Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
is an
archipelagic country
An archipelagic state is an island country that consists of an archipelago. The designation is legally defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). In various conferences, The Bahamas, Fiji, Indonesia, Papua New ...
comprising a
stratovolcanic archipelago over along the Pacific coast of East Asia.
It consists of 6,852 islands.
The five main islands are
Hokkaido,
Honshu,
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
,
Shikoku and
Okinawa. There are 6,847 remote islands.
The
Ryukyu Islands and
Nanpō Islands are south and east of the main islands.
The territory covers .
It is the
fourth largest island country in the world and the largest island country in
East Asia.
The country has the
6th longest coastline at and the 8th largest
Exclusive Economic Zone of in the world.
The terrain is mostly rugged and mountainous with 66% forest.
The
population is clustered in urban areas on the coast, plains and valleys.
Japan is located in the northwestern
Ring of Fire on multiple
tectonic plates.
East of the
Japanese archipelago are three
oceanic trenches. The
Japan Trench is created as the oceanic
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
subducts
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
beneath the continental
Okhotsk Plate.
The continuous subduction process causes frequent
earthquakes
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
,
tsunami and stratovolcanoes.
The islands are also affected by
typhoons. The subduction plates have pulled the Japanese archipelago eastward, created the
Sea of Japan and separated it from the
Asian continent
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
by
back-arc spreading 15 million years ago.
The climate varies from
humid continental in the north to
humid subtropical and
tropical rainforest in the south. These differences in climate and landscape have allowed the development of a diverse
flora and
fauna, with some rare endemic species, especially in the
Ogasawara Islands.
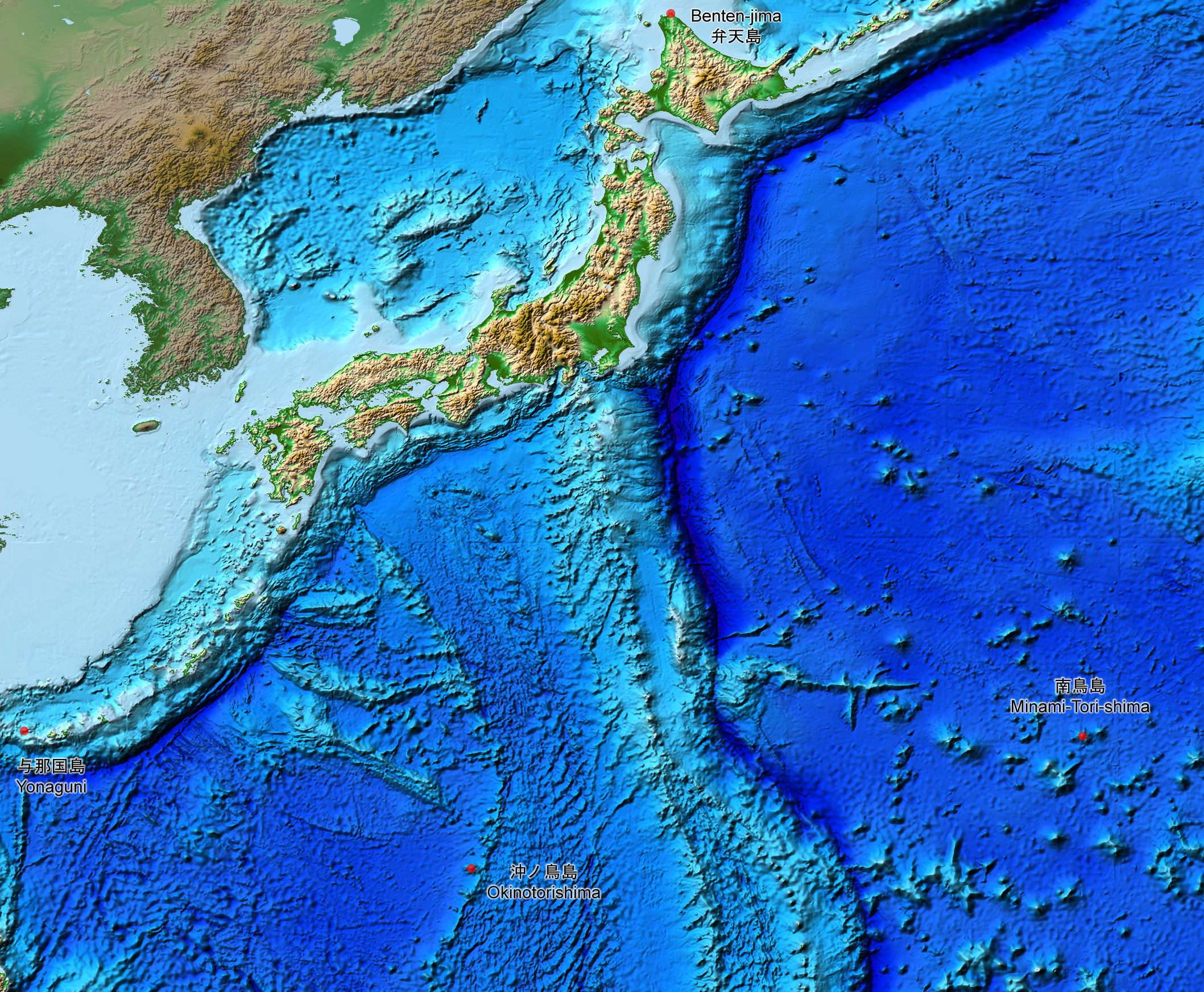
Japan extends from 20° to 45° north latitude (
Okinotorishima to
Benten-jima) and from 122° to 153° east longitude (
Yonaguni to
Minami Torishima).
Japan is surrounded by seas. To the north the
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
separates it from the
Russian Far East, to the west the Sea of Japan separates it from the
Korean Peninsula, to the southwest the
East China Sea
The East China Sea is an arm of the Western Pacific Ocean, located directly offshore from East China. It covers an area of roughly . The sea’s northern extension between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula is the Yellow Sea, separated b ...
separates the Ryukyu Islands from China and Taiwan, to the east is the Pacific Ocean.


The Japanese archipelago is over long in a north-to-southwardly direction from the Sea of Okhotsk to the
Philippine Sea
The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine archipelago (hence the name), the largest in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of . The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its ...
in the Pacific Ocean.
It is narrow, and no point in Japan is more than from the sea. There are 6,852 islands in total. The five main islands are (from north to south) Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu and Okinawa. Three of the four major islands (Honshu, Kyushu and Shikoku) are separated by narrow straits of the
Seto Inland Sea
The , sometimes shortened to the Inland Sea, is the body of water separating Honshū, Shikoku, and Kyūshū, three of the four main islands of Japan. It serves as a waterway connecting the Pacific Ocean to the Sea of Japan. It connects to Osaka ...
and form a natural entity. The 6,847 smaller islands are called remote islands.
This includes the
Bonin Islands,
Daitō Islands,
Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
,
Okinotorishima, the Ryukyu Islands, the
Volcano Islands,
Nansei Islands, and the Nanpō Islands, as well as numerous
islets, of which 430 are inhabited. The
Senkaku Islands
The are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan. They are located northeast of Taiwan, east of China, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known in main ...
are administered by Japan but disputed by China. This excludes the disputed
Northern Territories (Kuril islands) and
Liancourt Rocks. In total, as of 2021, Japan's territory is , of which is land and water.
Japan has the sixth longest coastline in the world (). It is the largest island country in East Asia and fourth largest island country in the world.
Because of Japan's many far-flung outlying islands and long coastline, the country has extensive
marine life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. M ...
and
mineral resources in the ocean. The Exclusive Economic Zone of Japan covers and is the 8th largest in the world. It is more than 11 times the land area of the country.
The Exclusive Economic Zone stretches from the baseline out to from its coast. Its territorial sea is , but between in the international straits—
La Pérouse (or Sōya Strait),
Tsugaru Strait, Ōsumi, and
Tsushima Strait.
Japan has a population of 126 million in 2019.
It is the
11th most populous country in the world and second most populous island country.
81% of the population lives on Honshu, 10% on Kyushu, 4.2% on Hokkaido, 3% on Shikoku, 1.1% in Okinawa Prefecture and 0.7% on other Japanese islands such as the Nanpō Islands.
Map of Japan

Japan is informally divided into eight regions from northeast (Hokkaidō) to southwest (Ryukyu Islands):
*
Hokkaidō
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
*
Tōhoku region
*
Kantō region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Slight ...
*
Chūbu region
The , Central region, or is a region in the middle of Honshu, Honshū, Japan, Japan's main island. In a wide, classical definition, it encompasses nine prefectures (''ken''): Aichi Prefecture, Aichi, Fukui Prefecture, Fukui, Gifu Prefecture ...
*
Kansai (or Kinki) region
*
Chūgoku region
*
Shikoku
*
Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
Each region contains several
prefectures, except the Hokkaido region, which comprises only Hokkaido Prefecture.
The regions are not official administrative units, but have been traditionally used as the regional division of Japan in a number of contexts. For example, maps and geography textbooks divide Japan into the eight regions, weather reports usually give the weather by region, and many businesses and institutions use their home region as part of their name (
Kinki Nippon Railway, Chūgoku Bank,
Tohoku University, etc.). While Japan has eight High Courts, their jurisdictions do not correspond with the eight regions.
Composition, topography and geography

About 73% of Japan is mountainous, with a mountain range running through each of the main islands. Japan's highest mountain is
Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest p ...
, with an elevation of . Japan's forest cover rate is 68.55% since the mountains are heavily forested. The only other developed nations with such a high forest cover percentage are Finland and Sweden.
Since there is little level ground, many hills and mountainsides at lower elevations around towns and cities are often cultivated. As Japan is situated in a volcanic zone along the Pacific deeps, frequent low-intensity earth tremors and occasional volcanic activity are felt throughout the islands. Destructive earthquakes occur several times a century.
Hot springs are numerous and have been exploited by the leisure industry.
The
Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
The , or GSI, is the national institution responsible for surveying and mapping the national land of Japan. The former name of the organization from 1949 until March 2010 was Geographical Survey Institute; despite the rename, it retains the same ...
measures Japan's territory annually in order to continuously grasp the state of the national land. As of July 1, 2021, Japan's territory is . It increases in area due to volcanic eruptions such as
Nishinoshima (西之島), the natural expansion of the islands, and land reclamation.
This table shows the land use in 2002.
Location
The Japanese archipelago is relatively far away from the Asian continent. Kyushu is closest to the southernmost point of the Korean peninsula with a distance of , which is almost 6 times farther away than from England to France across the
English Channel. Thus historically Kyushu was the gateway between Asia and Japan. China is separated by of sea from Japan's big
main islands. Hokkaido is near
Sakhalin, which was
occupied by Japan from 1905 to 1945. Most of the population lives on the Pacific coast side of Honshū. The west coast facing the Sea of Japan is less densely populated.
The Japanese archipelago was difficult to reach since before ancient history. During the
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
period around 20,000 BCE at the height of the
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, there was a land bridge between Hokkaido and Sakhalin which linked Japan with the Asian continent. The land bridge disappeared when the sea levels rose in the
Jōmon period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a c ...
around 10,000 BCE.
Japan's remote location, surrounded by vast seas, rugged, mountainous terrain and steep rivers make it secure against invaders and uncontrolled migration from the Asian continent. The Japanese can close their civilization with an
isolationist foreign policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
. During the
Edo period the
Tokugawa Shogunate enforced the
Sakoku
was the Isolationism, isolationist Foreign policy of Japan, foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, for a period of 265 years during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countri ...
policy which prohibited most foreign contact and trade from 1641 to 1853. In modern times, the inflow of people is managed via the seaports and airports. Thus Japan is fairly insulated from continental issues.
