|
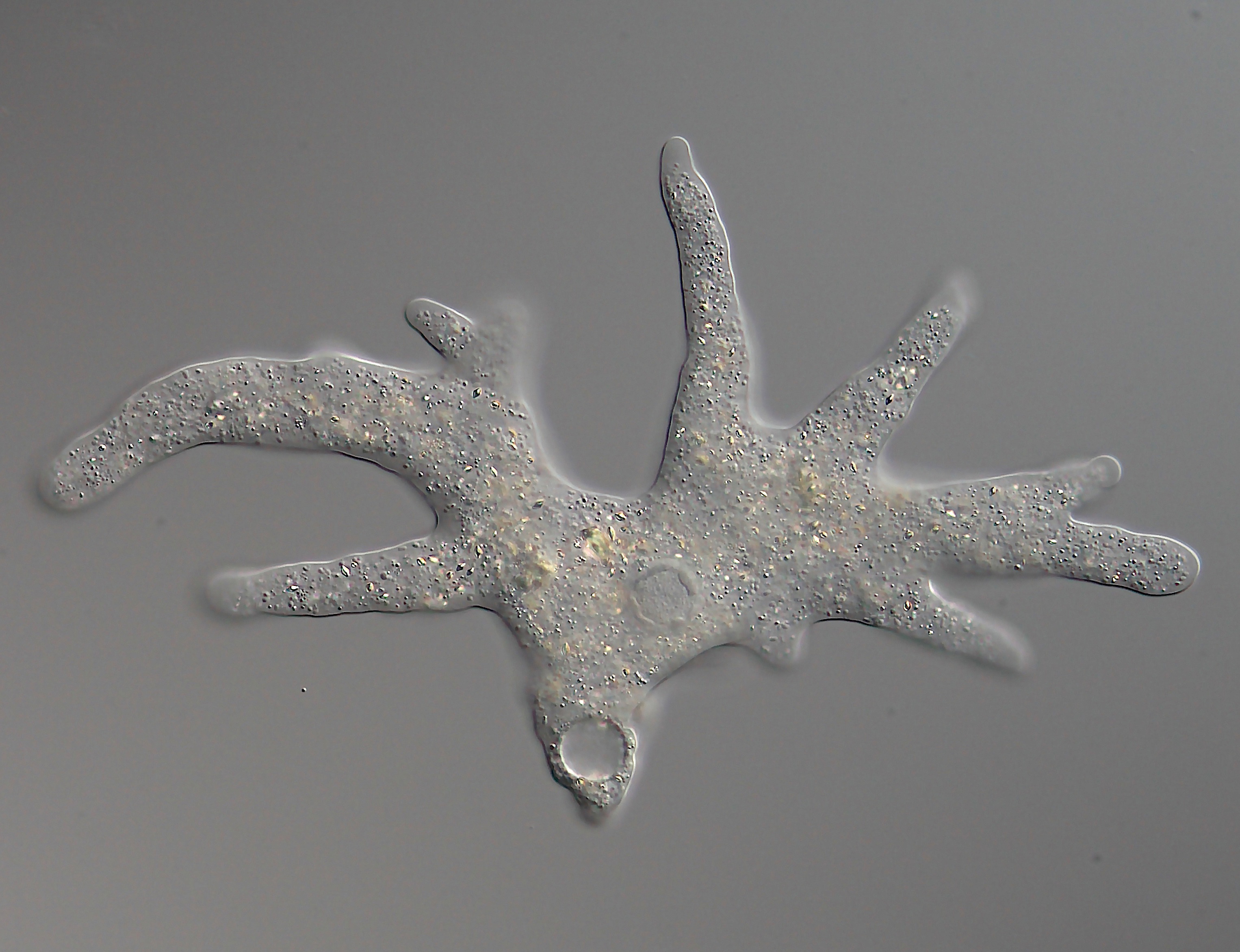
Spiculosiphon Oceana
''Spiculosiphon oceana'' is a giant species of foraminifera (a phylum of unicellular eukaryotes). Its appearance and lifestyle mimics that of a sponge. It was discovered in 2013 in underwater caves 30 miles off the coast of Spain. Description At () long, ''Spiculosiphon oceana'' is the largest foraminifera found in the Mediterranean. The species creates a test (shell) made out of sponge spicules, "gluing" them together with a protein it secretes, much like sponges do. The spicules it uses are carefully selected and laid parallel to the main stalk of the creature. Because of its large size and its appearance, ''S. oceana'' was originally mistaken as a multi-cellular animal from the sponge family. ''Spiculosiphon oceana'' lives on the sea floor. It lies in wait and extends its pseudopods outside its shell to capture prey, primarily plankton, that get trapped on the spicules of its shell. Thus, it captures prey much in the same way as carnivorous sponges. In addition to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge Spicules
Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three (Demospongiae, Hexactinellida, and Homoscleromorpha) produce skeletons of amorphous silica and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centro De Estudios Avanzados De Blanes
Centro may refer to: Places Brazil *Centro, Santa Maria, a neighborhood in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil * Centro, Porto Alegre, a neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil *Centro (Duque de Caxias), a neighborhood of Duque de Caxias, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *, a neighborhood of Niterói, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Centro, Rio de Janeiro, a neighborhood of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Centro (São Paulo), the historic downtown of São Paulo, Brazil *, Aracaju, Sergipe, Brazil Mexico *Centro, Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico *Centro, Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico *Centro Municipality, Tabasco, Mexico *Centro (borough), Tijuana, Baja California, Mexico * Centro, Yucatán, Mexico *Centro, the historic center of Mexico City, Mexico Elsewhere *Centro Habana, Cuba *Centro, Mandaue, a barangay in the Philippines *Centro Region, Portugal *Centro, Moca, Puerto Rico, a subdivision (also called a ''barrio'') of Moca, Puerto Rico *Centro (Madrid), a district of the city of Mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceana (non-profit Group)
Oceana, inc. is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit ocean conservation organization focused on influencing specific policy decisions on the national level to preserve and restore the world's oceans. It is headquartered in Washington D.C. with offices in Juneau, Alaska, Monterey, California, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, New York City, New York, Portland, Oregon, Toronto, Ontario, Mexico City, Madrid, Brussels, Copenhagen, Geneva, London, Manila, Belmopan, Brasilia, Santiago, and Lima, and it is the largest international advocacy group dedicated entirely to ocean conservation. Currently, Oceana has a staff of about 200 and 6,000 volunteers, and it has almost 50 million dollars of revenue (as of 2017). Oceana takes a multi-faceted approach to ocean conservation; It conducts its own scientific research in addition to making policy recommendations, lobbying for specific legislation, and filing and litigating lawsuits. History Oceana was established in 2001 by an international group of leading foundat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zootaxa
