Marine primary production on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
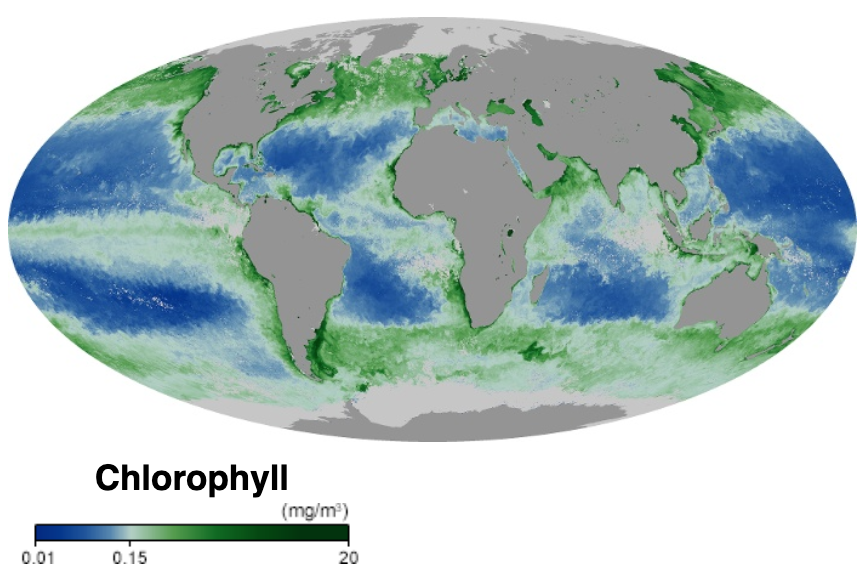 Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of
 The first primary producers that used photosynthesis were oceanic
The first primary producers that used photosynthesis were oceanic  The tiny marine cyanobacterium '' Prochlorococcus'', discovered in 1986, forms today part of the base of the ocean food chain and accounts for more than half the photosynthesis of the open ocean and an estimated 20% of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. It is possibly the most plentiful genus on Earth: a single millilitre of surface seawater may contain 100,000 cells or more.
Originally, biologists thought
The tiny marine cyanobacterium '' Prochlorococcus'', discovered in 1986, forms today part of the base of the ocean food chain and accounts for more than half the photosynthesis of the open ocean and an estimated 20% of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. It is possibly the most plentiful genus on Earth: a single millilitre of surface seawater may contain 100,000 cells or more.
Originally, biologists thought 


 In 2000 a team of microbiologists led by
In 2000 a team of microbiologists led by

File:Cyanidium O5A.jpg, Cyanidiophyceae colony, a class of unicellular red algae
File:Porphyra umbilicalis Helgoland.JPG, The seaweed ''
 Altogether, about 45 percent of the
Altogether, about 45 percent of the
File:Diatoms (248 05) Various diatoms.jpg,
File:Emiliania huxleyi.png, The ubiquitous '' Emiliania huxleyi''
File:Cwall99 lg.jpg, ''Emiliania huxleyi'' bloom off south England
File:CSIRO ScienceImage 7609 SEM dinoflagellate.jpg, Dinoflagellates
File:Karenia brevis.jpg, ''
File:Diplonema papillatum SEM image.gif, Diplonemids may be abundant in the world oceans
Traditionally the
A place in the sun - Algae is the crop of the future, according to researchers in Geel
Flanders Today, Retrieved 8 December 2012 Depending on the species, their sizes range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundred micrometers. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces.
File:Zooxanthellae.jpg,



File:Giant Kelp.jpg,
 The diagram on the right shows an evolutionary scenario for the conquest of land by streptophytes. Streptophyte algae include all
The diagram on the right shows an evolutionary scenario for the conquest of land by streptophytes. Streptophyte algae include all
 Back in the
Back in the
 Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
s from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotroph
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Wo ...
s.
Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain
Compared to terrestrial environments, marine environments have biomass pyramids which are inverted at the base. In particular, the biomass of consumers (copepods, krill, shrimp, forage fish) is larger than the biomass of primary producers. Thi ...
and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem engineer
An ecosystem engineer is any species that creates, significantly modifies, maintains or destroys a habitat. These organisms can have a large impact on species richness and landscape-level heterogeneity of an area. As a result, ecosystem engin ...
s which change the environment and provide habitats
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
for other marine life.
Primary production in the ocean can be contrasted with primary production on land. Globally the ocean and the land each produce about the same amount of primary production, but in the ocean primary production comes mainly from cyanobacteria and algae, while on land it comes mainly from vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
s.
Marine algae includes the largely invisible and often unicellular microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
, which together with cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
form the ocean phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
, as well as the larger, more visible and complex multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
commonly called seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and '' Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
. Seaweeds are found along coastal areas, living on the floor of continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
and washed up in intertidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species ...
s. Some seaweeds drift with plankton in the sunlit surface waters ( epipelagic zone) of the open ocean. Back in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleoz ...
, some phytoplankton evolved into red, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model ...
and green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
. These algae then invaded the land and started evolving into the land plants we know today. Later in the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
some of these land plants returned to the sea as mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
s and seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families ( Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the ...
es. These are found along coasts in intertidal regions and in the brackish water of estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
. In addition, some seagrasses, like seaweeds, can be found at depths up to 50 metres on both soft and hard bottoms of the continental shelf.
Marine primary producers
Primary producers are theautotroph
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Wo ...
organisms that make their own food instead of eating other organisms. This means primary producers become the starting point in the food chain for heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
organisms that do eat other organisms. Some marine primary producers are specialised bacteria and archaea which are chemotrophs, making their own food by gathering around hydrothermal vents
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspo ...
and cold seeps and using chemosynthesis. However, most marine primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
comes from organisms which use photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
on the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water. This process uses energy from sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
into sugars that can be used both as a source of chemical energy and of organic molecules that are used in the structural components of cells. Marine primary producers are important because they underpin almost all marine animal life by generating most of the oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and food that provide other organisms with the chemical energy they need to exist.
The principal marine primary producers are cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
and marine plants. The oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
released as a by-product of photosynthesis is needed by nearly all living things to carry out cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
. In addition, primary producers are influential in the global carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
cycles. They stabilize coastal areas and can provide habitats for marine animals. The term division has been traditionally used instead of phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
when discussing primary producers, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants
The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "trad ...
now accepts the terms as equivalent.
In a reversal of the pattern on land, in the oceans, almost all photosynthesis is performed by algae and cyanobacteria, with a small fraction contributed by vascular plants
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
and other groups. Algae encompass a diverse range of organisms, ranging from single floating cells to attached seaweeds. They include photoautotrophs from a variety of groups. Eubacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were amon ...
are important photosynthetizers in both oceanic and terrestrial ecosystems, and while some archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
are phototrophic, none are known to utilise oxygen-evolving photosynthesis. A number of eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s are significant contributors to primary production in the ocean, including green alga
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
e, brown alga
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and p ...
e and red algae, and a diverse group of unicellular groups. Vascular plants are also represented in the ocean by groups such as the seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families ( Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the ...
es.
Unlike terrestrial ecosystems, the majority of primary production in the ocean is performed by free-living microscopic organisms called phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
. It has been estimated that half of the world's oxygen is produced by phytoplankton. Larger autotrophs, such as the seagrasses and macroalgae (seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and '' Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s) are generally confined to the littoral zone and adjacent shallow waters, where they can attach to the underlying substrate but still be within the photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological pro ...
. There are exceptions, such as ''Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae ( seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral ...
'', but the vast majority of free-floating production takes place within microscopic organisms.
The factors limiting primary production in the ocean are also very different from those on land. The availability of water, obviously, is not an issue (though its salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
can be). Similarly, temperature, while affecting metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
rates (see Q10), ranges less widely in the ocean than on land because the heat capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K).
Heat cap ...
of seawater buffers temperature changes, and the formation of sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's o ...
insulates it at lower temperatures. However, the availability of light, the source of energy for photosynthesis, and mineral nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
, the building blocks for new growth, play crucial roles in regulating primary production in the ocean. Available Earth System Models suggest that ongoing ocean bio-geochemical changes could trigger reductions in ocean NPP between 3% and 10% of current values depending on the emissions scenario.
In 2020 researchers reported that measurements over the last two decades of primary production in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
show an increase of nearly 60% due to higher concentrations of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
. They hypothesize new nutrients are flowing in from other oceans and suggest this means the Arctic ocean may be able to support higher trophic level production and additional carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
in the future.
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
are a phylum (division) of bacteria, ranging from unicellular to filamentous
The word filament, which is descended from Latin ''filum'' meaning " thread", is used in English for a variety of thread-like structures, including:
Astronomy
* Galaxy filament, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
* Solar filamen ...
and including colonial species, which fix inorganic carbon into organic carbon compounds. They are found almost everywhere on earth: in damp soil, in both freshwater and marine environments, and even on Antarctic rocks. In particular, some species occur as drifting cells floating in the ocean, and as such were amongst the first of the phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
. These bacteria function like algae in that they can process nitrogen from the atmosphere when none is in the ocean.
 The first primary producers that used photosynthesis were oceanic
The first primary producers that used photosynthesis were oceanic cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
about 2.3 billion years ago. The release of molecular oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
by cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
as a by-product of photosynthesis induced global changes in the Earth's environment. Because oxygen was toxic to most life on Earth at the time, this led to the near-extinction of oxygen-intolerant organisms, a dramatic change which redirected the evolution of the major animal and plant species.
 The tiny marine cyanobacterium '' Prochlorococcus'', discovered in 1986, forms today part of the base of the ocean food chain and accounts for more than half the photosynthesis of the open ocean and an estimated 20% of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. It is possibly the most plentiful genus on Earth: a single millilitre of surface seawater may contain 100,000 cells or more.
Originally, biologists thought
The tiny marine cyanobacterium '' Prochlorococcus'', discovered in 1986, forms today part of the base of the ocean food chain and accounts for more than half the photosynthesis of the open ocean and an estimated 20% of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. It is possibly the most plentiful genus on Earth: a single millilitre of surface seawater may contain 100,000 cells or more.
Originally, biologists thought cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
was algae, and referred to it as "blue-green algae". The more recent view is that cyanobacteria are bacteria, and hence are not even in the same Kingdom as algae. Most authorities exclude all prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
, and hence cyanobacteria from the definition of algae.

Biological pigments
Biological pigments are any coloured material in plant or animal cells. All biological pigments selectively absorb certain wavelengths of light while reflecting others.Lee, DW (2007) Nature's palette - the science of plant color. University of Chicago Press The primary function of pigments in plants isphotosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
, which uses the green pigment chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to ...
and several colorful pigments that absorb as much light energy as possible. Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to ...
is the primary pigment in plants; it is a chlorin that absorbs yellow and blue wavelengths of light while reflecting green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
. It is the presence and relative abundance of chlorophyll that gives plants their green color. Green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
and plants possess two forms of this pigment: chlorophyll ''a'' and chlorophyll ''b''. Kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwa ...
s, diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising se ...
s, and other photosynthetic heterokonts contain chlorophyll ''c'' instead of ''b'', while red algae possess only chlorophyll ''a''. All chlorophylls serve as the primary means plants use to intercept light in order to fuel photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts

Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it i ...
s (from the Greek ''chloros'' for green, and ''plastes'' for "the one who forms") are organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s that conduct photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
, where the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to ...
captures the energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
from sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when ...
, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules while freeing oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
from water in plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
and algal
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
cells. They then use the stored energy to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
in a process known as the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
.
A chloroplast is a type of organelle known as a plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyan ...
, characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to ...
. They are highly dynamic—they circulate and are moved around within plant cells, and occasionally pinch in two to reproduce. Their behavior is strongly influenced by environmental factors like light color and intensity. Chloroplasts, like mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
, contain their own DNA, which is thought to be inherited from their ancestor—a photosynthetic cyanobacterium that was engulfed by an early eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
cell. Chloroplasts cannot be made by the plant cell and must be inherited by each daughter cell during cell division.
Most chloroplasts can probably be traced back to a single endosymbiotic event, when a cyanobacterium was engulfed by the eukaryote. Despite this, chloroplasts can be found in an extremely wide set of organisms, some not even directly related to each other—a consequence of many secondary
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature
* Secondary emission, of particles
** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products
* The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding i ...
and even tertiary endosymbiotic events.

Microbial rhodopsin
Phototrophic metabolism relies on one of three energy-converting pigments:chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to ...
, bacteriochlorophyll, and retinal. Retinal is the chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color.
The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the mo ...
found in rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
s. The significance of chlorophyll in converting light energy has been written about for decades, but phototrophy based on retinal pigments is just beginning to be studied.
 In 2000 a team of microbiologists led by
In 2000 a team of microbiologists led by Edward DeLong
Edward Francis DeLong (born 1958), is a marine microbiologist and professor in the Department of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii, Manoa, and is considered a pioneer in the field of metagenomics. He is best known for his discovery of the ...
made a crucial discovery in the understanding of the marine carbon and energy cycles. They discovered a gene in several species of bacteria responsible for production of the protein rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransductio ...
, previously unheard of in bacteria. These proteins found in the cell membranes are capable of converting light energy to biochemical energy due to a change in configuration of the rhodopsin molecule as sunlight strikes it, causing the pumping of a proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
from inside out and a subsequent inflow that generates the energy.''Bacteria with Batteries'', Popular Science, January 2001, Page 55. The archaeal-like rhodopsins have subsequently been found among different taxa, protists as well as in bacteria and archaea, though they are rare in complex multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni ...
s.
Research in 2019 shows these "sun-snatching bacteria" are more widespread than previously thought and could change how oceans are affected by global warming. "The findings break from the traditional interpretation of marine ecology found in textbooks, which states that nearly all sunlight in the ocean is captured by chlorophyll in algae. Instead, rhodopsin-equipped bacteria function like hybrid cars, powered by organic matter when available — as most bacteria are — and by sunlight when nutrients are scarce."
There is an astrobiological conjecture called the Purple Earth hypothesis
The Purple Earth hypothesis is an astrobiological hypothesis that photosynthetic life forms of early Earth were based on the simpler molecule retinal rather than the more complex chlorophyll, making Earth appear purple rather than green. An examp ...
which surmises that original life forms on Earth were retinal-based rather than chlorophyll-based, which would have made the Earth appear purple instead of green.
Marine algae

Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
is an informal term for a widespread and diverse collection of photosynthetic eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
organisms which are not necessarily closely related and are thus polyphyletic. Unlike higher plants, algae lack roots, stems, or leaves.
Algal groups
Marine algae have traditionally been placed in groups such as:green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
, red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
, brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and p ...
, diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising se ...
s, coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
s and dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates ( Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s.
Green algae
Green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
live most of their lives as single cells or are filamentous, while others form colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
made up from long chains of cells, or are highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. They form an informal group containing about 8,000 recognized species.
Red algae
Modernred algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
are mostly multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
with differentiated cells and include many notable seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and '' Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s. As coralline algae
Coralline algae are red algae in the order Corallinales. They are characterized by a thallus that is hard because of calcareous deposits contained within the cell walls. The colors of these algae are most typically pink, or some other shade of re ...
, they play an important role in the ecology of coral reefs. They form a (disputed) phylum containing about 7,000 recognized species.
Porphyra umbilicalis
Green laver (), known as ''aonori'' (; ) in Japan, ''sea cabbage'' () or ''hutai'' () in China, and ''parae'' () in Korean, is a type of edible green seaweed, including species from the genera ''Monostroma'' and ''Ulva'' ('' Ulva prolifera'', '' ...
''
Brown algae
Brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and p ...
are mostly multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
and include many seaweeds, including kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwa ...
. They form a class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differently ...
containing about 2,000 recognized species.
Diatoms
 Altogether, about 45 percent of the
Altogether, about 45 percent of the primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
in the oceans is contributed by diatoms
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
.
Diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising se ...
s are one of the most common types of phytoplankton
File:Diatoms through the microscope.jpg, They are a major algae group generating about 20% of world oxygen production.
File:Diatom algae Amphora sp.jpg, Diatoms have glass like cell walls called frustules which are made of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
.
File:Phytoplankton in the form of a diatom chain.jpg, Diatoms linked in a colonial chainCoccolithophores
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
s are almost exclusively marine and are found in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
. They have calcium carbonate plates (or scales) of uncertain function called ''coccolith
Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores (single-celled phytoplankton such as '' Emiliania huxleyi'') and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a ''coccosphere' ...
s'', which are important microfossils. Coccolithophores are of interest to those studying global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
because as ocean acidity increases, their coccoliths may become even more important as a carbon sink. The most abundant species of coccolithophore, '' Emiliania huxleyi'' is an ubiquitous component of the plankton base in marine food webs
Compared to terrestrial environments, marine environments have biomass pyramids which are inverted at the base. In particular, the biomass of consumers (copepods, krill, shrimp, forage fish) is larger than the biomass of primary producers. Thi ...
. Management strategies are being employed to prevent eutrophication-related coccolithophore blooms, as these blooms lead to a decrease in nutrient flow to lower levels of the ocean.
Dinoflagellate
Karenia brevis
''Karenia brevis'' is a microscopic, single-celled, photosynthetic organism in the genus '' Karenia''. It is a marine dinoflagellate commonly found in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. It is the organism responsible for the "Florida red tides" ...
'' produces red tides highly toxic to humans
File:Algal bloom(akasio) by Noctiluca in Nagasaki.jpg, Red tide
Mixotrophic algae
Other groups
phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
of microorganisms, such as the algal groups discussed above, was inferred and their taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
established based on studies of morphology. However developments in molecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
have allowed the evolutionary relationship of species to be established by analyzing their DNA and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
sequences. Many taxa, including the algal groups discussed above, are in the process of being reclassified or redefined using molecular phylogenetics. Recent developments in molecular sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure (sometimes incorrectly called the primary sequence) of an unbranched biopolymer. Sequencing results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which succi ...
have allowed for the recovery of genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
s directly from environmental samples and avoiding the need for culturing. This has led for example, to a rapid expansion in knowledge of the abundance and diversity of marine microorganisms. Molecular techniques such as genome-resolved metagenomics and single cell genomics
Single-cell sequencing examines the sequence information from individual cells with optimized next-generation sequencing technologies, providing a higher resolution of cellular differences and a better understanding of the function of an individua ...
are being used in combination with high throughput techniques.
Between 2009 and 2013, the ''Tara'' Oceans expedition traversed the world oceans collecting plankton and analysing them with contemporary molecular techniques. They found a huge range of previously unknown photosynthetic and mixotrophic algae. Among their findings were the diplonemids. These organisms are generally colourless and oblong in shape, typically about 20 µm long and with two flagella. Evidence from DNA barcoding suggests diplonemids may be among the most abundant and most species-rich of all marine eukaryote groups.
By size
Algae can be classified by size as ''microalgae'' or ''macroalgae''.Microalgae
Microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
are the microscopic types of algae, not visible to the naked eye. They are mostly unicellular species which exist as individuals or in chains or groups, though some are multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
. Microalgae are important components of the marine protists, as well as the marine phytoplankton. They are very diverse. It has been estimated there are 200,000-800,000 species of which about 50,000 species have been described.Starckx, Senne (31 October 2012A place in the sun - Algae is the crop of the future, according to researchers in Geel
Flanders Today, Retrieved 8 December 2012 Depending on the species, their sizes range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundred micrometers. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces.
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Sy ...
is a photosynthetic algae that lives inside hosts like coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
File:Paramecium bursaria.jpg, A single-celled ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
with green zoochlorellae
''Zoochlorella'' is a ''nomen rejiciendum'' for a genus of green algae assigned to ''Chlorella''. The term zoochlorella (plural zoochlorellae) is sometimes used to refer to any green algae that lives symbiotically within the body of a freshwater ...
living inside endosymbiotic
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within ...
ally
File:Euglena mutabilis - 400x - 1 (10388739803) (cropped).jpg, '' Euglena mutabilis'', a photosynthetic flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their ...
Macroalgae

Macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
are the larger, multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
and more visible types of algae, commonly called seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and '' Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s. Seaweeds usually grow in shallow coastal waters where they are anchored to the seafloor by a holdfast. Seaweed that becomes adrift can wash up on beaches. Kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwa ...
is a large brown seaweed that forms large underwater forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
covering about 25% of the world coastlines. They are among the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on Earth.Mann, K.H. 1973. Seaweeds: their productivity and strategy for growth. Science 182: 975-981. Some ''Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae ( seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral ...
'' seaweeds are planktonic (free-floating) and form floating drifts. Like microalgae, macroalgae (seaweeds) are technically marine protists since they are not true plants.

Giant kelp
''Macrocystis pyrifera'', commonly known as giant kelp or bladder kelp, is a species of kelp (large brown algae), and one of four species in the genus ''Macrocystis''. Despite its appearance, it is not a plant; it is a heterokont. Giant kelp is ...
is technically a protist since it is not a true plant, yet it is multicellular and can grow to 50 m
File:Sargassum on the beach, Cuba.JPG, ''Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae ( seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral ...
'' seaweed is a brown alga with air bladders that help it float
File:Histrio histrio by A. H. Baldwin.jpg, Sargassum fish
The sargassum fish, anglerfish, or frog fish (''Histrio histrio'') is a frogfish of the family (biology), family Antennariidae, Monotypic taxon, the only species in its genus. It lives among ''Sargassum'' seaweed which floats in subtropical ocea ...
are camouflaged to live among drifting ''Sargassum'' seaweed
File:Ventricaria ventricosa.JPG, This unicellular bubble algae lives in tidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species o ...
s. It can have a 4 cm diameter.
Evolution of land plants
 The diagram on the right shows an evolutionary scenario for the conquest of land by streptophytes. Streptophyte algae include all
The diagram on the right shows an evolutionary scenario for the conquest of land by streptophytes. Streptophyte algae include all green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
, and are the only photosynthetic eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s from which the macroscopic land flora evolved ''(red lines)''. That said, throughout the course of evolution, algae from various other lineages have colonized land ''(yellow lines)'' — but also streptophyte algae have continuously and independently made the wet to dry transition (convergence of red and yellow). Throughout history, numerous lineages have become extinct ''(X labels)''. Terrestrial algae of various taxonomic affiliations dwell on rock surfaces and form biological soil crusts. From the diversity of the paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
streptophyte algae, however, did an organism whose descendants eventually conquered land on a global scale emerge: a likely branched filamentous — or even parenchymatous
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word � ...
— organism that formed rhizoidal structures and experienced desiccation from time to time. From this "hypothetical hydro-terrestrial alga", the lineages of Zygnematophyceae
Zygnematophyceae (or Conjugatophyceae) is a class of green algae in the paraphylum streptophyte algae, also referred to as Charophyta, consisting of more than 4000 described species. It contains five orders: the Spirogloeales, the Serritaeniales ...
and embryophyte
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sist ...
s (land plants) arose. In its infancy, the trajectory leading to the embryophytes was represented by the — now extinct — earliest land plants.
The earliest land plants probably interacted with beneficial substrate microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found t ...
that aided them in obtaining nutrients from their substrate. Furthermore, the earliest land plants had to successfully overcome a barrage of terrestrial stressors (including ultraviolet light and photosynthetically active irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
, drought, drastic temperature shifts, etc.). They succeeded because they had the right set of traits — a mix of adaptations that were selected for in their hydro-terrestrial algal ancestors, exaptations, and the potential for co-option of a fortuitous set of genes and pathways. During the course of evolution, some members of the populations of the earliest land plants gained traits that are adaptive in terrestrial environments (such as some form of water conductance, stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
-like structures, embryos, etc.); eventually, the "hypothetical last common ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
of land plants" emerged. From this ancestor, the extant bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in ...
s and tracheophyte
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They a ...
s evolved. While the exact trait repertoire of the hypothetical last common ancestor of land plants is uncertain, it will certainly have entailed properties of vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
and non-vascular plant
Non-vascular plants are plants without a vascular system consisting of xylem and phloem. Instead, they may possess simpler tissues that have specialized functions for the internal transport of water.
Non-vascular plants include two distantly rel ...
s. What is also certain is that the last common ancestor of land plants had traits of algal ancestry.
Marine plants
 Back in the
Back in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleoz ...
, some phytoplankton evolved into red, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model ...
and green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
. Green algae then invaded the land and started evolving into the land plants we know today. Later, in the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
, some of these land plants returned to the sea as mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
s and seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families ( Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the ...
es.
Plant life can flourish in the brackish waters of estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
, where mangroves
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several ...
or cordgrass
''Spartina'' is a taxon of plants in the grass family, frequently found in coastal salt marshes. Its species are commonly known as cordgrass or cord-grass, and are native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean in western and southern Europe, north ...
or beach grass might grow. Flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s grow in sandy shallows in the form of seagrass meadow
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and ...
s, mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
s line the coast in tropical and subtropical regions and salt-tolerant
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles a ...
plants thrive in regularly inundated salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated ...
es. All of these habitats are able to sequester large quantities of carbon and support a biodiverse
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
range of larger and smaller animal life. Marine plants can be found in intertidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species ...
s and shallow waters, such as seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families ( Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the ...
es like eelgrass Eelgrass is a common name for several plants and may refer to:
* ''Zostera'', marine eelgrass
* ''Vallisneria'', freshwater eelgrass
{{Short pages monitor
''Primary Productivity in the Sea''
Springer. . * Falkowski, Paul and Raven, John A. (2013
''Aquatic Photosynthesis''
Second edition revised, Princeton University Press. . * Falkowski P and Knoll AH (2011
''Evolution of Primary Producers in the Sea''
Academic Press. . * Kirk, John T. O. (2010
''Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems''
Third edition revised, Cambridge University Press. . {{aquatic ecosystem topics, expanded=marine * Evolution-related timelines Marine botany Algae Seagrass Seaweeds Branches of botany
See also
*Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
* Aquatic plants
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ...
* Biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH ...
* Evolutionary history of plants
The evolution of plants has resulted in a wide range of complexity, from the earliest algal mats, through multicellular marine and freshwater green algae, terrestrial bryophytes, lycopods and ferns, to the complex gymnosperms and angiosperms ( ...
* Oceanic carbon cycle
The oceanic carbon cycle (or marine carbon cycle) is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere, Earth interior, and the seafloor. The carbon cycle is a result of many inte ...
* Plant evolution
Plant evolution is the subset of evolutionary phenomena that concern plants. Evolutionary phenomena are characteristics of populations that are described by averages, medians, distributions, and other statistical methods. This distinguishes pla ...
* Timeline of plant evolution
This article attempts to place key plant innovations in a geological context. It concerns itself only with novel adaptations and events that had a major ecological significance, not those that are of solely anthropological interest. The timeline ...
* Evolution of photosynthesis
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
References
Further reading
* Falkowski, Paul (Ed.) (2013''Primary Productivity in the Sea''
Springer. . * Falkowski, Paul and Raven, John A. (2013
''Aquatic Photosynthesis''
Second edition revised, Princeton University Press. . * Falkowski P and Knoll AH (2011
''Evolution of Primary Producers in the Sea''
Academic Press. . * Kirk, John T. O. (2010
''Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems''
Third edition revised, Cambridge University Press. . {{aquatic ecosystem topics, expanded=marine * Evolution-related timelines Marine botany Algae Seagrass Seaweeds Branches of botany