North Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The area is mostly
The area is mostly
 North Wales does not have any motorways, with the only motorways in Wales being present in South Wales, and nearest motorways (M53 motorway, M53 and M56 motorway, M56) being on the other side of the Wales-England border. There have been proposals to upgrade the A55 into a motorway or have more motorway-like features. Trunk roads in Wales, Trunk roads in the region are maintained by the North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent (NMWTRA).
The main roads spanning across North Wales, mostly span east to west, especially along the North Wales coast. This is mainly due to the mountainous terrain in the middle of Wales, leading most north-south connections to be slower, leading to diversions onto north-south roads in England. The emphasis on east-west roadways has led to North Wales having closer connections with North West England (centred on Liverpool and Manchester) rather than with South Wales.
The busiest road in North Wales is the A55 road, A55, the "North Wales Expressway", a dual carriageway primary road connecting Chester to Holyhead, along the North Wales coast and passing Deeside, Llandudno Junction, Conwy, and Bangor. It is described as the economic lifeline for North Wales, and the second most important road in all of Wales, only to the M4 motorway, M4 in South Wales. The road connects all the way to the Port of Holyhead following an extension in 2001, which provides ferry connections to the Republic of Ireland. The majority of the road is part of the International E-road network, E-road network as European route E22, E22 (until Ewloe, where it goes along the A494 road, A494 into England), and is a dual carriageway, grade-separated, for its entire 88-mile length.
A historically important road in the region is the A5 road (Great Britain), A5, a major road that was the primary link between the region and London (as the "''London-Holyhead Trunk Road"''). The road crosses the Menai Suspension Bridge and is regarded as a more scenic route, with its historical importance as a connection between London and the Port of Holyhead, superseded by the A55. Other roads transiting North Wales, from east to west include the A458 road, A458 from Halesowen to Mallwyd, and the A494 from Dolgellau to Saughall (originally to Birkenhead).
The busiest north-south road travelling through the region is the A483 road, A483 from Chester (originally from Manchester) through Wrexham and into England near Oswestry, before re-entering Montgomeryshire and passing Welshpool and Newtown, before continuing onto Swansea. Other major north-south roads include the single-carriageways of the A470 road, A470 from Llandudno to Cardiff via the Conwy valley, and the A487 road, A487 from Bangor to Haverfordwest via Caernarfon and Snowdonia.
North Wales does not have any motorways, with the only motorways in Wales being present in South Wales, and nearest motorways (M53 motorway, M53 and M56 motorway, M56) being on the other side of the Wales-England border. There have been proposals to upgrade the A55 into a motorway or have more motorway-like features. Trunk roads in Wales, Trunk roads in the region are maintained by the North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent (NMWTRA).
The main roads spanning across North Wales, mostly span east to west, especially along the North Wales coast. This is mainly due to the mountainous terrain in the middle of Wales, leading most north-south connections to be slower, leading to diversions onto north-south roads in England. The emphasis on east-west roadways has led to North Wales having closer connections with North West England (centred on Liverpool and Manchester) rather than with South Wales.
The busiest road in North Wales is the A55 road, A55, the "North Wales Expressway", a dual carriageway primary road connecting Chester to Holyhead, along the North Wales coast and passing Deeside, Llandudno Junction, Conwy, and Bangor. It is described as the economic lifeline for North Wales, and the second most important road in all of Wales, only to the M4 motorway, M4 in South Wales. The road connects all the way to the Port of Holyhead following an extension in 2001, which provides ferry connections to the Republic of Ireland. The majority of the road is part of the International E-road network, E-road network as European route E22, E22 (until Ewloe, where it goes along the A494 road, A494 into England), and is a dual carriageway, grade-separated, for its entire 88-mile length.
A historically important road in the region is the A5 road (Great Britain), A5, a major road that was the primary link between the region and London (as the "''London-Holyhead Trunk Road"''). The road crosses the Menai Suspension Bridge and is regarded as a more scenic route, with its historical importance as a connection between London and the Port of Holyhead, superseded by the A55. Other roads transiting North Wales, from east to west include the A458 road, A458 from Halesowen to Mallwyd, and the A494 from Dolgellau to Saughall (originally to Birkenhead).
The busiest north-south road travelling through the region is the A483 road, A483 from Chester (originally from Manchester) through Wrexham and into England near Oswestry, before re-entering Montgomeryshire and passing Welshpool and Newtown, before continuing onto Swansea. Other major north-south roads include the single-carriageways of the A470 road, A470 from Llandudno to Cardiff via the Conwy valley, and the A487 road, A487 from Bangor to Haverfordwest via Caernarfon and Snowdonia.
 The public Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network of the region is largely split into two sections. These sections are centred around the two main west-east railway lines transversing the region, as there are currently no north-south railway lines wholly in the region. This is largely due to the mountainous regions of Snowdonia resting between the two lines, and low passenger numbers of north-south lines leading to their closure. The public rail network is managed and maintained by Network Rail. Historically, the region had a more extensive rail network with more interconnectivity of the current lines and more connections to the south. However, due to falling passenger numbers, the emergence of automobiles and other factors, the region's railways came under review, resulting in the Beeching cuts to the network. Many former rail corridors of the once more extensive network were superseded by road infrastructure. The numerous heritage railways scattered across the region serve as a reminder of the former railways across the region.
The majority of lines operated in Wales are part of the Wales & Borders franchise, Wales & Borders Passenger rail franchising in Great Britain, franchise, the current operator is Transport for Wales Rail, a Welsh Government, Welsh-Government State-owned enterprises of the United Kingdom, owned company, although some services (from Holyhead and Wrexham) are operated by the West Coast Partnership operator, Avanti West Coast on services using the West Coast Main Line to Euston railway station, London Euston.
According to StatsWales, the number of rail journeys across the 6 principal areas of North Wales, made in 2017-18 was 1.4 million, an increase of 20,525 from 2007-8. The largest share of these rail journeys, at 38.4%, was within the boundaries of Gwynedd. Conwy was the principal area which saw the greatest increase in rail journeys as a percentage of journeys over the ten-year period, at 22.5%. The least amount of rail journeys in 2018-19 was in Anglesey.
As of 2020, there as 66 rail stations within the boundaries of the 6 northern principal areas, of which 2 are among the 20 busiest stations in Wales, Rhyl railway station, Rhyl, and Bangor railway station (Wales), Bangor. 41 of the rail stations are stations of the North Wales lines, whereas the remaining 25 are stations of the Mid Wales lines, specifically the Cambrian Line. There is a total of 5 rail routes in North Wales: the North Wales Coast Line, the Shrewsbury–Chester line, Shrewsbury—Chester Line, the Conwy Valley Line, the Borderlands Line (all part of the North Wales lines) and the Cambrian Line. All 5 routes together in 2018-19 had approximately 5,295,602 entries and exits through the 66 stations.
The North Wales Coast Line, the main rail line serving the north Wales coast, and connecting with Irish Ferries and Stena Line ferry services to Dublin Port in the Republic of Ireland. The Conwy Valley Line branches off at Llandudno Junction, heading north to Llandudno railway station, Llandudno and south to Blaenau Ffestiniog railway station, Blaenau Ffestiniog. The Shrewsbury—Chester line, connects Chester and Shrewsbury railway station, Shrewsbury via
The public Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network of the region is largely split into two sections. These sections are centred around the two main west-east railway lines transversing the region, as there are currently no north-south railway lines wholly in the region. This is largely due to the mountainous regions of Snowdonia resting between the two lines, and low passenger numbers of north-south lines leading to their closure. The public rail network is managed and maintained by Network Rail. Historically, the region had a more extensive rail network with more interconnectivity of the current lines and more connections to the south. However, due to falling passenger numbers, the emergence of automobiles and other factors, the region's railways came under review, resulting in the Beeching cuts to the network. Many former rail corridors of the once more extensive network were superseded by road infrastructure. The numerous heritage railways scattered across the region serve as a reminder of the former railways across the region.
The majority of lines operated in Wales are part of the Wales & Borders franchise, Wales & Borders Passenger rail franchising in Great Britain, franchise, the current operator is Transport for Wales Rail, a Welsh Government, Welsh-Government State-owned enterprises of the United Kingdom, owned company, although some services (from Holyhead and Wrexham) are operated by the West Coast Partnership operator, Avanti West Coast on services using the West Coast Main Line to Euston railway station, London Euston.
According to StatsWales, the number of rail journeys across the 6 principal areas of North Wales, made in 2017-18 was 1.4 million, an increase of 20,525 from 2007-8. The largest share of these rail journeys, at 38.4%, was within the boundaries of Gwynedd. Conwy was the principal area which saw the greatest increase in rail journeys as a percentage of journeys over the ten-year period, at 22.5%. The least amount of rail journeys in 2018-19 was in Anglesey.
As of 2020, there as 66 rail stations within the boundaries of the 6 northern principal areas, of which 2 are among the 20 busiest stations in Wales, Rhyl railway station, Rhyl, and Bangor railway station (Wales), Bangor. 41 of the rail stations are stations of the North Wales lines, whereas the remaining 25 are stations of the Mid Wales lines, specifically the Cambrian Line. There is a total of 5 rail routes in North Wales: the North Wales Coast Line, the Shrewsbury–Chester line, Shrewsbury—Chester Line, the Conwy Valley Line, the Borderlands Line (all part of the North Wales lines) and the Cambrian Line. All 5 routes together in 2018-19 had approximately 5,295,602 entries and exits through the 66 stations.
The North Wales Coast Line, the main rail line serving the north Wales coast, and connecting with Irish Ferries and Stena Line ferry services to Dublin Port in the Republic of Ireland. The Conwy Valley Line branches off at Llandudno Junction, heading north to Llandudno railway station, Llandudno and south to Blaenau Ffestiniog railway station, Blaenau Ffestiniog. The Shrewsbury—Chester line, connects Chester and Shrewsbury railway station, Shrewsbury via
North Wales Economic Ambition Board
* PDF book by Alfred Neobard Palmer published in 1910
Things to do in North Wales
{{Authority control North Wales, Regions of Wales Administrative divisions of Wales
, area_land_km2 = 6,172
, postal_code_type = Postcode
, postal_code = LL, CH, SY
, image_map1 = Wales North Wales locator map.svg
, map_caption1 = Six
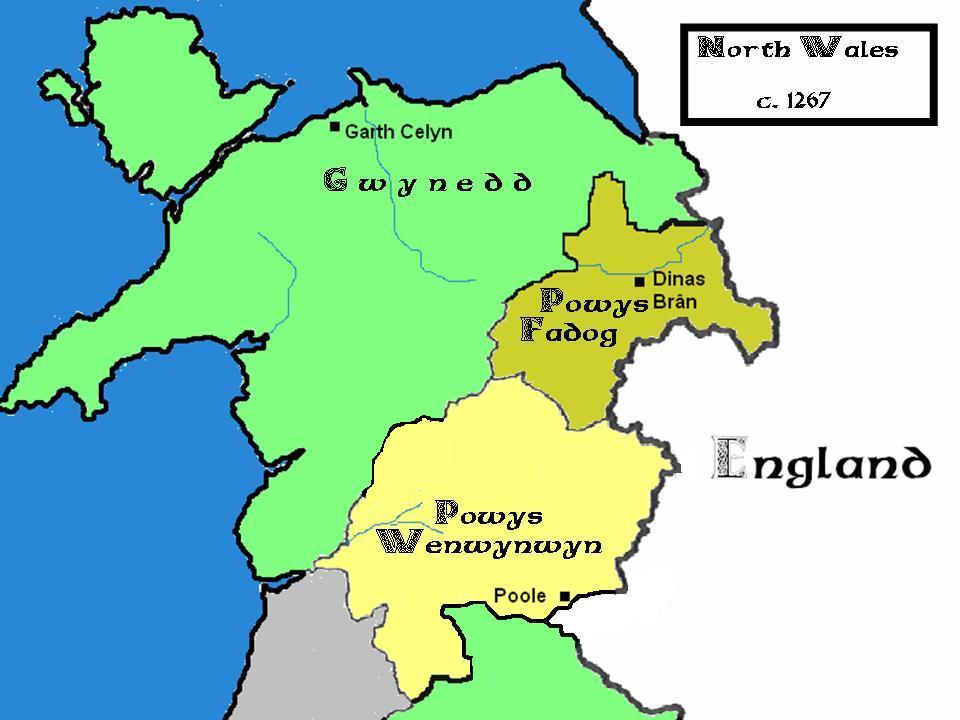 Historically, for most of North Wales, the region can be referred to as simply "''Gwynedd''", named after one of the last independent Welsh kingdoms, the
Historically, for most of North Wales, the region can be referred to as simply "''Gwynedd''", named after one of the last independent Welsh kingdoms, the

), regional tourism boards, principal areas of Wales
Since 1 April 1996, Wales has been divided into 22 single-tier principal areas ( cy, Awdurdodau unedol), styled as counties or county boroughs ( or ) for local government purposes. The elected councils of these areas are responsible for the pr ...
commonly defined to be North Wales, for policing, fire and rescue
A fire department (American English) or fire brigade (Commonwealth English), also known as a fire authority, fire district, fire and rescue, or fire service in some areas, is an organization that provides fire prevention and fire suppression se ...
, health
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
and regional economy.
North Wales ( cy, Gogledd Cymru) is a region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders Mid Wales to the south, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
to the east, and the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdonia National Park
Snowdonia or Eryri (), is a mountainous region in northwestern Wales and a national park of in area. It was the first to be designated of the three national parks in Wales, in 1951.
Name and extent
It was a commonly held belief that the nam ...
( and the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley
, iucn_category =V
, iucn_ref =
, photo =Sunny Hillside, Frosty Valley Dee Valley Wales (11014647076).jpg
, photo_width =
, photo_alt =Image of the view of the Dee Valley from Moel Y Gamelin
, photo_caption = ...
(), known for its mountains, waterfalls and trails, wholly within the region. Its population is concentrated in the north-east
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
and northern coastal areas, with significant Welsh-speaking populations in its western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and rural areas. North Wales is imprecisely defined, lacking any exact definition or administrative structure. It is commonly defined administratively as its six most northern principal areas {{Short description, Formal legal term for a county in England and Wales
In England and Wales local government legislation, a principal area is one of the sub-national areas established for control by a principal council. They include most of the ar ...
, but other definitions exist, with Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire, also known as ''Maldwyn'' ( cy, Sir Drefaldwyn meaning "the Shire of Baldwin's town"), is one of thirteen historic counties of Wales, historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. It is named after its county tow ...
historically considered to be part of the region.
Those from North Wales are sometimes referred to as "Gogs" (from "Gogledd" – the Welsh word for "north"); in comparison, those from South Wales are sometimes called "Hwntws" by those from North Wales.
The region includes the localities of Wrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
, Deeside
Deeside ( cy, Glannau Dyfrdwy) is the name given to a predominantly industrial conurbation of towns and villages in Flintshire and Cheshire on the Wales–England border lying near the canalised stretch of the River Dee that flows from nei ...
, Rhyl
Rhyl (; cy, Y Rhyl, ) is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. The town lies within the historic boundaries of Flintshire, on the north-east coast of Wales at the mouth of the River Clwyd ( Welsh: ''Afon Clwyd'').
To the we ...
, Colwyn Bay
Colwyn Bay ( cy, Bae Colwyn) is a town, community and seaside resort in Conwy County Borough on the north coast of Wales overlooking the Irish Sea. It lies within the historic county of Denbighshire. Eight neighbouring communities are incorpo ...
, Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fir ...
, Bangor, Llandudno, and Holyhead. The largest localities in North Wales are the city of Wrexham and the conurbations of Deeside and Rhyl/Prestatyn
Prestatyn is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. Historically a part of Flintshire, it is located on the Irish Sea coast, to the east of Rhyl. Prestatyn has a population of 19,085,
History Prehistory
There is evidence that ...
, where the main retail, cultural, educational, tourism, and transport infrastructure and services of North Wales are located. Bangor and St Asaph
St Asaph (; cy, Llanelwy "church on the Elwy") is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and community (Wales), community on the River Elwy in Denbighshire, Wales. In the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census it had a population of 3,355 ...
are the region's cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, Bangor is Wales' oldest city, whereas St Asaph is one of Wales' smallest and was awarded status in 2012. Wrexham, the region's largest settlement, became a city in 2022.
History
Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Based in northwest Wales, th ...
. This has led to a stronger sense of Welsh identity
Welsh national identity is a term referring to the sense of national identity, as embodied in the shared and characteristic culture, languages and traditions, of the Welsh people.
History
Celtic era
The Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons w ...
and home to more Welsh-language speakers, especially in North West Wales, than the rest of Wales. The term "North Wales" is rarely applied to all of Wales during the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic peoples, Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, ev ...
and the period of the Heptarchy
The Heptarchy were the seven petty kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England that flourished from the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain in the 5th century until they were consolidated in the 8th century into the four kingdoms of Mercia, Northumbria, Wess ...
, to distinguish it from "West Wales", known today as Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, although the term "Wales" or the names of the various petty kingdoms of Wales (''Gwynedd, and Powys
Powys (; ) is a Local government in Wales#Principal areas, county and Preserved counties of Wales, preserved county in Wales. It is named after the Kingdom of Powys which was a Welsh succession of states, successor state, petty kingdom and princi ...
'' in North Wales) are more commonly used to depict the region during this time.
The region is steeped in history, being a crucial component in Welsh medieval history, and was from the 5th to the 12th/13th centuries under the control of the influential Welsh kingdoms of Gwynedd, and Powys following the end of Roman rule in Britain. The Kingdom of Gwynedd controlled the majority of what is now the commonly defined 6 counties of North Wales, including all of the North Wales coast, with Powys retaining control over what is modern Powys, and parts of Wrexham and Flintshire, in addition to part of Shropshire. Through their over 800 year existences', their rulers acclaimed themselves to be the " King(s) of the Britons", and Gwynedd would lead the charge in the subsequent formation of the Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales ( cy, Tywysogaeth Cymru) was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the con ...
. The mountainous stronghold of Snowdonia formed the nucleus of that realm and would become the last redoubt of independent Medieval Wales — only overcome in 1283 by English forces under Edward I. To this day it remains a stronghold of the Welsh language and a centre for Welsh national and cultural identity.
World Heritage & Biosphere Sites
The area is home to three of the four UNESCOWorld Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s in Wales. These are Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal, the Slate Landscape of Northwest Wales and, collectively, the Edwardian castles and town walls of the region which comprise those at Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a royal town, community and port in Gwynedd, Wales, with a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the eastern shore of the Menai Strait, opposite the Isle of Anglesey. The city of Bangor is ...
, Beaumaris
Beaumaris ( ; cy, Biwmares ) is a town and community on the Isle of Anglesey in Wales, of which it is the former county town of Anglesey. It is located at the eastern entrance to the Menai Strait, the tidal waterway separating Anglesey from th ...
, Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy on ...
and Harlech
Harlech () is a seaside resort and community in Gwynedd, north Wales and formerly in the historic county of Merionethshire. It lies on Tremadog Bay in the Snowdonia National Park. Before 1966, it belonged to the Meirionydd District of the 19 ...
. It also shares with Powys and Ceredigion the distinction of hosting the only UNESCO Biosphere (from Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme to promote sustainable development) reserve in Wales, namely, Biosffer Dyfi Biosphere. London has only one more site than North Wales.
Definition
The boundaries and status of North Wales are undefined (compared toregions of England
The regions, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England, established in 1994. Between 1994 and 2011, nine regions had officially devolved functions within government. While they no ...
), definitions, and the boundary of North Wales with South or Mid Wales differs between organisations. It is strongly used culturally for comparison to the more urban
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
South Wales. The most common definition for statistical and administrative purposes of North Wales contains the 6 principal areas of: Isle of Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island, ...
, Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy on ...
, Denbighshire
Denbighshire ( ; cy, Sir Ddinbych; ) is a county in the north-east of Wales. Its borders differ from the historic county of the same name. This part of Wales contains the country's oldest known evidence of habitation – Pontnewydd (Bontnewy ...
, Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and C ...
, and Wrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
. Of which have a combined estimated population in 2018 of 698,400 people. Under this definition, the area borders the principal areas of Ceredigion
Ceredigion ( , , ) is a county in the west of Wales, corresponding to the historic county of Cardiganshire. During the second half of the first millennium Ceredigion was a minor kingdom. It has been administered as a county since 1282. Cer ...
, Powys
Powys (; ) is a Local government in Wales#Principal areas, county and Preserved counties of Wales, preserved county in Wales. It is named after the Kingdom of Powys which was a Welsh succession of states, successor state, petty kingdom and princi ...
, and the rest of Wales to the south, England and its counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
of Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to th ...
, and Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county t ...
to the east, and the Irish sea to the north and west. Other definitions, especially historical, commonly include Montgomeryshire
Montgomeryshire, also known as ''Maldwyn'' ( cy, Sir Drefaldwyn meaning "the Shire of Baldwin's town"), is one of thirteen historic counties of Wales, historic counties and a former administrative county of Wales. It is named after its county tow ...
, one of the historic counties of Wales
The historic counties of Wales are sub-divisions of Wales. They were used for various functions for several hundred years,Bryne, T., ''Local Government in Britain'', (1994) but for administrative purposes have been superseded by contemporary ...
, to be part of North Wales, although as part of Powys its more commonly considered Mid Wales today. The definitions of North and Mid Wales constantly overlap, with Meirionnydd
Meirionnydd is a coastal and mountainous region of Wales. It has been a kingdom, a cantref, a district and, as Merionethshire, a county.
Kingdom
Meirionnydd (Meirion, with -''ydd'' as a Welsh suffix of land, literally ''Land adjoined to Meirio ...
(southern part of the modern principal area of Gwynedd) sometimes considered Mid Wales. 
Capitalisation
North Wales may also be spelled as 'north Wales' with a lower case 'n' fornorth
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
, coined as the "to cap or not to cap" debate. It is argued that using a lower case 'n' is to be only used to signify "north" as merely a geographic identifier, and a capital 'N' to distinctly separate the region for cultural, organisational, or statistical purposes from the rest of Wales. Such usage may follow ideological lines, with North Wales used to confer the region as a distinctly separate entity from the rest of Wales, whilst north Wales as merely the northern bit of Wales. Organisations, where the region is administered the same as with the rest of Wales, may prefer to use a lower case for north. Whilst organisations only operating in the region or separate from any others in the rest of Wales may use a capitalised N. Local newspapers, such as the Daily Post describe themselves to be a "capper" capitalising the 'N', whereas other organisations such as BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadca ...
may use a lower case. The Welsh Government's style guide uses lowercase, whereas Visit Wales
Visit Wales ( cy, Croeso Cymru) is the Welsh Government's tourism organisation. Its aim is to promote Welsh tourism and assist the tourism industry.
History
The Wales Tourist Board was established in 1969 as a result of the Development of T ...
uses capitalised. David Williams, chairman of the North Wales Business Club, announced his support for capping the term "North", stating that North Wales should be a "very recognisable region in our own right".
Principal areas
For local administration, the region is made up of the following 6principal areas {{Short description, Formal legal term for a county in England and Wales
In England and Wales local government legislation, a principal area is one of the sub-national areas established for control by a principal council. They include most of the ar ...
, consisting of counties, and county boroughs, they are: the Isle of Anglesey, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, and Wrexham County Borough.
These principal areas are commonly divided into two groups, used for local news (e.g. BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...town and country planning
Town and country planning in the United Kingdom is the part of English land law which concerns land use planning. Its goal is to ensure sustainable economic development and a better environment. Each country of the United Kingdom has its own ...
, and were the proposed replacements to the existing 6 principal areas before proposals were scrapped in 2019. They are: North East Wales
North East Wales ( cy, Gogledd-Ddwyrain Cymru) refers to an area or region of Wales, commonly defined as a grouping of the principal areas of Denbighshire, Flintshire, and Wrexham County Borough in the north-east of the country. These principal ...
(Denbighshire, Flintshire, Wrexham), and North West Wales
North West Wales ( cy, Gogledd-Orllewin Cymru) refers to an area or region of Wales, commonly defined as a grouping of the principal areas of Conwy County Borough, Gwynedd and the Isle of Anglesey in the north-west of the country. These princi ...
(Anglesey, Conwy, Gwynedd) being the two most popular groupings, although a North Central Wales (Conwy and Denbighshire) grouping has been occasionally used, specifically for health administration.
Historical divisions
In addition to the six principal areas, North Wales is also divided into the following preserved counties for various ceremonial purposes: Clwyd (comprising Conwy, Denbighshire, Flintshire and Wrexham), and Gwynedd (comprisingGwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and C ...
and Isle of Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island, ...
) The preserved counties are based on the counties created by the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
and were used for local government purposes (with county councils) between 1974 and 1996. During this period up to the present, Montgomeryshire remained a part of Powys.
Prior to the preserved counties, there were counties, now referred to as historic counties. These are the oldest of the counties of North Wales, used for centuries. North Wales contained 6 historic counties during these times, the counties were; Anglesey, Caernarfonshire
, HQ= County Hall, Caernarfon
, Map=
, Image= Flag
, Motto= Cadernid Gwynedd (The strength of Gwynedd)
, year_start=
, Arms= ''Coat of arms of Caerna ...
, Denbighshire
Denbighshire ( ; cy, Sir Ddinbych; ) is a county in the north-east of Wales. Its borders differ from the historic county of the same name. This part of Wales contains the country's oldest known evidence of habitation – Pontnewydd (Bontnewy ...
, Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, Merionethshire
, HQ= Dolgellau
, Government= Merionethshire County Council (1889-1974)
, Origin=
, Status=
, Start= 1284
, End=
, Code= MER
, CodeName= ...
, and Montgomeryshire. The most notable difference between these six counties and the present six (seven with Montgomeryshire) is that Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire were combined into one principal area, initially called 'Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire' until a day after its formation where it took the name Gwynedd instead, and the formation of two county boroughs, Conwy carved out of Caernarfonshire and Denbighshire, and Wrexham carved out of Denbighshire and Flintshire.
The north of Wales was traditionally divided into three regions during the middle ages: Upper Gwynedd (or Gwynedd above the Conwy), defined as the area north of the River Dyfi
The River Dyfi ( cy, Afon Dyfi; ), also known as the River Dovey (; ), is an approximately long river in Wales.
Its large estuary forms the boundary between the counties of Gwynedd and Ceredigion, and its lower reaches have historically been c ...
and west of the River Conwy
, name_etymology =
, image = Boats in River Conwy.jpg
, image_size = 300
, image_caption = Boats in the river estuary at Conwy
, map =
, map_size =
, map_caption =
, push ...
; Lower Gwynedd (or Gwynedd below the Conwy), also known as the ''Perfeddwlad
Perfeddwlad or Y Berfeddwlad was an historic name for the territories in Wales lying between the River Conwy and the River Dee. comprising the cantrefi of Rhos, Rhufoniog, Dyffryn Clwyd and Tegeingl. Perfeddwlad thus was also known as the Four ...
("the middle country")'' and defined as the region east of the River Conwy and west of the River Dee; and Ynys Môn (or Anglesey), a large island off the north coast. English Maelor
English Maelor ( cy, Maelor Saesneg) comprises one half of the Maelor region on the Welsh side of the Wales-England border, being the area of the Maelor east of the River Dee. The region has changed counties several times, previously being par ...
, currently part of Wrexham County Borough, located east of the River Dee, as the name suggests, was part of England during a significant part of this period.
Electoral divisions
North Wales is electorally divided into constituencies andelectoral wards
The wards and electoral divisions in the United Kingdom are electoral districts at sub-national level, represented by one or more councillors. The ward is the primary unit of English electoral geography for civil parishes and borough and dist ...
to elect local representatives to multiple layers of government.
Parliamentary constituencies
There are eleven constituencies used for both theUK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremac ...
and the Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
(Welsh Parliament; ): Aberconwy ( UK / SN), Alyn and Deeside ( UK / SN), Arfon ( UK / SN), Clwyd South ( UK / SN), Clwyd West ( UK / SN), Delyn ( UK / SN), Dwyfor Meironnydd ( UK / SN), Montgomeryshire ( UK / SN, if considered North Wales), Vale of Clwyd ( UK / SN), Wrexham ( UK / SN), and Ynys Môn (Anglesey, UK / SN).
An electoral region for the Senedd, shares the name "North Wales", yet does not cover all of North Wales, only the northern coast, Anglesey, and northeast of Wales (specifically the entire area of the former pre-1996 county of Clwyd); the rest of North Wales (mainly Meirionnydd) is covered by the Mid and West Wales
Mid and West Wales or Mid and South West Wales refers to an ambiguous region of Wales that is sometimes used, consisting broadly of the preserved counties of Dyfed and Powys, sometimes Swansea and sometimes parts of Gwynedd. It is also used ...
Senedd electoral region. All constituencies aside Dwyfor Meironnydd, and Montgomeryshire are in the North Wales Senedd electoral region.
Between 1979 and 1994, all of North Wales (including Montgomery) was a single European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts ...
constituency (EPC), the North Wales European Parliament Constituency. In 1994, minor border changes put parts of Montgomeryshire in the neighbouring Mid and West Wales
Mid and West Wales or Mid and South West Wales refers to an ambiguous region of Wales that is sometimes used, consisting broadly of the preserved counties of Dyfed and Powys, sometimes Swansea and sometimes parts of Gwynedd. It is also used ...
constituency. In 1999, both of the constituencies ceased, when it was absorbed into the larger Wales constituency until 2020 when it was subsequently abolished following the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
's withdrawal
Withdrawal means "an act of taking out" and may refer to:
* Anchoresis (withdrawal from the world for religious or ethical reasons)
* ''Coitus interruptus'' (the withdrawal method)
* Drug withdrawal
* Social withdrawal
* Taking of money from a ban ...
from the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
on 31 January 2020.
Border to the south
The division with the rest of Wales is arbitrary and depends on the particular use being made. For example, the boundary of North Wales Police differs from the boundary of the North Wales area of theNatural Resources Wales
Natural Resources Wales ( cy, Cyfoeth Naturiol Cymru) is a Welsh Government sponsored body, which became operational from 1 April 2013, when it took over the management of the natural resources of Wales. It was formed from a merger of the Coun ...
and the North Wales Regional Transport Consortium (''Taith''). The historic boundary follows the pre-1996 county boundaries of Merionethshire and Denbighshire which in turn closely follow the geographic features of the River Dyfi
The River Dyfi ( cy, Afon Dyfi; ), also known as the River Dovey (; ), is an approximately long river in Wales.
Its large estuary forms the boundary between the counties of Gwynedd and Ceredigion, and its lower reaches have historically been c ...
to Aran Fawddwy, then crossing the high moorlands following the watershed until reaching Cadair Berwyn
Cadair Berwyn or Cader Berwyn is a mountain summit in north-east Wales with a height of above sea level. It is the highest point in the Berwyn range, the highest in North East Wales and the highest significant summit in Wales o ...
and then following the River Rhaeadr and River Tanat to the Shropshire border. The most common definition is that North Wales ends at the peripheries of the northern 6 principal areas, therefore the border is between Wrexham - Powys, Denbighshire - Powys, Gwynedd - Powys, and Gwynedd - Ceredigion (over the River Dyfi).
Geography
 The area is mostly
The area is mostly rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
with many mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and ...
s and valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers ...
s. This, in combination with its coast (on the Irish Sea), means tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
is the principal industry. Farming
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, which was once the principal economic force in the area, is now much reduced in importance. The average income per capita of the local population is the lowest in the UK.
The eastern part of North Wales contains the most populous areas, with more than 300,000 people living in the areas around Wrexham and Deeside. Wrexham, with a population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of 65,692 at the 2011 census in its built-up area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
, it is North Wales' largest city. The total population of North Wales is 696,300 (2017). The majority of other settlements are along the coast, including some popular resort town
A resort town, often called a resort city or resort destination, is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding ...
s, such as Rhyl
Rhyl (; cy, Y Rhyl, ) is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. The town lies within the historic boundaries of Flintshire, on the north-east coast of Wales at the mouth of the River Clwyd ( Welsh: ''Afon Clwyd'').
To the we ...
, Llandudno, Pwllheli
Pwllheli () is a market town and community of the Llŷn Peninsula ( cy, Penrhyn Llŷn) in Gwynedd, north-western Wales. It had a population of 4,076 in 2011 of whom a large proportion, 81%, are Welsh language, Welsh speaking. Pwllheli is the pl ...
, Prestatyn
Prestatyn is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. Historically a part of Flintshire, it is located on the Irish Sea coast, to the east of Rhyl. Prestatyn has a population of 19,085,
History Prehistory
There is evidence that ...
and Tywyn
Tywyn (Welsh: ; in English often ), formerly spelled Towyn, is a town, community, and seaside resort on the Cardigan Bay coast of southern Gwynedd, Wales. It was previously in the historic county of Merionethshire. It is famous as the lo ...
. There are two cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
cities Bangor and St. Asaphand a number of medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s (e.g. Criccieth Castle, Criccieth, Dolbadarn Castle, Dolbadarn, Dolwyddelan Castle, Dolwyddelan, Harlech, Caernarfon Castle, Beaumaris, Conwy) The area of North Wales is about 6,172 square kilometres, making it slightly larger than the country of Brunei, or the island of Bali.
The highest mountain in Wales is Snowdon (, in northwest Wales.
Transport
Roads
 North Wales does not have any motorways, with the only motorways in Wales being present in South Wales, and nearest motorways (M53 motorway, M53 and M56 motorway, M56) being on the other side of the Wales-England border. There have been proposals to upgrade the A55 into a motorway or have more motorway-like features. Trunk roads in Wales, Trunk roads in the region are maintained by the North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent (NMWTRA).
The main roads spanning across North Wales, mostly span east to west, especially along the North Wales coast. This is mainly due to the mountainous terrain in the middle of Wales, leading most north-south connections to be slower, leading to diversions onto north-south roads in England. The emphasis on east-west roadways has led to North Wales having closer connections with North West England (centred on Liverpool and Manchester) rather than with South Wales.
The busiest road in North Wales is the A55 road, A55, the "North Wales Expressway", a dual carriageway primary road connecting Chester to Holyhead, along the North Wales coast and passing Deeside, Llandudno Junction, Conwy, and Bangor. It is described as the economic lifeline for North Wales, and the second most important road in all of Wales, only to the M4 motorway, M4 in South Wales. The road connects all the way to the Port of Holyhead following an extension in 2001, which provides ferry connections to the Republic of Ireland. The majority of the road is part of the International E-road network, E-road network as European route E22, E22 (until Ewloe, where it goes along the A494 road, A494 into England), and is a dual carriageway, grade-separated, for its entire 88-mile length.
A historically important road in the region is the A5 road (Great Britain), A5, a major road that was the primary link between the region and London (as the "''London-Holyhead Trunk Road"''). The road crosses the Menai Suspension Bridge and is regarded as a more scenic route, with its historical importance as a connection between London and the Port of Holyhead, superseded by the A55. Other roads transiting North Wales, from east to west include the A458 road, A458 from Halesowen to Mallwyd, and the A494 from Dolgellau to Saughall (originally to Birkenhead).
The busiest north-south road travelling through the region is the A483 road, A483 from Chester (originally from Manchester) through Wrexham and into England near Oswestry, before re-entering Montgomeryshire and passing Welshpool and Newtown, before continuing onto Swansea. Other major north-south roads include the single-carriageways of the A470 road, A470 from Llandudno to Cardiff via the Conwy valley, and the A487 road, A487 from Bangor to Haverfordwest via Caernarfon and Snowdonia.
North Wales does not have any motorways, with the only motorways in Wales being present in South Wales, and nearest motorways (M53 motorway, M53 and M56 motorway, M56) being on the other side of the Wales-England border. There have been proposals to upgrade the A55 into a motorway or have more motorway-like features. Trunk roads in Wales, Trunk roads in the region are maintained by the North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent (NMWTRA).
The main roads spanning across North Wales, mostly span east to west, especially along the North Wales coast. This is mainly due to the mountainous terrain in the middle of Wales, leading most north-south connections to be slower, leading to diversions onto north-south roads in England. The emphasis on east-west roadways has led to North Wales having closer connections with North West England (centred on Liverpool and Manchester) rather than with South Wales.
The busiest road in North Wales is the A55 road, A55, the "North Wales Expressway", a dual carriageway primary road connecting Chester to Holyhead, along the North Wales coast and passing Deeside, Llandudno Junction, Conwy, and Bangor. It is described as the economic lifeline for North Wales, and the second most important road in all of Wales, only to the M4 motorway, M4 in South Wales. The road connects all the way to the Port of Holyhead following an extension in 2001, which provides ferry connections to the Republic of Ireland. The majority of the road is part of the International E-road network, E-road network as European route E22, E22 (until Ewloe, where it goes along the A494 road, A494 into England), and is a dual carriageway, grade-separated, for its entire 88-mile length.
A historically important road in the region is the A5 road (Great Britain), A5, a major road that was the primary link between the region and London (as the "''London-Holyhead Trunk Road"''). The road crosses the Menai Suspension Bridge and is regarded as a more scenic route, with its historical importance as a connection between London and the Port of Holyhead, superseded by the A55. Other roads transiting North Wales, from east to west include the A458 road, A458 from Halesowen to Mallwyd, and the A494 from Dolgellau to Saughall (originally to Birkenhead).
The busiest north-south road travelling through the region is the A483 road, A483 from Chester (originally from Manchester) through Wrexham and into England near Oswestry, before re-entering Montgomeryshire and passing Welshpool and Newtown, before continuing onto Swansea. Other major north-south roads include the single-carriageways of the A470 road, A470 from Llandudno to Cardiff via the Conwy valley, and the A487 road, A487 from Bangor to Haverfordwest via Caernarfon and Snowdonia.
Sea
The Port of Holyhead, on the isle of Anglesey, is the main commercial and ferry port in North Wales. The port had the third-largest volume of Cargo, freight traffic, in Wales, in 2018 (5.2 million tonnes), after Milford Haven Waterway, Milford Haven and Port of Port Talbot, Port Talbot, and it is the main port for freight and sea passenger transport with the Republic of Ireland, handling more than 2 million passengers each year. 81% of freight traffic going through Welsh ports to the Republic of Ireland, and 75.5% of sea passenger traffic between Wales and the Republic of Ireland went through Holyhead in 2018. Historically, there were two routes between Holyhead and the Irish ports of Dublin Port, Dublin and Dún Laoghaire, Dun Laoghaire. The route to Dun Laoghaire was the most popular in 1998 with over 1.7 million passengers ferried, however following a consistent decline in passenger traffic, it was removed in 2015. The other route to Dublin saw an overall increase in passenger numbers from just over 1 million in 1998 to just over 1.9 million in 2018, an increase of 82%. A Mostyn-Dublin ferry service once existed, on the now Port of Liverpool, Liverpool-Dublin route, attracting a peak of 48,000 passengers in 2003, before being discontinued in 2004.Rail
 The public Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network of the region is largely split into two sections. These sections are centred around the two main west-east railway lines transversing the region, as there are currently no north-south railway lines wholly in the region. This is largely due to the mountainous regions of Snowdonia resting between the two lines, and low passenger numbers of north-south lines leading to their closure. The public rail network is managed and maintained by Network Rail. Historically, the region had a more extensive rail network with more interconnectivity of the current lines and more connections to the south. However, due to falling passenger numbers, the emergence of automobiles and other factors, the region's railways came under review, resulting in the Beeching cuts to the network. Many former rail corridors of the once more extensive network were superseded by road infrastructure. The numerous heritage railways scattered across the region serve as a reminder of the former railways across the region.
The majority of lines operated in Wales are part of the Wales & Borders franchise, Wales & Borders Passenger rail franchising in Great Britain, franchise, the current operator is Transport for Wales Rail, a Welsh Government, Welsh-Government State-owned enterprises of the United Kingdom, owned company, although some services (from Holyhead and Wrexham) are operated by the West Coast Partnership operator, Avanti West Coast on services using the West Coast Main Line to Euston railway station, London Euston.
According to StatsWales, the number of rail journeys across the 6 principal areas of North Wales, made in 2017-18 was 1.4 million, an increase of 20,525 from 2007-8. The largest share of these rail journeys, at 38.4%, was within the boundaries of Gwynedd. Conwy was the principal area which saw the greatest increase in rail journeys as a percentage of journeys over the ten-year period, at 22.5%. The least amount of rail journeys in 2018-19 was in Anglesey.
As of 2020, there as 66 rail stations within the boundaries of the 6 northern principal areas, of which 2 are among the 20 busiest stations in Wales, Rhyl railway station, Rhyl, and Bangor railway station (Wales), Bangor. 41 of the rail stations are stations of the North Wales lines, whereas the remaining 25 are stations of the Mid Wales lines, specifically the Cambrian Line. There is a total of 5 rail routes in North Wales: the North Wales Coast Line, the Shrewsbury–Chester line, Shrewsbury—Chester Line, the Conwy Valley Line, the Borderlands Line (all part of the North Wales lines) and the Cambrian Line. All 5 routes together in 2018-19 had approximately 5,295,602 entries and exits through the 66 stations.
The North Wales Coast Line, the main rail line serving the north Wales coast, and connecting with Irish Ferries and Stena Line ferry services to Dublin Port in the Republic of Ireland. The Conwy Valley Line branches off at Llandudno Junction, heading north to Llandudno railway station, Llandudno and south to Blaenau Ffestiniog railway station, Blaenau Ffestiniog. The Shrewsbury—Chester line, connects Chester and Shrewsbury railway station, Shrewsbury via
The public Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network of the region is largely split into two sections. These sections are centred around the two main west-east railway lines transversing the region, as there are currently no north-south railway lines wholly in the region. This is largely due to the mountainous regions of Snowdonia resting between the two lines, and low passenger numbers of north-south lines leading to their closure. The public rail network is managed and maintained by Network Rail. Historically, the region had a more extensive rail network with more interconnectivity of the current lines and more connections to the south. However, due to falling passenger numbers, the emergence of automobiles and other factors, the region's railways came under review, resulting in the Beeching cuts to the network. Many former rail corridors of the once more extensive network were superseded by road infrastructure. The numerous heritage railways scattered across the region serve as a reminder of the former railways across the region.
The majority of lines operated in Wales are part of the Wales & Borders franchise, Wales & Borders Passenger rail franchising in Great Britain, franchise, the current operator is Transport for Wales Rail, a Welsh Government, Welsh-Government State-owned enterprises of the United Kingdom, owned company, although some services (from Holyhead and Wrexham) are operated by the West Coast Partnership operator, Avanti West Coast on services using the West Coast Main Line to Euston railway station, London Euston.
According to StatsWales, the number of rail journeys across the 6 principal areas of North Wales, made in 2017-18 was 1.4 million, an increase of 20,525 from 2007-8. The largest share of these rail journeys, at 38.4%, was within the boundaries of Gwynedd. Conwy was the principal area which saw the greatest increase in rail journeys as a percentage of journeys over the ten-year period, at 22.5%. The least amount of rail journeys in 2018-19 was in Anglesey.
As of 2020, there as 66 rail stations within the boundaries of the 6 northern principal areas, of which 2 are among the 20 busiest stations in Wales, Rhyl railway station, Rhyl, and Bangor railway station (Wales), Bangor. 41 of the rail stations are stations of the North Wales lines, whereas the remaining 25 are stations of the Mid Wales lines, specifically the Cambrian Line. There is a total of 5 rail routes in North Wales: the North Wales Coast Line, the Shrewsbury–Chester line, Shrewsbury—Chester Line, the Conwy Valley Line, the Borderlands Line (all part of the North Wales lines) and the Cambrian Line. All 5 routes together in 2018-19 had approximately 5,295,602 entries and exits through the 66 stations.
The North Wales Coast Line, the main rail line serving the north Wales coast, and connecting with Irish Ferries and Stena Line ferry services to Dublin Port in the Republic of Ireland. The Conwy Valley Line branches off at Llandudno Junction, heading north to Llandudno railway station, Llandudno and south to Blaenau Ffestiniog railway station, Blaenau Ffestiniog. The Shrewsbury—Chester line, connects Chester and Shrewsbury railway station, Shrewsbury via Wrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
, providing the main north Wales and south Wales connection. A former open-access operator Wrexham & Shropshire, used to provide a Wrexham General—Marylebone railway station, London Marylebone service until 2011. The Borderlands Line, intersects the Shrewsbury—Chester line at Wrexham General, branching south to Wrexham Central railway station, Wrexham Central (where it Terminal train station, terminates), and north to Bidston railway station, Bidston (Birkenhead), and the North Wales Coast Line at Shotton. Bidston connects to the Wirral line, providing Merseyrail services, west to West Kirby railway station, West Kirby, and east to Liverpool Central railway station, Liverpool Central. The Cambrian Line forms the other west-east line in the region (as the Mid-Wales line), it connects Shrewsbury, westwards with Mid Wales and towns along Cardigan Bay. The line is commonly split into two sections, the section from Shrewsbury to Aberystwyth railway station, Aberystwyth is sometimes referred to as the Cambrian Main Line, with the Cambrian Coast Line, splitting off from this line at Dovey Junction railway station, Dovey Junction, heading northwest to Pwllheli railway station, Pwllheli. The Welsh Marches Line connects Crewe railway station, Crewe to Newport railway station, Newport, via Shrewsbury, with services from Holyhead usually continuing to Cardiff Central railway station, Cardiff Central. It forms part of the Premier Service, North Wales South Wales service, along with the Shrewsbury—Chester, North Wales Coast Line, and South Wales Main Line. These lines form the main rail connection between North Wales and South Wales.
Chester provides the main travel connections for the North Wales Coast, as a major transport hub. As part of the North Wales Metro, from Chester ''(and Wrexham General at limited times),'' via the Halton Curve, direct trains run to Liverpool Lime Street railway station, Liverpool Lime Street, linking to the Merseyrail. Services to Manchester Piccadilly station, Manchester Piccadilly from Chester, via the Chester–Manchester line, Chester—Manchester line for Transport for Wales services, and the Mid-Cheshire line, Mid—Cheshire line for Northern Rail, Northern services, in addition to the Northern service to Leeds railway station, Leeds, provide North Wales' connections to Northern England. Shrewsbury provides the main travel connections for passengers from the Cambrian line (and those commuting south from other North Wales stations), providing services, in addition to those to South Wales, through England to Crewe, Birmingham International railway station, Birmingham International, and Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham New Street, and via the Heart of Wales line, services to Llanelli railway station, Llanelli.
Heritage and narrow gauge railway lines
There are numerous heritage railways in the region. Most of them are narrow-gauge railway, narrow-gauge. Several run on sections of historically longer lines. Heritage railways employ more than 300 people and generate over £50 million per year for the North Wales economy. The heritage railways in the region are: Several of these lines connect to the Cambrian line. Stations where the heritage railway uses the same station as Network Rail. At Fairbourne, the Fairbourne Railway connects to Barmouth Ferry railway station, Barmouth Ferry and the Ffestiniog Railway connects at . The Talyllyn Railway's station is a short walk from station on the Cambrian line, while on the Cambrian line is across town from on the Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway.Future developments
Many rail and bus lines of the region are part of an improvement project called the North Wales Metro or North East Wales Metro, which proposes improvements to the existing lines (specifically the Borderlands lines), improved connectivity between rail and other modes of transport, and more connections to North West England. For the Gobowen railway station, Gobowen to Oswestry railway station, Oswestry line, Cambrian Heritage Railways, the line's operator, is working on reopening the line (multiple sections of line), and the Anglesey Central Railway is also proposed to be restored.Tramways
In Llandudno, the Great Orme Tramway links to the Great Orme. It is the only remaining cable-operated street tramway in Great Britain, and one of only a few surviving in the world.Geology
North Wales has very diverse and complex geology with Precambrian schists along the Menai Strait and the great Cambrian dome behind Harlech and underlying much of western Snowdonia. In the Ordovician period much volcanism deposited a range of minerals and rocks over the northwestern parts of Gwynedd whilst to the east of the River Conwy lies a large area of upland rolling hills underlain by the Silurian mudstones and grits comprising the Denbigh and Migneint Moors. To the east, around Llangollen, to the north on Halkyn Mountain and the Great Orme and in eastern Anglesey are beds of limestone from which metals have been mined since pre-Roman times. Added to all this are the complexities posed by Parys Mountain and the outcrops of unusual minerals such as Jasper and Mona Marble which make the area of special interest to geologists.Demographics
Terms for people from the region include; North Welsh, and North Walian (also spelt as North Walean), or informally as "Gogs" from the Welsh word for North, "Gogledd". This term is mostly only used to distinguish from other parts of Wales (i.e. only used domestically in Wales), a majority of the population consider themselves as just "Welsh people, Welsh", and some additionally or only as "British people, British". Communities along the Wales-England border and northern coast may identify as "English people, English" as they are home to many of those of English ancestry.Population
According to Statistics for Wales (StatsWales), the North Wales region, consists of the 6 northern principal areas, and statistics provided by StatsWales only include these 6 areas. In 2018, the estimated population of the region was 698,400 people. North Wales exhibits the evenest distribution of population across the local authorities of any of the 4 statistical regions of Wales, with 4 of the 6 authorities home to over 100,000 residents, Flintshire, Wrexham, Gwynedd and Conwy. Flintshire is the most populated principal area of North Wales, home to an estimated 155,600 people, with the Isle of Anglesey being the least populated with an estimated 70,000 people. In 2018, North Wales has an estimated population density of 113.6 persons per square kilometre. Flintshire is the most densely populated of the 6 areas, at 355.6 persons per km2, with Gwynedd being the least dense principal area at 49.0 persons per km2. Between 2008, and 2018, the population density of North Wales grew by 2.3%, the third-highest rate of population density growth of the 4 statistical regions of Wales. Gwynedd, with 3.7% growth, had the highest population density growth rate in North Wales, whereas the Isle of Anglesey had the lowest population density growth rate at 0.1% from 2008 to 2018. The population growth for the region between 1998 and 2018 was 6.3%, however, the rate was lower between 2008 and 2018, than in 1998 and 2008. Conwy was the area with the highest population growth rate for the two decades at 8%, with Isle of Anglesey having the smallest growth rate at just over 3%. Population settlements North Wales' largest settlement (locality) is Wrexham, with 65,692 people in the 2011 census. Data from the census details that North Wales has a lower number and proportion of residents living in settlements of 25,000 or more, than South East and South West Wales, but higher than Mid Wales. StatsWales attributes this to North Wales' lack of a settlement of a population higher than 100,000 people. Age North Wales has an ageing population, as the proportion of residents over 65 has increased from 18.5% to 23.0%, and the proportion of the population under 15 has decreased from 19.8% to 17.8%.Language
Dialect North Wales has a distinct regional identity. Its dialect of the Welsh language differs from that of other regions, such as South Wales, in some ways: for example ' is used in most of the North instead of ' for "milk"; a simple sentence such as ''go upstairs now'' might be ' in North Wales, and ' in South Wales. Colloquialism, Colloquially, a person from North Wales (especially one who speaks with this dialect or accent) is known as a ''North Walian'', or a ''Gog'' (from the Welsh ', meaning "north"). There are Welsh medium education, Welsh medium schools scattered all across North Wales, ranging from primary to secondary schools.Welsh-speaking population
According to the 2011 census, there were 204,406 Welsh-speakers aged three and over in North Wales. Data from the Annual Population Survey, stated that Gwynedd had the largest proportion of speakers in North Wales and Wales as a whole, with 75.6% of residents aged 3 and over saying they can speak Welsh. Flintshire had the lowest rate of Welsh in North Wales, with only 22.5% saying they can speak it. North Wales is the most Welsh-speaking region of the 4 statistical regions of Wales, at 41.9% of the population speaking Welsh in the year ending September 2019, up approximately 2.4% from September 2009. However, Flintshire is one of 2 principal areas in Wales where the rate of Welsh has decreased over the past decade.Education
North Wales is home to two universities, Bangor University, and Wrexham Glyndŵr University, Wrexham Glyndwr University. In 2018-19, in total there were 17,500 enrolments on higher education courses in North Wales, representing 13.2% of student enrolments in all of Wales. Bangor University was home to a majority, 58.3% of these enrolments, with 10,195 enrolments in 2018-19, with Wrexham Glyndwr University following with 5,895 enrolments, and further education college Grŵp Llandrillo Menai providing the remaining 1,410 enrolments. Further education (FE) in Wales is provided by "colleges" (not to be confused with a university college), these are usually either Sixth form college, sixth form colleges, further education colleges, or sixth forms within Secondary school, secondary schools. Further education colleges are the largest further education institutions in North Wales, in which, at present, there are only 2; Grŵp Llandrillo Menai, and Coleg Cambria. Both of these colleges, are amalgamations of smaller further education or sixth form colleges, and are sometimes described as "super colleges". Grŵp Llandrillo Menai is a merger of Coleg Llandrillo, Coleg Menai, and Coleg Meirion-Dwyfor, providing courses for students of the Isle of Anglesey, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, and Gwynedd. Coleg Cambria is a merger Deeside College and Yale College, Wrexham, providing courses for students of Denbighshire, Flintshire, and Wrexham County Borough. There are no standalone sixth form colleges (sixth form only) in North Wales, as all colleges providing sixth form courses also provide non-sixth form courses. The other institutions providing sixth form further education in North Wales are secondary schools, which provide sixth form education themselves. Not all secondary schools in North Wales provide sixth form education, with it being common for students of a secondary school that does not provide sixth form education to study at a further education college. Grŵp Colegau NPTC Group of Colleges, a further education college formed from the merger of Neath Port Talbot College and Coleg Powys, is the main further education college for Powys, hosting a campus in Newtown.Health
Healthcare service
