Neuroinflammation Example on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neuroinflammation is
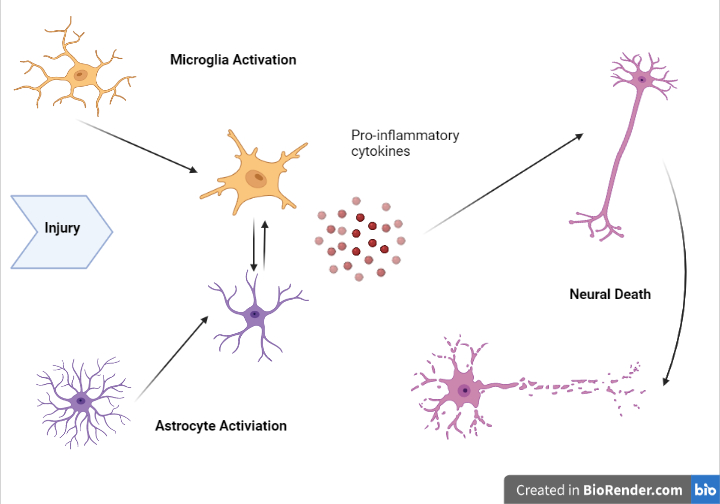 Viruses, bacteria, and other infectious agents activate the body’s defense systems and cause immune cells to protect the designed area from the damage. Some of these foreign pathogens can trigger a strong inflammatory response that can compromise the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and thus change the flow of inflammation in nearby tissue. The location along with the type of infection can determine what type of inflammatory response is activated and whether specific cytokines or immune cells will act.
Viruses, bacteria, and other infectious agents activate the body’s defense systems and cause immune cells to protect the designed area from the damage. Some of these foreign pathogens can trigger a strong inflammatory response that can compromise the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and thus change the flow of inflammation in nearby tissue. The location along with the type of infection can determine what type of inflammatory response is activated and whether specific cytokines or immune cells will act.

 As one of the major cytokines responsible for maintaining inflammatory balance, IL-6 can also be used as a biological marker to observe the correlation between age and neuroinflammation. The same levels of IL-6 observed in the brain after injury, have also been found in the elderly and indicate the potential for cognitive impairment to develop. The unnecessary upregulation of IL-6 in the elderly population is a result of dysfunctional mediation by glial cells that can lead to the priming of glial cells and result in a more sensitive neuroinflammatory response.
As one of the major cytokines responsible for maintaining inflammatory balance, IL-6 can also be used as a biological marker to observe the correlation between age and neuroinflammation. The same levels of IL-6 observed in the brain after injury, have also been found in the elderly and indicate the potential for cognitive impairment to develop. The unnecessary upregulation of IL-6 in the elderly population is a result of dysfunctional mediation by glial cells that can lead to the priming of glial cells and result in a more sensitive neuroinflammatory response.
 Exercise can help protect the mind and body by maintaining the brain’s internal environment, focusing on recruiting anti-inflammatory cytokines, and activating cellular processes that proactively protect against damage while also initiating recovery mechanisms. The ability of physical activity to stimulate immune defenses against neuroinflammation-related diseases has been observed in recent clinical studies. The application of various exercises under a range of different conditions resulted in higher neurological metabolism, stronger protection against free radicals, and stronger neuroplasticity against neurological diseases. The resulting increase in brain function was due to the induced change in gene expression, increase in trophic factors, and reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Exercise can help protect the mind and body by maintaining the brain’s internal environment, focusing on recruiting anti-inflammatory cytokines, and activating cellular processes that proactively protect against damage while also initiating recovery mechanisms. The ability of physical activity to stimulate immune defenses against neuroinflammation-related diseases has been observed in recent clinical studies. The application of various exercises under a range of different conditions resulted in higher neurological metabolism, stronger protection against free radicals, and stronger neuroplasticity against neurological diseases. The resulting increase in brain function was due to the induced change in gene expression, increase in trophic factors, and reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines.
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of the nervous tissue. It may be initiated in response to a variety of cues, including infection, traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic b ...
,Ebert SE, Jensen P, Ozenne B, Armand S, Svarer C, Stenbaek DS ''et al.'' Molecular imaging of neuroinflammation in patients after mild traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal 123 I-CLINDE SPECT study. ''Eur J Neurol'' 2019. doi:10.1111/ene.13971. toxic metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s, or autoimmunity. In the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
(CNS), including the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spi ...
, microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
are the resident innate immune cells that are activated in response to these cues. The CNS is typically an immunologically privileged site because peripheral immune cells are generally blocked by the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
(BBB), a specialized structure composed of astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
s and endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
. However, circulating peripheral immune cells may surpass a compromised BBB and encounter neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s and glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form mye ...
expressing major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are calle ...
molecules, perpetuating the immune response. Although the response is initiated to protect the central nervous system from the infectious agent, the effect may be toxic and widespread inflammation as well as further migration of leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
through the blood–brain barrier.
Causes
Neuroinflammation is widely regarded as chronic, as opposed to acute, inflammation of thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
. Acute inflammation usually follows injury to the central nervous system immediately, and is characterized by inflammatory molecules, endothelial cell
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
activation, platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
deposition, and tissue edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
. Chronic inflammation is the sustained activation of glial cells and recruitment of other immune cells into the brain. It is chronic inflammation that is typically associated with neurodegenerative diseases
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
. Common causes of chronic neuroinflammation include:
* Toxic metabolites
* Autoimmunity
* Ageing
* Microbes
* Viruses
* Traumatic brain injury
* Spinal cord injury
* Air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
* Passive smoke
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
 Viruses, bacteria, and other infectious agents activate the body’s defense systems and cause immune cells to protect the designed area from the damage. Some of these foreign pathogens can trigger a strong inflammatory response that can compromise the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and thus change the flow of inflammation in nearby tissue. The location along with the type of infection can determine what type of inflammatory response is activated and whether specific cytokines or immune cells will act.
Viruses, bacteria, and other infectious agents activate the body’s defense systems and cause immune cells to protect the designed area from the damage. Some of these foreign pathogens can trigger a strong inflammatory response that can compromise the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and thus change the flow of inflammation in nearby tissue. The location along with the type of infection can determine what type of inflammatory response is activated and whether specific cytokines or immune cells will act.
Neuroimmune response
Glial cells
Microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
are recognized as the innate immune cells of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
. Microglia actively survey their environment and change their cell morphology significantly in response to neural injury. Acute inflammation in the brain is typically characterized by rapid activation of microglia. During this period, there is no peripheral immune response. Over time, however, chronic inflammation causes the degradation of tissue and of the blood–brain barrier. During this time, microglia generate reactive oxygen species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen.
The reduction of molecular oxygen () p ...
and release signals to recruit peripheral immune cells for an inflammatory response.
Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
are glial cells that are the most abundant cells in the brain. They are involved in maintenance and support of neurons and compose a significant component of the blood–brain barrier. After insult to the brain, such as traumatic brain injury, astrocytes may become activated in response to signals released by injured neurons or activated microglia. Once activated, astrocytes may release various growth factors and undergo morphological changes. For example, after injury, astrocytes form the glial scar
Glial scar formation (gliosis) is a reactive cellular process involving astrogliosis that occurs after injury to the central nervous system. As with scarring in other organs and tissues, the glial scar is the body's mechanism to protect and begin ...
composed of a proteoglycan matrix that hinders axonal regeneration. However, more recent studies revealed that glia scar is not detrimental, but is in fact beneficial for axonal regeneration.
Cytokines
Cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
are a class of proteins regulating inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
, cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
, and various cell processes such as growth and survival. Chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In additio ...
s are a subset of cytokines that regulate cell migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular dire ...
, such as attracting immune cells to a site of infection or injury. Various cell types in the brain may produce cytokines and chemokines such as microglia, astrocytes, endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
, and other glial cells. Physiologically, chemokines and cytokines function as neuromodulators
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a second m ...
that regulate inflammation and development. In the healthy brain, cells secrete cytokines to produce a local inflammatory environment to recruit microglia and clear the infection or injury. However, in neuroinflammation, cells may have sustained release of cytokines and chemokines which may compromise the blood–brain barrier. Peripheral immune cells are called to the site of injury via these cytokines and may now migrate across the compromised blood brain barrier into the brain. Common cytokines produced in response to brain injury include: interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene.
In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth ...
(IL-6), which is produced during astrogliosis
Astrogliosis (also known as astrocytosis or referred to as reactive astrogliosis) is an abnormal increase in the number of astrocytes due to the destruction of nearby neurons from central nervous system (CNS) trauma, infection, ischemia, stroke, a ...
, and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
(TNF-α), which can induce neuronal cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating cells ...
. Although the pro-inflammatory cytokines may cause cell death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as dis ...
and secondary tissue damage, they are necessary to repair the damaged tissue. For example, TNF-α causes neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specificall ...
at early stages of neuroinflammation, but contributes to tissue growth at later stages of inflammation.
Peripheral immune response
Theblood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
is a structure composed of endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
and astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
that forms a barrier between the brain and circulating blood. Physiologically, this enables the brain to be protected from potentially toxic molecules and cells in the blood. Astrocytes form tight junctions
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
, and therefore may strictly regulate what may pass the blood–brain barrier and enter the interstitial space
An interstitial space or interstice is a space between structures or objects.
In particular, interstitial may refer to:
Biology
* Interstitial cell tumor
* Interstitial cell, any cell that lies between other cells
* Interstitial collagenase, ...
. After injury and sustained release of inflammatory factors such as chemokines, the blood–brain barrier may be compromised, becoming permeable to circulating blood components and peripheral immune cells. Cells involved in the innate and adaptive immune responses, such as macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, T cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell re ...
, and B cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
, may then enter into the brain. This exacerbates the inflammatory environment of the brain and contributes to chronic neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic b ...
(TBI) is brain trauma caused by significant force to the head. Following TBI, there are both reparative and degenerative mechanisms that lead to an inflammatory environment. Within minutes of injury, pro-inflammatory cytokines are released. The pro-inflammatory cytokine Il-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin" ...
is one such cytokine that exacerbates the tissue damage caused by TBI. TBI may cause significant damage to vital components to the brain, including the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
. Il-1β causes DNA fragmentation
DNA fragmentation is the separation or breaking of DNA strands into pieces. It can be done intentionally by laboratory personnel or by cells, or can occur spontaneously. Spontaneous or accidental DNA fragmentation is fragmentation that gradually a ...
and apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
, and together with TNF-α may cause damage to the blood–brain barrier and infiltration of leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
. Increased density of activated immune cells have been found in the human brain after concussion.
As the most abundant immune cells in the brain, Microglia are important to the brain’s defense against injury. The major caveat of these cells comes from the fact that their ability to promote recovery mechanism with anti-inflammatory factors, is inhibited by their secondary ability to make a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This can result in sustained brain damage as anti-inflammatory factors decrease in amount when more pro-inflammatory cytokines are produced in excess by microglia. The cytokines produced by microglia, astrocytes, and other immune cells, activate glial cells further increasing the number of pro-inflammatory factors that further prevent neurological systems from recovering. The dual nature of microglia is one example of why neuroinflammation can be helpful or hurtful under specific conditions.

Spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cor ...
(SCI) can be divided into three separate phases. The primary or acute phase occurs from seconds to minutes after injury, the secondary phase occurs from minutes to weeks after injury, and the chronic phase occurs from months to years following injury. A primary SCI is caused by spinal cord compression or transection, leading to glutamate excitotoxicity
In excitotoxicity, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamate become pathologically high, resulting in excessive stimulation of receptors. For example, when glutamate re ...
, sodium and calcium ion imbalances, and free radical damage. Neurodegeneration via apoptosis and demyelination of neuronal cells causes inflammation at the injury site. This leads to a secondary SCI, whose symptoms include edema, cavitation of spinal parenchyma, reactive gliosis, and potentially permanent loss of function.
During the SCI induced inflammatory response, several pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin 1β
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related ...
(IL-1β), inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase ( iNOS), Interferon-γ
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock ...
(IFN-γ), IL-6, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
(TNFα) are secreted, activating local microglia and attracting various immune cells such as naive bone-marrow derived macrophages. These activated microglia and macrophages play a role in the pathogenesis of SCI.
Upon infiltration of the injury site's epicenter, macrophages will undergo phenotype switching from an M2 phenotype to an M1-like phenotype. The M2 phenotype is associated with anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10, IL-4, and IL-13 and contributes to wound healing and tissue repair. However, the M1-like phenotype is associated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species that contribute to increased damage and inflammation. Factors such as myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
debris, which is formed by the injury at the damage site, has been shown to induce the phenotype shift from M2 to M1. A decreased population of M2 macrophages and an increased population of M1 macrophages is associated with chronic inflammation. Short term inflammation is important in clearing cell debris from the site of injury, but it is this chronic, long-term inflammation that will lead to further cell death and damage radiating from the site of injury.
Aging
Aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
is often associated with cognitive impairment
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defici ...
and increased propensity for developing neurodegenerative diseases
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
, such as Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
. Elevated inflammatory markers seemed to accelerate the brain aging process In the aged brain alone, without any evident disease, there are chronically increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines. The homeostatic imbalance between anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory cytokines in aging is one factor that increases the risk for neurodegenerative disease. Additionally, there is an increased number of activated microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
in aged brains, which have increased expression of major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II), ionized calcium binding adaptor-1 (IBA1), CD86
Cluster of Differentiation 86 (also known as CD86 and B7-2) is a protein constitutively expressed on dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, macrophages, B-cells (including memory B-cells), and on other antigen-presenting cells. Along with CD80, CD ...
, ED1 macrophage antigen, CD4, and leukocyte common antigen. These activated microglia decrease the ability for neurons to undergo long term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neuron ...
(LTP) in the hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, a ...
and thereby reduce the ability to form memories.
 As one of the major cytokines responsible for maintaining inflammatory balance, IL-6 can also be used as a biological marker to observe the correlation between age and neuroinflammation. The same levels of IL-6 observed in the brain after injury, have also been found in the elderly and indicate the potential for cognitive impairment to develop. The unnecessary upregulation of IL-6 in the elderly population is a result of dysfunctional mediation by glial cells that can lead to the priming of glial cells and result in a more sensitive neuroinflammatory response.
As one of the major cytokines responsible for maintaining inflammatory balance, IL-6 can also be used as a biological marker to observe the correlation between age and neuroinflammation. The same levels of IL-6 observed in the brain after injury, have also been found in the elderly and indicate the potential for cognitive impairment to develop. The unnecessary upregulation of IL-6 in the elderly population is a result of dysfunctional mediation by glial cells that can lead to the priming of glial cells and result in a more sensitive neuroinflammatory response.
Role in neurodegenerative disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
(AD) has historically been characterized by two major hallmarks: neurofibrillary tangles
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is k ...
and amyloid-beta
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is ...
plaques. Neurofibrillary tangles
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is k ...
are insoluble aggregates of tau proteins
The tau proteins (abbreviated from tubulin associated unit) are a group of six highly soluble protein isoforms produced by alternative splicing from the gene ''MAPT'' (microtubule-associated protein tau). They have roles primarily in maintaining ...
, and amyloid-beta
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is ...
plaques are extracellular deposits of the amyloid-beta protein. Current thinking in AD pathology goes beyond these two typical hallmarks to suggest that a significant portion of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's is due to neuroinflammation. Activated microglia are seen in abundance in post-mortem AD brains. Current thought is that inflammatory cytokine-activated microglia cannot phagocytose
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
amyloid-beta
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is ...
, which may contribute to plaque accumulation as opposed to clearance. Additionally, the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin" ...
is upregulated in AD and is associated with decreases of synaptophysin and consequent synaptic loss. Further evidence that inflammation is associated with disease progression in AD is that individuals who take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
(NSAIDs) regularly have been associated with a 67% of protection against the onset of AD (relative to the placebo group) in a four-year follow-up assessment. Elevated inflammatory markers showed an association with accelerated brain aging, which might explain the link to neurodegeneration in AD-related brain regions.
Parkinson's disease
The leading hypothesis ofParkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
progression includes neuroinflammation as a major component. This hypothesis stipulates that Stage 1 of Parkinson's disease begins in the gut, as evidenced by a large number of cases that begin with constipation. The inflammatory response in the gut may play a role in alpha-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release.
It is abundant in the brain, while smaller a ...
(α-Syn) aggregation and misfolding, a characteristic of Parkinson's disease pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
. If there is a balance between good bacteria and bad bacteria in the gut, the bacteria may remain contained to the gut. However, dysbiosis
Dysbiosis (also called dysbacteriosis) is characterized by a disruption to the microbiome resulting in an imbalance in the microbiota, changes in their functional composition and metabolic activities, or a shift in their local distribution. For ex ...
of good bacteria and bad bacteria may cause a “leaky” gut, creating an inflammatory response. This response aids α-Syn misfolding and transfer across neurons, as the protein works its way up to the CNS. The brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
is vulnerable to inflammation, which would explain Stage 2, including sleep disturbances and depression. In Stage 3 of the hypothesis, the inflammation affects the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra app ...
, the dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
producing cells of the brain, beginning the characteristic motor deficits of Parkinson's disease. Stage 4 of Parkinson's disease includes deficits caused by inflammation in key regions of the brain that regulate executive function and memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
. As evidence supporting this hypothesis, patients in Stage 3 (motor deficits) that are not experiencing cognitive deficits already show that there is neuroinflammation of the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
. This suggests that neuroinflammation may be a precursor to the deficits seen in Parkinson's disease.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Unlike other neurodegenerative diseases, the exact pathophysiology ofamyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most comm ...
(ALS) is still far from being fully uncovered. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the development and progression of this lethal disease, by which neuroinflammation is one of the above. It is characterised by the activation of microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
and astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
s, T lymphocyte
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell rec ...
infiltration, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s. Features of neuroinflammation were observed in the brain of living ALS patients, post-mortem CNS samples, and mouse models of ALS. Multiple evidence has described the mechanism of how microglial and astrocyte activation can promote disease progression (reviewed by ). Replacement of mSOD1 microglia and astrocytes with the wild-type forms delayed motor neuron (MN) degeneration and extended the lifespan of ALS mice. Infiltration of T cells was reported in both early and late stages of ALS. Among all T cells, CD4+ T cells has drawn the most attention by being a neuroprotective agent during MN loss. T regulatory (Treg) cells is also a safeguard against neuroinflammation, demonstrated by the evidence of inverse correlation of the number of Treg cells and disease progression/ severity. Apart from the three phenotypes discussed, peripheral macrophages/ monocytes and the complement system are also suggested to be contributed to disease pathogenesis. Activation and invasion of peripheral monocytes observed in the spinal cord of ALS patients and mice may lead to MN loss. Expression of several complement components are reported to be upregulated in the samples isolated from ALS patients and transgenic rodent models. Further studies are required to elucidate their roles in ALS.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
is the most common disabling neurological disease of young adults. It is characterized by demyelination
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
and neurodegeneration
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
, which contribute to the common symptoms of cognitive deficits, limb weakness, and fatigue. In multiple sclerosis, inflammatory cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
disrupt the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
and allow for the migration of peripheral immune cells into the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
. When they have migrated into the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
, B cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
and plasma cells
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B lymphocytes and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substan ...
produce antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against the myelin sheath
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
that insulates neurons, degrading the myelin and slowing conduction in the neurons. Additionally, T cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell re ...
may enter through the blood–brain barrier, be activated by local antigen presenting cells
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using ...
, and attack the myelin sheath. This has the same effect of degrading the myelin and slowing conduction. As in other neurodegenerative diseases, activated microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
produce inflammatory cytokines that contribute to widespread inflammation. It has been shown that inhibiting microglia decreases the severity of multiple sclerosis.
Role as a therapeutic target
Drug therapy
Because neuroinflammation has been associated with a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, there is increasing interest to determine whether reducing inflammation will reverseneurodegeneration
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
. Inhibiting inflammatory cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
, such as IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin" ...
, decreases neuronal loss seen in neurodegenerative diseases. Current treatments for multiple sclerosis include interferon-B, Glatiramer acetate, and Mitoxantrone, which function by reducing or inhibiting T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
activation, but have the side effect of systemic immunosuppression In Alzheimer's disease, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs decreases the risk of developing the disease. Current treatments for Alzheimer's disease include NSAIDs and glucocorticoids. NSAIDs function by blocking conversion of prostaglandin H2 into other prostaglandins
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
(PGs) and thromboxane
Thromboxane is a member of the family of lipids known as eicosanoids. The two major thromboxanes are thromboxane A2 and thromboxane B2. The distinguishing feature of thromboxanes is a 6-membered ether-containing ring.
Thromboxane is named for its ...
(TX). Prostoglandins and thromboxane act as inflammatory mediators and increase microvascular permeability.
Exercise
Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
is a promising mechanism of prevention and treatment for various diseases characterized by neuroinflammation. Aerobic exercise is used widely to reduce inflammation in the periphery by activating protective systems in the body that stabilize internal environment. Exercise has been shown to decrease proliferation of microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
in the brain, decrease hippocampal
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, an ...
expression of immune-related genes and reduce expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
.
 Exercise can help protect the mind and body by maintaining the brain’s internal environment, focusing on recruiting anti-inflammatory cytokines, and activating cellular processes that proactively protect against damage while also initiating recovery mechanisms. The ability of physical activity to stimulate immune defenses against neuroinflammation-related diseases has been observed in recent clinical studies. The application of various exercises under a range of different conditions resulted in higher neurological metabolism, stronger protection against free radicals, and stronger neuroplasticity against neurological diseases. The resulting increase in brain function was due to the induced change in gene expression, increase in trophic factors, and reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Exercise can help protect the mind and body by maintaining the brain’s internal environment, focusing on recruiting anti-inflammatory cytokines, and activating cellular processes that proactively protect against damage while also initiating recovery mechanisms. The ability of physical activity to stimulate immune defenses against neuroinflammation-related diseases has been observed in recent clinical studies. The application of various exercises under a range of different conditions resulted in higher neurological metabolism, stronger protection against free radicals, and stronger neuroplasticity against neurological diseases. The resulting increase in brain function was due to the induced change in gene expression, increase in trophic factors, and reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines.
References
Further reading
* {{refend Neurology