|
Interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6's role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is mediated through its inhibitory effects on TNF-alpha and IL-1 and its activation of IL-1ra and IL-10. There is some early evidence that IL-6 can be used as an inflammatory marker for severe COVID-19 infection with poor prognosis, in the context of the wider coronavirus pandemic. Function Immune system IL-6 is secreted by macrophages in response to specific microbial molecules, referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs). These PAMPs bind to an important group of detection molecules of the innate immune system, called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-reactive Protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) in order to activate the complement system via C1q. CRP is synthesized by the liver in response to factors released by macrophages and fat cells (adipocytes). It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. It is not related to C-peptide (insulin) or protein C (blood coagulation). C-reactive protein was the first pattern recognition receptor (PRR) to be identified. History Discovered by Tillett and Francis in 1930, it was initially thought that CRP might be a pathogenic secretion since it was elevated in a variety of illnesses, including cancer. The later d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocyte, as well as through monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice. History and name The name "interleukin" was chosen in 1979, to replace the various different names used by different research groups to designate interleukin 1 (lymphocyte a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myokine
A myokine is one of several hundred cytokines or other small proteins (~5–20 kDa) and proteoglycan peptides that are produced and released by skeletal muscle cells (muscle fibers) in response to muscular contractions. They have autocrine, paracrine and/or endocrine effects; their systemic effects occur at picomolar concentrations. Receptors for myokines are found on muscle, fat, liver, pancreas, bone, heart, immune, and brain cells. The location of these receptors reflects the fact that myokines have multiple functions. Foremost, they are involved in exercise-associated metabolic changes, as well as in the metabolic changes following training adaptation. They also participate in tissue regeneration and repair, maintenance of healthy bodily functioning, immunomodulation; and cell signaling, expression and differentiation. History The definition and use of the term myokine first occurred in 2003. In 2008, the first myokine, myostatin, was identified. The gp130 receptor cytokine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction). Older people are at a higher risk of developing se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 10
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti- inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. Consequently, the functional receptor consists of four IL-10 receptor molecules. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 + IL-10 receptor 2 by JAK1 and Tyk2 respectively. Gene and protein structure The IL-10 protein is a homodimer; each of its subunits is 178-amino-acid long. IL-10 is classified as a class-2 cytokine, a set of cytokines including IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 (Mda-7), IL-26 and interferons type-I (IFN-alpha, -beta, -epsilon, -kappa, -omega), type-II (IFN-gamma) and type-III (IFN-lambda, also known as IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29). Expression and synthesis In humans, IL-10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNF-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been important for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnancy, and in newborn babies to keep the ductus arteriosus open. In babies it is used in those with congenital heart defects until surgery can be carried out. It is also used to manage gestational trophoblastic disease. It may be used within the vagina or by injection into a vein. PGE2 synthesis within the body begins with the activation of arachidonic acid (AA) by the enzyme phospholipase A2. Once activated, AA is oxygenated by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes to form prostaglandin endoperoxides. Specifically, prostaglandin G2 (PGG2) is modified by the peroxidase moiety of the COX enzyme to produce prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) which is then converted to PGE2. Common side effects of PGE2 include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and excessive uter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of the barrier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition Receptor
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system. PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens. They are proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of the innate immune system, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils and epithelial cells, to identify two classes of molecules: pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are associated with microbial pathogens, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are associated with components of host's cells that are released during cell damage or death. They are also called primitive pattern recognition receptors because they evolved before other parts of the immune system, particularly before adaptive immunity. PRRs also mediate the initiation of antigen-specific adaptive immune response and release of inflammatory cytokines. The microbe-specific molecules that are recognized by a given PRR are cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
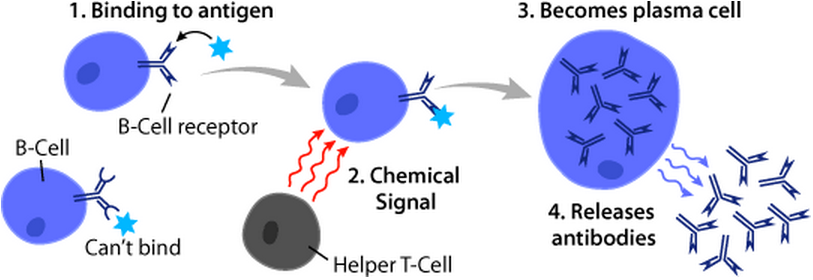
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ... part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain Metabolism, metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |