|
Denbighshire (historic)
, HQ= Denbigh and Ruthin , Arms= , Map= , Code= DEN , CodeName= Chapman code , Government= Denbighshire County Council (1889-1974) , PopulationFirst= 83,629Vision of Britain 1831 Census/ref> , PopulationFirstYear= 1831 , AreaFirst= , AreaFirstYear= 1831 , DensityFirst= 0.2/acre , DensityFirstYear= 1831 , PopulationSecond= 144,783Vision of Britain Denbighshire population an density , PopulationSecondYear= 1911 , AreaSecond= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
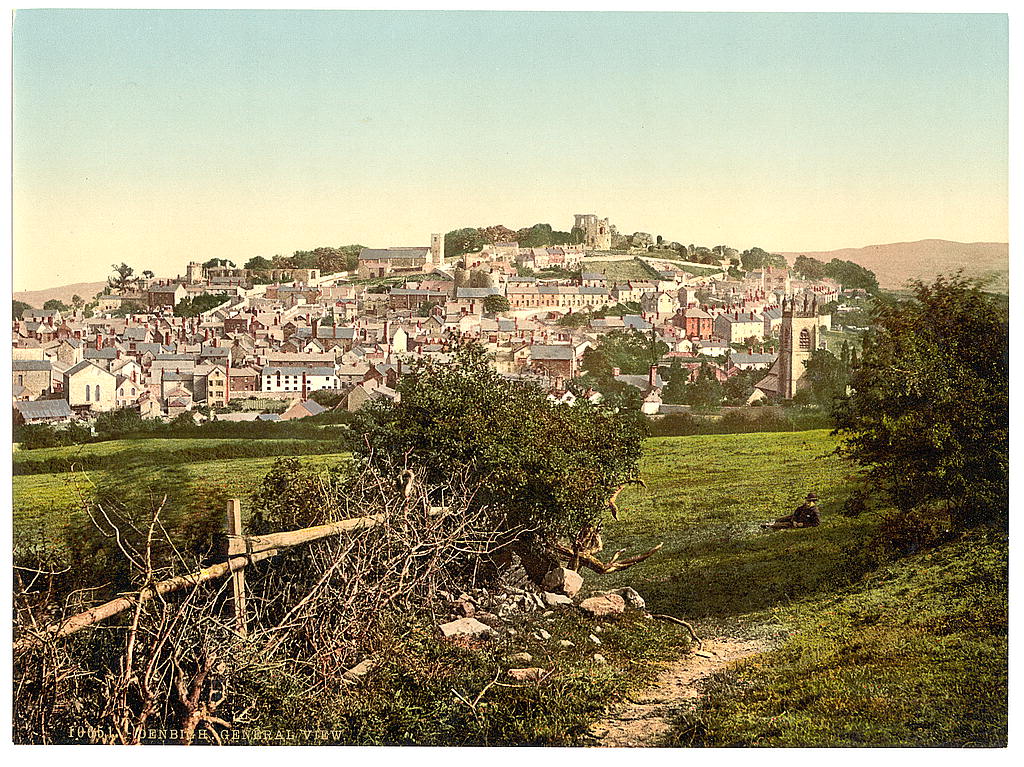
Denbigh
Denbigh (; cy, Dinbych; ) is a market town and a community in Denbighshire, Wales. Formerly, the county town, the Welsh name translates to "Little Fortress"; a reference to its historic castle. Denbigh lies near the Clwydian Hills. History Denbigh Castle, together with its town walls, was built in 1282 by order of King Edward I. The Burgess Gate, whose twin towers adorn the symbol on Denbigh's civic seal, was once the main entrance into the town. The first borough charter was granted to Denbigh in 1290, when the town was still contained within the old town walls. It was the centre of the Marcher Lordship of Denbigh. The town was involved in the revolt of Madog ap Llywelyn in 1294–1295; the castle was captured in the autumn, and on 11 November 1294 a relieving force was defeated by the Welsh rebels. The town was recaptured by Edward I in December. Denbigh was also burnt in 1400 during the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr. During the Wars of the Roses (1455-1487), the town was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74. Its pattern of two-tier metropolitan and non-metropolitan county and district councils remains in use today in large parts of England, although the metropolitan county councils were abolished in 1986, and both county and district councils have been replaced with unitary authorities in many areas since the 1990s. In Wales, too, the Act established a similar pattern of counties and districts, but these have since been entirely replaced with a system of unitary authorities. Elections were held to the new authorities in 1973, and they acted as "shadow authorities" until the handover date. Elections to county councils were held on 12 April, for metropolitan and Welsh districts on 10 May, and for non-metropolitan distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
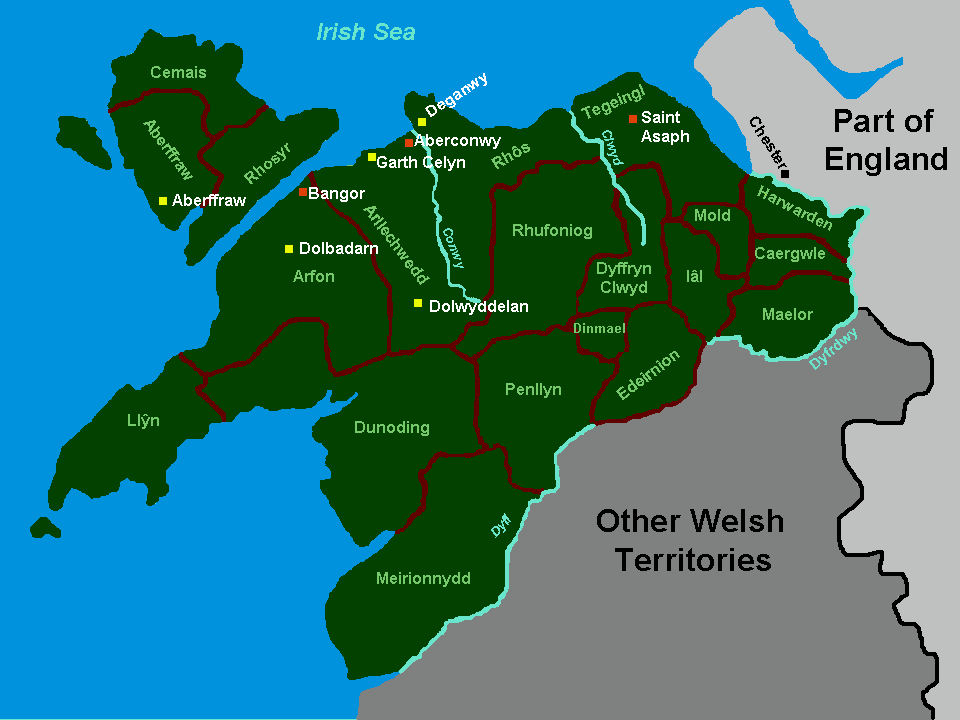
Cantref Iâl
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law. Description Land in medieval Wales was divided into ''cantrefi'', which were themselves divided into smaller ''cymydau'' (commotes). The word ''cantref'' is derived from ''cant'' ("a hundred") and ''tref'' ("town" in modern Welsh, but formerly used for much smaller settlements). The ''cantref'' is thought to be the original unit, with the commotes being a later division. ''Cantrefi'' could vary considerably in size: most were divided into two or three commotes, but the largest, the ''Cantref Mawr'' (or "Great Cantref") in Ystrad Tywi (now in Carmarthenshire) was divided into seven commotes. History The antiquity of the ''cantrefi'' is demonstrated by the fact that they often mark the boundary between dialects. Some were originally kingdoms in their own right; others may have been artificial units created later. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powys Fadog
Powys Fadog (English: ''Lower Powys'' or ''Madog's Powys'') was the northern portion of the former princely realm of Powys, which split in two following the death of Madog ap Maredudd in 1160. The realm was divided under Welsh law, with Madog's nephew Owain Cyfeiliog inheriting the south (see Powys Wenwynwyn) and his son Gruffydd Maelor I, who inherited the north. Gruffydd received the cantref of Maelor and the commote of Iâl as his portion and later added Nanheudwy, Cynllaith, Glyndyfrdwy and Mochnant Is Rhaeadr. This northern realm became known as Powys Fadog after the accession of his son Madog ap Gruffudd in 1191 who reigned until 1236, and after whom it may be named (see alternative translations above). During his reign, Madog initially adopted a neutral position between Gwynedd and England but by 1215 had settled on an alliance with Llywelyn ab Iorwerth of Gwynedd. This policy of alliance with Gwynedd altered under his successor Gruffudd II over his thirty-three year re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyffryn Clwyd
Dyffryn Clwyd was a cantref of Medieval Wales and from 1282 a marcher lordship. In 1536, it became part of the new county of Denbighshire. The name means Vale of Clwyd in English and is still the name for that region of north Wales in modern Welsh. Dyffryn Clwyd was one of the cantrefi of Perfeddwlad, and itself was made up of three commotes, Colion, Dogfeiling and Llannerch. The lordship was granted in 1282 to Reginald de Grey, 1st Baron Grey de Wilton,''The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales''. John Davies, Nigel Jenkins, Menna Baines and Peredur Lynch (2008) p. 334 Justice of Chester and Edward I's commander for his campaign of 1282 into north Wales. The lordship remained in the Grey family until Richard Grey, 6th Baron Grey de Ruthyn, 3rd Earl of Kent sold it to Henry VII in 1508. Marcher Lords of Dyffryn Clwyd *Reginald de Grey, 1st Baron Grey de Wilton (d. 1308) *John Grey, 2nd Baron Grey de Wilton (1268–1323) *Roger Grey, 1st Baron Grey de Ruthyn (died 1353) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantref Rhufoniog
{{coord, 52.950, -3.275, display=title, region:GB_scale:20000 Rhufoniog was a small sub-kingdom of the Dark Ages Gwynedd, and later a cantref in medieval Wales. Geography The cantref Rhos lay between it and the Irish Sea. Sometimes the two cantrefi were linked together as "Rhos and Rhufeiniog", which roughly corresponds to the territory of the old county of Denbighshire. The rivers Elwy, Clwyd and Clywedog formed a natural border to the north and east. As today, the countryside was bleak and isolated. There were three commotes in Rhufoniog, namely Upper Aled, Lower Aled and River Aled as a border between them, and the commote Ceinmerch (also known as 'Cymeirch' or 'Ystrad') in the north-east between the River Lliwen and the River Clywedog. History The early history of the cantref is unclear. According to tradition, it was ruled by its eponymous founder Rhufon, the third son of the first King of Gwynedd, Cunedda, and his direct descendants from the year 445 until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhos (north Wales)
Rhos means 'moor' or 'moorland' in Welsh. It is a region to the east of the River Conwy in north Wales. It started as a minor kingdom then became a medieval cantref, and was usually part of the Kingdom of Gwynedd (later the region became part of Denbighshire, then Clwyd, and is now in Conwy county borough). Kingdom: history and archaeology Rhos is identified as a small kingdom during the sub-Roman and early medieval periods in an Old Welsh genealogical document ‘Ancestry of the Kings and Princes of Wales’ listing thirteen of its kings (including two who are known to have ruled the wider region of Gwynedd). The most famous monarch was perhaps Cynlas Goch, the son of Owain Ddantgwyn, who lived in the early 6th century and was denounced by the monk, Gildas. He wrote (in Latin) that Cynlas was the “guider of the chariot which is the receptacle of the bear“. The latter may refer to a “Fort of the Bear”, possibly Dinerth, the name of a hillfort on Bryn Euryn in Llandrillo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Denbigh
The Lordship of Denbigh was a marcher lordship in North Wales created by Edward I in 1284 and granted to the Earl of Lincoln. It was centred on the borough of Denbigh and Denbigh Castle. The lordship was held successively by several of England's most prominent aristocratic families in the 14th and 15th centuries. Title to the lordship was disputed for much of the second half of the 14th century between two powerful noble families: the Mortimer Earls of March and the Montagu Earls of Salisbury. Eventually, the lordship returned to the crown when Edward, Duke of York, who had inherited the lordship through his grandmother, acceded to the throne in 1461 as Edward IV. In 1563, Elizabeth I revived the lordship and granted it to her favourite Lord Robert Dudley, later becoming the Earl of Leicester. Leicester mortgaged it to raise money and the lordship was finally returned to the crown when Elizabeth redeemed the mortgage in 1592/3. The crown disposed of much of the lordship's lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantref
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law. Description Land in medieval Wales was divided into ''cantrefi'', which were themselves divided into smaller ''cymydau'' (commotes). The word ''cantref'' is derived from ''cant'' ("a hundred") and ''tref'' ("town" in modern Welsh, but formerly used for much smaller settlements). The ''cantref'' is thought to be the original unit, with the commotes being a later division. ''Cantrefi'' could vary considerably in size: most were divided into two or three commotes, but the largest, the ''Cantref Mawr'' (or "Great Cantref") in Ystrad Tywi (now in Carmarthenshire) was divided into seven commotes. History The antiquity of the ''cantrefi'' is demonstrated by the fact that they often mark the boundary between dialects. Some were originally kingdoms in their own right; others may have been artificial units created later. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws In Wales Acts 1535-1542
The Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 ( cy, Y Deddfau Cyfreithiau yng Nghymru 1535 a 1542) were Act of Parliament, Acts of the Parliament of England, and were the parliamentary measures by which Wales was annexed to the Kingdom of England. Moreover, the English law, legal system of England was extended to Wales and the norms of English administration were introduced; with the intention to create a single State (polity), state and legal jurisdiction. The Acts were passed during the reign of King Henry VIII of England, who came from the Welsh House of Tudor, Tudor dynasty, and are sometimes referred to as the Acts of Union. Before these Acts, Wales was excluded from Parliamentary representation and divided between the Principality of Wales and many feudal statelets called the marcher Lordships. The Act declared King Henry's intentions, that because of differences in law and language: – and therefore: Names and dates They are sometimes misleadingly known as the Acts of Unio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denbighshire
Denbighshire ( ; cy, Sir Ddinbych; ) is a county in the north-east of Wales. Its borders differ from the historic county of the same name. This part of Wales contains the country's oldest known evidence of habitation – Pontnewydd (Bontnewydd-Llanelwy) Palaeolithic site has Neanderthal remains of some 225,000 years ago. Castles include Denbigh, Rhuddlan, Rhyl, Prestatyn, Trefnant, Llangollen and Ruthin, Castell Dinas Bran, Bodelwyddan and St Asaph Cathedral. Denbighshire is bounded by coastline to the north and hills to the east, south and west. The River Clwyd follows a broad valley with little industry: crops appear in the Vale of Clwyd and cattle and sheep in the uplands. The coast attracts summer visitors; hikers frequent the Clwydian Range, part of the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Llangollen International Musical Eisteddfod takes place each July. Formation The main area was formed on 1 April 1996 under the Local Government (Wale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government In Wales
Since 1 April 1996, Wales has been divided into 22 unitary authority, single-tier principal areas ( cy, Awdurdodau unedol), styled as counties or county boroughs ( or ) for local government purposes. The elected councils of these areas are responsible for the provision of all local government services, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highways. Below these there are also (in most, but not all, parts of the principal areas) elected community councils to which responsibility for specific aspects of the application of local policy may be devolved. The last set of 2022 Welsh local elections, local elections in Wales took place in 2022, with the 2027 Welsh local elections, next due to take place in 2027. Monarchy of the United Kingdom, The monarch appoints a Lord Lieutenant, lord lieutenant as a representative in each of the eight preserved counties of Wales, which are combinations of principal areas retained for ceremonial purposes. Subdivisions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Cantrefi_a_Chymydau_Cymru.jpg)
