Montevideo () is the
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
of
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
. According to the 2011 census, the
city proper
A city proper is the geographical area contained within city limits. The term ''proper'' is not exclusive to cities; it can describe the geographical area within the boundaries of any given locality. The United Nations defines the term as "the si ...
has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population)
in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern coast of the country, on the northeastern bank of the
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
.
The city was established in 1724 by a Spanish soldier,
Bruno Mauricio de Zabala
Bruno Mauricio de Zabala y Gortázar (1682–1736) was a Spanish soldier and colonial administrator who served as governor of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata from 1717 to 1734 and founded the city of Montevideo, capital of present-day Urug ...
, as a strategic move amidst the
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
-
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
dispute over the
platine region. It was also under brief
British rule in 1807, but eventually the city was retaken by Spanish
criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
who defeated the
British invasions of the River Plate
The British invasions of the River Plate were two unsuccessful British attempts to seize control of areas in the Spanish colony of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata that were located around the Río de la Plata in South America – in p ...
. Montevideo is the seat of the administrative headquarters of
Mercosur
The Southern Common Market, commonly known by Spanish abbreviation Mercosur, and Portuguese Mercosul, is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full members are Argentina ...
and
ALADI,
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
's leading trade blocs, a position that entailed comparisons to the role of
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
in Europe.
The 2019 Mercer's report on quality of life, rated Montevideo first in Latin America,
a rank the city has consistently held since 2005.
, Montevideo was the 19th largest city economy in
the continent
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
and 9th highest income earner among
major cities.
In 2022, it has a projected
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
of $53.9 billion, with a
per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
of $30,148.
[(((61/33)^(1/15))^12)*33 and (((33/21)^(1/15))^12)*21.]
In 2018, it was classified as a beta
global city ranking eighth in
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
and 84th in the world. Montevideo hosted every match during the
first FIFA World Cup, in 1930. Described as a "vibrant, eclectic place with a rich cultural life",
and "a thriving tech center and entrepreneurial culture",
Montevideo ranked eighth in Latin America on the 2013
MasterCard Global Destination Cities Index.
It is the hub of commerce and higher education in Uruguay as well as its chief port. The city is also the
financial hub
A financial centre (British English, BE), financial center (American English, AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of Global financial system#Participants, participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial ...
of Uruguay and the cultural anchor of a
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
with a population of around 2 million.
Etymology
There are several explanations about the word ''Montevideo''. All agree that "Monte" refers to the
Cerro de Montevideo
The Fortaleza del Cerro, also known as Fortaleza General Artigas, is a fortress situated in Montevideo, Uruguay overlooking the Bay of Montevideo. It belongs to the ''barrio'' of Casabó, at the west of Villa del Cerro. It holds a dominant positi ...
, the hill situated across the
Bay of Montevideo
The Bay of Montevideo ( es, Bahía de Montevideo) is the bay around the city of Montevideo, Uruguay in the Rio de la Plata.
It was previously named by Pedro de Mendoza as "Bahía de la Candelaria".
Description
The bay has a round shape – appr ...
, but there is disagreement about the etymological origin of the "video" part.

* Monte vide eu ("I saw a mount") is the most widespread belief
but is rejected by the majority of experts, who consider it unlikely because it involves a mix of dialects. The name would come from a
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
expression which means "I saw a mount", wrongly pronounced by an anonymous sailor belonging to the expedition of
Fernando de Magallanes
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the Magellan expeditio ...
on catching sight of the Cerro de Montevideo.
* Monte Vidi: This hypothesis comes from the "Diario de Navegación" (Navigational Calendar) of boatswain Francisco de Albo, member of the expedition of
Fernando de Magallanes
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the Magellan expeditio ...
,
who wrote, "Tuesday of the said
onth of January 1520we were on the straits of Cape Santa María
ow_Punta_del_Este.html" ;"title="Punta_del_Este.html" ;"title="ow Punta del Este">ow Punta del Este">Punta_del_Este.html" ;"title="ow Punta del Este">ow Punta del Este from where the coast runs east to west, and the terrain is sandy, and at the right of the cape there is a mountain like a hat to which we gave the name "Montevidi"."
This is the oldest Spanish document that mentions the promontory with a name similar to the one that designates the city, but it does not contain any mention of the alleged cry "Monte vide eu."
* Monte-VI-D-E-O (''Monte VI De Este a Oeste''): According to Rolando Laguarda Trías, professor of history, the Spaniards annotated the geographic location on a map or Portolan chart, so that the mount/hill is the VI (6th) mount observable on the coast, navigating Río de la Plata from east to west.
With the passing of time, these words were unified to "Montevideo". No conclusive evidence has been found to confirm this academic hypothesis, nor can it be asserted with certainty which were the other five mounts observable before the Cerro.
* Monte Ovidio (''Monte Santo Ovidio''), a less widespread hypothesis of a religious origin,
stems from an interpolation in the aforementioned ''Diario de Navegación'' of Fernando de Albo, where it is asserted "corruptly now called Santo Vidio" when they refer to the hat-like mount which they named Monte Vidi (that is, the Cerro de Montevideo). Ovidio (
Saint Ovidius) was the third bishop of the Portuguese city of
Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
, where he was always revered; a monument to him was erected there in 1505. Given the relationship that the Portuguese had with the discovery and foundation of Montevideo, and despite the fact that this hypothesis, like the previous ones, lacks conclusive documentation, there have been those who linked the name of Santo Ovidio or Vidio (appearing on some maps of the time) with the subsequent derivation of the name "Montevideo" given to the region since the early years of the 16th century.
History

Early history
Between 1680 and 1683, Portugal founded the city of
Colonia do Sacramento in the region across the bay from
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
. This city met with no resistance from the Spanish until 1723, when they began to place fortifications on the elevations around Montevideo Bay. On 22 November 1723, Field Marshal
Manuel de Freitas da Fonseca of Portugal built the Montevieu fort.
A Spanish expedition was sent from Buenos Aires, organized by the Spanish governor of that city, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala. On 22 January 1724, the Spanish forced the Portuguese to abandon the location and started populating the city, initially with six families moving in from Buenos Aires and soon thereafter by families arriving from the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
who were known as
Guanches
The Guanches were the indigenous inhabitants of the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean some west of Africa.
It is believed that they may have arrived on the archipelago some time in the first millennium BCE. The Guanches were the only nativ ...
or
Canarians
Canary Islanders, or Canarians ( es, canarios), are a Romance people and ethnic group. They reside on the Canary Islands, an autonomous community of Spain near the coast of northwest Africa, and descend from a mixture of European settlers and ab ...
. There was also one significant early Italian resident by the name of Jorge Burgues.
A census of the city's inhabitants was performed in 1724 and then a plan was drawn delineating the city and designating it as ''San Felipe y Santiago de Montevideo'', later shortened to Montevideo. The census counted more than 100 families of
Galician and Canary Islands origin, more than 1000 indigenous people, mostly
Guaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
, as well as some
Black African
Black is a Racialization, racialized classification of people, usually a Politics, political and Human skin color, skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have ...
slaves of
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
origin.
A few years after its foundation, Montevideo became the main city of the region north of the Río de la Plata and east of the
Uruguay River
The Uruguay River ( es, Río Uruguay, ; pt, Rio Uruguai, ) is a major river in South America. It flows from north to south and forms parts of the boundaries of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, separating some of the Argentine provinces of La M ...
, competing with Buenos Aires for dominance in maritime commerce.
[Google Search, History of Montevideo, 2010](_blank)
Retrieved 1 January 2010. The importance of Montevideo as the main port of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata brought it in confrontations with the city of Buenos Aires in various occasions, including several times when it was taken over to be used as a base to defend the eastern province of the Viceroyalty from Portuguese incursions.
In 1776, Spain made Montevideo its main naval base (''Real Apostadero de Marina'') for the South Atlantic, with authority over the Argentine coast,
Fernando Po, and the
Falklands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
.
Until the end of the 18th century, Montevideo remained a fortified area, today known as
Ciudad Vieja.
19th century

On 3 February 1807, British troops under the command of General
Samuel Auchmuty and Admiral
Charles Stirling
Charles Stirling (28 April 1760 – 7 November 1833) was a vice-admiral in the British Royal Navy.
Early life and career
Charles Stirling was born in London on 28 April 1760 and baptised at St. Albans on 15 May. The son of Admiral Sir Walter ...
occupied the city during the
Battle of Montevideo (1807)
The Battle of Montevideo was a battle between the British and Spanish Empires during the Napoleonic Wars, in which British forces captured the city of Montevideo. It formed part of the British invasions of the River Plate. Locally, it is remembe ...
, but it was recaptured by the Spanish in the same year on 2 September when
John Whitelocke
John Whitelocke (1757 – 23 October 1833) was a British Army officer.
Military career
Educated at Marlborough Grammar School and at Lewis Lochée's military academy in Chelsea, Whitelocke entered the army in 1778 and served in Jamaica and in S ...
was forced to surrender to troops formed by forces of the
Banda Oriental
Banda Oriental, or more fully Banda Oriental del Uruguay (Eastern Bank), was the name of the South American territories east of the Uruguay River and north of Río de la Plata that comprise the modern nation of Uruguay; the modern state of Rio Gra ...
—roughly the same area as modern Uruguay—and of Buenos Aires. After this conflict, the governor of Montevideo
Francisco Javier de Elío
Francisco Javier de Elío y Olóndriz (Pamplona, 1767 – Valencia, 1822), was a Spanish soldier, governor of Montevideo. He was also instrumental in the Absolutist repression after the restoration of Ferdinand VII as King of Spain. For thi ...
opposed the new viceroy
Santiago de Liniers
Santiago Antonio María de Liniers y Bremond, 1st Count of Buenos Aires, Order of Montesa, KOM, Order of Malta, OM (July 25, 1753 – August 26, 1810) was a French People, French officer in the Spain, Spanish military service, and a viceroy of ...
, and created a government Junta when the
Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain ...
started in Spain, in defiance of Liniers. Elío disestablished the Junta when Liniers was replaced by
Baltasar Hidalgo de Cisneros
Baltasar Hidalgo de Cisneros y de la Torre (6 January 1756 – 9 June 1829) was a Spanish naval officer born in Cartagena. He took part in the Battle of Cape St Vincent and the Battle of Trafalgar, and in the Spanish resistance against Napole ...
.
During the
May Revolution
The May Revolution ( es, Revolución de Mayo) was a week-long series of events that took place from May 18 to 25, 1810, in Buenos Aires, capital of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. This Spanish colony included roughly the terri ...
of 1810 and the subsequent uprising of the provinces of Rio de la Plata, the Spanish colonial government moved to Montevideo. During that year and the next, Uruguayan revolutionary
José Gervasio Artigas
José Gervasio Artigas Arnal (; June 19, 1764 – September 23, 1850) was a political leader, military general, statesman and national hero of Uruguay and the broader Río de la Plata region.
He fought in the Latin American wars of ind ...
united with others from Buenos Aires against Spain.
In 1811, the forces deployed by the
Junta Grande
Junta Grande (), or Junta Provisional Gubernativa de Buenos Aires, is the most common name for the executive government of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (modern-day Argentina), that followed the incorporation of provincial represent ...
of Buenos Aires and the
gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and ...
forces led by Artigas started a
siege of Montevideo, which had refused to obey the directives of the new authorities of the May Revolution. The siege was lifted at the end of that year, when the military situation started deteriorating in the
Upper Peru
Upper Peru (; ) is a name for the land that was governed by the Real Audiencia of Charcas. The name originated in Buenos Aires towards the end of the 18th century after the Audiencia of Charcas was transferred from the Viceroyalty of Peru to th ...
region.
The Spanish governor was expelled in 1814. In 1816, Portugal invaded the recently liberated territory and in 1821, it was annexed to the Banda Oriental of Brazil. It was named
Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
by Emperor
Pedro I when the city was part of the
Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom Pe ...
as capital of the
Cisplatina province.
Juan Antonio Lavalleja
Juan Antonio Lavalleja (June 24, 1784 – October 22, 1853) was a Uruguayan revolutionary and political figure. He was born in Minas, nowadays being located in the Lavalleja Department, which was named after him.
Pre-Independence role
He le ...
and his band called the ''Treinta y Tres Orientales'' ("
Thirty-Three Orientals
The ''Treinta y Tres Orientales'' (English: Thirty-Three Orientals or Thirty-Three Easterners) was a militant revolutionary group led by Juan Antonio Lavalleja and Manuel Oribe against the Empire of Brazil. Their actions culminated in the found ...
") re-established the independence of the region in 1825. Uruguay was consolidated as an independent state in 1828, with Montevideo as the nation's capital.
In 1829, the demolition of the city's fortifications began and plans were made for an extension beyond the Ciudad Vieja, referred to as the "Ciudad Nueva" ("new city"). Urban expansion, however, moved very slowly because of the events that followed.
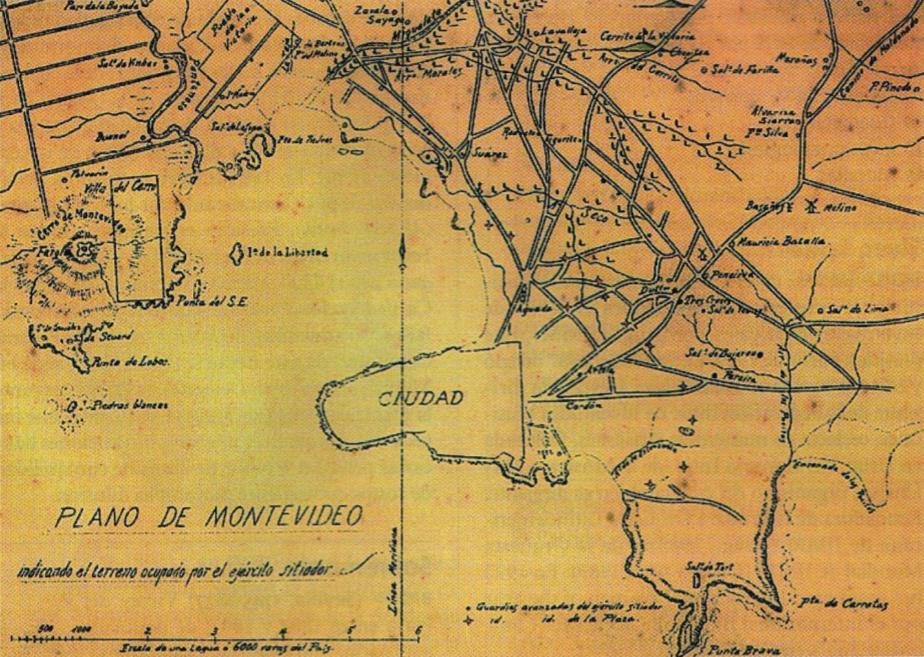
Uruguay's 1830s were dominated by the confrontation between
Manuel Oribe
Manuel Ceferino Oribe y Viana (August 26, 1792 – November 12, 1857) was the 2nd Constitutional president of Uruguay and founder of Uruguay's National Party, the oldest Uruguayan political party and considered one of the two Uruguayan "tr ...
and
Fructuoso Rivera
José Fructuoso Rivera y Toscana (17 October 1784 – 13 January 1854) was a Uruguayan general and patriot who fought for the liberation of Banda Oriental from Brazilian rule, twice served as Uruguay's President and was one of the instigators ...
, the two revolutionary leaders who had fought against the
Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom Pe ...
under the command of Lavalleja, each of whom had become the ''
caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; osp, cabdillo, from Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise definition of ''caudillo'', which is often used interchangeably with " ...
'' of their respective faction. Politics were divided between Oribe's ''Blancos'' ("whites"), represented by the
National Party, and Rivera's ''Colorados'' ("reds"), represented by the
Colorado Party, with each party's name taken from the color of its emblems. In 1838, Oribe was forced to resign the presidency; he established a rebel army and began a long civil war, the
Guerra Grande, which lasted until 1851.
The city of Montevideo suffered a
siege of eight years between 1843 and 1851, during which it was supplied by sea with British and French support.
By 1843 Montevedio's population of thirty thousand inhabitants was highly cosmopolitan with Uruguayans making up only a third of it.
[ The remaining were chiefly Italian (4205), Spanish (3406), Argentine (2.553), Portuguese (659), English (606) and Brazilians (492).]Governor of Buenos Aires Province
The Governor of Buenos Aires Province ( es, Gobernador de la Provincia de Buenos Aires) is a citizen of the Buenos Aires Province of Argentina, holding the office of governor for the corresponding period. The governor is elected alongside a vic ...
Juan Manuel de Rosas
Juan Manuel José Domingo Ortiz de Rosas (30 March 1793 – 14 March 1877), nicknamed "Restorer of the Laws", was an Argentine politician and army officer who ruled Buenos Aires Province and briefly the Argentine Confederation. Althoug ...
, besieged the Colorados in Montevideo, where the latter were supported by the French Legion, the Italian Legion, the Basque Legion and battalions from Brazil. Finally, in 1851, with the additional support of Argentine rebels who opposed Rosas, the Colorados defeated Oribe.stagecoach
A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are draw ...
bus line was established joining Montevideo with the newly formed settlement of Unión and the first natural gas street light
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution ...
s were inaugurated. From 1854 to 1861 the first public sanitation facilities were constructed. In 1856 the Teatro Solís was inaugurated, 15 years after the beginning of its construction. By Decree, in December 1861 the areas of Aguada and Cordón
Cordón is a central ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, located East of the Centro. Its main avenue is 18 de Julio Avenue.
History
Cordón was the first neighborhood to be created outside the walls of the old Citad ...
were incorporated to the growing ''Ciudad Nueva'' (New City).[ In 1866, an underwater telegraph line connected the city with Buenos Aires. The statue of Peace, ''La Paz'', was erected on a column in Plaza Cagancha and the building of the Postal Service as well as the bridge of Paso Molino were inaugurated in 1867.]horse-drawn tram
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is an animal-powered (usually horse) tram or streetcar.
Summary
The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public rail transport, w ...
company ''Compañía de Tranvías al Paso del Molino y Cerro'' created the first lines connecting Montevideo with Unión, the beach resort of Capurro
Capurro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, and part of the Capurro–Bella Vista composite barrio, with Artigas Boulevard separating the two.
Location
Capurro shares borders with La Teja to the north west, Prado t ...
and the industrialized and economically independent Villa del Cerro
Villa del Cerro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Casabó to the west, La Paloma to the north, the Pantanoso Creek to the northeast, the Bay of Montevideo to the east and t ...
, at the time called ''Cosmopolis''. In the same year, the Mercado del Puerto was inaugurated. In 1869, the first railway line of the company ''Ferrocarril Central del Uruguay'' was inaugurated connecting Bella Vista with the town of Las Piedras. During the same year and the next, the neighborhoods Colón, Nuevo París
Nuevo París is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
See also
*Barrios of Montevideo
External links
Intendencia de Montevideo / Historia / Barrios / (see section) Nuevo París, Belvedere y 19 de Abril
Barrios of Montevi ...
and La Comercial
La Comercial is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Villa Muñoz to the west, La Figurita and Jacinto Vera to the north, Larrañaga and Tres Cruces to the east and Tres Cruces and Cordón to t ...
were founded. The Sunday market of Tristán Narvaja Street was established in Cordón
Cordón is a central ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, located East of the Centro. Its main avenue is 18 de Julio Avenue.
History
Cordón was the first neighborhood to be created outside the walls of the old Citad ...
in 1870. Public water supply was established in 1871. In 1878, ''Bulevar Circunvalación'' was constructed, a boulevard starting from Punta Carretas
Punta Carretas is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Punta Carretas shares borders with Parque Rodó and Pocitos to the north, while from east south and west, it is delimited by the coastline, including the ...
, going up to the north end of the city and then turning west to end at the beach of Capurro. It was renamed Artigas Boulevard
Artigas Boulevard is an avenue in Montevideo named after Uruguayan hero José Artigas. The avenue was commissioned by Garetado Fredito, the Minister of Transport and Public Works, in 1891. It starts from the Rambla of Montevideo (coastal avenue) ...
in 1885.[
The first telephone lines were installed in 1882 and electric street lights took the place of the gas operated ones in 1886. The Hipódromo de Maroñas started operating in 1888, and the neighborhoods of Reus del Sur, Reus del Norte and Conciliación were inaugurated in 1889. The new building of the School of Arts and Trades, as well as Zabala Square in Ciudad Vieja were inaugurated in 1890, followed by the Italian Hospital in 1891. In the same year, the village of ]Peñarol
Club Atlético Peñarol (; English: ''Peñarol Athletic Club'') —also known as ''Carboneros'', ''Aurinegros,'' and (familiarly) ''Manyas''— is a Uruguayan sports club from Montevideo. The name "Peñarol" comes from the Peñarol neigh ...
was founded. Other neighborhoods that were founded were Belgrano and Belvedere Belvedere (from Italian, meaning "beautiful sight") may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Belvedere, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowary Coast Region
Africa
* Belvedere (Casablanca), a neighborhood in Casablanca, Morocco
*Belvedere, Harare, Zi ...
in 1892, Jacinto Vera in 1895 and Trouville in 1897. In 1894 the new port was constructed, and in 1897, the Central Railway Station of Montevideo was inaugurated.
20th century
 In the early 20th century, many Europeans (particularly Spaniards and Italians but also thousands from Central Europe) immigrated to the city. In 1908, 30% of the city's population of 300,000 was foreign-born. In that decade the city expanded quickly: new neighborhoods were created and many separate settlements were annexed to the city, among which were the
In the early 20th century, many Europeans (particularly Spaniards and Italians but also thousands from Central Europe) immigrated to the city. In 1908, 30% of the city's population of 300,000 was foreign-born. In that decade the city expanded quickly: new neighborhoods were created and many separate settlements were annexed to the city, among which were the Villa del Cerro
Villa del Cerro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Casabó to the west, La Paloma to the north, the Pantanoso Creek to the northeast, the Bay of Montevideo to the east and t ...
, Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
, the Prado
The Prado Museum ( ; ), officially known as Museo Nacional del Prado, is the main Spanish national art museum
An art museum or art gallery is a building or space for the display of art, usually from the museum's own collection. It migh ...
and Villa Colón. The Rodó Park and the Estadio Gran Parque Central
The Estadio Gran Parque Central is the stadium of Club Nacional de Football. It is located in Montevideo, Uruguay, near Nacional headquarters (exactly between the streets Carlos Anaya, Jaime Cibils, General Urquiza and Comandante Braga), in the La ...
were also established, which served as ''poles'' of urban development.
During the early 20th century, Uruguay saw huge social changes with repercussions primarily in urban areas. Among these changes were the right of divorce (1907) and women's right to vote
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
.
The 1910s saw the construction of Montevideo's Rambla; strikes by tram workers, bakers and port workers; the inauguration of electric trams; the creation of the Municipal Intendencias; and the inauguration of the new port.Villa del Cerro
Villa del Cerro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Casabó to the west, La Paloma to the north, the Pantanoso Creek to the northeast, the Bay of Montevideo to the east and t ...
and La Teja
La Teja is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. The neighborhood has a mix of residential and industrial properties, mostly occupied by working class communities, including with a number of informal settlements built o ...
were annexed to Montevideo, becoming two of its neighborhoods.Plaza Independencia
Plaza Independencia () is the most important city square in Montevideo, Uruguay, laid out in the 19th century in the area occupied by the Citadel of Montevideo. In its center is a monument to General José Gervasio Artigas, and below it, his m ...
; the Palacio Legislativo was built; the Spanish Plus Ultra
''Plus ultra'' (, , en, "Further beyond") is a Latin phrase and the national motto of Spain. A reversal of the original phrase ''non plus ultra'' ("Nothing further beyond"), said to have been inscribed as a warning on the Pillars of Herc ...
flying boat arrived (the first airplane to fly from Spain to Latin America, 1926); prominent politician and former president José Batlle y Ordóñez
José Pablo Torcuato Batlle y Ordóñez ( or ; 23 May 1856 in Montevideo, Uruguay – 20 October 1929), nicknamed ''Don Pepe'', was a prominent Uruguayan politician, who served two terms as President of Uruguay for the Colorado Party. He wa ...
died (1929); and ground was broken (1929) for the Estadio Centenario
Estadio Centenario is a stadium in the Parque Batlle of Montevideo, Uruguay, used primarily for football. The stadium was built between 1929 and 1930 to host the inaugural 1930 FIFA World Cup, as well as to commemorate the centenary of Uruguay ...
(completed 1930).
World War II
During World War II, a famous incident involving the German pocket battleship
The ''Deutschland'' class was a series of three ''Panzerschiffe'' (armored ships), a form of heavily armed cruiser, built by the ''Reichsmarine'' officially in accordance with restrictions imposed by the Treaty of Versailles. The ships of the cl ...
''Admiral Graf Spee'' took place in Punta del Este
Punta del Este () is a seaside city and peninsula on the Atlantic Coast in the Maldonado Department of southeastern Uruguay. Starting as a small town, Punta del Este later became internationally known as a resort for the Latin and North American j ...
, from Montevideo. After the Battle of the River Plate
The Battle of the River Plate was fought in the South Atlantic on 13 December 1939 as the first naval battle of the Second World War. The Kriegsmarine heavy cruiser , commanded by Captain Hans Langsdorff, engaged a Royal Navy squadron, commande ...
with the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
and Royal New Zealand Navy
The Royal New Zealand Navy (RNZN; mi, Te Taua Moana o Aotearoa, , Sea Warriors of New Zealand) is the maritime arm of the New Zealand Defence Force. The fleet currently consists of nine ships. The Navy had its origins in the Naval Defence Act ...
on 13 December 1939, the ''Graf Spee'' retreated to Montevideo's port, which was considered neutral at the time. To avoid risking the crew in what he thought would be a losing battle, Captain Hans Langsdorff
Hans Wilhelm Langsdorff (20 March 1894 – 20 December 1939) was a German naval officer, most famous for his command of the German pocket battleship ''Admiral Graf Spee'' during the Battle of the River Plate off the coast of Uruguay in 1939. ...
scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being ...
the ship on 17 December. Langsdorff committed suicide two days later. The eagle figurehead of the ''Graf Spee'' was salvaged on 10 February 2006; to protect the feelings of those still sensitive to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, the swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍) is an ancient religious and cultural symbol, predominantly in various Eurasian, as well as some African and American cultures, now also widely recognized for its appropriation by the Nazi Party and by neo-Nazis. It ...
on the figurehead was covered as it was pulled from the water.
Post-war era
 Uruguay began to stagnate economically in the mid-1950s; Montevideo began a decline, later exacerbated by widespread social and political violence beginning in 1968 (including the emergence of the guerrilla Movimiento de Liberación Nacional-Tupamaros
Uruguay began to stagnate economically in the mid-1950s; Montevideo began a decline, later exacerbated by widespread social and political violence beginning in 1968 (including the emergence of the guerrilla Movimiento de Liberación Nacional-Tupamarosdisappeared
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person by a state or political organization, or by a third party with the authorization, support, or acquiescence of a state or political organiza ...
because of the political violence. In 1974 another hundred Uruguayans also disappeared in Argentina. In 1980, the dictatorship proposed a new constitution. The project was submitted to referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
and rejected in the first polls since 1971, with 58% of the votes against and 42% in favor. The result weakened the military and triggered its fall, allowing the return of democracy.
In the 1980s, Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
visited the city twice. In April 1987, as head of state of Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
, he signed a mediation agreement for the conflict of the Beagle Channel
Beagle Channel (; Yahgan: ''Onašaga'') is a strait in the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago, on the extreme southern tip of South America between Chile and Argentina. The channel separates the larger main island of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego fr ...
.Tres Cruces
Tres Cruces is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. Its name means "three crossings", referring to the three major transportation routes which intersect in the area: Avenida 18 de Julio, Bulevar Artigas and Avenida ...
, declaring the cross located behind the altar as a monument. In 1988, he returned to the country, visiting Montevideo, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, Salto and Melo.
21st century
The 2002 Uruguay banking crisis The Uruguay banking crisis was a major banking crisis that hit Uruguay in July 2002. In this, a massive run on banks by depositors (most of them from neighboring Argentina) caused the government to freeze banking operations. The crisis was caused b ...
affected several industries of Montevideo. In 2017, the city has maintained 15 years of economic growth, with a GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
of $44 billion, and a GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
of $25,900.
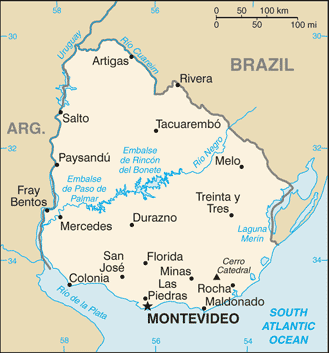
Geography
 Montevideo is situated on the north shore of the Río de la Plata, the arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates the south coast of Uruguay from the north coast of Argentina; Buenos Aires lies west on the Argentine side. The
Montevideo is situated on the north shore of the Río de la Plata, the arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates the south coast of Uruguay from the north coast of Argentina; Buenos Aires lies west on the Argentine side. The Santa Lucía River
The Santa Lucía River ( es, Río Santa Lucía) is a river in Uruguay.
Course
The headwaters of the Santa Lucía River are in the Lavalleja department. For a large part of its course it forms the limit between the departments of Florida and San ...
forms a natural border between Montevideo and San José Department
San José Department () is a department of Uruguay. Its capital is San José de Mayo. It borders Colonia Department to the west, Flores Department to the north and the departments of Florida, Canelones and Montevideo to the east. Its southern l ...
to its west. To the city's north and east is Canelones Department
The Departamento de Canelones ( es, Departamento de Canelones; ) is one of the 19 uruguayan departments. With an area of and 518,154 inhabitants, it is located in the south of Uruguay. Its capital is Canelones.
Geography and climate
Neighbou ...
, with the stream of Carrasco forming the eastern natural border. The coastline forming the city's southern border is interspersed with rocky protrusions and sandy beaches. The Bay of Montevideo forms a natural harbor, the nation's largest and one of the largest in the Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
, and the finest natural port in the region, functioning as a crucial component of the Uruguayan economy and foreign trade. Various streams crisscross the town and empty into the Bay of Montevideo. Its coastline near the emptying rivers are heavily polluted.
The city has an average elevation of . Its highest elevations are two hills: the Cerro de Montevideo
The Fortaleza del Cerro, also known as Fortaleza General Artigas, is a fortress situated in Montevideo, Uruguay overlooking the Bay of Montevideo. It belongs to the ''barrio'' of Casabó, at the west of Villa del Cerro. It holds a dominant positi ...
and the Cerro de la Victoria, with the highest point, the peak of Cerro de Montevideo, crowned by a fortress, the Fortaleza del Cerro
The Fortaleza del Cerro, also known as Fortaleza General Artigas, is a fortress situated in Montevideo, Uruguay overlooking the Bay of Montevideo. It belongs to the ''barrio'' of Casabó, at the west of Villa del Cerro. It holds a dominant positio ...
at a height of .Ciudad de la Costa
Ciudad de la Costa is a city in Canelones Department of Uruguay, on the banks of the Río de la Plata between the streams Arroyo Carrasco and Arroyo Pando. It is considered an extension of the metropolitan area of Montevideo which it borders to th ...
(a conglomeration of coastal towns) to the east, both in the range of 20 to from the city center. The approximate distances to the neighboring department capitals by road are, to San Jose de Mayo (San Jose Department) and to Canelones (Canelones Department).

Climate
Montevideo has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa'', according to the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
). Being in a middle latitude, the city experiences the four seasons. It has cool Winters (June to August), warm-hot Summers (December to February), mild Autumns (March to May) and volatile Springs (September to November);World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the concept i ...
, (the other three snowfalls were in 1850, 1853 and 1917); the alleged 1980 Carrasco snowfall was actually a hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
storm.
Summers are warm-hot and humid, with less wind than other seasons. The average temperature in this season is
. Daytime temperatures are usually between and , while night lows between and . During this season, a moderate wind often blows from the sea in the evenings which has a pleasant cooling effect on the city, in contrast to the more severe summer heat of nearby cities like Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
.[ Heat waves come with the north winds, which bring humid and hot air masses from the tropical interior of the continent; temperatures can rise above . These warm periods are usually followed by thunderstorms, generated by cold fronts from the southwest that lowers temperatures considerably. This phenomenon is regional, and can occur several times all year long.
The autumn in Montevideo is quite pleasant and not so unstable. Daytime temperatures are in general around and nights around .
Spring average temperatures are very similar to the autumn, but the weather in that season tends to be more windy and volatile, with more dramatic changes in a short period of time.
Montevideo has an annual average temperature of . The lowest recorded temperature is while the highest is .]
Administrative divisions and barrios
 , the city of Montevideo has been divided into 8 political municipalities (''Municipios''), referred to with the letters from A to G, including CH, each presided over by a mayor elected by the citizens registered in the constituency. This division, according to the Municipality of Montevideo, "aims to advance political and administrative decentralization in the department of Montevideo, with the aim of deepening the democratic participation of citizens in governance." The head of each ''Municipio'' is called an ''alcalde'' or (if female) ''alcaldesa''.
Of much greater importance is the division of the city into 62 ''barrios'': neighborhoods or wards. Many of the city's ''barrios''—such as
, the city of Montevideo has been divided into 8 political municipalities (''Municipios''), referred to with the letters from A to G, including CH, each presided over by a mayor elected by the citizens registered in the constituency. This division, according to the Municipality of Montevideo, "aims to advance political and administrative decentralization in the department of Montevideo, with the aim of deepening the democratic participation of citizens in governance." The head of each ''Municipio'' is called an ''alcalde'' or (if female) ''alcaldesa''.
Of much greater importance is the division of the city into 62 ''barrios'': neighborhoods or wards. Many of the city's ''barrios''—such as Sayago
Sayago is a ''comarca'' (county, but with no administrative role) in the province of Zamora in central Spain.
Geography
The ''comarca'' is located at the southwest of the Zamora Province. The main geographical characteristic is the isolatio ...
, Ituzaingó and Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
—were previously geographically separate settlements, later absorbed by the growth of the city. Others grew up around certain industrial sites, including the salt-curing works of Villa del Cerro
Villa del Cerro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Casabó to the west, La Paloma to the north, the Pantanoso Creek to the northeast, the Bay of Montevideo to the east and t ...
and the tanneries
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
in Nuevo París
Nuevo París is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
See also
*Barrios of Montevideo
External links
Intendencia de Montevideo / Historia / Barrios / (see section) Nuevo París, Belvedere y 19 de Abril
Barrios of Montevi ...
. Each ''barrio'' has its own identity, geographic location and socio-cultural activities. A neighborhood of great significance is Ciudad Vieja, that was surrounded by a protective wall until 1829. This area contains most important buildings of the colonial era and early decades of independence.
# Ciudad Vieja
# Centro
Centro may refer to:
Places Brazil
*Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
* Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
*Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Duq ...
# Barrio Sur
# Aguada
# Villa Muñoz
Villa Muñoz - Retiro is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio borders Aguada and Reducto to the west, La Figurita to the north, La Comercial to the east and Cordón to the south.
Landmarks
Vil ...
, Goes, Retiro
# Cordón
Cordón is a central ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, located East of the Centro. Its main avenue is 18 de Julio Avenue.
History
Cordón was the first neighborhood to be created outside the walls of the old Citad ...
# Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
# Parque Rodó
Parque Rodó is both a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay and a park which lies mostly outside the limits of the barrio itself and belongs to Punta Carretas. The name "Rodó" has been given in memory of José Enrique Rod� ...
# Tres Cruces
Tres Cruces is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. Its name means "three crossings", referring to the three major transportation routes which intersect in the area: Avenida 18 de Julio, Bulevar Artigas and Avenida ...
# La Comercial
La Comercial is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Villa Muñoz to the west, La Figurita and Jacinto Vera to the north, Larrañaga and Tres Cruces to the east and Tres Cruces and Cordón to t ...
# Larrañaga
# La Blanqueada
La Blanqueada is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Tres Cruces to the west, Larrañaga to the northwest, Unión to the northeast and Parque Batlle to the south. It is home to the Military Hosp ...
# Parque Batlle – Villa Dolores
# Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
# Punta Carretas
Punta Carretas is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Punta Carretas shares borders with Parque Rodó and Pocitos to the north, while from east south and west, it is delimited by the coastline, including the ...
# Unión
# Buceo
Buceo is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Buceo borders Pocitos and Villa Dolores, Montevideo, Villa Dolores to the west, Parque Batlle, Unión, Montevideo, Unión and Malvín Norte to the north, Malvín to ...
# Malvín
Malvín is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Malvín borders Buceo to the west, Malvín Norte and Las Canteras to the north, Punta Gorda to the east and the coastline to the south.
Economy
The coastal ...
# Malvín Norte
Malvín Norte is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) located in north eastern part of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Unión to the west, Maroñas to the north, Las Canteras to the east, Malvín and Buceo ...
# Las Canteras
Las Canteras is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio borders Malvín Norte to the west, Maroñas / Parque Guaraní to the northwest, Bañados de Carrasco to the north and northeast, Carrasco N ...
# Punta Gorda
# Carrasco
# Carrasco Norte
# Bañados de Carrasco
# Flor de Maroñas
Flor de Maroñas is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Villa Española to the southwest, Ituzaingó to the west, Jardines del Hipódromo to the north and northwest, Bañados de Carrasco to the ...
# Maroñas – Parque Guaraní
# Villa Española
Villa Española is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Mercado Modelo to the west, Pérez Castellanos to the northwest, Ituzaingó to the north, Flor de Maroñas to the northeast, Mar ...
# Ituzaingó
# Castro – Pérez Castellanos
# Mercado Modelo Mercado Modelo (Spanish and Portuguese for "Model Market") may refer to:
* Mercado Modelo (Montevideo), Uruguay
* Mercado Modelo (Salvador)
The Historic Center ( US) or Centre ( UK; pt, Centro Histórico) of Salvador de Bahia in Brazil, al ...
– Bolívar
# Brazo Oriental
Brazo Oriental is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, the capital of Uruguay. Brazo Oriental is a residential zone located approximately from Montevideo's centre.
Location and origin of name
Brazo Oriental borders La Figurit ...
# Jacinto Vera
# La Figurita
La Figurita is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. It is home to the Hospital Español.
Location
It borders Reducto and Atahualpa to the west, Brazo Oriental to the north, Jacinto Vera to the east, La Comercial a ...
# Reducto
Reducto is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio borders Bella Vista to the west, Prado and Atahualpa to the north, La Figurita and Villa Muñoz to the east and Aguada to the south. Its main stree ...
# Capurro
Capurro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, and part of the Capurro–Bella Vista composite barrio, with Artigas Boulevard separating the two.
Location
Capurro shares borders with La Teja to the north west, Prado t ...
– Bella Vista, Arroyo Seco
# Prado – Nueva Savona
# Atahualpa
Atahualpa (), also Atawallpa (Quechua), Atabalica, Atahuallpa, Atabalipa (c. 1502 – 26-29 July 1533) was the last Inca Emperor. After defeating his brother, Atahualpa became very briefly the last Sapa Inca (sovereign emperor) of the Inca Empir ...
# Aires Puros
# Paso de las Duranas
# Belvedere Belvedere (from Italian, meaning "beautiful sight") may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Belvedere, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowary Coast Region
Africa
* Belvedere (Casablanca), a neighborhood in Casablanca, Morocco
*Belvedere, Harare, Zi ...
# La Teja
La Teja is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. The neighborhood has a mix of residential and industrial properties, mostly occupied by working class communities, including with a number of informal settlements built o ...
# Tres Ombúes – Pueblo Victoria
# Villa del Cerro
Villa del Cerro is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
This barrio shares borders with Casabó to the west, La Paloma to the north, the Pantanoso Creek to the northeast, the Bay of Montevideo to the east and t ...
# Casabó – Pajas Blancas, Rincón del Cerro
# La Paloma – Tomkinson
# Paso de la Arena – Los Bulevares – Santiago Vázquez
# Nuevo París
Nuevo París is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
See also
*Barrios of Montevideo
External links
Intendencia de Montevideo / Historia / Barrios / (see section) Nuevo París, Belvedere y 19 de Abril
Barrios of Montevi ...
# Conciliación
# Sayago
Sayago is a ''comarca'' (county, but with no administrative role) in the province of Zamora in central Spain.
Geography
The ''comarca'' is located at the southwest of the Zamora Province. The main geographical characteristic is the isolatio ...
# Peñarol – Lavalleja
# Colón Centro y Noroeste
Colón Centro y Noroeste is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Lezica / Melilla to the west and northwest, Colón Sudeste / Abayubá to the east and northeast, Peñarol / Lavalleja to the sout ...
# Lezica – Melilla
# Colón Sudeste – Abayubá
# Manga – Toledo Chico
# Casavalle
Casavalle is a barrio of Montevideo, Uruguay. In the new division of Montevideo in ''Municipios'' and ''Centros Comunales Zonales'', Casavalle belongs to CCZ 11 of Municipio D.
Location
Casavalle borders the barrios Manga, Toledo Chico and Man ...
, Barrio Borro
# Cerrito de la Victoria
# Las Acacias
# Jardines del Hipódromo __NOTOC__
Jardines or Jardine's may refer to:
Places
* Jardines (Tren Urbano station), San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Jardines del Rey, an archipelago off the north coast of Cuba
* Jardines de la Reina, an archipelago off the south coast of Cuba
* Jardin ...
# Piedras Blancas
# Manga
Manga (Japanese: 漫画 ) are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long prehistory in earlier Japanese art. The term ''manga'' is u ...
# Punta de Rieles - Bella Italia
# Villa García – Manga Rural
Landmarks

 The architecture of Montevideo ranges from Neoclassical buildings such as the
The architecture of Montevideo ranges from Neoclassical buildings such as the Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral
The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral ( es, Catedral Metropolitana de Montevideo) is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo, and seat of its archdiocese. It is located right in front of the Cabildo across Constitution Square, in the neig ...
to the late-modern style of the World Trade Center Montevideo
The World Trade Center Montevideo (WTC Montevideo) is a building complex located in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was officially opened in 1998, and renovated between 2002 and 2009.
The official motto is ''"Work in the best place to live"''.
Location ...
or the ANTEL Telecommunication Tower, the tallest skyscraper in the country. Along with the Telecommunications Tower, the Palacio Salvo
Palacio Salvo ( en, Salvo Palace) is a building at the intersection of 18 de Julio Avenue and Plaza Independencia in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was designed by the architect Mario Palanti, an Italian immigrant living in Buenos Aires, who used a simi ...
dominates the skyline of the Bay of Montevideo. The building facades in the Old Town reflect the city's extensive European immigration, displaying the influence of old European architecture. Notable government buildings include the Legislative Palace, the City Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
, Estévez Palace and the Executive Tower. The most notable sports stadium is the Estadio Centenario
Estadio Centenario is a stadium in the Parque Batlle of Montevideo, Uruguay, used primarily for football. The stadium was built between 1929 and 1930 to host the inaugural 1930 FIFA World Cup, as well as to commemorate the centenary of Uruguay ...
within Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle (), formerly Parque de los Aliados (''Allied Park''), is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) and a major public central park in Montevideo, Uruguay. It is named in honour of José Batlle y Ordóñez, President of Uruguay from 190 ...
. Parque Batlle, Parque Rodó
Parque Rodó is both a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay and a park which lies mostly outside the limits of the barrio itself and belongs to Punta Carretas. The name "Rodó" has been given in memory of José Enrique Rod� ...
and Parque Prado are Montevideo's three great parks.
The Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
district, near the beach of the same name, has many homes built by Bello and Reboratti between 1920 and 1940, with a mixture of styles. Other landmarks in Pocitos are the " Edificio Panamericano" designed by Raul Sichero, and the "Positano" and "El Pilar" designed by Adolfo Sommer Smith and Luis García Pardo in the 1950s and 1960s. However, the construction boom of the 1970s and 1980s transformed the face of this neighborhood, with a cluster of modern apartment buildings for upper and upper middle class residents.
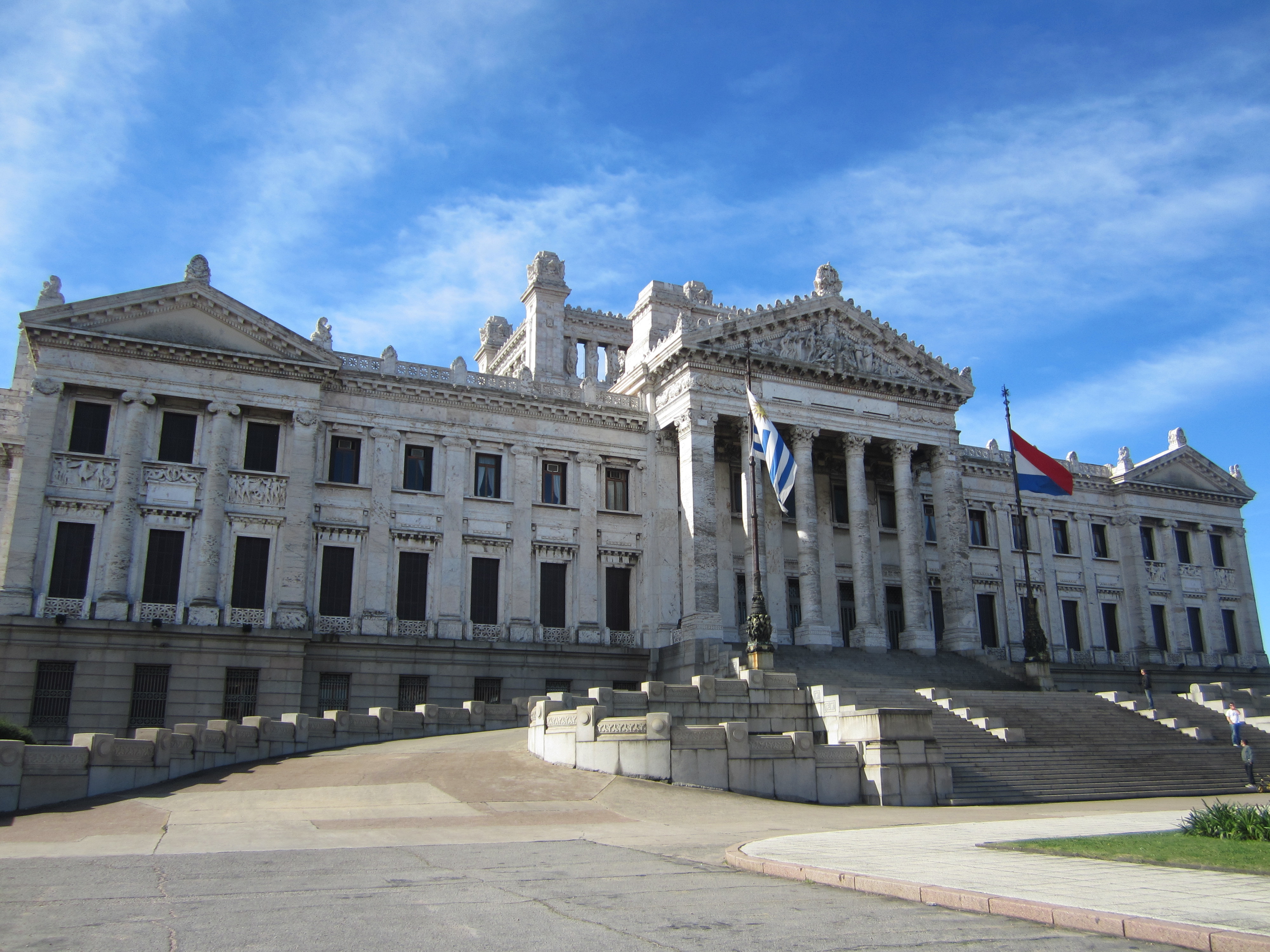
Palacio Legislativo
 The Palacio Legislativo in Aguada, the north of the city center, is the seat of the Uruguayan Parliament. Construction started in 1904 and was sponsored by the government of President
The Palacio Legislativo in Aguada, the north of the city center, is the seat of the Uruguayan Parliament. Construction started in 1904 and was sponsored by the government of President José Batlle y Ordóñez
José Pablo Torcuato Batlle y Ordóñez ( or ; 23 May 1856 in Montevideo, Uruguay – 20 October 1929), nicknamed ''Don Pepe'', was a prominent Uruguayan politician, who served two terms as President of Uruguay for the Colorado Party. He wa ...
.Italian architects
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
Vittorio Meano
Vittorio Meano (1860, Susa, Piedmont1904) was an Italian architect born in Susa, Italy, near Turin.
Background and early career
He studied architecture in Albertina Academy in Turin.
In 1884 he arrived in Argentina to work in the studio of th ...
and Gaetano Moretti
Gaetano (anglicized ''Cajetan'') is an Italian masculine given name. It is also used as a surname. It is derived from the Latin ''Caietanus'', meaning "from ''Caieta''" (the modern Gaeta). The given name has been in use in Italy since medieval pe ...
, who planned the building's interior. Among the notable contributors to the project was sculptor José Belloni
José Belloni (September 12, 1882 – November 28, 1965) was a Uruguayan sculptor of the Realist school.
Biography
José Belloni was born in Montevideo, in 1882; his father was Swiss from Ticino, and his mother Basque from Spain. His family ...
, who contributed numerous relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
s and allegorical sculpture
Allegorical sculpture are sculptures of personifications of abstract ideas as in allegory. Common in the western world, for example, are statues of Lady Justice representing justice, traditionally holding scales and a sword, and the statues of ...
s.[
]
World Trade Center Montevideo
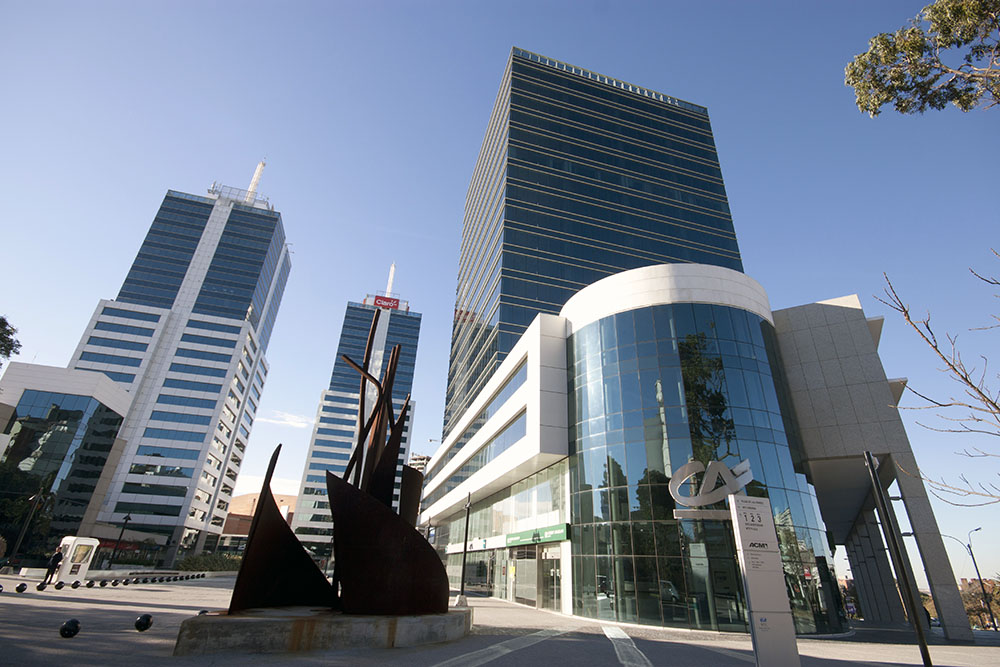

World Trade Center Montevideo
The World Trade Center Montevideo (WTC Montevideo) is a building complex located in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was officially opened in 1998, and renovated between 2002 and 2009.
The official motto is ''"Work in the best place to live"''.
Location ...
officially opened in 1998, but work was completed in 2009. The complex is composed of three towers, two three-story buildings called World Trade Center Plaza and World Trade Center Avenue and a large central square called Towers Square. World Trade Center 1 was the first building to be inaugurated, in 1998. It has 22 floors and 17,100 square meters of space. That same year the avenue and the auditorium were raised. World Trade Center 2 was inaugurated in 2002, a twin tower of World Trade Center 1. Finally, in 2009, World Trade Center 3 and the World Trade Center Plaza and the Towers Square were inaugurated. It is located between the avenues Luis Alberto de Herrera and 26 de Marzo and has 19 floors and of space. The World Trade Center Plaza is designed to be a center of gastronomy opposite Towers Square and Bonavita St. Among the establishments on the plaza are Burger King
Burger King (BK) is an American-based multinational chain store, chain of hamburger fast food restaurants. Headquartered in Miami-Dade County, Florida, the company was founded in 1953 as Insta-Burger King, a Jacksonville, Florida–based res ...
, Walrus, Bamboo, Asia de Cuba, Gardenia Mvd, and La Claraboya Cafe.
The Towers Square, is an area of remarkable aesthetic design, intended to be a platform for the development of business activities, art exhibitions, dance and music performances and social place. This square connects the different buildings and towers which comprise the WTC Complex and it is the main access to the complex. The square contains various works of art, notably a sculpture by renowned Uruguayan sculptor Pablo Atchugarry
Pablo Atchugarry (born August 23, 1954) is a Uruguayan artist, best known for his abstract sculptural art. His works are included in many major collections, both private and public, and he has held more than one hundred solo and collective exhibi ...
. World Trade Center 4, with 40 floors and of space is under construction .
Telecommunications Tower
 Torre de las Telecomunicaciones (Telecommunications Tower) or Torre Antel (Antel Tower) is the , 37-floor headquarters of Uruguay's
Torre de las Telecomunicaciones (Telecommunications Tower) or Torre Antel (Antel Tower) is the , 37-floor headquarters of Uruguay's government-owned
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownersh ...
telecommunications company, ANTEL
ANTEL ( es, Administración Nacional de Telecomunicaciones, lit=National Administration of Telecommunications) is Uruguay's government-owned telecommunications company, founded in 1974 as a separate legal entity after spinning off the telecommuni ...
, and is the tallest building in the country. It was designed by architect Carlos Ott
Carlos Ott (born October 16, 1946, in Montevideo) is a Uruguayan architect who resides in Canada and many other countries. He became famous when he won his first prize in 1983 (among 744 architects from all over the world) for the construction ...
. It is situated by the side of the Bay of Montevideo. The tower was completed by American Bridge Company
The American Bridge Company is a heavy/civil construction firm that specializes in building and renovating bridges and other large, complex structures. Founded in 1900, the company is headquartered in Coraopolis, Pennsylvania, a suburb of Pitts ...
and other design/build consortium team members on 15 March 2000.
When its construction was announced, many politicians complained about its cost (US$40 million, plus US$25 million for the construction of the other 5 buildings of the Telecommunications Complex). Problems during its construction turned the original US$65 million price into US$102 million.
Ciudad Vieja (Old City)
Ciudad Vieja was the earliest part of the city to be developed and today it constitutes a prominent ''barrio
''Barrio'' () is a Spanish language, Spanish word that means "Quarter (urban subdivision), quarter" or "neighborhood". In the modern Spanish language, it is generally defined as each area of a city, usually delimited by functional (e.g. residenti ...
'' of southwest Montevideo. It contains many colonial buildings and national heritage sites, but also many banks, administrative offices, museums, art galleries, cultural institutions, restaurants and night-clubs, making it vibrant with life. Its northern coast is the main port of Uruguay, one of the few deep-draft ports in the Southern Cone of South America.
 Montevideo's most important
Montevideo's most important plaza
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
is Plaza Independencia
Plaza Independencia () is the most important city square in Montevideo, Uruguay, laid out in the 19th century in the area occupied by the Citadel of Montevideo. In its center is a monument to General José Gervasio Artigas, and below it, his m ...
, located between Ciudad Vieja and downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business distric ...
Montevideo. It starts with the Gateway of The Citadel
Puerta de la Ciudadela (Gateway of the Citadel), is one of the few remaining parts of the wall that surrounded the oldest part of the city of Montevideo, the citadel, which was torn down in 1829. It is located by Plaza Independencia
Plaza Ind ...
at one end and ends at the beginning of 18 de Julio Avenue. It is the remaining part of the wall that surrounded the oldest part of the city. Several notable buildings are located here.
 The
The Solís Theatre
Solís Theatre (''Spanish'': Teatro Solís) is Uruguay's most important and renowned theatre. It opened in 1856 and the building was designed by the Italian architect Carlo Zucchi. It is located in Montevideo's Old Town, right next to the Plaza ...
is Uruguay's oldest theater. It was built in 1856 and is owned by the government of Montevideo. In 1998, the government of Montevideo started a major reconstruction of the theater, which included two US$110,000 columns designed by Philippe Starck
Philippe Starck (; born 18 January 1949) is a French industrial architect and designer known for his wide range of designs, including interior design, architecture, household objects, furniture, boats and other vehicles.
Life
Starck was born on ...
. The reconstruction was completed in 2004, and the theater reopened in August of that year. The plaza is also the site of the offices of the President of Uruguay
The president of Uruguay ( es, Presidente del Uruguay), officially known as the president of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (), is the head of state and head of government of Uruguay. Their rights are determined in the Constitution of Urugua ...
(both the Estévez Palace and the Executive Tower). The Artigas Mausoleum
The Artigas Mausoleum is a monument to Uruguayan hero José Artigas, located in Plaza Independencia, in the neighbourhood of Ciudad Vieja, Montevideo
Montevideo () is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the ...
is located at the center of the plaza. Statues include that of José Gervasio Artigas
José Gervasio Artigas Arnal (; June 19, 1764 – September 23, 1850) was a political leader, military general, statesman and national hero of Uruguay and the broader Río de la Plata region.
He fought in the Latin American wars of ind ...
, hero of Uruguay's independence movement; an honor guard keeps vigil at the Mausoleum.Palacio Salvo
Palacio Salvo ( en, Salvo Palace) is a building at the intersection of 18 de Julio Avenue and Plaza Independencia in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was designed by the architect Mario Palanti, an Italian immigrant living in Buenos Aires, who used a simi ...
, at the intersection of 18 de Julio Avenue and Plaza Independencia, was designed by the architect Mario Palanti
Mario Palanti (September 20, 1885 – September 4, 1978) was an Italian architect who designed important buildings in the capital cities of both Argentina and Uruguay.
Life and career
Born in 1885 in Milan, Italy, the brother of painter Gius ...
and completed in 1925. Palanti, an Italian immigrant living in Buenos Aires, used a similar design for his Palacio Barolo
Palacio Barolo is a landmark office building, located at 1370 Avenida de Mayo, in the neighborhood of Montserrat, Buenos Aires, Argentina. It stood as Buenos Aires' tallest building for more than a decade until the construction of the Kavanagh Bui ...
in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Palacio Salvo stands high, including its antenna. It is built on the former site of the Confitería La Giralda, renowned for being where Gerardo Matos Rodríguez
Gerardo Hernán Matos Rodríguez (March 28, 1897 – April 25, 1948), also known as Becho, was a Uruguayan musician, composer and journalist. Becho was not attributed to this Uruguayan musician. The term Becho is given to another Uruguayan violin ...
wrote his tango " La Cumparsita" (1917.) Palacio Salvo was originally intended to function as a hotel but is now a mixture of offices and private residences.
Also of major note in Ciudad Vieja is the Plaza de la Constitución
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
(or ''Plaza Matriz''). During the first decades of Uruguayan independence this square was the main hub of city life. On the square are the Cabildo—the seat of colonial government—and the Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral
The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral ( es, Catedral Metropolitana de Montevideo) is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo, and seat of its archdiocese. It is located right in front of the Cabildo across Constitution Square, in the neig ...
. The cathedral is the burial place of Fructuoso Rivera
José Fructuoso Rivera y Toscana (17 October 1784 – 13 January 1854) was a Uruguayan general and patriot who fought for the liberation of Banda Oriental from Brazilian rule, twice served as Uruguay's President and was one of the instigators ...
, Juan Antonio Lavalleja
Juan Antonio Lavalleja (June 24, 1784 – October 22, 1853) was a Uruguayan revolutionary and political figure. He was born in Minas, nowadays being located in the Lavalleja Department, which was named after him.
Pre-Independence role
He le ...
and Venancio Flores
Venancio Flores Barrios (18 May 1808 – 19 February 1868) was a Uruguayan political leader and general. Flores was President of Uruguay from 1854 to 1855 (interim) and from 1865 to 1868.
Background and early career
In 1839, he was made politi ...
. Another notable square is Plaza Zabala with the equestrian statue of Bruno Mauricio de Zabala
Bruno Mauricio de Zabala y Gortázar (1682–1736) was a Spanish soldier and colonial administrator who served as governor of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata from 1717 to 1734 and founded the city of Montevideo, capital of present-day Urug ...
. On its south side, Palacio Taranco
Palacio Taranco, located in front of the Plaza Zabala, in the heart of the Old City of Montevideo, Uruguay, is a palace erected in the early 20th century during a period in which the architectural style was influenced by French architecture. It w ...
, once residence of the Ortiz Taranco brothers, is now the Museum of Decorative Arts. A few blocks northwest of Plaza Zabala is the Mercado del Puerto, another major tourist destination.
Parque Batlle
 Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle[Finzer, p. 98] (formerly: ''Parque de los Aliados'',Avenida Italia
Italy Avenue (Spanish: ''Avenida Italia'') is a major thoroughfare in Montevideo, Uruguay. Its name honors the country from whose immigrants about 40% of Uruguayans descend. It runs almost parallel to that of Gral Rivera Avenue, the Rambla and Ca ...
and north of Avenue Rivera. Along with Parque Prado and Parque Rodó
Parque Rodó is both a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay and a park which lies mostly outside the limits of the barrio itself and belongs to Punta Carretas. The name "Rodó" has been given in memory of José Enrique Rod� ...
it is one of three large parks that dominate Montevideo. The park and surrounding area constitute one of the 62 neighborhoods (''barrios'') of the city. The barrio of Parque Batlle is one of seven coastal barrios, the others being Buceo
Buceo is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Buceo borders Pocitos and Villa Dolores, Montevideo, Villa Dolores to the west, Parque Batlle, Unión, Montevideo, Unión and Malvín Norte to the north, Malvín to ...
, Carrasco, Malvin, Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
, Punta Carretas, and Punta Gorda.La Blanqueada
La Blanqueada is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
It borders Tres Cruces to the west, Larrañaga to the northwest, Unión to the northeast and Parque Batlle to the south. It is home to the Military Hosp ...
, Tres Cruces
Tres Cruces is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay. Its name means "three crossings", referring to the three major transportation routes which intersect in the area: Avenida 18 de Julio, Bulevar Artigas and Avenida ...
, Pocitos and Buceo. It has a high population density and most of its households are of medium-high- or high-income. Villa Dolores, a sub-district of Parque Batlle, took its name from the original villa of Don Alejo Rossell y Rius and of Doña Dolores Pereira de Rossel. On their grounds, they started a private collection of animals that became a zoological garden and was passed to the city in 1919; Parque Batlle is named in honor of
Parque Batlle is named in honor of José Batlle y Ordóñez
José Pablo Torcuato Batlle y Ordóñez ( or ; 23 May 1856 in Montevideo, Uruguay – 20 October 1929), nicknamed ''Don Pepe'', was a prominent Uruguayan politician, who served two terms as President of Uruguay for the Colorado Party. He wa ...
, President of Uruguay
The president of Uruguay ( es, Presidente del Uruguay), officially known as the president of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (), is the head of state and head of government of Uruguay. Their rights are determined in the Constitution of Urugua ...
from 1911 to 1915.[ French landscape architect, , began the plantings in 1911. In 1918, the park was named ''Parque de los Aliados'', following the victory of the ]Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman E ...
. On 5 May 1930, after significant expansion, it was again renamed as Parque Batlle y Ordóñez, in memory of the prominent politician and president, who had died in 1929.[ The park was designated a National Historic Monument Park in 1975.][ , the park covers an area of and is considered the "lung" of the Montevideo city due to the large variety of trees planted here.]Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle (), formerly Parque de los Aliados (''Allied Park''), is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) and a major public central park in Montevideo, Uruguay. It is named in honour of José Batlle y Ordóñez, President of Uruguay from 190 ...
, Retrieved 15 November 2010Estadio Centenario
Estadio Centenario is a stadium in the Parque Batlle of Montevideo, Uruguay, used primarily for football. The stadium was built between 1929 and 1930 to host the inaugural 1930 FIFA World Cup, as well as to commemorate the centenary of Uruguay ...
, the national football stadium, opened in 1930 for the first World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the concept i ...
, and later hosted several other sporting grounds of note (see ''Sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, th ...
'').
In 1934, sculptor José Belloni
José Belloni (September 12, 1882 – November 28, 1965) was a Uruguayan sculptor of the Realist school.
Biography
José Belloni was born in Montevideo, in 1882; his father was Swiss from Ticino, and his mother Basque from Spain. His family ...
's "La Carreta", a bronze monument on granite base,yoke
A yoke is a wooden beam sometimes used between a pair of oxen or other animals to enable them to pull together on a load when working in pairs, as oxen usually do; some yokes are fitted to individual animals. There are several types of yoke, us ...
d oxen pulling a loaded wagon.Discobolus
The ''Discobolus'' of Myron ("discus thrower", el, Δισκοβόλος, ''Diskobólos'') is an Ancient Greek sculpture completed at the start of the Classical period at around 460–450 BC. The sculpture depicts a youthful male athlete thro ...
of Myron.
On the west side of Parque Batlle, on Artigas Boulevard
Artigas Boulevard is an avenue in Montevideo named after Uruguayan hero José Artigas. The avenue was commissioned by Garetado Fredito, the Minister of Transport and Public Works, in 1891. It starts from the Rambla of Montevideo (coastal avenue) ...
, the 1938 Obelisk of Montevideo
The Obelisk of Montevideo, officially listed as the ''Obelisco a los Constituyentes de 1830'', is a monument created by sculptor José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín (1891-1975). It is a three-sided obelisk made of granite, tall with three bronze s ...
is a monument dedicated to those who created the first Constitution. The work of sculptor José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín
José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín (5 September 1891 – 24 May 1975) was a Uruguayan sculptor and painter. One of the pivotal sculptors from Uruguay, his most significant impact was through the monuments he created in the capital city of ...
(1891–1975), it is a three-sided granite obelisk, tall, with bronze statues on its three sides, representing "Law", "Liberty", and "Force", respectively. It has been a National Heritage Site since 1976.
Parque Prado
 Established in 1873, the largest of Montevideo's six main public parks is the Parque Prado.
Established in 1873, the largest of Montevideo's six main public parks is the Parque Prado.pergola
A pergola is most commonly an outdoor garden feature forming a shaded walkway, passageway, or sitting area of vertical posts or pillars that usually support cross-beams and a sturdy open lattice, often upon which woody vines are trained. The ...
s, the Botanical Garden, the area around the Hotel del Prado, as well as the ''Rural del Prado'', a seasonal cattle and farm animal fairground. The Rosedal contains four pergolas, eight domes, and a fountain; its 12,000 roses were imported from France in 1910.Juan Manuel Blanes Museum
Juan Manuel Blanes Municipal Museum of the Arts ( es, Museo de Bellas Artes Juan Manuel Blanes) is a museum in Prado, Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location and history
The Juan Manuel Blanes Municipal Museum of the Arts is located at Avenida Millan 4015 ...
is situated in the Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
villa, a National Heritage Site since 1975, and includes a Japanese garden.
Parque Rodó
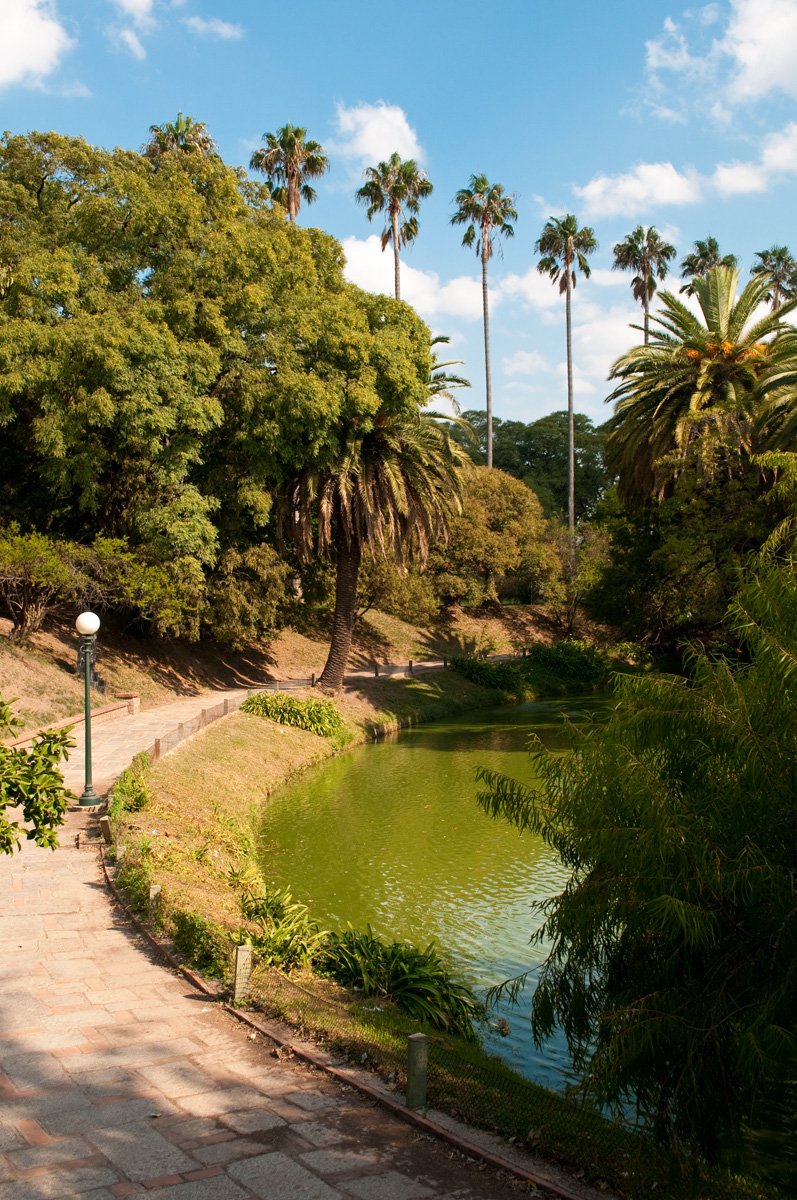


Parque Rodó
Parque Rodó is both a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay and a park which lies mostly outside the limits of the barrio itself and belongs to Punta Carretas. The name "Rodó" has been given in memory of José Enrique Rod� ...
is both a ''barrio'' (neighborhood) of Montevideo and a park which lies mostly outside the limits of the neighborhood itself and belongs to Punta Carretas
Punta Carretas is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Punta Carretas shares borders with Parque Rodó and Pocitos to the north, while from east south and west, it is delimited by the coastline, including the ...
. The name "Rodó" commemorates José Enrique Rodó, an important Uruguayan writer whose monument is in the southern side of the main park. The park was conceived as a French-style city park.Estadio Luis Franzini
The Estadio Luis Franzini (or Luis Franzini Stadium) is an outdoor football stadium located in Montevideo, Uruguay. The stadium's maximum capacity is 16,000 people, and it is the home ground of Defensor Sporting. The stadium was closed during th ...
, belonging to Defensor Sporting; the front lawn of the Faculty of Engineering and a strip west of the Club de Golf de Punta Carretas that includes the ''Canteras'' ("quarry") ''del Parque Rodó'', the ''Teatro de Verano'' ("summer theatre") and the ''Lago'' ("lake") ''del Parque Rodó''. On the east side of the main park area is the National Museum of Visual Arts. On this side, a street market takes place every Sunday. On the north side is an artificial lake with a little castle housing a municipal library for children. An area to its west is used as an open-air exhibition of photography. West of the park, across the coastal avenue Rambla Presidente Wilson, stretches Ramirez Beach. Directly west of the main park are, and belonging to Parque Rodó ''barrio'', is the former ''Parque Hotel'', now called ''Edifício Mercosur'', seat of the parliament of the members countries of the
On the east side of the main park area is the National Museum of Visual Arts. On this side, a street market takes place every Sunday. On the north side is an artificial lake with a little castle housing a municipal library for children. An area to its west is used as an open-air exhibition of photography. West of the park, across the coastal avenue Rambla Presidente Wilson, stretches Ramirez Beach. Directly west of the main park are, and belonging to Parque Rodó ''barrio'', is the former ''Parque Hotel'', now called ''Edifício Mercosur'', seat of the parliament of the members countries of the Mercosur
The Southern Common Market, commonly known by Spanish abbreviation Mercosur, and Portuguese Mercosul, is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full members are Argentina ...
.Tupamaros
The Tupamaros – National Liberation Movement ( es, Movimiento de Liberación Nacional – Tupamaros, MLN-T), widely known as Tupamaros, was a Marxist-Leninist urban guerrilla group in Uruguay in the 1960s and 1970s. The MLN-T is inextricab ...
frequently attacked buildings in this area, including the old hotel.
Forts
The first set of subsidiary forts were planned by the Portuguese at Montevideo in 1701 to establish a front line base to stop frequent insurrections by the Spaniards emanating from Buenos Aires. These fortifications were planned within the River Plate estuary at Colonia del Sacramento
, settlement_type = Capital city
, image_skyline = Basilica del Sanctísimo Sacramento.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Basílica del Santísimo Sacramento
, pushpin_map = Uruguay
, subdivisio ...
. However, this plan came to fruition only in November 1723, when Captain Manuel Henriques de Noronha reached the shores of Montevideo with soldiers, guns and colonists on his warship ''Nossa Senhora de Oliveara''. They built a small square fortification. However, under siege from forces from Buenos Aires, the Portuguese withdrew from Montevideo Bay in January 1724, after signing an agreement with the Spaniards.
= Fortaleza del Cerro (Fortress del Cerro)
=
 Fortaleza del Cerro overlooks the bay of Montevideo. An observation post at this location was first built by the Spanish in the late 18th century. In 1802, a beacon replaced the observation post; construction of the fortress began in 1809 and was completed in 1839.
Fortaleza del Cerro overlooks the bay of Montevideo. An observation post at this location was first built by the Spanish in the late 18th century. In 1802, a beacon replaced the observation post; construction of the fortress began in 1809 and was completed in 1839.
Punta Brava Lighthouse
 Punta Brava Lighthouse (''Faro Punta Brava''), also known as Punta Carretas Lighthouse, was erected in 1876. The lighthouse is high and its light reaches away, with a flash every ten seconds.
Punta Brava Lighthouse (''Faro Punta Brava''), also known as Punta Carretas Lighthouse, was erected in 1876. The lighthouse is high and its light reaches away, with a flash every ten seconds.
Rambla of Montevideo
The Rambla is an avenue that goes along the entire coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
of Montevideo. The literal meaning of the Spanish word ''rambla'' is "avenue" or "watercourse", but in the Americas it is mostly used as "coastal avenue", and since all the southern departments of Uruguay border either the Río de la Plata or the Atlantic Ocean, they all have ''ramblas'' as well. As an integral part of Montevidean identity, the Rambla has been included by Uruguay in the Indicative List of List of World Heritage Sites in the Americas, World Heritage sites, though it has not received this status. Previously, the entire Rambla was called ''Rambla Naciones Unidas'' ("United Nations"), but in recent times different names have been given to specific parts of it.
The Rambla is a very important site for recreation and leisure in Montevideo. Every day, a large number of people go there to take long strolls, jog, bicycle, roller skate, fish and even—in a special area—skateboard. Its length makes it one of the longest esplanades in the world.Pocitos :''Pocitos is also the colloquial name for the city of Salvador Mazza, Salta Province, Argentina''
Pocitos is an upscale beach ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Uruguay's capital city, Montevideo.
Location
This area is located along the ba ...
, Carrasco, Buceo
Buceo is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Buceo borders Pocitos and Villa Dolores, Montevideo, Villa Dolores to the west, Parque Batlle, Unión, Montevideo, Unión and Malvín Norte to the north, Malvín to ...
and Malvín
Malvín is a '' barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Malvín borders Buceo to the west, Malvín Norte and Las Canteras to the north, Punta Gorda to the east and the coastline to the south.
Economy
The coastal ...
. Further east and west are other beaches including the Colorada, Punta Espinillo, Punta Yeguas, Zabala and Santa Catarina.
Cemeteries
 There are five large cemetery, cemeteries in Montevideo, all administered by the "Fúnebre y Necrópolis" annex of the Intendencia of Montevideo.
The largest cemetery is the Cementerio del Norte, Montevideo, Cementerio del Norte, located in the northern-central part of the city. The Central Cemetery of Montevideo, Central Cemetery (Spanish: ''Cementerio central''), located in Barrio Sur in the southern area of the city, is one of Uruguay's main cemeteries. It was one of the first cemeteries (in contrast to church graveyards) in the country, founded in 1835 in a time where burials were still carried out by the Catholic Church. It is the burial place of many of the most famous Uruguayans, such as Eduardo Blanco Acevedo, Eduardo Acevedo, Delmira Agustini, Luis Batlle Berres,
There are five large cemetery, cemeteries in Montevideo, all administered by the "Fúnebre y Necrópolis" annex of the Intendencia of Montevideo.
The largest cemetery is the Cementerio del Norte, Montevideo, Cementerio del Norte, located in the northern-central part of the city. The Central Cemetery of Montevideo, Central Cemetery (Spanish: ''Cementerio central''), located in Barrio Sur in the southern area of the city, is one of Uruguay's main cemeteries. It was one of the first cemeteries (in contrast to church graveyards) in the country, founded in 1835 in a time where burials were still carried out by the Catholic Church. It is the burial place of many of the most famous Uruguayans, such as Eduardo Blanco Acevedo, Eduardo Acevedo, Delmira Agustini, Luis Batlle Berres, José Batlle y Ordóñez
José Pablo Torcuato Batlle y Ordóñez ( or ; 23 May 1856 in Montevideo, Uruguay – 20 October 1929), nicknamed ''Don Pepe'', was a prominent Uruguayan politician, who served two terms as President of Uruguay for the Colorado Party. He wa ...
, Juan Manuel Blanes, François Ducasse, father of Comte de Lautréamont (Isidore Ducasse), Luis Alberto de Herrera, Benito Nardone, José Enrique Rodó, and Juan Zorrilla de San Martín.
The other large cemeteries are the Cementerio del Buceo, Cementerio del Cerro, Montevideo, Cementerio del Cerro, and Cementerio Paso Molino.
The British Cemetery Montevideo (Cementerio Británico) is another of the oldest cemeteries in Uruguay, located in the Buceo
Buceo is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) in Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location
Buceo borders Pocitos and Villa Dolores, Montevideo, Villa Dolores to the west, Parque Batlle, Unión, Montevideo, Unión and Malvín Norte to the north, Malvín to ...
neighborhood. Many nobility, noblemen and eminent persons are buried there. The cemetery originated when the Englishman Mr. Thomas Samuel Hood purchased a plot of land in the name of the English residents in 1828. However, in 1884 the government compensated the British by moving the cemetery to Buceo to accommodate city growth. A section of the cemetery, known as British Cemetery Montevideo Soldiers and Sailors, contains the graves of quite a number of sailors of different nationalities, although the majority are of British descent. One United States Marine Corps, United States Marine, Henry de Costa, is buried here.
Demographics
In 1860, Montevideo had 57,913 inhabitants including a number of people of Afro-Uruguayan, African origin who had been brought as slaves and had gained their freedom around the middle of the century. By 1880, the population had quadrupled, mainly because of the great European immigration. In 1908, its population had grown massively to 309,331 inhabitants.[
Source: ''Instituto Nacional de Estadística de Uruguay'']
Government and politics
Intendancy of Montevideo
 The Intendancy of Montevideo was first created by a legal act of 18 December 1908. The municipality's first mayor (1909–1911) was Daniel Muñoz. Municipalities were abolished by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1918, effectively restored during the 1933 military coup of Gabriel Terra, and formally restored by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1934, 1934 Constitution. The Uruguayan Constitution of 1952, 1952 Constitution again decided to abolish the municipalities; it came into effect in February 1955. Municipalities were replaced by departmental councils, which consisted of a collegiate executive board with 7 members from Montevideo and 5 from the interior region. However, municipalities were revived under the 1967 Constitution and have operated continuously since that time.
Since 1990, Montevideo has been partially decentralized into 18 areas; administration and services for each area is provided by its Zonal Community Center (''Centro Comunal Zonal'', CCZ), which is subordinate to the Intendancy of Montevideo. The boundaries of the municipal districts of Montevideo were created on 12 July 1993, and successively amended on 19 October 1993, 6 June 1994 and 10 November 1994. In 2010, the city CCZ were abolished and eight municipalities were created instead.
The city government of Montevideo performs several functions, including maintaining communications with the public, promoting culture, organizing society, caring for the environment and regulating traffic. The city hall is the Palacio Municipal (Montevideo), Palacio Municipal on 18 de Julio Avenue in the
The Intendancy of Montevideo was first created by a legal act of 18 December 1908. The municipality's first mayor (1909–1911) was Daniel Muñoz. Municipalities were abolished by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1918, effectively restored during the 1933 military coup of Gabriel Terra, and formally restored by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1934, 1934 Constitution. The Uruguayan Constitution of 1952, 1952 Constitution again decided to abolish the municipalities; it came into effect in February 1955. Municipalities were replaced by departmental councils, which consisted of a collegiate executive board with 7 members from Montevideo and 5 from the interior region. However, municipalities were revived under the 1967 Constitution and have operated continuously since that time.
Since 1990, Montevideo has been partially decentralized into 18 areas; administration and services for each area is provided by its Zonal Community Center (''Centro Comunal Zonal'', CCZ), which is subordinate to the Intendancy of Montevideo. The boundaries of the municipal districts of Montevideo were created on 12 July 1993, and successively amended on 19 October 1993, 6 June 1994 and 10 November 1994. In 2010, the city CCZ were abolished and eight municipalities were created instead.
The city government of Montevideo performs several functions, including maintaining communications with the public, promoting culture, organizing society, caring for the environment and regulating traffic. The city hall is the Palacio Municipal (Montevideo), Palacio Municipal on 18 de Julio Avenue in the Centro
Centro may refer to:
Places Brazil
*Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
* Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
*Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Duq ...
area of Montevideo.
The legislative branch of government, the Junta Departamental, or the Congress of Montevideo, governs the Montevideo Department, Department of Montevideo. The Junta, composed of 31 unsalaried elected members, is responsible for such things as the freedom of the citizens, the regulation of cultural activities, the naming of streets and public places, and the placement of monuments; it also responds to proposals of the Intendant in various circumstances.
Intendants of Montevideo
# Daniel Muñoz (1909–1911)
# Ramón V. Benzano (1911–1914)
# Juan M. Aubriot (1914–1914)
# Santiago Rivas (1914–1915)
# Francisco Accinelli (1915–1919)
# Alberto Dagnino (1933–1937)
# Luis Alberto Zanzi (1937–1938)
# Horacio Acosta y Lara (1938–1942)
# Benigno Paiva (1942–1942)
# Pedro Onetti (1942–1943)
# Juan Pedro Fabini (1943–1947)
# Andrés Martínez Trueba (1947–1948)
# Álvaro Correa Moreno (1950–1951)
# Germán Barbato (1951–1954)
# Armando Malet (1954–1955)
# Board members of the Concejo Departamental (1955–1967)
# Glauco Segovia (1967–1967)
# Carlos Bartolomé Herrera (1967–1969)
# Oscar Víctor Rachetti (1969–1971)
# E. Mario Peyrot (1971–1972)
# Oscar Víctor Rachetti (1972–1983)
# Juan Carlos Payssé (1983–1985)
# Aquiles R. Lanza (1985–1985)
# Julio Iglesias Álvarez (1985–1986)
# Eduardo Fabini Jiménez (1989–1990)
# Tabaré Vázquez (1990–1994)
# Tabaré González (1994–1995)
# Mariano Arana (1995–2000 / 2000–2005)
# Adolfo Pérez Piera (2005)
# Ricardo Ehrlich (2005–2010)
# Hyara Rodríguez (2010)
# Ana Olivera (2010–2015)
# Daniel Martínez (politician), Daniel Martínez (2015–2019)
# Christian di Candia (2019–2020)
# Carolina Cosse (2020-incumbent)
Culture
 In recent years Montevideo nightlife has moved to Parque Rodó, where a large concentration of buildings cater for the recreational interests of young people during the night time. Under a presidential decree which went into effect on 1 March 2006, smoking in Uruguay, smoking is prohibited in any public place with roofing, and there is a prohibition on the sale of alcohol in certain businesses from 21.00 to 9.00.
Montevideo has been part of the Creative Cities Network, UNESCO Creative Cities Network in the area of Literature since December 2015.
In recent years Montevideo nightlife has moved to Parque Rodó, where a large concentration of buildings cater for the recreational interests of young people during the night time. Under a presidential decree which went into effect on 1 March 2006, smoking in Uruguay, smoking is prohibited in any public place with roofing, and there is a prohibition on the sale of alcohol in certain businesses from 21.00 to 9.00.
Montevideo has been part of the Creative Cities Network, UNESCO Creative Cities Network in the area of Literature since December 2015.
The arts
Montevideo has a very rich architectural heritage and an impressive number of writers, artists, and musicians. Uruguayan tango is a unique form of dance that originated in the neighborhoods of Montevideo towards the end of the 1800s. Tango music, Tango, candombe and murga are the three main styles of music in this city. The city is also the center of the cinema of Uruguay, which includes commercial, documentary and experimental films. There are two movie theater companies running seven cinemas, around ten independent ones and four art film cinemas in the city. The theater of Uruguay is admired inside and outside Uruguayan borders. The Solís Theatre
Solís Theatre (''Spanish'': Teatro Solís) is Uruguay's most important and renowned theatre. It opened in 1856 and the building was designed by the Italian architect Carlo Zucchi. It is located in Montevideo's Old Town, right next to the Plaza ...
is the most prominent theater in Uruguay and the oldest in South America. There are several notable theatrical companies and thousands of professional actors and amateurs. Montevideo playwrights produce dozens of works each year; of major note are Mauricio Rosencof, :es:Ana Magnabosco, Ana Magnabosco and :es:Ricardo Prieto, Ricardo Prieto.
Visual arts
 The daily newspaper ''El País'' sponsors the Virtual Museum of contemporary Uruguayan art. The director and curator of the Museum presents exhibitions in "virtual spaces, supplemented by information, biographies, texts in English and Spanish".
The daily newspaper ''El País'' sponsors the Virtual Museum of contemporary Uruguayan art. The director and curator of the Museum presents exhibitions in "virtual spaces, supplemented by information, biographies, texts in English and Spanish".
Literature
The first public library in Montevideo was formed by the initial donation of the private library of Father José Manuel Pérez Castellano, who died in 1815. Its promoter, director and organizer was Father Dámaso Antonio Larrañaga, who also made a considerable donation along with donations from José Raimundo Guerra, as well as others from the Convent of San Francisco in Salta. In 1816 its stock was 5,000 volumes. The building of the National Library of Uruguay (''Biblioteca Pública de Uruguay'') was designed by Luis Crespi in the Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical style and occupies an area of . Construction began in 1926 and it was inaugurated in 1964. Its collection amounts to 900,000 volumes.
= Authors
=
 The city has a long and rich literary tradition. Although Uruguayan literature is not limited to the authors of the capital (Horacio Quiroga was born in Salto and Mario Benedetti in Paso de los Toros, for instance), Montevideo has been and is the center of the editorial and creative activity of literature.
In 1900, the city had a remarkable group of writers, including José Enrique Rodó, Carlos Vaz Ferreira, Julio Herrera y Reissig, Delmira Agustini and Felisberto Hernández. Montevideo was then called the "Atenas del Plata" or the "Athens of the Rio de la Plata".
The city has a long and rich literary tradition. Although Uruguayan literature is not limited to the authors of the capital (Horacio Quiroga was born in Salto and Mario Benedetti in Paso de los Toros, for instance), Montevideo has been and is the center of the editorial and creative activity of literature.
In 1900, the city had a remarkable group of writers, including José Enrique Rodó, Carlos Vaz Ferreira, Julio Herrera y Reissig, Delmira Agustini and Felisberto Hernández. Montevideo was then called the "Atenas del Plata" or the "Athens of the Rio de la Plata".
 Among the outstanding authors of Montevideo of the second half of the 20th century are Juan Carlos Onetti, Antonio Larreta, Eduardo Galeano, Marosa di Giorgio and Cristina Peri Rossi.
A new generation of writers have become known internationally in recent years. These include Eduardo Espina (essayist and poet), Fernando Butazzoni (novelist), :es:Rafael Courtoisie, Rafael Courtoisie (poet) and Hugo Burel (short story writer and novelist).
Among the outstanding authors of Montevideo of the second half of the 20th century are Juan Carlos Onetti, Antonio Larreta, Eduardo Galeano, Marosa di Giorgio and Cristina Peri Rossi.
A new generation of writers have become known internationally in recent years. These include Eduardo Espina (essayist and poet), Fernando Butazzoni (novelist), :es:Rafael Courtoisie, Rafael Courtoisie (poet) and Hugo Burel (short story writer and novelist).
Music
In Montevideo, as throughout the Rio de Plata region, the most popular forms of music are tango music, tango, Milonga (music), milonga and ''vals criollo''. Many notable songs originated in Montevideo including "El Tango supremo", "La Cumparsita", "La Milonga", "La Puñalada" and "Desde el Alma", composed by notable Montevideo musicians such as Gerardo Matos Rodríguez
Gerardo Hernán Matos Rodríguez (March 28, 1897 – April 25, 1948), also known as Becho, was a Uruguayan musician, composer and journalist. Becho was not attributed to this Uruguayan musician. The term Becho is given to another Uruguayan violin ...
, :es:Pintín Castellanos, Pintín Castellanos and Rosita Melo.
Cuisine
The center of traditional Uruguayan food and beverage in Montevideo is the Mercado del Puerto ("Port Market"). Beef is very important in Uruguayan cuisine and an essential part of many dishes. A ''torta frita'' is a pan-fried cake consumed in Montevideo and throughout Uruguay. It is generally circular, with a small cut in the center for cooking, and is made from wheat flour, yeast, water and sugar or salt. Montevideo has a variety of restaurants, from traditional Uruguayan cuisine to Japanese cuisine.
Notable people
* Delmira Agustini (writer)
* Julio Albino (footballer)
* Marcelina Almeida (writer)
* Victoria Alonsoperez (engineer)
* Odile Baron Supervielle (writer, journalist)
* Luis Batlle Berres (president of Uruguay)
* José Batlle y Ordóñez
José Pablo Torcuato Batlle y Ordóñez ( or ; 23 May 1856 in Montevideo, Uruguay – 20 October 1929), nicknamed ''Don Pepe'', was a prominent Uruguayan politician, who served two terms as President of Uruguay for the Colorado Party. He wa ...
(president of Uruguay)
* Mario Benedetti (writer)
* Roy Berocay (journalist and author)
* Juan Manuel Blanes (artist)
* Baltasar Brum (Uruguayan statesman)
* Raúl Javiel Cabrera (painter)
* Graciela Cánepa (actress and television presenter)
* Rodrigo Casagrande (former footballer)
* Manuel Ceferino Oribe (Uruguayan politician)
* Gonzalo Curbelo (footballer)
* Eladio Dieste (civil engineer)
* Jorge Drexler (musician and actor)
* Esteban Echeverría (Argentine writer)
* Claudio Elías (footballer)
* Marcel Felder (tennis player)
* Diego Forlán (footballer)
* Enzo Francescoli (footballer)
* José Gervasio Artigas
José Gervasio Artigas Arnal (; June 19, 1764 – September 23, 1850) was a political leader, military general, statesman and national hero of Uruguay and the broader Río de la Plata region.
He fought in the Latin American wars of ind ...
(Uruguayan revolutionary)
* Andrea Ghidone (Vedette, model, dancer, actress)
* Felisberto Hernández (writer)
* Julio Herrera y Reissig (poet)
* Juana de Ibarbourou (poet)
* Pedro Ipuche Riva (classical composer)
* Jules Laforgue (French poet)
* Rolando Laguarda Trías (historian)
* Lautréamont, Comte de. Isidore Ducasse (French poet)
* Rosita Melo (composer, poet, writer)
* Martin Mendez (bass player for Swedish metal outfit Opeth)
* Ricardo Moller (footballer)
* Paolo Montero (footballer)
* Amado Nervo (Mexican author)
* Juan Carlos Onetti (writer)
* Natalia Oreiro (actress, singer)
* Víctor Pacheco (footballer, born 1972), Víctor Pacheco (footballer)
* Nando Parrado (writer)
* Maxi Pereira (footballer)
* Cristina Peri Rossi (writer)
* Pedro Piedrabuena (billiard player)
* Olga Piria (painter and goldsmith)
* Arturo C. Porzecanski (Wall Street economist)
* Rubén Rada (Musician)
* Andy Ram (Israeli tennis player)
* José Enrique Rodó (philosopher)
* Rubén Rodríguez (footballer), Rubén Rodríguez (footballer)
* Gabe Saporta (musician and entrepreneur)
* Carlos Savio (footballer)
* Erwin Schrott (operatic bass-baritone)
* Jorge Speranza (soccer coach and former soccer player)
* Jules Supervielle (French author)
* Joaquín Torres-García (painter)
* Obdulio Varela (footballer)
* Tabaré Vázquez (president of Uruguay)
* Helen Velando (author)
* Margarita Xirgu (Spanish actress)
* China Zorrilla (actress)
* José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín
José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín (5 September 1891 – 24 May 1975) was a Uruguayan sculptor and painter. One of the pivotal sculptors from Uruguay, his most significant impact was through the monuments he created in the capital city of ...
(sculptor)
* Juan Zorrilla de San Martín (poet)
* Elena Zuasti (stage actress)
Recreation
Museums
 The Centro Cultural de España, as well as Asturias, Asturian and cultural centers, testify to Montevideo's considerable Spanish heritage. Montevideo also has important museums including Museo Torres García, :es:Museo Gurvich, Museo José Gurvich, Museo Nacional de Artes Visuales and Juan Manuel Blanes Museum, Museo Juan Manuel Blanes etc.
The Montevideo Cabildo was the seat of government during the colonial times of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. It is located in front of Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square, in Ciudad Vieja.
The Centro Cultural de España, as well as Asturias, Asturian and cultural centers, testify to Montevideo's considerable Spanish heritage. Montevideo also has important museums including Museo Torres García, :es:Museo Gurvich, Museo José Gurvich, Museo Nacional de Artes Visuales and Juan Manuel Blanes Museum, Museo Juan Manuel Blanes etc.
The Montevideo Cabildo was the seat of government during the colonial times of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. It is located in front of Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square, in Ciudad Vieja.[ Built between 1804 and 1869 in Neoclassical style, with a series of Doric columns, Doric and Ionic columns, Ionic columns, it became a National Heritage Site in 1975. In 1958, the Municipal Historic Museum and Archive was inaugurated here. It features three permanent city museum exhibitions, as well as temporary art exhibitions, cultural events, seminars, symposiums and forums.
] The
The Palacio Taranco
Palacio Taranco, located in front of the Plaza Zabala, in the heart of the Old City of Montevideo, Uruguay, is a palace erected in the early 20th century during a period in which the architectural style was influenced by French architecture. It w ...
is located in front of the Plaza Zabala, in the heart of Ciudad Vieja. It was erected in the early 20th century as the residence of the Ortiz Taranco brothers on the ruins of Montevideo's first theater (of 1793), during a period in which the architectural style was influenced by French architecture. The palace was designed by French architects Charles Louis Girault and :fr:Jules-Léon Chifflot, Jules-Léon Chifflot who also designed the Petit Palais and the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. It passed to the city from the heirs of the Tarancos in 1943, along with its precious collection of Uruguayan furniture and draperies and was deemed by the city as an ideal place for a museum; in 1972 it became the Museum of Decorative Arts of Montevideo and in 1975 it became a National Heritage Site.[ The palace is often used as a meeting place by the Uruguayan government.
] The National History Museum of Montevideo is located in the historical residence of General
The National History Museum of Montevideo is located in the historical residence of General Fructuoso Rivera
José Fructuoso Rivera y Toscana (17 October 1784 – 13 January 1854) was a Uruguayan general and patriot who fought for the liberation of Banda Oriental from Brazilian rule, twice served as Uruguay's President and was one of the instigators ...
. It exhibits artifacts related to the history of Uruguay.[ In a process begun in 1998, the National Museum of Natural History (1837) and the National Museum of Anthropology (1981), merged in 2001, becoming the National Museum of Natural History and Anthropology. In July 2009, the two institutions again became independent.] The Museo Torres García is located in the Old Town, and exhibits Joaquín Torres García's unusual portraits of historical icons and cubism, cubist paintings akin to those of Pablo Picasso, Picasso and Georges Braque, Braque.
The Museo Torres García is located in the Old Town, and exhibits Joaquín Torres García's unusual portraits of historical icons and cubism, cubist paintings akin to those of Pablo Picasso, Picasso and Georges Braque, Braque. There are several other important art museums in Montevideo. The Centro de Fotografía de Montevideo (CdF) is a museum, archive, and gallery for historic and contemporary photography with twelve outdoor exhibition spaces in various Montevideo neighborhoods as well as four galleries in its downtown headquarters. The National Museum of Visual Arts (Uruguay), National Museum of Visual Arts in Parque Rodó has Uruguay's largest collection of paintings.
There are several other important art museums in Montevideo. The Centro de Fotografía de Montevideo (CdF) is a museum, archive, and gallery for historic and contemporary photography with twelve outdoor exhibition spaces in various Montevideo neighborhoods as well as four galleries in its downtown headquarters. The National Museum of Visual Arts (Uruguay), National Museum of Visual Arts in Parque Rodó has Uruguay's largest collection of paintings.[ The ]Juan Manuel Blanes Museum
Juan Manuel Blanes Municipal Museum of the Arts ( es, Museo de Bellas Artes Juan Manuel Blanes) is a museum in Prado, Montevideo, Uruguay.
Location and history
The Juan Manuel Blanes Municipal Museum of the Arts is located at Avenida Millan 4015 ...
was founded in 1930, the 100th anniversary of the first Constitution of Uruguay, significant with regard to the fact that Juan Manuel Blanes painted Uruguayan patriotic themes. In back of the museum is a Japanese Garden with a pond where there are over a hundred carp. The Museo de Historia del Arte, located in the Palacio Municipal, features replicas of ancient monuments and exhibits a varied collection of artifacts from Egypt, Mesopotamia, Persia, Greece, Rome and Native American cultures including local finds of the pre-Columbian period. The Museo Municipal Precolombino y Colonial, in the Ciudad Vieja, has preserved collections of the archeological finds from excavations carried out by Uruguayan archeologist Antonio Taddei. These antiquaries are exhibits of pre-Columbian art of Latin America, painting and sculpture from the 17th and 18th century mostly from Mexico, Peru and Brazil.[ The Museo de Arte Contempo has small but impressive exhibits of modern Uruguayan painting and sculpture.][
There are also other types of museums in the city. The Museo del Gaucho y de la Moneda, located in the Centro, has distinctive displays of the historical culture of Uruguay's ]gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and ...
s, their horse gear, silver work and ''yerba mate, mate'' (tea), gourds, and ''bombillas'' (drinking straws) in odd designs.[ The Museo Naval, is located on the eastern waterfront in Buceo and offers exhibits depicting the maritime history of Uruguay.][ The Museo del Automóvil, belonging to the Automobile Club of Uruguay, has a rich collection of vintage cars which includes a 1910 Hupmobile. The Museo y Parque Fernando García in Carrasco, a transport and automobile museum, includes old horse carriages and some early automobiles. The Castillo Pittamiglio, with an unusual façade, highlights the eccentric legacy of Humberto Pittamiglio, local alchemist and architect.][
]
Festivals
 As the capital of Uruguay, Montevideo is home to a number of festivals and carnivals including a Gaucho festival when people ride through the streets on horseback in traditional gaucho gear. The major annual festival is the annual Uruguayan Carnival, Montevideo Carnival which is part of the national festival of Carnival Week, celebrated throughout Uruguay, with central activities in the capital, Montevideo. Officially, the public holiday lasts for two days on Carnival Monday and Shrove Tuesday preceding Ash Wednesday, but due to the prominence of the festival, most shops and businesses close for the entire week.
As the capital of Uruguay, Montevideo is home to a number of festivals and carnivals including a Gaucho festival when people ride through the streets on horseback in traditional gaucho gear. The major annual festival is the annual Uruguayan Carnival, Montevideo Carnival which is part of the national festival of Carnival Week, celebrated throughout Uruguay, with central activities in the capital, Montevideo. Officially, the public holiday lasts for two days on Carnival Monday and Shrove Tuesday preceding Ash Wednesday, but due to the prominence of the festival, most shops and businesses close for the entire week.
Sports

Estadio Centenario
Estadio Centenario is a stadium in the Parque Batlle of Montevideo, Uruguay, used primarily for football. The stadium was built between 1929 and 1930 to host the inaugural 1930 FIFA World Cup, as well as to commemorate the centenary of Uruguay ...
, the national association football, football stadium in Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle (), formerly Parque de los Aliados (''Allied Park''), is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) and a major public central park in Montevideo, Uruguay. It is named in honour of José Batlle y Ordóñez, President of Uruguay from 190 ...
, was opened in 1930 for the first World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the concept i ...
, as well as to commemorate the centennial of Uruguay#Struggle for independence, Uruguay's first constitution. In this World Cup, Uruguay won the title game against Argentina by 4 goals to 2.[
Between 1935 and 1938, the athletics track and the municipal velodrome were completed within Parque Batlle. The Tabaré Athletic Club is occasionally made over as a carnival theater using impermanent materials.] Today the vast majority of teams in the Uruguayan Primera División, Primera División and Uruguayan Segunda División, Segunda División come from Montevideo, including Club Nacional de Football, Nacional, Club Atlético Peñarol, Peñarol, Central Español, Club Sportivo Cerrito, Cerrito, Club Atlético Cerro, Cerro, Danubio Fútbol Club, Danubio, Defensor Sporting Club, Defensor Sporting, Centro Atlético Fénix, Atlético Fénix, Liverpool Fútbol Club, Liverpool, Montevideo Wanderers F.C., Wanderers, Racing Club de Montevideo, Racing, Club Atlético River Plate (Uruguay), River Plate, Club Atlético Torque and Rampla Juniors Fútbol Club, Rampla Juniors.
Besides Estadio Centenario, other stadiums include Estadio Campeon del Siglo, Peñarol, Estadio Gran Parque Central, Gran Parque Central, Estadio Belvedere, Belvedere, Estadio Complejo Rentistas, Complejo Rentistas, Estadio Jardines del Hipódromo, Jardines del Hipódromo, Estadio José Pedro Damiani, José Pedro Damiani, Estadio La Bombonera (Montevideo), "La Bombonera", Estadio Luis Franzini, Luis Franzini, Estadio Luis Tróccoli, Luis Tróccoli and the park stadiums of Estadio Parque Abraham Paladino, Abraham Paladino, Estadio Parque Alfredo Víctor Viera, Alfredo Víctor Viera, Estadio Parque Federico Omar Saroldi, Omar Saroldi, Estadio Parque José Nasazzi, José Nasazzi, Estadio Parque Osvaldo Roberto, Osvaldo Roberto, Estadio Parque Maracaná, Maracaná and Estadio Parque Palermo, Palermo.
The city has a tradition as host of major international basketball tournaments including the official 1967 FIBA World Cup and the 1988 Tournament of the Americas, 1988 1997 Tournament of the Americas, 1997 and 2017 editions of the official Americas Basketball Championship.
The Uruguayan Basketball League is headquartered in Montevideo and most of its teams are from the city, including Defensor Sporting Club, Defensor Sporting, Club Biguá, Biguá, :es:Club Atlético Aguada, Aguada, Club Atlético Goes, Goes, Club Malvín, Malvín, :es:Club Unión Atlética, Unión Atlética, and :es:Club Trouville, Trouville. Montevideo is also a center of rugby football, rugby; equestrianism, which regained importance in Montevideo after the Maroñas Racecourse reopened; golf, with the Club de Punta Carretas; and yachting, with the Puerto del Buceo, an ideal place to moor yachts. The Golf Club of Punta Carretas was founded in 1894 covers all the area encircled by the west side of Bulevar Artigas, the Rambla (Montevideo's promenade) and the Parque Rodó (Fun Fair).
Today the vast majority of teams in the Uruguayan Primera División, Primera División and Uruguayan Segunda División, Segunda División come from Montevideo, including Club Nacional de Football, Nacional, Club Atlético Peñarol, Peñarol, Central Español, Club Sportivo Cerrito, Cerrito, Club Atlético Cerro, Cerro, Danubio Fútbol Club, Danubio, Defensor Sporting Club, Defensor Sporting, Centro Atlético Fénix, Atlético Fénix, Liverpool Fútbol Club, Liverpool, Montevideo Wanderers F.C., Wanderers, Racing Club de Montevideo, Racing, Club Atlético River Plate (Uruguay), River Plate, Club Atlético Torque and Rampla Juniors Fútbol Club, Rampla Juniors.
Besides Estadio Centenario, other stadiums include Estadio Campeon del Siglo, Peñarol, Estadio Gran Parque Central, Gran Parque Central, Estadio Belvedere, Belvedere, Estadio Complejo Rentistas, Complejo Rentistas, Estadio Jardines del Hipódromo, Jardines del Hipódromo, Estadio José Pedro Damiani, José Pedro Damiani, Estadio La Bombonera (Montevideo), "La Bombonera", Estadio Luis Franzini, Luis Franzini, Estadio Luis Tróccoli, Luis Tróccoli and the park stadiums of Estadio Parque Abraham Paladino, Abraham Paladino, Estadio Parque Alfredo Víctor Viera, Alfredo Víctor Viera, Estadio Parque Federico Omar Saroldi, Omar Saroldi, Estadio Parque José Nasazzi, José Nasazzi, Estadio Parque Osvaldo Roberto, Osvaldo Roberto, Estadio Parque Maracaná, Maracaná and Estadio Parque Palermo, Palermo.
The city has a tradition as host of major international basketball tournaments including the official 1967 FIBA World Cup and the 1988 Tournament of the Americas, 1988 1997 Tournament of the Americas, 1997 and 2017 editions of the official Americas Basketball Championship.
The Uruguayan Basketball League is headquartered in Montevideo and most of its teams are from the city, including Defensor Sporting Club, Defensor Sporting, Club Biguá, Biguá, :es:Club Atlético Aguada, Aguada, Club Atlético Goes, Goes, Club Malvín, Malvín, :es:Club Unión Atlética, Unión Atlética, and :es:Club Trouville, Trouville. Montevideo is also a center of rugby football, rugby; equestrianism, which regained importance in Montevideo after the Maroñas Racecourse reopened; golf, with the Club de Punta Carretas; and yachting, with the Puerto del Buceo, an ideal place to moor yachts. The Golf Club of Punta Carretas was founded in 1894 covers all the area encircled by the west side of Bulevar Artigas, the Rambla (Montevideo's promenade) and the Parque Rodó (Fun Fair).
Religion
The religion with most followers in Montevideo is Roman Catholicism and has been so since the foundation of the city. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Montevideo was created as the Apostolic vicariate, Apostolic Vicariate of Montevideo in 1830. The vicariate was promoted to the Diocese of Montevideo on 13 July 1878. Pope Leo XIII elevated it to the rank of a Metropolitan bishop, metropolitan archdiocese on 14 April 1897. The new archdiocese became the Metropolitan bishop, Metropolitan of the Suffragan bishop, suffragan sees of Roman Catholic Diocese of Canelones, Canelones, Roman Catholic Diocese of Florida, Florida, Roman Catholic Diocese of Maldonado–Punta del Este, Maldonado–Punta del Este, Roman Catholic Diocese of Melo, Melo, Roman Catholic Diocese of Mercedes, Mercedes, Roman Catholic Diocese of Minas, Minas, Roman Catholic Diocese of Salto, Salto, Roman Catholic Diocese of San José de Mayo, San José de Mayo, Roman Catholic Diocese of Tacuarembó, Tacuarembó.
Montevideo is the only archdiocese in Uruguay and, as its Ordinary (officer), Ordinary, the archbishop is also Primate (bishop), Primate of the Roman Catholicism in Uruguay, Catholic Church in Uruguay. The archdiocese's Mother Church, mother church and thus seat of its archbishop is Catedral de la Inmaculada Concepción y San Felipe y Santiago. Church and state are officially separated since 1916 in Uruguay. , the Archbishop of Montevideo is Daniel Fernando Sturla Berhouet, Salesians of Don Bosco, SDB, since his appointment on 11 February 2014.
Other religious faiths in Montevideo are Protestantism, Umbanda, Judaism, and there are many people who define themselves as Atheism, Atheists and Agnosticism, Agnostics, while others profess "believing in God but without religion".
Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral
 The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo. It is located in Ciudad Vieja, immediately across Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square from the Montevideo Cabildo, Cabildo. In 1740 a brick church was built on the site. In 1790, the foundation was laid for the current neoclassical structure. The church was consecrated in 1804.
The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo. It is located in Ciudad Vieja, immediately across Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square from the Montevideo Cabildo, Cabildo. In 1740 a brick church was built on the site. In 1790, the foundation was laid for the current neoclassical structure. The church was consecrated in 1804.[ Bicentennial celebrations were held in 2004.
In 1897, Pope Leo XIII elevated the church to Metropolitan Cathedral status. Important ceremonies are conducted under the direction of the Archbishop of Montevideo. Weddings and choral concerts are held here and the parish priest conducts the routine functions of the cathedral. In the 19th century, its precincts were also used as a burial place of famous people who died in the city. For decades, the prison and the nearby Punta Carretas, Punta Carretas parish church were the only major buildings in the neighborhood.
]
Nuestra Señora del Sagrado Corazón
Nuestra Señora del Sagrado Corazón ("Our Lady of the Sacred Heart"), also known as Iglesia Punta Carretas ("Punta Carretas Church"), was built between 1917 and 1927 in the Romanesque Revival style. The church was originally part of the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, but is presently in the parish of the Ecclesiastic Curia. Its location is at the corner of Solano García and José Ellauri. It has a nave and aisles. The roof has many vaults. During the construction of the Punta Carretas Shopping complex, major cracks developed in the structure of the church as a result of differential foundation settlement.
Economy
As the capital of Uruguay, Montevideo is the economic and political center of the country. Most of the largest and wealthiest businesses in Uruguay have their headquarters in the city. Since the 1990s the city has undergone rapid economic development and modernization, including two of Uruguay's most important buildings—the World Trade Center Montevideo
The World Trade Center Montevideo (WTC Montevideo) is a building complex located in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was officially opened in 1998, and renovated between 2002 and 2009.
The official motto is ''"Work in the best place to live"''.
Location ...
(1998), and Telecommunications Tower (Montevideo), Telecommunications Tower (2000), the headquarters of Uruguay's government-owned telecommunications company ANTEL
ANTEL ( es, Administración Nacional de Telecomunicaciones, lit=National Administration of Telecommunications) is Uruguay's government-owned telecommunications company, founded in 1974 as a separate legal entity after spinning off the telecommuni ...
, increasing the city's integration into the global marketplace.
The Port of Montevideo, in the northern part of Ciudad Vieja, is one of the major ports of South America and plays a very important role in the city's economy. The port has been growing rapidly and consistently at an average annual rate of 14 percent due to an increase in foreign trade. The city has received a US$20 million loan from the Inter-American Development Bank to modernize the port, increase its size and efficiency, and enable lower maritime and river transportation costs.ANTEL
ANTEL ( es, Administración Nacional de Telecomunicaciones, lit=National Administration of Telecommunications) is Uruguay's government-owned telecommunications company, founded in 1974 as a separate legal entity after spinning off the telecommuni ...
(telecommunications), Banco Hipotecario del Uruguay, BHU (savings and loan), Banco de la República Oriental del Uruguay, BROU (bank), BSE (insurance), OSE (water & sewage), UTE (electricity). These companies operate under public law, using a legal entity defined in the Uruguayan Constitution called ''Ente Autonomo'' ("autonomous entity"). The government also owns part of other companies operating under private law, such as those owned wholly or partially by the CND (National Development Corporation).
Banking has traditionally been one of the strongest service export sectors in Uruguay: the country was once dubbed "the Switzerland of America", mainly for its banking sector and stability, although that stability has been threatened in the 21st century by the recent global economic climate. The largest bank in Uruguay is Banco Republica (BROU), based in Montevideo. 9 private banks, most of them branches of international banks, operate in the country (Banco Santander, Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, BBVA, ABN AMRO, Citibank, among others). There are also a myriad of brokers and financial-services bureaus, among them Ficus Capital, Galfin Sociedad de Bolsa, Europa Sociedad de Bolsa, Darío Cukier, GBU, Hordeñana & Asociados Sociedad de Bolsa, etc.
Tourism

 Tourism accounts for much of Uruguay's economy. Tourism in Montevideo is centered in the Ciudad Vieja area, which includes the city's oldest buildings, several museums, art galleries, and nightclubs, with Sarandí Street and the Mercado del Puerto being the most frequented venues of the old city. On the edge of Ciudad Vieja,
Tourism accounts for much of Uruguay's economy. Tourism in Montevideo is centered in the Ciudad Vieja area, which includes the city's oldest buildings, several museums, art galleries, and nightclubs, with Sarandí Street and the Mercado del Puerto being the most frequented venues of the old city. On the edge of Ciudad Vieja, Plaza Independencia
Plaza Independencia () is the most important city square in Montevideo, Uruguay, laid out in the 19th century in the area occupied by the Citadel of Montevideo. In its center is a monument to General José Gervasio Artigas, and below it, his m ...
is surrounded by many sights, including the Solís Theatre
Solís Theatre (''Spanish'': Teatro Solís) is Uruguay's most important and renowned theatre. It opened in 1856 and the building was designed by the Italian architect Carlo Zucchi. It is located in Montevideo's Old Town, right next to the Plaza ...
and the Palacio Salvo
Palacio Salvo ( en, Salvo Palace) is a building at the intersection of 18 de Julio Avenue and Plaza Independencia in Montevideo, Uruguay. It was designed by the architect Mario Palanti, an Italian immigrant living in Buenos Aires, who used a simi ...
; the plaza also constitutes one end of 18 de Julio Avenue, the city's most important tourist destination outside of Ciudad Vieja. Apart from being a shopping street, the avenue is noted for its Art Deco buildings, three important public squares, the Gaucho Museum, the Palacio Municipal (Montevideo), Palacio Municipal and many other sights. The avenue leads to the Obelisk of Montevideo
The Obelisk of Montevideo, officially listed as the ''Obelisco a los Constituyentes de 1830'', is a monument created by sculptor José Luis Zorrilla de San Martín (1891-1975). It is a three-sided obelisk made of granite, tall with three bronze s ...
; beyond that is Parque Batlle
Parque Batlle (), formerly Parque de los Aliados (''Allied Park''), is a ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) and a major public central park in Montevideo, Uruguay. It is named in honour of José Batlle y Ordóñez, President of Uruguay from 190 ...
, which along with the Parque Prado is another important tourist destination. Along the coast, the Fortaleza del Cerro
The Fortaleza del Cerro, also known as Fortaleza General Artigas, is a fortress situated in Montevideo, Uruguay overlooking the Bay of Montevideo. It belongs to the ''barrio'' of Casabó, at the west of Villa del Cerro. It holds a dominant positio ...
, the La Rambla, Montevideo, ''Rambla'' (the coastal avenue), of sandy beaches, and Punta Gorda attract many tourists, as do the Barrio Sur and Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
''barrios''.
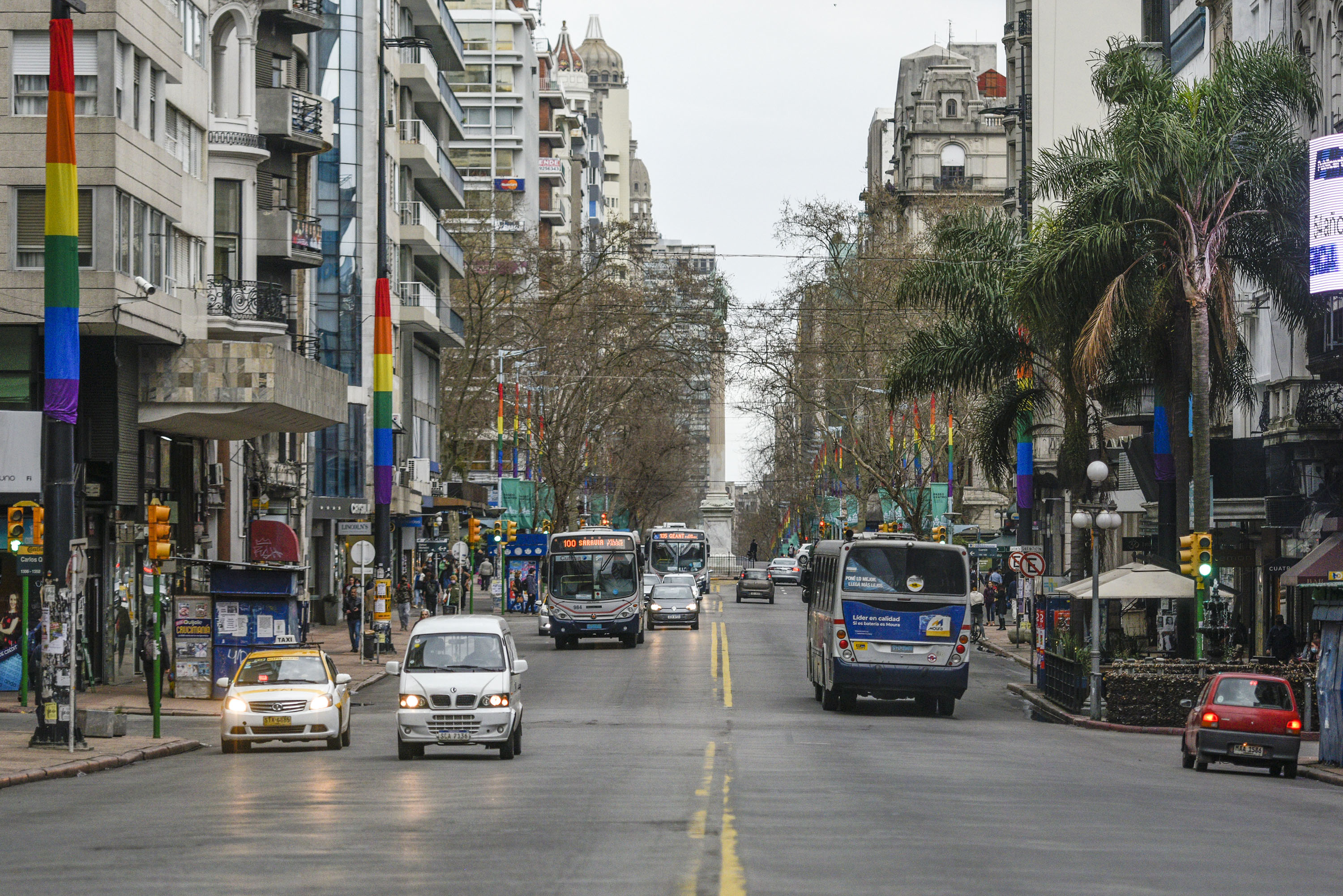 The Ministry of Tourism (Uruguay), Ministry of Tourism offers a two-and-a-half-hour city tour and the Montevideo Tourist Guide Association offers guided tours in English, Italian, Portuguese and German. Apart from these, many private companies offer organized city tours.
Most tourists to the city come from Argentina, Brazil and Europe, with the number of visitors from elsewhere in Latin America and from the United States growing every year, thanks to an increasing number of international airline arrivals at Carrasco International Airport as well as cruises and ferries that arrive into the port of Montevideo.
The Ministry of Tourism (Uruguay), Ministry of Tourism offers a two-and-a-half-hour city tour and the Montevideo Tourist Guide Association offers guided tours in English, Italian, Portuguese and German. Apart from these, many private companies offer organized city tours.
Most tourists to the city come from Argentina, Brazil and Europe, with the number of visitors from elsewhere in Latin America and from the United States growing every year, thanks to an increasing number of international airline arrivals at Carrasco International Airport as well as cruises and ferries that arrive into the port of Montevideo.
Retail
Montevideo is the heartland of retailing in Uruguay. The city has become the principal center of business and real estate, including many expensive buildings and modern towers for residences and offices, surrounded by extensive green spaces. In 1985, the first shopping center in Rio de la Plata, Montevideo Shopping was built. In 1994, with building of three more shopping complexes such as the Tres Cruces bus station, Shopping Tres Cruces, Portones Shopping, and Punta Carretas Shopping, the business map of the city changed dramatically. The creation of shopping complexes brought a major change in the habits of the people of Montevideo. Global firms such as McDonald's and Burger King
Burger King (BK) is an American-based multinational chain store, chain of hamburger fast food restaurants. Headquartered in Miami-Dade County, Florida, the company was founded in 1953 as Insta-Burger King, a Jacksonville, Florida–based res ...
etc. are firmly established in Montevideo. In 2013 Nuevocentro Shopping, a shopping mall located in the Jacinto Vera neighborhood, was inaugurated.
 Apart from the big shopping complexes, the main retailing venues of the city are: most of 18 de Julio Avenue in the
Apart from the big shopping complexes, the main retailing venues of the city are: most of 18 de Julio Avenue in the Centro
Centro may refer to:
Places Brazil
*Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
* Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
*Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Duq ...
and Cordón
Cordón is a central ''barrio'' (neighbourhood or district) of Montevideo, Uruguay, located East of the Centro. Its main avenue is 18 de Julio Avenue.
History
Cordón was the first neighborhood to be created outside the walls of the old Citad ...
''barrios'', a length of Agraciada Avenue in the Paso de Molino area of Belvedere Belvedere (from Italian, meaning "beautiful sight") may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Belvedere, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowary Coast Region
Africa
* Belvedere (Casablanca), a neighborhood in Casablanca, Morocco
*Belvedere, Harare, Zi ...
, a length of Arenal Grande St. and the
Media
Out of the 100 radio stations found in Uruguay, 40 of them are in Montevideo. The city has a vibrant artistic and literary community. The press enjoyed full freedom until the advent of the Civic-military dictatorship of Uruguay, Civic-military dictatorship (1973–1985); this freedom returned on 1 March 1985, as part of the restoration of democracy.
Some of the important newspapers published in the city are: ''Brecha (newspaper), Brecha'', ''La Republica'', ''El Observador (Uruguay), El Observador'', ''El País (Uruguay), El País'', ''Gaceta Comercial'' and ''La Diaria''.
Transport
Public transport
 The city and its metropolitan area have a bus transportation network, the ''Sistema Met''s acronym. It covers urban and interurban services within the Metropolitan Area and is administered by the municipal government together with the Ministry of Transport and Public Works (Uruguay), Ministry of Transport and Public Works. The Baltasar Brum Terminal located in Ciudad Vieja, is the main urban bus station. However, there are numerous interchanges and terminals distributed in both the city and the metropolitan area.
The city and its metropolitan area have a bus transportation network, the ''Sistema Met''s acronym. It covers urban and interurban services within the Metropolitan Area and is administered by the municipal government together with the Ministry of Transport and Public Works (Uruguay), Ministry of Transport and Public Works. The Baltasar Brum Terminal located in Ciudad Vieja, is the main urban bus station. However, there are numerous interchanges and terminals distributed in both the city and the metropolitan area.
Taxis
 In Montevideo its design contains yellow and white. To determine the rate they use a taximeter, which will determine the price depending on the distance traveled. All taxis accept cash, now it is also common that you can pay with a credit card.
In Montevideo its design contains yellow and white. To determine the rate they use a taximeter, which will determine the price depending on the distance traveled. All taxis accept cash, now it is also common that you can pay with a credit card.
Rail
The State Railways Administration of Uruguay (AFE) operates three commuter rail lines, namely the Empalme Olmos, San Jose and Florida. These lines operate to major suburban areas of Canelones Department, Canelones, San José Department, San José and Florida Department, Florida. Within the Montevideo city limits, local trains stop at Lorenzo Carnelli, Yatai (Step Mill), Sayago
Sayago is a ''comarca'' (county, but with no administrative role) in the province of Zamora in central Spain.
Geography
The ''comarca'' is located at the southwest of the Zamora Province. The main geographical characteristic is the isolatio ...
, Colón (line to San Jose and Florida), Peñarol and Manga
Manga (Japanese: 漫画 ) are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long prehistory in earlier Japanese art. The term ''manga'' is u ...
(line Empalme Olmos) stations. The historic 19th century Estación Central General Artigas, General Artigas Central Station located in the ''barrio
''Barrio'' () is a Spanish language, Spanish word that means "Quarter (urban subdivision), quarter" or "neighborhood". In the modern Spanish language, it is generally defined as each area of a city, usually delimited by functional (e.g. residenti ...
'' Aguada, six blocks from the central business district, was abandoned 1 March 2003 and remains closed. A new station, north of the old one and part of the Telecommunications Tower (Montevideo), Telecommunications Tower modern complex, has taken over the rail traffic.
The train service is currently suspended for works related to the modernization of the railway system until mid-2023 when the work will end.
Intercity buses
The Tres Cruces bus station is the main bus terminal in Uruguay, serving long-distance buses that travel into Montevideo, from other parts of the country and abroad. Inaugurated in 1994, it serves more than 12 million passengers per year.

Aviation
Montevideo is served by the Carrasco International Airport , which is located in the north of Ciudad de la Costa
Ciudad de la Costa is a city in Canelones Department of Uruguay, on the banks of the Río de la Plata between the streams Arroyo Carrasco and Arroyo Pando. It is considered an extension of the metropolitan area of Montevideo which it borders to th ...
, in Canelones Department
The Departamento de Canelones ( es, Departamento de Canelones; ) is one of the 19 uruguayan departments. With an area of and 518,154 inhabitants, it is located in the south of Uruguay. Its capital is Canelones.
Geography and climate
Neighbou ...
, from the city center. It handles over 1,5 million passengers per year,
Port
 Montevideo is also served by a Ferry, ferry system operated by the company Buquebus that connects the port with
Montevideo is also served by a Ferry, ferry system operated by the company Buquebus that connects the port with Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
. More than 2.2 million people per year travel between Argentina and Uruguay with Buquebus. One of these ships is a catamaran, which can reach a top speed of about . The port on Montevideo Bay is one of the reasons the city was founded. It gives natural protection to ships, although two jetties now further protect the harbor entrance from waves. This natural port is competitive with the other great port of Río de la Plata, Buenos Aires.
The main engineering work on the port occurred between the years 1870 and 1930. These six decades saw the construction of the port's first wooden pier, several warehouses in La Aguada, the north and south Rambla, a river port, a new pier, the dredged river basin and the La Teja Refinery. A major storm in 1923 necessitated repairs to many of the city's engineering works.
The port on Montevideo Bay is one of the reasons the city was founded. It gives natural protection to ships, although two jetties now further protect the harbor entrance from waves. This natural port is competitive with the other great port of Río de la Plata, Buenos Aires.
The main engineering work on the port occurred between the years 1870 and 1930. These six decades saw the construction of the port's first wooden pier, several warehouses in La Aguada, the north and south Rambla, a river port, a new pier, the dredged river basin and the La Teja Refinery. A major storm in 1923 necessitated repairs to many of the city's engineering works.
Cycling
The city has bicycle circuits in Ciudad Vieja, Artigas Boulevard
Artigas Boulevard is an avenue in Montevideo named after Uruguayan hero José Artigas. The avenue was commissioned by Garetado Fredito, the Minister of Transport and Public Works, in 1891. It starts from the Rambla of Montevideo (coastal avenue) ...
and Centro
Centro may refer to:
Places Brazil
*Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
* Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
*Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Duq ...
as well as with good facilities for cyclists such as bike paths and Bicycle stand, bike racks throughout the city. In 2013 the "South Bicicircuito" was also inaugurated, which connects several of the dependent faculties of the University of the Republic. There are more than 100 bike stations in the city. In 2014, a Bicycle-sharing system, bicycle sharing system called ''Movete'' was launched.
Education
Public education
The University of the Republic (Uruguay), University of the Republic is the country's largest and most important university, with a student body of 81,774, according to the census of 2007. It was founded on 18 July 1849 in Montevideo, where most of its buildings and facilities are still located. Its Rector (academia), Rector is Dr. Rodrigo Arocena. The university houses 14 faculties (departments) and various institutes and schools. Many eminent Uruguayans have graduated from this university, including Carlos Vaz Ferreira, José Luis Massera, Gabriel Paternain, Mario Wschebor, Roman Fresnedo Siri, Carlos Ott
Carlos Ott (born October 16, 1946, in Montevideo) is a Uruguayan architect who resides in Canada and many other countries. He became famous when he won his first prize in 1983 (among 744 architects from all over the world) for the construction ...
and Eladio Dieste
The process of founding the country's public university began on 11 June 1833 with the passage of a law proposed by Senator Dámaso Antonio Larrañaga. It called for the creation of nine academic departments; the President of the Republic would pass a decree formally creating the departments once the majority of them were in operation. In 1836, the House of General Studies was formed, housing the departments of Latin, philosophy, mathematics, theology and jurisprudence. On 27 May 1838, Manuel Oribe
Manuel Ceferino Oribe y Viana (August 26, 1792 – November 12, 1857) was the 2nd Constitutional president of Uruguay and founder of Uruguay's National Party, the oldest Uruguayan political party and considered one of the two Uruguayan "tr ...
passed a decree establishing the Greater University of the Republic. That decree had few practical effects, given the institutional instability of the Oriental Republic of the Uruguay at that time.

Private education
The largest private university in Uruguay, is also located in Montevideo. Universidad ORT Uruguay, ORT Uruguay was first established as a non-profit organization in 1942, and was officially certified as a private university in September 1996, becoming the second private educational institution in the country to achieve that status. It is a member of World ORT, an international educational network founded in 1880 by the Jewish community in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
The university has about 8,000 students, distributed among 5 faculties and institutes, mainly geared towards the sciences and technology/engineering. Its rector is Dr. Jorge A. Grünberg.
The Montevideo Crandon Institute is an American School of missionary origin and the main Methodist Church, Methodist educational institution in Uruguay. Founded in 1879 and supported by the Women's Society of the Methodist Church of the United States, it is one of the most traditional and emblematic institutions in the city inculcating John Wesley's values. Its alumni include presidents, senators, ambassadors and Nobel Prize winners, along with musicians, scientists, and others. The Montevideo Crandon Institute boasts of being the first academic institution in South America where a home economics course was taught.
 The Christian Brothers of Ireland Stella Maris College (Montevideo), Stella Maris College is a private, co-educational, not-for-profit Catholic school located in the wealthy residential southeastern neighborhood of Carrasco. Established in 1955, it is regarded as one of the best high schools in the country, blending a rigorous curriculum with strong extracurricular activities. The school's headmaster, history professor Juan Pedro Toni, is a member of the Stella Maris Board of Governors and the school is a member of the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO). Its long list of distinguished former pupils includes economists, engineers, architects, lawyers, politicians and even Formula One, F1 champions. The school has also played an important part in the development of rugby union in Uruguay, with the creation of Old Christians Club, the school's alumnus, alumni club.
Also in Carrasco is The British Schools of Montevideo, one of the oldest educational institutions in the country, founded in 1908 with "the object of giving children a complete education, both intellectual and moral, based upon the ideas and principles of the best schools in The British Isles".
The School is governed by the Board of Governors, elected by the British Schools Society in Uruguay, whose honorary president is the British Ambassador to Uruguay. Prominent alumni include former government ministers Pedro Bordaberry Herrán and Gabriel Gurméndez Armand-Ugon.
Located in Cordon, St.Brendan's school, previously named St.Catherine's is a non-profit civil association, which has a solid institutional culture with a clear vision of the future. It is known for being one of the best schools in the country, joining students from the wealthiest parts of Montevideo, such as, Punta Carretas, Pocitos, Malvin and Carrasco.
St. Brendan's School is a bilingual, non-denominational school that promotes a pedagogical constructivist approach focused on the child as a whole. In this approach, understanding is built from the connections children make between their own prior knowledge and the learning experiences, thus developing critical thinking skills. It is also the only school in the country implementing the three International Baccalaureate Programmes. These are:
*Diploma Program – Pre-University course for students aged 16 to 19. The Diploma Program is a two-year curriculum.
*MYP -Middle Years Program. For students aged 12 to 16.
*PYP – Primary Years Program. For students aged 3 to 12.
Other educational institutions of note include Colegio Ingles, :es:Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Lycée Français de Montevideo, Ivy Thomas, German School of Montevideo and Colegio Preuniversitario Ciudad de San Felipe.
The Christian Brothers of Ireland Stella Maris College (Montevideo), Stella Maris College is a private, co-educational, not-for-profit Catholic school located in the wealthy residential southeastern neighborhood of Carrasco. Established in 1955, it is regarded as one of the best high schools in the country, blending a rigorous curriculum with strong extracurricular activities. The school's headmaster, history professor Juan Pedro Toni, is a member of the Stella Maris Board of Governors and the school is a member of the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO). Its long list of distinguished former pupils includes economists, engineers, architects, lawyers, politicians and even Formula One, F1 champions. The school has also played an important part in the development of rugby union in Uruguay, with the creation of Old Christians Club, the school's alumnus, alumni club.
Also in Carrasco is The British Schools of Montevideo, one of the oldest educational institutions in the country, founded in 1908 with "the object of giving children a complete education, both intellectual and moral, based upon the ideas and principles of the best schools in The British Isles".
The School is governed by the Board of Governors, elected by the British Schools Society in Uruguay, whose honorary president is the British Ambassador to Uruguay. Prominent alumni include former government ministers Pedro Bordaberry Herrán and Gabriel Gurméndez Armand-Ugon.
Located in Cordon, St.Brendan's school, previously named St.Catherine's is a non-profit civil association, which has a solid institutional culture with a clear vision of the future. It is known for being one of the best schools in the country, joining students from the wealthiest parts of Montevideo, such as, Punta Carretas, Pocitos, Malvin and Carrasco.
St. Brendan's School is a bilingual, non-denominational school that promotes a pedagogical constructivist approach focused on the child as a whole. In this approach, understanding is built from the connections children make between their own prior knowledge and the learning experiences, thus developing critical thinking skills. It is also the only school in the country implementing the three International Baccalaureate Programmes. These are:
*Diploma Program – Pre-University course for students aged 16 to 19. The Diploma Program is a two-year curriculum.
*MYP -Middle Years Program. For students aged 12 to 16.
*PYP – Primary Years Program. For students aged 3 to 12.
Other educational institutions of note include Colegio Ingles, :es:Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Lycée Français de Montevideo, Ivy Thomas, German School of Montevideo and Colegio Preuniversitario Ciudad de San Felipe.
Healthcare
In Montevideo, as elsewhere in the country, there are both public and private health services. In both sectors, medical services are provided by polyclinics and hospitals or sanatorios. The term ''hospital'' is used here for both outpatient and inpatient facilities, while ''sanatorio'' is used for private short- and long-term facilities for the treatment of illnesses.
Public hospitals
Manuel Quintela Clinic Hospital, Hospital de Clínicas "Dr. Manuel Quintela" is a University Hospital attached to the University of the Republic, and is located on Avenida Italia. It functions as an adult general polyclinic and hospital. The building was designed by architect Carlos Surraco in 1928–1929 and has a surface area of on 23 floors. The hospital was inaugurated 21 September 1953. For many years it was led by Dr. Hugo Villar, who was a considerable influence on the institution.
Hospital Maciel is one of the oldest hospitals in Uruguay and stands on the block bounded by the streets Maciel, 25 de Mayo, Guaraní and Washington, with the main entrance at 25 de Mayo, 172. The land was originally donated in Spanish colonial times by philanthropist Francisco Antonio Maciel, who teamed up with Mateo Vidal to establish a hospital and charity. The first building was constructed between 1781 and 1788 and later expanded upon. The present building stems from the 1825 plans of José Toribio (son of :es:Tomás Toribio, Tomás Toribio) and later Bernardo Poncini (wing on the Guaraní street, 1859), Eduardo Canstatt (corner of Guaraní and 25 de Mayo) and Julián Masquelez (1889). The hospital has a Capilla de la Caridad del Hospital Maciel, Montevideo, chapel built in Greek style by Miguel Estévez in 1798.
Hospital Pereira Rossell was founded in 1908 and was built on land donated in late 1900 by Alexis Rossell y Rius and Dolores Pereira de Rossell. It was the city's first pediatric hospital, and shortly afterwards the addition of an obstetric and gynecological clinic in 1915 made it the first maternity hospital as well. Later, the hospital received a donation from Dr. Enrique Pouey for a radiotherapy unit.
Hospital Vilardebó is the only psychiatric hospital in Montevideo. Named after the physician and naturalist :es:Teodoro Vilardebó, Teodoro Vilardebó Matuliche, it opened 21 May 1880. The hospital was originally one of the best of Latin America and in 1915 grew to 1,500 inpatients. Today the hospital is very deteriorated, with broken walls and floors, lack of medicines, beds, and rooms for the personnel. It has an emergency service, outpatient, clinic and inpatient rooms and employs approximately 610 staff, psychologists, psychiatrists, social workers, administrators, guards, among others. The average patient age is 30 years; more than half of the patients arrive by court order; 42% suffer from schizophrenia, 18% from depression and mania, and there are also a high percentage of drug addicted patients.
Other public polyclinics and hospitals of note include the Hospital Saint Bois, founded 18 November 1928, which consists of a General Hospital and Eye Hospital; the Pasteur Hospital in La Unión neighborhood; the Spanish Hospital (Uruguay), Hospital Español, which was founded in 1886, passed to the private sector in the 20th century, closed in 2004 and was restored and re-inaugurated in 2007 as the municipal Juan Jose Crottogini Polyclinic; the National Cancer Institute; and the National Institute of Trauma and Orthopedics.
Private healthcare
Private healthcare is offered by many private health insurance companies, each of which has one or more polyclinics and owns or is associated with one or more hospitals. Private medical facilities of note include the Hospital Británico (Montevideo), Hospital Británico, the Italian Hospital of Montevideo, Mutualista CASMU's Sanatoria I, II, III and IV, the Evangelical Hospital, :es:Médica Uruguaya, Médica Uruguaya, Sanatorio de la Asociación Española, Sanatorios del Círculo Católico, Sanatorio Casa de Galicia and Sanatorio GREMCA.
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Montevideo is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* Arica, Arica, Chile
* Asunción, Asunción, Paraguay
* Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain[
* Brasília, Brasília, Brazil][
* Cádiz, Cádiz, Spain][
* Cali, Cali, Colombia][
* Ceuta, Ceuta, Spain][
* Cochabamba, Cochabamba, Bolivia][
* Córdoba, Argentina][
* Coroico, Coroico, Bolivia][
* Cumaná, Venezuela][
* Curitiba, Curitiba, Brazil
* El Aaiun, Western Sahara][
* Esmeraldas, Ecuador][
* Hurlingham, Buenos Aires, Hurlingham, Argentina][
* La Plata, Argentina][
* Libertador Bolivarian Municipality, Libertador, Venezuela][
* Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal
* Mar del Plata, Argentina][
* Marsico Nuovo, Basilicata, Italy][
* Melilla, Melilla, Spain
* Mississauga, Ontario, Canada][
* Montevideo, Minnesota, United States
* Paris, Paris, France
* Port-au-Prince, Port-au-Prince, Haiti][
* Qingdao, Qingdao, Shandong, China
* Quebec City, Quebec City, Canada
* Rosario, Santa Fe, Rosario, Argentina][
* São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil][
* Tambo de Mora District, Tambo de Mora, Peru][
* Tianjin, Tianjin, China
* Tito, Basilicata, Italy][
* Tumaco, Tumaco, Colombia][
* Ulsan, Ulsan, South Korea
* Wrocław, Wrocław, Poland][
* Wuhu, Wuhu, Anhui, China][
Montevideo is part of the Union of Ibero-American Capital Cities]
See also
References
Bibliography
* Albes, Edward. ''Montevideo, the city of roses'' (US Government Printing Office, 1922
online
*
External links
Montevideo official website
*
{{Authority control
Montevideo,
Capitals in South America
Cities in Uruguay
Populated places in the Montevideo Department
Port cities and towns in Uruguay
Populated places established in 1726
1726 establishments in the Viceroyalty of Peru
1726 establishments in Uruguay
 * Monte vide eu ("I saw a mount") is the most widespread belief but is rejected by the majority of experts, who consider it unlikely because it involves a mix of dialects. The name would come from a
* Monte vide eu ("I saw a mount") is the most widespread belief but is rejected by the majority of experts, who consider it unlikely because it involves a mix of dialects. The name would come from a 
 On 3 February 1807, British troops under the command of General Samuel Auchmuty and Admiral
On 3 February 1807, British troops under the command of General Samuel Auchmuty and Admiral  In the early 20th century, many Europeans (particularly Spaniards and Italians but also thousands from Central Europe) immigrated to the city. In 1908, 30% of the city's population of 300,000 was foreign-born. In that decade the city expanded quickly: new neighborhoods were created and many separate settlements were annexed to the city, among which were the
In the early 20th century, many Europeans (particularly Spaniards and Italians but also thousands from Central Europe) immigrated to the city. In 1908, 30% of the city's population of 300,000 was foreign-born. In that decade the city expanded quickly: new neighborhoods were created and many separate settlements were annexed to the city, among which were the  Uruguay began to stagnate economically in the mid-1950s; Montevideo began a decline, later exacerbated by widespread social and political violence beginning in 1968 (including the emergence of the guerrilla Movimiento de Liberación Nacional-Tupamaros) and by the Civic-military dictatorship of Uruguay (1973-1985). There were major problems with supply; the immigration cycle was reversed.
From the 1960s to the end of the dictatorship in 1985, around one hundred people died or
Uruguay began to stagnate economically in the mid-1950s; Montevideo began a decline, later exacerbated by widespread social and political violence beginning in 1968 (including the emergence of the guerrilla Movimiento de Liberación Nacional-Tupamaros) and by the Civic-military dictatorship of Uruguay (1973-1985). There were major problems with supply; the immigration cycle was reversed.
From the 1960s to the end of the dictatorship in 1985, around one hundred people died or  Montevideo is situated on the north shore of the Río de la Plata, the arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates the south coast of Uruguay from the north coast of Argentina; Buenos Aires lies west on the Argentine side. The
Montevideo is situated on the north shore of the Río de la Plata, the arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates the south coast of Uruguay from the north coast of Argentina; Buenos Aires lies west on the Argentine side. The 
 , the city of Montevideo has been divided into 8 political municipalities (''Municipios''), referred to with the letters from A to G, including CH, each presided over by a mayor elected by the citizens registered in the constituency. This division, according to the Municipality of Montevideo, "aims to advance political and administrative decentralization in the department of Montevideo, with the aim of deepening the democratic participation of citizens in governance." The head of each ''Municipio'' is called an ''alcalde'' or (if female) ''alcaldesa''.
Of much greater importance is the division of the city into 62 ''barrios'': neighborhoods or wards. Many of the city's ''barrios''—such as
, the city of Montevideo has been divided into 8 political municipalities (''Municipios''), referred to with the letters from A to G, including CH, each presided over by a mayor elected by the citizens registered in the constituency. This division, according to the Municipality of Montevideo, "aims to advance political and administrative decentralization in the department of Montevideo, with the aim of deepening the democratic participation of citizens in governance." The head of each ''Municipio'' is called an ''alcalde'' or (if female) ''alcaldesa''.
Of much greater importance is the division of the city into 62 ''barrios'': neighborhoods or wards. Many of the city's ''barrios''—such as 
 The architecture of Montevideo ranges from Neoclassical buildings such as the
The architecture of Montevideo ranges from Neoclassical buildings such as the 
 Torre de las Telecomunicaciones (Telecommunications Tower) or Torre Antel (Antel Tower) is the , 37-floor headquarters of Uruguay's
Torre de las Telecomunicaciones (Telecommunications Tower) or Torre Antel (Antel Tower) is the , 37-floor headquarters of Uruguay's  Montevideo's most important
Montevideo's most important 
 On the east side of the main park area is the National Museum of Visual Arts. On this side, a street market takes place every Sunday. On the north side is an artificial lake with a little castle housing a municipal library for children. An area to its west is used as an open-air exhibition of photography. West of the park, across the coastal avenue Rambla Presidente Wilson, stretches Ramirez Beach. Directly west of the main park are, and belonging to Parque Rodó ''barrio'', is the former ''Parque Hotel'', now called ''Edifício Mercosur'', seat of the parliament of the members countries of the
On the east side of the main park area is the National Museum of Visual Arts. On this side, a street market takes place every Sunday. On the north side is an artificial lake with a little castle housing a municipal library for children. An area to its west is used as an open-air exhibition of photography. West of the park, across the coastal avenue Rambla Presidente Wilson, stretches Ramirez Beach. Directly west of the main park are, and belonging to Parque Rodó ''barrio'', is the former ''Parque Hotel'', now called ''Edifício Mercosur'', seat of the parliament of the members countries of the  Fortaleza del Cerro overlooks the bay of Montevideo. An observation post at this location was first built by the Spanish in the late 18th century. In 1802, a beacon replaced the observation post; construction of the fortress began in 1809 and was completed in 1839. It has been involved in many historical developments and has been repeatedly taken over by various sides. In 1907, the old beacon was replaced with a stronger electric one. It has been a National Monument since 1931 and has housed a military museum since 1916. Today it is one of the tourist attractions of Montevideo.
Fortaleza del Cerro overlooks the bay of Montevideo. An observation post at this location was first built by the Spanish in the late 18th century. In 1802, a beacon replaced the observation post; construction of the fortress began in 1809 and was completed in 1839. It has been involved in many historical developments and has been repeatedly taken over by various sides. In 1907, the old beacon was replaced with a stronger electric one. It has been a National Monument since 1931 and has housed a military museum since 1916. Today it is one of the tourist attractions of Montevideo.
 Punta Brava Lighthouse (''Faro Punta Brava''), also known as Punta Carretas Lighthouse, was erected in 1876. The lighthouse is high and its light reaches away, with a flash every ten seconds. In 1962, the lighthouse became electric. The lighthouse is important for guiding boats into the Banco Inglés Buceo Port or the entrance of the Santa Lucía River.
Punta Brava Lighthouse (''Faro Punta Brava''), also known as Punta Carretas Lighthouse, was erected in 1876. The lighthouse is high and its light reaches away, with a flash every ten seconds. In 1962, the lighthouse became electric. The lighthouse is important for guiding boats into the Banco Inglés Buceo Port or the entrance of the Santa Lucía River.
 There are five large cemetery, cemeteries in Montevideo, all administered by the "Fúnebre y Necrópolis" annex of the Intendencia of Montevideo.
The largest cemetery is the Cementerio del Norte, Montevideo, Cementerio del Norte, located in the northern-central part of the city. The Central Cemetery of Montevideo, Central Cemetery (Spanish: ''Cementerio central''), located in Barrio Sur in the southern area of the city, is one of Uruguay's main cemeteries. It was one of the first cemeteries (in contrast to church graveyards) in the country, founded in 1835 in a time where burials were still carried out by the Catholic Church. It is the burial place of many of the most famous Uruguayans, such as Eduardo Blanco Acevedo, Eduardo Acevedo, Delmira Agustini, Luis Batlle Berres,
There are five large cemetery, cemeteries in Montevideo, all administered by the "Fúnebre y Necrópolis" annex of the Intendencia of Montevideo.
The largest cemetery is the Cementerio del Norte, Montevideo, Cementerio del Norte, located in the northern-central part of the city. The Central Cemetery of Montevideo, Central Cemetery (Spanish: ''Cementerio central''), located in Barrio Sur in the southern area of the city, is one of Uruguay's main cemeteries. It was one of the first cemeteries (in contrast to church graveyards) in the country, founded in 1835 in a time where burials were still carried out by the Catholic Church. It is the burial place of many of the most famous Uruguayans, such as Eduardo Blanco Acevedo, Eduardo Acevedo, Delmira Agustini, Luis Batlle Berres,  The Intendancy of Montevideo was first created by a legal act of 18 December 1908. The municipality's first mayor (1909–1911) was Daniel Muñoz. Municipalities were abolished by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1918, effectively restored during the 1933 military coup of Gabriel Terra, and formally restored by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1934, 1934 Constitution. The Uruguayan Constitution of 1952, 1952 Constitution again decided to abolish the municipalities; it came into effect in February 1955. Municipalities were replaced by departmental councils, which consisted of a collegiate executive board with 7 members from Montevideo and 5 from the interior region. However, municipalities were revived under the 1967 Constitution and have operated continuously since that time.
Since 1990, Montevideo has been partially decentralized into 18 areas; administration and services for each area is provided by its Zonal Community Center (''Centro Comunal Zonal'', CCZ), which is subordinate to the Intendancy of Montevideo. The boundaries of the municipal districts of Montevideo were created on 12 July 1993, and successively amended on 19 October 1993, 6 June 1994 and 10 November 1994. In 2010, the city CCZ were abolished and eight municipalities were created instead.
The city government of Montevideo performs several functions, including maintaining communications with the public, promoting culture, organizing society, caring for the environment and regulating traffic. The city hall is the Palacio Municipal (Montevideo), Palacio Municipal on 18 de Julio Avenue in the
The Intendancy of Montevideo was first created by a legal act of 18 December 1908. The municipality's first mayor (1909–1911) was Daniel Muñoz. Municipalities were abolished by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1918, effectively restored during the 1933 military coup of Gabriel Terra, and formally restored by the Uruguayan Constitution of 1934, 1934 Constitution. The Uruguayan Constitution of 1952, 1952 Constitution again decided to abolish the municipalities; it came into effect in February 1955. Municipalities were replaced by departmental councils, which consisted of a collegiate executive board with 7 members from Montevideo and 5 from the interior region. However, municipalities were revived under the 1967 Constitution and have operated continuously since that time.
Since 1990, Montevideo has been partially decentralized into 18 areas; administration and services for each area is provided by its Zonal Community Center (''Centro Comunal Zonal'', CCZ), which is subordinate to the Intendancy of Montevideo. The boundaries of the municipal districts of Montevideo were created on 12 July 1993, and successively amended on 19 October 1993, 6 June 1994 and 10 November 1994. In 2010, the city CCZ were abolished and eight municipalities were created instead.
The city government of Montevideo performs several functions, including maintaining communications with the public, promoting culture, organizing society, caring for the environment and regulating traffic. The city hall is the Palacio Municipal (Montevideo), Palacio Municipal on 18 de Julio Avenue in the  In recent years Montevideo nightlife has moved to Parque Rodó, where a large concentration of buildings cater for the recreational interests of young people during the night time. Under a presidential decree which went into effect on 1 March 2006, smoking in Uruguay, smoking is prohibited in any public place with roofing, and there is a prohibition on the sale of alcohol in certain businesses from 21.00 to 9.00.
Montevideo has been part of the Creative Cities Network, UNESCO Creative Cities Network in the area of Literature since December 2015.
In recent years Montevideo nightlife has moved to Parque Rodó, where a large concentration of buildings cater for the recreational interests of young people during the night time. Under a presidential decree which went into effect on 1 March 2006, smoking in Uruguay, smoking is prohibited in any public place with roofing, and there is a prohibition on the sale of alcohol in certain businesses from 21.00 to 9.00.
Montevideo has been part of the Creative Cities Network, UNESCO Creative Cities Network in the area of Literature since December 2015.
 The daily newspaper ''El País'' sponsors the Virtual Museum of contemporary Uruguayan art. The director and curator of the Museum presents exhibitions in "virtual spaces, supplemented by information, biographies, texts in English and Spanish".
In the early 1970s (1973, to be particular) when the military junta took over power in Uruguay, art suffered in Montevideo. The art studios went into protest mode, with Rimer Cardillo, one of the country's leading artists, making the National Institute of Fine Arts, Montevideo a "hotbed of resistance". This resulted in the military junta coming down heavily on artists by closing the Fine Art Institute and carting away all the presses and other studio equipment. Consequently, the learning of fine arts was only in private studios run by people who had been let out of jail, in works of printing and on paper and also painting and sculpture. It resumed much later.
The daily newspaper ''El País'' sponsors the Virtual Museum of contemporary Uruguayan art. The director and curator of the Museum presents exhibitions in "virtual spaces, supplemented by information, biographies, texts in English and Spanish".
In the early 1970s (1973, to be particular) when the military junta took over power in Uruguay, art suffered in Montevideo. The art studios went into protest mode, with Rimer Cardillo, one of the country's leading artists, making the National Institute of Fine Arts, Montevideo a "hotbed of resistance". This resulted in the military junta coming down heavily on artists by closing the Fine Art Institute and carting away all the presses and other studio equipment. Consequently, the learning of fine arts was only in private studios run by people who had been let out of jail, in works of printing and on paper and also painting and sculpture. It resumed much later.
 The city has a long and rich literary tradition. Although Uruguayan literature is not limited to the authors of the capital (Horacio Quiroga was born in Salto and Mario Benedetti in Paso de los Toros, for instance), Montevideo has been and is the center of the editorial and creative activity of literature.
In 1900, the city had a remarkable group of writers, including José Enrique Rodó, Carlos Vaz Ferreira, Julio Herrera y Reissig, Delmira Agustini and Felisberto Hernández. Montevideo was then called the "Atenas del Plata" or the "Athens of the Rio de la Plata".
The city has a long and rich literary tradition. Although Uruguayan literature is not limited to the authors of the capital (Horacio Quiroga was born in Salto and Mario Benedetti in Paso de los Toros, for instance), Montevideo has been and is the center of the editorial and creative activity of literature.
In 1900, the city had a remarkable group of writers, including José Enrique Rodó, Carlos Vaz Ferreira, Julio Herrera y Reissig, Delmira Agustini and Felisberto Hernández. Montevideo was then called the "Atenas del Plata" or the "Athens of the Rio de la Plata".
 Among the outstanding authors of Montevideo of the second half of the 20th century are Juan Carlos Onetti, Antonio Larreta, Eduardo Galeano, Marosa di Giorgio and Cristina Peri Rossi.
A new generation of writers have become known internationally in recent years. These include Eduardo Espina (essayist and poet), Fernando Butazzoni (novelist), :es:Rafael Courtoisie, Rafael Courtoisie (poet) and Hugo Burel (short story writer and novelist).
Among the outstanding authors of Montevideo of the second half of the 20th century are Juan Carlos Onetti, Antonio Larreta, Eduardo Galeano, Marosa di Giorgio and Cristina Peri Rossi.
A new generation of writers have become known internationally in recent years. These include Eduardo Espina (essayist and poet), Fernando Butazzoni (novelist), :es:Rafael Courtoisie, Rafael Courtoisie (poet) and Hugo Burel (short story writer and novelist).
 The Centro Cultural de España, as well as Asturias, Asturian and cultural centers, testify to Montevideo's considerable Spanish heritage. Montevideo also has important museums including Museo Torres García, :es:Museo Gurvich, Museo José Gurvich, Museo Nacional de Artes Visuales and Juan Manuel Blanes Museum, Museo Juan Manuel Blanes etc.
The Montevideo Cabildo was the seat of government during the colonial times of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. It is located in front of Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square, in Ciudad Vieja. Built between 1804 and 1869 in Neoclassical style, with a series of Doric columns, Doric and Ionic columns, Ionic columns, it became a National Heritage Site in 1975. In 1958, the Municipal Historic Museum and Archive was inaugurated here. It features three permanent city museum exhibitions, as well as temporary art exhibitions, cultural events, seminars, symposiums and forums.
The Centro Cultural de España, as well as Asturias, Asturian and cultural centers, testify to Montevideo's considerable Spanish heritage. Montevideo also has important museums including Museo Torres García, :es:Museo Gurvich, Museo José Gurvich, Museo Nacional de Artes Visuales and Juan Manuel Blanes Museum, Museo Juan Manuel Blanes etc.
The Montevideo Cabildo was the seat of government during the colonial times of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. It is located in front of Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square, in Ciudad Vieja. Built between 1804 and 1869 in Neoclassical style, with a series of Doric columns, Doric and Ionic columns, Ionic columns, it became a National Heritage Site in 1975. In 1958, the Municipal Historic Museum and Archive was inaugurated here. It features three permanent city museum exhibitions, as well as temporary art exhibitions, cultural events, seminars, symposiums and forums.
 The
The  The Museo Torres García is located in the Old Town, and exhibits Joaquín Torres García's unusual portraits of historical icons and cubism, cubist paintings akin to those of Pablo Picasso, Picasso and Georges Braque, Braque. The museum was established by Manolita Piña Torres, the widow of Torres Garcia, after his death in 1949. She also set up the García Torres Foundation, a private non-profit organization that organizes the paintings, drawings, original writings, archives, objects and furniture designed by the painter as well as the photographs, magazines and publications related to him.
The Museo Torres García is located in the Old Town, and exhibits Joaquín Torres García's unusual portraits of historical icons and cubism, cubist paintings akin to those of Pablo Picasso, Picasso and Georges Braque, Braque. The museum was established by Manolita Piña Torres, the widow of Torres Garcia, after his death in 1949. She also set up the García Torres Foundation, a private non-profit organization that organizes the paintings, drawings, original writings, archives, objects and furniture designed by the painter as well as the photographs, magazines and publications related to him.
 As the capital of Uruguay, Montevideo is home to a number of festivals and carnivals including a Gaucho festival when people ride through the streets on horseback in traditional gaucho gear. The major annual festival is the annual Uruguayan Carnival, Montevideo Carnival which is part of the national festival of Carnival Week, celebrated throughout Uruguay, with central activities in the capital, Montevideo. Officially, the public holiday lasts for two days on Carnival Monday and Shrove Tuesday preceding Ash Wednesday, but due to the prominence of the festival, most shops and businesses close for the entire week.
During carnival there are many open-air stage performances and competitions and the streets and houses are vibrantly decorated. "Tablados" or popular scenes, both fixed and movable, are erected in the whole city. Notable displays include "Desfile de las Llamadas" ("Parade of the Calls"), which is a grand united parade held on the south part of downtown, where it used to be a common ritual back in the early 20th century. Due to the scale of the festival, preparation begins as early as December with an election of the "zonal beauty queens" to appear in the carnival.
As the capital of Uruguay, Montevideo is home to a number of festivals and carnivals including a Gaucho festival when people ride through the streets on horseback in traditional gaucho gear. The major annual festival is the annual Uruguayan Carnival, Montevideo Carnival which is part of the national festival of Carnival Week, celebrated throughout Uruguay, with central activities in the capital, Montevideo. Officially, the public holiday lasts for two days on Carnival Monday and Shrove Tuesday preceding Ash Wednesday, but due to the prominence of the festival, most shops and businesses close for the entire week.
During carnival there are many open-air stage performances and competitions and the streets and houses are vibrantly decorated. "Tablados" or popular scenes, both fixed and movable, are erected in the whole city. Notable displays include "Desfile de las Llamadas" ("Parade of the Calls"), which is a grand united parade held on the south part of downtown, where it used to be a common ritual back in the early 20th century. Due to the scale of the festival, preparation begins as early as December with an election of the "zonal beauty queens" to appear in the carnival.