The 6 counties of North Wales are all part of the Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board (BCUHB), it is the largest of the Local health board, local health boards which divide up NHS Wales services in Wales. Formed from the merger of the North Wales NHS Trust (itself a merger of North East Wales NHS Trust, North East Wales, and Conwy & Denbighshire NHS Trust, Conwy & Denbighshire NHS trust, NHS Trusts), the North West Wales NHS Trust, and the Local Health Boards of the six counties of Anglesey, Conwy, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, and Wrexham. There are 3 main district general hospitals in North Wales; Ysbyty Gwynedd in Bangor, Glan Clwyd Hospital, Ysbyty Glan Clwyd Hospital in Bodelwyddan, and Wrexham Maelor Hospital. Each hospital is the main centre of healthcare for the west, central, and east parts of North Wales respectively. North Wales additionally has a network of 22 acute and Community hospital, community hospitals, with patients commonly referred to hospitals in National Health Service (England), England for rare, more specialised treatment, unavailable under BCUHB, notably to Countess of Chester Hospital, Countess of Chester, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Royal Liverpool University, and Royal Shrewsbury Hospital, Royal Shrewsbury hospitals.Economy
According to the Annual Population Survey and Office for National Statistics, the unemployment rate of the six principal areas of North Wales was collectively 3.9% for the population aged 16 and over; the employment rate was 75.9% of those aged 16-64, and the economic inactivity rate (excluding students) for the population aged 16-64 was 17.9%.North Wales Growth Deal
In 2016 the UK Government invited North Wales to submit a Growth Deal Bid, to "create thousands of jobs, boost the economy, improve transport and communication links, focus on renewable energy, support tourism and more". A bid was prepared by the North Wales Business Council, which consists of the Leaders and Chief Executives of the 6 councils, the Vice Chancellors of Wrexham Glyndŵr University and Bangor University the Chief Executives of Coleg Cambria and Grwp Llandrillo Menai, and North Wales Mersey Dee Business Council. In the 2018 budget Philip Hammond announced that £120M would be made available by the UK Government to support the Growth Deal. In December 2018, Ken Skates confirmed that the Welsh Government would match the UK Government funding, and also offered to match any additional funding support which the UK Government might make available. In November 2019 the Heads of Terms Agreement for the North Wales Growth Deal was signed by the representatives of the North Wales Economic Ambition Board, Alun Cairns the UK Government Secretary of State for Wales, and Eluned Morgan, Baroness Morgan of Ely on behalf of Welsh Government.Local media
Local newspapers
Two daily newspapers are published in the region. The region-wide "North Wales edition" of the ''Daily Post'', based at Bryn Eirias on Colwyn Bay's Abergele Road, is distributed from Monday to Saturday, whilst ''The Leader (Welsh newspaper), The Leader'' (formerly the ''Evening Leader'') publishes two editions for Wrexham and Flintshire and is based at the headquarters of Newsquest in Mold, Flintshire, Mold after NWN Media Ltd dissolved after existing since 1920. Additionally, nine weekly newspapers provide local and community news:Reach PLC titles
* ''Caernarfon and Denbigh Herald'' (Arfon and Dwyfor editions) * ''The Mail'' (Bangor/Anglesey and Holyhead/Anglesey editions) * ''North Wales Weekly News'' (General, Colwyn Bay and Conwy Valley editions)Newsquest titles
* ''Denbighshire Free Press'' * ''Flintshire Standard'' * ''The Journal'' (Rhyl, Prestatyn and Abergele editions) * ''North Wales Chronicle'' (North Gwynedd and Anglesey) * ''North Wales Pioneer'' (Llandudno and Colwyn Bay editions) * ''Leader'' The weekly Aberystwyth-based ''Cambrian News'' covers southern Gwynedd and publishes separate editions for the Arfon/Dwyfor and Meirionydd districts. A weekly Welsh-language newspaper, ''Y Cymro'' is published each week by the ''Cambrian News'' from its Porthmadog office alongside two localised Welsh titles, ''Y Cyfnod'' (Bala) and ''Y Dydd'' (Dolgellau). ''Yr Herald Gymraeg'' is distributed by Trinity Mirror as a pull-out section in the Wednesday edition of the ''Daily Post''. There are also 24 Papur Bro, Papurau Bro (''area papers'') providing community news and generally published each month.Online
Several hyperlocal websites in the area provide locally sourced news online. In Conwy county, BaeColwyn.com has provided Welsh language coverage of the Colwyn Bay area since 2011 and AbergelePost.com has been serving the Abergele area since 2010. Wrexham.com is a full-time operation covering Wrexham and the surrounding area, and is based at offices in Wrexham city centre. A full-time citizen-led online news site Deeside.com started in early 2013 and covers Connah's Quay, Mancot, Pentre, Shotton, Flintshire, Shotton, Queensferry, Flintshire, Queensferry, Sealand, Flintshire, Sealand, Broughton, Flintshire, Broughton, Hawarden, Ewloe, Sandycroft and parts of Saltney.Radio
Although no BBC local radio stations exist in Wales, the corporation's national services BBC Radio Wales and BBC Radio Cymru cover the region from their broadcasting centres in Bangor, and Wrexham. The Bangor studios produce a large number of Radio Cymru programmes with some music and feature output for Radio Wales originating from Wrexham. Three commercial radio stations serve the area — Capital North West and Wales broadcasts local drivetime programming for Wrexham, Flintshire, Denbighshire and Conwy county as well as Cheshire and the Wirral with a Welsh language opt-out service for the former Heart North Wales Coast, Coast FM area on 96.3 FM. Capital Cymru airs an extended local programming service, predominantly in the Welsh language, for Gwynedd and Anglesey. Across the entire region, Heart North Wales also airs local peak-time programming in English, including an extended news programme on weeknights. All three stations broadcast from studios in Gwersyllt on the outskirts of Wrexham. Three community radio stations broadcast on FM — Calon FM serving Wrexham County Borough and parts of southern Flintshire, Tudno FM broadcasting to Llandudno & surrounding areas and Môn FM across the Isle of Anglesey and parts of Gwynedd. Radio Glan Clwyd - an extension of hospital service Radio Ysbyty Glan Clwyd - broadcasts on 1287 AM in the Bodelwyddan, St Asaph, Rhuddlan, Towyn and Kinmel Bay areas. Towards the western side of North Wales, local hills mean national BBC FM coverage can be quite poor, often suffering interference from Irish stations from the west.Television
News coverage of North Wales is generally provided within the BBC's ''Wales Today'', ''Newyddion'' and ''Ffeil'' programmes (the latter two broadcast on S4C) and on ITV (TV channel), ITV's ''ITV News Cymru Wales''. BBC Cymru Wales news teams are based at the corporation's Bangor and Wrexham studios, while ITV Wales & West, ITV Cymru Wales runs a newsroom inColwyn Bay
Colwyn Bay ( cy, Bae Colwyn) is a town, community and seaside resort in Conwy County Borough on the north coast of Wales overlooking the Irish Sea. It lies within the historic county of Denbighshire. Eight neighbouring communities are incorpo ...
.
S4C has an administrative office in Caernarfon, where a cluster of independent production companies are also based or partly based including Rondo Media, Cwmni Da, Antena, Owain Roberts Animations and Tinopolis.
Sport
Football
Wrexham A.F.C. play in the English football league system; having been a member of the Football League for over 80 years, in 2008 they were relegated into the Conference National for the first time in their existence. They now play in the Vanarama National League. They play at the Racecourse Ground in Wrexham and train at Colliers Park, Gresford. Several teams including Connah's Quay Nomads F.C. and Bangor City F.C. have appeared in UEFA competitions, playing within the mostly semi-professional Welsh leagues the Cymru Premier and the Cymru North. Due to the proximity of North Wales to the North West of England, support for the English clubs of Liverpool F.C., Everton F.C. and Manchester United F.C. has been historically strong.Rugby League
Wales was represented in the Super League by the Crusaders Rugby League, Crusaders RL, they re-located to Wrexham for the 2010 season from South Wales. They played at the Racecourse Ground and trained at Stansty Park both in Wrexham before folding in 2011. They have now been replaced by the RFL League 1, League 1 side, North Wales Crusaders. North Wales has its own amateur league, in the fifth tier of the British rugby league system, the North Wales Championship.Rugby Union
In September 2008 it was announced by the Welsh Rugby Union that a development team based in North Wales would be created, with a long-term goal of becoming the fifth Welsh team in the Pro14, Celtic League. It was envisaged that this would both help the growth of the game in the area, and provide a larger pool of players for the Wales national rugby union team, Welsh national team to be selected from. The team was named RGC 1404.See also
* Geography of Wales * West Wales * Mid Wales * North Wales Police * North Wales Police and Crime Commissioner * North Wales Fire and Rescue ServiceNotes
References
External links
North Wales Economic Ambition Board
* PDF book by Alfred Neobard Palmer published in 1910
Things to do in North Wales
{{Authority control North Wales, Regions of Wales Administrative divisions of Wales