Nonfigurative Art on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world.
Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world.
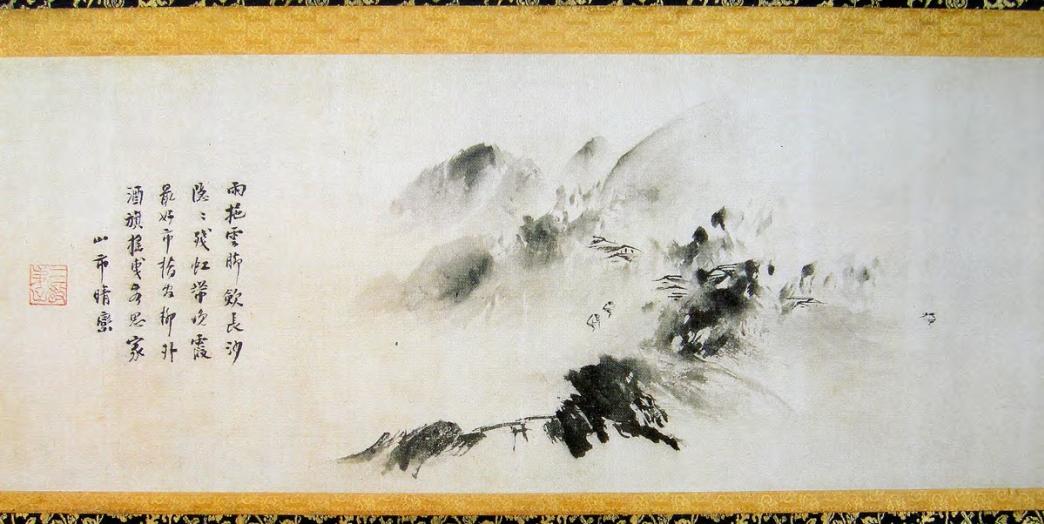 In Chinese painting, abstraction can be traced to the
In Chinese painting, abstraction can be traced to the
 Patronage from the church diminished and private patronage from the public became more capable of providing a livelihood for artists. Three
Patronage from the church diminished and private patronage from the public became more capable of providing a livelihood for artists. Three
 At the beginning of the 20th century
At the beginning of the 20th century
 Many of the abstract artists in Russia became Constructivists believing that art was no longer something remote, but life itself. The artist must become a technician, learning to use the tools and materials of modern production. ''Art into life!'' was
Many of the abstract artists in Russia became Constructivists believing that art was no longer something remote, but life itself. The artist must become a technician, learning to use the tools and materials of modern production. ''Art into life!'' was
 During the 1930s Paris became the host to artists from Russia, Germany, the Netherlands and other European countries affected by the rise of totalitarianism. Sophie Tauber and Jean Arp collaborated on paintings and sculpture using organic/geometric forms. The Polish Katarzyna Kobro applied mathematically based ideas to sculpture. The many types of abstraction now in close proximity led to attempts by artists to analyse the various conceptual and aesthetic groupings. An exhibition by forty-six members of the Cercle et Carré group organized by Joaquín Torres-García assisted by Michel Seuphor contained work by the Neo-Plasticists as well as abstractionists as varied as Kandinsky, Anton Pevsner and Kurt Schwitters. Criticized by Theo van Doesburg to be too indefinite a collection he published the journal ''Art Concret'' setting out a manifesto defining an abstract art in which the line, color and surface only, are the concrete reality. Abstraction-Création founded in 1931 as a more open group, provided a point of reference for abstract artists, as the political situation worsened in 1935, and artists again regrouped, many in London. The first exhibition of British abstract art was held in England in 1935. The following year the more international ''Abstract and Concrete'' exhibition was organized by Nicolete Gray including work by
During the 1930s Paris became the host to artists from Russia, Germany, the Netherlands and other European countries affected by the rise of totalitarianism. Sophie Tauber and Jean Arp collaborated on paintings and sculpture using organic/geometric forms. The Polish Katarzyna Kobro applied mathematically based ideas to sculpture. The many types of abstraction now in close proximity led to attempts by artists to analyse the various conceptual and aesthetic groupings. An exhibition by forty-six members of the Cercle et Carré group organized by Joaquín Torres-García assisted by Michel Seuphor contained work by the Neo-Plasticists as well as abstractionists as varied as Kandinsky, Anton Pevsner and Kurt Schwitters. Criticized by Theo van Doesburg to be too indefinite a collection he published the journal ''Art Concret'' setting out a manifesto defining an abstract art in which the line, color and surface only, are the concrete reality. Abstraction-Création founded in 1931 as a more open group, provided a point of reference for abstract artists, as the political situation worsened in 1935, and artists again regrouped, many in London. The first exhibition of British abstract art was held in England in 1935. The following year the more international ''Abstract and Concrete'' exhibition was organized by Nicolete Gray including work by
 During the Nazi rise to power in the 1930s many artists fled Europe to the United States. By the early 1940s the main movements in modern art, expressionism, cubism, abstraction, surrealism, and dada were represented in New York: Marcel Duchamp,
During the Nazi rise to power in the 1930s many artists fled Europe to the United States. By the early 1940s the main movements in modern art, expressionism, cubism, abstraction, surrealism, and dada were represented in New York: Marcel Duchamp,
File:Albert Gleizes, 1910-12, Les Arbres, oil on canvas, 41 x 27 cm. Reproduced in Du "Cubisme", 1912.jpg, Albert Gleizes, 1910–1912, ''Les Arbres (The Trees)'', oil on canvas, 41 × 27 cm. Reproduced in ''Du "Cubisme"'', 1912
File:Arthur Dove, 1911-12, Based on Leaf Forms and Spaces, pastel on unidentified support. Now lost.jpg, Arthur Dove, 1911–12, ''Based on Leaf Forms and Spaces'', pastel on unidentified support. Now lost
File:Francis Picabia, 1912, Tarentelle, oil on canvas, 73.6 x 92.1 cm, Museum of Modern Art, New York.jpg,
The term "Abstraction" spoken about at Museum of Modern Art by Nelson Goodman of Grove Art Online
Tate UK "Abstract art is..."
