|
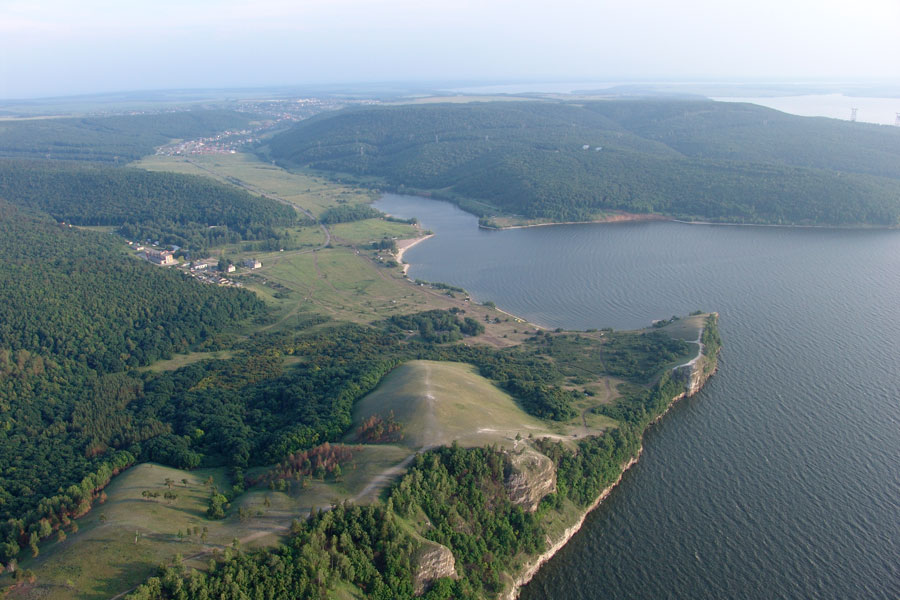
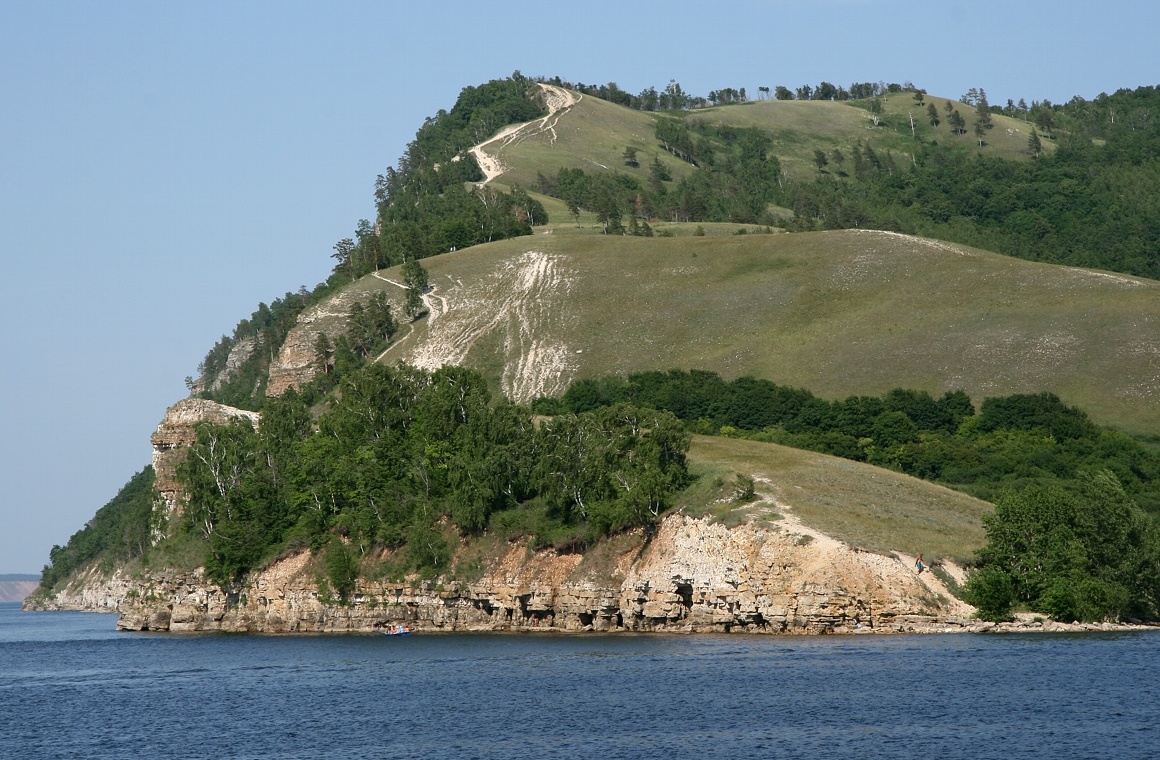
Samara Bend
The Samara Bend (''Samarskaya Luka''; ) is a large hairpin bend of the middle Volga River to the east where it meets the Samara River. It is situated in the Samara region of Russia. As the Volga enters its middle course it reaches the Zhiguli Mountains. The Samara Bend is formed as the river circles these hills. The Samara Bend National Park, one of the first in the USSR, was established in 1984. Some pockets of the park's territory are among the northernmost points of the Great European Steppe. The Samara Bend is noted for a remarkable succession of archaeological cultures from 7000 BC to 4000 BC. These sites have revealed Europe's earliest pottery ( Elshanka culture), the world's oldest horse burial and signs of horse worship (the Syezzheye cemetery of Samara culture), and the earliest kurgans associated with Proto-Indo-Europeans (e.g., Krivoluchye assigned to Khvalynsk culture Marija Gimbutas. ''The Prehistory of Eastern Europe''. Part 1 (1956). P. 55.). See also * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samara River 51
Samara ( rus, Сама́ра, p=sɐˈmarə), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara rivers, with a population of over 1.14 million residents, up to 1.22 million residents in the urban agglomeration, not including Novokuybyshevsk, which is not conurbated. The city covers an area of , and is the eighth-largest city in Russia and tenth agglomeration, the third-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Formerly a closed city, Samara is now a large and important social, political, economic, industrial, and cultural centre in Russia and hosted the European Union—Russia Summit in May 2007. It has a continental climate characterised by hot summers and cold winters. The life of Samara's citizens has always been intrinsically linked to the Volga River, which has not only served as the main commercial thoroughfare of Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Worship
Horse worship is a spiritual practice with archaeological evidence of its existence during the Iron Age and, in some places, as far back as the Bronze Age. The horse was seen as divine, as a sacred animal associated with a particular deity, or as a totem animal impersonating the king or warrior. Horse cults and horse sacrifice were originally a feature of Eurasian nomad cultures. While horse worship has been almost exclusively associated with Indo-European culture, by the Early Middle Ages it was also adopted by Turkic peoples. Horse worship still exists today in various regions of South Asia. Bronze Age The history of horse domestication is still a debated topic. The most widely accepted theory is that the horse was domesticated somewhere in the western Eurasian steppes. Various archaeological cultures including the Botai in Kazakhstan and Dereivka in Ukraine are proposed as possible candidates. However, widespread use of horses on the steppes is only noted from the late part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Russia
Russia (russian: link=no, Россия) is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,192 km2 (6,612,074 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations. Russia is a transcontinental country stretching vastly over two continents, Europe and Asia. It spans the northernmost edge of Eurasia, and has the world's fourth-longest coastline, at . Russia, alongside Canada, is one of the world's only two countries with a coast along three oceans,(however connection to the Atlantic ocean is extremely remote, while USA and Canada both have large coast lines on three oceans) due to which it has links with over thirteen marginal seas. It lies between latitudes 41° and 82° N, and longitudes 19° E and 169° W. Russia is larger than three continents of the world, and has the same surface area as Pluto. Global posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Samara Bend
The Battle of Samara Bend (russian: Монгольско-булгарское сражение, lit=Mongolian-Bulgar battle), also known as the Battle of Kernek, was the first battle between the Volga Bulgaria and the Mongol Empire. It is famous for being the first battle that the Mongol Horde lost. The battle took place during the autumn of 1223 at the southern border of Volga Bulgaria. The battle began with the Bulgar forces retreating and the Mongols pursuing them. The Mongols were then successfully led into an ambush. The Bulgars then countered the Mongols, which led to the Bulgars winning the battle. Background Volga Bulgars The Volga Bulgars were of Turkic origin. By the second half of the second century, the Bulgars had built a powerful state between the Sea of Azov and the Kuban region. They were related to the Kutrigur Huns. A section of the Volga Bulgars migrated to Central Europe, forming an empire in the Balkans, while another settled northward in the dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marija Gimbutas
Marija Gimbutas ( lt, Marija Gimbutienė, ; January 23, 1921 – February 2, 1994) was a Lithuanian archaeologist and anthropologist known for her research into the Neolithic and Bronze Age cultures of " Old Europe" and for her Kurgan hypothesis, which located the Proto-Indo-European homeland in the Pontic Steppe. Biography Early life Marija Gimbutas was born as Marija Birutė Alseikaitė to Veronika Janulaitytė-Alseikienė and Danielius Alseika in Vilnius, the capital of the Republic of Central Lithuania; her parents were members of the Lithuanian intelligentsia. Her mother received a doctorate in ophthalmology at the