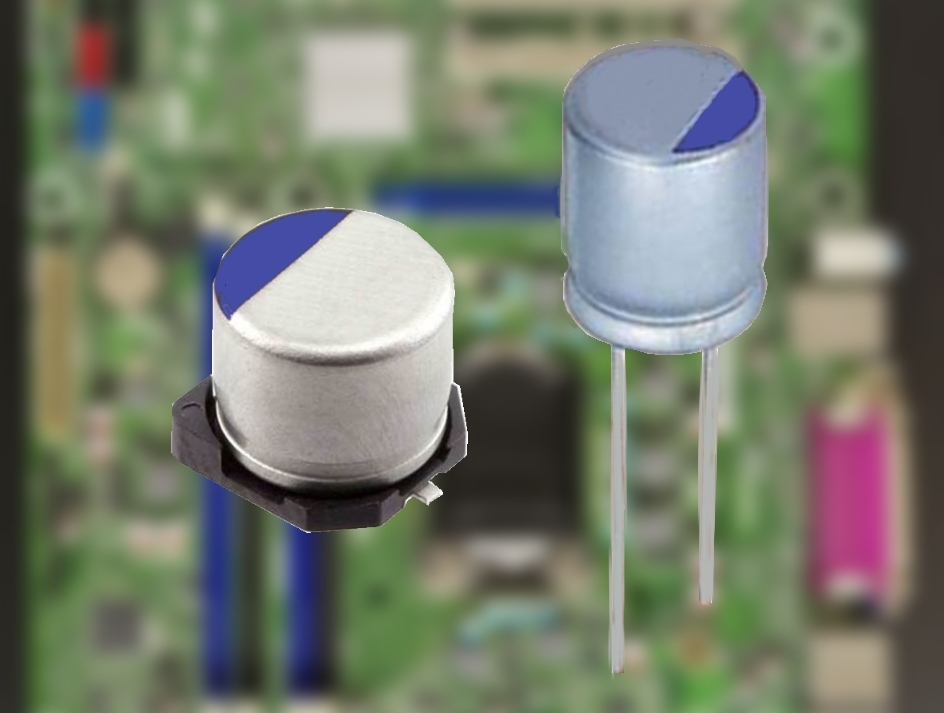
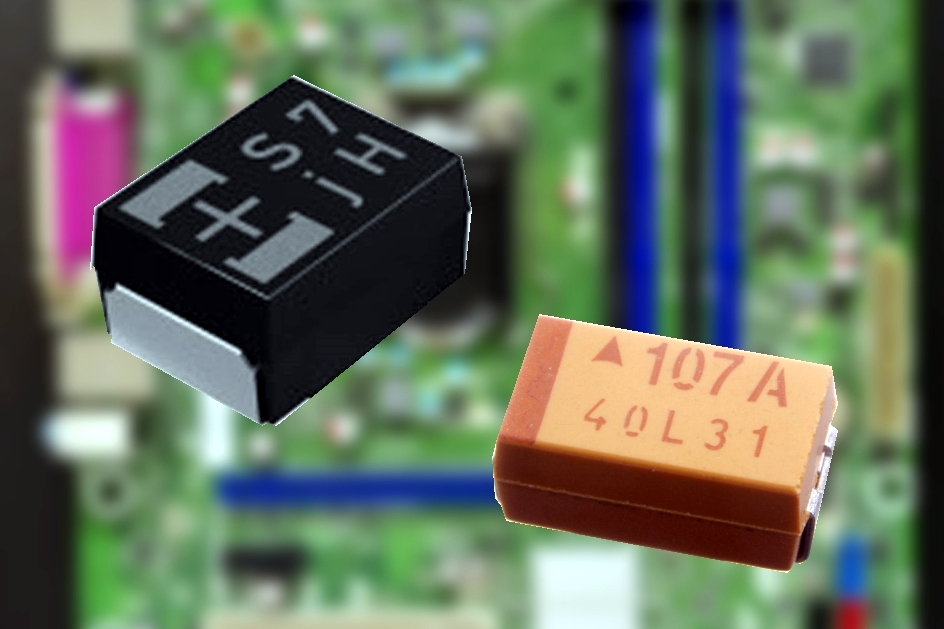

A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an
electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid
conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dis ...
. There are four different types:
* Polymer
tantalum electrolytic capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounded ...
(Polymer Ta-e-cap)
* Polymer
aluminium electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Al-e-cap)
* Hybrid polymer capacitor (Hybrid polymer Al-e-cap)
* Polymer
niobium electrolytic capacitors
Polymer Ta-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (
SMD) chip style. Polymer Al-e-caps and hybrid polymer Al-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (SMD) chip style, in cylindrical SMDs (V-chips) style or as radial leaded versions (single-ended).
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are characterized by particularly low internal
equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
s (ESR) and high ripple current ratings. Their electrical parameters have similar temperature dependence, reliability and service life compared to solid tantalum capacitors, but have a much better temperature dependence and a considerably longer service life than aluminium electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes. In general polymer e-caps have a higher leakage current rating than the other solid or non-solid electrolytic capacitors.
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are also available in a hybrid construction. The hybrid polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors combine a solid polymer electrolyte with a liquid electrolyte. These types are characterized by low ESR values but have low leakage currents and are insensitive to transients,
however they have a temperature-dependent service life similar to non-solid e-caps.
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are mainly used in
power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a res ...
of integrated electronic circuits as buffer, bypass and decoupling capacitors, especially in devices with flat or compact design. Thus they compete with
MLCC capacitor
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. It is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes. The composition of the ceramic material de ...
s, but offer higher capacitance values than MLCC, and they display no
microphonic
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which ...
effect (such as class 2 and 3
ceramic capacitors).
History
Aluminium
electrolytic capacitors
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel ...
(Al-e-caps) with liquid
electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dis ...
s were invented in 1896 by
Charles Pollak.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid
manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell ...
(MnO
2) electrolytes were invented by
Bell Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
in the early 1950s, as a miniaturized and more reliable low-voltage support capacitor to complement the newly invented
transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
, see
Tantalum capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounde ...
. The first Ta-e-caps with MnO
2 electrolytes had 10 times better
conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
and a higher ripple current load than earlier types Al-e-caps with liquid electrolyte. Additionally, unlike standard Al-e-caps, the
equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
(ESR) of Ta-caps is stable in varying temperatures.

During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower
ESR and lower
equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and resistors tends to ...
(ESL) for bypass and decoupling capacitors used in power supply lines were needed.
see
Role of ESR, ESL and capacitance.
A breakthrough came in 1973, with the discovery by A. Heeger and F. Wudl of an organic conductor, the charge-transfer salt TCNQ. TCNQ (
7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) is the organic compound with the formula . This cyanocarbon, a relative of para-quinone, is an electron acceptor that is used to prepare charge transfer salts, which are of interest in molecular electronics.
P ...
or N-n-butyl isoquinolinium in combination with TTF (
Tetrathiafulvalene
Tetrathiafulvalene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, , by replacement of four CH groups w ...
)) is a chain molecule of almost perfect one-dimensional structure that has a 10-fold better conductivity along the chains than does MnO
2, and has a 100-fold better conductivity than non-solid electrolytes.

The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from
Sanyo
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka, Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiari ...
. These were wound, cylindrical capacitors with 10x increased electrolyte conductivity compared with MnO
2
These capacitors were used in devices for applications that required the lowest possible ESR or highest possible ripple current. One OS-CON e-cap could replace three more bulky "wet" e-caps or two Ta-caps.
[J. Both, "Electrolytic Capacitors from the Postwar Period to the Present", IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, Vol.32, Issue:2, pp.8-26, March–April 2016, ,]
/ref> By 1995, the Sanyo OS-CON became the preferred decoupling capacitor for Pentium processor-based IBM personal computers.
The Sanyo OS-CON e-cap product line was sold in 2010 to Panasonic. Panasonic then replaced the TCNQ salt with a conducting polymer under the same brand.
The next step in ESR reduction was the development of conducting polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s by Alan J. Heeger, Alan MacDiarmid
Alan Graham MacDiarmid, ONZ FRS (14 April 1927 – 7 February 2007) was a New Zealand-born American chemist, and one of three recipients of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 2000.
Early life and education
MacDiarmid was born in Masterton, New ...
and Hideki Shirakawa
is a Japanese chemist, engineer, and Professor Emeritus at the University of Tsukuba and Zhejiang University. He is best known for his discovery of conductive polymers. He was co-recipient of the 2000 Nobel Prize in Chemistry jointly with Alan Ma ...
in 1975. The conductivity of conductive polymers such as polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
History ...
(PPy) PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene, 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Baye ...
is better than that of TCNQ by a factor of 100 to 500, and close to the conductivity of metals.
In 1988 the first polymer electrolyte e-cap, "APYCAP" with PPy polymer electrolyte, was launched by the Japanese manufacturer Nitsuko. The product was not successful, in part because it was not available in SMD versions.
