Norman Cavalry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Horses in the Middle Ages differed in size, build and breed from the modern horse, and were, on average, smaller. They were also more central to society than their modern counterparts, being essential for war, agriculture, and transport.
Consequently, specific types of horse developed, many of which have no modern equivalent. While an understanding of modern horse breeds and
Horses in the Middle Ages differed in size, build and breed from the modern horse, and were, on average, smaller. They were also more central to society than their modern counterparts, being essential for war, agriculture, and transport.
Consequently, specific types of horse developed, many of which have no modern equivalent. While an understanding of modern horse breeds and
 During the
During the
"The Spanish Mustang: The Origin and Relationships of the Mustang, Barb, and Arabian Horse"
. ''Frank Hopkins''. Retrieved 2008-08-14. It is also possible that other sources of oriental bloodstock came from what was called the '' Nisaean breed'' (possibly akin to the Turkoman horse) from Iran and Anatolia, another type of oriental horse brought back from the Crusades. "Spanish" horses, whatever their breeding, were the most expensive. In fact, in Germany the word ''spanjol'' became the term for quality war horses. However, German literary sources also refer to fine horses from Scandinavia.Bumke, p. 178 France also produced good war horses. Some scholars attribute this to the strong
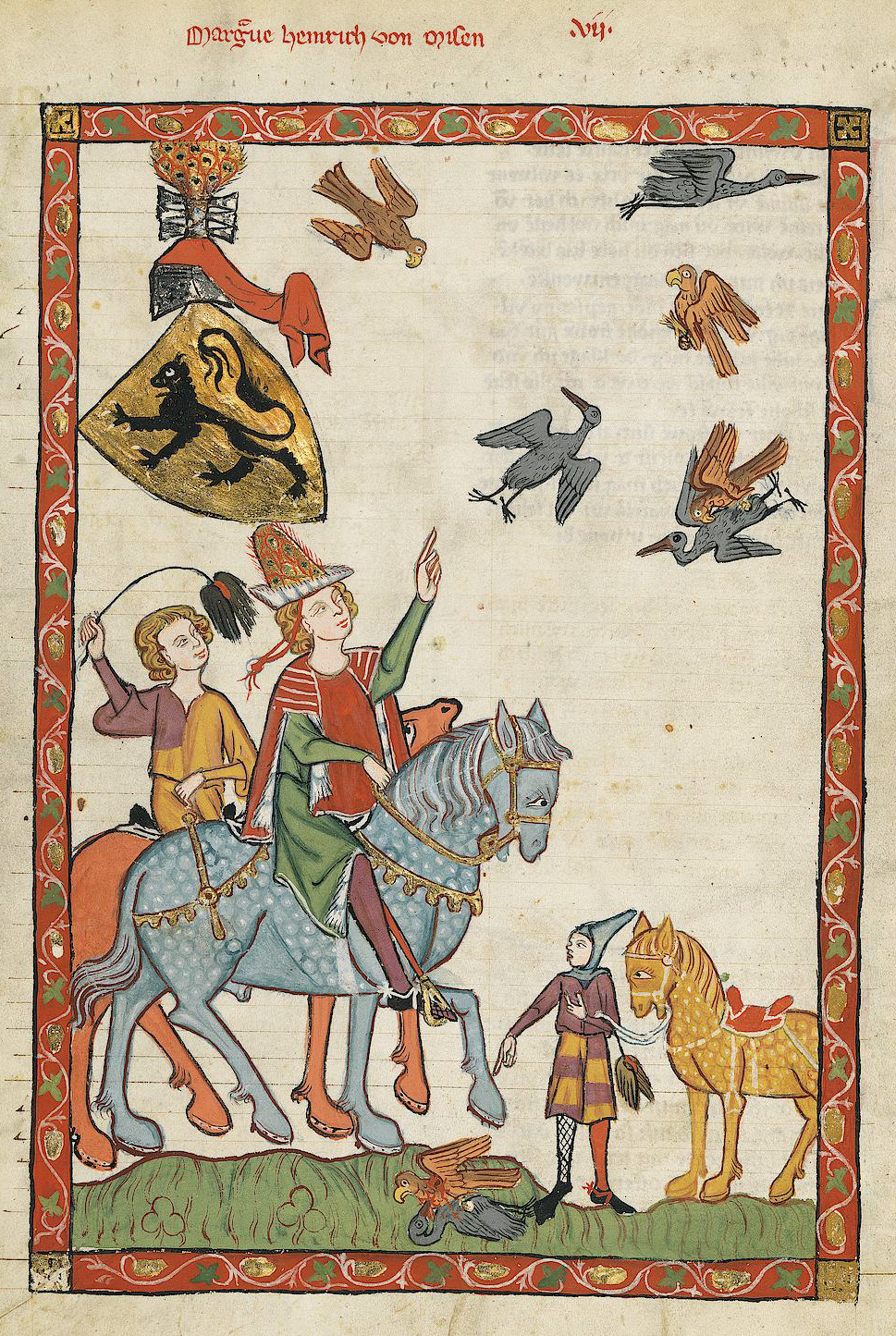 One of the best-known of the medieval horses was the destrier, renowned and admired for its capabilities in war. It was well trained, and was required to be strong, fast and agile. A 14th-century writer described them as "tall and majestic and with great strength". In contemporary sources, the destrier was frequently referred to as the "great horse" because of its size and reputation.Oakeshott (1998), p. 11 Being a subjective term, it gives no firm information about its actual height or weight, but since the average horse of the time was , a "great horse" by medieval standards might appear small to our modern eyes. The destrier was highly prized by knights and men-at-arms, but was actually not very common, and appears to have been most suited to the joust.
Coursers were generally preferred for hard battle as they were light, fast and strong. They were valuable, but not as costly as the destrier. They were also used frequently for
One of the best-known of the medieval horses was the destrier, renowned and admired for its capabilities in war. It was well trained, and was required to be strong, fast and agile. A 14th-century writer described them as "tall and majestic and with great strength". In contemporary sources, the destrier was frequently referred to as the "great horse" because of its size and reputation.Oakeshott (1998), p. 11 Being a subjective term, it gives no firm information about its actual height or weight, but since the average horse of the time was , a "great horse" by medieval standards might appear small to our modern eyes. The destrier was highly prized by knights and men-at-arms, but was actually not very common, and appears to have been most suited to the joust.
Coursers were generally preferred for hard battle as they were light, fast and strong. They were valuable, but not as costly as the destrier. They were also used frequently for
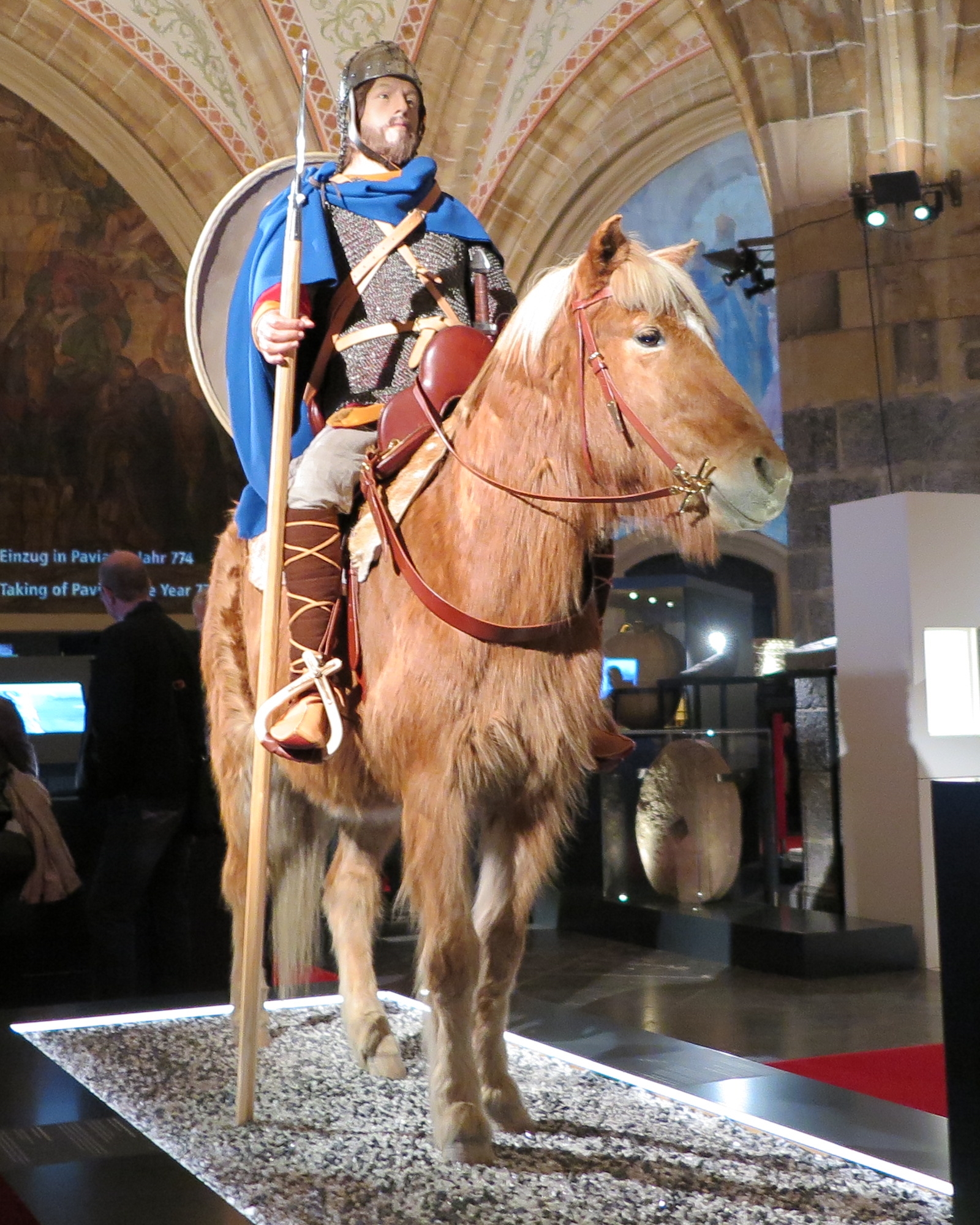 While
While
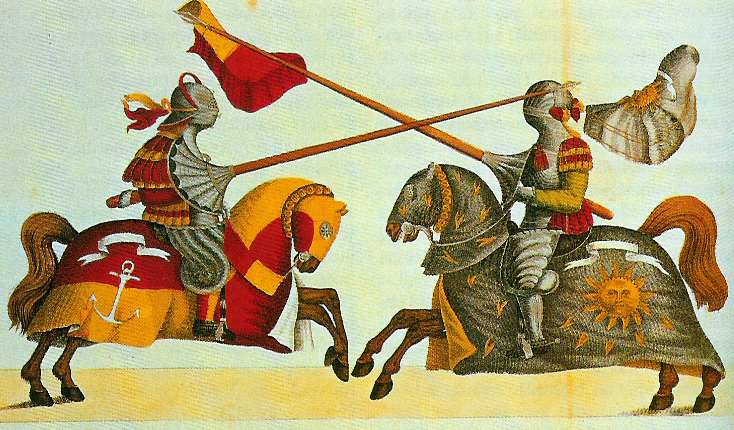 Tournaments and hastiludes began in the 11th century as both a sport and to provide training for battle. Usually taking the form of a melee, the participants used the horses,
Tournaments and hastiludes began in the 11th century as both a sport and to provide training for battle. Usually taking the form of a melee, the participants used the horses,
 The most well-known horse of the medieval era of Europe is the destrier, known for carrying knights into war. However, most knights and mounted
The most well-known horse of the medieval era of Europe is the destrier, known for carrying knights into war. However, most knights and mounted
 There is dispute in medievalist circles over the size of the war horse, with some notable historians claiming a size of , as large as a modern Shire horse. However, there are practical reasons for this dispute. Analysis of existing horse armour located in the Royal Armouries indicates the equipment was originally worn by horses of , or about the size and build of a modern
There is dispute in medievalist circles over the size of the war horse, with some notable historians claiming a size of , as large as a modern Shire horse. However, there are practical reasons for this dispute. Analysis of existing horse armour located in the Royal Armouries indicates the equipment was originally worn by horses of , or about the size and build of a modern  Perhaps one reason for the pervasive belief that the medieval war horse had to be of draught horse type is the assumption, still held by many, that medieval armour was heavy. In fact, even the heaviest tournament armour (for knights) weighed little more than , and field (war) armour ; barding, or horse armour, rarely weighed more than . Allowing for the weight of the rider and other equipment, horses can carry approximately 30% of their weight; thus such loads could certainly be carried by a heavy riding horse in the range, and a draught horse was not needed.
Although a large horse is not required to carry an armoured knight, it is held by some historians that a large horse was desirable to increase the power of a lance strike. However, practical experiments by re-enactors have suggested that the rider's weight and strength is of more relevance than the size of the mount, and that little of the horse's weight is translated to the lance.Alvarez, Richard
Perhaps one reason for the pervasive belief that the medieval war horse had to be of draught horse type is the assumption, still held by many, that medieval armour was heavy. In fact, even the heaviest tournament armour (for knights) weighed little more than , and field (war) armour ; barding, or horse armour, rarely weighed more than . Allowing for the weight of the rider and other equipment, horses can carry approximately 30% of their weight; thus such loads could certainly be carried by a heavy riding horse in the range, and a draught horse was not needed.
Although a large horse is not required to carry an armoured knight, it is held by some historians that a large horse was desirable to increase the power of a lance strike. However, practical experiments by re-enactors have suggested that the rider's weight and strength is of more relevance than the size of the mount, and that little of the horse's weight is translated to the lance.Alvarez, Richard
"Saddle, Lance and Stirrup: An Examination of the Mechanics of Shock Combat and the Development of Shock Tactics"
. ''Classical Fencing''. Retrieved 2007-03-08. Further evidence for a 14-16 hand () war horse is that it was a matter of pride to a knight to be able to vault onto his horse in full armour, without touching the
 Riding horses were used by a variety of people during the Middle Ages, and so varied greatly in quality, size and breeding. Knights and nobles kept riding horses in their war-trains, saving their warhorses for the battle. The names of horses referred to a ''type'' of horse, rather than a breed. Many horses were named by the region where they or their immediate ancestors were foaled. For example, in Germany, Hungarian horses were commonly used for riding. Individual horses were often described by their gait (' trotters' or ' amblers'), by their colouring, or by the name of their breeder.
The most typical riding horse was known as a
Riding horses were used by a variety of people during the Middle Ages, and so varied greatly in quality, size and breeding. Knights and nobles kept riding horses in their war-trains, saving their warhorses for the battle. The names of horses referred to a ''type'' of horse, rather than a breed. Many horses were named by the region where they or their immediate ancestors were foaled. For example, in Germany, Hungarian horses were commonly used for riding. Individual horses were often described by their gait (' trotters' or ' amblers'), by their colouring, or by the name of their breeder.
The most typical riding horse was known as a
 The Romans had used a two-field crop rotation agricultural system, but from the 8th century on, a three-field system became more common. One field would be sown with a winter crop, the second with a spring crop, and the third left fallow. This allowed a greater amount of spring crop of oats to be grown, which provided
The Romans had used a two-field crop rotation agricultural system, but from the 8th century on, a three-field system became more common. One field would be sown with a winter crop, the second with a spring crop, and the third left fallow. This allowed a greater amount of spring crop of oats to be grown, which provided
 The development of equestrian technology proceeded at a similar pace as the development of
The development of equestrian technology proceeded at a similar pace as the development of
"Who Invented Horseshoeing?"
''Science of Motion'', Retrieved on 2011-11-06. Additional archaeological evidence suggests they were used in Siberia during the 9th and 10th centuries, and had spread to
Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. World Decade Secretariat.
A theory known as The Great Stirrup Controversy argues that the advantages in warfare that stemmed from use of the stirrup led to the birth of feudalism itself. Other scholars, however, dispute this assertion, suggesting that stirrups provided little advantage in shock warfare, being useful primarily for allowing a rider to lean farther to the left and right on the saddle while fighting, and simply reduce the risk of falling off. Therefore, it is argued, they are not the reason for the switch from infantry to cavalry in Medieval militaries, nor the reason for the emergence of Feudalism. There was a variety of headgear used to control horses, predominantly
 A significant development which increased the importance and use of horses in
A significant development which increased the importance and use of horses in

 It was not uncommon for a girl to learn her father's trade and for a woman to share her husband's trade, since the entire family often helped run medieval shops and farms. Many guilds also accepted the membership of widows, so they might continue their husband's business. Under this system, some women trained in horse-related trades, and there are records of women working as farriers and saddle-makers. On farms, where every hand was needed, excessive emphasis on division of labour was impracticable, and women often worked alongside men (on their own farms or as hired help), leading the farm horses and oxen, and managing their care.
Despite the difficulties of travel, it was customary for many people, including women, to travel long distances. Upper-class wives frequently accompanied their husbands on crusade or to tournaments, and many women traveled for social or family engagements; both nuns and laywomen would perform pilgrimages. When not on foot, women would usually travel on horseback or, if weakened or infirm, be carried in a wagon or a litter. If roads permitted, women sometimes rode in early carriages developed from freight wagons, pulled by three or four horses. After the invention of better suspension systems, travel in carriages became more comfortable. Women of the nobility also rode horses for sport, accompanying men in activities that included
It was not uncommon for a girl to learn her father's trade and for a woman to share her husband's trade, since the entire family often helped run medieval shops and farms. Many guilds also accepted the membership of widows, so they might continue their husband's business. Under this system, some women trained in horse-related trades, and there are records of women working as farriers and saddle-makers. On farms, where every hand was needed, excessive emphasis on division of labour was impracticable, and women often worked alongside men (on their own farms or as hired help), leading the farm horses and oxen, and managing their care.
Despite the difficulties of travel, it was customary for many people, including women, to travel long distances. Upper-class wives frequently accompanied their husbands on crusade or to tournaments, and many women traveled for social or family engagements; both nuns and laywomen would perform pilgrimages. When not on foot, women would usually travel on horseback or, if weakened or infirm, be carried in a wagon or a litter. If roads permitted, women sometimes rode in early carriages developed from freight wagons, pulled by three or four horses. After the invention of better suspension systems, travel in carriages became more comfortable. Women of the nobility also rode horses for sport, accompanying men in activities that included
Warhorse: the archaeology of a medieval revolution?
AHRC funded research project by the University of Exeter and the University of East Anglia {{good article Transport in the Middle Ages Warfare of the Middle Ages Horse history and evolution Types of horse Medieval society Horse trade
 Horses in the Middle Ages differed in size, build and breed from the modern horse, and were, on average, smaller. They were also more central to society than their modern counterparts, being essential for war, agriculture, and transport.
Consequently, specific types of horse developed, many of which have no modern equivalent. While an understanding of modern horse breeds and
Horses in the Middle Ages differed in size, build and breed from the modern horse, and were, on average, smaller. They were also more central to society than their modern counterparts, being essential for war, agriculture, and transport.
Consequently, specific types of horse developed, many of which have no modern equivalent. While an understanding of modern horse breeds and equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, Driving (horse), driving, and Equestrian vaulting, vaulting ...
is vital for any analysis of the medieval horse, researchers also need to consider documentary (both written and pictorial) and archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence.
Horses in the Middle Ages were rarely differentiated by breed, but rather by use. This led them to be described, for example, as " chargers" (war horses), " palfreys" (riding horses), cart horses or packhorse
A packhorse, pack horse, or sumpter refers to a horse, mule, donkey, or pony used to carry goods on its back, usually in sidebags or panniers. Typically packhorses are used to cross difficult terrain, where the absence of roads prevents the use of ...
s. Reference is also given to their place of origin, such as "Spanish horses," but whether this referred to one breed or several is unknown. Another difficulty arising during any study of medieval documents or literature is the flexibility of the medieval languages, where several words can be used for one thing (or, conversely, several objects are referred to by one word). Words such as ' courser' and 'charger' are used interchangeably (even within one document), and where one epic may speak disparagingly of a rouncey, another praises its skill and swiftness.
Significant technological advances in equestrian equipment, often introduced from other cultures, allowed for significant changes in both warfare and agriculture. In particular, improved designs for the solid-treed saddle as well as the arrival of the stirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ( ...
, horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
and horse collar were significant advances in medieval society.
Consequently, the assumptions and theories developed by historians are not definitive, and debate still rages on many issues, such as the breeding or size of the horse, and a number of sources must be consulted in order to understand the breadth of the subject.
Breeding
 During the
During the Decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
and the Early Middle Ages, much of the quality breeding stock developed during the classical period was lost due to uncontrolled breeding and had to be built up again over the following centuries.Carey et al., p. 112 In the west, this may have been due in part to the reliance of the British and Scandinavians on infantry-based warfare, where horses were only used for riding and pursuit.
However, there were exceptions; in the 7th century a Merovingian kingdom still retained at least one active Roman horse-breeding centre.Nicolle, p. 267 The Spanish also retained many quality horses, in part due to the historic reputation of the region as a horse-breeding land, and partially due to the cultural influences related to the Islamic conquest of the Iberian peninsula between the 8th and 15th centuries.Bennett (1998)
The origins of the medieval war horse are obscure, although it is believed they had some Barb and Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
blood through the Spanish Jennet, a forerunner to the modern Friesian and Andalusian horse
The Andalusian, also known as the Pure Spanish Horse or PRE (Spanish language literally translates to “Spanish pure breed”. This name is sometimes capitalized when used in English-language publications, but is all lower-case in Spanish, wh ...
.Bennett, Deb (2004"The Spanish Mustang: The Origin and Relationships of the Mustang, Barb, and Arabian Horse"
. ''Frank Hopkins''. Retrieved 2008-08-14. It is also possible that other sources of oriental bloodstock came from what was called the '' Nisaean breed'' (possibly akin to the Turkoman horse) from Iran and Anatolia, another type of oriental horse brought back from the Crusades. "Spanish" horses, whatever their breeding, were the most expensive. In fact, in Germany the word ''spanjol'' became the term for quality war horses. However, German literary sources also refer to fine horses from Scandinavia.Bumke, p. 178 France also produced good war horses. Some scholars attribute this to the strong
Feudal society
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
there,Gies & Gies, p. 88 but an equally probable explanation is the historic influence of the Roman horse breeding traditions preserved by the Merovingians, combined with the addition of valuable Spanish and oriental bloodstock captured in the wake of the victory of Charles Martel over the Islamic Umayyad invaders at the Battle of Tours in 732. Following this battle, the Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
s began to increase their heavy cavalry, which resulted in the seizure of land (for fodder production), and a change in tribute payment from cattle to horses.
As the importance of horse breeding to successful warfare was realized, planned breeding programs increased. Many changes were due to the influence of Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
culture through both the Crusades and the Moorish invasions
The Muslim conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (), also known as the Arab conquest of Spain, by the Umayyad Caliphate occurred between approximately 711 and the 720s. The conquest resulted in the destruction of the Christian Visigothic Kingdom of ...
of Spain; the Arabs kept extensive pedigrees of their Barb and Arabian horses via an oral tradition. Some of the earliest written pedigrees in recorded European history were kept by Carthusian monks, who were among those who bred the Spanish Jennet. Because they could read and write, thus kept careful records, monastics were given the responsibility for horse breeding by certain members of the nobility, particularly in Spain. In England, a common source of warhorses were the wild moorland ponies, which were rounded up annually by horse-breeders, including the Cistercians
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint ...
, for use as campaign riding horses, or light cavalry; one such breed was the Fell pony, which had similar ancestry to the Friesian horse.
It is also hard to trace what happened to the bloodlines of destriers when this type seems to disappear from record during the 17th century.Prestwich, p. 30 Many modern draft breeds claim some link to the medieval "great horse," with some historians considering breeds such as the Percheron, Belgian and Suffolk Punch likely descendants of the destrier. However, other historians discount this theory, since the historical record suggests the medieval warhorse was quite a different 'type' to the modern draught horse. Such a theory would suggest the war horses were crossed once again with "cold blooded" work horses, since war horses, and the destrier in particular, were renowned for their hot-blooded nature.
Types of horse
Throughout the period, horses were rarely considered breeds, but instead were defined by ''type'': by describing their purpose or their physical attributes. Many of the definitions were not precise, or were interchangeable. Prior to approximately the 13th century, few pedigrees were written down. Thus, many terms for horses in the Middle Ages did not refer to breeds as we know them today, but rather described appearance or purpose. One of the best-known of the medieval horses was the destrier, renowned and admired for its capabilities in war. It was well trained, and was required to be strong, fast and agile. A 14th-century writer described them as "tall and majestic and with great strength". In contemporary sources, the destrier was frequently referred to as the "great horse" because of its size and reputation.Oakeshott (1998), p. 11 Being a subjective term, it gives no firm information about its actual height or weight, but since the average horse of the time was , a "great horse" by medieval standards might appear small to our modern eyes. The destrier was highly prized by knights and men-at-arms, but was actually not very common, and appears to have been most suited to the joust.
Coursers were generally preferred for hard battle as they were light, fast and strong. They were valuable, but not as costly as the destrier. They were also used frequently for
One of the best-known of the medieval horses was the destrier, renowned and admired for its capabilities in war. It was well trained, and was required to be strong, fast and agile. A 14th-century writer described them as "tall and majestic and with great strength". In contemporary sources, the destrier was frequently referred to as the "great horse" because of its size and reputation.Oakeshott (1998), p. 11 Being a subjective term, it gives no firm information about its actual height or weight, but since the average horse of the time was , a "great horse" by medieval standards might appear small to our modern eyes. The destrier was highly prized by knights and men-at-arms, but was actually not very common, and appears to have been most suited to the joust.
Coursers were generally preferred for hard battle as they were light, fast and strong. They were valuable, but not as costly as the destrier. They were also used frequently for hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
.
A more general-purpose horse was the rouncey (also ''rounsey''), which could be kept as a riding horse or trained for war. It was commonly used by squires, men-at-arms
A man-at-arms was a soldier of the High Medieval to Renaissance periods who was typically well-versed in the use of arms and served as a fully-armoured heavy cavalryman. A man-at-arms could be a knight, or other nobleman, a member of a knig ...
or poorer knights. A wealthy knight would keep rounceys for his retinue
A retinue is a body of persons "retained" in the service of a noble, royal personage, or dignitary; a ''suite'' (French "what follows") of retainers.
Etymology
The word, recorded in English since circa 1375, stems from Old French ''retenue'', it ...
. Sometimes the expected nature of warfare dictated the choice of horse; when a summons to war was sent out in England, in 1327, it expressly requested rounceys, for swift pursuit, rather than destriers. Rounceys were sometimes used as pack horses (but never as cart horses).
The well-bred palfrey, which could equal a destrier in price, was popular with nobles and highly ranked knights for riding, hunting and ceremonial use.Oakeshott (1998), p. 14 Ambling
An ambling gait or amble is any of several four-beat intermediate horse gaits, all of which are faster than a walk but usually slower than a canter and always slower than a gallop. Horses that amble are sometimes referred to as "gaited", particu ...
was a desirable trait in a palfrey, as the smooth gait allowed the rider to cover long distances quickly in relative comfort.
Other horse types included the jennet, a small horse first bred in Spain from Barb and Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
bloodstock. Their quiet and dependable nature, as well as size, made them popular as riding horses for ladies; however, they were also used as cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
horses by the Spanish.
The hobby was a lightweight horse, about , developed in Ireland from Spanish or Libyan (Barb) bloodstock. This type of quick and agile horse was popular for skirmishing, and was often ridden by light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily rai ...
known as '' Hobelars''. Hobbies were used successfully by both sides during the Wars of Scottish Independence, with Edward I of England trying to gain advantage by preventing Irish exports of the horses to Scotland. Robert Bruce employed the hobby for his guerilla warfare and mounted raids, covering a day.
Horses in warfare
 While
While light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily rai ...
had been used in warfare for many centuries, the medieval era saw the rise of heavy cavalry, particularly the European knight. Historians are uncertain when the use of heavy cavalry in the form of mounted shock troops first occurred, but the technique had become widespread by the mid-12th century. The heavy cavalry charge itself was not a common occurrence in warfare. Pitched battles were avoided if at all possible, with most offensive warfare in the early Middle Ages taking the form of sieges, or swift mounted raids called ''chevauchée
A ''chevauchée'' (, "promenade" or "horse charge", depending on context) was a raiding method of medieval warfare for weakening the enemy, primarily by burning and pillaging enemy territory in order to reduce the productivity of a region, in add ...
s'', with the warriors lightly armed on swift horses and their heavy war horses safely in the stable. Pitched battles were sometimes unavoidable, but were rarely fought on land suitable for heavy cavalry. While mounted riders remained effective for initial attacks, by the 14th century, it was common for knights to dismount to fight. Horses were sent to the rear, and kept ready for pursuit.Sadler, p. 32
By the Late Middle Ages (approx 1300-1550), large battles became more common, probably because of the success of infantry tactics and changes in weaponry. However, because such tactics left the knight unmounted, the role of the war horse also changed. By the 17th century, the medieval charger had become a thing of the past, replaced by lighter, unarmoured horses.
Throughout the period, light horse, or ''prickers'', were used for scouting and reconnaissance; they also provided a defensive screen for marching armies. Large teams of draught horses, or oxen, were used for pulling the heavy early cannon. Other horses pulled wagons and carried supplies for the armies.
Tournaments
 Tournaments and hastiludes began in the 11th century as both a sport and to provide training for battle. Usually taking the form of a melee, the participants used the horses,
Tournaments and hastiludes began in the 11th century as both a sport and to provide training for battle. Usually taking the form of a melee, the participants used the horses, armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
and weapons of war. The sport of jousting grew out of the tournament and, by the 15th century, the art of tilting became quite sophisticated. In the process, the pageantry and specialization became less war-like, perhaps because of the knight's changing role in war.
Horses were specially bred for the joust, and heavier horse armour developed. However, this did not necessarily lead to significantly larger horses. Interpreters at the Royal Armouries, Leeds, re-created the joust, using specially bred horses and replica armour. Their horses accurately represented the medieval mount, being compactly built and not particularly tall.
Types of war horse
 The most well-known horse of the medieval era of Europe is the destrier, known for carrying knights into war. However, most knights and mounted
The most well-known horse of the medieval era of Europe is the destrier, known for carrying knights into war. However, most knights and mounted men-at-arms
A man-at-arms was a soldier of the High Medieval to Renaissance periods who was typically well-versed in the use of arms and served as a fully-armoured heavy cavalryman. A man-at-arms could be a knight, or other nobleman, a member of a knig ...
rode smaller horses known as coursers and rounceys. (A common generic name for medieval war horses was ''charger,'' which was interchangeable with the other terms). In Spain, the jennet was used as a light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily rai ...
horse.
Stallion
A stallion is a male horse that has not been gelded (castrated).
Stallions follow the conformation and phenotype of their breed, but within that standard, the presence of hormones such as testosterone may give stallions a thicker, "cresty" nec ...
s were often used as war horses in Europe due to their natural aggression and hot-blooded tendencies. A 13th-century work describes destriers "biting and kicking" on the battlefield,Bumke, p. 175 and, in the heat of battle, war horses were often seen fighting each other. However, the use of mares by European warriors cannot be discounted from literary references.Bumke, p. 177 Mares were the preferred war horse of the Moors.Edwards They also were preferred by the Mongols.
War horses were more expensive than normal riding horses, and destriers the most prized, but figures vary greatly from source to source. Destriers are given a values ranging from seven times the price of an ordinary horse to 700 times. The Bohemian king Wenzel II rode a horse "valued at one thousand marks" in 1298. At the other extreme, a 1265 French ordinance ruled that a squire could not spend more than twenty marks on a rouncey.Oakeshott (1998), p. 12 Knights were expected to have at least one war horse (as well as riding horses and packhorses), with some records from the later Middle Ages showing knights bringing twenty-four horses on campaign. Five horses was perhaps the standard.
Size of war horses
 There is dispute in medievalist circles over the size of the war horse, with some notable historians claiming a size of , as large as a modern Shire horse. However, there are practical reasons for this dispute. Analysis of existing horse armour located in the Royal Armouries indicates the equipment was originally worn by horses of , or about the size and build of a modern
There is dispute in medievalist circles over the size of the war horse, with some notable historians claiming a size of , as large as a modern Shire horse. However, there are practical reasons for this dispute. Analysis of existing horse armour located in the Royal Armouries indicates the equipment was originally worn by horses of , or about the size and build of a modern field hunter
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
or ordinary riding horse.Gravett, p. 59 Research undertaken at the Museum of London, using literary, pictorial and archaeological sources, supports military horses of , distinguished from a riding horse by its strength and skill, rather than its size. This average does not seem to vary greatly across the medieval period. Horses appear to have been selectively bred for increased size from the 9th and 10th centuries, and by the 11th century the average warhorse was probably , a size verified by studies of Norman horseshoes as well as the depictions of horses on the Bayeux Tapestry. Analysis of horse transports suggests 13th-century destriers were a stocky build, and no more than . Three centuries later, warhorses were not significantly bigger; the Royal Armouries used a Lithuanian Heavy Draught mare as a model for the statues displaying various 15th- and 16th-century horse armours, as her body shape was an excellent fit.
 Perhaps one reason for the pervasive belief that the medieval war horse had to be of draught horse type is the assumption, still held by many, that medieval armour was heavy. In fact, even the heaviest tournament armour (for knights) weighed little more than , and field (war) armour ; barding, or horse armour, rarely weighed more than . Allowing for the weight of the rider and other equipment, horses can carry approximately 30% of their weight; thus such loads could certainly be carried by a heavy riding horse in the range, and a draught horse was not needed.
Although a large horse is not required to carry an armoured knight, it is held by some historians that a large horse was desirable to increase the power of a lance strike. However, practical experiments by re-enactors have suggested that the rider's weight and strength is of more relevance than the size of the mount, and that little of the horse's weight is translated to the lance.Alvarez, Richard
Perhaps one reason for the pervasive belief that the medieval war horse had to be of draught horse type is the assumption, still held by many, that medieval armour was heavy. In fact, even the heaviest tournament armour (for knights) weighed little more than , and field (war) armour ; barding, or horse armour, rarely weighed more than . Allowing for the weight of the rider and other equipment, horses can carry approximately 30% of their weight; thus such loads could certainly be carried by a heavy riding horse in the range, and a draught horse was not needed.
Although a large horse is not required to carry an armoured knight, it is held by some historians that a large horse was desirable to increase the power of a lance strike. However, practical experiments by re-enactors have suggested that the rider's weight and strength is of more relevance than the size of the mount, and that little of the horse's weight is translated to the lance.Alvarez, Richard"Saddle, Lance and Stirrup: An Examination of the Mechanics of Shock Combat and the Development of Shock Tactics"
. ''Classical Fencing''. Retrieved 2007-03-08. Further evidence for a 14-16 hand () war horse is that it was a matter of pride to a knight to be able to vault onto his horse in full armour, without touching the
stirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ( ...
. This arose not from vanity, but necessity: if unhorsed during battle, a knight would remain vulnerable if unable to mount by himself. In reality, of course, a wounded or weary knight might find it difficult, and rely on a vigilant squire to assist him. Incidentally, a knight's armour served in his favour in any fall. With his long hair twisted on his head to form a springy padding under his padded-linen hood, and his helm placed on top, he had head protection not dissimilar to a modern bicycle or equestrian helmet.
Transportation
Throughout the Middle Ages it was customary for people of all classes and background to travel, often widely. The households of the upper classes and royal courts moved between manors and estates; the demands of diplomacy, war andcrusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
s took men to distant countries; priests travelled between churches, monasteries and formed emissaries to Rome; people of all classes went on pilgrimage, or travelled to find work; others travelled as a pastime. Most people undertook small journeys on foot and hired horses for longer journeys.Clark, p. 8 For the upper classes, travel was accompanied by a great deal of pomp and display, with fine horses, large retinues and magnificent cavalcades in order to display their wealth as well as to ensure personal comfort.Labarge, p. xiii For example, in 1445, the English royal household contained 60 horses in the king's stable and 186 kept for "chariots" (carriages) and cart
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people.
It is different from the flatbed tr ...
s.
During much of the Middle Ages, there was no system of interconnected roads and bridges ''Roads and Bridges'' is a 2000 film by Abraham Lim about a Chinese-American man facing racial prejudice in the American Midwest. Lim plays the main character, Johnson Lee, a Chinese-American man who is placed on a Kansas road-cleaning crew by his p ...
. Though parts of Europe still had remnants of Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
s built before the collapse of the Roman Empire, most had long fallen into disrepair.Nicolle, p. 267 Because of the necessity to ride long distances over uncertain roads, smooth- gaited horses were preferred, and most ordinary riding horses were of greater value if they could do one of the smooth but ground-covering four-beat gaits collectively known as an '' amble'' rather than the more jarring trot.
Mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two pos ...
trains, for land travel, and barges, for river and canal travel, were the most common form of long-distance haulage, although wheeled horse-drawn vehicle
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have m ...
s were used for shorter journeys.Tuchman, p. 57 In areas with good roads, regular carrier services were established between major towns.Clark, pp. 9-10 However, because medieval roads were generally so poor, carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
s for human passengers were rare. When roads permitted, early carriages were developed from freight wagons. Carriage travel was made more comfortable in the late 14th century with the introduction of the ''chariot branlant'', which had strap suspension.Gies & Gies, p. 56
The speed of travel varied greatly. Large retinues could be slowed by the presence of slow-paced carts and litters, or by servants and attendants on foot, and could rarely cover more than fifteen to twenty miles a day. Small mounted companies might travel 30 miles a day. However, there were exceptions: stopping only for a change of horses midway, Richard II of England
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father die ...
once managed the 70 miles between Daventry and Westminster in a night.
For breeding, war and travel purposes, it was also necessary to be able to transport horses themselves. For this purpose, boats were adapted and built to be used as horse transports. William of Normandy's invasion of England
The term Invasion of England may refer to the following planned or actual invasions of what is now modern England, successful or otherwise.
Pre-English Settlement of parts of Britain
* The 55 and 54 BC Caesar's invasions of Britain.
* The 43 AD ...
in 1066 required the transfer of over 2000 horses from Normandy. Similarly, when travelling to France in 1285–6, Edward I of England ferried over 1000 horses across the English Channel to provide the royal party with transport.Clark, p. 6
Riding horses
 Riding horses were used by a variety of people during the Middle Ages, and so varied greatly in quality, size and breeding. Knights and nobles kept riding horses in their war-trains, saving their warhorses for the battle. The names of horses referred to a ''type'' of horse, rather than a breed. Many horses were named by the region where they or their immediate ancestors were foaled. For example, in Germany, Hungarian horses were commonly used for riding. Individual horses were often described by their gait (' trotters' or ' amblers'), by their colouring, or by the name of their breeder.
The most typical riding horse was known as a
Riding horses were used by a variety of people during the Middle Ages, and so varied greatly in quality, size and breeding. Knights and nobles kept riding horses in their war-trains, saving their warhorses for the battle. The names of horses referred to a ''type'' of horse, rather than a breed. Many horses were named by the region where they or their immediate ancestors were foaled. For example, in Germany, Hungarian horses were commonly used for riding. Individual horses were often described by their gait (' trotters' or ' amblers'), by their colouring, or by the name of their breeder.
The most typical riding horse was known as a rouncy
The term rouncey (also spelt rouncy or rounsey) was used during the Middle Ages to refer to an ordinary, all-purpose Horses in the Middle Ages, horse. They were used for Equestrianism, riding, but could also be trained for Horses in warfare, war. ...
. It was relatively small and inexpensive. The best riding horses were known as palfreys; another breed of horse was developed in the 14th century in England called a hackney, from which the modern term " hack" is derived. Because the hackney had a trotting gait it was not considered a comfortable ride for most purposes. Women sometimes rode rouncies, palfreys or small horses known as jennets.
Harness and pack horses
A variety of work horses were used throughout the Middle Ages. The pack horse (or "sumpter horse") carried equipment and belongings. Common riding horses, often called "hackneys", could be used as pack horses. Cart horses pulled wagons for trading and freight haulage, on farms, or as part of a military campaign. These draught horses were smaller than their modern counterparts; pictorial and archaeological evidence suggests that they were stout but short, approximately , and capable of drawing a load of per horse.Clark, pp. 27-28 Four-wheeled wagons and two-wheeled carts were more common in towns, such as London and, depending on type of vehicle and weight of the load, were usually pulled by teams of two, three, or four horses harnessed in tandem. Starting in the 12th century, in England the use of oxen to pull carts was gradually superseded by the use of horses, a process that extended through the 13th century. This change came because horse-drawn transport moved goods quicker and over greater distances than ox-drawn methods of transport.Dyer ''Making a Living'' p. 129Agriculture
 The Romans had used a two-field crop rotation agricultural system, but from the 8th century on, a three-field system became more common. One field would be sown with a winter crop, the second with a spring crop, and the third left fallow. This allowed a greater amount of spring crop of oats to be grown, which provided
The Romans had used a two-field crop rotation agricultural system, but from the 8th century on, a three-field system became more common. One field would be sown with a winter crop, the second with a spring crop, and the third left fallow. This allowed a greater amount of spring crop of oats to be grown, which provided fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agriculture, agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, domestic rabbit, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food g ...
for horses.Slocum, pp. 140-1 Another advance during the Middle Ages was the development of the heavy mouldboard plough, which allowed dense and heavy soils to be tilled easily; this technology required the use of larger teams of draught animals
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for t ...
including oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
and horses, as well as the adoption of larger fields.Slocum, pp. 141-2 Particularly after the 12th century, the increased use of both the horse collar and use of iron horse shoes allowed horsepower to be directed more efficiently.Slocum, p. 143 Horse teams usually were four horses, or perhaps six, as compared to eight oxen, and the lesser numbers compensated for the fact that the horses needed to be fed grain on top of pasture, unlike oxen. The increased speed of horses also allowed more land to be ploughed in a day, with an eight ox plough team averaging half of an acre per day, but a horse team averaged a full acre per day.
For farm work, such as ploughing and harrowing, the draught horses utilized for these purposes were, in England, called 'affers' and 'stotts' ( and in medieval Latin). These horses were usually smaller and cheaper than the cart horse. The difference between ''affers'' and ''stotts'' was largely nominal. Medieval English records from south-east England and East Anglia typically use the term 'stott', while 'affer' is used in documents from across the rest of the country. While oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
were traditionally used as work animals on farms, horses began to be used in greater numbers after the development of the horse collar. Oxen and horses were sometimes harnessed together. The transition from oxen to horses for farm work was documented in pictorial sources (for example, the 11th-century Bayeux tapestry depicts working horses), and also clear from the change from the Roman two-field crop-rotation system to a new three-field system, which increased the cultivation of fodder crops (predominantly oats, barley and beans). Horses were also used to process crops; they were used to turn the wheels in mills (such as corn mills), and transport crops to market.Gies & Gies, p. 273 The change to horse-drawn teams also meant a change in ploughs, as horses were more suited to a wheeled plough, unlike oxen.
Equestrian equipment and technological innovations
 The development of equestrian technology proceeded at a similar pace as the development of
The development of equestrian technology proceeded at a similar pace as the development of horse breeding
Horse breeding is reproduction in horses, and particularly the human-directed process of selective breeding of animals, particularly purebred horses of a given breed. Planned matings can be used to produce specifically desired characteristics in ...
and utilisation. The changes in warfare during the Early Middle Ages to heavy cavalry both precipitated and relied on the arrival of the stirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ( ...
, solid-treed saddle, and horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
from other cultures.
The development of the nailed horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
enabled longer, faster journeys on horseback, particularly in the wetter lands in northern Europe, and were useful for campaigns on varied terrains.Bennet et al., p. 74 By providing protection and support, nailed horse shoes also improved the efficiency of draught horse teams. Though the Romans had developed an iron " hipposandal" that resembled a hoof boot, there is much debate over the actual origins of the nailed horseshoe, though it does appear to be of European origin. There is little evidence of nailed-on shoes prior to AD 500 or 600, though there is speculation that the Celtic Gauls were the first to nail on metal horseshoes.McBane, pp. 57-60 The earliest clear written record of iron horseshoes is a reference to "crescent figured irons and their nails" in a list of cavalry equipment from AD 910.Heymering, Henry, RJF, CJF"Who Invented Horseshoeing?"
''Science of Motion'', Retrieved on 2011-11-06. Additional archaeological evidence suggests they were used in Siberia during the 9th and 10th centuries, and had spread to
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
soon afterward; by the 11th century, horseshoes were commonly used in Europe. By the time the Crusades began in 1096, horseshoes were widespread and frequently mentioned in various written sources.
Riding technology
The saddle with a solid tree provided a bearing surface to protect the horse from the weight of the rider. The Romans are credited with the invention of the solid-treed saddle, possibly as early as the 1st century BC, and it was widespread by the 2nd century AD.Hope, Chapters 1 and 2 Early medieval saddles resembled the Roman "four-horn" saddle, and were used without stirrups.Oakeshott (1998), p. 40 The development of the solid saddle tree was significant; it raised the rider above the horse's back, and distributed the rider's weight, reducing the pressure on any one part of the horse's back, thus greatly increasing the comfort of the horse and prolonging its useful life. Horses could carry more weight when distributed across a solid saddle tree. It also allowed a more built up seat to give the rider greater security in the saddle. From the 12th century on, the high war-saddle became more common, providing protection as well as added security. The built up cantle of a solid-treed saddle enabled horsemen to use lance more effectively. Beneath the saddle, caparisons or saddle cloths were sometimes worn; these could be decorated or embroidered with heraldic colours and arms.Wagner et al., p. 65 War horses could be equipped with additional covers, blankets and armour collectively referred to as barding; this could be for decorative or protective purposes. Early forms of horse armour, usually restricted to tournaments, comprised padded leather pieces, covered by a trapper (a decorated cloth), which was not particularly heavy.Barker, pp. 175-6 Mail and plate armour was also occasionally used; there are literary references to horse armour (an "iron blanket") starting in the late 12th century.Bumke, p. 176 The solid tree allowed for effective use of thestirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ( ...
. The stirrup was developed in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and in widespread use there by 477 AD. By the 7th century, primarily due to invaders from Central Asia, such as the Avars, stirrups arrived in Europe, and European riders had adopted them by the 8th century. Among other advantages, stirrups provided greater balance and support to the rider, which allowed the knight to use a sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
more efficiently without falling, especially against infantry.
The increased use of the stirrup from the 8th century on aided the warrior's stability and security in the saddle when fighting. This may have led to greater use of shock tactics, although a couched lance could be used effectively without stirrups. In particular, Charles Martel recognized the military potential of the stirrup, and distributed seized lands to his retainers on condition that they serve him by fighting in the new manner.World Decade for Cultural Development 1988–1997. United Nations Page 3Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. World Decade Secretariat.
A theory known as The Great Stirrup Controversy argues that the advantages in warfare that stemmed from use of the stirrup led to the birth of feudalism itself. Other scholars, however, dispute this assertion, suggesting that stirrups provided little advantage in shock warfare, being useful primarily for allowing a rider to lean farther to the left and right on the saddle while fighting, and simply reduce the risk of falling off. Therefore, it is argued, they are not the reason for the switch from infantry to cavalry in Medieval militaries, nor the reason for the emergence of Feudalism. There was a variety of headgear used to control horses, predominantly
bridle
A bridle is a piece of equipment used to direct a horse. As defined in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the "bridle" includes both the that holds a bit that goes in the mouth of a horse, and the reins that are attached to the bit.
Headgear w ...
s with assorted designs of bits. Many of the bits used during the Middle Ages resemble the bradoon, snaffle bit and curb bit that are still in common use today. However, they often were decorated to a greater degree: the bit rings or shanks were frequently covered with large, ornamental "bosses." Some designs were also more extreme and severe than those used today. The curb bit was known during the classical period, but was not generally used during the Middle Ages until the mid-14th century.Oakeshott (1998), p. 38 Some styles of snaffle bit used during the Middle Ages had the lower cheek extended, in the manner of the modern half-cheek or full cheek snaffle. Until the late 13th century, bridles generally had a single pair of reins; after this period it became more common for knights to use two sets of reins, similar to that of the modern double bridle, and often at least one set was decorated.Oakeshott (1998), p. 39
Spurs were commonly used throughout the period, especially by knights, with whom they were regularly associated. A young man was said to have "won his spurs" when he achieved knighthood. Wealthy knights and riders frequently wore decorated and filigreed spurs. Attached to the rider's heel by straps, spurs could be used both to encourage horses to quickly move forward or to direct lateral movement.Wagner et al., p. 66 Early spurs had a short shanks or "neck", placing the rowel relatively close to the rider's heel; further developments in the spur shape lengthened the neck, making it easier to touch the horse with less leg movement on the part of the rider.Wagner et al., p. 67
Harness technology
 A significant development which increased the importance and use of horses in
A significant development which increased the importance and use of horses in harness
A harness is a looped restraint or support. Specifically, it may refer to one of the following harness types:
* Bondage harness
* Child harness
* Climbing harness
* Dog harness
* Pet harness
* Five-point harness
* Horse harness
* Parrot harness
* ...
, particularly for plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
ing and other farm work, was the horse collar. The horse collar was invented in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
during the 5th century, arrived in Europe during the 9th century,Chamberlin and became widespread throughout Europe by the 12th century.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 317. It allowed horses to pull greater weight than they could when hitched to a vehicle by means of yokes or breastcollars used in earlier times.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 322. The yoke was designed for oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
and not suited to the anatomy of horses, it required horses to pull with their shoulders rather than using the power of their hindquarters. Harnessed in such a manner, horse teams could pull no more than 500 kg. The breastplate-style harness that had flat straps across the neck and chest of the animal, while useful for pulling light vehicles, was of little use for heavy work. These straps pressed against the horse's sterno-cephalicus muscle and trachea, which restricted breathing and reduced the pulling power of the horse.Needham, Volume 4, part 2, 305 Two horses harnessed with a breastcollar harness were limited to pulling a combined total of about .Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 312 In contrast, the horse collar rested on horses' shoulders and did not impede breathing. It allowed a horse to use its full strength, by pushing forward with its hindquarters into the collar rather than to pull with its shoulders. With the horse collar, a horse could provide a work effort of 50% more foot-pounds per second than an ox, because it could move at a greater speed, as well as having generally greater endurance and the ability to work more hours in a day. A single horse with a more efficient collar harness could draw a weight of about .
A further improvement was managed by altering the arrangement of the teams; by hitching horses one behind the other, rather than side by side, weight could be distributed more evenly, and pulling power increased.Gimpel, p. 34 This increase in horse power is demonstrated in the building accounts of Troyes
Troyes () is a commune and the capital of the department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within the Champagne wine region and is near to ...
, which show carters hauling stone from quarries distant; the carts weighed, on average, , on which of stone was regularly loaded, sometimes increasing to – a significant increase from Roman-era loads.Gimpel, p. 32
Horse trades and professions
The elite horseman of the Middle Ages was the knight. Generally raised from the middle and upper classes, the knight was trained from childhood in the arts of war and management of the horse. In most languages, the term for knight reflects his status as a horseman: the French ''chevalier'', Spanish ''caballero'' and German ''Ritter''. The French word for horse-mastery – ''chevalerie'' – gave its name to the highest concept of knighthood:chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christianity, Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours we ...
.
A large number of trades and positions arose to ensure the appropriate management and care of horses. In aristocratic households, the marshal
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
was responsible for all aspects relating to horses: the care and management of all horses from the chargers to the pack horses, as well as all travel logistics.Labarge, p. 41 The position of marshal (literally "horse servant") was a high one in court circles and the king's marshal (such as the Earl Marshal in England) was also responsible for managing many military matters.Norman, p. 133 Also present within the great households was the constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in criminal law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. A constable is commonly the rank of an officer within the police. Other peop ...
(or "count of the stable"), who was responsible for protection and the maintenance of order within the household and commanding the military component and, with marshals, might organise hastiludes and other chivalrous events. Within lower social groupings, the 'marshal' acted as a farrier. The highly skilled marshal made and fitted horseshoes, cared for the hoof, and provided general veterinary care
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutri ...
for horses; throughout the Middle Ages, a distinction was drawn between the marshal and the blacksmith, whose work was more limited.
A number of tradesmen dealt with the provision of horses. Horse dealers (frequently called "horse coursers" in England) bought and sold horses, and frequently had a reputation as dishonest figures, responsible for the brisk trade in stolen horses.Clark, p. 8 Others, such as the "hackneymen" offered horses for hire, and many formed large establishments on busy roads, often branding their horses to deter theft.
Women and horses

 It was not uncommon for a girl to learn her father's trade and for a woman to share her husband's trade, since the entire family often helped run medieval shops and farms. Many guilds also accepted the membership of widows, so they might continue their husband's business. Under this system, some women trained in horse-related trades, and there are records of women working as farriers and saddle-makers. On farms, where every hand was needed, excessive emphasis on division of labour was impracticable, and women often worked alongside men (on their own farms or as hired help), leading the farm horses and oxen, and managing their care.
Despite the difficulties of travel, it was customary for many people, including women, to travel long distances. Upper-class wives frequently accompanied their husbands on crusade or to tournaments, and many women traveled for social or family engagements; both nuns and laywomen would perform pilgrimages. When not on foot, women would usually travel on horseback or, if weakened or infirm, be carried in a wagon or a litter. If roads permitted, women sometimes rode in early carriages developed from freight wagons, pulled by three or four horses. After the invention of better suspension systems, travel in carriages became more comfortable. Women of the nobility also rode horses for sport, accompanying men in activities that included
It was not uncommon for a girl to learn her father's trade and for a woman to share her husband's trade, since the entire family often helped run medieval shops and farms. Many guilds also accepted the membership of widows, so they might continue their husband's business. Under this system, some women trained in horse-related trades, and there are records of women working as farriers and saddle-makers. On farms, where every hand was needed, excessive emphasis on division of labour was impracticable, and women often worked alongside men (on their own farms or as hired help), leading the farm horses and oxen, and managing their care.
Despite the difficulties of travel, it was customary for many people, including women, to travel long distances. Upper-class wives frequently accompanied their husbands on crusade or to tournaments, and many women traveled for social or family engagements; both nuns and laywomen would perform pilgrimages. When not on foot, women would usually travel on horseback or, if weakened or infirm, be carried in a wagon or a litter. If roads permitted, women sometimes rode in early carriages developed from freight wagons, pulled by three or four horses. After the invention of better suspension systems, travel in carriages became more comfortable. Women of the nobility also rode horses for sport, accompanying men in activities that included hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
and hawking.
Most medieval women rode astride. Although an early chair-like sidesaddle with handles and a footrest was available by the 13th century and allowed women of the nobility to ride while wearing elaborate gowns, they were not universally adopted during the Middle Ages. This was largely due to the insecure seat they offered, which necessitated a smooth-gaited horse being led by another handler. The sidesaddle did not become practical for everyday riding until the 16th-century development of the pommel horn that allowed a woman to hook her leg around the saddle and hence use the reins to control her own horse. Even then, sidesaddle riding remained a precarious activity until the invention of the second, "leaping horn" in the 19th century.
It was not unknown for women to ride war horses, and take their part in warfare. Joan of Arc is probably the most famous female warrior of the medieval period, but there were many others, including the Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as ...
who, armoured and mounted, led an army against her cousin Stephen of Blois, and Stephen's wife Matilda of Boulogne in the 12th century. The 15th-century writer Christine de Pizan
Christine de Pizan or Pisan (), born Cristina da Pizzano (September 1364 – c. 1430), was an Italian poet and court writer for King Charles VI of France and several French dukes.
Christine de Pizan served as a court writer in medieval France ...
advised aristocratic ladies that they must "know the laws of arms and all things pertaining to warfare, ever prepared to command her men if there is need of it."
See also
* Horse transports in the Middle Ages * Domestication of the horseNotes
References
* Barber, Richard (2005) ''The Reign of Chivalry'', 2nd Ed. UK: The Boydell Press * Barker, Juliet (1986) ''The Tournament in England: 1100-1400.'' UK: The Boydell Press *Bennet, Matthew; Bradbury, Jim; DeVries, Kelly; Dickie, Iain; Jestice, Phyllis G. (2005) ''Fighting Techniques of the Medieval World: AD 500-AD 1500'', London: Amber Books *Bennett, Deb (1998) ''Conquerors: The Roots of New World Horsemanship.'' Amigo Publications Inc; 1st edition. *Bumke, Joachim (2000) ''Courtly Culture: Literature and Society in the High Middle Ages,'' translated by Thomas Dunlap, USA: Overlook Duckworth (First published in 1986 as ''Höfische Kultur: Literatur und Gesellschaft im holen Mittelalter'' by Deutscher Taschenbuch Verlag) *Carey, Brian Todd; Allfree, Joshua B; Cairns, John (2006) ''Warfare in the Medieval World.'' UK: Pen & Sword Military *Chamberlin, J. Edward (2006) ''Horse: How the Horse Has Shaped Civilizations.'' Bluebridge *Clark, John (Ed) (2004) ''The Medieval Horse and its Equipment: c. 1150-c. 1450.'' Rev. 2nd Ed, UK: The Boydell Press * Davis, R. (1989) ''The Medieval Warhorse.'' London:Thames and Hudson * de Pisan, Christine. ''A Medieval Woman's Mirror of Honor: The Treasury of the City of Ladies.'' trans & ed. by C Willard and M Cosman, 1989 *Devereux, Frederick L. (1941) ''The Cavalry Manual of Horse Management'' * *Edwards, Gladys Brown (1973) ''The Arabian: War Horse to Show Horse.'' Arabian Horse Association of Southern California, Revised Collector's Edition, Rich Publishing *Gawronski, R.S. (2004) "Some Remarks on the Origins and Construction of the Roman Military Saddle." ''Archeologia (Archaeology)'', Volume 55 * Gies, Frances; Gies, Joseph (2005) ''Daily Life in Medieval Times.'' UK: Grange Books(originally published by Harper Collins in three volumes, 1969, 1974, 1990) *Gimpel, Jean (1977) ''The Medieval Machine: The Industrial Revolution of the Middle Ages.'' London: victor Gollancz Ltd * Gravett, Christopher (2002) ''English Medieval Knight 1300-1400''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing * Hobson, John M. (2004). ''The Eastern Origins of Western Civilisation''. Cambridge University Press. . *Hope, Lt. Col. C.E.G. (1972) ''The Horseman's Manual''. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. * Hyland, Ann (1994) ''The Medieval Warhorse From Byzantium to the Crusades.'' UK: Grange Books *Hyland, Ann (1998) ''The Warhorse 1250-1600.'' UK: Sutton Publishing * Labarge, Margaret Wade (1982) ''Medieval Travellers: The Rich and the Restless'', republished 2005 UK: Phoenix, * Leyser, Henrietta (1996) ''Medieval Women: A Social History of Women in England 450-1500.'' UK: Phoenix Press *McBane, Susan (1992) ''A Natural Approach to Horse Management'', London: Methuen *Needham, Joseph
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, init ...
(1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part 2, Mechanical Engineering''. Taipei: Caves Books Ltd.
* Nicolle, David (1999) ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom.'' UK: Brockhampton Press
*Norman, Vesey (1971) ''The Medieval Soldier'' repub. 2006 UK: Pen & Sword Military Classics
*Oakeshott, Ewart
Ronald Ewart Oakeshott (25 May 1916 – 30 September 2002) was a British illustrator, collector, and amateur historian who wrote prodigiously on medieval arms and armour. He was a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries, a Founder Member of the Ar ...
(1998) ''A Knight and His Horse.'' Rev. 2nd Ed. USA:Dufour Editions
*Oakeshott, Ewart (1999) ''A Knight and His Armour'' Rev. 2nd Ed. USA: Dufour Editions
* Power, Eileen (1975) ''Medieval Women.'' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
* Prestwich, Michael (1996) ''Armies and Warfare in the Middle Ages: The English Experience.'' New Haven: Yale University Press
* Sadler, John (2005) ''Border Fury: England and Scotland at War 1296-1568'', UK: Pearson Education Ltd,
* Slocum, Kay (2005) ''Medieval Civilisation.'' London: Laurence King Publishing
* Tuchman, Barbara W (1978) ''A Distant Mirror: The Calamitous 14th Century.'' New York: Ballantine Books
* Wagner, Eduard; Drobiná, Zoroslava; Durdik, Jan; (2000) ''Medieval Costume, Armour and Weapons'', trans. by Jean Layton, NY: Dover Publications (first published in 1956 as ''Kroje, zbroj a zbrane doby predhusitské a husitské''; first published in English in 1958 by Andrew Dakers)
* White Jr., Lynn. (1966)''Medieval Technology and Social Change''. Oxford University Press.
Further reading
* *External link
Warhorse: the archaeology of a medieval revolution?
AHRC funded research project by the University of Exeter and the University of East Anglia {{good article Transport in the Middle Ages Warfare of the Middle Ages Horse history and evolution Types of horse Medieval society Horse trade