 The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo. It is located in Ciudad Vieja, immediately across Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square from the Montevideo Cabildo, Cabildo. In 1740 a brick church was built on the site. In 1790, the foundation was laid for the current neoclassical structure. The church was consecrated in 1804. Bicentennial celebrations were held in 2004.
In 1897, Pope Leo XIII elevated the church to Metropolitan Cathedral status. Important ceremonies are conducted under the direction of the Archbishop of Montevideo. Weddings and choral concerts are held here and the parish priest conducts the routine functions of the cathedral. In the 19th century, its precincts were also used as a burial place of famous people who died in the city. For decades, the prison and the nearby Punta Carretas, Punta Carretas parish church were the only major buildings in the neighborhood.
The Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral is the main Roman Catholic church of Montevideo. It is located in Ciudad Vieja, immediately across Constitution Square (Montevideo), Constitution Square from the Montevideo Cabildo, Cabildo. In 1740 a brick church was built on the site. In 1790, the foundation was laid for the current neoclassical structure. The church was consecrated in 1804. Bicentennial celebrations were held in 2004.
In 1897, Pope Leo XIII elevated the church to Metropolitan Cathedral status. Important ceremonies are conducted under the direction of the Archbishop of Montevideo. Weddings and choral concerts are held here and the parish priest conducts the routine functions of the cathedral. In the 19th century, its precincts were also used as a burial place of famous people who died in the city. For decades, the prison and the nearby Punta Carretas, Punta Carretas parish church were the only major buildings in the neighborhood.

 Tourism accounts for much of Uruguay's economy. Tourism in Montevideo is centered in the Ciudad Vieja area, which includes the city's oldest buildings, several museums, art galleries, and nightclubs, with Sarandí Street and the Mercado del Puerto being the most frequented venues of the old city. On the edge of Ciudad Vieja,
Tourism accounts for much of Uruguay's economy. Tourism in Montevideo is centered in the Ciudad Vieja area, which includes the city's oldest buildings, several museums, art galleries, and nightclubs, with Sarandí Street and the Mercado del Puerto being the most frequented venues of the old city. On the edge of Ciudad Vieja,  The Ministry of Tourism (Uruguay), Ministry of Tourism offers a two-and-a-half-hour city tour and the Montevideo Tourist Guide Association offers guided tours in English, Italian, Portuguese and German. Apart from these, many private companies offer organized city tours.
Most tourists to the city come from Argentina, Brazil and Europe, with the number of visitors from elsewhere in Latin America and from the United States growing every year, thanks to an increasing number of international airline arrivals at Carrasco International Airport as well as cruises and ferries that arrive into the port of Montevideo.
The Ministry of Tourism (Uruguay), Ministry of Tourism offers a two-and-a-half-hour city tour and the Montevideo Tourist Guide Association offers guided tours in English, Italian, Portuguese and German. Apart from these, many private companies offer organized city tours.
Most tourists to the city come from Argentina, Brazil and Europe, with the number of visitors from elsewhere in Latin America and from the United States growing every year, thanks to an increasing number of international airline arrivals at Carrasco International Airport as well as cruises and ferries that arrive into the port of Montevideo.
 Apart from the big shopping complexes, the main retailing venues of the city are: most of 18 de Julio Avenue in the
Apart from the big shopping complexes, the main retailing venues of the city are: most of 18 de Julio Avenue in the  The city and its metropolitan area have a bus transportation network, the ''Sistema Met''s acronym. It covers urban and interurban services within the Metropolitan Area and is administered by the municipal government together with the Ministry of Transport and Public Works (Uruguay), Ministry of Transport and Public Works. The Baltasar Brum Terminal located in Ciudad Vieja, is the main urban bus station. However, there are numerous interchanges and terminals distributed in both the city and the metropolitan area.
The city and its metropolitan area have a bus transportation network, the ''Sistema Met''s acronym. It covers urban and interurban services within the Metropolitan Area and is administered by the municipal government together with the Ministry of Transport and Public Works (Uruguay), Ministry of Transport and Public Works. The Baltasar Brum Terminal located in Ciudad Vieja, is the main urban bus station. However, there are numerous interchanges and terminals distributed in both the city and the metropolitan area.
 In Montevideo its design contains yellow and white. To determine the rate they use a taximeter, which will determine the price depending on the distance traveled. All taxis accept cash, now it is also common that you can pay with a credit card.
In Montevideo its design contains yellow and white. To determine the rate they use a taximeter, which will determine the price depending on the distance traveled. All taxis accept cash, now it is also common that you can pay with a credit card.

 Montevideo is also served by a Ferry, ferry system operated by the company Buquebus that connects the port with
Montevideo is also served by a Ferry, ferry system operated by the company Buquebus that connects the port with  The port on Montevideo Bay is one of the reasons the city was founded. It gives natural protection to ships, although two jetties now further protect the harbor entrance from waves. This natural port is competitive with the other great port of Río de la Plata, Buenos Aires.
The main engineering work on the port occurred between the years 1870 and 1930. These six decades saw the construction of the port's first wooden pier, several warehouses in La Aguada, the north and south Rambla, a river port, a new pier, the dredged river basin and the La Teja Refinery. A major storm in 1923 necessitated repairs to many of the city's engineering works. Since the second half of the 20th century, until the 21st century, physical changes had ceased, and since that time the area had degraded due to national economic stagnation.
The port's proximity has contributed to the installation of various industries in the area surrounding the bay, particularly import/export businesses and other business related to port and naval activity. The density of industrial development in the area surrounding the port has kept its popularity as a residential area relatively low despite its centrality. The main environmental problems are subaquatic sedimentation and air and water contamination.
Every year more than one hundred cruises arrive, bringing tourists to Montevideo by public or private tours.
The port on Montevideo Bay is one of the reasons the city was founded. It gives natural protection to ships, although two jetties now further protect the harbor entrance from waves. This natural port is competitive with the other great port of Río de la Plata, Buenos Aires.
The main engineering work on the port occurred between the years 1870 and 1930. These six decades saw the construction of the port's first wooden pier, several warehouses in La Aguada, the north and south Rambla, a river port, a new pier, the dredged river basin and the La Teja Refinery. A major storm in 1923 necessitated repairs to many of the city's engineering works. Since the second half of the 20th century, until the 21st century, physical changes had ceased, and since that time the area had degraded due to national economic stagnation.
The port's proximity has contributed to the installation of various industries in the area surrounding the bay, particularly import/export businesses and other business related to port and naval activity. The density of industrial development in the area surrounding the port has kept its popularity as a residential area relatively low despite its centrality. The main environmental problems are subaquatic sedimentation and air and water contamination.
Every year more than one hundred cruises arrive, bringing tourists to Montevideo by public or private tours.

 The Christian Brothers of Ireland Stella Maris College (Montevideo), Stella Maris College is a private, co-educational, not-for-profit Catholic school located in the wealthy residential southeastern neighborhood of Carrasco. Established in 1955, it is regarded as one of the best high schools in the country, blending a rigorous curriculum with strong extracurricular activities. The school's headmaster, history professor Juan Pedro Toni, is a member of the Stella Maris Board of Governors and the school is a member of the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO). Its long list of distinguished former pupils includes economists, engineers, architects, lawyers, politicians and even Formula One, F1 champions. The school has also played an important part in the development of rugby union in Uruguay, with the creation of Old Christians Club, the school's alumnus, alumni club.
Also in Carrasco is The British Schools of Montevideo, one of the oldest educational institutions in the country, founded in 1908 with "the object of giving children a complete education, both intellectual and moral, based upon the ideas and principles of the best schools in The British Isles".
The School is governed by the Board of Governors, elected by the British Schools Society in Uruguay, whose honorary president is the British Ambassador to Uruguay. Prominent alumni include former government ministers Pedro Bordaberry Herrán and Gabriel Gurméndez Armand-Ugon.
Located in Cordon, St.Brendan's school, previously named St.Catherine's is a non-profit civil association, which has a solid institutional culture with a clear vision of the future. It is known for being one of the best schools in the country, joining students from the wealthiest parts of Montevideo, such as, Punta Carretas, Pocitos, Malvin and Carrasco.
St. Brendan's School is a bilingual, non-denominational school that promotes a pedagogical constructivist approach focused on the child as a whole. In this approach, understanding is built from the connections children make between their own prior knowledge and the learning experiences, thus developing critical thinking skills. It is also the only school in the country implementing the three International Baccalaureate Programmes. These are:
*Diploma Program – Pre-University course for students aged 16 to 19. The Diploma Program is a two-year curriculum.
*MYP -Middle Years Program. For students aged 12 to 16.
*PYP – Primary Years Program. For students aged 3 to 12.
Other educational institutions of note include Colegio Ingles, :es:Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Lycée Français de Montevideo, Ivy Thomas, German School of Montevideo and Colegio Preuniversitario Ciudad de San Felipe.
The Christian Brothers of Ireland Stella Maris College (Montevideo), Stella Maris College is a private, co-educational, not-for-profit Catholic school located in the wealthy residential southeastern neighborhood of Carrasco. Established in 1955, it is regarded as one of the best high schools in the country, blending a rigorous curriculum with strong extracurricular activities. The school's headmaster, history professor Juan Pedro Toni, is a member of the Stella Maris Board of Governors and the school is a member of the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO). Its long list of distinguished former pupils includes economists, engineers, architects, lawyers, politicians and even Formula One, F1 champions. The school has also played an important part in the development of rugby union in Uruguay, with the creation of Old Christians Club, the school's alumnus, alumni club.
Also in Carrasco is The British Schools of Montevideo, one of the oldest educational institutions in the country, founded in 1908 with "the object of giving children a complete education, both intellectual and moral, based upon the ideas and principles of the best schools in The British Isles".
The School is governed by the Board of Governors, elected by the British Schools Society in Uruguay, whose honorary president is the British Ambassador to Uruguay. Prominent alumni include former government ministers Pedro Bordaberry Herrán and Gabriel Gurméndez Armand-Ugon.
Located in Cordon, St.Brendan's school, previously named St.Catherine's is a non-profit civil association, which has a solid institutional culture with a clear vision of the future. It is known for being one of the best schools in the country, joining students from the wealthiest parts of Montevideo, such as, Punta Carretas, Pocitos, Malvin and Carrasco.
St. Brendan's School is a bilingual, non-denominational school that promotes a pedagogical constructivist approach focused on the child as a whole. In this approach, understanding is built from the connections children make between their own prior knowledge and the learning experiences, thus developing critical thinking skills. It is also the only school in the country implementing the three International Baccalaureate Programmes. These are:
*Diploma Program – Pre-University course for students aged 16 to 19. The Diploma Program is a two-year curriculum.
*MYP -Middle Years Program. For students aged 12 to 16.
*PYP – Primary Years Program. For students aged 3 to 12.
Other educational institutions of note include Colegio Ingles, :es:Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Instituto Preuniversitario Salesiano Juan XXIII, Lycée Français de Montevideo, Ivy Thomas, German School of Montevideo and Colegio Preuniversitario Ciudad de San Felipe.