In 1991 Panasonic launched its polymer Al-e-cap series "SP-Cap", These e-caps used PPy polymer electrolyte and reached ESR values that were directly comparable to Ceramic capacitor, ceramic multilayer capacitors (MLCCs). They were still less expensive than tantalum capacitors and with their flat design useful in compact devices such as laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
s and cell phones they competed with tantalum chip capacitors as well.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with PPy polymer electrolyte cathode followed three years later. In 1993 NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
introduced its SMD polymer Ta-e-caps called "NeoCap". In 1997 Sanyo followed with the "POSCAP" polymer tantalum chips.
A new conductive polymer for tantalum polymer capacitors was presented by Kemet at the "1999 Carts" conference. This capacitor used the newly developed organic conductive polymer PEDT ( Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)), also known as PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene, 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Baye ...
(trade name Baytron®).
Two years later at the 2001 APEC Conference, Kemet introduced PEDOT polymer aluminium e-caps to the market. PEDOT polymer has a higher temperature stability, and as PEDOT:PSS solution this electrolyte could be inserted only by dipping instead of in-situ polymerization like for PPy which makes the production faster and cheaper.
Application basics
Role of ESR, ESL and capacitance
The predominant application of all electrolytic capacitors is in power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a res ...
. They are used in input and output smoothing capacitors, as decoupling capacitor
A decoupling capacitor is a capacitor used to decouple one part of an electrical network (circuit) from another. Noise caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing its effect on the rest of the circuit. For hig ...
s to circulate the harmonic current in a short loop, as bypass capacitor
A decoupling capacitor is a capacitor used to decouple one part of an electrical network (circuit) from another. Noise caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing its effect on the rest of the circuit. For hig ...
s to shunt AC noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arise ...
to the ground by bypassing the power supply lines, as backup capacitors to mitigate the drop in line voltage during sudden power demand or as filter capacitor
Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose.
Energy storage
A capacitor can store electric energy when it is c ...
in low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter des ...
to reduce switching noises. The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an
The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
is simple. If the circuit, f. e. a microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
, has a sudden power demand, the supply voltage drops by ESL, ESR and capacitance charge loss. Because in case of a sudden current demand the voltage of the power line drops:
:Δ''U'' = ESR × ''I''.
For example:
Electrolytic capacitors – basics
Anodic oxidation
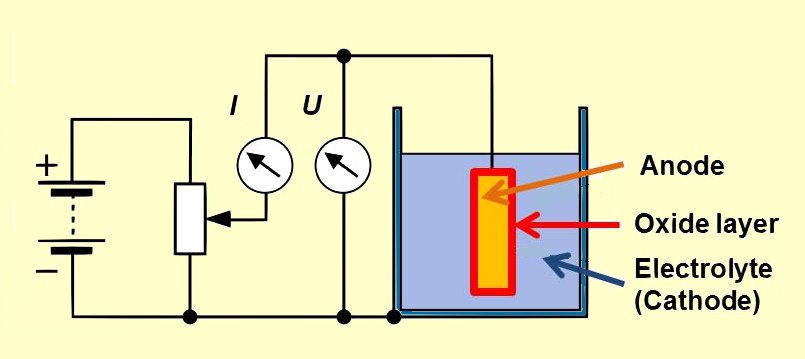 Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by
Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by anodic
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
form an insulating oxide layer. By applying a positive voltage to the anode (+) material in an electrolytic bath an oxide barrier layer with a thickness corresponding to the applied voltage can be formed. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric in an e-cap. To increase the capacitors capacitance the anode surface is roughened and so the oxide layer surface also is roughened. To complete a capacitor a counter electrode has to match the rough insulating oxide surface. This is accomplished by the electrolyte, which acts as the cathode (-) electrode of an electrolytic capacitor.
The main difference between the polymer capacitors is the anode material and its oxide used as the dielectric:
* Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors use high purity sintered tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
powder as an anode with tantalum pentoxide
Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. is an inert material with a high refract ...
(Ta2O5) as a dielectric and
* Polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors use a high purity and electrochemically etched (roughened) aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
foil as an anode with aluminium oxide (Al2O3) as the dielectric
The properties of the aluminium oxide layer compared with tantalum pentoxide dielectric layer are given in the following table:
 Every e-cap in principle forms a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance is an increasing function of the electrode area A, the permittivity ε of the dielectric material and the thickness of the dielectric (d).
:
Capacitance is proportional to the product of the area of one plate multiplied by the permittivity and divided by the dielectric thickness.
The dielectric thickness is in the range of
Every e-cap in principle forms a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance is an increasing function of the electrode area A, the permittivity ε of the dielectric material and the thickness of the dielectric (d).
:
Capacitance is proportional to the product of the area of one plate multiplied by the permittivity and divided by the dielectric thickness.
The dielectric thickness is in the range of nanometers
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
per volt. On the other hand, the breakdown voltage of these oxide layers is quite high. Using etched or sintered anodes, with their much higher surface area compared to a smooth surface of the same size or volume, e-caps can achieve a high volumetric capacitance. The latest developments in high etched or sintered anodes increases the capacitance value, depending on the rated voltage, by a factor of up to 200 for Al-e-caps or Ta-e-caps compared with smooth anodes.
Electrolytes
The most important electrical property of an electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dis ...
in an electrolytic capacitor is its electrical conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
. The electrolyte forms the counter electrode, of the e-cap, the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
. The roughened structures of the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
surface continue in the structure of the oxide layer, the dielectric, the cathode must adapt precisely to the roughened structure. With a liquid, as in the conventional "wet" e-caps that is easy to achieve. In polymer e-caps in which a solid conductive polymer forms the electrolyte, this is much more difficult to achieve, because its conductivity comes by a chemical process of polymerization. However, the benefits of a solid polymer electrolyte, the significantly lower ESR of the capacitor and the low temperature dependence of the electrical parameters, in many cases justify the additional production steps as well as higher costs.
Conducting salt TCNQ electrolyte
 Electrolytic capacitors with the charge transfer salt
Electrolytic capacitors with the charge transfer salt tetracyanoquinodimethane
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) is the organic compound with the formula . This cyanocarbon, a relative of para-quinone, is an electron acceptor that is used to prepare charge transfer salts, which are of interest in molecular electronics.
P ...
TCNQ as electrolyte, formerly produced by Sanyo
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka, Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiari ...
with the trade name "OS-CON", in the true sense of the term "polymer" were not "polymer capacitors". TCNQ electrolytic capacitors are mentioned here to point out the danger of confusion with 'real' polymer capacitors, which are sold nowadays under the same trade name OS-CON. The original OS-CON capacitors with TCNQ electrolyte sold by the former manufacturer Sanyo has been discontinued with the integration of Sanyo capacitor businesses by Panasonic 2010.
Polymer electrolyte
Polymers are formed by a chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
, polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer, monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are ...
. In this reaction monomers are continuously attached to a growing polymer strand.[Clayden, J., Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2000)]
''Organic chemistry''
Oxford University Press pp. 1450–1466 Usually polymers are electrically insulators, at best, semiconductors. For use as an electrolyte in e-caps, electrical conductive
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is gene ...
polymers are employed. The conductivity of a polymer is obtained by conjugated double bonds
In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. It is conventionally represented as ...
which permit free movement of charge carriers in the doped state. As charge carriers serve electron hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or ...
s. That means, the conductivity of conducting polymers, which is nearly comparable with metallic conductors, only starts when the polymers are doped oxidatively or reductively.
A polymer electrolyte must be able to penetrate the anode's finest pores to form a complete, homogeneous layer, because only anode oxide sections covered by the electrolyte contribute to the capacitance. For this the precursors of the polymer has to consist of very small base materials that can penetrate even the smallest pores. The size of this precursors are the limiting factor in the size of the pores in the etched aluminium anode foils or of the size of tantalum powder. The rate of polymerization must be controlled for capacitor manufacturing. Too rapid polymerization does not lead to a complete anode coverage, while too slow polymerization increases production costs. Neither the precursors nor the polymer or its residues may attack the anodes oxide chemically or mechanically. The polymer electrolyte must have high stability over a wide temperature range over long times. The polymer film is not only the counter electrode of the e-cap it also protects the dielectric even against external influences such as the direct contact of graphite in this capacitors, which are provided with a cathode contact via graphite and silver.
Polymer e-caps employ either polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
History ...
(PPy) or polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocyclic compound, heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s hav ...
(PEDOT or PEDT)
Polypyrrole PPy


Polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
History ...
(PPy) is a conducting polymer formed by oxidative
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
polymerization of pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4 H4 NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-meth ...
. A suitable oxidizing agent is iron (III) chloride (FeCl3). Water, methanol, ethanol, acetonitrile and other polar solvents may be used for the synthesis of PPy. As a solid conducting polymer electrolyte It reaches conductivities up to 100 S/m. Polypyrrole was the first conductive polymer used in polymer Al-e-caps as well as in polymer Ta-e-caps.