Throughout history, Japan was never fully invaded nor colonized by other countries. The
Mongols tried to invade Japan twice and failed in 1274 and 1281. Japan capitulated only once after nuclear attacks in World War II. At the time Japan did not have
nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors an ...
. The insular geography is a major factor for the isolationist, semi-open and
expansionist
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who ...
periods of
Japanese history.
Mountains and volcanoes
The mountainous islands of the Japanese archipelago form a crescent off the eastern coast of Asia.
They are separated from the continent by the Sea of Japan, which serves as a protective barrier. Japan has 108 active
volcanoes (10% of the world's active volcanoes) because of active plate tectonics in the Ring of Fire.
Around 15 million years ago, the volcanic shoreline of the Asian continent was pushed out into a series of volcanic island arcs.
This created the "back-arc basins" known as the
Sea of Japan and
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
with the formal shaping of the Japanese archipelago.
The archipelago also has summits of mountain ridges that were uplifted near the outer edge of the
continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
.
[ About 73 percent of Japan's area is mountainous, and scattered plains and intermontane basins (in which the population is concentrated) cover only about 27 percent.][ A long chain of mountains runs down the middle of the archipelago, dividing it into two halves, the "face", fronting on the Pacific Ocean, and the "back", toward the Sea of Japan.][ On the Pacific side are steep mountains 1,500 to 3,000 meters high, with deep valleys and gorges.][
Central Japan is marked by the convergence of the three mountain chains—the Hida, Kiso, and ]Akaishi mountains
The are a mountain range in central Honshū, Japan, bordering Nagano, Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures. It is also called the , as it joins with the Hida Mountains ("Northern Alps") and the Kiso Mountains ("Central Alps") to form the Japa ...
—that form the Japanese Alps
The is a series of mountain ranges in Japan which bisect the main island of Honshu. The peaks that tower over central Honshu have long been the object of veneration and pilgrimage. These mountains had long been exploited by local people for raw m ...
(''Nihon Arupusu''), several of whose peaks are higher than .[ The highest point in the Japanese Alps is Mount Kita at .][ The highest point in the country is ]Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest p ...
(Fujisan, also erroneously called Fujiyama), a volcano dormant since 1707 that rises to above sea level in Shizuoka Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Shizuoka Prefecture has a population of 3,637,998 and has a geographic area of . Shizuoka Prefecture borders Kanagawa Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the northea ...
.[ On the Sea of Japan side are plateaus and low mountain districts, with altitudes of 500 to 1,500 meters.][
]
Plains
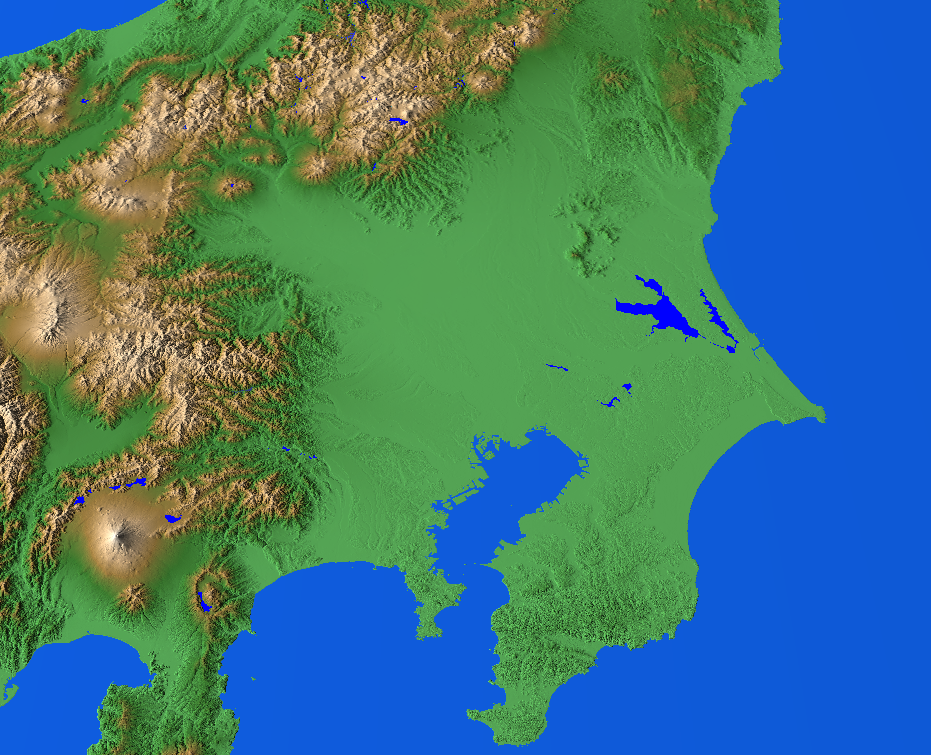 There are three major plains in central Honshū. The largest is the Kantō Plain which covers in the
There are three major plains in central Honshū. The largest is the Kantō Plain which covers in the Kantō region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Slight ...
. The capital Tokyo and the largest metropolitan population is located there. The second largest plain in Honshū is the Nōbi Plain with the third-most-populous urban area Nagoya. The third largest plain in Honshū is the Osaka Plain which covers in the Kinki region. It features the second largest urban area of Osaka (part of the Keihanshin
is a metropolitan region in the Kansai region of Japan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka in Osaka Prefecture and Kobe in Hyōgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population () of 19,302,746 o ...
metropolitan area). Osaka and Nagoya extend inland from their bays until they reach steep mountains. The Osaka Plain is connected with Kyoto and Nara. Kyoto is located in the Yamashiro Basin Yamashiro is a Japanese word with ''kanji'' often meaning ''mountain castle'' (山城). There are however other kanji spellings.
* Yamashiro, Kyoto, former town in Japan
* Yamashiro, Tokushima, former town in Japan
* Yamashiro Province, former Jap ...
and Nara is in the Nara Basin .
The Kantō Plain, Osaka Plain and Nōbi Plain are the most important economic, political and cultural areas of Japan. These plains had the largest agricultural production and large bays with ports for fishing and trade. This made them the largest population centers. Kyoto and Nara are the ancient capitals and cultural heart of Japan. The Kantō Plain became Japan's center of power, because it is the largest plain with a central location and historically it had the most agricultural production that could be taxed. The Tokugawa Shogunate established a '' bakufu'' in Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
in 1603. This evolved into the capital of Tokyo by 1868.
Hokkaido has multiple plains such as the Ishikari Plain , Tokachi Plain , the Kushiro Plain
is a city in Kushiro Subprefecture on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. It serves as the subprefecture's capital and it is the most populated city in the eastern part of the island.
Geography
Mountains
* Mount Oakan
* Mount Meakan
* Mount Akan- ...
is the largest wetland in Japan and Sarobetsu Plain . There are many farms that produce a plethora of agricultural products. The average farm size in Hokkaido is 26 hectares per farmer in 2013. That is nearly 11 times larger than the national average of 2.4 hectares. This made Hokkaido the most agriculturally rich prefecture of Japan.Sendai
is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, desig ...
in northeastern Honshū.[ Many of these plains are along the coast, and their areas have been increased by land reclamation throughout recorded history.][
]
Rivers
 Rivers are generally steep and swift, and few are suitable for navigation except in their lower reaches. Although most rivers are less than in length, their rapid flow from the mountains is what provides hydroelectric power.
Rivers are generally steep and swift, and few are suitable for navigation except in their lower reaches. Although most rivers are less than in length, their rapid flow from the mountains is what provides hydroelectric power.[ Seasonal variations in flow have led to extensive development of flood control measures.][ The longest, the Shinano River, which winds through ]Nagano Prefecture
is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the ...
to Niigata Prefecture and flows into the Sea of Japan, is long.
Lakes and coasts
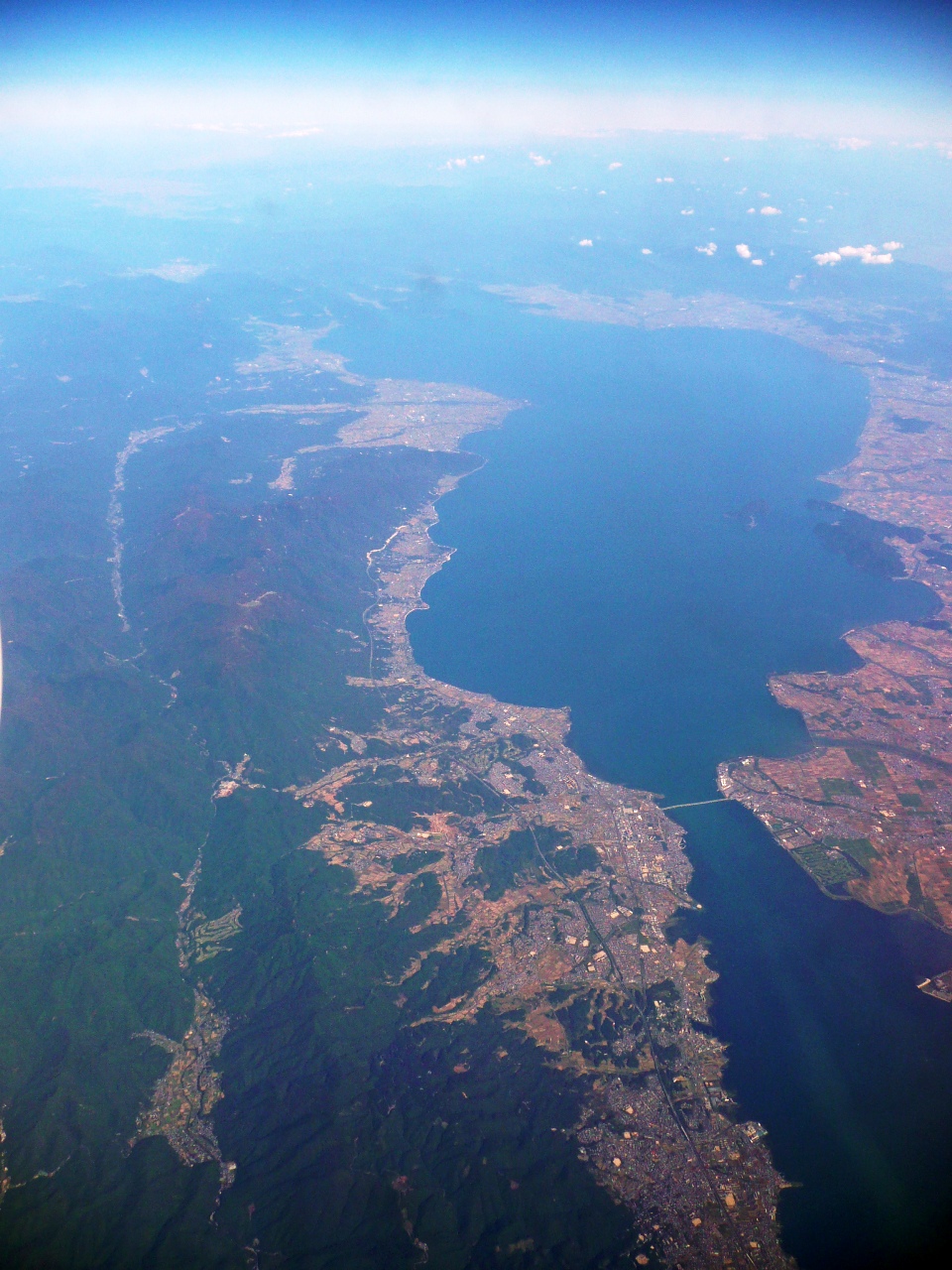 The largest freshwater lake is Lake Biwa , northeast of Kyoto in Shiga Prefecture.
The largest freshwater lake is Lake Biwa , northeast of Kyoto in Shiga Prefecture.[ It has consistently carried water for millions of years. Lake Biwa was created by plate tectonics in an active rift zone. This created a very deep lake with a maximum depth of . Thus it has not naturally filled with sediment. Over the course of millions of years, a diverse ecosystem evolved in the lake. It has more than 1,000 species and subspecies. There are 46 native fish species and subspecies,][Kawanabe, H.; Nishino, M.; and Maehata, M., editors (2012). ''Lake Biwa: Interactions between Nature and People.'' pp 119-120. ] including 11 species and 5 subspecies that are endemic or near-endemic.[ Approximately 5,000 water birds visit the lake each year.
The following are the 10 largest lakes of Japan.][ 国土地理院 平成29年全国都道府県市区町村別面積�]
付1 湖沼面積(平成29年10月1日版)
2018年2月10日閲覧。
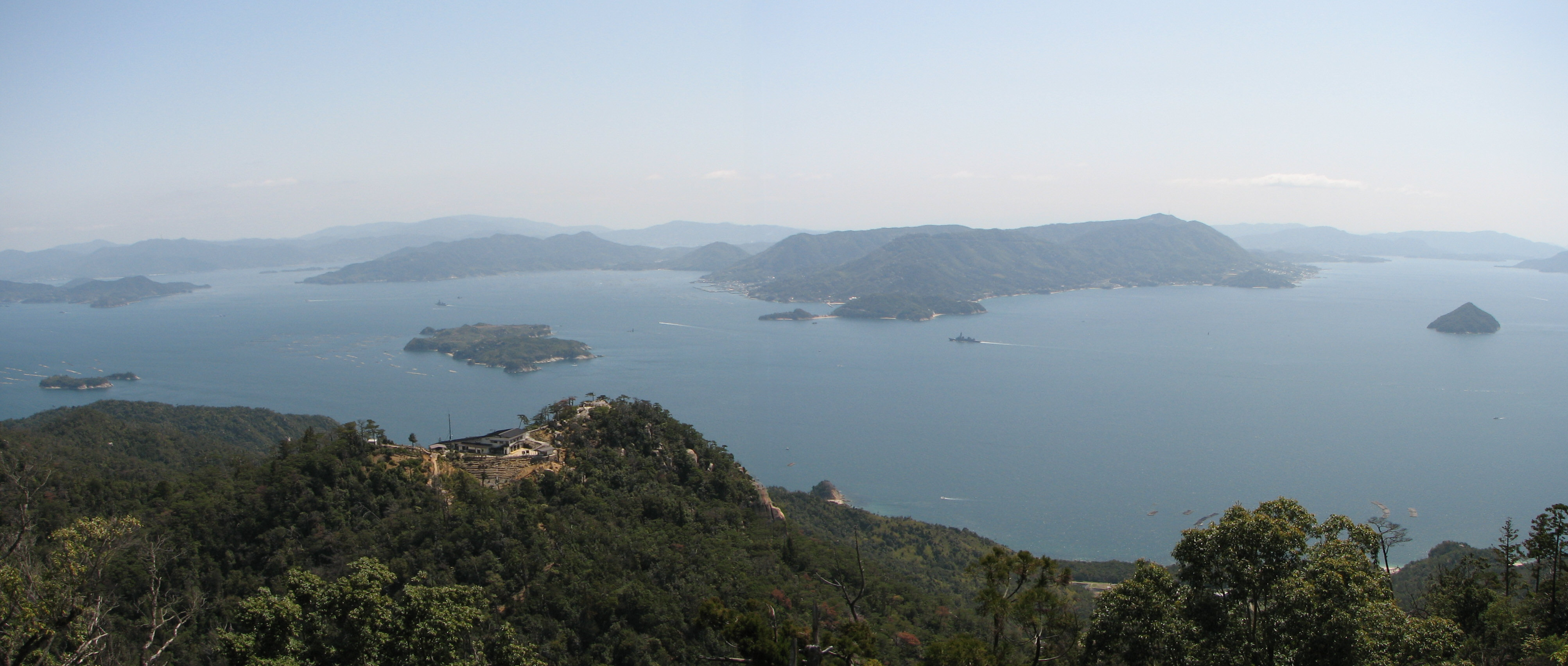 Extensive coastal shipping, especially around the Seto Inland Sea, compensates for the lack of navigable rivers.
Extensive coastal shipping, especially around the Seto Inland Sea, compensates for the lack of navigable rivers.[ The Pacific coastline south of Tokyo is characterized by long, narrow, gradually shallowing inlets produced by sedimentation, which has created many natural harbors.][ The Pacific coastline north of Tokyo, the coast of Hokkaidō, and the Sea of Japan coast are generally unindented, with few natural harbors.][
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 765 km² of tidal flats in Japan, making it the 35th ranked country in terms of tidal flat extent.
]
Land reclamation
 The Japanese archipelago has been transformed by humans into a sort of continuous land, in which the four main islands are entirely reachable and passable by rail and road transportation thanks to the construction of huge bridges and tunnels that connect each other and various islands.
Approximately 0.5% of Japan's total area is reclaimed land (''umetatechi'').
The Japanese archipelago has been transformed by humans into a sort of continuous land, in which the four main islands are entirely reachable and passable by rail and road transportation thanks to the construction of huge bridges and tunnels that connect each other and various islands.
Approximately 0.5% of Japan's total area is reclaimed land (''umetatechi'').[ The majority of ]land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
projects occurred after World War II during the Japanese economic miracle. Reclamation of 80% to 90% of all the tidal flatland was done. Large land reclamation projects with landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
were done in coastal areas for maritime and industrial factories, such as Higashi Ogishima Higashi is the Japanese word for ''east''. In kanji it is represented as 東.
Higashi may also refer to:
Places
* Higashi, Shibuya, a district of Shibuya, Tokyo
* Higashi, Fukushima, a village in Fukushima Prefecture
*Higashi, Okinawa, a village ...
in Kawasaki
Kawasaki ( ja, 川崎, Kawasaki, river peninsula, links=no) may refer to:
Places
*Kawasaki, Kanagawa, a Japanese city
**Kawasaki-ku, Kawasaki, a ward in Kawasaki, Kanagawa
**Kawasaki City Todoroki Arena
**Kawasaki Stadium, a multi-sport stadium
*K ...
, Osaka Bay and Nagasaki Airport. Port Island, Rokkō Island and Kobe Airport were built in Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
. Late 20th and early 21st century projects include artificial islands such as Chubu Centrair International Airport in Ise Bay, Kansai International Airport in the middle of Osaka Bay, Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise and Wakayama Marina City
Wakayama Marina City is a resort town built on an artificial island of 49 hectares (121 acres) in size, in Wakaura Bay, part of the larger Osaka Bay. It is also part of Wakayama, Wakayama, Wakayama-shi (City) Wakayama-ken (Prefecture) on the Kans ...
.Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
– first man-made island built by Taira no Kiyomori in 1173Odaiba
today is a large artificial island in Tokyo Bay, Japan, across the Rainbow Bridge from central Tokyo. Odaiba was initially built in this area for defensive purposes in the 1850s. Reclaimed land offshore Shinagawa was dramatically expanded durin ...
, a series of island forts constructed to protect Tokyo from sea attacks (1853).Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
, Japan – (1995).Central Breakwater
The is a breakwater and artificial island located in Tokyo Bay, adjacent to the Tokyo Gate Bridge.
History
The Central Breakwater was first constructed in 1973 and has been used as a site for waste disposal from Tokyo since then, forming two ar ...
–
Much reclaimed land is made up of landfill from waste materials, dredged earth, sand, sediment, sludge and soil removed from construction sites. It is used to build man-made islands in harbors and embankments in inland areas.2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes ...
region. This rubble was processed, and when it had the appropriate radiation levels it was used as landfill to build new artificial islands in Tokyo Bay. Yamashita Park in Yokohama City was made with rubble from the great Kantō earthquake
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
in 1923.
Oceanography and seabed of Japan
 Japan's sea territory is .
Japan's sea territory is .undersea mountain ranges
Undersea mountain ranges are mountain ranges that are mostly or entirely underwater, and specifically under the surface of an ocean. If originated from current tectonic forces, they are often referred to as a ''mid-ocean ridge''. In contrast, if ...
stretch from Japan's main islands to the south. They occasionally reach above the sea surface as islands. East of the undersea mountain ranges are three oceanic trenches: the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench (max depth ), Japan Trench (max depth ) and Izu–Ogasawara Trench (max depth ).
There are large quantities of marine life and mineral resources in the ocean and seabed of Japan. At a depth of over there are minerals such as manganese nodules, cobalt in the crust and hydrothermal deposits.
Geology
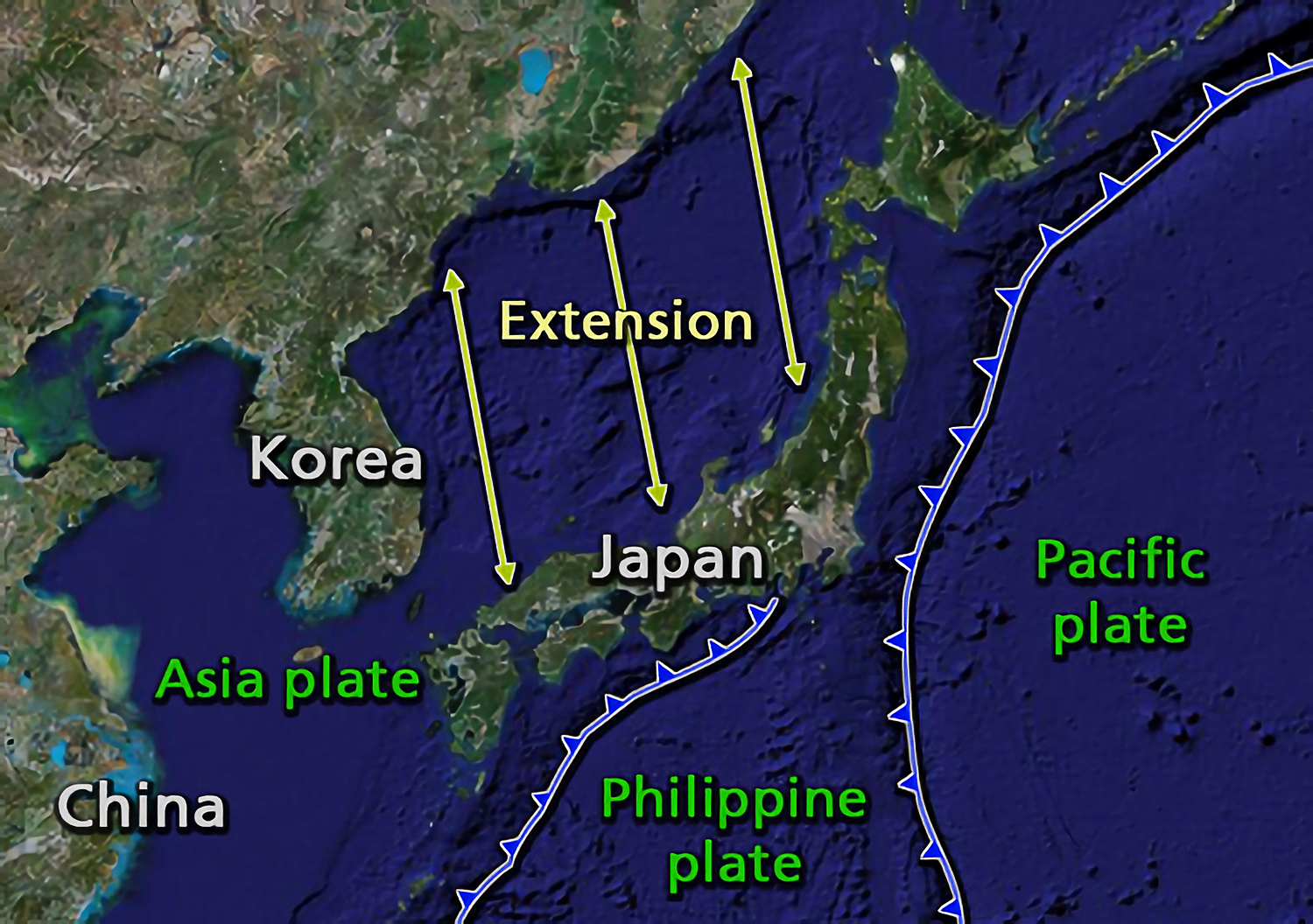
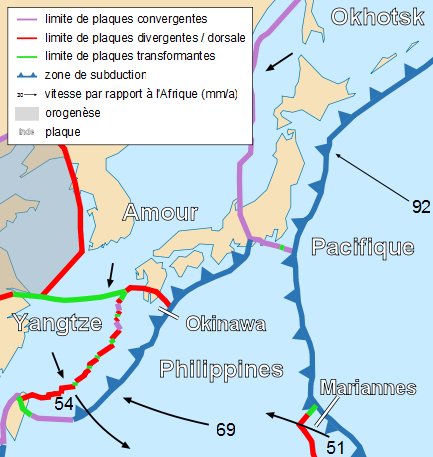
Tectonic plates
The Japanese archipelago is the result of subducting tectonic plates over several 100 millions of years from the mid-Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
(443.8 Mya) to the Pleistocene (11,700 years ago). Approximately of oceanic floor has passed under the Japanese archipelago in the last 450 million years, with most being fully subducted. It is considered a mature island arc.
The islands of Japan were created by tectonic plate movements:
* Tohoku (upper half of Honshu), Hokkaido, Kuril islands and Sakhalin are located on the Okhotsk Plate. This is a minor tectonic plate bounded to the north by the North American Plate. The Okhotsk Plate is bounded on the east by the Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
at the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench and the Japan Trench. It is bounded on the south by the Philippine Sea Plate at the Nankai Trough. On the west it is bounded by the Eurasian Plate and possibly on the southwest by the Amurian Plate. The northeastern boundary the Ulakhan Fault The Ulakhan Fault is a left-lateral moving transform fault that runs along the boundary between two tectonic plates in northeast Asia, the North American Plate, and the Okhotsk Plate. It runs from a triple junction in the Chersky Range in the west ...
.
* The southern half of Honshu, Shikoku and most of Kyushu are located on the Amurian Plate.
* The southern tip of Kyushu and the Ryukyu islands are located on the Okinawa Plate.
* The Nanpō Islands are on the Philippine Sea Plate.
The Pacific Plate and Philippine Sea Plate are subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
plates. They are deeper than the Eurasian plate. The Philippine Sea Plate moves beneath the continental Amurian Plate and Okinawa Plate to the south. The Pacific Plate moves under the Okhotsk Plate to the north. These subduction plates have pulled Japan eastward and opened the Sea of Japan by back-arc spreading around 15 million years ago.Strait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary or Gulf of Tartary (russian: Татарский пролив; ; ja, 間宮海峡, Mamiya kaikyō, Mamiya Strait; ko, 타타르 해협) is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia ...
and the Korea Strait opened much later. La Pérouse Strait formed about 60,000 to 11,000 years ago closing the path used by mammoths which had earlier moved to northern Hokkaido.
Median Tectonic Line
The Japan Median Tectonic Line (MTL) is Japan's longest fault system.Mikawa Bay
Mikawa Bay (Landsat photo)
Mikawa Bay (三河湾 ''Mikawa-wan'') is a bay to the south of Aichi Prefecture, Japan, surrounded by Chita Peninsula to the west and Atsumi Peninsula to the east and south. Its area is approximately 604 km2. Pollu ...
, then through the Seto Inland Sea from the Kii Channel and Naruto Strait to Shikoku along the Sadamisaki Peninsula and the Bungo Channel and Hōyo Strait to Kyūshū.
Oceanic trenches
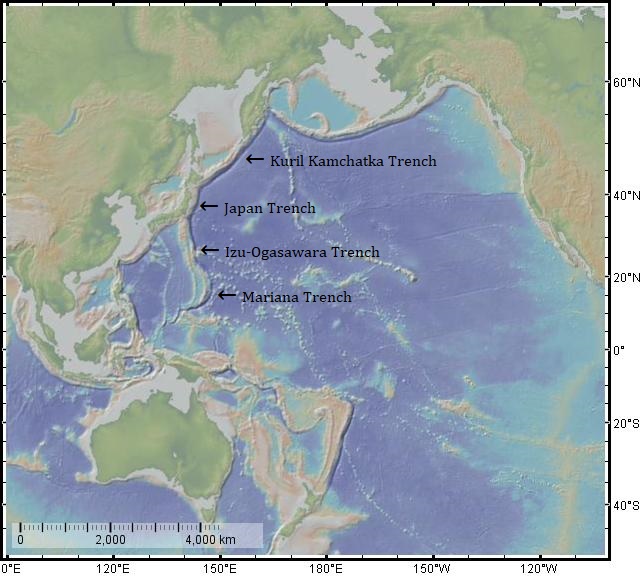 East of the Japanese archipelago are three oceanic trenches.
* The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench is in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido.
East of the Japanese archipelago are three oceanic trenches.
* The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench is in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido.[Rhea, S., et al., 2010, ''Seismicity of the Earth 1900–2007, Kuril–Kamchatka arc and vicinity'', U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2010-1083-C, 1 map sheet, scale 1:5,000,000 http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1083/c/]
* The Japan Trench extends from the Kuril Islands to the northern end of the Izu Islands. Its deepest part is . The Japan Trench is created as the oceanic Pacific Plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate. The subduction process causes bending of the down going plate, creating a deep trench. Continuous movement on the subduction zone associated with the Japan Trench is one of the main causes of tsunamis and earthquakes in northern Japan, including the megathrust 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. The rate of subduction associated with the Japan Trench has been recorded at about /yr.
Composition
The Japanese islands are formed of the mentioned geological units parallel to the subduction front. The parts of islands facing the Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
are typically younger and display a larger proportion of volcanic products, while island parts facing the Sea of Japan are mostly heavily faulted and folded sedimentary deposits. In northwest Japan are thick quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
deposits. This makes determination of the geological history and composition difficult and it is not yet fully understood.
Growing archipelago
The Japanese archipelago grows gradually because of perpetual tectonic plate movements, earthquakes, stratovolcanoes and land reclamation in the Ring of Fire.
For example, during the 20th century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shō off the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific.
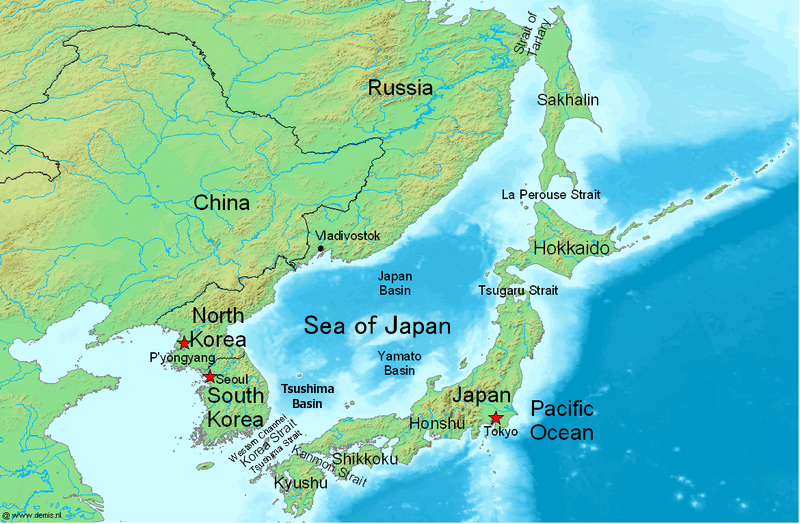
Sea of Japan
History
During the Pleistocene (2.58 million years BCE) glacial cycles, the Japanese islands may have occasionally been connected to the Eurasian Continent via the Korea Strait and the Korean Peninsula or Sakhalin. The Sea of Japan was considered to be a frozen inner lake because of the lack of the warm Tsushima Current. Various plants and large animals, such as the ''Palaeoloxodon naumanni
''Palaeoloxodon naumanni'', occasionally called Naumann's elephant, is an extinct species belonging to the genus ''Palaeoloxodon'' found in the Japanese archipelago during the Middle to Late Pleistocene around 430,000 to 24,000 years ago. It is na ...
'' migrated into the Japanese archipelago.[Kameda Y. & Kato M. (2011). "Terrestrial invasion of pomatiopsid gastropods in the heavy-snow region of the Japanese Archipelago". '' BMC Evolutionary Biology'' 11: 118. .] The Early Miocene period was when the Sea of Japan started to open, and the northern and southern parts of the Japanese archipelago separated from each other.Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million ye ...
. The orogenesis of the high mountain ranges in northeastern Japan started in the Late Miocene and lasted in the Pliocene. During the advance of the last Ice Age, the world sea level dropped. This dried and closed the exit straits of the Sea of Japan one by one. The deepest, and thus the last to close, was the western channel of the Korea Strait. There is controversy as to whether the Sea of Japan became a huge cold inland lake.
During the advance of the last Ice Age, the world sea level dropped. This dried and closed the exit straits of the Sea of Japan one by one. The deepest, and thus the last to close, was the western channel of the Korea Strait. There is controversy as to whether the Sea of Japan became a huge cold inland lake.[ The Japanese archipelago had a taiga biome (open boreal woodlands). It was characterized by ]coniferous
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant ...
forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches. Hokkaido, Sakhalin, and the Kuril islands had mammoth steppe biome (steppe-tundra). The vegetation was dominated by palatable high-productivity grasses, herbs and willow shrubs.
Present
The Sea of Japan has a surface area of , a mean depth of and a maximum depth of . It has a carrot-like shape, with the major axis extending from southwest to northeast and a wide southern part narrowing toward the north. The coastal length is about with the largest part () belonging to Russia. The sea extends from north to south for more than and has a maximum width of about .[Sea of Japan]
'' Great Soviet Encyclopedia''
There are three major basins: the ''Yamato Basin'' in the southeast, the ''Japan Basin'' in the north and the ''Tsushima Basin
The or Ulleung Basin (울릉분지 ulleung bunji) is an oceanic basin located where the Sea of Japan meets the Korea Strait. It lies immediately south of Ulleung-do and Liancourt Rocks, in the eastern end of the South Korean EEZ and the weste ...
'' in the southwest.[Sea of Japan]
Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The Japan Basin has an oceanic crust and it is the deepest part of the sea, whereas the Tsushima Basin is the shallowest with depths below . The Yamato Basin and Tsushima Basin have thick ocean crusts.[ The ]continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
of the sea are wide on the eastern shores along Japan. On the western shores, they are narrow particularly along the Korean and Russian coast, averaging about .
The geographical location of the Japanese archipelago has defined the Sea of Japan for millions of years. Without the Japanese archipelago it would just be the Pacific Ocean. The term has been the international standard since at least the early 19th century.
Ocean currents
 The Japanese archipelago is surrounded by eight ocean currents.
* The is a warm north-flowing ocean current on the west side of the Ryukyu Islands and along the east coast of Kyushu, Shikoku and Honshu. It is a strong western boundary current and part of the North Pacific
The Japanese archipelago is surrounded by eight ocean currents.
* The is a warm north-flowing ocean current on the west side of the Ryukyu Islands and along the east coast of Kyushu, Shikoku and Honshu. It is a strong western boundary current and part of the North Pacific ocean gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine ...
.
* The Kuroshio Current starts in the east coast of Luzon, Philippines, Taiwan and flows northeastward past Japan, where it merges with the easterly drift of the North Pacific Current.Philippine Sea
The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine archipelago (hence the name), the largest in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of . The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its ...
.
** The winter spawning Japanese Flying Squid are associated with the Kuroshio Current. The eggs and larvae develop during winter in the East China Sea
The East China Sea is an arm of the Western Pacific Ocean, located directly offshore from East China. It covers an area of roughly . The sea’s northern extension between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula is the Yellow Sea, separated b ...
and the adults travel with minimum energy via the Kuroshio Current to the rich northern feeding grounds near northwestern Honshu and Hokkaido.[Mann, K.H. and J.R.N. Lazier. (2006). ''Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems''. Blackwell Scientific Publications, 2nd Edition]
* The is a branch of the Kuroshio Current. It flows along the west coast of Kyushu and Honshu into the Sea of Japan.
* The current is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows southward and circulates counterclockwise along the east coast of Hokkaido and northeastern Honshu in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean and flow southward via the Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Ameri ...
, passing through the Bering Strait and transporting cold water from the Arctic Sea into the Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
. It collides with the Kuroshio Current off the eastern shore of Japan to form the North Pacific Current. The nutrient-rich Oyashio is named for its metaphorical role as the that provides for and nurtures marine organisms.
* The Liman Current is a southward flowing cold ocean current that flows from the Strait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary or Gulf of Tartary (russian: Татарский пролив; ; ja, 間宮海峡, Mamiya kaikyō, Mamiya Strait; ko, 타타르 해협) is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia ...
along the Asian continent in the Sea of Japan.
* The originates when the Tsushima Current is divided in two as it flows through the west entrance of the Tsugaru Strait, and along the La Perouse Strait at the north coast of Hokkaido it becomes the . The flow rate is 1 to 3 knots. There is a relatively stronger flow in the summer than in the winter.[北海道周辺の海流 第一管区海上保安本部](_blank)
/ref>
Natural resources
Land resources
There are small deposits of coal, oil, iron and minerals in the Japanese archipelago.
Marine resources
 The Exclusive economic zone of Japan has an estimated large quantities of mineral resources such as methane clathrate, natural gas, metallic minerals and
The Exclusive economic zone of Japan has an estimated large quantities of mineral resources such as methane clathrate, natural gas, metallic minerals and rare-earth mineral
A rare-earth mineral contains one or more rare-earth elements as major metal constituents. Rare-earth minerals are usually found in association with alkaline to peralkaline igneous complexes, in pegmatites associated with alkaline magmas and in o ...
reserves. Seabed mineral resources such as manganese nodules, cobalt-rich crust and submarine hydrothermal deposits are located at depths over .[藤田和男ほか監修 佐々木詔雄ほか編著 『天然ガスの本』 日刊工業新聞 2008年3月25日初版1刷発行 ] As of 2019, the methane clathrate in the deep sea remains unexploited, because the necessary technology is not established yet. This is why currently Japan has very limited proven reserves like crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
.
The Kantō region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Slight ...
alone is estimated to have over 400 billion cubic meters of natural gas reserves. It forms a Minami Kantō gas field in the area spanning Saitama, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Ibaraki, and Chiba
Chiba may refer to:
Places China
* (), town in Jianli County, Jingzhou, Hubei
Japan
* Chiba (city), capital of Chiba Prefecture
** Chiba Station, a train station
* Chiba Prefecture, a sub-national jurisdiction in the Greater Tokyo Area on ...
prefectures. However, mining is strictly regulated in many areas because it is directly below Tokyo, and is only slightly mined in the Bōsō Peninsula. In Tokyo and Chiba Prefecture, there have been frequent accidents with natural gas that was released naturally from the Minami Kantō gas field.
In 2018, south of Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
at deep, approximately 16 million tons of rare-earth mineral
A rare-earth mineral contains one or more rare-earth elements as major metal constituents. Rare-earth minerals are usually found in association with alkaline to peralkaline igneous complexes, in pegmatites associated with alkaline magmas and in o ...
s were discovered by JAMSTEC in collaboration with Waseda University and the University of Tokyo.
Marine life
Japan maintains one of the world's largest fishing fleets and accounts for nearly 15% of the global catch (2014).[
]
Energy
, 46.1% of energy in Japan was produced from petroleum, 21.3% from coal, 21.4% from natural gas, 4.0% from nuclear power and 3.3% from hydropower. Nuclear power is a major domestic source of energy and produced 9.2 percent of Japan's electricity, , down from 24.9 percent the previous year. Following the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes ...
disaster in 2011, the nuclear reactors were shut down. Thus Japan's industrial sector became even more dependent than before on imported fossil fuels. By May 2012 all of the country's nuclear power plants were taken offline because of ongoing public opposition following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
in March 2011, though government officials continued to try to sway public opinion in favor of returning at least some of Japan's 50 nuclear reactors to service. Shinzo Abe's government seeks to restart the nuclear power plants that meet strict new safety standards and is emphasizing nuclear energy's importance as a base-load electricity source.Kagoshima prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
, and several other reactors around the country have since resumed operations. Opposition from local governments has delayed several restarts that remain pending.
Reforms of the electricity and gas sectors, including full liberalization of Japan's energy market in April 2016 and gas market in April 2017, constitute an important part of Prime Minister Abe's economic program.Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry
Ministry may refer to:
Government
* Ministry (collective executive), the complete body of government ministers under the leadership of a prime minister
* Ministry (government department), a department of a government
Religion
* Christian mi ...
is exploring over 40 locations for potential geothermal energy plants.
On 3 July 2018, Japan's government pledged to increase renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
sources from 15% to 22–24% including wind and solar by 2030. Nuclear energy will provide 20% of the country's energy needs as an emissions-free energy source. This will help Japan meet climate change commitments.
National Parks and Scenic Beauty
National Parks
 Japan has 34 and 56 in 2019. These are designated and managed for protection and sustainable usage by the Ministry of the Environment under the of 1957. The Quasi-National Parks have slightly less beauty, size, diversity, or preservation. They are recommended for ministerial designation and managed by the prefectures under the supervision of the Ministry of the Environment.
The Japanese archipelago has diverse landscapes.
Japan has 34 and 56 in 2019. These are designated and managed for protection and sustainable usage by the Ministry of the Environment under the of 1957. The Quasi-National Parks have slightly less beauty, size, diversity, or preservation. They are recommended for ministerial designation and managed by the prefectures under the supervision of the Ministry of the Environment.
The Japanese archipelago has diverse landscapes.subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and ...
with numerous species of subtropical and tropical plants, and mangrove forests.List of Ramsar sites in Japan
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. Adopted in 1971, it entered into force in 1975 and as of April 2022 had 1 ...
* Cultural Landscapes
Cultural landscape is a term used in the fields of geography, ecology, and heritage studies, to describe a symbiosis of human activity and environment. As defined by the World Heritage Committee, it is the "cultural properties hatrepresent the co ...
Places of Scenic Beauty
 The Places of Scenic Beauty and Natural Monuments are selected by the government via the
The Places of Scenic Beauty and Natural Monuments are selected by the government via the Agency for Cultural Affairs
The is a special body of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). It was set up in 1968 to promote Japanese arts and culture.
The agency's budget for FY 2018 rose to ¥107.7 billion.
Overview
The ag ...
in order to protect Japan's cultural heritage. As of 2017, there are 1,027 and 410 . The highest classification are 75 and 36 .
Three Views of Japan
The is the canonical list of Japan's three most celebrated scenic sights, attributed to 1643 and scholar Hayashi Gahō. These are traditionally the pine-clad islands of Matsushima
is a group of islands in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. There are some 260 tiny islands (''shima'') covered in pines (''matsu'') – hence the name – and it is considered to be one of the Three Views of Japan.
Nearby cultural properties ...
in Miyagi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Miyagi Prefecture has a population of 2,305,596 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Miyagi Prefecture borders Iwate Prefecture to the north, Akita Prefecture to the nort ...
, the pine-clad sandbar of Amanohashidate in Kyoto Prefecture, and Itsukushima Shrine
is a Shinto jinja (shrine), shrine on the island of Itsukushima (popularly known as Miyajima, Hiroshima, Miyajima), best known for its "floating" ''torii'' gate.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric (2005)"''Itsukushima-jinja''"in ''Japa ...
in Hiroshima Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Hiroshima Prefecture has a population of 2,811,410 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 8,479 km² (3,274 sq mi). Hiroshima Prefecture borders Okayama ...
. In 1915, the New Three Views of Japan were selected with a national election by the Jitsugyo no Nihon Sha (株式会社実業之日本社). In 2003, the Three Major Night Views of Japan were selected by the ''New Three Major Night Views of Japan and the 100 Night Views of Japan Club'' (新日本三大夜景・夜景100選事務局).
Matsushima miyagi z.JPG, Pine-clad islands of Matsushima
is a group of islands in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. There are some 260 tiny islands (''shima'') covered in pines (''matsu'') – hence the name – and it is considered to be one of the Three Views of Japan.
Nearby cultural properties ...
Amanohashidate view from Mt Moju02s3s4592.jpg, Sandbar of Amanohashidate
20131012_07_Miyajima_-_Torii_(10491662566).jpg, Torii at Itsukushima Shrine
is a Shinto jinja (shrine), shrine on the island of Itsukushima (popularly known as Miyajima, Hiroshima, Miyajima), best known for its "floating" ''torii'' gate.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric (2005)"''Itsukushima-jinja''"in ''Japa ...
Climate
 Most regions of Japan, such as much of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu, belong to the temperate zone with
Most regions of Japan, such as much of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu, belong to the temperate zone with humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
( Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') characterized by four distinct seasons. However, its climate varies from cool humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfb'') in the north such as northern Hokkaido, to warm tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south such as the Yaeyama Islands and Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
.
Climate zones


 Japan's varied geographical features divide it into six principal climatic zones.
* Hokkaido belongs to the humid continental climate, with long, cold winters and cool summers. Precipitation is sparse; however, winter brings large snowfalls of hundreds of inches in areas such as Sapporo and Asahikawa.
* In the Sea of Japan, the northwest seasonal wind in winter gives heavy snowfall, which south of Tōhoku mostly melts before the beginning of spring. In summer, it is a little less rainy than the Pacific area but sometimes experiences extreme high temperatures because of the foehn wind phenomenon.
* Central Highland: a typical inland climate gives large temperature variations between summers and winters and between days and nights. Precipitation is lower than on the coast because of rain shadow effects.
* Seto Inland Sea: the mountains in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions block the seasonal winds and bring mild climate and many fine days throughout the year.
* Pacific Ocean: the climate varies greatly between the north and the south, but generally winters are significantly milder and sunnier than those of the side that faces the Sea of Japan. Summers are hot because of the southeast seasonal wind. Precipitation is very heavy in the south and heavy in the summer in the north. The climate of the Ogasawara Island chain ranges from a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') to tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') with temperatures being warm to hot all year round.
* The climate of the Ryukyu Islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south with warm winters and hot summers. Precipitation is very high and is especially affected by the rainy season and typhoons.
Japan's varied geographical features divide it into six principal climatic zones.
* Hokkaido belongs to the humid continental climate, with long, cold winters and cool summers. Precipitation is sparse; however, winter brings large snowfalls of hundreds of inches in areas such as Sapporo and Asahikawa.
* In the Sea of Japan, the northwest seasonal wind in winter gives heavy snowfall, which south of Tōhoku mostly melts before the beginning of spring. In summer, it is a little less rainy than the Pacific area but sometimes experiences extreme high temperatures because of the foehn wind phenomenon.
* Central Highland: a typical inland climate gives large temperature variations between summers and winters and between days and nights. Precipitation is lower than on the coast because of rain shadow effects.
* Seto Inland Sea: the mountains in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions block the seasonal winds and bring mild climate and many fine days throughout the year.
* Pacific Ocean: the climate varies greatly between the north and the south, but generally winters are significantly milder and sunnier than those of the side that faces the Sea of Japan. Summers are hot because of the southeast seasonal wind. Precipitation is very heavy in the south and heavy in the summer in the north. The climate of the Ogasawara Island chain ranges from a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') to tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') with temperatures being warm to hot all year round.
* The climate of the Ryukyu Islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south with warm winters and hot summers. Precipitation is very high and is especially affected by the rainy season and typhoons.
Rainfall
Japan is generally a rainy country with high humidity.[ Because of its wide range of latitude,][ seasonal winds and different types of ocean currents, Japan has a variety of climates, with a latitude range of the inhabited islands from 24°N – 46°N, which is comparable to the range between Nova Scotia and The Bahamas in the east coast of North America.][ Tokyo is between 35°N – 36°N, which is comparable to that of Tehran, Athens, or Las Vegas.][
As Mount Fuji and the coastal Japanese Alps provide a rain shadow, Nagano and Yamanashi Prefectures receive the least precipitation in Honshu, though it still exceeds annually. A similar effect is found in Hokkaido, where Okhotsk Subprefecture receives as little as per year. All other prefectures have coasts on the Pacific Ocean, Sea of Japan, Seto Inland Sea or have a body of salt water connected to them. Two prefectures— Hokkaido and Okinawa—are composed entirely of islands.
]
Summer
The climate from June to September is marked by hot, wet weather brought by tropical airflows from the Pacific Ocean and Southeast Asia.[ These air flows are full of moisture and deposit substantial amounts of rain when they reach land.][ There is a marked rainy season, beginning in early June and continuing for about a month.][ It is followed by hot, sticky weather.][ Five or six typhoons pass over or near Japan every year from early August to early October, sometimes resulting in significant damage.][ Annual precipitation averages between except for the areas such as Kii Peninsula and Yakushima Island which is Japan's wettest place with the annual precipitation being one of the world's highest at 4,000 to 10,000 mm.
Maximum precipitation, like the rest of East Asia, occurs in the summer months except on the Sea of Japan coast where strong northerly winds produce a maximum in late autumn and early winter. Except for a few sheltered inland valleys during December and January, precipitation in Japan is above of rainfall equivalent in all months of the year, and in the wettest coastal areas it is above per month throughout the year.
Mid June to mid July is generally the rainy season in Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu, excluding Hokkaidō since the seasonal rain front or dissipates in northern Honshu before reaching Hokkaido. In Okinawa, the rainy season starts early in May and continues until mid June. Unlike the rainy season in mainland Japan, it rains neither everyday nor all day long during the rainy season in Okinawa. Between July and October, typhoons, grown from tropical depressions generated near the equator, can attack Japan with furious rainstorms.
]
Winter
 In winter, the Siberian High develops over the Eurasian land mass and the Aleutian Low develops over the northern Pacific Ocean.
In winter, the Siberian High develops over the Eurasian land mass and the Aleutian Low develops over the northern Pacific Ocean.[ The result is a flow of cold air southeastward across Japan that brings freezing temperatures and heavy snowfalls to the central mountain ranges facing the Sea of Japan, but clear skies to areas fronting on the Pacific.][
The warmest winter temperatures are found in the Nanpō and Bonin Islands, which enjoy a tropical climate due to the combination of latitude, distance from the ]Asian continent
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, and warming effect of winds from the Kuroshio, as well as the Volcano Islands (at the latitude of the southernmost of the Ryukyu Islands, 24° N). The coolest summer temperatures are found on the northeastern coast of Hokkaidō in Kushiro and Nemuro Subprefectures.
Sunshine
Sunshine, in accordance with Japan's uniformly heavy rainfall, is generally modest in quantity, though no part of Japan receives the consistently gloomy fogs that envelope the Sichuan Basin or Taipei. Amounts range from about six hours per day in the Inland Sea coast and sheltered parts of the Pacific Coast and Kantō Plain to four hours per day on the Sea of Japan coast of Hokkaidō. In December there is a very pronounced sunshine gradient between the Sea of Japan and Pacific coasts, as the former side can receive less than 30 hours and the Pacific side as much as 180 hours. In summer, however, sunshine hours are lowest on exposed parts of the Pacific coast where fogs from the Oyashio current create persistent cloud cover similar to that found on the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin.
Extreme temperature records
The highest recorded temperature in Japan was 41.1 °C (106.0 °F) on 23 July 2018, an unverified record of 42.7 °C was taken in Adachi, Tokyo on 20 July 2004. The high humidity and the maritime influence make temperatures in the 40s rare, with summers dominated by a more stable subtropical monsoon pattern through most of Japan. The lowest was −41.0 °C (−41.8 °F) in Asahikawa on 25 January 1902. However an unofficial −41.5 °C was taken in Bifuka on 27 January 1931. Mount Fuji broke the Japanese record lows for each month except January, February, March, and December. Record lows for any month were taken as recent as 1984.
Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
has a tropical savanna climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') and the highest average temperature in Japan of 25 degrees Celsius.
Population distribution
 Japan has a population of 126.3 million in 2019.
Japan has a population of 126.3 million in 2019.Kanto
Kantō (Japanese)
Kanto is a simplified spelling of , a Japanese word, only omitting the diacritics.
In Japan
Kantō may refer to:
*Kantō Plain
*Kantō region
*Kantō-kai, organized crime group
*Kanto (Pokémon), a geographical region in the ' ...
, Kinki, and Chukyo metropolitan areas.
Honshu
is the largest island of Japan and the second most populous island in the world. It has a population of 104,000,000 with a population density of (2010).metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
( megacity) in the world with people (2016).[Japan Statistics Bureau – Keihin'yō Major Metropolitan Area]
and has a population density of 2,642 persons/km2.
Kyushu
is the third largest island of Japan of the five main islands.
Shikoku
is the second smallest of the five main islands (after Okinawa island), . It is located south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. It has the second smallest population of 3,845,534 million (2015)
Hokkaido
is the second largest island of Japan, and the largest and northernmost prefecture. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaido from Honshu.[ Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaido" in ] It has the third largest population of the five main islands with 5,383,579 (2015)
Okinawa Prefecture
is the southernmost prefecture of Japan. It encompasses two thirds of the Ryukyu Islands over long. It has a population of 1,445,812 (2017) and a density of 662 persons/km2. is the smallest and most southwestern of the five main islands, .
Nanpō Islands
are the groups of islands that are located to the south and east of the main islands of the Japanese archipelago. They extend from the Izu Peninsula
The is a large mountainous peninsula with a deeply indented coastline to the west of Tokyo on the Pacific coast of the island of Honshu, Japan. Formerly known as Izu Province, Izu peninsula is now a part of Shizuoka Prefecture. The peninsul ...
west of Tokyo Bay southward for about , to within of the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
. The Nanpō Islands are all administered by Tokyo Metropolis.
Taiheiyō Belt
 The Taiheiyō Belt is a megalopolis that includes the Greater Tokyo Area and
The Taiheiyō Belt is a megalopolis that includes the Greater Tokyo Area and Keihanshin
is a metropolitan region in the Kansai region of Japan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka in Osaka Prefecture and Kobe in Hyōgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population () of 19,302,746 o ...
megapoles. It is almost long from Ibaraki Prefecture in the northeast to Fukuoka Prefecture in the southwest. Satellite images at night show a dense and continuous strip of light (demarcating urban zones) that delineates the region with overlapping metropolitan areas in Japan. It has a total population of approximately 81,859,345 (2016).
* Taiheiyō Belt – includes Ibaraki, Saitama, Chiba
Chiba may refer to:
Places China
* (), town in Jianli County, Jingzhou, Hubei
Japan
* Chiba (city), capital of Chiba Prefecture
** Chiba Station, a train station
* Chiba Prefecture, a sub-national jurisdiction in the Greater Tokyo Area on ...
, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku ...
, Mie, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Wakayama, Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
, Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
, Yamaguchi, Fukuoka, and Ōita. (81,859,345 people)
** Greater Tokyo Area – Part of the larger Kantō region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Slight ...
, broadly includes Tokyo and Yokohama. (38,000,000 people)
** Keihanshin
is a metropolitan region in the Kansai region of Japan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka in Osaka Prefecture and Kobe in Hyōgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population () of 19,302,746 o ...
– Part of the larger Kansai region, includes Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
. (19,341,976 people)
Underwater habitats
There are plans to build underwater habitats in Japan's Exclusive Economic Zone. Currently no underwater city is constructed yet. For example, the Ocean Spiral by Shimizu Corporation would have a floating dome 500 meters in diameter with hotels, residential and commercial complexes. It could be 15 km long. This allows mining of the seabed, research and production of methane from carbon dioxide with micro-organisms. The Ocean Spiral was co-developed with JAMSTEC and Tokyo University.
Extreme points
 Japan extends from 20° to 45° north latitude ( Okinotorishima to Benten-jima) and from 122° to 153° east longitude ( Yonaguni to Minami Torishima).
Japan extends from 20° to 45° north latitude ( Okinotorishima to Benten-jima) and from 122° to 153° east longitude ( Yonaguni to Minami Torishima).
Japan's main islands
The five main islands of Japan are Hokkaidō, Honshū, Kyūshū, Shikoku and Okinawa. These are also called the mainland.
Extreme altitudes
Largest islands of Japan


 These are the 50 largest islands of Japan. It excludes the disputed Kuril islands known as the northern territories.
These are the 50 largest islands of Japan. It excludes the disputed Kuril islands known as the northern territories.
Northern Territories
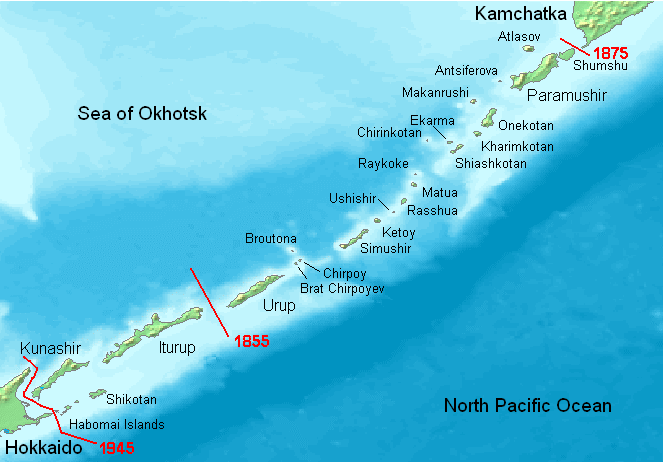 Japan has a longstanding claim of the Southern Kuril Islands ( Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, and the Habomai Islands). These islands were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. The Kuril Islands historically belong to Japan. The Kuril Islands were first inhabited by the
Japan has a longstanding claim of the Southern Kuril Islands ( Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, and the Habomai Islands). These islands were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. The Kuril Islands historically belong to Japan. The Kuril Islands were first inhabited by the Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Y ...
and then controlled by the Japanese Matsumae clan in the Edo Period. The Soviet Union did not sign the San Francisco Treaty
The , also called the , re-established peaceful relations between Japan and the Allied Powers on behalf of the United Nations by ending the legal state of war and providing for redress for hostile actions up to and including World War II. It ...
in 1951. The U.S. Senate Resolution of April 28, 1952, ratifying of the San Francisco Treaty, explicitly stated that the USSR had no title to the Kurils.[James E. Goodby, Vladimir I. Ivanov, Nobuo Shimotomai, ''Northern territories and beyond: Russian, Japanese, and American Perspectives'', Praeger Publishers, 1995] This dispute has prevented the signing of a peace treaty between Japan and Russia.
Geographically the Kuril Islands are a northeastern extension of Hokkaido. Kunashiri and the Habomai Islands are visible from the northeastern coast of Hokkaido. Japan considers the northern territories (aka Southern Chishima) part of Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture.
Time zone
There is one time zone in the whole Japanese archipelago. It is 9 hours ahead of UTC. There is no daylight saving time. The easternmost Japanese island Minami-Tori-shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
also uses Japan Standard Time while it is geographically southeast of Tokyo and in the UTC+10:00 time zone.
Sakhalin uses UTC+11:00 even though it is located directly north of Hokkaido. The Northern Territories and the Kuril islands use UTC+11:00 although they are geographically in UTC+10:00
Natural hazards
Earthquakes and tsunami
 Japan is substantially prone to earthquakes, tsunami and volcanoes because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. It has the 15th highest natural disaster risk as measured in the 2013 World Risk Index.
Japan is substantially prone to earthquakes, tsunami and volcanoes because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. It has the 15th highest natural disaster risk as measured in the 2013 World Risk Index.[2013 World Risk Report](_blank)
As many as 1,500 earthquakes are recorded yearly, and magnitudes of 4 to 6 are common.[ Minor tremors occur almost daily in one part of the country or another, causing slight shaking of buildings.][ ]Undersea earthquake
A submarine, undersea, or underwater earthquake is an earthquake that occurs underwater at the bottom of a body of water, especially an ocean. They are the leading cause of tsunamis. The magnitude can be measured scientifically by the use of the ...
s also expose the Japanese coastline to danger from .[
Destructive earthquakes, often resulting in tsunami, occur several times each century.]1923 Tokyo earthquake
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20
* one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film
Music ...
killed over 140,000 people. More recent major quakes are the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake and the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake
Eleven or 11 may refer to:
*11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12
* one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11
Literature
* ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn
*''El ...
, a 9.1-magnitudeFukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
, one of the worst disasters in the history of nuclear power.Sendai
is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, desig ...
, and created a massive tsunami that devastated Japan's northeastern coastal areas. At least 100 aftershocks registering a 6.0 magnitude or higher have followed the main shock. At least 15,000 people died as a result.
Researchers found the source of great thrust earthquakes and associated tsunamis in the Greater Tokyo Area at the Izu-Ogasawara Trench.Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
.liquefaction
In materials science, liquefaction is a process that generates a liquid from a solid or a gas or that generates a non-liquid phase which behaves in accordance with fluid dynamics.
It occurs both naturally and artificially. As an example of the ...
during an earthquake. As a result, there are specific earthquake resistance standards and ground reform work that applies to all construction in these areas. In an area that was possibly reclaimed in the past, old maps and land condition drawings are checked and drilling is carried out to determine the strength of the ground. However this can be very costly, so for a private residential block of land, a Swedish weight sounding test is more common.[ The development of advanced technology has permitted the construction of ]skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
s even in earthquake-prone areas.[ Extensive civil defence efforts focus on training in protection against earthquakes, in particular against accompanying fire, which represents the greatest danger.][
]
Volcanic eruptions
 Japan has 108 active volcanoes. That's 10% of all active volcanoes in the world. Japan has stratovolcanoes near the subduction zones of the tectonic plates. During the 20th century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shō off the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific.
Japan has 108 active volcanoes. That's 10% of all active volcanoes in the world. Japan has stratovolcanoes near the subduction zones of the tectonic plates. During the 20th century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shō off the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific.lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
at its summit. Beginning in June, repeated collapse of this erupting dome generated ash flows that swept down the mountain's slopes at speeds as high as . Unzen
is an active volcanic group of several overlapping stratovolcanoes, near the city of Shimabara, Nagasaki on the island of Kyushu, Japan's southernmost main island.
In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a megatsu ...
erupted in 1792 and killed more than 15,000 people. It is the worst volcanic disaster in the country's recorded history.dormant
Dormant, "sleeping", may refer to:
Science
*Dormancy
Dormancy is a period in an organism's life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolic activity and therefore helps ...
stratovolcano that last erupted on 16 December 1707 till about 1 January 1708.Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
almost away. Cinders and ash fell like rain in Izu, Kai, Sagami, and Musashi provinces. In Edo, the volcanic ash was several centimeters thick. The eruption is rated a 5 on the Volcanic Explosivity Index. There are three VEI-7 volcanoes in Japan. These are the Aira Caldera, Kikai Caldera and Aso Caldera. These giant caldera are remnants of past eruptions. Mount Aso is the largest active volcano in Japan. 300,000 to 90,000 years ago there were four eruptions of Mount Aso which emitted huge amounts of volcanic ash that covered all of Kyushu and up to Yamaguchi Prefecture.
* The Aira Caldera is 17 kilometers long and 23 km wide located in south Kyushu. The city of Kagoshima and the Sakurajima volcano are within the Aira Caldera. Sakurajima is the most active volcano in Japan.
* The Aso Caldera stretches 25 kilometers north to south and 18 kilometers east to west in Kumamoto Prefecture, Kyushu. It has erupted 4 times: 266,000 and 141,000 years ago with 32 DRE km3 ( dense-rock equivalent) each; 130,000 years ago with 96 DRE km3; and 90,000 years ago with 384 DRE km3.
There are three VEI-7 volcanoes in Japan. These are the Aira Caldera, Kikai Caldera and Aso Caldera. These giant caldera are remnants of past eruptions. Mount Aso is the largest active volcano in Japan. 300,000 to 90,000 years ago there were four eruptions of Mount Aso which emitted huge amounts of volcanic ash that covered all of Kyushu and up to Yamaguchi Prefecture.
* The Aira Caldera is 17 kilometers long and 23 km wide located in south Kyushu. The city of Kagoshima and the Sakurajima volcano are within the Aira Caldera. Sakurajima is the most active volcano in Japan.
* The Aso Caldera stretches 25 kilometers north to south and 18 kilometers east to west in Kumamoto Prefecture, Kyushu. It has erupted 4 times: 266,000 and 141,000 years ago with 32 DRE km3 ( dense-rock equivalent) each; 130,000 years ago with 96 DRE km3; and 90,000 years ago with 384 DRE km3.[阿蘇カルデラ](_blank)
産総研
* The Kikai Caldera is a massive, mostly submerged caldera up to 19 kilometres (12 mi) in diameter in the Ōsumi Islands of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. It is the remains of the ancient eruption of a colossal volcano. Kikai Caldera was the source of the Akahoya eruption, one of the largest eruptions during the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present). About 4,300 BC, pyroclastic flows from that eruption reached the coast of southern Kyūshū up to away, and ash fell as far as Hokkaidō. The eruption produced about 150 km³ of tephra, giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7 The Jōmon culture of at least southern Kyushu was destroyed, and it took nearly 1,000 years to recover.submarine volcano
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges ...
Fukutoku-Okanoba damaged fisheries, tourism, the environment, 11 ports in Okinawa and 19 ports in Kagoshima prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
.geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pres ...
and electricity.
Typhoons
Since recording started in 1951, an average of 2.6 typhoons reached the main islands of Kyushu, Shikoku, Honshu and Hokkaido per year. Approximately 10.3 typhoons approach within the 300 kilometer range near the coast of Japan. Okinawa is, due to its geographic location, most vulnerable to typhoons with an average of 7 storms per year. The most destructive was Isewan Typhoon
Typhoon Vera, also known as the , was an exceptionally intense tropical cyclone that struck Japan in September 1959, becoming the strongest and deadliest typhoon on record to make landfall on the country as a Category 5 equivalent storm. ...
with 5,000 casualties in the Tokai region in September 1959. In October 2004, Typhoon Tokage caused heavy rain in Kyushu and central Japan with 98 casualties. Until the 1960s the death toll was hundreds of people per typhoon. Since the 1960s improvements in construction, flood prevention, high tides detection and early warnings substantially reduced the death toll which rarely exceeds a dozen people per typhoon. Japan also has special search and rescue units to save people in distress.landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s, flooding, and avalanches.
Environmental issues
In the 2006 environment annual report,Annual Report on the Environment in Japan 2006
Ministry of the Environment the Ministry of Environment reported that current major issues are: global warming and preservation of the ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rela ...
, conservation of the atmospheric environment, water and soil, waste management and recycling, measures for chemical substances, conservation of the natural environment and the participation in the international cooperation.
See also
* List of peninsulas of Japan
* Japanese addressing system
References
Japan
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency..
External links
"Colton's Japan: Nippon, Kiusiu, Sikok, Yesso and the Japanese Kuriles"
a map from 1855
Terrain of Japan
– GJI Maps (Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
The , or GSI, is the national institution responsible for surveying and mapping the national land of Japan. The former name of the organization from 1949 until March 2010 was Geographical Survey Institute; despite the rename, it retains the same ...
)
{{Asia topic, Climate of
Lists of subdivisions of Japan

 The Japanese archipelago is over long in a north-to-southwardly direction from the Sea of Okhotsk to the
The Japanese archipelago is over long in a north-to-southwardly direction from the Sea of Okhotsk to the  Japan is informally divided into eight regions from northeast (Hokkaidō) to southwest (Ryukyu Islands):
*
Japan is informally divided into eight regions from northeast (Hokkaidō) to southwest (Ryukyu Islands):
*  About 73% of Japan is mountainous, with a mountain range running through each of the main islands. Japan's highest mountain is
About 73% of Japan is mountainous, with a mountain range running through each of the main islands. Japan's highest mountain is  There are three major plains in central Honshū. The largest is the Kantō Plain which covers in the
There are three major plains in central Honshū. The largest is the Kantō Plain which covers in the  Rivers are generally steep and swift, and few are suitable for navigation except in their lower reaches. Although most rivers are less than in length, their rapid flow from the mountains is what provides hydroelectric power. Seasonal variations in flow have led to extensive development of flood control measures. The longest, the Shinano River, which winds through
Rivers are generally steep and swift, and few are suitable for navigation except in their lower reaches. Although most rivers are less than in length, their rapid flow from the mountains is what provides hydroelectric power. Seasonal variations in flow have led to extensive development of flood control measures. The longest, the Shinano River, which winds through  The largest freshwater lake is Lake Biwa , northeast of Kyoto in Shiga Prefecture. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake and estimated to be the 13th oldest lake in the world dating to at least 4 million years ago. It has consistently carried water for millions of years. Lake Biwa was created by plate tectonics in an active rift zone. This created a very deep lake with a maximum depth of . Thus it has not naturally filled with sediment. Over the course of millions of years, a diverse ecosystem evolved in the lake. It has more than 1,000 species and subspecies. There are 46 native fish species and subspecies,Kawanabe, H.; Nishino, M.; and Maehata, M., editors (2012). ''Lake Biwa: Interactions between Nature and People.'' pp 119-120. including 11 species and 5 subspecies that are endemic or near-endemic. Approximately 5,000 water birds visit the lake each year.
The following are the 10 largest lakes of Japan. 国土地理院 平成29年全国都道府県市区町村別面積�
The largest freshwater lake is Lake Biwa , northeast of Kyoto in Shiga Prefecture. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake and estimated to be the 13th oldest lake in the world dating to at least 4 million years ago. It has consistently carried water for millions of years. Lake Biwa was created by plate tectonics in an active rift zone. This created a very deep lake with a maximum depth of . Thus it has not naturally filled with sediment. Over the course of millions of years, a diverse ecosystem evolved in the lake. It has more than 1,000 species and subspecies. There are 46 native fish species and subspecies,Kawanabe, H.; Nishino, M.; and Maehata, M., editors (2012). ''Lake Biwa: Interactions between Nature and People.'' pp 119-120. including 11 species and 5 subspecies that are endemic or near-endemic. Approximately 5,000 water birds visit the lake each year.
The following are the 10 largest lakes of Japan. 国土地理院 平成29年全国都道府県市区町村別面積� Extensive coastal shipping, especially around the Seto Inland Sea, compensates for the lack of navigable rivers. The Pacific coastline south of Tokyo is characterized by long, narrow, gradually shallowing inlets produced by sedimentation, which has created many natural harbors. The Pacific coastline north of Tokyo, the coast of Hokkaidō, and the Sea of Japan coast are generally unindented, with few natural harbors.
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 765 km² of tidal flats in Japan, making it the 35th ranked country in terms of tidal flat extent.
Extensive coastal shipping, especially around the Seto Inland Sea, compensates for the lack of navigable rivers. The Pacific coastline south of Tokyo is characterized by long, narrow, gradually shallowing inlets produced by sedimentation, which has created many natural harbors. The Pacific coastline north of Tokyo, the coast of Hokkaidō, and the Sea of Japan coast are generally unindented, with few natural harbors.
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 765 km² of tidal flats in Japan, making it the 35th ranked country in terms of tidal flat extent.
 The Japanese archipelago has been transformed by humans into a sort of continuous land, in which the four main islands are entirely reachable and passable by rail and road transportation thanks to the construction of huge bridges and tunnels that connect each other and various islands.
Approximately 0.5% of Japan's total area is reclaimed land (''umetatechi''). It began in the 12th century. Land was reclaimed from the sea and from river deltas by building dikes and drainage and rice paddies on terraces carved into mountainsides. The majority of
The Japanese archipelago has been transformed by humans into a sort of continuous land, in which the four main islands are entirely reachable and passable by rail and road transportation thanks to the construction of huge bridges and tunnels that connect each other and various islands.
Approximately 0.5% of Japan's total area is reclaimed land (''umetatechi''). It began in the 12th century. Land was reclaimed from the sea and from river deltas by building dikes and drainage and rice paddies on terraces carved into mountainsides. The majority of  Japan's sea territory is . Japan ranks fourth with its exclusive economic zone ocean water volume from 0 to depth. Japan ranks fifth with sea volume of 2,000–3,000 meters, fourth with 3,000–4,000 meters, third with 4,000–5,000 meters and first with volume of 5,000 to over 6,000 meters. The relief map of the Japanese archipelago shows that 50% of Japan's sea territory has an ocean volume between 0 and depth. The other 50% has a depth of to over . 19% has a depth of 0 to . Thus Japan possesses one of the largest ocean territories with a combination of all depths from shallow to very deep sea. Multiple long
Japan's sea territory is . Japan ranks fourth with its exclusive economic zone ocean water volume from 0 to depth. Japan ranks fifth with sea volume of 2,000–3,000 meters, fourth with 3,000–4,000 meters, third with 4,000–5,000 meters and first with volume of 5,000 to over 6,000 meters. The relief map of the Japanese archipelago shows that 50% of Japan's sea territory has an ocean volume between 0 and depth. The other 50% has a depth of to over . 19% has a depth of 0 to . Thus Japan possesses one of the largest ocean territories with a combination of all depths from shallow to very deep sea. Multiple long 

 East of the Japanese archipelago are three oceanic trenches.
* The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench is in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido.Rhea, S., et al., 2010, ''Seismicity of the Earth 1900–2007, Kuril–Kamchatka arc and vicinity'', U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2010-1083-C, 1 map sheet, scale 1:5,000,000 http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1083/c/
* The Japan Trench extends from the Kuril Islands to the northern end of the Izu Islands. Its deepest part is . The Japan Trench is created as the oceanic Pacific Plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate. The subduction process causes bending of the down going plate, creating a deep trench. Continuous movement on the subduction zone associated with the Japan Trench is one of the main causes of tsunamis and earthquakes in northern Japan, including the megathrust 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. The rate of subduction associated with the Japan Trench has been recorded at about /yr.
* The Izu–Ogasawara Trench is south of the Japan Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of the Izu Trench (at the north) and the Bonin Trench (at the south, west of the Ogasawara Plateau). It stretches to the northernmost section of the Mariana Trench. The Izu–Ogasawara Trench is an extension of the Japan Trench. There the Pacific Plate is being subducted beneath the Philippine Sea Plate, creating the Izu Islands and Bonin Islands on the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc system.
East of the Japanese archipelago are three oceanic trenches.
* The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench is in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido.Rhea, S., et al., 2010, ''Seismicity of the Earth 1900–2007, Kuril–Kamchatka arc and vicinity'', U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2010-1083-C, 1 map sheet, scale 1:5,000,000 http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1083/c/
* The Japan Trench extends from the Kuril Islands to the northern end of the Izu Islands. Its deepest part is . The Japan Trench is created as the oceanic Pacific Plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate. The subduction process causes bending of the down going plate, creating a deep trench. Continuous movement on the subduction zone associated with the Japan Trench is one of the main causes of tsunamis and earthquakes in northern Japan, including the megathrust 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. The rate of subduction associated with the Japan Trench has been recorded at about /yr.
* The Izu–Ogasawara Trench is south of the Japan Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of the Izu Trench (at the north) and the Bonin Trench (at the south, west of the Ogasawara Plateau). It stretches to the northernmost section of the Mariana Trench. The Izu–Ogasawara Trench is an extension of the Japan Trench. There the Pacific Plate is being subducted beneath the Philippine Sea Plate, creating the Izu Islands and Bonin Islands on the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc system.

 The Exclusive economic zone of Japan has an estimated large quantities of mineral resources such as methane clathrate, natural gas, metallic minerals and
The Exclusive economic zone of Japan has an estimated large quantities of mineral resources such as methane clathrate, natural gas, metallic minerals and  Japan has 34 and 56 in 2019. These are designated and managed for protection and sustainable usage by the Ministry of the Environment under the of 1957. The Quasi-National Parks have slightly less beauty, size, diversity, or preservation. They are recommended for ministerial designation and managed by the prefectures under the supervision of the Ministry of the Environment.
The Japanese archipelago has diverse landscapes. For example, the northern part of Hokkaido has a taiga biome. Hokkaido has 22% of Japan's forestland with coniferous trees ( Sakhalin fir and Sakhalin spruce) and broad-leaved trees ( Japanese oak, birch and Painted maple). The seasonal views change throughout the year. In the south, the Yaeyama Islands are in the
Japan has 34 and 56 in 2019. These are designated and managed for protection and sustainable usage by the Ministry of the Environment under the of 1957. The Quasi-National Parks have slightly less beauty, size, diversity, or preservation. They are recommended for ministerial designation and managed by the prefectures under the supervision of the Ministry of the Environment.
The Japanese archipelago has diverse landscapes. For example, the northern part of Hokkaido has a taiga biome. Hokkaido has 22% of Japan's forestland with coniferous trees ( Sakhalin fir and Sakhalin spruce) and broad-leaved trees ( Japanese oak, birch and Painted maple). The seasonal views change throughout the year. In the south, the Yaeyama Islands are in the  The Places of Scenic Beauty and Natural Monuments are selected by the government via the
The Places of Scenic Beauty and Natural Monuments are selected by the government via the 

 Japan's varied geographical features divide it into six principal climatic zones.
* Hokkaido belongs to the humid continental climate, with long, cold winters and cool summers. Precipitation is sparse; however, winter brings large snowfalls of hundreds of inches in areas such as Sapporo and Asahikawa.
* In the Sea of Japan, the northwest seasonal wind in winter gives heavy snowfall, which south of Tōhoku mostly melts before the beginning of spring. In summer, it is a little less rainy than the Pacific area but sometimes experiences extreme high temperatures because of the foehn wind phenomenon.
* Central Highland: a typical inland climate gives large temperature variations between summers and winters and between days and nights. Precipitation is lower than on the coast because of rain shadow effects.
* Seto Inland Sea: the mountains in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions block the seasonal winds and bring mild climate and many fine days throughout the year.
* Pacific Ocean: the climate varies greatly between the north and the south, but generally winters are significantly milder and sunnier than those of the side that faces the Sea of Japan. Summers are hot because of the southeast seasonal wind. Precipitation is very heavy in the south and heavy in the summer in the north. The climate of the Ogasawara Island chain ranges from a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') to tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') with temperatures being warm to hot all year round.
* The climate of the Ryukyu Islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south with warm winters and hot summers. Precipitation is very high and is especially affected by the rainy season and typhoons.
Japan's varied geographical features divide it into six principal climatic zones.
* Hokkaido belongs to the humid continental climate, with long, cold winters and cool summers. Precipitation is sparse; however, winter brings large snowfalls of hundreds of inches in areas such as Sapporo and Asahikawa.
* In the Sea of Japan, the northwest seasonal wind in winter gives heavy snowfall, which south of Tōhoku mostly melts before the beginning of spring. In summer, it is a little less rainy than the Pacific area but sometimes experiences extreme high temperatures because of the foehn wind phenomenon.
* Central Highland: a typical inland climate gives large temperature variations between summers and winters and between days and nights. Precipitation is lower than on the coast because of rain shadow effects.
* Seto Inland Sea: the mountains in the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions block the seasonal winds and bring mild climate and many fine days throughout the year.
* Pacific Ocean: the climate varies greatly between the north and the south, but generally winters are significantly milder and sunnier than those of the side that faces the Sea of Japan. Summers are hot because of the southeast seasonal wind. Precipitation is very heavy in the south and heavy in the summer in the north. The climate of the Ogasawara Island chain ranges from a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') to tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') with temperatures being warm to hot all year round.
* The climate of the Ryukyu Islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south with warm winters and hot summers. Precipitation is very high and is especially affected by the rainy season and typhoons.
 In winter, the Siberian High develops over the Eurasian land mass and the Aleutian Low develops over the northern Pacific Ocean. The result is a flow of cold air southeastward across Japan that brings freezing temperatures and heavy snowfalls to the central mountain ranges facing the Sea of Japan, but clear skies to areas fronting on the Pacific.
The warmest winter temperatures are found in the Nanpō and Bonin Islands, which enjoy a tropical climate due to the combination of latitude, distance from the
In winter, the Siberian High develops over the Eurasian land mass and the Aleutian Low develops over the northern Pacific Ocean. The result is a flow of cold air southeastward across Japan that brings freezing temperatures and heavy snowfalls to the central mountain ranges facing the Sea of Japan, but clear skies to areas fronting on the Pacific.
The warmest winter temperatures are found in the Nanpō and Bonin Islands, which enjoy a tropical climate due to the combination of latitude, distance from the 
 Japan extends from 20° to 45° north latitude ( Okinotorishima to Benten-jima) and from 122° to 153° east longitude ( Yonaguni to Minami Torishima). These are the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in Japan.
Japan extends from 20° to 45° north latitude ( Okinotorishima to Benten-jima) and from 122° to 153° east longitude ( Yonaguni to Minami Torishima). These are the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in Japan.


 Japan has a longstanding claim of the Southern Kuril Islands ( Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, and the Habomai Islands). These islands were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. The Kuril Islands historically belong to Japan. The Kuril Islands were first inhabited by the
Japan has a longstanding claim of the Southern Kuril Islands ( Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, and the Habomai Islands). These islands were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. The Kuril Islands historically belong to Japan. The Kuril Islands were first inhabited by the  Japan is substantially prone to earthquakes, tsunami and volcanoes because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. It has the 15th highest natural disaster risk as measured in the 2013 World Risk Index.2013 World Risk Report
Japan is substantially prone to earthquakes, tsunami and volcanoes because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. It has the 15th highest natural disaster risk as measured in the 2013 World Risk Index.2013 World Risk Report Japan has 108 active volcanoes. That's 10% of all active volcanoes in the world. Japan has stratovolcanoes near the subduction zones of the tectonic plates. During the 20th century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shō off the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific. In 1991, Japan's Unzen Volcano on Kyushu about east of Nagasaki, awakened from its 200-year slumber to produce a new
Japan has 108 active volcanoes. That's 10% of all active volcanoes in the world. Japan has stratovolcanoes near the subduction zones of the tectonic plates. During the 20th century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shō off the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific. In 1991, Japan's Unzen Volcano on Kyushu about east of Nagasaki, awakened from its 200-year slumber to produce a new