{{DEFAULTSORT:Abstract Art Abstract art, Art movements Dada, P Modern art Paintings by movement or period
 Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world.
Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world.
Western art
The art of Europe, or Western art, encompasses the history of visual art in Europe. European prehistoric art started as mobile Upper Paleolithic rock and cave painting and petroglyph art and was characteristic of the period between the Paleol ...
had been, from the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
up to the middle of the 19th century, underpinned by the logic of perspective and an attempt to reproduce an illusion of visible reality. By the end of the 19th century many artists felt a need to create a new kind of art which would encompass the fundamental changes taking place in technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
and philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
. The sources from which individual artists drew their theoretical arguments were diverse, and reflected the social and intellectual preoccupations in all areas of Western culture at that time.
Abstract art, non-figurative art, non-objective art, and non-representational art are all closely related terms. They have similar, but perhaps not identical, meanings.
Abstraction indicates a departure from reality in depiction of image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
ry in art. This departure from accurate representation can be slight, partial, or complete. Abstraction exists along a continuum. Even art that aims for verisimilitude of the highest degree can be said to be abstract, at least theoretically, since perfect representation is impossible. Artwork which takes liberties, e.g. altering color or form in ways that are conspicuous, can be said to be partially abstract. Total abstraction bears no trace of any reference to anything recognizable. In geometric abstraction
Geometric abstraction is a form of abstract art based on the use of geometric forms sometimes, though not always, placed in non-illusionistic space and combined into non-objective (non-representational) compositions. Although the genre was popu ...
, for instance, one is unlikely to find references to naturalistic entities. Figurative art
Figurative art, sometimes written as figurativism, describes artwork (particularly paintings and sculptures) that is clearly derived from real object sources and so is, by definition, representational. The term is often in contrast to abstract a ...
and total abstraction are almost mutually exclusive. But figurative and representational (or realistic) art often contain partial abstraction.
Both geometric abstraction and lyrical abstraction
Lyrical abstraction is either of two related but distinct trends in Post-war Modernist painting:
''European Abstraction Lyrique'' born in Paris, the French art critic Jean José Marchand being credited with coining its name in 1947, considered ...
are often totally abstract. Among the very numerous art movements that embody partial abstraction would be for instance fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
in which color is conspicuously and deliberately altered vis-a-vis reality, and cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
, which alters the forms of the real-life entities depicted.
History
Prehistoric
Much of the art of earlier cultures – signs and marks on pottery, textiles, and inscriptions and paintings on rock – used simple, geometric and linear forms which might have had a symbolic or decorative purpose. It is at this level of visual meaning that abstract art communicates. One can enjoy the beauty of Chinese calligraphy orIslamic calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is the artistic practice of handwriting and calligraphy, in the languages which use Arabic alphabet or the alphabets derived from it. It includes Arabic, Persian, Ottoman, and Urdu calligraphy.Chapman, Caroline (2012). '' ...
without being able to read it.
Classical antiquity
Islamic world
Islam's sometimes negative view of figurative art has led to the proliferation of complex non-figurative artistic expression across the Islamic world. Non-figurative Islamic art is nearly as old as Islam itself, and some of the oldest examples of it can be found on such early buildings as theDome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
. While Islamic art may have reservations about painting humans and animals, it does not, however, feel the same about plants and inanimate objects.
Islamic art traditionally revolves around calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "t ...
, tessellating geometric patterns, and vegetal motifs called arabesque
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foli ...
s. These elements can be found in all Islamic applied arts, including architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, rugmaking, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and por ...
, glassmaking
Glass production involves two main methods – the float glass process that produces sheet glass, and glassblowing that produces bottles and other containers. It has been done in a variety of ways during the history of glass.
Glass container ...
, and metalwork, as well as decorating the borders of otherwise figurative paintings.
As a result of the extensive dialogue between the Christian and Islamic world brought about by the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, Islamic patterns and techniques would also come to be applied to European decorative arts, especially in Italy and Spain. Prominent examples include Spanish Mudéjar art
Mudéjar art, also known as Mudéjar style, refers to a type of ornamentation and decoration used in the Iberian Peninsula, Iberian Christian kingdoms, primarily between the 13th and 16th centuries. It was applied to Romanesque architecture, Rom ...
and Venetian Gothic architecture
Venetian Gothic is the particular form of Italian Gothic architecture typical of Venice, originating in local building requirements, with some influence from Byzantine architecture, and some from Islamic architecture, reflecting Venice's trading ...
.
East Asia
 In Chinese painting, abstraction can be traced to the
In Chinese painting, abstraction can be traced to the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
painter Wang Mo (王墨), who is credited to have invented the splashed-ink painting style. While none of his paintings remain, this style is clearly seen in some Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
Paintings. The Chan buddhist painter Liang Kai (梁楷, c. 1140–1210) applied the style to figure painting in his "Immortal in splashed ink" in which accurate representation is sacrificed to enhance spontaneity linked to the non-rational mind of the enlightened. A late Song painter named Yu Jian, adept to Tiantai buddhism, created a series of splashed ink landscapes that eventually inspired many Japanese Zen painters. His paintings show heavily misty mountains in which the shapes of the objects are barely visible and extremely simplified. This type of painting was continued by Sesshu Toyo in his later years.
Another instance of abstraction in Chinese painting is seen in Zhu Derun
Zhu Derun ()(1294–1365), Zemin () by style name, Suiyang Shanren () by pseudonym, was a Chinese painter and poet in Yuan Dynasty. He was a native of Suiyang (now Shangqiu), Henan Province, and later lived in Suzhou.Cihai: Page 88. He was at ...
's ''Cosmic Circle''. On the left side of this painting is a pine tree in rocky soil, its branches laced with vines that extend in a disorderly manner to the right side of the painting in which a perfect circle (probably made with help of a compass) floats in the void. The painting is a reflection of the Daoist metaphysics in which chaos and reality are complementary stages of the regular course of nature.
In Tokugawa Japan, some Zen monk-painters created Enso, a circle who represents the absolute enlightenment. Usually made in one spontaneous brush stroke, it became the paradigm of the minimalist aesthetic that guided part of the Zen painting.
19th century
 Patronage from the church diminished and private patronage from the public became more capable of providing a livelihood for artists. Three
Patronage from the church diminished and private patronage from the public became more capable of providing a livelihood for artists. Three art movement
An art movement is a tendency or style in art with a specific common philosophy or goal, followed by a group of artists during a specific period of time, (usually a few months, years or decades) or, at least, with the heyday of the movement defin ...
s which contributed to the development of abstract art were Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
, Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating ...
and Expressionism
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it rad ...
. Artistic independence for artists was advanced during the 19th century. An ''objective interest in what is seen'', can be discerned from the paintings of John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
, J M W Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbule ...
, Camille Corot
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot ( , , ; July 16, 1796 – February 22, 1875), or simply Camille Corot, is a French landscape and portrait painter as well as a printmaker in etching. He is a pivotal figure in landscape painting and his vast o ...
and from them to the Impressionists who continued the ''plein air
''En plein air'' (; French for 'outdoors'), or ''plein air'' painting, is the act of painting outdoors.
This method contrasts with studio painting or academic rules that might create a predetermined look. The theory of 'En plein air' painting ...
'' painting of the Barbizon school.
Early intimations of a new art had been made by James McNeill Whistler
James Abbott McNeill Whistler (; July 10, 1834July 17, 1903) was an American painter active during the American Gilded Age and based primarily in the United Kingdom. He eschewed sentimentality and moral allusion in painting and was a leading pr ...
who, in his painting '' Nocturne in Black and Gold: The falling Rocket'', (1872), placed greater emphasis on visual sensation than the depiction of objects. Even earlier than that, with her 'spirit' drawings, Georgiana Houghton's choice to work with abstract shapes correlate with the unnatural nature of her subject, in a time when abstraction” isn't yet a concept (she organized an exhibit in 1871).
Expressionist
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it rad ...
painters explored the bold use of paint surface, drawing distortions and exaggerations, and intense color. Expressionists produced emotionally charged paintings that were reactions to and perceptions of contemporary experience; and reactions to Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating ...
and other more conservative directions of late 19th-century painting. The Expressionists drastically changed the emphasis on subject matter in favor of the portrayal of psychological states of being. Although artists like Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( , ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His best known work, ''The Scream'' (1893), has become one of Western art's most iconic images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the dr ...
and James Ensor drew influences principally from the work of the Post-Impressionists they were instrumental to the advent of abstraction in the 20th century.
Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a ...
had begun as an Impressionist but his aim – to make a logical construction of reality based on a view from a single point, with modulated color in flat areas – became the basis of a new visual art, later to be developed into Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
.
Additionally in the late 19th century in Eastern Europe mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
and early modernist religious philosophy as expressed by theosophist Mme. Blavatsky had a profound impact on pioneer geometric
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ca ...
artists like Hilma af Klint and Wassily Kandinsky. The mystical teaching of Georges Gurdjieff
George Ivanovich Gurdjieff (; rus, Гео́ргий Ива́нович Гурджи́ев, r=Geórgy Ivánovich Gurdzhíev, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪd͡ʑ ɡʊrd͡ʐˈʐɨ(j)ɪf; hy, Գեորգի Իվանովիչ Գյուրջիև; c. 1 ...
and P.D. Ouspensky
Pyotr Demianovich Ouspenskii (known in English as Peter D. Ouspensky; rus, Пётр Демья́нович Успе́нский, Pyotr Demyánovich Uspénskiy; 5 March 1878 – 2 October 1947) was a Russian esotericist known for his expositions ...
also had an important influence on the early formations of the geometric abstract styles of Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
and his colleagues in the early 20th century. The spiritualism
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase) ...
also inspired the abstract art of Kasimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich ; german: Kasimir Malewitsch; pl, Kazimierz Malewicz; russian: Казими́р Севери́нович Мале́вич ; uk, Казимир Северинович Малевич, translit=Kazymyr Severynovych ...
and František Kupka.
Early 20th century
Fauvism and Cubism
 At the beginning of the 20th century
At the beginning of the 20th century Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known prima ...
and several other young artists including the pre-cubist Georges Braque
Georges Braque ( , ; 13 May 1882 – 31 August 1963) was a major 20th-century List of French artists, French painter, Collage, collagist, Drawing, draughtsman, printmaker and sculpture, sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his all ...
, André Derain
André Derain (, ; 10 June 1880 – 8 September 1954) was a French artist, painter, sculptor and co-founder of Fauvism with Henri Matisse.
Biography
Early years
Derain was born in 1880 in Chatou, Yvelines, Île-de-France, just outside Paris. I ...
, Raoul Dufy and Jean Metzinger
Jean Dominique Antony Metzinger (; 24 June 1883 – 3 November 1956) was a major 20th-century French painter, theorist, writer, critic and poet, who along with Albert Gleizes wrote the first theoretical work on Cubism. His earliest works, from 1 ...
revolutionized the Paris art world with "wild", multi-colored, expressive landscapes and figure paintings that the critics called Fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
. The raw language of color as developed by the Fauves directly influenced another pioneer of abstraction, Wassily Kandinsky.
Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
, based on Cézanne's idea that all depiction of nature can be reduced to cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only r ...
, sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
and cone became, along with Fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
, the art movement that directly opened the door to abstraction in the early 20th century.
Early Abstract Art
During the 1912 Salon de la Section d'Or, where František Kupka exhibited his abstract painting ''Amorpha, Fugue en deux couleurs'' (''Fugue in Two Colors'') (1912), the poet Guillaume Apollinaire named the work of several artists includingRobert Delaunay
Robert Delaunay (12 April 1885 – 25 October 1941) was a French artist who, with his wife Sonia Delaunay and others, co-founded the Orphism art movement, noted for its use of strong colours and geometric shapes. His later works were more abstra ...
, Orphism. He defined it as, "the art of painting new structures out of elements that have not been borrowed from the visual sphere, but had been created entirely by the artist...it is a pure art."
Since the turn of the century, cultural connections between artists of the major European cities had become extremely active as they strove to create an art form equal to the high aspirations of modernism
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
. Ideas were able to cross-fertilize by means of artist's books, exhibitions and manifestos
A manifesto is a published declaration of the intentions, motives, or views of the issuer, be it an individual, group, political party or government. A manifesto usually accepts a previously published opinion or public consensus or promotes a ...
so that many sources were open to experimentation and discussion, and formed a basis for a diversity of modes of abstraction. The following extract from ''The World Backwards'' gives some impression of the inter-connectedness of culture at the time: "David Burliuk
David Davidovich Burliuk (Давид Давидович Бурлюк; 21 July 1882 – 15 January 1967) was a Russian-language poet, artist and publicist associated with the Futurist and Neo-Primitivist movements. Burliuk has been described as ...
's knowledge of modern art movements must have been extremely up-to-date, for the second Knave of Diamonds exhibition, held in January 1912 (in Moscow) included not only paintings sent from Munich, but some members of the German Die Brücke
The Brücke (Bridge), also Künstlergruppe Brücke or KG Brücke was a group of German expressionist artists formed in Dresden in 1905. Founding members were Fritz Bleyl, Erich Heckel, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl Schmidt-Rottluff. Later memb ...
group, while from Paris came work by Robert Delaunay
Robert Delaunay (12 April 1885 – 25 October 1941) was a French artist who, with his wife Sonia Delaunay and others, co-founded the Orphism art movement, noted for its use of strong colours and geometric shapes. His later works were more abstra ...
, Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known prima ...
and Fernand Léger
Joseph Fernand Henri Léger (; February 4, 1881 – August 17, 1955) was a French painting, painter, sculpture, sculptor, and film director, filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism (known as "tubism") which he gradually ...
, as well as Picasso. During the Spring David Burliuk gave two lectures on cubism and planned a polemical publication, which the Knave of Diamonds was to finance. He went abroad in May and came back determined to rival the almanac '' Der Blaue Reiter'' which had emerged from the printers while he was in Germany".
From 1909 to 1913 many experimental works in the search for this 'pure art' had been created by a number of artists: Francis Picabia
Francis Picabia (: born Francis-Marie Martinez de Picabia; 22January 1879 – 30November 1953) was a French avant-garde painter, poet and typographist. After experimenting with Impressionism and Pointillism, Picabia became associated with Cubism ...
painted '' Caoutchouc'', c. 1909, '' The Spring'', 1912, ''Dances at the Spring'' and ''The Procession, Seville'', 1912; Wassily Kandinsky painted ''Untitled (First Abstract Watercolor)'', 1913, ''Improvisation 21A'', the ''Impression'' series, and ''Picture with a Circle'' (1911); František Kupka had painted the Orphist works, ''Discs of Newton'' (Study for ''Fugue in Two Colors''), 1912 and ''Amorpha, Fugue en deux couleurs'' (''Fugue in Two Colors''), 1912; Robert Delaunay
Robert Delaunay (12 April 1885 – 25 October 1941) was a French artist who, with his wife Sonia Delaunay and others, co-founded the Orphism art movement, noted for its use of strong colours and geometric shapes. His later works were more abstra ...
painted a series entitled ''Simultaneous Windows'' and ''Formes Circulaires, Soleil n°2'' (1912–13); Léopold Survage
Léopold Frédéric Léopoldowitsch Survage (31 July 1879 – 31 October 1968) was a French painter of Finnish origin. Trained in Moscow, he identified with the Russian avant-garde before moving to Paris, where he shared a studio with Amedeo Modi ...
created ''Colored Rhythm'' (Study for the film), 1913; Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
, painted ''Tableau No. 1'' and ''Composition No. 11'', 1913.
With his expressive use of color and his free and imaginative drawing Henri Matisse comes very close to pure abstraction in ''French Window at Collioure'' (1914), ''View of Notre-Dame
''View of Notre-Dame'' (French: ''Une vue de Notre-Dame'') is an oil painting by Henri Matisse from 1914.
Experimental period
Along with works such as ''Woman on a High Stool'', it belongs to the "experimental period" of Matisse's oeuvre. Penti ...
'' (1914), and '' The Yellow Curtain'' from 1915.
And the search continued: The Rayist (Luchizm) drawings of Natalia Goncharova and Mikhail Larionov
Mikhail Fyodorovich Larionov (Russian: Михаи́л Фёдорович Ларио́нов; June 3, 1881 – May 10, 1964) was a Russian avant-garde painter who worked with radical exhibitors and pioneered the first approach to abstract Rus ...
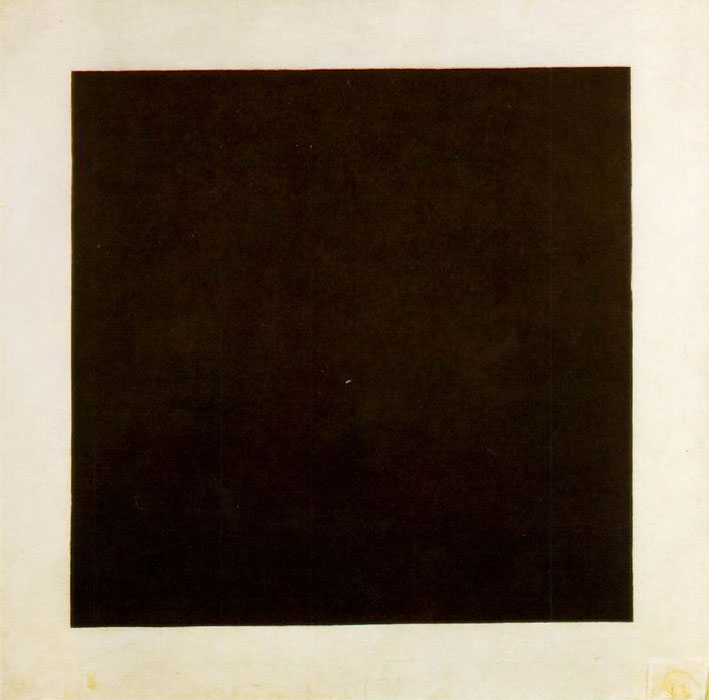
, used lines like rays of light to make a construction. Kasimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich ; german: Kasimir Malewitsch; pl, Kazimierz Malewicz; russian: Казими́р Севери́нович Мале́вич ; uk, Казимир Северинович Малевич, translit=Kazymyr Severynovych ...
completed his first entirely abstract work, the Suprematist, '' Black Square'', in 1915. Another of the Suprematist group' Liubov Popova, created the Architectonic Constructions and Spatial Force Constructions between 1916 and 1921. Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
was evolving his abstract language, of horizontal and vertical lines with rectangles of color, between 1915 and 1919, Neo-Plasticism
''De Stijl'' (; ), Dutch for "The Style", also known as Neoplasticism, was a Dutch art movement founded in 1917 in Leiden. De Stijl consisted of artists and architects. In a more narrow sense, the term ''De Stijl'' is used to refer to a body o ...
was the aesthetic which Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg and other in the group De Stijl intended to reshape the environment of the future.
Russian avant-garde
 Many of the abstract artists in Russia became Constructivists believing that art was no longer something remote, but life itself. The artist must become a technician, learning to use the tools and materials of modern production. ''Art into life!'' was
Many of the abstract artists in Russia became Constructivists believing that art was no longer something remote, but life itself. The artist must become a technician, learning to use the tools and materials of modern production. ''Art into life!'' was Vladimir Tatlin
Vladimir Yevgrafovich Tatlin ( – 31 May 1953) was a Russian and Soviet painter, architect and stage-designer. Tatlin achieved fame as the architect who designed The Monument to the Third International, more commonly known as Tatlin's Tower, whi ...
's slogan, and that of all the future Constructivists. Varvara Stepanova and Alexandre Exter and others abandoned easel painting and diverted their energies to theatre design and graphic works.
On the other side stood Kazimir Malevich, Anton Pevsner and Naum Gabo. They argued that art was essentially a spiritual activity; to create the individual's place in the world, not to organize life in a practical, materialistic sense. Many of those who were hostile to the materialist production idea of art left Russia. Anton Pevsner went to France, Gabo went first to Berlin, then to England and finally to America. Kandinsky studied in Moscow then left for the Bauhaus. By the mid-1920s the revolutionary period (1917 to 1921) when artists had been free to experiment was over; and by the 1930s only socialist realism was allowed.
Music
As visual art becomes more abstract, it develops some characteristics of music: an art form which uses the abstract elements of sound and divisions of time. Wassily Kandinsky, himself an amateur musician, was inspired by the possibility of marks and associative color ''resounding in the soul.'' The idea had been put forward by Charles Baudelaire, that all our senses respond to various stimuli but the senses are connected at a deeper aesthetic level. Closely related to this, is the idea that art has ''The spiritual dimension'' and can transcend 'every-day' experience, reaching a spiritual plane. The Theosophical Society popularized the ancient wisdom of the sacred books of India and China in the early years of the century. It was in this context thatPiet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
, Wassily Kandinsky, Hilma af Klint and other artists working towards an 'objectless state' became interested in the occult as a way of creating an 'inner' object.
The universal and timeless shapes found in geometry: the circle, square and triangle become the spatial elements in abstract art; they are, like color, fundamental systems underlying visible reality.
The Bauhaus
The Bauhaus at Weimar, Germany was founded in 1919 by Walter Gropius. The philosophy underlying the teaching program was unity of all the visual and plastic arts from architecture and painting to weaving and stained glass. This philosophy had grown from the ideas of the Arts and Crafts movement in England and the Deutscher Werkbund. Among the teachers were Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, Johannes Itten, Josef Albers, Anni Albers, and László Moholy-Nagy. In 1925 the school was moved to Dessau and, as the Nazi party gained control in 1932, The Bauhaus was closed. In 1937 an exhibition of degenerate art, 'Entartete Kunst' contained all types of avant-garde art disapproved of by the Nazi party. Then the exodus began: not just from the Bauhaus but from Europe in general; to Paris, London and America. Paul Klee went to Switzerland but many of the artists at the Bauhaus went to America.Abstraction in Paris and London
 During the 1930s Paris became the host to artists from Russia, Germany, the Netherlands and other European countries affected by the rise of totalitarianism. Sophie Tauber and Jean Arp collaborated on paintings and sculpture using organic/geometric forms. The Polish Katarzyna Kobro applied mathematically based ideas to sculpture. The many types of abstraction now in close proximity led to attempts by artists to analyse the various conceptual and aesthetic groupings. An exhibition by forty-six members of the Cercle et Carré group organized by Joaquín Torres-García assisted by Michel Seuphor contained work by the Neo-Plasticists as well as abstractionists as varied as Kandinsky, Anton Pevsner and Kurt Schwitters. Criticized by Theo van Doesburg to be too indefinite a collection he published the journal ''Art Concret'' setting out a manifesto defining an abstract art in which the line, color and surface only, are the concrete reality. Abstraction-Création founded in 1931 as a more open group, provided a point of reference for abstract artists, as the political situation worsened in 1935, and artists again regrouped, many in London. The first exhibition of British abstract art was held in England in 1935. The following year the more international ''Abstract and Concrete'' exhibition was organized by Nicolete Gray including work by
During the 1930s Paris became the host to artists from Russia, Germany, the Netherlands and other European countries affected by the rise of totalitarianism. Sophie Tauber and Jean Arp collaborated on paintings and sculpture using organic/geometric forms. The Polish Katarzyna Kobro applied mathematically based ideas to sculpture. The many types of abstraction now in close proximity led to attempts by artists to analyse the various conceptual and aesthetic groupings. An exhibition by forty-six members of the Cercle et Carré group organized by Joaquín Torres-García assisted by Michel Seuphor contained work by the Neo-Plasticists as well as abstractionists as varied as Kandinsky, Anton Pevsner and Kurt Schwitters. Criticized by Theo van Doesburg to be too indefinite a collection he published the journal ''Art Concret'' setting out a manifesto defining an abstract art in which the line, color and surface only, are the concrete reality. Abstraction-Création founded in 1931 as a more open group, provided a point of reference for abstract artists, as the political situation worsened in 1935, and artists again regrouped, many in London. The first exhibition of British abstract art was held in England in 1935. The following year the more international ''Abstract and Concrete'' exhibition was organized by Nicolete Gray including work by Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
, Joan Miró, Barbara Hepworth and Ben Nicholson. Hepworth, Nicholson and Gabo moved to the St. Ives group in Cornwall to continue their 'constructivist' work.
Late 20th century
 During the Nazi rise to power in the 1930s many artists fled Europe to the United States. By the early 1940s the main movements in modern art, expressionism, cubism, abstraction, surrealism, and dada were represented in New York: Marcel Duchamp,
During the Nazi rise to power in the 1930s many artists fled Europe to the United States. By the early 1940s the main movements in modern art, expressionism, cubism, abstraction, surrealism, and dada were represented in New York: Marcel Duchamp, Fernand Léger
Joseph Fernand Henri Léger (; February 4, 1881 – August 17, 1955) was a French painting, painter, sculpture, sculptor, and film director, filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism (known as "tubism") which he gradually ...
, Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
, Jacques Lipchitz, André Masson, Max Ernst, and André Breton, were just a few of the exiled Europeans who arrived in New York. The rich cultural influences brought by the European artists were distilled and built upon by local New York painters. The climate of freedom in New York allowed all of these influences to flourish. The art galleries that primarily had focused on European art began to notice the local art community and the work of younger American artists who had begun to mature. Certain artists at this time became distinctly abstract in their mature work. During this period Piet Mondrian's painting ''Composition No. 10'', 1939–1942, characterized by primary colors, white ground and black grid lines clearly defined his radical but classical approach to the rectangle and abstract art in general.
Some artists of the period defied categorization, such as Georgia O'Keeffe who, while a modernist abstractionist, was a pure maverick in that she painted highly abstract forms while not joining any specific group of the period.
Eventually American artists who were working in a great diversity of styles began to coalesce into cohesive stylistic groups. The best-known group of American artists became known as the Abstract expressionists and the New York School (art), New York School. In New York City there was an atmosphere which encouraged discussion and there was a new opportunity for learning and growing. Artists and teachers John D. Graham and Hans Hofmann became important bridge figures between the newly arrived European Modernists and the younger American artists coming of age. Mark Rothko, born in Russia, began with strongly surrealist imagery which later dissolved into his powerful color compositions of the early 1950s. The action painting, expressionistic gesture and the act of painting itself, became of primary importance to Jackson Pollock, Robert Motherwell, and Franz Kline. While during the 1940s Arshile Gorky's and Willem de Kooning's figurative work evolved into abstraction by the end of the decade. New York City became the center, and artists worldwide gravitated towards it; from other places in America as well.
21st century
Digital art, hard-edge painting,geometric abstraction
Geometric abstraction is a form of abstract art based on the use of geometric forms sometimes, though not always, placed in non-illusionistic space and combined into non-objective (non-representational) compositions. Although the genre was popu ...
, minimalism, lyrical abstraction
Lyrical abstraction is either of two related but distinct trends in Post-war Modernist painting:
''European Abstraction Lyrique'' born in Paris, the French art critic Jean José Marchand being credited with coining its name in 1947, considered ...
, op art, abstract expressionism, color field painting, monochrome painting, assemblage (art), assemblage, neo-Dada, shaped canvas painting, are a few directions relating to abstraction in the second half of the 20th century.
In the United States, ''Art as Object'' as seen in the Minimalist sculpture of Donald Judd and the paintings of Frank Stella are seen today as newer permutations. Other examples include Lyrical Abstraction and the sensuous use of color seen in the work of painters as diverse as Robert Motherwell, Patrick Heron, Kenneth Noland, Sam Francis, Cy Twombly, Richard Diebenkorn, Helen Frankenthaler, Joan Mitchell.
Elements
Analysis
One socio-historical explanation that has been offered for the growing prevalence of the abstract in modern art – an explanation linked to the name of Theodor W. Adorno – is that such abstraction is a response to, and a reflection of, the growing abstraction of social relations in industrial society. Frederic Jameson similarly sees modernist abstraction as a function of the abstract power of money, equating all things equally as exchange-values. The social ''content'' of abstract art is then precisely the abstract nature of social existence – legal formalities, bureaucratic impersonalization, information/power – in the world of late modernity. Analytical psychology#Post-Jungian approaches, Post-Jungians by contrast would see the quantum theories with their disintegration of conventional ideas of form and matter as underlying the divorce of the concrete and the abstract in modern art.Aniela Jaffé, in C. G. Jung ed., ''Man and his Symbols'' (1978) pp. 288–89, 303Gallery
Francis Picabia
Francis Picabia (: born Francis-Marie Martinez de Picabia; 22January 1879 – 30November 1953) was a French avant-garde painter, poet and typographist. After experimenting with Impressionism and Pointillism, Picabia became associated with Cubism ...
, 1912, ''Tarentelle'', oil on canvas, 73.6 × 92.1 cm, Museum of Modern Art, New York. Reproduced in ''Du "Cubisme"''
File:Vassily Kandinsky, 1912 - Improvisation 27, Garden of Love II.jpg, Wassily Kandinsky, 1912, ''Improvisation 27'' (''Garden of Love'' II), oil on canvas, 120.3 × 140.3 cm, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. Exhibited at the 1913 Armory Show
File:Pablo Picasso, 1913-14, Head (Tête), cut and pasted colored paper, gouache and charcoal on paperboard, 43.5 x 33 cm, Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh.jpg, Pablo Picasso, 1913–14, ''Head'' (''Tête''), cut and pasted colored paper, gouache and charcoal on paperboard, 43.5 × 33 cm, Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh
File:Porte-Fenetre a Collioure 1914.jpg, Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known prima ...
, 1914, ''French Window at Collioure'', Centre Georges Pompidou, Paris
File:Hilma af Klint Svanen.jpg, Hilma af Klint, ''Svanen'' (''The Swan''), No. 17, Group IX, Series SUW, October 1914–March 1915. This abstract work was never exhibited during af Klint's lifetime.
File:Theo van Doesburg Composition VII (the three graces).jpg, Theo van Doesburg, Neo-Plasticism
''De Stijl'' (; ), Dutch for "The Style", also known as Neoplasticism, was a Dutch art movement founded in 1917 in Leiden. De Stijl consisted of artists and architects. In a more narrow sense, the term ''De Stijl'' is used to refer to a body o ...
: 1917, ''Composition VII'' (''The Three Graces'')
File:Leger railway crossing.jpg, Fernand Léger
Joseph Fernand Henri Léger (; February 4, 1881 – August 17, 1955) was a French painting, painter, sculpture, sculptor, and film director, filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism (known as "tubism") which he gradually ...
1919, ''The Railway Crossing'', oil on canvas, 53.8 × 64.8 cm, The Art Institute of Chicago
File:Joseph Csaky, Deux figures, 1920, relief, limestone, polychrome, 80 cm, Kröller-Müller Museum, Otterlo, Holland.jpg, Joseph Csaky, ''Deux figures'', 1920, relief, limestone, polychrome, 80 cm, Kröller-Müller Museum, Otterlo
File:Albert Gleizes, 1921, Composition bleu et jaune (Composition jaune), oil on canvas, 200.5 x 110 cm DSC00547.jpg, Albert Gleizes, 1921, ''Composition bleu et jaune'' (''Composition jaune''), oil on canvas, 200.5 × 110 cm
File:Piet Mondrian - Lozenge Composition with Yellow, Black, Blue, Red, and Gray - 1921 - The Art Institute of Chicago.jpg, Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being ...
, ''Composition with Yellow, Black, Blue, Red, and Gray'', 1921, Art Institute of Chicago
File:Fire in the Evening.JPG, Paul Klee, ''Fire in the Evening'', 1929
File:Carlsund Rapid (1930).jpg, Otto Gustaf Carlsund, ''Rapid'' (1930), a Concrete Art restaurant mural, Stockholm
File:Newman-Onement 1.jpg, Barnett Newman, ''Onement 1'', 1948, Museum of Modern Art, New YorkSee also
; In other media * Abstract animation * Abstract comics * Abstract photography * Experimental film * Literary nonsense * Musique concréte * Noise musicReferences
Sources
* * * *External links
The term "Abstraction" spoken about at Museum of Modern Art by Nelson Goodman of Grove Art Online
Tate UK "Abstract art is..."
{{DEFAULTSORT:Abstract Art Abstract art, Art movements Dada, P Modern art Paintings by movement or period