and send troops to aid Finland, but their primary objective in the landing was to encircle Germany and cut the Germans off from Scandinavian resources. Around the same time, Germany moved troops into Denmark. The Phoney War continued.
In May 1940, Germany Battle of France, attacked France through the Low Countries. France capitulated in June 1940. By August, Germany had begun a Battle of Britain, bombing offensive against the United Kingdom but failed to convince the Britons to give up.''National Geographic'', 510. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa.''National Geographic'', 532. On 7 December 1941 Empire of Japan, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire, and other Allies of World War II, allied forces.''National Geographic'', 511.''National Geographic'', 519.
After the staggering Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback. The Battle of Kursk, which involved the largest Battle of Prokhorovka, tank battle in history, was the last major German offensive on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. In June 1944, British and American forces invaded France in the Normandy landings, D-Day landings, opening a new front against Germany. Berlin finally Battle of Berlin, fell in 1945, ending the Second World War in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with World War II casualties, 60 million dead across the world.''National Geographic'', 439. More than 40 million people in Europe had died as a result of the Second World War, including between 11 and 17 million people who perished during the Holocaust. The Soviet Union World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, lost around 27 million people (mostly civilians) during the war, about half of all Second World War casualties. By the end of the Second World War, Europe had more than 40 million refugees. Several World War II evacuation and expulsion, post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe displaced a total of about 20 million people.
The First World War, and especially the Second World War, diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After the Second World War the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an "
The social revolutions sweeping through Russia also affected other European nations following The Great War: in 1919, with the Weimar Republic in Germany and the First Austrian Republic; in 1922, with Benito Mussolini, Mussolini's one-party Fascism, fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy and in Atatürk's Turkey, Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet and state secularism.
Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This, and the Wall Street Crash of 1929, brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis, social instability and the threat of communism, Fascism, fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler in power of what became Nazi Germany.''National Geographic'', 438.
In 1933, Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards his goal of building Greater Germany. Germany re-expanded and took back the Saarland and Rhineland in 1935 and 1936. In 1938, Austria became a part of Germany following the Anschluss. Later that year, following the Munich Agreement signed by Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Italy, Germany annexed the Sudetenland, which was a part of Czechoslovakia inhabited by ethnic Germans, and in early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic. At the time, the United Kingdom and France preferred a policy of appeasement.
With tensions mounting between Germany and Second Polish Republic, Poland over the future of Gdańsk, Danzig, the Germans turned to the Soviets and signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which allowed the Soviets to invade the Baltic states and parts of Poland and Romania. Germany Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on 3 September, opening the European Theatre of World War II, European Theatre of the Second World War.National Geographic, 465. The Soviet invasion of Poland started on 17 September and Poland fell soon thereafter. On 24 September, the Soviet Union attacked the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states (1940), Baltic countries and, on 30 November, Finland, the latter of which was followed by the devastating Winter War for the Red Army. The British hoped to land at Battles of Narvik, Narvik and send troops to aid Finland, but their primary objective in the landing was to encircle Germany and cut the Germans off from Scandinavian resources. Around the same time, Germany moved troops into Denmark. The Phoney War continued.
In May 1940, Germany Battle of France, attacked France through the Low Countries. France capitulated in June 1940. By August, Germany had begun a Battle of Britain, bombing offensive against the United Kingdom but failed to convince the Britons to give up.''National Geographic'', 510. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa.''National Geographic'', 532. On 7 December 1941 Empire of Japan, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire, and other Allies of World War II, allied forces.''National Geographic'', 511.''National Geographic'', 519.
After the staggering Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback. The Battle of Kursk, which involved the largest Battle of Prokhorovka, tank battle in history, was the last major German offensive on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. In June 1944, British and American forces invaded France in the Normandy landings, D-Day landings, opening a new front against Germany. Berlin finally Battle of Berlin, fell in 1945, ending the Second World War in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with World War II casualties, 60 million dead across the world.''National Geographic'', 439. More than 40 million people in Europe had died as a result of the Second World War, including between 11 and 17 million people who perished during the Holocaust. The Soviet Union World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, lost around 27 million people (mostly civilians) during the war, about half of all Second World War casualties. By the end of the Second World War, Europe had more than 40 million refugees. Several World War II evacuation and expulsion, post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe displaced a total of about 20 million people.
The First World War, and especially the Second World War, diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After the Second World War the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an "Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. The term symbolizes the efforts by the Soviet Union (USSR) to block itself and its s ...
". The United States and Western Europe established the NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
alliance and, later, the Soviet Union and Central Europe established the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
.National Geographic, 530. Particular hot spots after the Second World War were Berlin and Trieste, whereby the Free Territory of Trieste, founded in 1947 with the UN, was dissolved in 1954 and 1975, respectively. The Berlin blockade in 1948 and 1949 and the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961 were one of the great international crises of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
.
The two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, became locked in a fifty-year-long Cold War, centred on nuclear proliferation. At the same time decolonisation, which had already started after the First World War, gradually resulted in the independence of most of the European colonies in Asia and Africa.
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. The term symbolizes the efforts by the Soviet Union (USSR) to block itself and its s ...
at the Pan-European Picnic then set in motion a peaceful chain reaction, at the end of which the Eastern bloc, the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
and other Revolutions of 1989, communist states collapsed, and the Cold War ended. Germany was reunited, after the symbolic Berlin Wall#Fall of the Wall, fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the maps of Central and Eastern Europe were redrawn once more. This made old previously interrupted cultural and economic relationships possible, and previously isolated cities such as Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest and Trieste were now again in the centre of Europe.
European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic integration, economic, political, legal, social integration, social, and cultural Regional integration, integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integrat ...
also grew after the Second World War. In 1949 the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
was founded, following a speech by Sir Winston Churchill, with the idea of unifying Europe to achieve common goals. It includes all European states except for Belarus, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, and Vatican City. The Treaty of Rome in 1957 established the European Economic Community between six Western European states with the goal of a unified economic policy and common market.National Geographic, 536. In 1967 the EEC, European Coal and Steel Community, and Euratom formed the European Community, which in 1993 became the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
. The EU established a European Parliament, parliament, European Court of Justice, court and European Central Bank, central bank, and introduced the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
as a unified currency.National Geographic, 537. Between 2004 and 2013, more Central European countries began joining, Enlargement of the European Union, expanding the EU to 28 European countries and once more making Europe a major economical and political centre of power.National Geographic, 535. However, the United Kingdom withdrew from the EU on 31 January 2020, as a result of a 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, June 2016 referendum on EU membership. The Russo-Ukrainian War, Russo-Ukrainian conflict, which has been ongoing since 2014, steeply escalated when Russia launched a 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, full-scale invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022, marking the largest humanitarian and refugee crisis in Europe since the Second World War and the Yugoslav Wars.
Geography
Europe makes up the western fifth of theEurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
n landmass. It has a higher ratio of coast to landmass than any other continent or subcontinent. Its maritime borders consist of the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean, Black and Caspian Seas to the south.
Land relief in Europe shows great variation within relatively small areas. The southern regions are more mountainous, while moving north the terrain descends from the high Alps, Pyrenees and Carpathians, through hilly uplands, into broad, low northern plains, which are vast in the east. This extended lowland is known as the Great European Plain and at its heart lies the North German Plain. An arc of uplands also exists along the north-western seaboard, which begins in the western parts of the islands of Britain and Ireland, and then continues along the mountainous, fjord-cut spine of Norway.
This description is simplified. Subregions such as the Iberian Peninsula and the Italian Peninsula contain their own complex features, as does mainland Central Europe itself, where the relief contains many plateaus, river valleys and basins that complicate the general trend. Sub-regions like Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, Britain and Ireland are special cases. The former is a land unto itself in the northern ocean that is counted as part of Europe, while the latter are upland areas that were once joined to the mainland until sea level rise, rising sea levels cut them off.
Climate
 Europe lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being subjected to prevailing westerlies. The climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore, the average temperature throughout the year of Aveiro, Portugal, Aveiro is , while it is only in New York City which is almost on the same latitude, bordering the same ocean. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in far south-eastern Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average around higher than those in Calgary and they are almost higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk.
The large water masses of the
Europe lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being subjected to prevailing westerlies. The climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore, the average temperature throughout the year of Aveiro, Portugal, Aveiro is , while it is only in New York City which is almost on the same latitude, bordering the same ocean. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in far south-eastern Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average around higher than those in Calgary and they are almost higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk.
The large water masses of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, which equalise the temperatures on an annual and daily average, are also of particular importance. The water of the Mediterranean extends from the Sahara desert to the Alpine arc in its northernmost part of the Adriatic Sea near Trieste.
In general, Europe is not just colder towards the north compared to the south, but it also gets colder from the west towards the east. The climate is more oceanic in the west and less so in the east. This can be illustrated by the following table of average temperatures at locations roughly following the 64th, 60th, 55th, 50th, 45th and 40th latitudes. None of them is located at high altitude; most of them are close to the sea. (location, approximate latitude and longitude, coldest month average, hottest month average and annual average temperatures in degrees C)
Geology
 The geological history of Europe traces back to the formation of the Baltic Shield (Fennoscandia) and the Sarmatian craton, both around 2.25 billion years ago, followed by the Volgo–Uralia shield, the three together leading to the East European craton (≈ Baltica) which became a part of the supercontinent Columbia (supercontinent), Columbia. Around 1.1 billion years ago, Baltica and Arctica (as part of the Laurentia block) became joined to Rodinia, later resplitting around 550 million years ago to reform as Baltica. Around 440 million years ago Euramerica was formed from Baltica and Laurentia; a further joining with Gondwana then leading to the formation of Pangea. Around 190 million years ago, Gondwana and Laurasia split apart due to the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. Finally and very soon afterwards, Laurasia itself split up again, into Laurentia (North America) and the Eurasian continent. The land connection between the two persisted for a considerable time, via Greenland, leading to interchange of animal species. From around 50 million years ago, rising and falling sea levels have determined the actual shape of Europe and its connections with continents such as Asia. Europe's present shape dates to the late Tertiary period about five million years ago.
The geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary. Europe's most significant feature is the dichotomy between highland and mountainous Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern plain ranging from Ireland in the west to the
The geological history of Europe traces back to the formation of the Baltic Shield (Fennoscandia) and the Sarmatian craton, both around 2.25 billion years ago, followed by the Volgo–Uralia shield, the three together leading to the East European craton (≈ Baltica) which became a part of the supercontinent Columbia (supercontinent), Columbia. Around 1.1 billion years ago, Baltica and Arctica (as part of the Laurentia block) became joined to Rodinia, later resplitting around 550 million years ago to reform as Baltica. Around 440 million years ago Euramerica was formed from Baltica and Laurentia; a further joining with Gondwana then leading to the formation of Pangea. Around 190 million years ago, Gondwana and Laurasia split apart due to the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. Finally and very soon afterwards, Laurasia itself split up again, into Laurentia (North America) and the Eurasian continent. The land connection between the two persisted for a considerable time, via Greenland, leading to interchange of animal species. From around 50 million years ago, rising and falling sea levels have determined the actual shape of Europe and its connections with continents such as Asia. Europe's present shape dates to the late Tertiary period about five million years ago.
The geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary. Europe's most significant feature is the dichotomy between highland and mountainous Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern plain ranging from Ireland in the west to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
in the east. These two halves are separated by the mountain chains of the Pyrenees and Alps/Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians. The northern plains are delimited in the west by the Scandinavian Mountains and the mountainous parts of the British Isles. Major shallow water bodies submerging parts of the northern plains are the Celtic Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea complex and Barents Sea.
The northern plain contains the old geological continent of Baltica and so may be regarded geologically as the "main continent", while peripheral highlands and mountainous regions in the south and west constitute fragments from various other geological continents. Most of the older geology of western Europe existed as part of the ancient microcontinent Avalonia.
Flora
 Having lived side by side with agricultural peoples for millennia, Europe's animals and plants have been profoundly affected by the presence and activities of man. With the exception of Fennoscandia and northern Russia, few areas of untouched wilderness are currently found in Europe, except for various national parks.
The main natural vegetation cover in Europe is mixed forest. The conditions for growth are very favourable. In the north, the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift warm the continent. Southern Europe could be described as having a warm, but mild climate. There are frequent summer droughts in this region. Mountain ridges also affect the conditions. Some of these (Alps, Pyrenees) are oriented east–west and allow the wind to carry large masses of water from the ocean in the interior. Others are oriented south–north (Scandinavian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, Dinarides, Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, Apennine Mountains, Apennines) and because the rain falls primarily on the side of mountains that is oriented towards the sea, forests grow well on this side, while on the other side, the conditions are much less favourable. Few corners of mainland Europe have not been grazed by livestock at some point in time, and the cutting down of the preagricultural forest habitat caused disruption to the original plant and animal ecosystems.
Having lived side by side with agricultural peoples for millennia, Europe's animals and plants have been profoundly affected by the presence and activities of man. With the exception of Fennoscandia and northern Russia, few areas of untouched wilderness are currently found in Europe, except for various national parks.
The main natural vegetation cover in Europe is mixed forest. The conditions for growth are very favourable. In the north, the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift warm the continent. Southern Europe could be described as having a warm, but mild climate. There are frequent summer droughts in this region. Mountain ridges also affect the conditions. Some of these (Alps, Pyrenees) are oriented east–west and allow the wind to carry large masses of water from the ocean in the interior. Others are oriented south–north (Scandinavian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, Dinarides, Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, Apennine Mountains, Apennines) and because the rain falls primarily on the side of mountains that is oriented towards the sea, forests grow well on this side, while on the other side, the conditions are much less favourable. Few corners of mainland Europe have not been grazed by livestock at some point in time, and the cutting down of the preagricultural forest habitat caused disruption to the original plant and animal ecosystems.
 Possibly 80 to 90 percent of Europe was once covered by forest. It stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Although over half of Europe's original forests disappeared through the centuries of deforestation, Europe still has over one quarter of its land area as forest, such as the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest, broadleaf and mixed forests, taiga of Scandinavia and Russia, mixed rainforests of the Caucasus and the Cork oak forests in the western Mediterranean. During recent times, deforestation has been slowed and many trees have been planted. However, in many cases monoculture plantations of Pinophyta, conifers have replaced the original mixed natural forest, because these grow quicker. The plantations now cover vast areas of land, but offer poorer habitats for many European forest dwelling species which require a mixture of tree species and diverse forest structure. The amount of natural forest in Western Europe is just 2–3% or less, while in its Western Russia its 5–10%. The European country with the List of countries by forest area, smallest percentage of forested area is
Possibly 80 to 90 percent of Europe was once covered by forest. It stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Although over half of Europe's original forests disappeared through the centuries of deforestation, Europe still has over one quarter of its land area as forest, such as the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest, broadleaf and mixed forests, taiga of Scandinavia and Russia, mixed rainforests of the Caucasus and the Cork oak forests in the western Mediterranean. During recent times, deforestation has been slowed and many trees have been planted. However, in many cases monoculture plantations of Pinophyta, conifers have replaced the original mixed natural forest, because these grow quicker. The plantations now cover vast areas of land, but offer poorer habitats for many European forest dwelling species which require a mixture of tree species and diverse forest structure. The amount of natural forest in Western Europe is just 2–3% or less, while in its Western Russia its 5–10%. The European country with the List of countries by forest area, smallest percentage of forested area is Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
(1%), while the most forested country is Finland (77%).
In temperate Europe, mixed forest with both flowering plant, broadleaf and coniferous trees dominate. The most important species in central and western Europe are beech and oak. In the north, the taiga is a mixed spruce–pine–birch forest; further north within Russia and extreme northern Scandinavia, the taiga gives way to tundra as the Arctic is approached. In the Mediterranean, many olive trees have been planted, which are very well adapted to its arid climate; Cupressus sempervirens, Mediterranean Cypress is also widely planted in southern Europe. The semi-arid Mediterranean region hosts much scrub forest. A narrow east–west tongue of Eurasian grassland (the steppe) extends westwards from Ukraine and southern Russia and ends in Hungary and traverses into taiga to the north.
Fauna
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
the bears' habitats were limited to more or less inaccessible mountains with sufficient forest cover. Today, the European brown bear, brown bear lives primarily in the Balkan, Balkan peninsula, Scandinavia and Russia; a small number also persist in other countries across Europe (Austria, Pyrenees etc.), but in these areas brown bear populations are fragmented and marginalised because of the destruction of their habitat. In addition, polar bears may be found on Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago far north of Scandinavia. The Eurasian wolf, wolf, the second largest predator in Europe after the brown bear, can be found primarily in Central and Eastern Europe and in the Balkans, with a handful of packs in pockets of Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
(Scandinavia, Spain, etc.).
 European wild cat, foxes (especially the red fox), jackal and different species of martens, hedgehogs, different species of reptiles (like snakes such as vipers and grass snakes) and amphibians, different birds (owls, hawks and other birds of prey).
Important European herbivores are snails, larvae, fish, different birds and mammals, like rodents, deer and roe deer, boars and living in the mountains, marmots, steinbocks, chamois among others. A number of insects, such as the small tortoiseshell butterfly, add to the biodiversity.
The extinction of the Cretan Dwarf Hippopotamus, dwarf hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on the islands of the Mediterranean.
Sea creatures are also an important part of European flora and fauna. The sea flora is mainly phytoplankton. Important animals that live in European seas are zooplankton, molluscs, echinoderms, different crustaceans, squids and octopuses, fish, dolphins and whales.
Biodiversity is protected in Europe through the Council of Europe's Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats, Bern Convention, which has also been signed by the European Community as well as non-European states.
European wild cat, foxes (especially the red fox), jackal and different species of martens, hedgehogs, different species of reptiles (like snakes such as vipers and grass snakes) and amphibians, different birds (owls, hawks and other birds of prey).
Important European herbivores are snails, larvae, fish, different birds and mammals, like rodents, deer and roe deer, boars and living in the mountains, marmots, steinbocks, chamois among others. A number of insects, such as the small tortoiseshell butterfly, add to the biodiversity.
The extinction of the Cretan Dwarf Hippopotamus, dwarf hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on the islands of the Mediterranean.
Sea creatures are also an important part of European flora and fauna. The sea flora is mainly phytoplankton. Important animals that live in European seas are zooplankton, molluscs, echinoderms, different crustaceans, squids and octopuses, fish, dolphins and whales.
Biodiversity is protected in Europe through the Council of Europe's Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats, Bern Convention, which has also been signed by the European Community as well as non-European states.
Politics
The political map of Europe is substantially derived from the re-organisation of Europe following theNapoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
in 1815. The prevalent form of government in Europe is parliamentary democracy, in most cases in the form of Republic; in 1815, the prevalent form of government was still the Monarchies in Europe, Monarchy. Europe's remaining eleven monarchies are constitutional monarchy, constitutional.
European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic integration, economic, political, legal, social integration, social, and cultural Regional integration, integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integrat ...
is the process of political, legal, economic (and in some cases social and cultural) integration of European states as it has been pursued by the powers sponsoring the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
since the end of the Second World War The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
has been the focus of economic integration on the continent since its foundation in 1993. More recently, the Eurasian Economic Union has been established as a counterpart comprising former Soviet states.
27 European states are members of the politico-economic European Union, 26 of the border-free Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
and 19 of the monetary union Eurozone. Among the smaller European organisations are the Nordic Council, the Benelux, the Baltic Assembly and the Visegrád Group.
List of states and territories
The list below includes all internationally recognized sovereign countries falling even partially under any regions of Europe, common geographical or political definitions of Europe. Within the above-mentioned states are several de facto independent countries with list of states with limited recognition, limited to no international recognition. None of them are members of the UN: Several dependencies and similar territories with broad autonomy are also found within or close to Europe. This includes Åland (an counties of Finland, autonomous county of Finland), two Danish Realm, autonomous territories of the Kingdom of Denmark (other than Denmark proper), three Crown Dependencies and two British Overseas Territories. Svalbard is also included due to its unique status within Norway, although it is not autonomous. Not included are the three countries of the United Kingdom with devolved powers and the two Autonomous Regions of Portugal, which despite having a unique degree of autonomy, are not largely self-governing in matters other than international affairs. Areas with little more than a unique tax status, such as the Canary Islands and Heligoland, are also not included for this reason.Economy
euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
as a common currency.
Five European countries rank in the top ten of the world's largest List of countries by GDP (PPP), national economies in GDP (PPP). This includes (ranks according to the The World Factbook, CIA): Germany (6), Russia (7), the United Kingdom (10), France (11) and Italy (13).
There is huge disparity between many European countries in terms of their income. The richest in terms of nominal GDP is Monaco with its US$185,829 per capita (2018) and the poorest is Ukraine with its US$3,659 per capita (2019). Monaco is the richest country in terms of GDP per capita in the world according to the World Bank report.
As a whole, Europe's GDP per capita is US$21,767 according to a 2016 International Monetary Fund assessment.
Economic history
;Industrial growth (1760–1945) Capitalism has been dominant in the Western world since the end of feudalism. From Britain, it gradually spread throughout Europe. TheIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
started in Europe, specifically the United Kingdom in the late 18th century, and the 19th century saw Western Europe industrialise. Economies were disrupted by the First World War, but by the beginning of the Second World War, they had recovered and were having to compete with the growing economic strength of the United States. The Second World War, again, damaged much of Europe's industries.
;Cold War (1945–1991)

Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and thus were members of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON)."Germany (East)", Library of Congress Country StudyAppendix B: The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
The states which retained a free-market system were given a large amount of aid by the United States under the Marshall Plan. The western states moved to link their economies together, providing the basis for the EU and increasing cross border trade. This helped them to enjoy rapidly improving economies, while those states in COMECON were struggling in a large part due to the cost of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. Until 1990, the European Community was expanded from 6 founding members to 12. The emphasis placed on resurrecting the West German economy led to it overtaking the UK as Europe's largest economy.
;Reunification (1991–present)
 With the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe in 1991, the post-socialist states began free market reforms.
After East Germany, East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, the economy of West Germany struggled as it had to support and largely rebuild the infrastructure of East Germany.
By the millennium change, the EU dominated the economy of Europe, comprising the five largest European economies of the time: Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. In 1999, 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone replacing their former national currencies by the common euro. The three who chose to remain outside the Eurozone were the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Sweden. The European Union is now the largest economy in the world.
Figures released by Eurostat in 2009 confirmed that the Eurozone had gone into Late 2000s recession in Europe, recession in 2008. It impacted much of the region. In 2010, fears of a European sovereign-debt crisis, sovereign debt crisis developed concerning some countries in Europe, especially Greece, Ireland, Spain and Portugal. As a result, measures were taken, especially for Greece, by the leading countries of the Eurozone. The European Union, EU-27 unemployment rate was 10.3% in 2012. For those aged 15–24 it was 22.4%.Unemployment statistics
With the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe in 1991, the post-socialist states began free market reforms.
After East Germany, East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, the economy of West Germany struggled as it had to support and largely rebuild the infrastructure of East Germany.
By the millennium change, the EU dominated the economy of Europe, comprising the five largest European economies of the time: Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. In 1999, 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone replacing their former national currencies by the common euro. The three who chose to remain outside the Eurozone were the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Sweden. The European Union is now the largest economy in the world.
Figures released by Eurostat in 2009 confirmed that the Eurozone had gone into Late 2000s recession in Europe, recession in 2008. It impacted much of the region. In 2010, fears of a European sovereign-debt crisis, sovereign debt crisis developed concerning some countries in Europe, especially Greece, Ireland, Spain and Portugal. As a result, measures were taken, especially for Greece, by the leading countries of the Eurozone. The European Union, EU-27 unemployment rate was 10.3% in 2012. For those aged 15–24 it was 22.4%.Unemployment statistics. Eurostat. April 2012.
Demographics
Population Reference Bureau. The population of Europe has grown in the past century, but in other areas of the world (in particular Africa and Asia) the population has grown far more quickly. Among the continents, Europe has a relatively high population density, second only to Asia. Most of Europe is in a mode of sub-replacement fertility, which means that each new(-born) generation is being less populous than the older. The most densely populated country in Europe (and in the world) is the microstate of Monaco.
Ethnic groups
Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "peoples of Europe", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minority, ethnic minorities. According to UN population projection, Europe's population may fall to about 7% of world population by 2050, or 653 million people (medium variant, 556 to 777 million in low and high variants, respectively). Within this context, significant disparities exist between regions in relation to fertility rates. The average number of List of countries and territories by fertility rate, children per female of child-bearing age is 1.52. According to some sources, this rate is higher among Islam in Europe, Muslims in Europe. The UN predicts a steady population decline in Central and Eastern Europe as a result of emigration and low birth rates.Migration
North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographical terms and is coextensive with the Asian part of Russia, and consists of three Russian regions east of the Ural Mountains: ...
and some parts of Northern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
.
Languages
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
; the Germanic languages, whose ancestor language came from southern Scandinavia; and the Slavic languages. Slavic languages are mostly spoken in Southern, Central and Eastern Europe. Romance languages are spoken primarily in Western and Southern Europe, as well as in Switzerland in Central Europe and Romania and Moldova in Eastern Europe. Germanic languages are spoken in Western, Northern and Central Europe as well as in Gibraltar and Malta in Southern Europe. Languages in adjacent areas show significant overlaps (such as in English (language), English, for example). Other Indo-European languages outside the three main groups include the Baltic languages, Baltic group (Latvian language, Latvian and Lithuanian language, Lithuanian), the Celtic languages, Celtic group (Irish language, Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Manx language, Manx, Welsh language, Welsh, Cornish language, Cornish and Breton language, Breton), Greek language, Greek, Armenian language, Armenian and Albanian language, Albanian.
A distinct non-Indo-European family of Uralic languages (Estonian language, Estonian, Finnish language, Finnish, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Erzya language, Erzya, Komi language, Komi, Mari language, Mari, Moksha language, Moksha and Udmurt language, Udmurt) is spoken mainly in Estonia, Finland, Hungary and parts of Russia. Turkic languages include Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani, Kazakh language, Kazakh and Turkish language, Turkish, in addition to smaller languages in Eastern and Southeast Europe (Balkan Gagauz Turkish, Bashkir language, Bashkir, Chuvash language, Chuvash, Crimean Tatar language, Crimean Tatar, Karachay-Balkar language, Karachay-Balkar, Kumyk language, Kumyk, Nogai language, Nogai and Tatar language, Tatar). Kartvelian languages (Georgian language, Georgian, Mingrelian language, Mingrelian and Svan language, Svan) are spoken primarily in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. Two other language families reside in the North Caucasus (termed Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian, most notably including Chechen language, Chechen, Avar language, Avar and Lezgian language, Lezgin; and Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian, most notably including Adyghe language, Adyghe). Maltese language, Maltese is the only Semitic language that is official within the EU, while Basque language, Basque is the only European language isolate.
Multilingualism and the protection of regional and minority languages are recognised political goals in Europe today. The Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities and the Council of Europe's European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages set up a legal framework for language rights in Europe.
Religion
history of religion, Historically, religion in Europe has been a major influence on Western art history, European art, culture of Europe, culture, Western philosophy, philosophy and European Union law, law. There are six patron saints of Europe venerated in Roman Catholicism, five of them so declared by Pope John Paul II between 1980 and 1999: Saints Cyril and Methodius, Bridget of Sweden, Catherine of Siena and Edith Stein, Teresa Benedicta of the Cross (Edith Stein). Benedict of Nursia had already been declared "Patron Saint of all Europe" by Pope Paul VI in 1964. The largest religion in Europe isChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, with 76.2% of Europeans considering themselves Christians, including Catholic, Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and various Protestant denominations. Among Protestants, the most popular are historically state-supported European denominations such as Lutheranism, Anglicanism and the Reformed faith. Other Protestant denominations such as historically significant ones like Anabaptists were never supported by any state and thus are not so widespread, as well as these newly arriving from the United States such as Pentecostalism, Adventism, Methodism, Baptists and various Evangelical Protestants; although Methodism and Baptists both have European origins. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom"; many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Historically, Europe has been the centre and "cradle of Christian civilization". Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, including the Roman Catholic Church, has played a prominent role in the shaping of Western civilisation, Western civilization since at least the 4th century,Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p. 2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Jose Orlandis, 1993, "A Short History of the Catholic Church," 2nd edn. (Michael Adams, Trans.), Dublin:Four Courts Press, , preface, se, accessed 8 December 2014.Thomas E. Woods and Antonio Canizares, 2012, "How the Catholic Church Built Western Civilization," Reprint edn., Washington, DC: Regnery History, , se
accessed 8 December 2014. p. 1: "Western civilization owes far more to Catholic Church than most people – Catholic included – often realize. The Church in fact built Western civilization."
/ref> and for at least a millennium and a half, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture, even though the religion was inherited from the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
. Christian culture was the predominant force in western civilisation, western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, art and science. In 2012 Europe had the Christianity by country, world's largest Christian population.
The second most popular religion is Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
(4.9%) concentrated mainly in the Balkans (Albania and Bosnia and Herzegovina) and Transcontinental country, transcontinental countries located at the boundary of Europe and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
(Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
and Turkey. Other religions, including Judaism, Hinduism and Buddhism are minority religions (though Tibetan Buddhism is the majority religion of Russia's Republic of Kalmykia). The 20th century saw the revival of Neopaganism through movements such as Wicca and Druidry.
Europe has become a relatively secular continent, with an increasing number and proportion of irreligion, irreligious, atheism, atheist and agnosticism, agnostic people, who make up about 18.3% of Europe's population, currently the largest secular population in the Western religion, Western world. There are a particularly high number of self-described non-religious people in the Czech Republic, Estonia, Sweden, former East Germany and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
Major cities and urban areas
The three largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban areas of Europe are Moscow, London and Paris. All have over 10 million residents, and as such have been described as megacity, megacities. While Istanbul has the highest total city population, it lies partly inAsia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. 64.9% of the residents live on the European side and 35.1% on the Asian side.
The next largest cities in order of population are Madrid, Saint Petersburg, Milan, Barcelona, Berlin, and Rome each having over 3 million residents.
When considering the commuter belts or List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan areas, within Europe (for which comparable data is available) Moscow covers the largest population, followed in order by Istanbul, London, Paris, Madrid, Milan, Ruhr Area, Saint Petersburg, Rhein-Süd, Barcelona and Berlin.
Culture
ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
and its cultures. The boundaries of Europe were historically understood as those of Christendom (or more specifically Latin Christendom), as established or defended throughout the medieval and early modern history of Europe, especially Islamic conquests, against Islam, as in the Reconquista and the Ottoman wars in Europe.Hilaire BellocEurope and the Faith
, Chapter I This shared cultural heritage is combined by overlapping indigenous national cultures and folklores, roughly divided into Slavic Europe, Slavic, Romance-speaking Europe, Latin (Romance) and Germanic Europe, Germanic, but with several components not part of either of these group (notably Greek culture, Greek, Basque culture, Basque and Celtic Europe, Celtic). Historically, special examples with overlapping cultures are Strasbourg with Latin (Romance) and Germanic or Trieste with Latin, Slavic and Germanic roots. Cultural contacts and mixtures shape a large part of the regional cultures of Europe. Europe is often described as "maximum cultural diversity with minimal geographical distances". Different cultural events are organized in Europe, with the aim of bringing different cultures closer together and raising awareness of their importance, such as the European Capital of Culture, the European Region of Gastronomy, the European Youth Capital and the European Capital of Sport.
Sport
See also
;History * Baltica * Genetic history of Europe * Prehistoric Europe * Classical antiquity *Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
* Early modern Europe
* Modernity
* History of Europe
;Politics
* Eurodistrict
* Euroregion
* Flags of Europe
* List of sovereign states by date of formation
* Names of European cities in different languages
* Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe statistics, OSCE countries statistics
* European Union as a potential superpower
;Demographics
* Area and population of European countries
* European Union statistics
* List of European cities by population within city limits
* List of cities of the European Union by population within city limits, Largest cities of the EU
* List of urban areas in the European Union
* List of cities in Europe
* List of metropolitan areas in Europe
* List of villages in Europe
* Pan-European identity
;Economics
* Economy of the European Union
* Financial and social rankings of European countries
* Healthcare in Europe
* Telecommunications in Europe
* List of European television stations
* List of European countries by GDP (nominal)
;Culture
* European Capital of Culture
* European Region of Gastronomy
* European Youth Capital
;Sports
*European Games
Notes
References
Sources
* National Geographic Society (2005). ''National Geographic Visual History of the World''. Washington, DC: National Geographic Society. . * * * *External links
Council of Europe
European Union
The Columbia Gazetteer of the World Online
Columbia University Press
"Introducing Europe"
fro
Lonely Planet
Travel Guides and Information Historical Maps
Borders in Europe 3000BC to the present
Geacron Historical atlas
Online history of Europe in 21 maps
{{Authority control Europe, Continents