The problem with the polymerization of PPy was the rate of polymerization. When pyrrole is mixed with the desired oxidizing agents at room temperature, the polymerization reaction begins immediately. Thus polypyrrole begins to form, before the chemical solution can get into the anode pores. The polymerization rate can be controlled by cryogenic cooling or by electrochemical polymerization.
The cooling method requires a very great technical effort and is unfavorable for mass production. In the electrochemical polymerization at first an auxiliary electrode layer on the dielectric has to be applied and to be connected to the anode.
Polythiopene PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS
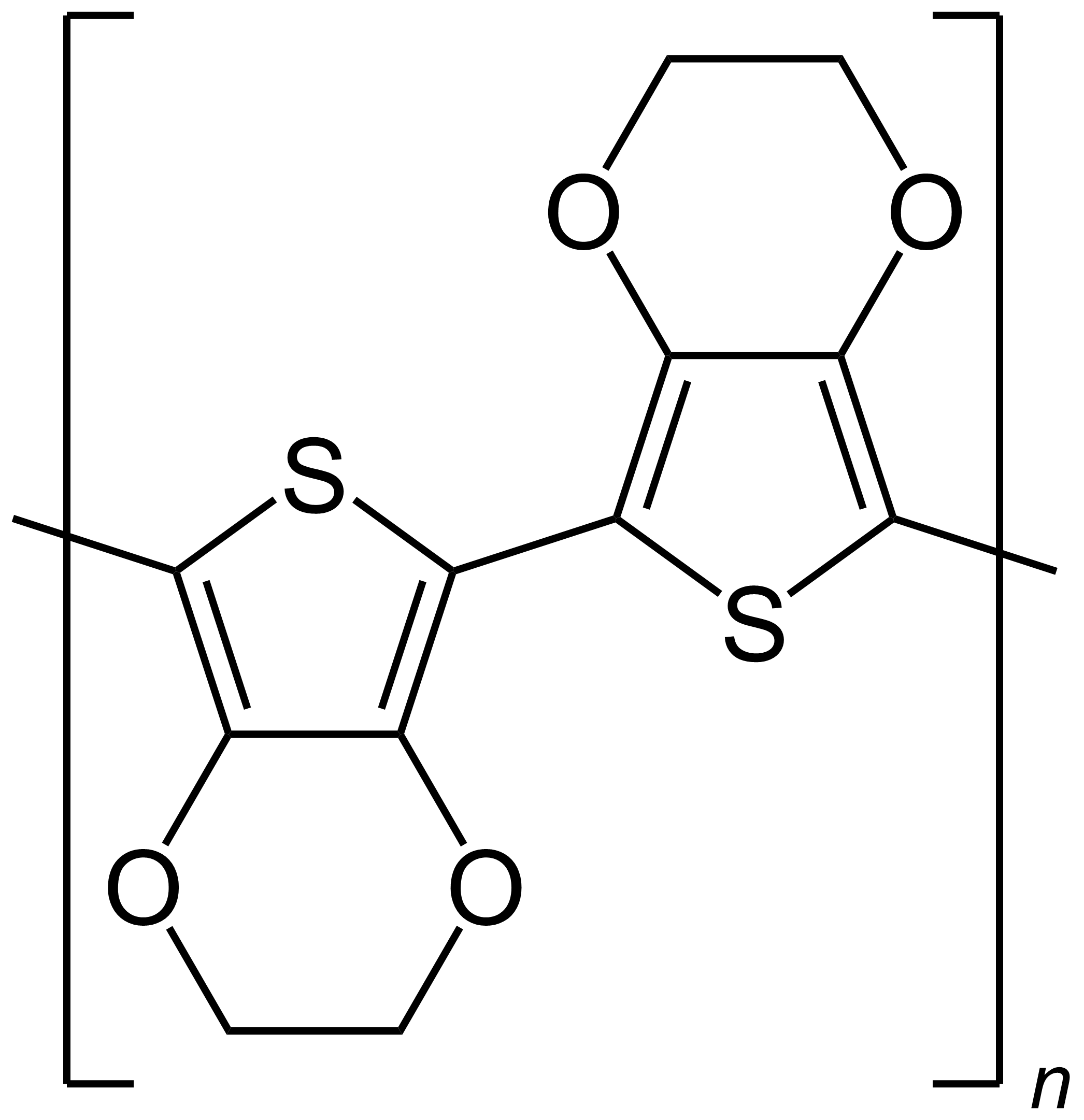
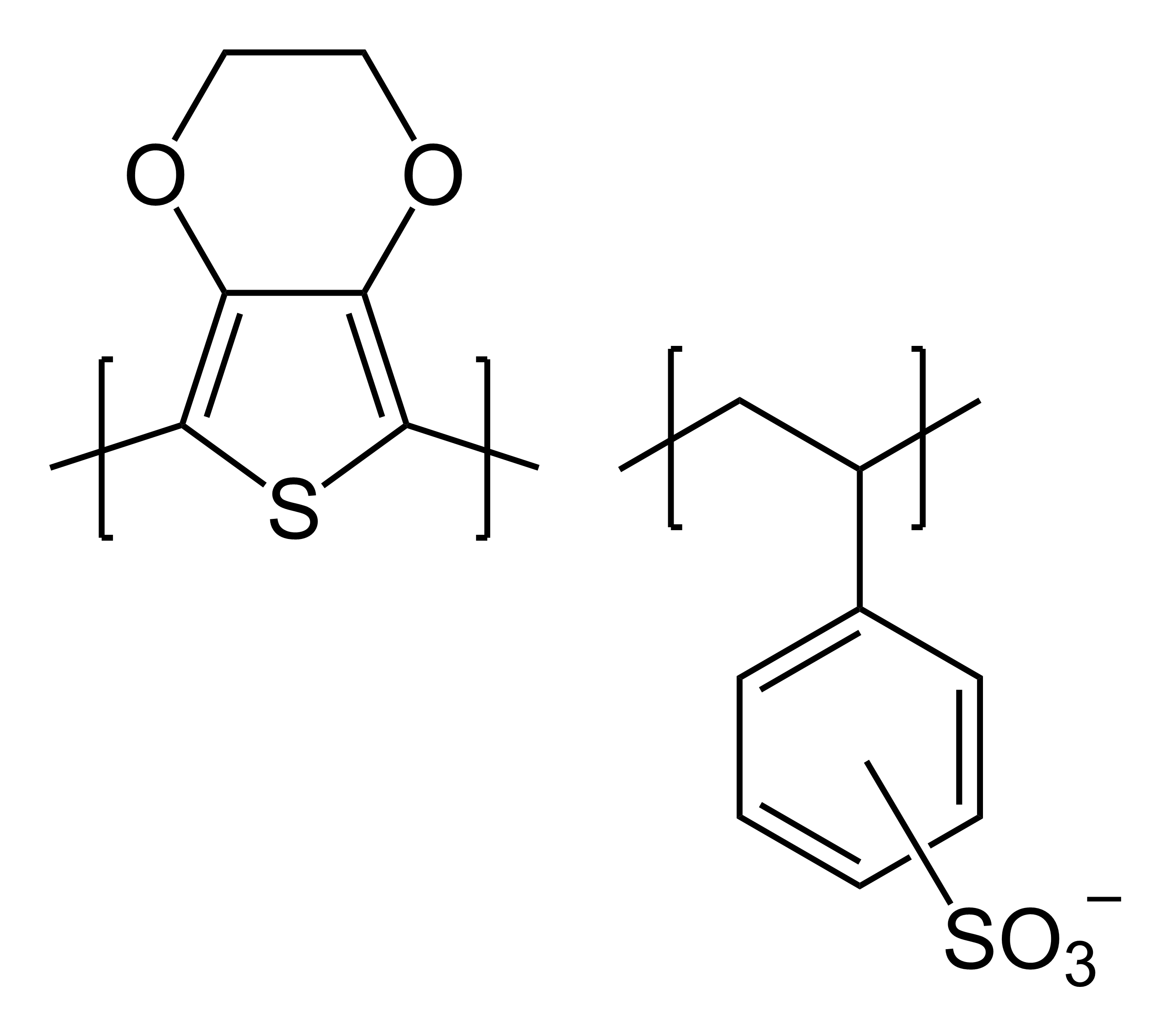 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), abbreviated
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), abbreviated PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene, 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Baye ...
or PEDTSodium persulfate
Sodium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Sodium, Na2Sulfur, S2Oxygen, O8. It is the sodium salt of peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8, an oxidizing agent. It is a white solid that dissolves in water. It is almost non-hygroscopic an ...
. Advantages of PEDOT are optical transparency
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable light scattering by particles, scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale ...
in its conducting
Conducting is the art of directing a musical performance, such as an orchestral or choral concert. It has been defined as "the art of directing the simultaneous performance of several players or singers by the use of gesture." The primary duti ...
state, non toxic, stable up to temperatures of 280 °C and a conductivity up to 500 S/m.sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
polystyrene sulfonate
Polystyrene sulfonates are a group of medications used to treat high blood potassium. Effects generally take hours to days. They are also used to remove potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical applications.
Common side effect ...
(PSS) and dissolved in water.[U. Merker, K. Reuter, K. Wussow, S. Kirchmeyer, and U. Tracht, „PEDT as conductive polymer cathode in electrolytic capacitors". CARTS Europe 2002] The complete polymer layer on the dielectric is then composed of pre-polymerized particles from the dispersion. These dispersions are known as PEDOT: PSS, trade names Baytron P® and Clevios™,
Hybrid electrolyte
Hybrid polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors combine a coating of the roughened and oxidized aluminium anode structure with a conductive polymer together with a liquid electrolyte. The liquid electrolyte is soaked in the separator (spacer) and achieves with its ion conductivity the electrical contact between the two polymer layers covering the dielectric and on the cathode foil. The liquid electrolyte can supply the oxygen for self-healing processes of the capacitor, which reduces the leakage current, so that values such as in conventional "wet" the electrolytic capacitor can be achieved. In addition the safety margin for the required oxide thickness for a desired rated voltage can be reduced.
The detrimental effects of the liquid electrolyte on ESR and temperature characteristics are relatively low. By using appropriate organic electrolytes and a good sealing of the capacitors a long service life can be achieved.
Types and styles
Based on the used anode metal and the combination of a polymer electrolyte together with a liquid electrolyte, there are three different types:
*Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounded ...
*Polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitor
*Hybrid polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitor
These three different types or families, are produced in two different styles,
* Rectangular SMD chip, usually molded with a plastic case, available with sintered tantalum anode or with stacked aluminium anode foils and
* Cylindrical style with a wound cell in a metal case, available as cylindrical SMDs (V-chips) style or as radial leaded versions (single-ended)
Polymer-Quader-Polarität.jpg, Rectangular SMD chips are available with sintered tantalum anode or with stacked aluminum anode foils
V-Chip.jpg, Cylindrical styles with a wound cell in a metal case are available as SMDs (V-chips) or as radial leaded versions (single-ended) for polymer or hybrid polymer aluminum capacitors
Rectangular chip style
In the early 1990s polymer Ta-caps coincided with the emergence of flat devices such as mobile phones and laptops using SMD assembly technology. The rectangular base surface achieves the maximum mounting space, which is not possible with round base surfaces. The sintered cell can be manufactured so that the finished component has a desired height, typically the height of other components. Typical heights range from about 0.8 to 4 mm.
Polymer tantalum chip capacitors
Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors are essentially tantalum capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounde ...
s in which the electrolyte is a conductive polymer instead of manganese dioxide, see also tantalum capacitor#Materials, production and styles
Tantalum capacitors are manufactured from a powder of relatively pure elemental tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
metal.dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
layer is then formed over all the tantalum particle surfaces of the anode by the electrochemical process of anodization
Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
The process is called ''anodizing'' because the part to be treated forms the anode electrode of an electr ...
or forming. To achieve this, the “pellet” is submerged into a very weak solution of acid and DC voltage is applied. The total dielectric thickness is determined by the final voltage applied during the forming process. Thereafter, the oxidized sintered block is impregnated with the precursors of the polymer, to achieve the polymer electrolyte, the counter electrode. This polymerized pellet now is successively dipped into conducting graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
and then silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
to provide a good connection to the conducting polymer. This layers achieves the cathode connection of the capacitor. The capacitive cell then is generally molded by a synthetic resin.
File:Tantalum-Polymer-Capacitor.jpg, Layer structure of a polymer tantalum capacitor with graphit/silver cathode connection
File:SMD-Polymer-Tantalum-Chip.tif, Basic cross-section of a rectangular polymer tantalum chip capacitor
File:Polymer-Tantalum-Quader.jpg, Rectangular polymer tantalum chip capacitor
Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors have ESR values that are approximately only 1/10 of the value of tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte of the same size. By a multi-anode technique in which several anode blocks are connected in parallel in one case, the ESR value can be reduced again. The advantage of the multi-anode technology in addition to the very low ESR values is the lower inductance ESL, whereby the capacitors are suitable for higher frequencies.
The disadvantage of all polymer tantalum capacitors is the higher leakage current, which is approximately by a factor of 10 higher compared to the capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte. Polymer SMD Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors are available up to a size of 7.3x4.3x4.3 mm (length × width × height) with a capacity of 1000 µF at 2.5 V. They cover temperature ranges from −55 °C to +125 °C and are available in rated voltage values from 2.5 to 63 V.
New designs – lowering ESR and ESL
 Lowering ESR and ESL remains a major research and development objective for all polymer capacitors. Some constructive measures can have also a major impact on the electrical parameters of capacitors. Smaller ESR values can be achieved for example by parallel connection of several conventional capacitor cells in one case. Three parallel capacitors with an ESR of 60 mΩ each have a resulting ESR of 20 mΩ. This technology is called “multi-anode” construction and is used in very low ESR polymer tantalum capacitors.
Lowering ESR and ESL remains a major research and development objective for all polymer capacitors. Some constructive measures can have also a major impact on the electrical parameters of capacitors. Smaller ESR values can be achieved for example by parallel connection of several conventional capacitor cells in one case. Three parallel capacitors with an ESR of 60 mΩ each have a resulting ESR of 20 mΩ. This technology is called “multi-anode” construction and is used in very low ESR polymer tantalum capacitors. Polymer tantalum chip capacitors with these new design enhancements, that both the ESR and the ESL decreased reaching properties, approaching ever closer to those of MLCC capacitors.
Polymer tantalum chip capacitors with these new design enhancements, that both the ESR and the ESL decreased reaching properties, approaching ever closer to those of MLCC capacitors.
Polymer aluminium chip capacitors
Rectangular polymer Al-caps have one or more layered aluminium anode foils and a conductive polymer electrolyte. The layered anode foils are at one side contacted with each other, this block is anodically oxidized to achieve the dielectric, and the block is impregnated with the precursors of the polymer to achieve the polymer electrolyte, the counter electrode. Like for polymer tantalum capacitors this polymerized block now is successively dipped into conducting graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
and then silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
to provide a good connection to the conducting polymer. This layers achieves the cathode connection of the capacitor. The capacitive cell then generally is molded by a synthetic resin.
File:E-cap-construction-principle-4-polymer-graphite-silver.png, Layer structure of a polymer aluminum capacitor with graphit/silver cathode connection
File:Polymer-Al-Chip-stacked.png, Basic cross-section of a rectangular polymer aluminum chip capacitor
File:Polymer-Aluminium-Quader.jpg, Rectangular polymer aluminum chip capacitor. The external appearance has no indication of the used internally anode material.
The layered anode foils in the rectangular shaped polymer Al-chip-e-caps are electrically parallel connected single capacitors. Thus, the ESR and ESL values are connected in parallel reducing ESR and ESL correspondingly, and allowing them to operate at higher frequencies.
These rectangular polymer Al-chip-e-caps are available in the "D"-case with dimensions of 7.3x4.3 mm and heights of between 2 and 4 mm. They provide a competitive alternative to Ta-caps.
Comparing mechanical comparable polymer Al-chip-e-caps and polymer Ta-chip-e-caps shows that the different permittivities of aluminium oxide and tantalum pentoxide have little impact on the specific capacity due to different safety margins in oxide layers. Polymer Ta-e-caps use an oxide layer thickness that corresponds to approximately four times the rated voltage, while the polymer Al-e-caps have about twice the rated voltage.
Cylindrical (radial) style
Cylindrical polymer aluminium capacitors based on the technique of wound aluminium electrolytic capacitors with liquid electrolytes. They are available only with aluminium as anode material.
They are intended for larger capacitance values compared to rectangular polymer capacitors. Due to their design, they may vary in height on a given surface mounting area so that larger capacitance values can be achieved by a taller case without increasing the mounting surface. This is primarily useful for printed circuit boards
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struct ...
without a height limit.
Cylindrical polymer aluminium capacitors
Cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps are made of two aluminum foils, an etched and formed anode and a cathode foil that are mechanically separated by a separator and wound together. The winding is impregnated with the polymer precursors to achieve the polymerized conducting polymer to form cathode the polymer electrode, electrically connected to the cathode foil. The winding then is built into an aluminum case and sealed with a rubber sealing. For the SMD version (Vertical chip= V-chip) the case is provided with a bottom plate.
File:E-cap-winding.tif, Winding of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor
File:E-cap-construction-principle-2-polymer.png, Cross-sectional view of the capacitive cell of a wound polymer aluminum capacitor with polymer electrolyte
File:Polymer-zylindric-Al-e-caps.png, Cylindrical polymer aluminum capacitors with wound cell in cylindrical metal case, in radial leaded (single-ended) and SMD style (V-chip)
The cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps are less expensive than corresponding polymer tantalum capacitors for a given CV value (capacitance × rated voltage). They are available up to a size of 10×13 mm (diameter × height) with a CV value of 3900 µF×2.5 V They can cover temperature ranges from -55 °C to +125 °C and are available in nominal voltage values from 2.5 to 200 V
Hybrid polymer aluminum capacitors
 Hybrid polymer capacitors are available only in the cylindrical style construction thus corresponds to the above-described cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps leaded in the radial (single-ended) design or with a base plate in the SMD version (V-chip). The difference is that the polymer only covers the surface of the roughened structure of the dielectric Al2O3 and the surface of the cathode foil as thin layers. With this especially the high-ohmic parts in the small pores of the anode foil can be made low-ohmic to reduce the capacitors ESR. As electrical connection between both polymer layers serve a liquid electrolyte like in conventional wet Al-e-caps impregnating the separator. The small distance the non-solid electrolyte conduct increases the ESR a little bit, however in fact not dramatically. Advantage of this construction is that the liquid electrolyte in operation delivers the oxygen which is necessary for self-healing of the dielectric layer in the presence of any small defects.
The current that flows through a small defect results in selective heating, which normally destroys the overlying polymer film, isolating, but not healing, the defect. In hybrid polymer capacitors liquid can flow to the defect, delivering oxygen and healing the dielectric by generating new oxides, decreasing the leakage current. Hybrid polymer Al-e-caps have a much lower leakage current than standard polymer Al-e-caps.
Hybrid polymer capacitors are available only in the cylindrical style construction thus corresponds to the above-described cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps leaded in the radial (single-ended) design or with a base plate in the SMD version (V-chip). The difference is that the polymer only covers the surface of the roughened structure of the dielectric Al2O3 and the surface of the cathode foil as thin layers. With this especially the high-ohmic parts in the small pores of the anode foil can be made low-ohmic to reduce the capacitors ESR. As electrical connection between both polymer layers serve a liquid electrolyte like in conventional wet Al-e-caps impregnating the separator. The small distance the non-solid electrolyte conduct increases the ESR a little bit, however in fact not dramatically. Advantage of this construction is that the liquid electrolyte in operation delivers the oxygen which is necessary for self-healing of the dielectric layer in the presence of any small defects.
The current that flows through a small defect results in selective heating, which normally destroys the overlying polymer film, isolating, but not healing, the defect. In hybrid polymer capacitors liquid can flow to the defect, delivering oxygen and healing the dielectric by generating new oxides, decreasing the leakage current. Hybrid polymer Al-e-caps have a much lower leakage current than standard polymer Al-e-caps.
Comparison of the polymer families
Comparison of benchmarks
The polymer electrolyte, the two different anode materials, aluminum and tantalum, together with the different designs led to multiple polymer e-cap families with different specifications. For comparison, the basic parameters of the tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte are also listed.
(As of April 2015)
Comparison of electrical parameters
Electrical properties of polymer capacitors can best be compared, using consistent capacitance, rated voltage and dimensions. The values for the ESR and the ripple current are the most important parameters for the use of for polymer capacitors in electronic equipment. The leakage current is significant, because it is higher than that of e-caps with non-polymer electrolytes. The respective values of Ta-e-caps with MnO2 electrolyte and wet Al-e-caps are included.
:1 Manufacturer, series, capacitance/rated voltage.
:2 W×L×H for rectangular style (chip), D×L for cylindrical style.
:3 Calculated for a 100 µF, 10 V capacitor.
(As of June 2015)
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of polymer e-caps against wet Al-e-caps:
* lower ESR values.
* higher ripple current capability
* lower temperature depending characteristics
* no evaporation of electrolyte, longer service life
* no burning or exploding in case of shorts
Disadvantages of polymer e-caps against wet Al-e-caps:
* more expensive
* higher leakage current
* damageable by transients and higher voltages spikes
Advantages of hybrid polymer Al-e-caps:
* less expensive than polymer aluminum e-caps
* lower leakage current
* impassible against transients
Disadvantage of hybrid polymer Al-e-caps:
* limited service life due to evaporation
Advantages of polymer Ta and Al-e-caps against MLCCs (ceramic):
* no voltage dependent capacitance (except type 1 ceramics)
* no microphonic (except type 1 ceramics)
* higher capacitance values possible
Electrical characteristics
Series-equivalent circuit
 The electrical characteristics of capacitors are harmonized by the international generic specification IEC 60384-1. In this standard, the electrical characteristics of capacitors are described by an idealized series-equivalent circuit with electrical components which model all ohmic losses, capacitive and inductive parameters of electrolytic capacitors:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''ESR, the
The electrical characteristics of capacitors are harmonized by the international generic specification IEC 60384-1. In this standard, the electrical characteristics of capacitors are described by an idealized series-equivalent circuit with electrical components which model all ohmic losses, capacitive and inductive parameters of electrolytic capacitors:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''ESR, the equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
which summarizes all ohmic losses of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESR"
* ''L''ESL, the equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and resistors tends to ...
which is the effective self-inductance of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESL".
* ''R''leak, the resistance representing the leakage current
In electronics, leakage is the gradual transfer of electrical energy across a boundary normally viewed as insulating, such as the spontaneous discharge of a charged capacitor, magnetic coupling of a transformer with other components, or flow of cu ...
of the capacitor
Rated capacitance, standard values and tolerances
 The capacitance value of polymer electrolytic capacitors depends on measuring frequency and temperature. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes show a broader aberration over frequency and temperature ranges than polymer capacitors.
The standardized measuring condition for polymer Al-e-caps is an AC measuring method with 0.5 V at a frequency of 100/120 Hz and a temperature of 20 °C. For polymer Ta-e-caps a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage ≤2.5 V, or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V, may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage.
The capacitance value measured at the frequency of 1 kHz is about 10% less than the 100/120 Hz value. Therefore, the capacitance values of polymer e-caps are not directly comparable and differ from those of
The capacitance value of polymer electrolytic capacitors depends on measuring frequency and temperature. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes show a broader aberration over frequency and temperature ranges than polymer capacitors.
The standardized measuring condition for polymer Al-e-caps is an AC measuring method with 0.5 V at a frequency of 100/120 Hz and a temperature of 20 °C. For polymer Ta-e-caps a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage ≤2.5 V, or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V, may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage.
The capacitance value measured at the frequency of 1 kHz is about 10% less than the 100/120 Hz value. Therefore, the capacitance values of polymer e-caps are not directly comparable and differ from those of film capacitor
Film capacitors, plastic film capacitors, film dielectric capacitors, or polymer film capacitors, generically called film caps as well as power film capacitors, are electrical capacitors with an insulating plastic film as the dielectric, sometime ...
s or ceramic capacitors, whose capacitance is measured at 1 kHz or higher.
The basic unit of a polymer electrolytic capacitor's capacitance is the microfarad
The farad (symbol: F) is the unit of electrical capacitance, the ability of a body to store an electrical charge, in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the English physicist Michael Faraday (1791–1867). In SI base unit ...
(μF). The capacitance value specified in manufacturers data sheets is called the rated capacitance CR or nominal capacitance CN. It is given according to IEC 60063 in values corresponding to the E series E series may refer to:
* BMC E-series engine, a series of automobile engines
* Electronic E series of preferred numbers, a series of preferred values for electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, zener diodes
* Entwicklung seri ...
. These values are specified with a capacitance tolerance in accordance with IEC 60062 preventing overlaps.
The actual measured capacitance value must be within the tolerance limits.
Rated and category voltage
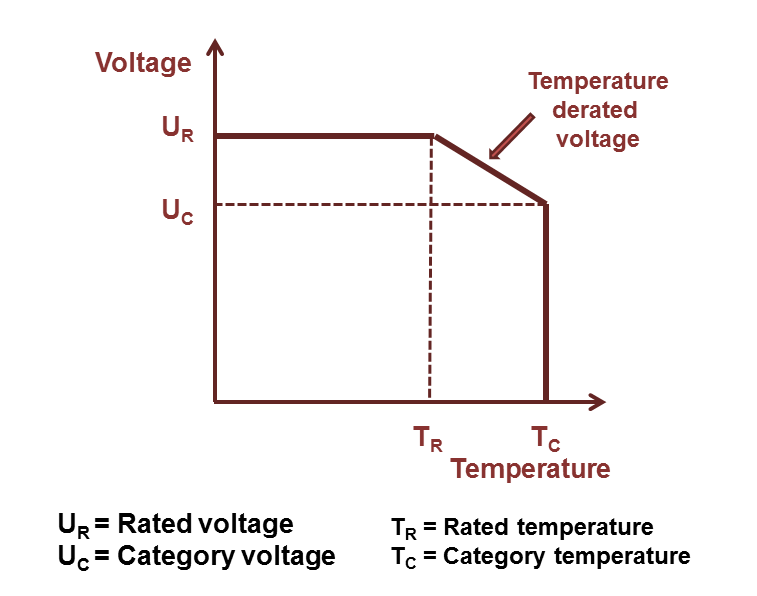 Referring to IEC 60384-1, the allowed operating voltage for polymer e-caps is called the "rated voltage UR". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR.
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture at right.
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
Applying a lower voltage may have a positive influence on polymer electrolytic capacitors. For hybrid polymer Al-e-caps a lower applied voltage in some cases can extend the lifetime.
Referring to IEC 60384-1, the allowed operating voltage for polymer e-caps is called the "rated voltage UR". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR.
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture at right.
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
Applying a lower voltage may have a positive influence on polymer electrolytic capacitors. For hybrid polymer Al-e-caps a lower applied voltage in some cases can extend the lifetime.
Rated and category temperature
The relation between rated temperature TR and rated voltage UR as well as higher category temperature TC and derated category voltage UC is given in the picture at right.
Surge Voltage
Polymer e-cap oxide layers are formed for safety reasons at a higher voltage than the rated voltage, called a surge voltage. Therefore, it is allowed to apply a surge voltage for short times and a limited number of cycles.
The surge voltage indicates the maximum peak voltage value that may be applied during their application for a limited number of cycles.
Transient Voltage
Transients
Transience or transient may refer to:
Music
* ''Transient'' (album), a 2004 album by Gaelle
* ''Transience'' (Steven Wilson album), 2015
* Transience (Wreckless Eric album)
Science and engineering
* Transient state, when a process variable or ...
are fast and high voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
Fast, short duration electrical transients ...
s. Polymer electrolytic capacitors, aluminum as well as tantalum polymer capacitors can not withstand transients or peak voltages higher than surge voltage. Transients for this type of e-caps may destroy the components.zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great varie ...
An unambiguous and general specification of tolerable transients or peak voltages is not possible. In every case transients arise, the application must be individually assessed.
Reverse voltage
Polymer electrolytic capacitors, tantalum as well as aluminum polymer capacitors are polarized capacitors and generally requires the anode electrode voltage to be positive relative to the cathode voltage. Nevertheless, they can withstand for short instants a type dependent reverse voltage for a limited number of cycles. A reverse voltage higher than the type-dependent threshold level applied for a long time to the polymer electrolyte capacitor leads to short-circuit and to destruction of the capacitor.
To minimize the likelihood of a polarized electrolytic being incorrectly inserted into a circuit, polarity has to be very clearly indicated on the case, see the section on "Polarity marking" below.
Impedance and ESR
See also: Electrolytic capacitor#Impedance and Electrolytic capacitor#ESR and dissipation factor tan δ
The impedance is the complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of the voltage to the current in an AC circuit, and expresses as AC resistance both magnitude and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
at a particular frequency. In the data sheets of polymer electrolyte capacitors only the impedance magnitude '', Z, '' is specified, and simply written as ''"Z"''. Regarding the IEC 60384-1 standard, the impedance values of polymer electrolytic capacitors are measured and specified at 100 kHz.
In the special case of resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillatin ...
, in which the both reactive resistances ''XC'' and ''XL'' have the same value (''XC=XL''), the impedance will be determined by only equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
''ESR'', which summarizes all resistive losses of the capacitor. At 100 kHz the impedance and the ESR have nearly the same value for polymer e-caps with capacitance values in the µF range. With frequencies above the resonance the impedance increases again due to ''ESL'' of the capacitor, turning the capacitor into an inductor.

 Impedance and ESR, as shown in the curves, as shown in the curves, heavily depend on the used electrolyte. The curves show the progressively lower impedance and ESR values of "wet" Al-e-caps and MnO2 Ta-e-caps, Al/TCNQ and tantalum polymer e-caps. The curve of a ceramic Class 2 MLCC capacitor, with still lower Z and ESR values is also shown, but whose capacitance is voltage-dependent.
An advantage of the polymer e-caps over non-solid Al-e-caps is low temperature dependence and almost linear curve of the ESR over the specified temperature range. This applies both to polymer tantalum, polymer aluminum, as well as for hybrid polymer aluminum e-caps.
Impedance and ESR are also dependent on design and materials of the capacitors. Cylindrical Al-e-caps with the same capacitance as rectangular Al-e-caps have higher inductance than rectangular Al-e-caps with layered electrodes and therefore they have a lower resonant frequency. This effect is amplified by multi-anode construction, in which individual inductances are reduced by their parallel connection
Impedance and ESR, as shown in the curves, as shown in the curves, heavily depend on the used electrolyte. The curves show the progressively lower impedance and ESR values of "wet" Al-e-caps and MnO2 Ta-e-caps, Al/TCNQ and tantalum polymer e-caps. The curve of a ceramic Class 2 MLCC capacitor, with still lower Z and ESR values is also shown, but whose capacitance is voltage-dependent.
An advantage of the polymer e-caps over non-solid Al-e-caps is low temperature dependence and almost linear curve of the ESR over the specified temperature range. This applies both to polymer tantalum, polymer aluminum, as well as for hybrid polymer aluminum e-caps.
Impedance and ESR are also dependent on design and materials of the capacitors. Cylindrical Al-e-caps with the same capacitance as rectangular Al-e-caps have higher inductance than rectangular Al-e-caps with layered electrodes and therefore they have a lower resonant frequency. This effect is amplified by multi-anode construction, in which individual inductances are reduced by their parallel connection
Ripple current
 A "ripple current" is the
A "ripple current" is the root mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of the ...
(RMS) value of a superimposed AC current of any frequency and any waveform of the current curve for continuous operation within the specified temperature range. It arises mainly in power supplies (including switched-mode power supplies
A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, switched power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently.
Like ...
) after rectifying an AC voltage and flows as charge and discharge current through the decoupling or smoothing capacitor.thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of particles in matter. Thermal radiation is generated when heat from the movement of charges in the material (electrons and protons in common forms of matter) is ...
, convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
, and thermal conduction. The temperature of the capacitor, which is the net balance between heat produced and distributed, must not exceed the capacitor's maximum specified temperature.
The ripple current for polymer e-caps is specified as a maximum effective (RMS) value at 100 kHz at upper rated temperature. Non-sinusoidal ripple currents have to be analyzed and separated into their individual single frequencies by means of Fourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Josep ...
and summarized by squared addition to calculate a RMS value.
Current surge, peak or pulse current
Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors are sensitive to peak or pulse currents.
Leakage current
 The DC leakage current (DCL) is a unique characteristic for electrolytic capacitors other conventional capacitors do not have. It is the DC current that flows when a DC voltage of correct polarity is applied. This current is represented by the resistor ''Rleak'' in parallel with the capacitor in the series-equivalent circuit of e-caps. The main causes of DCL for solid polymer capacitors are f. e. points of electrical dielectric breakdown after soldering, unwanted conductive paths due to impurities or due to poor anodization, and for rectangular types bypassing of dielectric due to excess MnO2, due to moisture paths or cathode conductors (carbon, silver).
Datasheet leakage current specification is given by multiplication of the rated capacitance value ''CR'' with the value of the rated voltage ''UR'' together with an added figure, measured after 2 or 5 minutes, for example a formula for non-solid Al-e-caps:
:
Leakage current in solid polymer e-caps generally drops very fast but then remain on the reached level. The value depends on the voltage applied, temperature, measuring time and influence of moisture caused by case sealing conditions.
Polymer e-caps have relatively high leakage current values. This leakage current cannot be reduced by "healing" in the sense of generating new oxide, because under normal conditions polymer electrolytes cannot deliver oxygen for forming processes. Annealing of defects in the dielectric layer only can be carried out through local overheating and polymer evaporation.
The leakage current values for polymer electrolyte capacitors are between ''0.2 CRUR'' to ''0.04 CRUR'', depending on the manufacturer and series. Thus the value of the leakage current for polymer capacitors is higher than for "wet" Al-e-caps and MnO2 Ta-e-caps.
This higher leakage of current disadvantage of solid polymer Al-e-caps is avoided by hybrid Al-e-caps. Their liquid electrolyte provides the oxygen that is necessary for the reforming of oxide defects, so that the hybrids achieve the same values as wet Al-e-caps.
The DC leakage current (DCL) is a unique characteristic for electrolytic capacitors other conventional capacitors do not have. It is the DC current that flows when a DC voltage of correct polarity is applied. This current is represented by the resistor ''Rleak'' in parallel with the capacitor in the series-equivalent circuit of e-caps. The main causes of DCL for solid polymer capacitors are f. e. points of electrical dielectric breakdown after soldering, unwanted conductive paths due to impurities or due to poor anodization, and for rectangular types bypassing of dielectric due to excess MnO2, due to moisture paths or cathode conductors (carbon, silver).
Datasheet leakage current specification is given by multiplication of the rated capacitance value ''CR'' with the value of the rated voltage ''UR'' together with an added figure, measured after 2 or 5 minutes, for example a formula for non-solid Al-e-caps:
:
Leakage current in solid polymer e-caps generally drops very fast but then remain on the reached level. The value depends on the voltage applied, temperature, measuring time and influence of moisture caused by case sealing conditions.
Polymer e-caps have relatively high leakage current values. This leakage current cannot be reduced by "healing" in the sense of generating new oxide, because under normal conditions polymer electrolytes cannot deliver oxygen for forming processes. Annealing of defects in the dielectric layer only can be carried out through local overheating and polymer evaporation.
The leakage current values for polymer electrolyte capacitors are between ''0.2 CRUR'' to ''0.04 CRUR'', depending on the manufacturer and series. Thus the value of the leakage current for polymer capacitors is higher than for "wet" Al-e-caps and MnO2 Ta-e-caps.
This higher leakage of current disadvantage of solid polymer Al-e-caps is avoided by hybrid Al-e-caps. Their liquid electrolyte provides the oxygen that is necessary for the reforming of oxide defects, so that the hybrids achieve the same values as wet Al-e-caps.
Dielectric absorption (soakage)
Dielectric absorption occurs when a capacitor that has remained charged for a long time discharges only incompletely when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would reach zero volts after discharge, real capacitors develop a small voltage from time-delayed dipole discharging, a phenomenon that is also called dielectric relaxation
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mater ...
, "soakage" or "battery action".
For polymer tantalum as well as aluminum electrolytic capacitors no figures for dielectric absorption are available.
Reliability and lifetime
Reliability (failure rate)
 The
The reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), a ...
of a component is a property that indicates how reliably this component performs its function in a time interval. It is subject to a stochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appea ...
and can be described qualitatively and quantitatively, but is not directly measurable. The reliability of electrolytic capacitors is empirically determined by identifying the failure rate
Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed in failures per unit of time. It is usually denoted by the Greek letter λ (lambda) and is often used in reliability engineering.
The failure rate of a ...
in production accompanying endurance tests. Reliability normally is shown as a bathtub curve
The bathtub curve is widely used in reliability engineering and deterioration modeling. It describes a particular form of the hazard function which comprises three parts:
*The first part is a decreasing failure rate, known as early failures.
*Th ...
and is divided into three areas: early failures or infant mortality failures, constant random failures and wear out failures. Failures totalized in a failure rate are short circuit, open circuit, and degradation failures (exceeding electrical parameters). For polymer Ta-e-caps the failure rate is also influenced by the circuit series resistor, which is not required for polymer Al-e-caps.
Billions of test unit-hours are needed to verify failure rates in the very low level range which are required today to ensure the production of large quantities of components without failures. This requires about a million units tested over a long period, which means a large staff and considerable financing. The tested failure rates are often complemented with feedback from the field from large users (field failure rate), which mostly lowers failure rate estimates
For historical reasons the failure rate units of Ta-e-caps and Al-e-caps are different. For Al-e-caps the reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), a ...
prediction is generally expressed in a failure rate
Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed in failures per unit of time. It is usually denoted by the Greek letter λ (lambda) and is often used in reliability engineering.
The failure rate of a ...
''λ'', with the unit Failures In Time (FIT) at standard operating conditions 40 °C and 0.5 UR during the period of constant random failures. This is the number of failures that can be expected in one billion (109) component-hours of operation (e.g., 1000 components for 1 million hours, or 1 million components for 1000 hours which is 1 ppm/1000 hours) at the standard operating conditions. This failure rate model implicitly assumes that failures are random. Individual components fail at random times but at a predictable rate. The reciprocal value of FIT is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
For Ta-e-caps the failure rate "FTa" is specified with the unit "n % failures per 1000 hours" at 85 °C, U = UR and a circuit resistance of 0.1 Ω/V. This is the failure percentage that can be expected in 1000 hours of operation at much more demanding operational conditions compared with the “FIT” model.
The failure rates “λ” and "FTa" depend on operational conditions including temperature, voltage applied, and various environmental factors such as humidity, shocks or vibrations and of the capacitance value of the capacitor.
Lifetime, service life
The life time, service life
A product's service life is its period of use in service. Several related terms describe more precisely a product's life, from the point of manufacture, storage, and distribution, and eventual use.
Service life has been defined as "a product li ...
, load life or useful life of electrolytic capacitors is a special characteristic of non-solid electrolytic capacitors, whose liquid electrolyte can evaporate over the time leading to wear-out failures. Solid tantalum capacitors with MnO2 electrolyte have no wear-out mechanism so that the constant failure rate least up to the point all capacitors have failed. They do not have a lifetime specification like non-solid Al-e-caps.
However, polymer tantalum as well as polymer aluminum electrolytic capacitors do have a life time specification. The polymer electrolyte has a small conductivity deterioration by a thermal degradation mechanism of the conductive polymer. The electrical conductivity decreases as a function of time, in agreement with a granular metal type structure, in which aging is due to the shrinking of the conductive polymer grains.accelerating
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by th ...
endurance test according to IEC 60384-24/-25/-26 with rated voltage at the upper category temperature. Test conditions for passing the test are
* no short circuit or open circuit
* reduction of capacitance by less than 20%
* increase of ESR, impedance or loss factor less than factor of 2
The specified limits for polymer capacitor degradation failures are much closer than for non-solid Al-e-caps. That means, the life time behavior of polymer e-caps are much more stable than for wet Al-e-caps.
The lifetime specification for polymer capacitors is specified in similar terms to non-solid Al-e-caps with a time in hours at maximum voltage and temperature, for example: 2000h/105 °C. This value can be used for an estimation of an operational life time at individual conditions by a formula called "20-degree-rule":
:
* ''Lx'' = life time to be estimated
* ''LSpec'' = specified life time (useful life, load life, service life)
* ''T0'' = upper category temperature (°C)
* ''TA'' = temperature (°C) of the e-cap case or ambient temperature near the capacitor
This rule characterizes the change of thermic polymer reactions speed within the specified degradation limits. According to this formula the theoretical expected service life of a 2000 h/105 °C polymer capacitor, which is operated at 65 °C, can be calculated (better estimated) with about 200,000 hours or approximately 20 years.
For hybrid polymer Al-e-caps the 20-degree rule does not apply. The expected life of these polymer hybrid e-caps can be calculated using the 10-degree rule. For above conditions e-caps with a liquid electrolyte can expect a life time of 32,000 hours or approximately 3.7 years.
Failure modes, self-healing mechanism and application rules
Field crystallization
Polymer capacitors, tantalum as well as aluminum, are reliable at the same high level as other electronic components with very low failure rates. However, all tantalum electrolytic capacitors, including polymer tantalum, have a unique failure mode called “field crystallization". Field crystallization followed by a
Field crystallization followed by a dielectric breakdown
Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrical insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes an electrical conductor and electric current flows through it. All insulating mate ...
is characterized by a sudden rise in leakage current, within a few milliseconds, from nano-ampere magnitude to ampere magnitude in low-impedance circuits. Increasing current flow can be accelerate as an “avalanche effect” and rapidly spread through the metal/oxide. This can result in various degrees of destruction ranging from rather small, burned areas on the oxide to zigzag burned streaks covering large areas of the pellet or complete oxidation of the metal.short circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit ...
. However, if the current source is limited in solid MnO2 Ta-e-caps a self-healing process take place oxidizing MnO2 into insulating Mn2O3
In polymer Ta-e-caps combustion is not a risk. Field crystallization may occur, however. In this case, the polymer layer is selectively heated and burned away by the increasing leakage current so that the faulty point is isolated. Since the polymer material does not provide oxygen, the leakage current can not accelerate. However, the faulty area no longer contributes to the capacitors capacitance.
Self-healing
Polymer Al-e-caps exhibit the same self-healing mechanism as polymer Ta-e-caps. After application of a voltage at weakened spots in the oxide, a localised higher leakage current path is formed. This leads to a local heating of the polymer; whereby the polymer either oxidises and becomes highly resistive – or evaporates. Also, hybrid polymer Al-e-caps show this self-healing mechanism. However, liquid electrolyte can flow to the faulty spot and can deliver oxygen to build up new dielectric oxide. This is the reason for relatively low leakage current values for hybrid polymer capacitors.
Application rules
The many different types of polymer electrolytic capacitors show differences in electrical long-term behavior, their inherent failure modes, and their self-healing mechanism. To ensure safe operation, manufacturers recommend different application rules, oriented on type behavior, see following table:
Additional informations
Capacitor symbol
Electrolytic capacitor symbols
Polarity marking
Polarity marking for polymer electrolytic capacitors
Imprinted markings
Polymer electrolytic capacitors, given sufficient space, have coded imprinted markings to indicate
* manufacturer's name or trademark;
* manufacturer's type designation;
* polarity
* rated capacitance;
* tolerance on rated capacitance
* rated voltage
* climatic category or rated temperature;
* year and month (or week) of manufacture;
For very small capacitors no marking is possible.
The code of the markings vary by manufacturer.
Standardization
Electronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not ...
s and related technologies standardization follows the rules given by the International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
(IEC), a non-profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
, non-governmental international standards organization
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpr ...
.
The definition of the characteristics and the procedure of the test methods for capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
s for use in electronic equipment are set out in the Generic specification:
* IEC/EN 60384-1 – Fixed capacitors for use in electronic equipment
The tests and requirements to be met by polymer tantalum and polymer aluminum electrolytic capacitors for use in electronic equipment for approval as standardized types are set out in the following sectional specifications:
* IEC/EN 60384-24—''Surface mount fixed tantalum electrolytic capacitors with conductive polymer solid electrolyte''
* IEC/EN 60384-25—''Surface mount fixed aluminium electrolytic capacitors with conductive polymer solid electrolyte''
* IEC/EN 60384-26—''Fixed aluminium electrolytic capacitors with conductive polymer solid electrolyte''
Technological competition
The ESR and ESL characteristics of polymer electrolytic capacitors are converging to those of MLCC capacitors. Conversely, the specific capacitance of Class 2-MLCC capacitors is approaching that of tantalum chip capacitors. However, apart from this increasing comparability there are arguments in favor of or against certain types of capacitors. Many capacitor manufacturers compose these crucial arguments of their technologies against the competition in presentations and articles, f. e.:
* Al-Polymer e-caps against MLCC: Panasonic
* MLCC against Polymer and "wet" e-caps:Murata
* Al-Polymer e-caps against "wet" e-caps: NCC,
Manufacturers and products
As of July 2016
See also
* Aluminum electrolytic capacitor
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminum foil with an etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminum oxide by anodization that acts ...
* Electrolytic capacitor
* Niobium capacitor
A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose anode (+) is made of passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide, on which an insulating niobium pentoxide layer acts as a dielect ...
* SAL electrolytic capacitor
* Tantalum capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounde ...
* Capacitor types
Capacitors are manufactured in many styles, forms, dimensions, and from a large variety of materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors, called ''plates'', separated by an insulating layer (''dielectric''). Capacitors are wide ...
References
External links
{{wikimedia, Capacitor, collapsible=true
Capacitors
Electronic design

 A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid
A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid  During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower
During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower  The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from
The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from  The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an
The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an  Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by
Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by 

 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), abbreviated
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), abbreviated  Lowering ESR and ESL remains a major research and development objective for all polymer capacitors. Some constructive measures can have also a major impact on the electrical parameters of capacitors. Smaller ESR values can be achieved for example by parallel connection of several conventional capacitor cells in one case. Three parallel capacitors with an ESR of 60 mΩ each have a resulting ESR of 20 mΩ. This technology is called “multi-anode” construction and is used in very low ESR polymer tantalum capacitors. In this construction up to six individual anodes in one case are connected. This design is offered as polymer tantalum chip capacitors as well as lower expensive tantalum chip capacitors with MnO2 electrolyte. Multi-anode polymer tantalum capacitors have ESR values on the single-digit milliohm range.
Another simple constructive measure changes the parasitic inductance of the capacitor, the ESL. Since the length of the leads inside the capacitor case has a large amount of the total ESL the inductance of the capacitor can be reduced by reducing the length of the internal leads by asymmetric sintering of the anode lead. This technique is called “face-down” construction. Due to the lower ESL of this face-down construction the resonance of the capacitor is shifted to higher frequencies, which take into account the faster load changes of digital circuits with ever-higher switching frequencies.
Lowering ESR and ESL remains a major research and development objective for all polymer capacitors. Some constructive measures can have also a major impact on the electrical parameters of capacitors. Smaller ESR values can be achieved for example by parallel connection of several conventional capacitor cells in one case. Three parallel capacitors with an ESR of 60 mΩ each have a resulting ESR of 20 mΩ. This technology is called “multi-anode” construction and is used in very low ESR polymer tantalum capacitors. In this construction up to six individual anodes in one case are connected. This design is offered as polymer tantalum chip capacitors as well as lower expensive tantalum chip capacitors with MnO2 electrolyte. Multi-anode polymer tantalum capacitors have ESR values on the single-digit milliohm range.
Another simple constructive measure changes the parasitic inductance of the capacitor, the ESL. Since the length of the leads inside the capacitor case has a large amount of the total ESL the inductance of the capacitor can be reduced by reducing the length of the internal leads by asymmetric sintering of the anode lead. This technique is called “face-down” construction. Due to the lower ESL of this face-down construction the resonance of the capacitor is shifted to higher frequencies, which take into account the faster load changes of digital circuits with ever-higher switching frequencies.
 Polymer tantalum chip capacitors with these new design enhancements, that both the ESR and the ESL decreased reaching properties, approaching ever closer to those of MLCC capacitors.
Polymer tantalum chip capacitors with these new design enhancements, that both the ESR and the ESL decreased reaching properties, approaching ever closer to those of MLCC capacitors.
 Hybrid polymer capacitors are available only in the cylindrical style construction thus corresponds to the above-described cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps leaded in the radial (single-ended) design or with a base plate in the SMD version (V-chip). The difference is that the polymer only covers the surface of the roughened structure of the dielectric Al2O3 and the surface of the cathode foil as thin layers. With this especially the high-ohmic parts in the small pores of the anode foil can be made low-ohmic to reduce the capacitors ESR. As electrical connection between both polymer layers serve a liquid electrolyte like in conventional wet Al-e-caps impregnating the separator. The small distance the non-solid electrolyte conduct increases the ESR a little bit, however in fact not dramatically. Advantage of this construction is that the liquid electrolyte in operation delivers the oxygen which is necessary for self-healing of the dielectric layer in the presence of any small defects.
The current that flows through a small defect results in selective heating, which normally destroys the overlying polymer film, isolating, but not healing, the defect. In hybrid polymer capacitors liquid can flow to the defect, delivering oxygen and healing the dielectric by generating new oxides, decreasing the leakage current. Hybrid polymer Al-e-caps have a much lower leakage current than standard polymer Al-e-caps.
Hybrid polymer capacitors are available only in the cylindrical style construction thus corresponds to the above-described cylindrical polymer Al-e-caps leaded in the radial (single-ended) design or with a base plate in the SMD version (V-chip). The difference is that the polymer only covers the surface of the roughened structure of the dielectric Al2O3 and the surface of the cathode foil as thin layers. With this especially the high-ohmic parts in the small pores of the anode foil can be made low-ohmic to reduce the capacitors ESR. As electrical connection between both polymer layers serve a liquid electrolyte like in conventional wet Al-e-caps impregnating the separator. The small distance the non-solid electrolyte conduct increases the ESR a little bit, however in fact not dramatically. Advantage of this construction is that the liquid electrolyte in operation delivers the oxygen which is necessary for self-healing of the dielectric layer in the presence of any small defects.
The current that flows through a small defect results in selective heating, which normally destroys the overlying polymer film, isolating, but not healing, the defect. In hybrid polymer capacitors liquid can flow to the defect, delivering oxygen and healing the dielectric by generating new oxides, decreasing the leakage current. Hybrid polymer Al-e-caps have a much lower leakage current than standard polymer Al-e-caps.
 The capacitance value of polymer electrolytic capacitors depends on measuring frequency and temperature. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes show a broader aberration over frequency and temperature ranges than polymer capacitors.
The standardized measuring condition for polymer Al-e-caps is an AC measuring method with 0.5 V at a frequency of 100/120 Hz and a temperature of 20 °C. For polymer Ta-e-caps a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage ≤2.5 V, or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V, may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage.
The capacitance value measured at the frequency of 1 kHz is about 10% less than the 100/120 Hz value. Therefore, the capacitance values of polymer e-caps are not directly comparable and differ from those of
The capacitance value of polymer electrolytic capacitors depends on measuring frequency and temperature. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes show a broader aberration over frequency and temperature ranges than polymer capacitors.
The standardized measuring condition for polymer Al-e-caps is an AC measuring method with 0.5 V at a frequency of 100/120 Hz and a temperature of 20 °C. For polymer Ta-e-caps a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage ≤2.5 V, or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V, may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage.
The capacitance value measured at the frequency of 1 kHz is about 10% less than the 100/120 Hz value. Therefore, the capacitance values of polymer e-caps are not directly comparable and differ from those of  Referring to IEC 60384-1, the allowed operating voltage for polymer e-caps is called the "rated voltage UR". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR.
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture at right.
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
Applying a lower voltage may have a positive influence on polymer electrolytic capacitors. For hybrid polymer Al-e-caps a lower applied voltage in some cases can extend the lifetime. For polymer Ta-e-caps lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.
Referring to IEC 60384-1, the allowed operating voltage for polymer e-caps is called the "rated voltage UR". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR.
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture at right.
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
Applying a lower voltage may have a positive influence on polymer electrolytic capacitors. For hybrid polymer Al-e-caps a lower applied voltage in some cases can extend the lifetime. For polymer Ta-e-caps lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.

 A "ripple current" is the
A "ripple current" is the  The
The  Field crystallization followed by a
Field crystallization followed by a