''Zootaxa'' is a peer-reviewed scientific mega journal for animal taxonomists. It is published by Magnolia Press (Auckland, New Zealand). The journal was established by Zhi-Qiang Zhang in 2001 and new issues are published multiple times a week. From 2001 to 2020, more than 60,000 new species have been described in the journal accounting for around 25% of all new taxa indexed in The Zoological Record in the last few years. Print and online versions are available. Temporary suspension from JCR The journal exhibited high levels of self-citation and its journal impact factor of 2019 was suspended from ''Journal Citation Reports'' in 2020, a sanction which hit 34 journals in total. Biologist Ross Mounce noted that high levels of self-citation may be inevitable for a journal which publishes a large share of new species classification. Later that year this decision was reversed and it was admitted that levels of self-citation are appropriate considering the large proportion of papers f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such flat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seco De Palos
Seco or SECO may refer to: Gastronomy * Seco (wine), dry wine * Seco (food), an Ecuadorian meat dish * Seco Herrerano, the national alcoholic beverage of Panamá People * David Seco (born 1973), Spanish professional racing cyclist *Hugo Seco (born 1988), Portuguese professional footballer * Manuel Seco (born 1928), Spanish lexicographer * María Luisa Seco (1948–1988), Spanish television presenter * Myriam Seco (born 1967), Spanish archaeologist Places * Seco River may refer to Arroyo Seco (other) or Río Seco (other) * Seco, Kentucky, a small town in the United States * The ICAO airport code for Francisco de Orellana Airport, Ecuador * Seco Island, in the Philippines Science * seco-, chemical prefix indicating cleavage of a ring with addition of one or more hydrogen atoms at each terminal group * Secobarbital * ''Seco'' (butterfly), a genus of metalmark butterflies in the tribe Riodinini * Seco (tobacco), the mid-level leaves of a tobacco plant * ''Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Institute For Species Exploration
The International Institute for Species Exploration (IISE) is a research institute located in Syracuse, New York. Its mission is to improve taxonomical exploration and the cataloging of new species of flora and fauna. Since 2008, IISE has published a yearly "Top 10" of the most unusual or unique biota newly identified in the previous year, with the aim of drawing attention to the work done in taxonomy across the world over the previous year. In 2011, the institute contributed towards the estimate that Earth was home to approximately 8.7 million species. Overview The International Institute for Species Exploration (IISE) is a research facility dedicated to cataloging the Earth's species across all biological kingdoms. IISE cites three reasons why an improved taxonomic understanding of life is important: without knowing what exists today, humans will be unable to tell when species go extinct; the diversity of life driven by billions of years of natural selection means nature lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |