marine protists on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Marine protists are defined by their habitat as


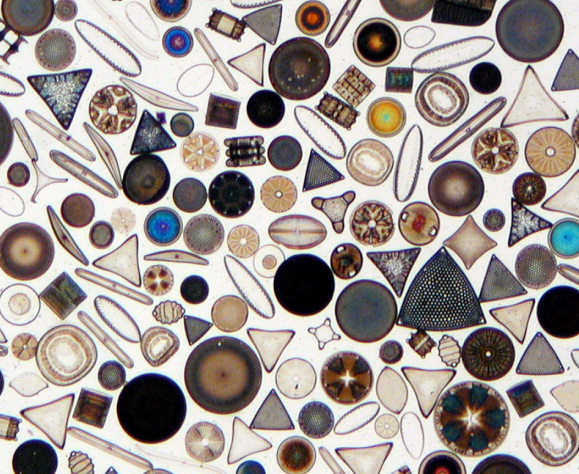
File:Diatoms through the microscope.jpg,
/ref> File:Triceratium morlandii var. morlandii.jpg, Fossil diatom frustule from 32 to 40 mya File:Podocyrtis papalis Ehrenberg - Radiolarian (30448963206).jpg,
File:Frontonia ingesting a diatom.ogg, Ciliate ingesting a diatom
File:Amoeba engulfing diatom.ogv, Amoeba engulfing a diatom
The fungus-like protist saprobes are specialized to absorb nutrients from nonliving organic matter, such as dead organisms or their wastes. For instance, many types of
23.4 "Ecology of Protists"
OpenStax, Houston, Texas. Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
File:Tintinnid ciliate Favella.jpg,
 Flagella are used in prokaryotes (archaea and bacteria) as well as protists. In addition, both flagella and
Flagella are used in prokaryotes (archaea and bacteria) as well as protists. In addition, both flagella and
2004, accessed 2011-01-01. to emphasize their distinctive wavy appendage role in cellular function or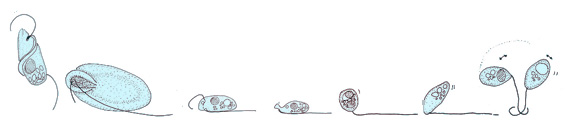

File:Chlamydomonas (10000x).jpg, Green algal flagellate (''
A place in the sun - Algae is the crop of the future, according to researchers in Geel
Flanders Today, Retrieved 8 December 2012 Depending on the species, their sizes range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundred micrometers. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces.
File:Chlamydomonas globosa - 400x (13263097835).jpg, ''Chlamydomonas globosa'', a unicellular green alga with two

 Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Diatoms are enclosed in protective silica (glass) shells called
"Plankton - Plant plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019. Dead diatoms drift to the ocean floor where, over millions of years, the remains of their frustules can build up as much as half a mile deep. Diatoms have relatively high sinking speeds compared with other phytoplankton groups, and they account for about 40% of particulate carbon exported to ocean depths.
File:Diatoms (248 05) Various diatoms.jpg,
 Physically driven seasonal enrichments in surface nutrients favour
Physically driven seasonal enrichments in surface nutrients favour
File:Diatom algae Amphora sp.jpg, Silicified frustule of a pennate diatom with two overlapping halves
File:Fjouenne sbrmvr012w 20070924163039 small.jpg, ''Guinardia delicatula'', a diatom responsible for
File:CSIRO ScienceImage 7233 diatom.jpg, Linked diatoms
File:Pennate diatom infected with two chytrid-like fungal pathogens.png, Pennate diatom from an Arctic meltpond, infected with two chytrid-like fungal pathogens. Scale bar = 10 µm.
"A coccolithophore"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.
File:Emiliania huxleyi.jpg, The
File:Gyrodinium dinoflagellate.jpg, ''
Dinoflagellates often live in
File:Ceratium tripos.jpg, ''Tripos muelleri'' is recognisable by its U-shaped horns
File:Archives de zoologie expérimentale et générale (1920) (20299351186).jpg, ''
File:Algal bloom(akasio) by Noctiluca in Nagasaki.jpg,
"Plankton - Animal plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.
File:Mikrofoto.de-Radiolarien 6.jpg, Like diatoms, radiolarians come in many shapes
File:Theocotylissa ficus Ehrenberg - Radiolarian (34638920262).jpg, Also like diatoms, radiolarian shells are usually made of silicate
File:Acantharian radiolarian Xiphacantha (Haeckel).jpg, However
File:Cladococcus abietinus.jpg, ''Cladococcus abietinus''
File:Cleveiplegma boreale.jpg, ''Cleveiplegma boreale''
File:EB1911 Foraminifera - Section of Rotalia beccarii.jpg, section showing chambers of a spiral foram
File:Live Ammonia tepida.jpg, Live ''
A number of forams are
File:Amoeba proteus 2.jpg, Naked amoeba showing food vacuoles and ingested diatom
File:Arcella sp.jpg, Shell or test of a
Penard's Amoeba Collection
 Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Phytoplankton primary production supports higher Although many ciliates are heterotrophs, a number of pelagic species are
Although many ciliates are heterotrophs, a number of pelagic species are
File:Faure FremietTspCamp.jpg, ''Tintinnopsis campanula''
File:Oxytricha chlorelligera - 400x (10403483023).jpg, '' Oxytricha chlorelligera''
File:Stylonychia putrina - 160x - II (13215594964).jpg, '' Stylonychia putrina''
File:Strombidium rassoulzadegani.jpg, The marine ciliate ''Strombidium rassoulzadegani''
File:Holophyra ovum - 400x (9836710085).jpg, ''Holophyra'' ovum
File:Mikrofoto.de-Blepharisma japonicum 15.jpg, '' Blepharisma japonicum''
File:Из жизни инфузорий.webm, Several taxa of ciliates interacting
File:Blepharisma americana.ogv, '' Blepharisma americanum'' swimming in a drop of pond water with other microorganisms
unicellular macroalgae → )" mode=packed heights=130px style=float:left;>
File:Chaos carolinensis Wilson 1900.jpg, The single-celled ''
 Interaction between microbial species has played important roles in evolution and speciation. One of the best examples is that the origin of
Interaction between microbial species has played important roles in evolution and speciation. One of the best examples is that the origin of
 Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
 Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
There are also costs for protists that carry protective shells. The diagram on the right above shows some of the energetic costs coccolithophore incur from carrying coccoliths. In the diagram, the energetic costs are reported in percentage of total photosynthetic budget. (A) represents transport processes include the transport into the cell from the surrounding seawater of primary calcification substrates Ca2+ and HCO3− (black arrows) and the removal of the end product H+ from the cell (gray arrow). The transport of Ca2+ through the cytoplasm to the coccolith vesicle (CV) is the dominant cost associated with calcification. (B) represents metabolic processes include the synthesis of coccolith-associated
 Available under
Available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * {{microorganisms, state=expanded Microorganisms Marine organisms Planktology Biological oceanography Marine biology Protista
protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish water, ...
of seas or oceans or the brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
water of coastal estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
(lacking a common ancestor for all descendants).
Most protists are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They are highly diverse organisms currently organised into 18 phyla, but not easy to classify. Studies have shown high protist diversity exists in oceans, deep sea-vents and river sediments, suggesting large numbers of eukaryotic microbial communities have yet to be discovered. There has been little research on mixotrophic A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
protists, but recent studies in marine environments found mixotrophic protists contribute a significant part of the protist biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
. Since protists are eukaryotes (and not prokaryotes) they possess within their cell at least one nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, as well as organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s such as mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
and Golgi bodies
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles in ...
. Many protist species can switch between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction involving meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately resu ...
and fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
.
In contrast to the cells of prokaryotes, the cells of eukaryotes are highly organised. Plants, animals and fungi are usually multi-celled and are typically macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenomena an ...
. Most protists are single-celled and microscopic. But there are exceptions. Some single-celled marine protists are macroscopic. Some marine slime molds have unique life cycles that involve switching between unicellular, colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
, and multicellular forms. Other marine protist are neither single-celled nor microscopic, such as seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
.
Protists have been described as a taxonomic grab bag of misfits where anything that doesn't fit into one of the main biological kingdoms can be placed. Some modern authors prefer to exclude multicellular organisms from the traditional definition of a protist, restricting protists to unicellular organisms. This more constrained definition excludes all brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used ...
, the multicellular red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
, and, sometimes, slime mold
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to several kinds of unrelated eukaryotic organisms with a life cycle that includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic mu ...
s (slime molds excluded when multicellularity is defined as "complex").
Background
The ocean represents the largest continuous planetary ecosystem, hosting an enormous variety of organisms, which include microscopic biota such as unicellular eukaryotes (protists). Despite their small size, protists play key roles inmarine biogeochemical cycles
Marine biogeochemical cycles are biogeochemical cycles that occur within marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. These biogeochemical cycles are the pathways chemical substanc ...
and harbour tremendous evolutionary diversity. Notwithstanding their significance for understanding the evolution of life on Earth and their role in marine food web
Compared to terrestrial environments, marine environments have biomass pyramids which are inverted at the base. In particular, the biomass of consumers (copepods, krill, shrimp, forage fish) is larger than the biomass of primary producers. Th ...
s, as well as driving biogeochemical cycles to maintain habitability, little is known about their cell biology including reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and signaling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
. Most of the biological knowledge available is based on comparison of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s from cultured species to homolog
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of prima ...
s in genetically tractable model taxa. A main impediment to understanding the cell biology of these diverse eukaryotes is that protocols for genetic modification are available for only a small number of species that represent neither the most ecologically relevant protists nor the breadth of eukaryotic diversity. Even so, in the decade to 2020, genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
and transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The t ...
sequencing initiatives have resulted in nearly 120 million unigene
UniGene was a NCBI database of the transcriptome and thus, despite the name, not primarily a database for genes. Each entry is a set of transcripts that appear to stem from the same transcription locus (i.e. gene or expressed pseudogene). Inform ...
s being identified in protists, which is facilitating the development of genetic tools for model species.


Trophic modes
Protists can be divided broadly into four groups depending on whether their nutrition is plant-like, animal-like, fungal-like, or a mixture of these.Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s are a major algae group generating about 20% of world oxygen production.The Air You're Breathing? A Diatom Made That/ref> File:Triceratium morlandii var. morlandii.jpg, Fossil diatom frustule from 32 to 40 mya File:Podocyrtis papalis Ehrenberg - Radiolarian (30448963206).jpg,
Radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elab ...
File:Gephyrocapsa oceanica color (lightened).jpg, Single-celled alga, ''Gephyrocapsa oceanica
''Gephyrocapsa oceanica'' is a species of coccolithophorid. It is the type species of the genus ''Gephyrocapsa''. The species is an important Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (g ...
''
File:CSIRO ScienceImage 7609 SEM dinoflagellate.jpg, Two dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s
File:Paramecium bursaria.jpg, A single-celled ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
with green zoochlorellae
''Zoochlorella'' is a ''nomen rejiciendum'' for a genus of green algae assigned to ''Chlorella''. The term zoochlorella (plural zoochlorellae) is sometimes used to refer to any green algae that lives symbiotically within the body of a freshwater ...
living inside endosymbiotic
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within ...
ally
File:Euglenoid movement.jpg, Euglenoid
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical o ...
File:The ciliate Frontonia sp.jpg, This ciliate is digesting cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
. The cytostome
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacuole ...
or mouth is at the bottom right.
oomycete
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the resul ...
s grow on dead animals or algae. Marine saprobic protists have the essential function of returning inorganic nutrients to the water. This process allows for new algal growth, which in turn generates sustenance for other organisms along the food chain. Indeed, without saprobe species, such as protists, fungi, and bacteria, life would cease to exist as all organic carbon became "tied up" in dead organisms.Clark M A, Douglas M and Choi J (2018) ''Biology 2e''23.4 "Ecology of Protists"
OpenStax, Houston, Texas.
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Mixotrophs
Mixotroph A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
s have no single trophic mode. A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
at one end to heterotrophy
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. There are two types of eukaryotic mixotrophs: those with their own chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s, and those with endosymbiont
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
s—and others that acquire them through kleptoplasty
Kleptoplasty or kleptoplastidy is a symbiotic phenomenon whereby plastids, notably chloroplasts from algae, are sequestered by host organisms. The word is derived from ''Kleptes'' (κλέπτης) which is Greek for thief. The alga is eaten norma ...
or by enslaving the entire phototrophic cell.
The distinction between plants and animals often breaks down in very small organisms. Possible combinations are photo- and chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototro ...
y, litho- and organotroph
An organotroph is an organism that obtains hydrogen or electrons from organic substrates. This term is used in microbiology to classify and describe organisms based on how they obtain electrons for their respiration processes. Some organotrophs su ...
y, auto- and heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
y or other combinations of these. Mixotrophs can be either eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
or prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a Unicellular organism, single-celled organism that lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:πρό#Ancient Greek, πρό (, 'before') a ...
. They can take advantage of different environmental conditions.
Recent studies of marine microzooplankton found 30–45% of the ciliate abundance was mixotrophic, and up to 65% of the amoeboid, foram and radiolarian biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
was mixotrophic.
''Phaeocystis
''Phaeocystis'' is a genus of algae belonging to the Prymnesiophyte class and to the larger division of Haptophyta. It is a widespread marine phytoplankton and can function at a wide range of temperatures (eurythermal) and salinities (euryhalin ...
'' is an important algal genus found as part of the marine phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
around the world. It has a polymorphic life cycle, ranging from free-living cells to large colonies. It has the ability to form floating colonies, where hundreds of cells are embedded in a gel matrix, which can increase massively in size during blooms. As a result, ''Phaeocystis'' is an important contributor to the marine carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
and sulfur cycle
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. It is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element ( CHNOPS), being a const ...
s. ''Phaeocystis'' species are endosymbionts to acantharian
The Acantharea (Acantharia) are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several ...
radiolarians.
Tintinnid
Tintinnids are ciliates of the choreotrich order Tintinnida, distinguished by vase-shaped shells, the name deriving from a Latin source meaning a small tinkling bell, that are called'' loricae'', which are mostly protein but may incorporate min ...
ciliate ''Favella''
File:Euglena mutabilis - 400x - 1 (10388739803) (cropped).jpg, '' Euglena mutabilis'', a photosynthetic flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their ...
File:Stichotricha secunda - 400x (14974779356).jpg, Zoochlorellae
''Zoochlorella'' is a ''nomen rejiciendum'' for a genus of green algae assigned to ''Chlorella''. The term zoochlorella (plural zoochlorellae) is sometimes used to refer to any green algae that lives symbiotically within the body of a freshwater ...
(green) living inside the ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
''Stichotricha secunda''
Protist locomotion
Another way of categorising protists is according to their mode of locomotion. Many unicellular protists, particularly protozoans, aremotile
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
and can generate movement using flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
, cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
or pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filamen ...
s. Cells which use flagella for movement are usually referred to as flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their ...
s, cells which use cilia are usually referred to as ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
s, and cells which use pseudopods are usually referred to as amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and ret ...
or amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopo ...
s. Other protists are not motile, and consequently have no movement mechanism.
cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
are widely used in eukaryotic cells (plant and animal) apart from protists.
The regular beat patterns of eukaryotic cilia and flagella generates motion on a cellular level. Examples range from the propulsion of single cells such as the swimming of spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, ...
to the transport of fluid along a stationary layer of cells such as in a respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
. Though eukaryotic flagella and motile cilia are ultrastructurally identical, the beating pattern of the two organelles can be different. In the case of flagella, the motion is often planar and wave-like, whereas the motile cilia often perform a more complicated three-dimensional motion with a power and recovery stroke.
Eukaryotic flagella—those of animal, plant, and protist cells—are complex cellular projections that lash back and forth. Eukaryotic flagella are classed along with eukaryotic motile cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
as undulipodia
An undulipodium or undulopodium (a Greek word meaning "swinging foot"), or a 9+2 organelle is a motile filamentous extracellular projection of eukaryotic cells. It is basically synonymous to flagella and cilia which are differing terms for simi ...
A Dictionary of Biology2004, accessed 2011-01-01. to emphasize their distinctive wavy appendage role in cellular function or
motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
. Primary cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
are immotile, and are not undulipodia.


Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
s generally have hundreds to thousands of cilia that are densely packed together in arrays. Like the flagella, the cilia are powered by specialised molecular motor
Molecular motors are natural (biological) or artificial molecular machines that are the essential agents of movement in living organisms. In general terms, a motor is a device that consumes energy in one form and converts it into motion or mecha ...
s. An efficient forward stroke is made with a stiffened flagellum, followed by an inefficient backward stroke made with a relaxed flagellum. During movement, an individual cilium deforms as it uses the high-friction power strokes and the low-friction recovery strokes. Since there are multiple cilia packed together on an individual organism, they display collective behaviour in a metachronal rhythm
A metachronal rhythm or metachronal wave refers to wavy movements produced by the sequential action (as opposed to synchronized) of structures such as cilia, segments of worms, or legs. These movements produce the appearance of a travelling wave. ...
. This means the deformation of one cilium is in phase with the deformation of its neighbor, causing deformation waves that propagate along the surface of the organism. These propagating waves of cilia are what allow the organism to use the cilia in a coordinated manner to move. A typical example of a ciliated microorganism is the ''Paramecium
''
''Paramecium'' ( , ; also spelled ''Paramoecium'') is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. ''Paramecia'' are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and a ...
'', a one-celled, ciliated protozoan covered by thousands of cilia. The cilia beating together allow the ''Paramecium'' to propel through the water at speeds of 500 micrometers per second.
Chlamydomonas
''Chlamydomonas'' is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 speciesSmith, G.M. 1955 ''Cryptogamic Botany Volume 1. Algae and Fungi'' McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, ...
'')
File:Инфузория туфелька поедает бактерии!.gif, Paramecium
''
''Paramecium'' ( , ; also spelled ''Paramoecium'') is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. ''Paramecia'' are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and a ...
feeding on bacteria
File:Oxytricha trifallax.jpg, The ciliate ''Oxytricha trifallax
''Sterkiella histriomuscorum'', formerly ''Oxytricha trifallax'', is a ciliate species in the genus ''Sterkiella'', known for its highly fragmented genomes which have been used as a Model organism, model for ciliate genetics.
Genetics
Like all ...
'' with cilia clearly visible
File:Collection Penard MHNG Specimen 05bis-1-1 Amoeba proteus.tif, Amoeba with ingested diatoms
Marine algae
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
is an informal term for a widespread and diverse group of photosynthetic protists
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the excl ...
which are not necessarily closely related and are thus polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of converg ...
. Marine algae can be divided into six groups: green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
, red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and po ...
, euglenophyte
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by three major clades, i.e., Kinetoplastea, D ...
s, dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s and diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s.
Dinoflagellates and diatoms are important components of marine algae and have their own sections below. Euglenophyte
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by three major clades, i.e., Kinetoplastea, D ...
s are a phylum of unicellular flagellates with only a few marine members.
Not all algae are microscopic. Green, red and brown algae all have multicellular macroscopic forms that make up the familiar seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s. Green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
, an informal group, contains about 8,000 recognised species. Many species live most of their lives as single cells or are filamentous, while others form colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
made up from long chains of cells, or are highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. Red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
, a (disputed) phylum contains about 7,000 recognised species, mostly multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
and including many notable seaweeds. Brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and po ...
form a class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
containing about 2,000 recognised species, mostly multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
and including many seaweeds such as kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwat ...
.
Unlike higher plants, algae lack roots, stems, or leaves. They can be classified by size as ''microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
'' or ''macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as k ...
''.
Microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
are the microscopic types of algae, not visible to the naked eye. They are mostly unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
species which exist as individuals or in chains or groups, though some are multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
. Microalgae are important components of the marine protists discussed above, as well as the phytoplankton discussed below. They are very diverse. It has been estimated there are 200,000-800,000 species of which about 50,000 species have been described.Starckx, Senne (31 October 2012A place in the sun - Algae is the crop of the future, according to researchers in Geel
Flanders Today, Retrieved 8 December 2012 Depending on the species, their sizes range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundred micrometers. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces.
flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
just visible at bottom left
File:Инфузории Ophridium versatile.jpg, ''Chlorella vulgaris
''Chlorella vulgaris'' is a species of green microalga in the division Chlorophyta. It is mainly used as a dietary supplement or protein-rich food additive in Japan.
Description
''C. vulgaris'' is a green eukaryotic microalga in the genus ...
'', a common green microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
, in endosymbiosis
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
with a ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
File:Centric diatom.jpg, Centric diatom
File:Dinoflagellates.jpg, Dinoflagellates
Macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as k ...
are the larger, multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
and more visible types of algae, commonly called seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s. Seaweeds usually grow in shallow coastal waters where they are anchored to the seafloor by a holdfast. Like microalgae, macroalgae (seaweeds) can be regarded as marine protists
Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in Marine habitat, marine environments, that is, in the saline water, saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal Estuary, estuaries. Life originated as marine ...
since they are not true plants. But they are not microorganisms, so they are not within the scope of this article.
Unicellular organisms are usually microscopic, less than one tenth of a millimeter long. There are exceptions. Mermaid's wineglass, a genus of subtropical green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
, is single-celled but remarkably large and complex in form with a single large nucleus, making it a model organism for studying cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
. Another single-celled algae, ''Caulerpa taxifolia
''Caulerpa taxifolia'' is a species of green seaweed, an alga of the genus ''Caulerpa'', native to tropical waters of the Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, and Caribbean Sea. The species name ''taxifolia'' arises from the resemblance of its leaf-like ...
'', has the appearance of a vascular plant including "leaves" arranged neatly up stalks like a fern. Selective breeding in aquariums to produce hardier strains resulted in an accidental release into the Mediterranean where it has become an invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ...
known colloquially as ''killer algae''.
Diatoms

Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s are photosynthetic unicellular algae populating the oceans and other waters around the globe. They form a (disputed) phylum containing about 100,000 recognised species. Diatoms generate about 20 percent of all oxygen produced on the planet each year, and take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
each year from the waters in which they live. They produce 25–45% of the total primary production of organic material in the oceans, owing to their prevalence in open-ocean regions when total phytoplankton biomass is maximal. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Diatoms are enclosed in protective silica (glass) shells called
frustule
A frustule is the hard and porous cell wall or external layer of diatoms. The frustule is composed almost purely of silica, made from silicic acid, and is coated with a layer of organic substance, which was referred to in the early literature on d ...
s. They are classified by the shape of these glass cages in which they live, and which they build as they grow. Each frustule is made from two interlocking parts covered with tiny holes through which the diatom exchanges nutrients and wastes.Wassilieff, Maggy (2006"Plankton - Plant plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019. Dead diatoms drift to the ocean floor where, over millions of years, the remains of their frustules can build up as much as half a mile deep. Diatoms have relatively high sinking speeds compared with other phytoplankton groups, and they account for about 40% of particulate carbon exported to ocean depths.
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s are one of the most common types of phytoplankton
File:Diatom Helipelta metil.jpg, Their protective shells (frustles) are made of silicon
File:Diatom - Triceratium favus.jpg
File:Diatom - Isthmia nervosa - 400x (16237138292).jpg,
 Physically driven seasonal enrichments in surface nutrients favour
Physically driven seasonal enrichments in surface nutrients favour diatom bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasse ...
s. Anthropogenic climate change will directly affect these seasonal cycles, changing the timing of blooms and diminishing their biomass, which will reduce primary production and CO2 uptake. Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth ...
data suggests there was a global decline of diatoms between 1998 and 2012, particularly in the North Pacific, associated with shallowing of the surface mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporat ...
and lower nutrient concentrations.
diatom bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasse ...
s in the North Sea
File:Pinnularia major.jpg, There are over 100,000 species of diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s accounting for 25–45% of the ocean's primary production
Coccolithophores
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdo ...
s are minute unicellular photosynthetic protists with two flagella for locomotion. Most of them are protected by calcium carbonate shells covered with ornate circular plates or scales called coccolith
Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores (single-celled phytoplankton such as ''Emiliania huxleyi'') and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a ''coccosphere''. ...
s. The term coccolithophore derives from the Greek for a ''seed carrying stone'', referring to their small size and the coccolith stones they carry. Under the right conditions they bloom, like other phytoplankton, and can turn the ocean milky white.Wassilieff, Maggy (2006"A coccolithophore"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.

coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdo ...
''Emiliania huxleyi
''Emiliania huxleyi'' is a species of coccolithophore found in almost all ocean ecosystems from the equator to sub-polar regions, and from nutrient rich upwelling zones to nutrient poor oligotrophic waters. It is one of thousands of different ...
''
File:Cwall99 lg.jpg, Algae bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in Fresh water, freshwater or Ocean, marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ...
of ''Emiliania huxleyi'' off the southern coast of England
File:JRYSEM-247-05-azurapl.jpg,
Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s are usually positioned as part of the algae group, and form a phylum of unicellular flagellates with about 2,000 marine species. The name comes from the Greek "dinos" meaning ''whirling'' and the Latin "flagellum" meaning a ''whip'' or ''lash''. This refers to the two whip-like attachments (flagella) used for forward movement. Most dinoflagellates are protected with red-brown, cellulose armour. Like other phytoplankton, dinoflagellates are r-strategists which under right conditions can bloom and create red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural phycotoxin, algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are ...
s. Excavates may be the most basal flagellate lineage.
By trophic orientation dinoflagellates are all over the place. Some dinoflagellates are known to be photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ca ...
). Some species are endosymbiont
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
s of marine animals and other protists, and play an important part in the biology of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s. Others predate other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic. Many dinoflagellates are mixotrophic A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
and could also be classified as phytoplankton.
The toxic dinoflagellate ''Dinophysis acuta
''Dinophysis acuta'' is a species of flagellated planktons belonging to the genus ''Dinophysis''. It is one of the few unusual photosynthetic protists that acquire plastids from algae by endosymbiosis. By forming massive blooms, particularly ...
'' acquire chloroplasts from its prey. "It cannot catch the cryptophytes by
itself, and instead relies on ingesting ciliates such as the red ''Mesodinium rubrum
''Mesodinium rubrum'' (or ''Myrionecta rubra'') is a species of ciliates. It constitutes a plankton community and is found throughout the year, most abundantly in spring and fall, in coastal areas. Although discovered in 1908, its scientific im ...
'', which sequester their chloroplasts from a
specific cryptophyte clade (Geminigera/Plagioselmis/Teleaulax)".
Gyrodinium
''Gyrodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates belonging to the order Gymnodiniales within class Dinophyceae.
The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. World Register of Marine Species lists 141 species, with many synonyms.
They are heterotrophi ...
'', one of the few naked dinoflagellates which lack armour
File:Protoperidinium dinoflagellate.jpg, The dinoflagellate ''Protoperidinium'' extrudes a large feeding veil to capture prey
File:Radiolarian - Podocyrtis (Lampterium) mitra Ehrenberg - 160x.jpg, Nassellarian radiolarians can be in symbiosis with dinoflagellates
File:Dinophysis acuta.jpg, The dinoflagellate ''Dinophysis acuta''
symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
with other organisms. Many nassellarian radiolarians house dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
symbionts within their tests. The nassellarian provides ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary a ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
for the dinoflagellate, while the dinoflagellate provides the nassellarian with a mucous membrane useful for hunting and protection against harmful invaders. There is evidence from DNA analysis that dinoflagellate symbiosis with radiolarians evolved independently from other dinoflagellate symbioses, such as with foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and ot ...
.
Some dinoflagellates are bioluminescent
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorganisms including ...
. At night, ocean water can light up internally and sparkle with blue light because of these dinoflagellates. Bioluminescent dinoflagellates possess scintillons
Scintillons are small structures in cytoplasm that produce light. Among bioluminescent organisms, only dinoflagellates have scintillons.
Description Dinoflagellate light production
Marine dinoflagellates at night can emit blue light by biolumi ...
, individual cytoplasmic
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. Th ...
bodies which contain dinoflagellate luciferase, the main enzyme involved in the luminescence. The luminescence, sometimes called ''the phosphorescence of the sea'', occurs as brief (0.1 sec) blue flashes or sparks when individual scintillons are stimulated, usually by mechanical disturbances from, for example, a boat or a swimmer or surf.
Oodinium
''Oodinium'' is a genus of parasitic dinoflagellates. Their hosts are salt- and fresh-water fish, causing a type of fish velvet disease (also called gold dust disease). One species has also been recorded on various cnidarians.
The host typical ...
'', a genus of parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ...
dinoflagellates, causes velvet disease
Velvet disease (also called gold-dust, rust and coral disease) is a fish disease caused by dinoflagellate parasites of the genera '' Amyloodinium'' in marine fish, and ''Oodinium'' in freshwater fish. The disease gives infected organisms a dusty ...
in fish
File:Karenia brevis.jpg, '' Karenia brevis'' produces red tides highly toxic to humans
Red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural phycotoxin, algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are ...
File:Noctiluca scintillans unica.jpg, ''Noctiluca scintillans
''Noctiluca scintillans'' is a marine life, marine species of dinoflagellate that can exist in a green or red form, depending on the pigmentation in its vacuoles. It can be found cosmopolitan distribution, worldwide, but its geographical species ...
'', a bioluminescent dinoflagellate
File:Ornithocercus heteroporus (probably).jpg, ''Ornithocercus heteroporus'' - prominent lists on display
Marine protozoans
Protozoan
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
s are protists which feed on organic matter such as other microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s or organic tissues and debris. Historically, the protozoa were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
-like behaviours, such as motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
and predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
, and lack a cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
, as found in plants and many algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
. Although the traditional practice of grouping protozoa with animals is no longer considered valid, the term continues to be used in a loose way to identify single-celled organisms that can move independently and feed by heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
y.
Marine protozoans include zooflagellates, foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and ot ...
ns, radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elab ...
s and some dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s.
Radiolarians
Radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elab ...
s are unicellular predatory protists
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the excl ...
encased in elaborate globular shells, typically between 0.1 and 0.2 millimetres in size, usually made of silica and pierced with holes. Their name comes from the Latin for "radius". They catch prey by extending parts of their body through the holes. As with the silica frustules of diatoms, radiolarian shells can sink to the ocean floor when radiolarians die and become preserved as part of the ocean sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly ...
. These remains, as microfossils
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, ...
, provide valuable information about past oceanic conditions.Wassilieff, Maggy (2006"Plankton - Animal plankton"
''Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Accessed: 2 November 2019.
acantharian
The Acantharea (Acantharia) are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several ...
radiolarians have shells made from strontium sulfate
Strontium sulfate (SrSO4) is the sulfuric acid, sulfate salt of strontium. It is a white crystalline powder and occurs in nature as the mineral Celestine (mineral), celestine. It is poorly soluble in water to the extent of 1 part in 8,800. It is mo ...
crystals
File:Spherical radiolarian 2.jpg, Cutaway schematic diagram of a spherical radiolarian shell
Foraminiferans
Like radiolarians,foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and ot ...
ns (''forams'' for short) are single-celled predatory protists, also protected with shells that have holes in them. Their name comes from the Latin for "hole bearers". Their shells, often called tests
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
, are chambered (forams add more chambers as they grow). The shells are usually made of calcite, but are sometimes made of agglutinated sediment particles or chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail s ...
, and (rarely) of silica. Most forams are benthic, but about 40 species are planktic. They are widely researched with well established fossil records which allow scientists to infer a lot about past environments and climates.
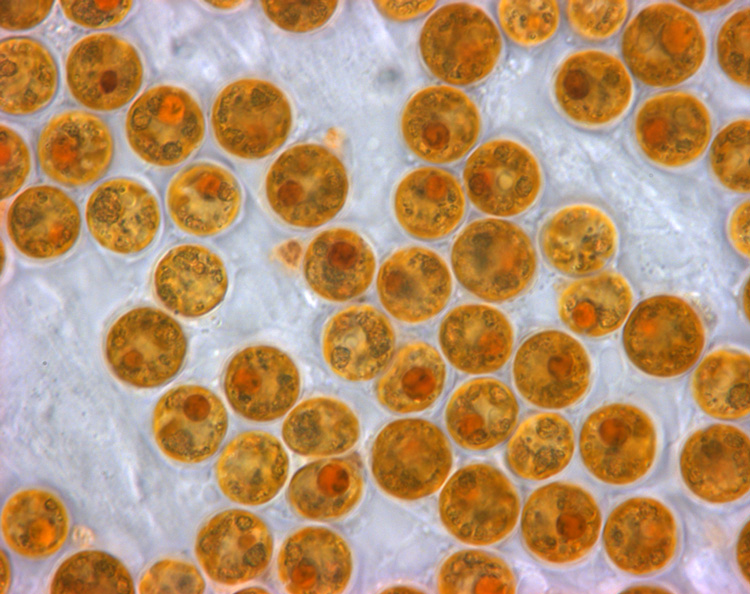
Ammonia tepida
''Ammonia tepida'' is a benthic foraminifer living in the sediment of brackish waters. It is very similar to ''Ammonia beccarii'', but the latter lives on the surface of red algae. Once considered a globally widespread taxon, a recent genetic an ...
'' streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food
File:Planktic Foraminifera of the northern Gulf of Mexico.jpg, Group of planktonic forams
File:Nummulitids.jpg, Fossil nummulitid forams of various sizes from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
File:All Gizah Pyramids.jpg, The Egyptian pyramid
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Sources cite at least 118 identified "Egyptian" pyramids. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. Of ...
s were constructed from limestone that contained nummulite
A nummulite is a large lenticular fossil, characterized by its numerous coils, subdivided by septa into chambers. They are the shells of the fossil and present-day marine protozoan ''Nummulites'', a type of foraminiferan. Nummulites commonly vary ...
s.
mixotroph A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
ic ( see below). These have unicellular algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
as endosymbiont
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
s, from diverse lineages such as the green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
, red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
, golden algae
The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae or golden algae are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, '' Prymnesium parvum'', whic ...
, diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s, and dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s. Mixotrophic foraminifers are particularly common in nutrient-poor oceanic waters. Some forams are kleptoplastic, retaining chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s from ingested algae to conduct photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
.
Amoeba
testate amoeba
Testate amoebae (formerly thecamoebians, Testacea or Thecamoeba) are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the ...
, ''Arcella
''Arcella'' is a genus of testate amoebae in the order Arcellinida, usually found in freshwaters and mosses, and rarely in soils. A key characteristic of ''Arcella'' is the circular test with a hole on its center from where finger-like pseudopod ...
'' sp.
File:Collection Penard MHNG Specimen 533-2-1 Pamphagus granulatus.tif, Xenogenic
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compo ...
testate amoeba covered in diatoms (froPenard's Amoeba Collection
Ciliates
Marine ciliates are major grazers of the phytoplankton.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Phytoplankton primary production supports higher
trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it i ...
s and fuels microbial remineralization
In biogeochemistry, remineralisation (or remineralization) refers to the breakdown or transformation of organic matter (those molecules derived from a biological source) into its simplest inorganic forms. These transformations form a crucial link ...
. The dominant pelagic grazers of phytoplankton are typically associated with distinct operating modes of the food web compartments and nutrient cycling
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cycli ...
. Heterotrophic
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
protist grazers and microzooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
dominance is usually associated with the microbial loop
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phy ...
and regenerated production; while mesozooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
is associated with a linear food chain and export production
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone t ...
. Grazing on particulate primary production in the global ocean surface is ~10–15% for mesozooplankton and 59–75% for microzooplankton, with estimates for coastal and estuarine systems usually in the a lower range.
Ciliates constitute an important component of the microzooplankton community with preference for small-sized preys, in contrast to mesozooplankton, and many ciliate species are also grazed by mesozooplankton. Thus, ciliates can be an important link between small cells and higher trophic levels. Besides their significant role in carbon transfer, ciliates are also considered high quality food, as a source of proteinaceous compounds with a low C:N ratio in comparison to phytoplankton.
 Although many ciliates are heterotrophs, a number of pelagic species are
Although many ciliates are heterotrophs, a number of pelagic species are mixotrophic A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
, combining both phagotrophic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
and phototroph
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a common misconcep ...
ic nutrition (Stoecker, 1998). The recognition of mixotrophy in the marine plankton food web has challenged the classical understanding of pelagic food webs, as autotrophy and heterotrophy are not necessarily two distinct functional compartments. Classical understanding of ecological interactions among plankton, such as competition for nutrients, indicates that nutrient uptake affinity decreases with organism size, favoring smaller sizes under resource limiting conditions. Mixotrophy is advantageous to organisms under nutrient limited conditions, allowing them to reduce direct competition by grazing on smaller prey and increase direct ingestion of nutrients. Modeling results suggest that mixotrophy favors larger organisms, and therefore enhances trophic transfer efficiency. On top of that, mixotrophy appears to be important over both, space and time, in marine systems. stressing the need for ecological field studies to further elucidate the role of mixotrophy.
Macroscopic protists
giant amoeba
''Chaos'' is a genus of single-celled amoeboid organisms in the family Amoebidae. The largest and best-known species, the so-called "giant amoeba" ''Chaos carolinensis'', can reach lengths of 5 mm, although most specimens fall between 1 an ...
'' has up to 1000 nuclei and reaches lengths of 5 mm
File:Gromia in situ closeup.png, ''Gromia sphaerica
''Gromia sphaerica'' is a large spherical testate amoeba, a single-celled eukaryotic organism and the largest of its genus, '' Gromia''. The genus itself contains about 13 known species, 3 of which have been recently discovered. It was discovered ...
'' is a large spherical testate amoeba
Testate amoebae (formerly thecamoebians, Testacea or Thecamoeba) are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the ...
which makes mud trails. Its diameter is up to 3.8 cm.
File:Spiculosiphon oceana AB.png, '' Spiculosiphon oceana'', a unicellular foraminiferan
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an ...
with an appearance and lifestyle that mimics a sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through t ...
, grows to 5 cm long.
File:Xenophyophore.jpg, The xenophyophore, another single-celled foraminiferan, lives in abyssal zone
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. "Abyss" derives from the Greek word , meaning bottomless. At depths of , this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean a ...
s. It has a giant shell up to 20 cm across.
File:Giant Kelp.jpg, Giant kelp
''Macrocystis pyrifera'', commonly known as giant kelp or bladder kelp, is a species of kelp (large brown algae), and one of four species in the genus ''Macrocystis''. Despite its appearance, it is not a plant; it is a heterokont. Giant kelp is ...
, a brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and po ...
, is not a true plant, yet it is multicellular and can grow to 50m
Planktonic protists
Interactome

 Interaction between microbial species has played important roles in evolution and speciation. One of the best examples is that the origin of
Interaction between microbial species has played important roles in evolution and speciation. One of the best examples is that the origin of eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
is grounded in the interaction-events of endosymbiosis
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
; giving rise to mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s, and other metabolic capacities in the eukaryotic cell, Microbial interactions guarantee ecosystem function, having crucial roles in, for instance, carbon channeling in photosymbiosis, control of microalgae blooms by parasites, and phytoplankton-associated bacteria influencing the growth and health of their host.
Despite their importance, understanding of microbial interactions in the ocean and other aquatic systems is rudimentary, and the majority of them are still unknown. The earliest surveys of interactions between aquatic microbes date back to the 19th century. In 1851, while on board HMS ''Rattlesnake'' in the Pacific Ocean, Thomas Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stor ...
discovered small yellow–green cells inside the conspicuous planktonic radiolarians which he thought were organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s/ Later, Karl Brandt
Karl Brandt (8 January 1904 – 2 June 1948) was a German physician and ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) officer in Nazi Germany. Trained in surgery, Brandt joined the Nazi Party in 1932 and became Adolf Hitler's escort doctor in August 1934. A member of ...
established the yellowish cells were symbiotic alga and named them zooxanthella
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus '' Sym ...
. Since these early studies, hundreds of others have reported microbial interactions by using classic tools, mainly microscopy, but this knowledge has not yet been gathered into one accessible database. In recent years the high throughput sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The ...
(HTS) of environmental DNA
Environmental DNA or eDNA is DNA that is collected from a variety of environmental samples such as soil, seawater, snow or air, rather than directly sampled from an individual organism. As various organisms interact with the environment, DNA ...
or RNA has transformed understanding of microbial diversity and evolution, as well as generating hypotheses on microbial interactions based on correlations of estimated microbial abundances over spatiotemporal scales.
The diagram on the right is an overview of the interactions between planktonic protists recorded in a manually curated Protist Interaction DAtabase (PIDA). The network is based on 2422 ecological interactions in the PIDA registered from ~500 publications spanning the last 150 years. The nomenclature and taxonomic order of Eukaryota is based on Adl et al. 2019. The nomenclature and taxonomic order of Bacteria is based on Schultz et al. 2017.
The nodes are grouped (outer circle) according to eukaryotic supergroups (or ''Incertae sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
''), Bacteria and Archaea. All major protistan lineages were involved in interactions as hosts, symbionts (mutualists and commensalists), parasites, predators, and/or prey. Predation was the most common interaction (39%), followed by symbiosis (29%), parasitism (18%), and unresolved interactions (14%, where it is uncertain whether the interaction is beneficial or antagonistic). Nodes represent eukaryotic and prokaryotic taxa and are colored accordingly. Node size indicates the number of edges/links that are connected to that node. Each node/taxon is assigned a number, which corresponds with the numbers for taxa in B, C and D. Edges represent interactions between two taxa and are colored according to ecological interaction type: predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
(orange), symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
(green), and parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
(purple).
The network is undirected, meaning that a node can contain both parasites/symbionts/prey and hosts/predators. To avoid cluttering of the figure, "Self-loops", which represent cases where both interacting organisms belong to the same taxon (e.g., a dinoflagellate eating another dinoflagellate) are not shown as edges/links in this figure, but are considered in the size of nodes. The outermost circle groups taxa in the different eukaryotic ‘supergroups’ or the prokaryotic domains Bacteria and Archaea. Ancryomonadidae is abbreviated An. Telonema
''Telonema'' is a genus of single-celled organisms.
Some sources group ''Telonema'' within the cryptomonads-haptophytes assemblage. It is sometimes assigned to a unique phylum, Telonemia
Telonemia is a phylum of microscopic eukaryote, single-c ...
is not placed into any of the supergroups, but classified as ''Incertae sedis'' (abbreviated I.S. in the figure). In B, B, and D the following abbreviations for supergroups are used: Ar Archaea, Ba Bacteria, Rh Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foramini ...
, Al Alveolata, St Stramenopile
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have be ...
s, Ha Haptista
Haptista is a proposed group of protists made up of centrohelids and haptophytes. Phylogenomic studies indicate that Haptista, together with ''Ancoracysta twista'', forms a sister clade to the SAR+Telonemia supergroup, but it may also be sister t ...
, Cy Cryptista
Cryptista is a clade of algae-like eukaryotes. It is most likely related to Archaeplastida which includes plants and many algae, within the larger group Diaphoretickes.
Although it has sometimes placed along with Haptista in the group Hacrobia, ...
, Ap Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae ''sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced /ɑːrkɪ'plastɪdə/) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group ...
, Ex Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
, Ob Obazoa, Am Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classi ...
, Cu CRuMS, An Ancryomonadidae, Is ''Incertae sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
''.
B: Predator–prey interactions in PIDA. The node numbers correspond to taxa node numbers in a. Abbreviations for supergroups are described above. Background and nodes are colored according to functional role in the interaction: Prey are colored light orange (left part of figure), while predators are depicted in dark orange (right part of figure). The size of each node represents the number of edges connected to that node.
C. Symbiont–host interactions included in PIDA. The node numbers correspond to node numbers in A. Abbreviations for supergroups are described above. Symbionts are to the left, colored light green, and their hosts are to the right in dark green. The size of each node represents the number of edges connected to that node.
D: Parasite–host interactions included in PIDA. The node numbers correspond to node numbers in A. Abbreviations for supergroups are described above. Parasite taxa are depicted in light purple (left), hosts in dark purple (right).
It was found that protist predators seem to be "multivorous" while parasite–host and symbiont–host interactions appear to have moderate degrees of specialization. The SAR supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". T ...
(i.e., Stramenopiles, Alveolata, and Rhizaria) heavily dominated PIDA, and comparisons against a global-ocean molecular survey ( Tara expedition) indicated that several SAR lineages, which are abundant and diverse in the marine realm, were underrepresented among the recorded interactions.
Protist shells
Many protists have protective shells ortests
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
, usually made from calcium carbonate (chalk) or silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
(glass). Protists are mostly single-celled and microscopic. Their shells are often tough mineralised forms that resist degradation, and can survive the death of the protist as a microfossil
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, ...
. Although protists are very small, they are ubiquitous. Their numbers are such that their shells play a huge part in the formation of ocean sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly ...
s, and in the global cycling of elements and nutrients.
Diatom shells are called frustule
A frustule is the hard and porous cell wall or external layer of diatoms. The frustule is composed almost purely of silica, made from silicic acid, and is coated with a layer of organic substance, which was referred to in the early literature on d ...
s and are made from silica. These glass structures have accumulated for over 100 million years leaving rich deposits of nano and microstructured silicon oxide in the form of diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 μm to le ...
around the globe. The evolutionary causes for the generation of nano and microstructured silica by photosynthetic algae are not yet clear. However, in 2018 it was shown that reflection of ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
by nanostructured silica protects the DNA in the algal cells, and this may be an evolutionary cause for the formation of the glass cages.De Tommasi, E., Congestri, R., Dardano, P., De Luca, A.C., Managò, S., Rea, I. and De Stefano, M. (2018) "UV-shielding and wavelength conversion by centric diatom nanopatterned frustules". ''Nature: Scientific Reports'', 8(1): 1–14. . Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdo ...
s are protected by a shell constructed from ornate circular plates or scales called coccolith
Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores (single-celled phytoplankton such as ''Emiliania huxleyi'') and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a ''coccosphere''. ...
s. The coccoliths are made from calcium carbonate or chalk. The term coccolithophore derives from the Greek for a ''seed carrying stone'', referring to their small size and the coccolith stones they carry.
There are benefits for protists that carry protective shells. The diagram on the left above shows some benefits coccolithophore get from carrying coccoliths. In the diagram, (A) represents accelerated photosynthesis including carbon concentrating mechanisms (CCM) and enhanced light uptake via scattering of scarce photons for deep-dwelling species. (B) represents protection from photodamage including sunshade protection from ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
(UV) and photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) and energy dissipation under high-light conditions. (C) represents armour protection includes protection against viral/bacterial infections and grazing by selective and nonselective grazers.Monteiro, F.M., Bach, L.T., Brownlee, C., Bown, P., Rickaby, R.E., Poulton, A.J., Tyrrell, T., Beaufort, L., Dutkiewicz, S., Gibbs, S. and Gutowska, M.A. (2016) "Why marine phytoplankton calcify". ''Science Advances'', 2(7): e1501822. . Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
There are also costs for protists that carry protective shells. The diagram on the right above shows some of the energetic costs coccolithophore incur from carrying coccoliths. In the diagram, the energetic costs are reported in percentage of total photosynthetic budget. (A) represents transport processes include the transport into the cell from the surrounding seawater of primary calcification substrates Ca2+ and HCO3− (black arrows) and the removal of the end product H+ from the cell (gray arrow). The transport of Ca2+ through the cytoplasm to the coccolith vesicle (CV) is the dominant cost associated with calcification. (B) represents metabolic processes include the synthesis of coccolith-associated
polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s (CAPs – gray rectangles) by the Golgi complex
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles insi ...
(white rectangles) that regulate the nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that deter ...
and geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
of CaCO3 crystals. The completed coccolith (gray plate) is a complex structure of intricately arranged CAPs and CaCO3 crystals. (C) Mechanical and structural processes account for the secretion of the completed coccoliths that are transported from their original position adjacent to the nucleus to the cell periphery, where they are transferred to the surface of the cell.
See also
*Cavalier-Smith's system of classification
The biological classification system of life introduced by British zoologist Thomas Cavalier-Smith involves systematic arrangements of all life forms on earth. Following and improving the classification systems introduced by Carl Linnaeus, Ernst ...
References
Further references
*Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * {{microorganisms, state=expanded Microorganisms Marine organisms Planktology Biological oceanography Marine biology Protista