University of Berlin in 1908, while her father received his medical degree from the University of Tartu in 1910. After Lithuania regained independence in 1918, Gimbutas's parents organized the Lithuanian Association of Sanitary Aid which founded the first Lithuanian hospital in the capital. During this period, her father also served as the publisher of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khvalynsk Culture
The Khvalynsk culture was a Middle Copper Age (" Eneolithic") culture (c. 4900 – 3500 BC) of the middle Volga region. It takes its name from Khvalynsk in Saratov Oblast. The Khvalynsk culture extended from the Samara Bend in the north (the location of some of the most important sites such as Krivoluchye) to the North Caucasus in the south, from the Sea of Azov in the west to the Ural River in the east. It was preceded by the Early Eneolithic Samara culture, from which it came, and succeeded by the Late Eneolithic, Early Yamna culture, into which it developed. The Khvalynsk culture is associated with speakers of an early stage of the Proto-Indo-European language. Dating A number of calibrated C-14 readings obtained from material in the graves of the type site date the culture certainly to the approximate window, 5000–4500 BCE. This material is from Khvalynsk I, or Early Khvalynsk. Khvalynsk II, or Late Khvalynsk, is Late Eneolithic. Asko Parpola regards Khvalynsk cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
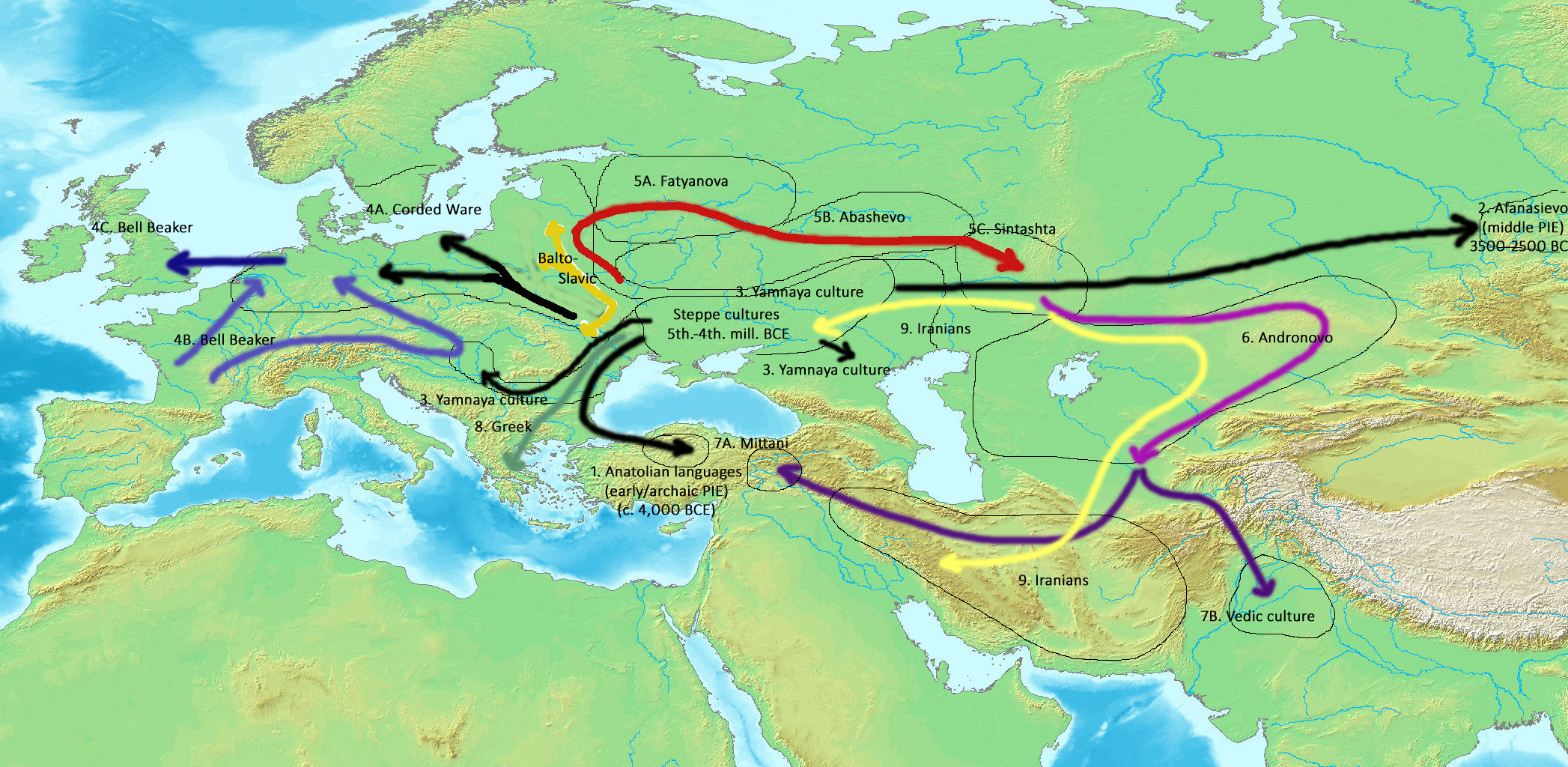
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe ( Corded W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western and Northern Europe during the 3rd millennium BC. The earliest kurgans date to the 4th millennium BC in the Caucasus, and a part of researchers associate these with the Indo-Europeans. Kurgans were built in the Eneolithic, Bronze, Iron, Antiquity and Middle Ages, with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia. Etymology According to the Etymological dictionary of the Ukrainian language the word "kurhan" is borrowed directly from the "Polovtsian" language ( Kipchak, part of the Turkic languages) and means: fortress, embankment, high grave. The word has two possible etymologies, either from the Old Turkic root ''qori-'' "to close, to block, to guard, to protect", or ''qur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samara Culture
The Samara culture was an Eneolithic (Copper Age) culture that flourished around the turn of the 5th millennium BCE, at the Samara Bend of the Volga River (modern Russia). The Samara culture is regarded as related to contemporaneous or subsequent prehistoric cultures of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, such as the Khvalynsk, Repin and Yamna (or Yamnaya) cultures. The Proto-Indo-European homeland is often linked to one or more of these cultures. Place and time The Samara culture was an Eneolithic culture of the early 5th millennium BCE at the Samara bend region of the middle Volga, at the northern edge of the steppe zone. It was discovered during archaeological excavations in 1973 near the village of Syezzheye (Съезжее) near Bogatoye. Related sites are Varfolomeyevka on the Russian-Kazakh border (5500 BCE), which has parallels in Dzhangar (Kalmykia), and Mykol'ske, on the Dnieper. The later stages of the Samara culture are contemporaneous with its successor culture in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Burial
Horse burial is the practice of burying a horse as part of the ritual of human burial, and is found among many Indo-European speaking peoples and others, including Chinese and Turkic peoples. The act indicates the high value placed on horses in the particular cultures and provides evidence of the migration of peoples with a horse culture. Human burials that contain other livestock are rare; in Britain, for example, 31 horse burials have been discovered but only one cow burial, unique in Europe. This process of horse burial is part of a wider tradition of horse sacrifice. An associated ritual is that of chariot burial, in which an entire chariot, with or without a horse, is buried with a dead person. Background and detail The horse carries great symbolic meaning in human cultures (see horse worship). In Celtic and Germanic cultures, for instance, the horse "could be associated with the journeying sun", and horses were deified and used in divination, but Celtic horse sacrific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of . It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average at delta – between and – and of |
Elshanka Culture
The Elshanka culture (Russian: Елшанская культура) was a Subneolithic or very early Neolithic culture that flourished in the middle Volga region in the 7th millennium BC. The sites are mostly individual graves scattered along the Samara and Sok rivers. They revealed Europe's oldest pottery. The culture extended along the Volga from Ulyanovsk Oblast in the north through the Samara Bend towards Khvalynsk Hills and the Buzuluk District in the south. No signs of permanent dwellings have been found. Elshanka people appear to have been hunters and fishermen who had seasonal settlements at the confluences of rivers. Most grave goods come from such settlements. Elshanka is believed to be the source from which the art of pottery spread south and westward towards the Balkans (with one particularly important site being the Surskoy Island in the Dnieper Rapids where pottery was made from 6200 BC to 5800 BC). Elshanka pots, dated from 6700 BC onwards, usually have simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |