Music in the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The music of the United States reflects the country's multi-ethnic population through a diverse array of styles. It is a mixture of music influenced by the

 Music intertwines with aspects of American social and cultural identity, including through
Music intertwines with aspects of American social and cultural identity, including through
 The United States is often said to be a cultural
The United States is often said to be a cultural
 Folk music in the US is varied across the country's numerous ethnic groups. The Native American tribes each play their own varieties of folk music, most of it spiritual in nature. African American music includes
Folk music in the US is varied across the country's numerous ethnic groups. The Native American tribes each play their own varieties of folk music, most of it spiritual in nature. African American music includes
 The United States is a
The United States is a
 During the colonial era, there were two distinct fields of what is now considered classical music. One was associated with amateur composers and pedagogues, whose style was originally drawn from simple hymns and gained sophistication over time. The other colonial tradition was that of the mid-Atlantic cities like Philadelphia and Baltimore, which produced a number of prominent composers who worked almost entirely within the European model; these composers were mostly English in origin, and worked specifically in the style of prominent English composers of the day.
During the colonial era, there were two distinct fields of what is now considered classical music. One was associated with amateur composers and pedagogues, whose style was originally drawn from simple hymns and gained sophistication over time. The other colonial tradition was that of the mid-Atlantic cities like Philadelphia and Baltimore, which produced a number of prominent composers who worked almost entirely within the European model; these composers were mostly English in origin, and worked specifically in the style of prominent English composers of the day.

 The New York classical music scene included Charles Griffes, originally from
The New York classical music scene included Charles Griffes, originally from
 The patriotic lay songs of the American Revolution constituted the first kind of mainstream popular music. These included "The Liberty Tree" by Thomas Paine. Cheaply printed as
The patriotic lay songs of the American Revolution constituted the first kind of mainstream popular music. These included "The Liberty Tree" by Thomas Paine. Cheaply printed as  Following the Civil War, minstrel shows became the first distinctively American form of music expression. The minstrel show was an indigenous form of American entertainment consisting of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music, usually performed by white people in
Following the Civil War, minstrel shows became the first distinctively American form of music expression. The minstrel show was an indigenous form of American entertainment consisting of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music, usually performed by white people in
 The blues is a genre of African American folk music that is the basis for much of modern American popular music. Blues can be seen as part of a continuum of musical styles like country, jazz, ragtime, and gospel; though each genre evolved into distinct forms, their
The blues is a genre of African American folk music that is the basis for much of modern American popular music. Blues can be seen as part of a continuum of musical styles like country, jazz, ragtime, and gospel; though each genre evolved into distinct forms, their  Ragtime was originally a piano style, featuring syncopated rhythms and
Ragtime was originally a piano style, featuring syncopated rhythms and
 Jazz is a kind of music characterized by swung and blue notes, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and
Jazz is a kind of music characterized by swung and blue notes, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and  Though jazz had long since achieved some limited popularity, it was
Though jazz had long since achieved some limited popularity, it was
 Country music is primarily a fusion of African American blues and spirituals with Appalachian folk music, adapted for pop audiences and popularized beginning in the 1920s. The origins of country are in rural Southern folk music, which was primarily Irish and British, with African and continental European musics. Anglo-Celtic tunes, dance music, and balladry were the earliest predecessors of modern country, then known as ''hillbilly music''. Early
Country music is primarily a fusion of African American blues and spirituals with Appalachian folk music, adapted for pop audiences and popularized beginning in the 1920s. The origins of country are in rural Southern folk music, which was primarily Irish and British, with African and continental European musics. Anglo-Celtic tunes, dance music, and balladry were the earliest predecessors of modern country, then known as ''hillbilly music''. Early  The roots of commercial country music are generally traced to 1927, when music talent scout Ralph Peer recorded
The roots of commercial country music are generally traced to 1927, when music talent scout Ralph Peer recorded
 R&B, an abbreviation for ''rhythm and blues'', is a style that arose in the 1930s and 1940s. Early R&B consisted of large rhythm units "smashing away behind screaming blues singers (who) had to shout to be heard above the clanging and strumming of the various electrified instruments and the churning rhythm sections". R&B was not extensively recorded and promoted because record companies felt that it was not suited for most audiences, especially middle-class whites, because of the suggestive lyrics and driving rhythms. Bandleaders like
R&B, an abbreviation for ''rhythm and blues'', is a style that arose in the 1930s and 1940s. Early R&B consisted of large rhythm units "smashing away behind screaming blues singers (who) had to shout to be heard above the clanging and strumming of the various electrified instruments and the churning rhythm sections". R&B was not extensively recorded and promoted because record companies felt that it was not suited for most audiences, especially middle-class whites, because of the suggestive lyrics and driving rhythms. Bandleaders like  Pure soul was popularized by Otis Redding and the other artists of Stax Records in Memphis, Tennessee. By the late 1960s, Atlantic recording artist
Pure soul was popularized by Otis Redding and the other artists of Stax Records in Memphis, Tennessee. By the late 1960s, Atlantic recording artist
Village Voice Media. Retrieved on 2008-07-10. while his unique sound with Brian Jackson influenced neo soul artists. During the mid-1970s, highly slick and commercial bands such as Philly soul group
During the mid-1970s, highly slick and commercial bands such as Philly soul group  By 1983, the concept of popular music crossover became inextricably associated with Michael Jackson. ''Thriller'' saw unprecedented success, selling over 10 million copies in the United States alone. By 1984, the album captured over 140 gold and platinum awards and was recognized by the ''Guinness Book of World Records'' as the best-selling record of all-time, a title it still holds today. MTV's broadcast of " Billie Jean" was the first for any black artist, thereby breaking the "color barrier" of pop music on the small screen. ''Thriller'' remains the only music video recognized by the National Film Registry.
By 1983, the concept of popular music crossover became inextricably associated with Michael Jackson. ''Thriller'' saw unprecedented success, selling over 10 million copies in the United States alone. By 1984, the album captured over 140 gold and platinum awards and was recognized by the ''Guinness Book of World Records'' as the best-selling record of all-time, a title it still holds today. MTV's broadcast of " Billie Jean" was the first for any black artist, thereby breaking the "color barrier" of pop music on the small screen. ''Thriller'' remains the only music video recognized by the National Film Registry.

 Pop Music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. ''Rock'' and ''pop'' remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which ''pop'' became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible. Although much of the music that appears on record charts is seen as pop music, the genre is distinguished from chart music.
Pop Music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. ''Rock'' and ''pop'' remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which ''pop'' became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible. Although much of the music that appears on record charts is seen as pop music, the genre is distinguished from chart music.
 Rock and roll developed out of country, blues, and R&B. Rock's exact origins and early influences have been hotly debated, and are the subjects of much scholarship. Though squarely in the blues tradition, rock took elements from
Rock and roll developed out of country, blues, and R&B. Rock's exact origins and early influences have been hotly debated, and are the subjects of much scholarship. Though squarely in the blues tradition, rock took elements from  The 1960s saw several important changes in popular music, especially rock. Many of these changes took place through the British Invasion where bands such as The Beatles, The Who, and The Rolling Stones, became immensely popular and had a profound effect on American culture and music. These changes included the move from professionally composed songs to the
The 1960s saw several important changes in popular music, especially rock. Many of these changes took place through the British Invasion where bands such as The Beatles, The Who, and The Rolling Stones, became immensely popular and had a profound effect on American culture and music. These changes included the move from professionally composed songs to the  Following the turbulent political, social and musical changes of the 1960s and early 1970s, rock music diversified. What was formerly a discrete genre known as ''rock and roll'' evolved into a catchall category called simply '' rock music'', which came to include diverse styles developed in the US like punk rock. During the 1970s most of these styles were evolving in the underground music scene, while mainstream audiences began the decade with a wave of
Following the turbulent political, social and musical changes of the 1960s and early 1970s, rock music diversified. What was formerly a discrete genre known as ''rock and roll'' evolved into a catchall category called simply '' rock music'', which came to include diverse styles developed in the US like punk rock. During the 1970s most of these styles were evolving in the underground music scene, while mainstream audiences began the decade with a wave of  Punk was a form of rebellious rock that began in the 1970s, and was loud, aggressive, and often very simple. Punk began as a reaction against the popular music of the period, especially
Punk was a form of rebellious rock that began in the 1970s, and was loud, aggressive, and often very simple. Punk began as a reaction against the popular music of the period, especially  Hardcore, punk, and garage rock were the roots of '' alternative rock'', a diverse grouping of rock subgenres that were explicitly opposed to mainstream music, and that arose from the punk and post-punk styles. In the United States, many cities developed local alternative rock scenes, including Minneapolis and Seattle. Seattle's local scene produced grunge music, a dark and brooding style inspired by hardcore, psychedelia, and alternative rock. With the addition of a more melodic element to the sound of bands like Nirvana,
Hardcore, punk, and garage rock were the roots of '' alternative rock'', a diverse grouping of rock subgenres that were explicitly opposed to mainstream music, and that arose from the punk and post-punk styles. In the United States, many cities developed local alternative rock scenes, including Minneapolis and Seattle. Seattle's local scene produced grunge music, a dark and brooding style inspired by hardcore, psychedelia, and alternative rock. With the addition of a more melodic element to the sound of bands like Nirvana,  Heavy metal is characterized by aggressive, driving rhythms, amplified and distorted guitars, grandiose lyrics, and virtuosic instrumentation. Heavy metal's origins lie in the hard rock bands who took blues and rock and created a heavy sound built on guitar and drums. The first major American bands came in the early 1970s, like Blue Öyster Cult, KISS, and
Heavy metal is characterized by aggressive, driving rhythms, amplified and distorted guitars, grandiose lyrics, and virtuosic instrumentation. Heavy metal's origins lie in the hard rock bands who took blues and rock and created a heavy sound built on guitar and drums. The first major American bands came in the early 1970s, like Blue Öyster Cult, KISS, and
 Unlike Motown which predicated its mainstream success on the class appeal of its acts that rendered racial identity irrelevant, hip hop of 1980s, particularly hip hop that crossed over to rock-and-roll, was predicated on its (implicit but emphatic) primary identification with black identity. By the beginning of the 1980s, there were popular hip hop songs, and the celebrities of the scene, like LL Cool J, gained mainstream renown. Other performers experimented with politicized lyrics and social awareness, or fused hip hop with jazz, heavy metal, techno, funk and soul. New styles appeared in the latter part of the 1980s, like alternative hip hop and the closely related jazz rap fusion, pioneered by rappers like De La Soul.
Gangsta rap is a kind of hip hop, most importantly characterized by a lyrical focus on macho sexuality, physicality, and a dangerous criminal image. Though the origins of gangsta rap can be traced back to the mid-1980s style of Philadelphia's Schoolly D and the West Coast's Ice-T, the style broadened and came to apply to many different regions in the country, to rappers from New York, such as Notorious B.I.G. and influential hip hop group Wu-Tang Clan, and to rappers on the West Coast, such as Too Short and N.W.A. A distinctive West Coast rap scene spawned the early 1990s G-funk sound, which paired gangsta rap lyrics with a thick and hazy sound, often from 1970s funk sampling (music), samples; the best-known proponents were the rappers 2Pac, Dr. Dre, Ice Cube, and Snoop Dogg. Gangsta rap continued to exert a major presence in American popular music through the end of the 1990s and early into the 21st century.
The dominance of gangsta rap in mainstream hip-hop was supplanted in the late-2000s, largely due to the mainstream success of hip-hop artists such as Kanye West. The outcome of a highly publicized Graduation (album)#Release, sales competition between the simultaneous release of his and gangsta rapper 50 Cent's third studio albums, ''Graduation (album), Graduation'' and ''Curtis (50 Cent album), Curtis'' respectively, has since been accredited to the decline. The competition resulted in record-breaking sales performances by both albums and West outsold 50 Cent, selling nearly a million copies of ''Graduation'' in the first week alone. Industry observers remark that West's victory over 50 Cent proved that rap music did not have to conform to gangsta-rap conventions in order to be commercially successful. West effectively paved the way for a new wave of hip-hop artists, including Drake (rapper), Drake, Kendrick Lamar and J. Cole, who did not follow the hardcore hip hop, hardcore-gangsta rap, gangster mold and became platinum-selling artists.
Jay-Z became an internationally renowned hip hop icon in the wake of the deaths of The Notorious B.I.G. and Tupac Shakur in the mid-1990s. Kanye West was mentored by Jay-Z and produced for him, before attaining a similar level of success.
Unlike Motown which predicated its mainstream success on the class appeal of its acts that rendered racial identity irrelevant, hip hop of 1980s, particularly hip hop that crossed over to rock-and-roll, was predicated on its (implicit but emphatic) primary identification with black identity. By the beginning of the 1980s, there were popular hip hop songs, and the celebrities of the scene, like LL Cool J, gained mainstream renown. Other performers experimented with politicized lyrics and social awareness, or fused hip hop with jazz, heavy metal, techno, funk and soul. New styles appeared in the latter part of the 1980s, like alternative hip hop and the closely related jazz rap fusion, pioneered by rappers like De La Soul.
Gangsta rap is a kind of hip hop, most importantly characterized by a lyrical focus on macho sexuality, physicality, and a dangerous criminal image. Though the origins of gangsta rap can be traced back to the mid-1980s style of Philadelphia's Schoolly D and the West Coast's Ice-T, the style broadened and came to apply to many different regions in the country, to rappers from New York, such as Notorious B.I.G. and influential hip hop group Wu-Tang Clan, and to rappers on the West Coast, such as Too Short and N.W.A. A distinctive West Coast rap scene spawned the early 1990s G-funk sound, which paired gangsta rap lyrics with a thick and hazy sound, often from 1970s funk sampling (music), samples; the best-known proponents were the rappers 2Pac, Dr. Dre, Ice Cube, and Snoop Dogg. Gangsta rap continued to exert a major presence in American popular music through the end of the 1990s and early into the 21st century.
The dominance of gangsta rap in mainstream hip-hop was supplanted in the late-2000s, largely due to the mainstream success of hip-hop artists such as Kanye West. The outcome of a highly publicized Graduation (album)#Release, sales competition between the simultaneous release of his and gangsta rapper 50 Cent's third studio albums, ''Graduation (album), Graduation'' and ''Curtis (50 Cent album), Curtis'' respectively, has since been accredited to the decline. The competition resulted in record-breaking sales performances by both albums and West outsold 50 Cent, selling nearly a million copies of ''Graduation'' in the first week alone. Industry observers remark that West's victory over 50 Cent proved that rap music did not have to conform to gangsta-rap conventions in order to be commercially successful. West effectively paved the way for a new wave of hip-hop artists, including Drake (rapper), Drake, Kendrick Lamar and J. Cole, who did not follow the hardcore hip hop, hardcore-gangsta rap, gangster mold and became platinum-selling artists.
Jay-Z became an internationally renowned hip hop icon in the wake of the deaths of The Notorious B.I.G. and Tupac Shakur in the mid-1990s. Kanye West was mentored by Jay-Z and produced for him, before attaining a similar level of success.
 Female rappers Nicki Minaj, Cardi B, Saweetie, Doja Cat, Iggy Azalea, City Girls and Megan Thee Stallion also entered the mainstream. There are many women that have notably influenced the hip hop culture. However, a few names that cannot go unsaid are MC Sha-rock, MC Lyte, Queen Latifah, Lauryn Hill, Missy Elliot, Lil Kim, Erykah Badu, Foxy Brown (rapper), Foxy Brown, and many more. Of this list MC Sha-rock is considered the historian/pioneer of female hip-hop culture. She started her career as a break-dancer in the Bronx, New York and later became "The hip-hop's culture's first female emcee/rapper". Her career has been long-lived. From being a former member of the Funky 4+1 more to having MC rhyming battles with groups such as Grandmaster Flash and Furious 5. Another notable pioneer of female hip-hop is the famous Queen Latifah, Born Dana Elaine Owens in Newark,NJ. Queen Latifah started her career from a young age, as early as 17. But, not long after it began it soon took-off. She released her first full length album, ''All Hail the Queen'' in 1989. As she continued to release music she grew more and more popular, and her fame increased amidst the hip-hop culture. However, Queen Latifah was not an ordinary rapper. She rapped about the issues surrounding being a black woman and overall social injustice issues that appear in the music industry. These early pioneers have led female rap culture and impacted today's popular female hip-hop artists. For example, such popular artists may include Cardi B, Megan Thee Stallion, Miss Mulatto, Flo Milli, Cupcakke and many others. Each artists has their own identity in the rap game, however as hip-hop evolves so does the style of music. Cardi B's first studio album, ''Invasion of Privacy (album), Invasion of Privacy'' (2018), debuted at number one on the Billboard 200, '' Billboard'' 200 and was named the number-one female rap album of the 2010s by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard''. Critically acclaimed, it made Cardi B the only woman to win the Grammy Award for Best Rap Album as a solo artist, and marked the first female rap album in fifteen years to be nominated for Grammy Award for Album of the Year, Album of the Year.
Female rappers Nicki Minaj, Cardi B, Saweetie, Doja Cat, Iggy Azalea, City Girls and Megan Thee Stallion also entered the mainstream. There are many women that have notably influenced the hip hop culture. However, a few names that cannot go unsaid are MC Sha-rock, MC Lyte, Queen Latifah, Lauryn Hill, Missy Elliot, Lil Kim, Erykah Badu, Foxy Brown (rapper), Foxy Brown, and many more. Of this list MC Sha-rock is considered the historian/pioneer of female hip-hop culture. She started her career as a break-dancer in the Bronx, New York and later became "The hip-hop's culture's first female emcee/rapper". Her career has been long-lived. From being a former member of the Funky 4+1 more to having MC rhyming battles with groups such as Grandmaster Flash and Furious 5. Another notable pioneer of female hip-hop is the famous Queen Latifah, Born Dana Elaine Owens in Newark,NJ. Queen Latifah started her career from a young age, as early as 17. But, not long after it began it soon took-off. She released her first full length album, ''All Hail the Queen'' in 1989. As she continued to release music she grew more and more popular, and her fame increased amidst the hip-hop culture. However, Queen Latifah was not an ordinary rapper. She rapped about the issues surrounding being a black woman and overall social injustice issues that appear in the music industry. These early pioneers have led female rap culture and impacted today's popular female hip-hop artists. For example, such popular artists may include Cardi B, Megan Thee Stallion, Miss Mulatto, Flo Milli, Cupcakke and many others. Each artists has their own identity in the rap game, however as hip-hop evolves so does the style of music. Cardi B's first studio album, ''Invasion of Privacy (album), Invasion of Privacy'' (2018), debuted at number one on the Billboard 200, '' Billboard'' 200 and was named the number-one female rap album of the 2010s by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard''. Critically acclaimed, it made Cardi B the only woman to win the Grammy Award for Best Rap Album as a solo artist, and marked the first female rap album in fifteen years to be nominated for Grammy Award for Album of the Year, Album of the Year.
 The American music industry is dominated by large companies that produce, market, and distribute certain kinds of music. Generally, these companies do not produce, or produce in only very limited quantities, recordings in styles that do not appeal to very large audiences. Smaller companies often fill in the void, offering a wide variety of recordings in styles ranging from
The American music industry is dominated by large companies that produce, market, and distribute certain kinds of music. Generally, these companies do not produce, or produce in only very limited quantities, recordings in styles that do not appeal to very large audiences. Smaller companies often fill in the void, offering a wide variety of recordings in styles ranging from  The single largest niche industry is based on Latin music. Latin music has long influenced American popular music, and was an especially crucial part of the development of jazz. Modern pop Latin styles include a wide array of genres imported from across Latin America, including Colombian cumbia, Puerto Rican reggaeton, and Mexican
The single largest niche industry is based on Latin music. Latin music has long influenced American popular music, and was an especially crucial part of the development of jazz. Modern pop Latin styles include a wide array of genres imported from across Latin America, including Colombian cumbia, Puerto Rican reggaeton, and Mexican
 The government of the United States regulates the music industry, enforces intellectual property laws, and promotes and collects certain kinds of music. Under United States copyright law, American copyright law, musical works, including recordings and compositions, are protected as intellectual property as soon as they are fixed in a tangible form. Copyright holders often register their work with the Library of Congress, which maintains a collection of the material. In addition, the Library of Congress has actively sought out culturally and musicologically significant materials since the early 20th century, such as by sending researchers to record folk music. These researchers include the pioneering American folk song collector Alan Lomax, whose work helped inspire the roots revival of the mid-20th century. The federal government also funds the National Endowment for the Arts, National Endowments for the Arts and National Endowment for the Humanities, Humanities, which allocate grants to musicians and other artists, the Smithsonian Institution, which conducts research and educational programs, and the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, which funds non-profit and television broadcasters.
Music has long affected the politics of the United States. Political parties and movements frequently use music and song to communicate their ideals and values, and to provide entertainment at political functions. The presidential campaign of William Henry Harrison was the first to greatly benefit from music, after which it became standard practice for major candidates to use songs to create public enthusiasm. In more recent decades, politicians often chose theme songs, some of which have become iconic; the song "Happy Days Are Here Again", for example, has been associated with the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party since the 1932 campaign of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Since the 1950s, however, music has declined in importance in politics, replaced by televised campaigning with little or no music. Certain forms of music became more closely associated with political protest, especially in the 1960s. Gospel music, Gospel stars like Mahalia Jackson became important figures in the Civil Rights Movement, while the American folk revival helped spread the counterculture of the 1960s and opposition to the Vietnam War.
The government of the United States regulates the music industry, enforces intellectual property laws, and promotes and collects certain kinds of music. Under United States copyright law, American copyright law, musical works, including recordings and compositions, are protected as intellectual property as soon as they are fixed in a tangible form. Copyright holders often register their work with the Library of Congress, which maintains a collection of the material. In addition, the Library of Congress has actively sought out culturally and musicologically significant materials since the early 20th century, such as by sending researchers to record folk music. These researchers include the pioneering American folk song collector Alan Lomax, whose work helped inspire the roots revival of the mid-20th century. The federal government also funds the National Endowment for the Arts, National Endowments for the Arts and National Endowment for the Humanities, Humanities, which allocate grants to musicians and other artists, the Smithsonian Institution, which conducts research and educational programs, and the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, which funds non-profit and television broadcasters.
Music has long affected the politics of the United States. Political parties and movements frequently use music and song to communicate their ideals and values, and to provide entertainment at political functions. The presidential campaign of William Henry Harrison was the first to greatly benefit from music, after which it became standard practice for major candidates to use songs to create public enthusiasm. In more recent decades, politicians often chose theme songs, some of which have become iconic; the song "Happy Days Are Here Again", for example, has been associated with the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party since the 1932 campaign of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Since the 1950s, however, music has declined in importance in politics, replaced by televised campaigning with little or no music. Certain forms of music became more closely associated with political protest, especially in the 1960s. Gospel music, Gospel stars like Mahalia Jackson became important figures in the Civil Rights Movement, while the American folk revival helped spread the counterculture of the 1960s and opposition to the Vietnam War.
 The United States has the world's global music industry market share data, largest music market with a total retail value of 4.9 billion dollars in 2014, The American music industry includes a number of fields, ranging from record companies to radio in the United States, radio stations and community orchestras. Total industry revenue is about $40 billion worldwide, and about $12 billion in the United States. Most of the world's major label, major record companies are based in the United States; they are represented by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). The major record companies produce material by artists that have signed to one of their record labels, a brand name often associated with a particular genre or record producer. Record companies may also promote and market their artists, through advertising, public performances and concerts, and television appearances. Record companies may be affiliated with other music media companies, which produce a product related to popular recorded music. These include television channels like
The United States has the world's global music industry market share data, largest music market with a total retail value of 4.9 billion dollars in 2014, The American music industry includes a number of fields, ranging from record companies to radio in the United States, radio stations and community orchestras. Total industry revenue is about $40 billion worldwide, and about $12 billion in the United States. Most of the world's major label, major record companies are based in the United States; they are represented by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). The major record companies produce material by artists that have signed to one of their record labels, a brand name often associated with a particular genre or record producer. Record companies may also promote and market their artists, through advertising, public performances and concerts, and television appearances. Record companies may be affiliated with other music media companies, which produce a product related to popular recorded music. These include television channels like  Radio stations in the United States often broadcast popular music. Each music station has a radio format, format, or a category of songs to be played; these are generally similar to but not the same as ordinary generic classification. Many radio stations in the United States are locally owned and operated, and may offer an eclectic assortment of recordings; many other stations are owned by large companies like Clear Channel Communications, Clear Channel, and are generally formatted on smaller, more repetitive playlists. Commercial sales of recordings are tracked by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard'' magazine, which compiles a number of music charts for various fields of recorded music sales. The Billboard Hot 100, ''Billboard'' Hot 100 is the top pop music chart for single (music), singles, a recording consisting of a handful of songs; longer pop recordings are albums, and are tracked by the Billboard 200, ''Billboard'' 200. Though recorded music is commonplace in American homes, many of the music industry's revenue comes from a small number of devotees; for example, 62% of album sales come from less than 25% of the music-buying audience. Total CD sales in the United States topped 705 million units sold in 2005, and singles sales just under three million.
Though the major record companies dominate the American music industry, an indie music, independent music industry (''indie music'') does exist. Most indie record labels have limited, if any, retail distribution outside a small region. Artists sometimes record for an indie label and gain enough acclaim to be signed to a major label; others choose to remain at an indie label for their entire careers. Indie music may be in styles generally similar to mainstream music, but is often inaccessible, unusual, or otherwise unappealing to many people. Indie musicians often release some or all of their songs over the Internet for fans and others to download and listen. In addition to recording artists of many kinds, there are numerous fields of professional musicianship in the United States, many of whom rarely record, including community orchestras, wedding singers and bands, lounge singers, and nightclub DJs. The American Federation of Musicians is the largest American trade union, labor union for professional musicians. However, only 15% of the Federation's members have steady music employment.
Radio stations in the United States often broadcast popular music. Each music station has a radio format, format, or a category of songs to be played; these are generally similar to but not the same as ordinary generic classification. Many radio stations in the United States are locally owned and operated, and may offer an eclectic assortment of recordings; many other stations are owned by large companies like Clear Channel Communications, Clear Channel, and are generally formatted on smaller, more repetitive playlists. Commercial sales of recordings are tracked by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard'' magazine, which compiles a number of music charts for various fields of recorded music sales. The Billboard Hot 100, ''Billboard'' Hot 100 is the top pop music chart for single (music), singles, a recording consisting of a handful of songs; longer pop recordings are albums, and are tracked by the Billboard 200, ''Billboard'' 200. Though recorded music is commonplace in American homes, many of the music industry's revenue comes from a small number of devotees; for example, 62% of album sales come from less than 25% of the music-buying audience. Total CD sales in the United States topped 705 million units sold in 2005, and singles sales just under three million.
Though the major record companies dominate the American music industry, an indie music, independent music industry (''indie music'') does exist. Most indie record labels have limited, if any, retail distribution outside a small region. Artists sometimes record for an indie label and gain enough acclaim to be signed to a major label; others choose to remain at an indie label for their entire careers. Indie music may be in styles generally similar to mainstream music, but is often inaccessible, unusual, or otherwise unappealing to many people. Indie musicians often release some or all of their songs over the Internet for fans and others to download and listen. In addition to recording artists of many kinds, there are numerous fields of professional musicianship in the United States, many of whom rarely record, including community orchestras, wedding singers and bands, lounge singers, and nightclub DJs. The American Federation of Musicians is the largest American trade union, labor union for professional musicians. However, only 15% of the Federation's members have steady music employment.
 Music is an important part of education in the United States, and is a part of most or all school systems in the country. Music education is generally mandatory in public elementary schools, and is an elective in later years.
Music is an important part of education in the United States, and is a part of most or all school systems in the country. Music education is generally mandatory in public elementary schools, and is an elective in later years.
 The scholarly study of music in the United States includes work relating music to social class, racial, ethnic and religious identity, gender and sexuality, as well as studies of music history, musicology, and other topics. The academic study of American music can be traced back to the late 19th century, when researchers like Alice Fletcher and Francis La Flesche studied the music of the Omaha (tribe), Omaha peoples, working for the Bureau of American Ethnology and the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. In the 1890s and into the early 20th century, musicological recordings were made among indigenous, Hispanic, African-American and Anglo-American peoples of the United States. Many worked for the Library of Congress, first under the leadership of Oscar Sonneck, chief of the Library's Music Divisions.Blum, Stephen, "Sources, Scholarship and Historiography" in the ''Garland Encyclopedia of World Music''. These researchers included Robert W. Gordon, founder of the Archive of American Folk Song, and John Lomax, John and Alan Lomax; Alan Lomax was the most prominent of several folk song collectors who helped to inspire the 20th century roots revival of American folk culture.
The scholarly study of music in the United States includes work relating music to social class, racial, ethnic and religious identity, gender and sexuality, as well as studies of music history, musicology, and other topics. The academic study of American music can be traced back to the late 19th century, when researchers like Alice Fletcher and Francis La Flesche studied the music of the Omaha (tribe), Omaha peoples, working for the Bureau of American Ethnology and the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. In the 1890s and into the early 20th century, musicological recordings were made among indigenous, Hispanic, African-American and Anglo-American peoples of the United States. Many worked for the Library of Congress, first under the leadership of Oscar Sonneck, chief of the Library's Music Divisions.Blum, Stephen, "Sources, Scholarship and Historiography" in the ''Garland Encyclopedia of World Music''. These researchers included Robert W. Gordon, founder of the Archive of American Folk Song, and John Lomax, John and Alan Lomax; Alan Lomax was the most prominent of several folk song collectors who helped to inspire the 20th century roots revival of American folk culture.
 Early 20th scholarly analysis of American music tended to interpret European-derived classical traditions as the most worthy of study, with the folk, religious, and traditional musics of the common people denigrated as low-class and of little artistic or social worth. American music history was compared to the much longer historical record of European nations, and was found wanting, leading writers like the composer Arthur Farwell to ponder what sorts of musical traditions might arise from American culture, in his 1915 ''Music in America''. In 1930, John Tasker Howard's ''Our American Music'' became a standard analysis, focusing on largely on concert music composed in the United States.Crawford, p. x. Since the analysis of musicologist Charles Seeger in the mid-20th century, American music history has often been described as intimately related to perceptions of race and ancestry. Under this view, the diverse racial and ethnic background of the United States has both promoted a sense of musical separation between the races, while still fostering constant acculturation, as elements of European, African, and indigenous musics have shifted between fields. Gilbert Chase's ''America's Music, from the Pilgrims to the Present'', was the first major work to examine the music of the entire United States, and recognize folk traditions as more culturally significant than music for the concert hall. Chase's analysis of a diverse American musical identity has remained the dominant view among the academic establishment. Until the 1960s and 1970s, however, most musical scholars in the United States continued to study European music, limiting themselves only to certain fields of American music, especially European-derived classical and operatic styles, and sometimes African American jazz. More modern musicologists and ethnomusicologists have studied subjects ranging from the national musical identity to the individual styles and techniques of specific communities in a particular time of American history. Prominent recent studies of American music include Charles Hamm's ''Music in the New World'' from 1983 and Richard Crawford (music historian), Richard Crawford's ''America's Musical Life'' from 2001.Crawford, p. x–xi.
Early 20th scholarly analysis of American music tended to interpret European-derived classical traditions as the most worthy of study, with the folk, religious, and traditional musics of the common people denigrated as low-class and of little artistic or social worth. American music history was compared to the much longer historical record of European nations, and was found wanting, leading writers like the composer Arthur Farwell to ponder what sorts of musical traditions might arise from American culture, in his 1915 ''Music in America''. In 1930, John Tasker Howard's ''Our American Music'' became a standard analysis, focusing on largely on concert music composed in the United States.Crawford, p. x. Since the analysis of musicologist Charles Seeger in the mid-20th century, American music history has often been described as intimately related to perceptions of race and ancestry. Under this view, the diverse racial and ethnic background of the United States has both promoted a sense of musical separation between the races, while still fostering constant acculturation, as elements of European, African, and indigenous musics have shifted between fields. Gilbert Chase's ''America's Music, from the Pilgrims to the Present'', was the first major work to examine the music of the entire United States, and recognize folk traditions as more culturally significant than music for the concert hall. Chase's analysis of a diverse American musical identity has remained the dominant view among the academic establishment. Until the 1960s and 1970s, however, most musical scholars in the United States continued to study European music, limiting themselves only to certain fields of American music, especially European-derived classical and operatic styles, and sometimes African American jazz. More modern musicologists and ethnomusicologists have studied subjects ranging from the national musical identity to the individual styles and techniques of specific communities in a particular time of American history. Prominent recent studies of American music include Charles Hamm's ''Music in the New World'' from 1983 and Richard Crawford (music historian), Richard Crawford's ''America's Musical Life'' from 2001.Crawford, p. x–xi.
Audio clips: Traditional music of the United States.
Musée d'Ethnographie de Genève. Accessed November 25, 2010.
American Guild of Music
6 Ever American Trending Music Stars
Music Publisher's Association
Music Library Association
Historic American Sheet Music
Lester S. Levy Sheet Music Collection
popular American music, 1780–1960 {{DEFAULTSORT:Music Of The United States American music, Performing arts pages with videographic documentation
music of Europe
The culture of Europe is rooted in its art, architecture, film, different types of music, economics, literature, and philosophy. European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage".
Definition
T ...
, Indigenous peoples, West Africa, Latin America, Middle East, North Africa, amongst many other places. The country's most internationally renowned genres are traditional pop, jazz, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
, country, bluegrass, rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, rock and roll, R&B, pop
Pop or POP may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* Pop music, a musical genre Artists
* POP, a Japanese idol group now known as Gang Parade
* Pop!, a UK pop group
* Pop! featuring Angie Hart, an Australian band
Albums
* ''Pop'' (G ...
, hip hop, soul, funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African Americans in the m ...
, gospel, disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric pia ...
, house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
, techno, ragtime, doo-wop
Doo-wop (also spelled doowop and doo wop) is a genre of rhythm and blues music that originated in African-American communities during the 1940s, mainly in the large cities of the United States, including New York, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Chica ...
, folk music, americana, boogaloo
Boogaloo or bugalú (also: shing-a-ling, Latin boogaloo, Latin R&B) is a genre of Latin music and dance which was popular in the United States in the 1960s. Boogaloo originated in New York City mainly among teenage African Americans and Latinos ...
, tejano
Tejanos (, ; singular: ''Tejano/a''; Spanish for "Texan", originally borrowed from the Caddo ''tayshas'') are the residents of the state of Texas who are culturally descended from the Mexican population of Tejas and Coahuila that lived in the ...
, reggaeton, surf, and salsa
Salsa most often refers to:
* Salsa (Mexican cuisine), a variety of sauces used as condiments
* Salsa music, a popular style of Latin American music
* Salsa (dance), a Latin dance associated with Salsa music
Salsa or SALSA may also refer to:
A ...
. American music is heard around the world. Since the beginning of the 20th century, some forms of American popular music have gained a near global audience.
Native Americans were the earliest inhabitants of the land that is today known as the United States and played its first music. Beginning in the 17th century, settlers
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
from the United Kingdom, Ireland, Spain, Germany, and France began arriving in large numbers, bringing with them new styles and instruments. Slaves from West Africa brought their musical traditions, and each subsequent wave of immigrants contributed to a melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
.
There are also some African-American influences in the musical tradition of the European-American settlers, such as jazz, blues, rock, country and bluegrass. The United States has also seen documented folk music and recorded popular music produced in the ethnic styles of the Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, Irish, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
, Hispanic, and Jewish communities, among others.
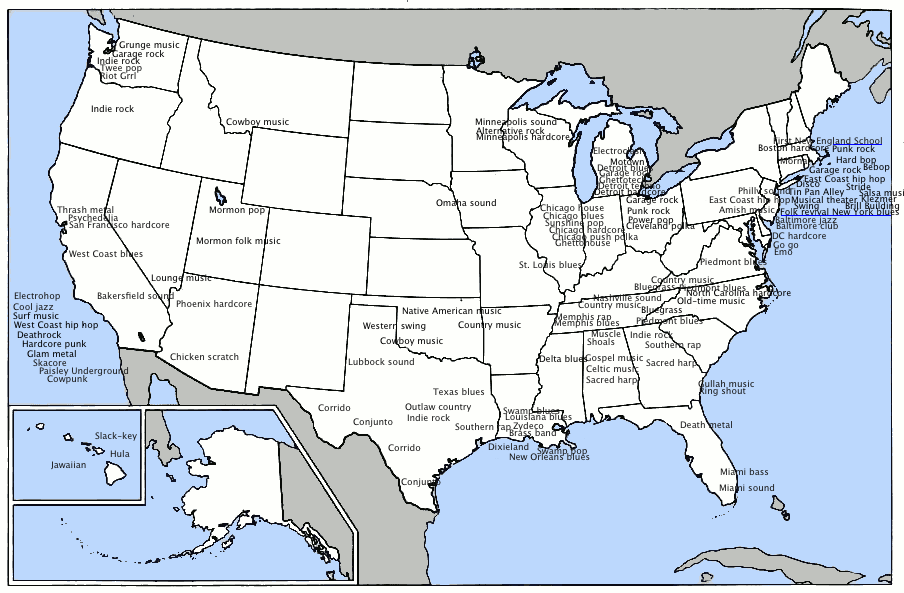
Many American cities and towns have vibrant music scenes which, in turn, support a number of regional musical styles. Musical centers around the country have all have produced and contributed to the many distinctive styles of American music. The Cajun and Creole traditions in Louisiana music
''Louisiana Music'' is a website presenting classical music videos produced by the Louisiana Museum of Modern Art.
Content
The Great Romantics (2007 to 2009)
* Brahms - Trio with clarinet interpreted by Paul Meyer, Jing Zhao and Éric Le S ...
, the folk and popular styles of Hawaiian music, and the bluegrass and old time music of the Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
states are a few examples of diversity in American music.
Characteristics
The music of the United States can be characterized by the use ofsyncopation
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "place ...
and asymmetrical rhythms, long, irregular melodies, which are said to "reflect the wide open geography of (the American landscape)" and the "sense of personal freedom characteristic of American life". Some distinct aspects of American music, like the call-and-response format, are derived from African techniques and instruments.
Throughout the later part of American history, and into modern times, the relationship between American and European music has been a discussed topic among scholars of American music. Some have urged for the adoption of more purely European techniques and styles, which are sometimes perceived as more refined or elegant, while others have pushed for a sense of musical nationalism that celebrates distinctively American styles. Modern classical music scholar John Warthen Struble has contrasted American and European, concluding that the music of the United States is inherently distinct because the United States has not had centuries of musical evolution as a nation. Instead, the music of the United States is that of dozens or hundreds of indigenous and immigrant groups, all of which developed largely in regional isolation until the American Civil War, when people from across the country were brought together in army units, trading musical styles and practices. Struble deemed the ballads of the Civil War "the first American folk music with discernible features that can be considered unique to America: the first 'American' sounding music, as distinct from any regional style derived from another country."
The Civil War, and the period following it, saw a general flowering of American art, literature and music. Amateur musical ensembles of this era can be seen as the birth of American popular music. Music author David Ewen describes these early amateur bands as combining "the depth and drama of the classics with undemanding technique, eschewing complexity in favor of direct expression. If it was vocal music, the words would be in English, despite the snobs who declared English an unsingable language. In a way, it was part of the entire awakening of America that happened after the Civil War, a time in which American painters, writers, and 'serious' composers addressed specifically American themes." During this period the roots of blues, gospel, jazz, and country music took shape; in the 20th century, these became the core of American popular music, which further evolved into the styles like rhythm and blues, rock and roll, and hip hop music.
Social identity
 Music intertwines with aspects of American social and cultural identity, including through
Music intertwines with aspects of American social and cultural identity, including through social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the Upper class, upper, Middle class, middle and Working class, lower classes. Membership in a social class can for ...
, race and ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, geography, religion, language, gender, and sexuality
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied ...
. The relationship between music and race is perhaps the most potent determiner of musical meaning in the United States. The development of an African American musical identity, out of disparate sources from Africa and Europe, has been a constant theme in the music history of the United States. Little documentation exists of colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
-era African American music, when styles, songs, and instruments from across West Africa commingled with European styles and instruments, leading to the creation of new genres and self expression from enslaved people. By the mid-19th century, a distinctly African American folk tradition was well-known and widespread, and African American musical techniques, instruments, and images became a part of mainstream American music through spirituals, minstrel shows, and slave songs. African American musical styles became an integral part of American popular music through blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
, jazz, rhythm and blues, and then rock and roll, soul, and hip hop; all of these styles were consumed by Americans of all races, but were created in African American styles and idioms before eventually becoming common in performance and consumption across racial lines. In contrast, country music derives from both African and European, as well as Native American and Hawaiian, traditions and has long been perceived as a form of white music.
Economic and social classes separates American music through the creation and consumption of music, such as the upper-class patronage of symphony
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning com ...
-goers, and the generally poor performers of rural and ethnic folk musics. Musical divisions based on class are not absolute, however, and are sometimes as much perceived as actual; popular American country music, for example, is a commercial genre designed to "appeal to a working-class identity, whether or not its listeners are actually working class". Country music is also intertwined with geographic identity, and is specifically rural in origin and function; other genres, like R&B and hip hop, are perceived as inherently urban. For much of American history, music-making has been a "feminized activity". In the 19th century, amateur piano and singing were considered proper for middle- and upper-class women. Women were also a major part of early popular music performance, though recorded traditions quickly become more dominated by men. Most male-dominated genres of popular music include female performers as well, often in a niche appealing primarily to women; these include gangsta rap
Gangsta rap or gangster rap, initially called reality rap, emerged in the mid- to late 1980s as a controversial hip-hop subgenre whose lyrics assert the culture and values typical of American street gangs and street hustlers. Many gangsta rappe ...
and heavy metal.
History
Diversity
 The United States is often said to be a cultural
The United States is often said to be a cultural melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
, taking in influences from across the world and creating distinctively new methods of cultural expression. Though aspects of American music can be traced back to specific origins, claiming any particular original culture for a musical element is inherently problematic, due to the constant evolution of American music through transplanting and hybridizing techniques, instruments and genres. Elements of foreign musics arrived in the United States both through the formal sponsorship of educational and outreach events by individuals and groups, and through informal processes, as in the incidental transplantation of West African music through slavery, and Irish music through immigration. The most distinctly American musics are a result of cross-cultural hybridization through close contact. Slavery, for example, mixed persons from numerous tribes in tight living quarters, resulting in a shared musical tradition that was enriched through further hybridizing with elements of indigenous, Latin, and European music.Cowdery, James R. with Anne Lederman, "Blurring the Boundaries of Social and Musical Identities" in the ''Garland Encyclopedia of World Music'', pp. 322–333. American ethnic, religious, and racial diversity has also produced such intermingled genres as the French-African music of the Louisiana Creoles
Louisiana Creoles (french: Créoles de la Louisiane, lou, Moun Kréyòl la Lwizyàn, es, Criollos de Luisiana) are people descended from the inhabitants of colonial Louisiana before it became a part of the United States during the period of bo ...
, the Native, Mexican and European fusion Tejano music, and the thoroughly hybridized slack-key guitar
Slack-key guitar (from Hawaiian ''kī hōalu'', which means "loosen the uningkey") is a fingerstyle genre of guitar music that originated in Hawaii after Portuguese cowboys introduced Spanish guitars there in the late 19th century. The Hawaiian ...
and other styles of modern Hawaiian music.
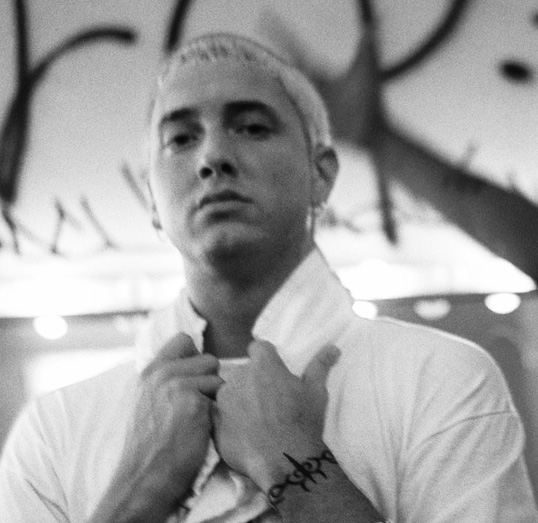
The process of transplanting music between cultures is not without criticism. The folk revival of the mid-20th century, for example, appropriated the musics of various rural peoples, in part to promote certain political causes, which has caused some to question whether the process caused the "commercial commodification of other peoples' songs ... and the inevitable dilution of mean" in the appropriated musics. The use of African American musical techniques, images, and conceits in popular music largely by and for white Americans has been widespread since at least the mid-19th century songs of Stephen Foster and the rise of minstrel shows. The American music industry has actively attempted to popularize white performers of African American music because they are more palatable to mainstream and middle-class Americans. This process has been related to the rise of stars as varied as Benny Goodman
Benjamin David Goodman (May 30, 1909 – June 13, 1986) was an American clarinetist and bandleader known as the "King of Swing".
From 1936 until the mid-1940s, Goodman led one of the most popular swing big bands in the United States. His co ...
, Eminem
Marshall Bruce Mathers III (born October 17, 1972), known professionally as Eminem (; often stylized as EMINƎM), is an American rapper and record producer. He is credited with popularizing hip hop in middle America and is critically acclai ...
, and Elvis Presley, as well as popular styles like blue-eyed soul
Blue-eyed soul (also called white soul) is rhythm and blues (R&B) and soul music performed by white artists. The term was coined in the mid-1960s, to describe white artists whose sound was similar to that of the predominantly-black Motown and Stax ...
and rockabilly.
Folk music
 Folk music in the US is varied across the country's numerous ethnic groups. The Native American tribes each play their own varieties of folk music, most of it spiritual in nature. African American music includes
Folk music in the US is varied across the country's numerous ethnic groups. The Native American tribes each play their own varieties of folk music, most of it spiritual in nature. African American music includes blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
and gospel, descendants of West African music brought to the Americas by slaves and mixed with Western European music. During the colonial era, English, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Spanish styles and instruments were brought to the Americas. By the early 20th century, the United States had become a major center for folk music from around the world, including polka
Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.
History
Etymology
The term ...
, Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
fiddling, Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
, Klezmer
Klezmer ( yi, קלעזמער or ) is an instrumental musical tradition of the Ashkenazi Jews of Central and Eastern Europe. The essential elements of the tradition include dance tunes, ritual melodies, and virtuosic improvisations played for l ...
, and several kinds of Latin music.
The Native Americans played the first folk music in what is now the United States, using a wide variety of styles and techniques. Some commonalities are near universal among Native American traditional music, however, especially the lack of harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However ...
and polyphony, and the use of vocables and descending melodic figures. Traditional instrumentations use the flute
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, meaning they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedless ...
and many kinds of percussion instruments, like drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a she ...
s, rattles, and shakers
The United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing, more commonly known as the Shakers, are a Millenarianism, millenarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian sect founded in England and then organized in the Unit ...
. Since European and African contact was established, Native American folk music has grown in new directions, into fusions with disparate styles like European folk dances and Tejano music. Modern Native American music may be best known for pow wow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native American and First Nations communities. Powwows today allow Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their cultures. Powwows may be private or pu ...
s, pan-tribal gatherings at which traditionally styled dances and music are performed.
The Thirteen Colonies of the original United States were all former English possessions, and Anglo culture became a major foundation for American folk and popular music. Many American folk songs are identical to British songs in arrangements, but with new lyrics, often as parodies of the original material. American-Anglo songs are also characterized as having fewer pentatonic tunes, less prominent accompaniment (but with heavier use of drones
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
) and more melodies in major. Anglo-American traditional music also includes a variety of broadside ballads, humorous stories and tall tales, and disaster songs regarding mining, shipwrecks, and murder. Legendary heroes like Joe Magarac
Joe Magarac () is a pseudo-legendary American folk hero. He is presented to readers as having been the protagonist of tales of oral folklore told by steelworkers in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, which later spread throughout the industrial areas of ...
, John Henry, and Jesse James
Jesse Woodson James (September 5, 1847April 3, 1882) was an American outlaw, bank and train robber, guerrilla and leader of the James–Younger Gang. Raised in the " Little Dixie" area of Western Missouri, James and his family maintained stro ...
are part of many songs. Folk dances of British origin include the square dance
A square dance is a dance for four couples, or eight dancers in total, arranged in a square, with one couple on each side, facing the middle of the square. Square dances contain elements from numerous traditional dances and were first documente ...
, descended from the quadrille, combined with the American innovation of a caller instructing the dancers. The religious communal society known as the Shakers
The United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing, more commonly known as the Shakers, are a Millenarianism, millenarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian sect founded in England and then organized in the Unit ...
emigrated from England during the 18th century and developed their own folk dance style. Their early songs can be dated back to British folk song models. Other religious societies established their own unique musical cultures early in American history, such as the music of the Amish, the Harmony Society, and the Ephrata Cloister in Pennsylvania.
The ancestors of today's African American population were brought to the United States as slaves, working primarily in the plantations of the South. They were from hundreds of tribes across West Africa, and they brought with them certain traits of West African music including call and response vocals and complexly rhythmic music, as well as syncopated
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "place ...
beats and shifting accents. The African musical focus on rhythmic singing and dancing was brought to the New World, where it became part of a distinct folk culture that helped Africans "retain continuity with their past through music". The first slaves in the United States sang work songs, field hollers and, following Christianization, hymns. In the 19th century, a Great Awakening
Great Awakening refers to a number of periods of religious revival in American Christian history. Historians and theologians identify three, or sometimes four, waves of increased religious enthusiasm between the early 18th century and the late ...
of religious fervor gripped people across the country, especially in the South. Protestant hymns written mostly by New England preachers became a feature of camp meetings held among devout Christians across the South. When blacks began singing adapted versions of these hymns, they were called Negro spirituals. It was from these roots, of spiritual songs, work songs, and field hollers, that blues, jazz, and gospel developed.
Blues and spirituals
Spirituals were primarily expressions of religious faith, sung by slaves on southern plantations. In the mid to late 19th century, spirituals spread out of the U.S. South. In 1871Fisk University
Fisk University is a private historically black liberal arts college in Nashville, Tennessee. It was founded in 1866 and its campus is a historic district listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
In 1930, Fisk was the first Africa ...
became home to the Fisk Jubilee Singers, a pioneering group that popularized spirituals across the country. In imitation of this group, gospel quartets arose, followed by increasing diversification with the early 20th-century rise of jackleg and singing preachers, from whence came the popular style of gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music, and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music varies according to culture and social context. Gospel music is com ...
.
Blues is a combination of African work songs, field hollers, and shouts. It developed in the rural South in the first decade of the 20th century. The most important characteristics of the blues is its use of the blue scale, with a flatted or indeterminate third, as well as the typically lamenting lyrics; though both of these elements had existed in African American folk music prior to the 20th century, the codified form of modern blues (such as with the AAB structure) did not exist until the early 20th century.''Rolling Stone'', p. 20.
Other immigrant communities
melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
consisting of numerous ethnic groups. Many of these peoples have kept alive the folk traditions of their homeland, often producing distinctively American styles of foreign music. Some nationalities have produced local scenes in regions of the country where they have clustered, like Cape Verdean music
Cape Verde is known internationally for '' morna'', a form of folk music usually sung in the Cape Verdean Creole, accompanied by clarinet, violin, guitar and cavaquinho. ''Funaná'', ''Coladeira'', '' Batuque'' and '' Cabo love'' are other musical ...
in New England, Armenian music in California, and Italian and Ukrainian music
Ukrainian music covers diverse and multiple component elements of the music that is found in the Western and Eastern musical civilization. It also has a very strong indigenous Slavic and Christian uniqueness whose elements were used among the a ...
in New York City.
The Creoles are a community with varied non-Anglo ancestry, mostly descendant of people who lived in Louisiana before its purchase by the U.S. The Cajuns are a group of Francophones who arrived in Louisiana after leaving Acadia in Canada. The city of New Orleans, Louisiana, being a major port, has acted as a melting pot for people from all over the Caribbean basin. The result is a diverse and syncretic set of styles of Cajun music and Creole music.
Spain and subsequently Mexico controlled much of what is now the western United States until the Mexican–American War, including the entire state of Texas. After Texas joined the United States, the native Tejano
Tejanos (, ; singular: ''Tejano/a''; Spanish for "Texan", originally borrowed from the Caddo ''tayshas'') are the residents of the state of Texas who are culturally descended from the Mexican population of Tejas and Coahuila that lived in the ...
s living in the state began culturally developing separately from their neighbors to the south, and remained culturally distinct from other Texans. Central to the evolution of early Tejano music was the blend of traditional Mexican forms such as mariachi
Mariachi (, , ) is a genre of regional Mexican music that dates back to at least the 18th century, evolving over time in the countryside of various regions of western Mexico. The usual mariachi group today consists of as many as eight violins, t ...
and the corrido
The corrido () is a popular narrative metrical tale and poetry that forms a ballad. The songs are often about oppression, history, daily life for criminals, the vaquero lifestyle, and other socially relevant topics. Corridos were widely popular ...
, and Continental European styles introduced by German and Czech settlers in the late 19th century. In particular, the accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German ''Akkordeon'', from ''Akkord''—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free-reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a reed ...
was adopted by Tejano folk musicians around the start of the 20th century, and it became a popular instrument for amateur musicians in Texas and Northern Mexico.
Classical music
Classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" also ...
was brought to the United States with some of the first colonists. European classical music is rooted in the traditions of European art, ecclesiastical and concert music. The central norms of this tradition developed between 1550 and 1825, centering on what is known as the common practice period. Many American classical composers attempted to work entirely within European models until late in the 19th century. When Antonín Dvořák
Antonín Leopold Dvořák ( ; ; 8 September 1841 – 1 May 1904) was a Czechs, Czech composer. Dvořák frequently employed rhythms and other aspects of the folk music of Moravian traditional music, Moravia and his native Bohemia, following t ...
, a prominent Czech composer, visited the United States from 1892 to 1895, he iterated the idea that American classical music needed its own models instead of imitating European composers; he helped to inspire subsequent composers to make a distinctly American style of classical music. By the beginning of the 20th century, many American composers were incorporating disparate elements into their work, ranging from jazz and blues to Native American music.
Early classical music

Classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" also ...
was brought to the United States during the colonial era. Many American composers of this period worked exclusively with European models, while others, such as William Billings, Supply Belcher, and Justin Morgan, also known as the ''First New England School'', developed a style almost entirely independent of European models. Of these composers, Billings is the most well-remembered; he was also influential "as the founder of the American church choir, as the first musician to use a pitch pipe, and as the first to introduce a violoncello into church service". Many of these composers were amateur singers who developed new forms of sacred music suitable for performance by amateurs, and often using harmonic methods which would have been considered bizarre by contemporary European standards. These composers' styles were untouched by "the influence of their sophisticated European contemporaries", using modal or pentatonic scales or melodies and eschewing the European rules of harmony.
In the early 19th century, America produced diverse composers such as Anthony Heinrich
Anthony Philip Heinrich (March 11, 1781 – May 3, 1861) was the first "full-time" American composer, and the most prominent before the American Civil War. He did not start composing until he was 36, after losing his business fortune in the N ...
, who composed in an idiosyncratic, intentionally American style and was the first American composer to write for a symphony orchestra. Many other composers, most famously William Henry Fry and George Frederick Bristow, supported the idea of an American classical style, though their works were very European in orientation. It was John Knowles Paine, however, who became the first American composer to be accepted in Europe. Paine's example inspired the composers of the ''Second New England School'', which included such figures as Amy Beach, Edward MacDowell, and Horatio Parker.
Louis Moreau Gottschalk
Louis Moreau Gottschalk (May 8, 1829 – December 18, 1869) was an American composer and pianist, best known as a virtuoso performer of his own romantic piano works. He spent most of his working career outside the United States.
Life and car ...
is perhaps the best-remembered American composer of the 19th century, said by music historian Richard Crawford to be known for "bringing indigenous or folk, themes and rhythms into music for the concert hall". Gottschalk's music reflected the cultural mix of his home city, New Orleans, Louisiana, which was home to a variety of Latin, Caribbean, African American, Cajun, and Creole music. He was well acknowledged as a talented pianist in his lifetime, and was also a known composer who remains admired though little performed.
20th century
 The New York classical music scene included Charles Griffes, originally from
The New York classical music scene included Charles Griffes, originally from Elmira, New York
Elmira () is a city and the county seat of Chemung County, New York, United States. It is the principal city of the Elmira, New York, metropolitan statistical area, which encompasses Chemung County. The population was 26,523 at the 2020 cens ...
, who began publishing his most innovative material in 1914. His early collaborations were attempts to use non-Western musical themes. The best-known New York composer was George Gershwin. Gershwin was a songwriter with Tin Pan Alley and the Broadway theatres, and his works were strongly influenced by jazz, or rather the precursors to jazz that were extant during his time. Gershwin's work made American classical music more focused, and attracted an unheard of amount of international attention. Following Gershwin, the first major composer was Aaron Copland from Brooklyn, who used elements of American folk music, though it remained European in technique and form. Later, he turned to the ballet and then serial music.Struble, p. 122. Charles Ives
Charles Edward Ives (; October 20, 1874May 19, 1954) was an American modernist composer, one of the first American composers of international renown. His music was largely ignored during his early career, and many of his works went unperformed f ...
was one of the earliest American classical composers of enduring international significance, producing music in a uniquely American style, though his music was mostly unknown until after his death in 1954.
Many of the later 20th-century composers, such as John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one of the leading fi ...
, John Corigliano
John Paul Corigliano Jr. (born February 16, 1938) is an American composer of contemporary classical music. His scores, now numbering over one hundred, have won him the Pulitzer Prize, five Grammy Awards, Grawemeyer Award for Music Composition, an ...
, Terry Riley, Steve Reich
Stephen Michael Reich ( ; born October 3, 1936) is an American composer known for his contribution to the development of minimal music in the mid to late 1960s. Reich's work is marked by its use of repetitive figures, slow harmonic rhythm, a ...
, John Adams, and Miguel del Aguila
-->
Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to:
Places
*Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands
*São Miguel (disambi ...
, used modernist and minimalist techniques. Reich discovered a technique known as phasing, in which two musical activities begin simultaneously and are repeated, gradually drifting out of sync, creating a natural sense of development. Reich was also very interested in non-Western music, incorporating African rhythmic techniques in his compositions.Struble, ''The History of American Classical Music''. Recent composers and performers are strongly influenced by the minimalist works of Philip Glass
Philip Glass (born January 31, 1937) is an American composer and pianist. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential composers of the late 20th century. Glass's work has been associated with minimal music, minimalism, being built up fr ...
, a Baltimore native based out of New York, Meredith Monk, and others.Unterberger, p. 1–65.
Popular music
The United States has produced many popular musicians and composers in the modern world. Beginning with the birth of recorded music, American performers have continued to lead the field of popular music, which out of "all the contributions made by Americans to world culture... has been taken to heart by the entire world". Most histories of popular music start with American ragtime or Tin Pan Alley; others, however, trace ''popular music'' to the Renaissance and throughbroadsheet
A broadsheet is the largest newspaper format and is characterized by long Vertical and horizontal, vertical pages, typically of . Other common newspaper formats include the smaller Berliner (format), Berliner and Tabloid (newspaper format), ta ...
s, ballads, and other popular traditions. Other authors typically look at popular sheet music, tracing ''American popular music'' to spirituals, minstrel shows, vaudeville, and the patriotic songs of the Civil War.
Early popular song
 The patriotic lay songs of the American Revolution constituted the first kind of mainstream popular music. These included "The Liberty Tree" by Thomas Paine. Cheaply printed as
The patriotic lay songs of the American Revolution constituted the first kind of mainstream popular music. These included "The Liberty Tree" by Thomas Paine. Cheaply printed as broadsheet
A broadsheet is the largest newspaper format and is characterized by long Vertical and horizontal, vertical pages, typically of . Other common newspaper formats include the smaller Berliner (format), Berliner and Tabloid (newspaper format), ta ...
s, early patriotic songs spread across the colonies and were performed at home and at public meetings. Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
songs were especially celebrated, and were performed on fields of battle during the American Revolution. The longest lasting of these fife songs is " Yankee Doodle", still well known today. The melody dates back to 1755 and was sung by both American and British troops. Patriotic songs were based mostly on English melodies, with new lyrics added to denounce British colonialism; others, however, used tunes from Ireland, Scotland or elsewhere, or did not utilize a familiar melody. The song " Hail, Columbia" was a major work that remained an unofficial national anthem until the adoption of " The Star-Spangled Banner". Much of this early American music still survives in Sacred Harp. Although relatively unknown outside of Shaker Communities, Simple Gifts was written in 1848 by Elder Joseph Brackett and the tune has since become internationally famous.
During the Civil War, when soldiers from across the country commingled, the multifarious strands of American music began to cross-fertilize each other, a process that was aided by the burgeoning railroad industry and other technological developments that made travel and communication easier. Army units included individuals from across the country, and they rapidly traded tunes, instruments and techniques. The war was an impetus for the creation of distinctly American songs that became and remained wildly popular.Struble, p. xvii. The most popular songs of the Civil War era included " Dixie", written by Daniel Decatur Emmett
Daniel Decatur Emmett (October 29, 1815June 28, 1904) was an American songwriter, entertainer, and founder of the first troupe of the blackface minstrel tradition, the Virginia Minstrels. He is most remembered as the composer of the song "Dixie" ...
. The song, originally titled "Dixie's Land", was made for the closing of a minstrel show; it spread to New Orleans first, where it was published and became "one of the great song successes of the pre-Civil War period". In addition to popular patriotic songs, the Civil War era also produced a great body of brass band pieces.
 Following the Civil War, minstrel shows became the first distinctively American form of music expression. The minstrel show was an indigenous form of American entertainment consisting of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music, usually performed by white people in
Following the Civil War, minstrel shows became the first distinctively American form of music expression. The minstrel show was an indigenous form of American entertainment consisting of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music, usually performed by white people in blackface
Blackface is a form of theatrical makeup used predominantly by non-Black people to portray a caricature of a Black person.
In the United States, the practice became common during the 19th century and contributed to the spread of racial stereo ...
. Minstrel shows used African American elements in musical performances, but only in simplified ways; storylines in the shows depicted blacks as natural-born slaves and fools, before eventually becoming associated with abolitionism
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
. The minstrel show was invented by Daniel Decatur Emmett and the Virginia Minstrels. Minstrel shows produced the first well-remembered popular songwriters in American music history: Thomas D. Rice
Thomas Dartmouth Rice (May 20, 1808 – September 19, 1860) was an American performer and playwright who performed in blackface and used African American vernacular speech, song and dance to become one of the most popular minstrel show ente ...
, Daniel Decatur Emmett, and, most famously, Stephen Foster. After minstrel shows' popularity faded, coon songs, a similar phenomenon, became popular.
The composer John Philip Sousa is closely associated with the most popular trend in American popular music just before the start of the 20th century. Formerly the bandmaster of the United States Marine Band, Sousa wrote military marches like " The Stars and Stripes Forever" that reflected his "nostalgia for ishome and country", giving the melody a "stirring virile character".
In the early 20th century, American musical theater was a major source for popular songs, many of which influenced blues, jazz, country, and other extant styles of popular music. The center of development for this style was in New York City, where the Broadway theatres became among the most renowned venues in the city. Theatrical composers and lyricists like the brothers George and Ira Gershwin
Ira Gershwin (born Israel Gershovitz; December 6, 1896 – August 17, 1983) was an American lyricist who collaborated with his younger brother, composer George Gershwin, to create some of the most memorable songs in the English language of the 2 ...
created a uniquely American theatrical style that used American vernacular speech and music. Musicals featured popular songs and fast-paced plots that often revolved around love and romance.
Blues and gospel
 The blues is a genre of African American folk music that is the basis for much of modern American popular music. Blues can be seen as part of a continuum of musical styles like country, jazz, ragtime, and gospel; though each genre evolved into distinct forms, their
The blues is a genre of African American folk music that is the basis for much of modern American popular music. Blues can be seen as part of a continuum of musical styles like country, jazz, ragtime, and gospel; though each genre evolved into distinct forms, their origins
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Comics and manga
* ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002
* ''The Origin'' (Buffy comic), a 1999 ''Buffy the Vampire Sl ...
were often indistinct. Early forms of the blues evolved in and around the Mississippi Delta in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The earliest blues music was primarily call and response vocal music, without harmony or accompaniment and without any formal musical structure. Slaves and their descendants created the blues by adapting the field shouts and hollers, turning them into passionate solo songs. When mixed with the Christian spiritual songs of African American churches and revival meetings, blues became the basis of gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music, and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music varies according to culture and social context. Gospel music is com ...
. Modern gospel began in African American churches in the 1920s, in the form of worshipers proclaiming their faith in an improvised, often musical manner (testifying). Composers like Thomas A. Dorsey
Thomas Andrew Dorsey (July 1, 1899 – January 23, 1993) was an American musician, composer, and Evangelism, Christian evangelist influential in the development of early blues and 20th-century gospel music. He penned 3,000 songs, a third of them ...
composed gospel works that used elements of blues and jazz in traditional hymns and spiritual songs.
 Ragtime was originally a piano style, featuring syncopated rhythms and
Ragtime was originally a piano style, featuring syncopated rhythms and chromaticism
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic scale, diatonic pitch (music), pitches and chord (music), chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. In simple terms, within each octave, diatonic music uses o ...
s. It is primarily a form of dance music utilizing the walking bass, and is generally composed in sonata form. Ragtime is a refined and evolved form of the African American cakewalk dance, mixed with styles ranging from European marches and popular songs to jigs and other dances played by large African American bands in northern cities during the end of the 19th century. The most famous ragtime performer and composer was Scott Joplin
Scott Joplin ( 1868 – April 1, 1917) was an American composer and pianist. Because of the fame achieved for his ragtime compositions, he was dubbed the "King of Ragtime." During his career, he wrote over 40 original ragtime pieces, one ra ...
, known for works such as "Maple Leaf Rag".Garofalo, p. 26.
Blues became a part of American popular music in the 1920s, when classic female blues singers like Bessie Smith grew popular. At the same time, record companies launched the field of race music, which was mostly blues targeted at African American audiences. The most famous of these acts went on to inspire much of the later popular development of the blues and blues-derived genres, including the legendary delta blues
Delta blues is one of the earliest-known styles of blues. It originated in the Mississippi Delta, and is regarded as a regional variant of country blues. Guitar and harmonica are its dominant instruments; slide guitar is a hallmark of the s ...
musician Robert Johnson and Piedmont blues
Piedmont blues (also known as East Coast, or Southeastern blues) refers primarily to a guitar style, which is characterized by a fingerpicking approach in which a regular, alternating thumb bass string rhythmic pattern supports a syncopated melo ...
musician Blind Willie McTell. By the end of the 1940s, however, pure blues was only a minor part of popular music, having been subsumed by offshoots like rhythm & blues and the nascent rock and roll style. Some styles of electric, piano-driven blues, like boogie-woogie, retained a large audience. A bluesy style of gospel also became popular in mainstream America in the 1950s, led by singer Mahalia Jackson.Werner. The blues genre experienced major revivals in the 1950s with Chicago blues musicians such as Muddy Waters and Little Walter, as well as in the 1960s in the British Invasion and American folk music revival
The American folk music revival began during the 1940s and peaked in popularity in the mid-1960s. Its roots went earlier, and performers like Josh White, Burl Ives, Woody Guthrie, Lead Belly, Big Bill Broonzy, Billie Holiday, Richard Dyer-Benn ...
when country blues musicians like Mississippi John Hurt and Reverend Gary Davis were rediscovered. The seminal blues musicians of these periods had tremendous influence on rock musicians such as Chuck Berry in the 1950s, as well as on the British blues and blues rock
Blues rock is a fusion music genre that combines elements of blues and rock music. It is mostly an electric ensemble-style music with instrumentation similar to electric blues and rock (electric guitar, electric bass guitar, and drums, sometimes w ...
scenes of the 1960s and 1970s, including Eric Clapton
Eric Patrick Clapton (born 1945) is an English rock and blues guitarist, singer, and songwriter. He is often regarded as one of the most successful and influential guitarists in rock music. Clapton ranked second in ''Rolling Stone''s list of ...
in Britain and Johnny Winter in Texas.
Jazz
 Jazz is a kind of music characterized by swung and blue notes, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and
Jazz is a kind of music characterized by swung and blue notes, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation
Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr ...
. Though originally a kind of dance music, jazz has been a major part of popular music, and has also become a major element of Western classical music. Jazz has roots in West African cultural and musical expression, and in African American music traditions including blues and ragtime, as well as European military band music. Early jazz was closely related to ragtime, with which it could be distinguished by the use of more intricate rhythmic improvisation. The earliest jazz bands adopted much of the vocabulary of the blues, including bent and blue notes and instrumental "growls" and smears otherwise not used on European instruments. Jazz's roots come from the city of New Orleans, Louisiana, populated by Cajuns and black Creoles, who combined the French-Canadian culture of the Cajuns with their own styles of music in the 19th century. Large Creole bands that played for funerals and parades became a major basis for early jazz, which spread from New Orleans to Chicago and other northern urban centers.
 Though jazz had long since achieved some limited popularity, it was
Though jazz had long since achieved some limited popularity, it was Louis Armstrong
Louis Daniel Armstrong (August 4, 1901 – July 6, 1971), nicknamed "Satchmo", "Satch", and "Pops", was an American trumpeter and vocalist. He was among the most influential figures in jazz. His career spanned five decades and several era ...
who became one of the first popular stars and a major force in the development of jazz, along with his friend pianist Earl Hines
Earl Kenneth Hines, also known as Earl "Fatha" Hines (December 28, 1903 – April 22, 1983), was an American jazz pianist and bandleader. He was one of the most influential figures in the development of jazz piano and, according to one source, " ...
. Armstrong, Hines, and their colleagues were improvisers, capable of creating numerous variations on a single melody. Armstrong also popularized scat singing, an improvisational vocal technique in which nonsensical syllables ( vocables) are sung. Armstrong and Hines were influential in the rise of a kind of pop big band jazz called ''swing
Swing or swinging may refer to:
Apparatus
* Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth
* Pendulum, an object that swings
* Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus
* Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse
* Swing rid ...
''. Swing is characterized by a strong rhythm section, usually consisting of double bass and drums, medium to fast tempo, and rhythmic devices like the swung note, which is common to most jazz. Swing is primarily a fusion of 1930s jazz fused with elements of the blues and Tin Pan Alley. Swing used bigger bands than other kinds of jazz, leading to bandleaders tightly arranging the material which discouraged improvisation, previously an integral part of jazz. Swing became a major part of African American dance, and came to be accompanied by a popular dance called the swing dance.
Jazz influenced many performers of all the major styles of later popular music, though jazz itself never again became such a major part of American popular music as during the swing era. The later 20th-century American jazz scene did, however, produce some popular crossover stars, such as Miles Davis. In the middle of the 20th century, jazz evolved into a variety of subgenres, beginning with bebop. Bebop is a form of jazz characterized by fast tempos, improvisation based on harmonic structure rather than melody, and use of the flatted fifth
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a interval (music), musical interval composed of three adjacent Major second, whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can ...
. Bebop was developed in the early and mid-1940s, later evolving into styles like hard bop and free jazz. Innovators of the style included Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie
John Birks "Dizzy" Gillespie (; October 21, 1917 – January 6, 1993) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, composer, educator and singer. He was a trumpet virtuoso and improviser, building on the virtuosic style of Roy Eldridge but addi ...
, who arose from small jazz clubs in New York City.Clarke.
Country music
 Country music is primarily a fusion of African American blues and spirituals with Appalachian folk music, adapted for pop audiences and popularized beginning in the 1920s. The origins of country are in rural Southern folk music, which was primarily Irish and British, with African and continental European musics. Anglo-Celtic tunes, dance music, and balladry were the earliest predecessors of modern country, then known as ''hillbilly music''. Early
Country music is primarily a fusion of African American blues and spirituals with Appalachian folk music, adapted for pop audiences and popularized beginning in the 1920s. The origins of country are in rural Southern folk music, which was primarily Irish and British, with African and continental European musics. Anglo-Celtic tunes, dance music, and balladry were the earliest predecessors of modern country, then known as ''hillbilly music''. Early hillbilly
Hillbilly is a term (often derogatory) for people who dwell in rural, mountainous areas in the United States, primarily in southern Appalachia and the Ozarks. The term was later used to refer to people from other rural and mountainous areas west ...
also borrowed elements of the blues and drew upon more aspects of 19th-century pop songs as hillbilly music evolved into a commercial genre eventually known as ''country and western'' and then simply ''country''. The earliest country instrumentation revolved around the European-derived fiddle
A fiddle is a bowed string musical instrument, most often a violin. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including classical music. Although in many cases violins and fiddles are essentially synonymous, th ...
and the African-derived banjo
The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, and usually made of plastic, or occasionally animal skin. Early forms of the instrument were fashi ...
, with the guitar later added. String instruments like the ukulele and steel guitar
A steel guitar ( haw, kīkākila) is any guitar played while moving a steel bar or similar hard object against plucked strings. The bar itself is called a "steel" and is the source of the name "steel guitar". The instrument differs from a conve ...
became commonplace due to the popularity of Hawaiian musical groups in the early 20th century.
 The roots of commercial country music are generally traced to 1927, when music talent scout Ralph Peer recorded
The roots of commercial country music are generally traced to 1927, when music talent scout Ralph Peer recorded Jimmie Rodgers
James Charles Rodgers (September 8, 1897 – May 26, 1933) was an American singer-songwriter and musician who rose to popularity in the late 1920s. Widely regarded as "the Father of Country Music", he is best known for his distinctive rhythmi ...
and The Carter Family. Popular success was very limited, though a small demand spurred some commercial recording. After World War II, there was increased interest in specialty styles like country music, producing a few major pop stars. The most influential country musician of the era was Hank Williams
Hank Williams (born Hiram Williams; September 17, 1923 – January 1, 1953) was an American singer, songwriter, and musician. Regarded as one of the most significant and influential American singers and songwriters of the 20th century, he reco ...
, a bluesy country singer from Alabama. He remains renowned as one of country music's greatest songwriters and performers, viewed as a "folk poet" with a "honky-tonk swagger" and "working-class sympathies". Throughout the decade the roughness of honky-tonk gradually eroded as the Nashville sound grew more pop-oriented. Producers like Chet Atkins created the Nashville sound by stripping the hillbilly elements of the instrumentation and using smooth instrumentation and advanced production techniques. Eventually, most records from Nashville were in this style, which began to incorporate strings and vocal choirs.
By the early part of the 1960s, however, the Nashville sound had become perceived as too watered-down by many more traditionalist performers and fans, resulting in a number of local scenes like the Bakersfield sound. A few performers retained popularity, however, such as the long-standing cultural icon Johnny Cash
John R. Cash (born J. R. Cash; February 26, 1932 – September 12, 2003) was an American country singer-songwriter. Much of Cash's music contained themes of sorrow, moral tribulation, and redemption, especially in the later stages of his ca ...
. The Bakersfield sound began in the mid to late 1950s when performers like Wynn Stewart and Buck Owens began using elements of Western swing and rock, such as the breakbeat
Breakbeat is a broad type of electronic music that tends to use drum breaks sampled from early recordings of funk, jazz, and R&B. Breakbeats have been used in styles such as hip hop, jungle, drum and bass, big beat, breakbeat hardcore, and UK ...
, in their music. In the 1960s performers like Merle Haggard popularized the sound. In the early 1970s, Haggard was also part of outlaw country, alongside singer-songwriters such as Willie Nelson and Waylon Jennings. Outlaw country was rock-oriented and lyrically focused on the criminal antics of the performers, in contrast to the clean-cut country singers of the Nashville sound. By the middle of the 1980s, the country music charts were dominated by pop singers, alongside a nascent revival of honky-tonk-style country with the rise of performers like Dwight Yoakam. The 1980s also saw the development of alternative country
Alternative country, or alternative country rock (sometimes alt-country, insurgent country, Americana, or y'allternative), is a loosely defined subgenre of country music and/or country rock that includes acts that differ significantly in style ...
performers like Uncle Tupelo, who were opposed to the more pop-oriented style of mainstream country. At the beginning of the 2000s, rock-oriented country acts remained among the best-selling performers in the United States, especially Garth Brooks
Troyal Garth Brooks (born February 7, 1962) is an American country music singer and songwriter. His integration of pop and rock elements into the country genre has earned him popularity, particularly in the United States with success on the co ...
.Garofalo.
Soul, R&B and funk
 R&B, an abbreviation for ''rhythm and blues'', is a style that arose in the 1930s and 1940s. Early R&B consisted of large rhythm units "smashing away behind screaming blues singers (who) had to shout to be heard above the clanging and strumming of the various electrified instruments and the churning rhythm sections". R&B was not extensively recorded and promoted because record companies felt that it was not suited for most audiences, especially middle-class whites, because of the suggestive lyrics and driving rhythms. Bandleaders like
R&B, an abbreviation for ''rhythm and blues'', is a style that arose in the 1930s and 1940s. Early R&B consisted of large rhythm units "smashing away behind screaming blues singers (who) had to shout to be heard above the clanging and strumming of the various electrified instruments and the churning rhythm sections". R&B was not extensively recorded and promoted because record companies felt that it was not suited for most audiences, especially middle-class whites, because of the suggestive lyrics and driving rhythms. Bandleaders like Louis Jordan
Louis Thomas Jordan (July 8, 1908 – February 4, 1975) was an American saxophonist, multi-instrumentalist, songwriter and bandleader who was popular from the late 1930s to the early 1950s. Known as " the King of the Jukebox", he earned his high ...
innovated the sound of early R&B, using a band with a small horn section and prominent rhythm instrumentation. By the end of the 1940s, he had had several hits, and helped pave the way for contemporaries like Wynonie Harris
Wynonie Harris (August 24, 1915 – June 14, 1969) was an American blues shouter and rhythm-and-blues singer of upbeat songs, featuring humorous, often ribald lyrics. He had fifteen Top 10 hits between 1946 and 1952. Harris is attributed by ma ...
and John Lee Hooker
John Lee Hooker (August 22, 1912 or 1917 – June 21, 2001) was an American blues singer, songwriter, and guitarist. The son of a sharecropper, he rose to prominence performing an electric guitar-style adaptation of Delta blues. Hooker often ...
. Many of the most popular R&B songs were not performed in the rollicking style of Jordan and his contemporaries; instead they were performed by white musicians like Pat Boone in a more palatable mainstream style, which turned into pop hits. By the end of the 1950s, however, there was a wave of popular black blues rock and country-influenced R&B performers like Chuck Berry gaining unprecedented fame among white listeners.
Motown Records
Motown Records is an American record label owned by the Universal Music Group. It was founded by Berry Gordy, Berry Gordy Jr. as Tamla Records on June 7, 1958, and incorporated as Motown Record Corporation on April 14, 1960. Its name, a portmant ...
became highly successful during the early and mid-1960s for producing music of black American roots that defied racial segregation in the music industry and consumer market. Music journalist Jerry Wexler
Jerry may refer to:
Animals
* Jerry (Grand National winner), racehorse, winner of the 1840 Grand National
* Jerry (St Leger winner), racehorse, winner of 1824 St Leger Stakes
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Jerry'' (film), a 2006 Indian fil ...
(who coined the phrase "rhythm and blues") once said of Motown: " heydid something that you would have to say on paper is impossible. They took black music and beamed it directly to the white American teenager." Berry Gordy founded Motown in 1959 in Detroit, Michigan. It was one of few R&B record labels that sought to transcend the R&B market (which was definitively black in the American mindset) and specialize in crossover music. The company emerged as the leading producer (or "assembly line," a reference to its motor-town origins) of black popular music by the early 1960s and marketed its products as "The Motown Sound" or "The Sound of Young America"—which combined elements of soul, funk, disco and R&B. Notable Motown acts include the Four Tops
The Four Tops are an American vocal quartet from Detroit who helped to define the city's Motown sound of the 1960s. The group's repertoire has included soul music, R&B, disco, adult contemporary, doo-wop, jazz, and show tunes.
Founded as the ...
, the Temptations, the Supremes, Smokey Robinson
William "Smokey" Robinson Jr. (born February 19, 1940) is an American singer, songwriter, record producer, and former record executive director. He was the founder and front man of the Motown vocal group the Miracles, for which he was also chief ...
, Stevie Wonder
Stevland Hardaway Morris ( Judkins; May 13, 1950), known professionally as Stevie Wonder, is an American singer-songwriter, who is credited as a pioneer and influence by musicians across a range of genres that include rhythm and blues, Pop musi ...
, and the Jackson 5. Visual representation was central to Motown's rise; they placed greater emphasis on visual media than other record labels. Many people's first exposure to Motown was by television and film. Motown artists' image of successful black Americans who held themselves with grace and aplomb broadcast a distinct form of middle-class blackness to audiences, which was particularly appealing to whites.
Soul music is a combination of rhythm and blues and gospel which began in the late 1950s in the United States. It is characterized by its use of gospel-music devices, with a greater emphasis on vocalists and the use of secular themes. The 1950s recordings of Ray Charles, Sam Cooke
Samuel Cook (January 22, 1931 – December 11, 1964), known professionally as Sam Cooke, was an American singer and songwriter. Considered to be a pioneer and one of the most influential soul artists of all time, Cooke is commonly referred ...
, and James Brown
James Joseph Brown (May 3, 1933 – December 25, 2006) was an American singer, dancer, musician, record producer and bandleader. The central progenitor of funk music and a major figure of 20th century music, he is often referred to by the honor ...
are commonly considered the beginnings of soul. Charles' '' Modern Sounds'' (1962) records featured a fusion of soul and country music, country soul, and crossed racial barriers in music at the time. One of Cooke's most well-known songs " A Change Is Gonna Come" (1964) became accepted as a classic and an anthem of the American Civil Rights Movement during the 1960s. According to AllMusic, James Brown was critical, through "the gospel-impassioned fury of his vocals and the complex polyrhythms of his beats", in "two revolutions in black American music. He was one of the figures most responsible for turning R&B into soul and he was, most would agree, the figure most responsible for turning soul music into the funk of the late '60s and early '70s."
 Pure soul was popularized by Otis Redding and the other artists of Stax Records in Memphis, Tennessee. By the late 1960s, Atlantic recording artist
Pure soul was popularized by Otis Redding and the other artists of Stax Records in Memphis, Tennessee. By the late 1960s, Atlantic recording artist Aretha Franklin
Aretha Louise Franklin ( ; March 25, 1942 – August 16, 2018) was an American singer, songwriter and pianist. Referred to as the " Queen of Soul", she has twice been placed ninth in ''Rolling Stone''s "100 Greatest Artists of All Time". With ...
had emerged as the most popular female soul star in the country. Also by this time, soul had splintered into several genres, influenced by psychedelic rock and other styles. The social and political ferment of the 1960s inspired artists like Marvin Gaye
Marvin Pentz Gay Jr., who also spelled his surname as Gaye (April 2, 1939 – April 1, 1984), was an American singer and songwriter. He helped to shape the sound of Motown in the 1960s, first as an in-house session player and later as a solo ar ...
and Curtis Mayfield to release albums with hard-hitting social commentary, while another variety became more dance-oriented music, evolving into funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African Americans in the m ...
. Despite his previous affinity with politically and socially-charged lyrical themes, Gaye helped popularize sexual and romance-themed music and funk,Edmonds (2001), pp. 15–18. while his 70s recordings, including '' Let's Get It On'' (1973) and '' I Want You'' (1976) helped develop the quiet storm sound and format. One of the most influential albums ever recorded, Sly & the Family Stone's ''There's a Riot Goin' On
''There's a Riot Goin' On'' (sometimes referred to as ''Riot'') is the fifth studio album by American funk and soul band Sly and the Family Stone. It was recorded from 1970 to 1971 at Record Plant Studios in Sausalito, California and released lat ...
'' (1971) has been considered among the first and best examples of the matured version of funk music, after prototypical instances of the sound in the group's earlier work. Artists such as Gil Scott-Heron
Gilbert Scott-Heron (April 1, 1949 – May 27, 2011) was an American Jazz poetry, jazz poet, singer, musician, and author, known primarily for his work as a spoken-word performer in the 1970s and 1980s. His collaborative efforts with musician ...
and The Last Poets practiced an eclectic blend of poetry, jazz-funk, and soul, featuring critical political and social commentary with afrocentric sentiment. Scott-Heron's Proto-rap
Rapping (also rhyming, spitting, emceeing or MCing) is a musical form of vocal delivery that incorporates "rhyme, rhythmic speech, and street vernacular". It is performed or chanted, usually over a backing beat or musical accompaniment. The ...
work, including " The Revolution Will Not Be Televised" (1971) and ''Winter in America
''Winter in America'' is a studio album by American vocalist Gil Scott-Heron and keyboardist Brian Jackson. It was recorded in September to October 1973 at D&B Sound Studio in Silver Spring, Maryland and released in May 1974 by Strata-East Reco ...
'' (1974), has had a considerable impact on later hip hop artists,Catching Up with Gil – Music – Houston PressVillage Voice Media. Retrieved on 2008-07-10. while his unique sound with Brian Jackson influenced neo soul artists.
The O'Jays
The O'Jays are an American R&B group from Canton, Ohio, formed in 1958 and originally consisting of Eddie Levert, Walter Lee Williams, William Powell, Bobby Massey, and Bill Isles. The O'Jays made their first chart appearance with the minor hi ...
and blue-eyed soul
Blue-eyed soul (also called white soul) is rhythm and blues (R&B) and soul music performed by white artists. The term was coined in the mid-1960s, to describe white artists whose sound was similar to that of the predominantly-black Motown and Stax ...
group Hall & Oates achieved mainstream success. By the end of the 1970s, most music genres, including soul, had been disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric pia ...
-influenced. With the introduction of influences from electro music
Electro (or electro- funk)Rap meets ...
and funk in the late 1970s and early 1980s, soul music became less raw and more slickly produced, resulting in a genre of music that was once again called ''R&B'', usually distinguished from the earlier rhythm and blues by identifying it as '' contemporary R&B''.
The first contemporary R&B stars arose in the 1980s, with the dance-pop star Michael Jackson, funk-influenced singer Prince, and a wave of female vocalists like Tina Turner and Whitney Houston. Michael Jackson and Prince have been described as the most influential figures in contemporary R&B and popular music because of their eclectic use of elements from a variety of genres. Prince was largely responsible for creating the Minneapolis sound: "a blend of horns, guitars, and electronic synthesizers supported by a steady, bouncing rhythm." Jackson's work focused on smooth balladry or disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric pia ...
-influenced dance music; as an artist, he "pulled dance music out of the disco doldrums with his 1979 adult solo debut, ''Off the Wall
''Off the Wall'' is the fifth studio album by American singer Michael Jackson, released on August 10, 1979, by Epic Records. It was Jackson's first album released through Epic Records, the label he recorded under until his death in 2009, and t ...
'', merged R&B with rock on ''Thriller
Thriller may refer to:
* Thriller (genre), a broad genre of literature, film and television
** Thriller film, a film genre under the general thriller genre
Comics
* ''Thriller'' (DC Comics), a comic book series published 1983–84 by DC Comics i ...
'', and introduced stylized steps such as the robot and moonwalk over the course of his career." Jackson is often recognized as the "King of Pop" for his achievements.
 By 1983, the concept of popular music crossover became inextricably associated with Michael Jackson. ''Thriller'' saw unprecedented success, selling over 10 million copies in the United States alone. By 1984, the album captured over 140 gold and platinum awards and was recognized by the ''Guinness Book of World Records'' as the best-selling record of all-time, a title it still holds today. MTV's broadcast of " Billie Jean" was the first for any black artist, thereby breaking the "color barrier" of pop music on the small screen. ''Thriller'' remains the only music video recognized by the National Film Registry.
By 1983, the concept of popular music crossover became inextricably associated with Michael Jackson. ''Thriller'' saw unprecedented success, selling over 10 million copies in the United States alone. By 1984, the album captured over 140 gold and platinum awards and was recognized by the ''Guinness Book of World Records'' as the best-selling record of all-time, a title it still holds today. MTV's broadcast of " Billie Jean" was the first for any black artist, thereby breaking the "color barrier" of pop music on the small screen. ''Thriller'' remains the only music video recognized by the National Film Registry.

Janet Jackson
Janet Damita Jo Jackson (born May 16, 1966) is an American singer, songwriter, actress, and dancer. She is noted for her innovative, socially conscious and sexually provocative records, as well as elaborate stage shows. Her sound and choreog ...
collaborated with former Prince associates Jimmy Jam and Terry Lewis on her third studio album '' Control'' (1986); the album's second single "Nasty
Nasty may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Music
* ''Nasty'' (album), a 1996 album by Cameo
* ''Nasty'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Rico Nasty
* ''Nasty'', a 1981 album by Ronald Shannon Jackson
* "Nasty" (Bandit Gang Marco song), ...
" has been described as the origin of the new jack swing
New jack swing, new jack, or swingbeat is a fusion genre of the rhythms and production techniques of hip hop and dance-pop, and the urban contemporary sound of R&B. Spearheaded by producers Teddy Riley and Bernard Belle, new jack swing was mos ...
sound, a genre innovated by Teddy Riley. Riley's work on Keith Sweat
Keith Sweat (born July 22, 1961) is an American singer, songwriter, record producer, and an early figure in the new jack swing musical movement. He is known for his collection of hits including "I Want Her", " Make It Last Forever", "I'll Give A ...
's '' Make It Last Forever'' (1987), Guy's '' Guy'' (1988), and Bobby Brown's '' Don't Be Cruel'' (1998) made new jack swing a staple of contemporary R&B into the mid-1990s. New jack swing was a style and trend of vocal music, often featuring rapped verses and drum machines. The crossover appeal of early contemporary R&B artists in mainstream popular music, including works by Prince, Michael and Janet Jackson, Whitney Houston, Tina Turner, Anita Baker, and The Pointer Sisters became a turning point for black artists in the industry, as their success "was perhaps the first hint that the greater cosmopolitanism of a world market might produce some changes in the complexion of popular music."
The use of melisma, a gospel tradition adapted by vocalists Whitney Houston and Mariah Carey
Mariah Carey (; born March 27, 1969) is an American singer, songwriter, actress, and record producer. Referred to as the " Songbird Supreme", she is noted for her five-octave vocal range, melismatic singing style and signature use of the whi ...
would become a cornerstone of contemporary R&B singers beginning in the late 1980s and throughout the 1990s. Whitney Houston's R&B hits included " All the Man That I Need" (1990) and "I Will Always Love You
"I Will Always Love You" is a song written and originally recorded in 1973 by American singer-songwriter Dolly Parton. Written as a farewell to her business partner and mentor Porter Wagoner, expressing Parton's decision to pursue a solo career, ...
" (1992), later became the best-selling physical single by a female act of all time, with sales of over 20 million copies worldwide. Her 1992 hit soundtrack ''The Bodyguard'', spent 20 weeks on top of the ''Billboard'' Hot 200, sold over 45 million copies worldwide and remains the best-selling soundtrack album of all time.
Hip hop came to influence contemporary R&B later in the 1980s, first through new jack swing and then in a related series of subgenres called hip hop soul and neo soul. Hip hop soul and neo soul developed later, in the 1990s. Typified by the work of Mary J. Blige
Mary Jane Blige ( ; born January 11, 1971) is an American singer, songwriter, and actress. Often referred to as the " Queen of Hip-Hop Soul" and " Queen of R&B", Blige has won nine Grammy Awards, a Primetime Emmy Award, four American Music Award ...
, R. Kelly
Robert Sylvester Kelly (born January 8, 1967) is an American singer, songwriter, record producer, and sex offender convicted of racketeering and multiple sex offenses.
During his recording career, Kelly sold over 75 million records worldwid ...
and Bobby Brown, the former is a mixture of contemporary R&B with hip hop beats, while the images and themes of gangsta rap
Gangsta rap or gangster rap, initially called reality rap, emerged in the mid- to late 1980s as a controversial hip-hop subgenre whose lyrics assert the culture and values typical of American street gangs and street hustlers. Many gangsta rappe ...
may be present. The latter is a more experimental, edgier, and generally less mainstream combination of 1960s and 1970s-style soul vocals with some hip hop influence, and has earned some mainstream recognition through the work of D'Angelo
Michael Eugene Archer (born February 11, 1974), better known by his stage name D'Angelo (), is an American singer, songwriter, multi-instrumentalist, and record producer. He first garnered attention after co-producing the single "U Will Know" ...
, Erykah Badu, Alicia Keys, and Lauryn Hill. D'Angelo's critically acclaimed album ''Voodoo
Voodoo may refer to:
Religions
* African or West African Vodun, practiced by Gbe-speaking ethnic groups
* African diaspora religions, a list of related religions sometimes called Vodou/Voodoo
** Candomblé Jejé, also known as Brazilian Vodu ...
'' (2000) has been recognized by music writers as a masterpiece and the cornerstone of the neo soul genre.
Pop music
 Pop Music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. ''Rock'' and ''pop'' remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which ''pop'' became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible. Although much of the music that appears on record charts is seen as pop music, the genre is distinguished from chart music.
Pop Music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. ''Rock'' and ''pop'' remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which ''pop'' became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible. Although much of the music that appears on record charts is seen as pop music, the genre is distinguished from chart music. Bing Crosby
Harry Lillis "Bing" Crosby Jr. (May 3, 1903 – October 14, 1977) was an American singer, musician and actor. The first multimedia star, he was one of the most popular and influential musical artists of the 20th century worldwide. He was a ...
was one of the first artists to be nicknamed "King of Song" or "King of Popular Music". Indie pop, which developed in the late 1970s, marked another departure from the glamour of contemporary pop music, with guitar bands formed on the then-novel premise that one could record and release their own music without having to procure a record contract from a major label. By the early 1980s, the promotion of pop music had been greatly affected by the rise of music television channels like MTV
MTV (Originally an initialism of Music Television) is an American cable channel that launched on August 1, 1981. Based in New York City, it serves as the flagship property of the MTV Entertainment Group, part of Paramount Media Networks, a di ...
, which "favoured those artists such as Michael Jackson and Madonna
Madonna Louise Ciccone (; ; born August 16, 1958) is an American singer-songwriter and actress. Widely dubbed the " Queen of Pop", Madonna has been noted for her continual reinvention and versatility in music production, songwriting, a ...
who had a strong visual appeal". The 1980s are commonly remembered for an increase in the use of digital recording, associated with the usage of synthesizer
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and ...
s, with synth-pop
Synth-pop (short for synthesizer pop; also called techno-pop; ) is a subgenre of new wave music that first became prominent in the late 1970s and features the synthesizer as the dominant musical instrument. It was prefigured in the 1960s ...
music and other electronic genres featuring non-traditional instruments increasing in popularity. By 2014, pop music worldwide had been permeated by electronic dance music. In 2018, researchers at the University of California, Irvine, concluded that pop music has become 'sadder' since the 1980s. The elements of happiness and brightness have eventually been replaced with the electronic beats making the pop music more 'sad yet danceable'. Kelly Clarkson is the only American singer to be a two-time winners of the Grammy Award for Best Pop Vocal Album as of 2021, Clarkson being the first to win twice. Clarkson and Justin Timberlake
Justin Randall Timberlake (born January 31, 1981) is an American singer, songwriter, and actor. He is one of the world's best-selling music artists, with sales of over 88 million records. Timberlake is the recipient of numerous awards and ac ...
have both been nominated five times, more than any other artist, though Clarkson is the only artist to have the most solo albums nominated. Three of Timberlake's are solo, two are from NSYNC
NSYNC (, ; also stylized as *NSYNC or 'N Sync) was an American boy band formed by Chris Kirkpatrick in Orlando, Florida, in 1995 and launched in Germany by BMG Ariola Munich. Their self-titled debut album was successfully released to European ...
.
Rock, metal, and punk
 Rock and roll developed out of country, blues, and R&B. Rock's exact origins and early influences have been hotly debated, and are the subjects of much scholarship. Though squarely in the blues tradition, rock took elements from
Rock and roll developed out of country, blues, and R&B. Rock's exact origins and early influences have been hotly debated, and are the subjects of much scholarship. Though squarely in the blues tradition, rock took elements from Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
and Latin musical techniques. Rock was an urban style, formed in the areas where diverse populations resulted in the mixtures of African American, Latin and European genres ranging from the blues and country to polka
Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.
History
Etymology
The term ...
and zydeco. Rock and roll first entered popular music through a style called '' rockabilly'', which fused the nascent sound with elements of country music. Black-performed rock and roll had previously had limited mainstream success, but it was the white performer Elvis Presley who first appealed to mainstream audiences with a black style of music, becoming one of the best-selling musicians in history, and brought rock and roll to audiences across the world.
 The 1960s saw several important changes in popular music, especially rock. Many of these changes took place through the British Invasion where bands such as The Beatles, The Who, and The Rolling Stones, became immensely popular and had a profound effect on American culture and music. These changes included the move from professionally composed songs to the
The 1960s saw several important changes in popular music, especially rock. Many of these changes took place through the British Invasion where bands such as The Beatles, The Who, and The Rolling Stones, became immensely popular and had a profound effect on American culture and music. These changes included the move from professionally composed songs to the singer-songwriter
A singer-songwriter is a musician who writes, composes, and performs their own musical material, including lyrics and melodies. In the United States, the category is built on the folk-acoustic tradition, although this role has transmuted thr ...
, and the understanding of popular music as an art, rather than a form of commerce or pure entertainment. These changes led to the rise of musical movements connected to political goals, such as the American Civil Rights Movement and the opposition to the Vietnam War. Rock was at the forefront of this change.
In the early 1960s, rock spawned several subgenres, beginning with surf. Surf was an instrumental guitar genre characterized by a distorted sound, associated with the Southern California surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitabl ...
youth culture. Inspired by the lyrical focus of surf, The Beach Boys began recording in 1961 with an elaborate, pop-friendly, and harmonic sound. As their fame grew, The Beach Boys' songwriter Brian Wilson
Brian Douglas Wilson (born June 20, 1942) is an American musician, singer, songwriter, and record producer who co-founded the Beach Boys. Often called a genius for his novel approaches to pop composition, extraordinary musical aptitude, and m ...
experimented with new studio techniques and became associated with the counterculture. The counterculture was a movement that embraced political activism, and was closely connected to the hippie
A hippie, also spelled hippy, especially in British English, is someone associated with the counterculture of the 1960s, originally a youth movement that began in the United States during the mid-1960s and spread to different countries around ...
subculture. The hippies were associated with folk rock, country rock
Country rock is a genre of music which fuses rock and country. It was developed by rock musicians who began to record country-flavored records in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These musicians recorded rock records using country themes, vocal s ...
, and psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
. Folk and country rock were associated with the rise of politicized folk music, led by Pete Seeger and others, especially at the Greenwich Village music scene in New York. Folk rock entered the mainstream in the middle of the 1960s, when the singer-songwriter Bob Dylan began his career. AllMusic editor Stephen Thomas Erlewine
Stephen Thomas Erlewine (; born June 18, 1973) is an American music critic and senior editor for the online music database AllMusic. He is the author of many artist biographies and record reviews for AllMusic, as well as a freelance writer, occ ...
attributes The Beatles' shift toward introspective songwriting in the mid-1960s to Bob Dylan's influence at the time. He was followed by a number of country-rock bands and soft, folky singer-songwriters. Psychedelic rock was a hard-driving kind of guitar-based rock, closely associated with the city of San Francisco. Though Jefferson Airplane
Jefferson Airplane was an American rock band based in San Francisco, California, that became one of the pioneering bands of psychedelic rock. Formed in 1965, the group defined the San Francisco Sound and was the first from the Bay Area to ac ...
was the only local band to have a major national hit, the Grateful Dead
The Grateful Dead was an American rock music, rock band formed in 1965 in Palo Alto, California. The band is known for its eclectic style, which fused elements of rock, Folk music, folk, country music, country, jazz, bluegrass music, bluegrass, ...
, a country and bluegrass-flavored jam band, became an iconic part of the psychedelic counterculture, associated with hippies, LSD and other symbols of that era. Some say that the Grateful Dead
The Grateful Dead was an American rock music, rock band formed in 1965 in Palo Alto, California. The band is known for its eclectic style, which fused elements of rock, Folk music, folk, country music, country, jazz, bluegrass music, bluegrass, ...
were truly the most American patriotic rock band
A rock band or pop band is a small musical ensemble that performs rock music, pop music, or a related genre. A four-piece band is the most common configuration in rock and pop music. In the early years, the configuration was typically two guita ...
to have ever existed; forming and molding a culture that defines Americans today.
singer-songwriter
A singer-songwriter is a musician who writes, composes, and performs their own musical material, including lyrics and melodies. In the United States, the category is built on the folk-acoustic tradition, although this role has transmuted thr ...
s who drew on the deeply emotional and personal lyrics of 1960s folk rock. The same period saw the rise of bombastic arena rock bands, bluesy Southern rock groups and mellow soft rock
Soft rock is a form of rock music that originated in the late 1960s in Southern California and the United Kingdom which smoothed over the edges of singer-songwriter and pop rock, relying on simple, melodic songs with big, lush productions. S ...
stars. Beginning in the later 1970s, the rock singer and songwriter Bruce Springsteen
Bruce Frederick Joseph Springsteen (born September 23, 1949) is an American singer and songwriter. He has released 21 studio albums, most of which feature his backing band, the E Street Band. Originally from the Jersey Shore, he is an originat ...
became a major star, with anthemic songs and dense, inscrutable lyrics that celebrated the poor and working class.
 Punk was a form of rebellious rock that began in the 1970s, and was loud, aggressive, and often very simple. Punk began as a reaction against the popular music of the period, especially
Punk was a form of rebellious rock that began in the 1970s, and was loud, aggressive, and often very simple. Punk began as a reaction against the popular music of the period, especially disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric pia ...
and arena rock. American bands in the field included, most famously, The Ramones and Talking Heads, the latter playing a more avant-garde style that was closely associated with punk before evolving into mainstream new wave. Other major acts include Blondie, Patti Smith, and Television. In the 1980s some punk fans and bands became disillusioned with the growing popularity of the style, resulting in an even more aggressive style called hardcore punk. Hardcore was a form of sparse punk, consisting of short, fast, intense songs that spoke to disaffected youth, with such influential bands as Bad Religion
Bad Religion is an American punk rock band that formed in Los Angeles, California, in 1980. The band's lyrics cover topics related to religion, politics, society, the media and science. Musically, they are noted for their melodic sensibilitie ...
, Bad Brains, Black Flag, Dead Kennedys, and Minor Threat. Hardcore began in metropolises like Washington, D.C., though most major American cities had their own local scenes in the 1980s.
 Hardcore, punk, and garage rock were the roots of '' alternative rock'', a diverse grouping of rock subgenres that were explicitly opposed to mainstream music, and that arose from the punk and post-punk styles. In the United States, many cities developed local alternative rock scenes, including Minneapolis and Seattle. Seattle's local scene produced grunge music, a dark and brooding style inspired by hardcore, psychedelia, and alternative rock. With the addition of a more melodic element to the sound of bands like Nirvana,
Hardcore, punk, and garage rock were the roots of '' alternative rock'', a diverse grouping of rock subgenres that were explicitly opposed to mainstream music, and that arose from the punk and post-punk styles. In the United States, many cities developed local alternative rock scenes, including Minneapolis and Seattle. Seattle's local scene produced grunge music, a dark and brooding style inspired by hardcore, psychedelia, and alternative rock. With the addition of a more melodic element to the sound of bands like Nirvana, Pearl Jam
Pearl Jam is an American rock band formed in Seattle, Washington, in 1990. The band's lineup consists of founding members Jeff Ament (bass guitar), Stone Gossard (rhythm guitar), Mike McCready (lead guitar), and Eddie Vedder (lead vocals, guita ...
, Soundgarden, and Alice in Chains, grunge became wildly popular across the United States in 1991. Three years later, bands like Green Day
Green Day is an American rock band formed in the East Bay of California in 1987 by lead vocalist and guitarist Billie Joe Armstrong, together with bassist and backing vocalist Mike Dirnt. For most of the band's career, they have been a powe ...
, The Offspring, Rancid, Bad Religion
Bad Religion is an American punk rock band that formed in Los Angeles, California, in 1980. The band's lyrics cover topics related to religion, politics, society, the media and science. Musically, they are noted for their melodic sensibilitie ...
, and NOFX
NOFX () is an American punk rock band formed in Los Angeles, California in 1983. Vocalist/bassist Fat Mike, guitarist Eric Melvin and drummer Erik Sandin are original founding and longest-serving members of the band, who have appeared on every ...
hit the mainstream (with their respective then-new albums '' Dookie'', '' Smash'', '' Let's Go'', '' Stranger than Fiction'' and '' Punk in Drublic'') and brought the California punk scene exposure worldwide.
 Heavy metal is characterized by aggressive, driving rhythms, amplified and distorted guitars, grandiose lyrics, and virtuosic instrumentation. Heavy metal's origins lie in the hard rock bands who took blues and rock and created a heavy sound built on guitar and drums. The first major American bands came in the early 1970s, like Blue Öyster Cult, KISS, and
Heavy metal is characterized by aggressive, driving rhythms, amplified and distorted guitars, grandiose lyrics, and virtuosic instrumentation. Heavy metal's origins lie in the hard rock bands who took blues and rock and created a heavy sound built on guitar and drums. The first major American bands came in the early 1970s, like Blue Öyster Cult, KISS, and Aerosmith
Aerosmith is an American Rock music, rock band formed in Boston in 1970. The group consists of Steven Tyler (lead vocals), Joe Perry (musician), Joe Perry (guitar), Tom Hamilton (musician), Tom Hamilton (bass), Joey Kramer (drums) and Brad Whi ...
. Heavy metal remained, however, a largely underground phenomenon. During the 1980s the first major pop-metal style arose and dominated the charts for several years kicked off by metal act Quiet Riot and dominated by bands such as Mötley Crüe
Mötley Crüe is an American heavy metal band formed in Los Angeles in 1981. The group was founded by bassist Nikki Sixx, drummer Tommy Lee, lead guitarist Mick Mars and lead singer Vince Neil. Mötley Crüe has sold over 100 million albums ...
and Ratt; this was glam metal, a hard rock and pop fusion with a raucous spirit and a glam-influenced visual aesthetic. Some of these bands, like Bon Jovi
Bon Jovi is an American Rock music, rock band formed in 1983 in Sayreville, New Jersey. It consists of singer Jon Bon Jovi, keyboardist David Bryan, drummer Tico Torres, guitarist Phil X, and bassist Hugh McDonald (American musician), Hugh McD ...
, became international stars. The band Guns N' Roses
Guns N' Roses is an American hard rock band from Los Angeles, California, formed in 1985. When they signed to Geffen Records in 1986, the band comprised vocalist Axl Rose, lead guitarist Slash, rhythm guitarist Izzy Stradlin, bassist Duff McKa ...
rose to fame near the end of the decade with an image that was a reaction against the glam metal aesthetic.
By the mid-1980s heavy metal had branched in so many different directions that fans, record companies, and fanzines created numerous subgenres. The United States was especially known for one of these subgenres, thrash metal, which was innovated by bands like Metallica
Metallica is an American heavy metal band. The band was formed in 1981 in Los Angeles by vocalist/guitarist James Hetfield and drummer Lars Ulrich, and has been based in San Francisco for most of its career. The band's fast tempos, instrume ...
, Megadeth
Megadeth is an American thrash metal band formed in Los Angeles in 1983 by vocalist/guitarist Dave Mustaine. Known for their technically complex guitar work and musicianship, Megadeth is one of the "big four" of American thrash metal along wit ...
, Slayer
Slayer was an American thrash metal band from Huntington Park, California. The band was formed in 1981 by guitarists Kerry King and Jeff Hanneman, drummer Dave Lombardo and bassist/vocalist Tom Araya. Slayer's fast and aggressive musical style ...
, and Anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The sk ...
, with Metallica being the most commercially successful. The United States was known as one of the birthplaces of death metal
Death metal is an extreme subgenre of heavy metal music. It typically employs heavily distorted and low-tuned guitars, played with techniques such as palm muting and tremolo picking; deep growling vocals; aggressive, powerful drumming, feat ...
during the mid to late 1980s. The Florida scene was the most well-known, featuring bands like Death, Cannibal Corpse
Cannibal Corpse is an American death metal band formed in Buffalo, New York in 1988, now based out of Tampa, Florida. The band has released fifteen studio albums, two box sets, four video albums, and two live albums. The band has had little radi ...
, Morbid Angel, Deicide, and many others. There are now countless death metal and deathgrind bands across the country.
Hip hop
Hip hop is a cultural movement, of which music is a part. Hip hop music for the most part is itself composed of two parts:rapping
Rapping (also rhyming, spitting, emceeing or MCing) is a musical form of vocal delivery that incorporates "rhyme, rhythmic speech, and street vernacular". It is performed or chanted, usually over a backing beat or musical accompaniment. The ...
, the delivery of swift, highly rhythmic and lyrical vocals; and DJing and/or music production, producing, the production of instrumentation through sampling (music), sampling, musical instrument, instrumentation, turntablism, or beatboxing, the production of musical sounds through vocalized tones. Hip hop arose in the early 1970s in The Bronx, New York City. Jamaican immigrant DJ Kool Herc is widely regarded as the progenitor of hip hop; he brought with him from Jamaica the practice of Deejay (Jamaican), toasting over the rhythms of popular songs. Emcees originally arose to introduce the soul, funk, and R&B songs that the DJs played, and to keep the crowd excited and dancing; over time, the DJs began isolating the percussion break of songs (when the rhythm climaxes), producing a repeated beat that the emcees rapped over.
 Unlike Motown which predicated its mainstream success on the class appeal of its acts that rendered racial identity irrelevant, hip hop of 1980s, particularly hip hop that crossed over to rock-and-roll, was predicated on its (implicit but emphatic) primary identification with black identity. By the beginning of the 1980s, there were popular hip hop songs, and the celebrities of the scene, like LL Cool J, gained mainstream renown. Other performers experimented with politicized lyrics and social awareness, or fused hip hop with jazz, heavy metal, techno, funk and soul. New styles appeared in the latter part of the 1980s, like alternative hip hop and the closely related jazz rap fusion, pioneered by rappers like De La Soul.
Gangsta rap is a kind of hip hop, most importantly characterized by a lyrical focus on macho sexuality, physicality, and a dangerous criminal image. Though the origins of gangsta rap can be traced back to the mid-1980s style of Philadelphia's Schoolly D and the West Coast's Ice-T, the style broadened and came to apply to many different regions in the country, to rappers from New York, such as Notorious B.I.G. and influential hip hop group Wu-Tang Clan, and to rappers on the West Coast, such as Too Short and N.W.A. A distinctive West Coast rap scene spawned the early 1990s G-funk sound, which paired gangsta rap lyrics with a thick and hazy sound, often from 1970s funk sampling (music), samples; the best-known proponents were the rappers 2Pac, Dr. Dre, Ice Cube, and Snoop Dogg. Gangsta rap continued to exert a major presence in American popular music through the end of the 1990s and early into the 21st century.
The dominance of gangsta rap in mainstream hip-hop was supplanted in the late-2000s, largely due to the mainstream success of hip-hop artists such as Kanye West. The outcome of a highly publicized Graduation (album)#Release, sales competition between the simultaneous release of his and gangsta rapper 50 Cent's third studio albums, ''Graduation (album), Graduation'' and ''Curtis (50 Cent album), Curtis'' respectively, has since been accredited to the decline. The competition resulted in record-breaking sales performances by both albums and West outsold 50 Cent, selling nearly a million copies of ''Graduation'' in the first week alone. Industry observers remark that West's victory over 50 Cent proved that rap music did not have to conform to gangsta-rap conventions in order to be commercially successful. West effectively paved the way for a new wave of hip-hop artists, including Drake (rapper), Drake, Kendrick Lamar and J. Cole, who did not follow the hardcore hip hop, hardcore-gangsta rap, gangster mold and became platinum-selling artists.
Jay-Z became an internationally renowned hip hop icon in the wake of the deaths of The Notorious B.I.G. and Tupac Shakur in the mid-1990s. Kanye West was mentored by Jay-Z and produced for him, before attaining a similar level of success.
Unlike Motown which predicated its mainstream success on the class appeal of its acts that rendered racial identity irrelevant, hip hop of 1980s, particularly hip hop that crossed over to rock-and-roll, was predicated on its (implicit but emphatic) primary identification with black identity. By the beginning of the 1980s, there were popular hip hop songs, and the celebrities of the scene, like LL Cool J, gained mainstream renown. Other performers experimented with politicized lyrics and social awareness, or fused hip hop with jazz, heavy metal, techno, funk and soul. New styles appeared in the latter part of the 1980s, like alternative hip hop and the closely related jazz rap fusion, pioneered by rappers like De La Soul.
Gangsta rap is a kind of hip hop, most importantly characterized by a lyrical focus on macho sexuality, physicality, and a dangerous criminal image. Though the origins of gangsta rap can be traced back to the mid-1980s style of Philadelphia's Schoolly D and the West Coast's Ice-T, the style broadened and came to apply to many different regions in the country, to rappers from New York, such as Notorious B.I.G. and influential hip hop group Wu-Tang Clan, and to rappers on the West Coast, such as Too Short and N.W.A. A distinctive West Coast rap scene spawned the early 1990s G-funk sound, which paired gangsta rap lyrics with a thick and hazy sound, often from 1970s funk sampling (music), samples; the best-known proponents were the rappers 2Pac, Dr. Dre, Ice Cube, and Snoop Dogg. Gangsta rap continued to exert a major presence in American popular music through the end of the 1990s and early into the 21st century.
The dominance of gangsta rap in mainstream hip-hop was supplanted in the late-2000s, largely due to the mainstream success of hip-hop artists such as Kanye West. The outcome of a highly publicized Graduation (album)#Release, sales competition between the simultaneous release of his and gangsta rapper 50 Cent's third studio albums, ''Graduation (album), Graduation'' and ''Curtis (50 Cent album), Curtis'' respectively, has since been accredited to the decline. The competition resulted in record-breaking sales performances by both albums and West outsold 50 Cent, selling nearly a million copies of ''Graduation'' in the first week alone. Industry observers remark that West's victory over 50 Cent proved that rap music did not have to conform to gangsta-rap conventions in order to be commercially successful. West effectively paved the way for a new wave of hip-hop artists, including Drake (rapper), Drake, Kendrick Lamar and J. Cole, who did not follow the hardcore hip hop, hardcore-gangsta rap, gangster mold and became platinum-selling artists.
Jay-Z became an internationally renowned hip hop icon in the wake of the deaths of The Notorious B.I.G. and Tupac Shakur in the mid-1990s. Kanye West was mentored by Jay-Z and produced for him, before attaining a similar level of success.
 Female rappers Nicki Minaj, Cardi B, Saweetie, Doja Cat, Iggy Azalea, City Girls and Megan Thee Stallion also entered the mainstream. There are many women that have notably influenced the hip hop culture. However, a few names that cannot go unsaid are MC Sha-rock, MC Lyte, Queen Latifah, Lauryn Hill, Missy Elliot, Lil Kim, Erykah Badu, Foxy Brown (rapper), Foxy Brown, and many more. Of this list MC Sha-rock is considered the historian/pioneer of female hip-hop culture. She started her career as a break-dancer in the Bronx, New York and later became "The hip-hop's culture's first female emcee/rapper". Her career has been long-lived. From being a former member of the Funky 4+1 more to having MC rhyming battles with groups such as Grandmaster Flash and Furious 5. Another notable pioneer of female hip-hop is the famous Queen Latifah, Born Dana Elaine Owens in Newark,NJ. Queen Latifah started her career from a young age, as early as 17. But, not long after it began it soon took-off. She released her first full length album, ''All Hail the Queen'' in 1989. As she continued to release music she grew more and more popular, and her fame increased amidst the hip-hop culture. However, Queen Latifah was not an ordinary rapper. She rapped about the issues surrounding being a black woman and overall social injustice issues that appear in the music industry. These early pioneers have led female rap culture and impacted today's popular female hip-hop artists. For example, such popular artists may include Cardi B, Megan Thee Stallion, Miss Mulatto, Flo Milli, Cupcakke and many others. Each artists has their own identity in the rap game, however as hip-hop evolves so does the style of music. Cardi B's first studio album, ''Invasion of Privacy (album), Invasion of Privacy'' (2018), debuted at number one on the Billboard 200, '' Billboard'' 200 and was named the number-one female rap album of the 2010s by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard''. Critically acclaimed, it made Cardi B the only woman to win the Grammy Award for Best Rap Album as a solo artist, and marked the first female rap album in fifteen years to be nominated for Grammy Award for Album of the Year, Album of the Year.
Female rappers Nicki Minaj, Cardi B, Saweetie, Doja Cat, Iggy Azalea, City Girls and Megan Thee Stallion also entered the mainstream. There are many women that have notably influenced the hip hop culture. However, a few names that cannot go unsaid are MC Sha-rock, MC Lyte, Queen Latifah, Lauryn Hill, Missy Elliot, Lil Kim, Erykah Badu, Foxy Brown (rapper), Foxy Brown, and many more. Of this list MC Sha-rock is considered the historian/pioneer of female hip-hop culture. She started her career as a break-dancer in the Bronx, New York and later became "The hip-hop's culture's first female emcee/rapper". Her career has been long-lived. From being a former member of the Funky 4+1 more to having MC rhyming battles with groups such as Grandmaster Flash and Furious 5. Another notable pioneer of female hip-hop is the famous Queen Latifah, Born Dana Elaine Owens in Newark,NJ. Queen Latifah started her career from a young age, as early as 17. But, not long after it began it soon took-off. She released her first full length album, ''All Hail the Queen'' in 1989. As she continued to release music she grew more and more popular, and her fame increased amidst the hip-hop culture. However, Queen Latifah was not an ordinary rapper. She rapped about the issues surrounding being a black woman and overall social injustice issues that appear in the music industry. These early pioneers have led female rap culture and impacted today's popular female hip-hop artists. For example, such popular artists may include Cardi B, Megan Thee Stallion, Miss Mulatto, Flo Milli, Cupcakke and many others. Each artists has their own identity in the rap game, however as hip-hop evolves so does the style of music. Cardi B's first studio album, ''Invasion of Privacy (album), Invasion of Privacy'' (2018), debuted at number one on the Billboard 200, '' Billboard'' 200 and was named the number-one female rap album of the 2010s by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard''. Critically acclaimed, it made Cardi B the only woman to win the Grammy Award for Best Rap Album as a solo artist, and marked the first female rap album in fifteen years to be nominated for Grammy Award for Album of the Year, Album of the Year.
Other niche styles and Latin American music
 The American music industry is dominated by large companies that produce, market, and distribute certain kinds of music. Generally, these companies do not produce, or produce in only very limited quantities, recordings in styles that do not appeal to very large audiences. Smaller companies often fill in the void, offering a wide variety of recordings in styles ranging from
The American music industry is dominated by large companies that produce, market, and distribute certain kinds of music. Generally, these companies do not produce, or produce in only very limited quantities, recordings in styles that do not appeal to very large audiences. Smaller companies often fill in the void, offering a wide variety of recordings in styles ranging from polka
Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.
History
Etymology
The term ...
to salsa
Salsa most often refers to:
* Salsa (Mexican cuisine), a variety of sauces used as condiments
* Salsa music, a popular style of Latin American music
* Salsa (dance), a Latin dance associated with Salsa music
Salsa or SALSA may also refer to:
A ...
. Many small music industries are built around a core fanbase who may be based largely in one region, such as Tejano music, Tejano or music of Hawaii, Hawaiian music, or they may be widely dispersed, such as the audience for Jewish klezmer.
Among the Hispanic American musicians who were pioneers in the early stages of rock and roll were Ritchie Valens, who scored several hits, most notably "La Bamba (song), La Bamba" and Herman Santiago wrote the lyrics to the iconic rock and roll song "Why Do Fools Fall in Love (song), Why Do Fools Fall in Love". Songs that became popular in the United States and are heard during the Holiday/Christmas season are "¿Dónde Está Santa Claus?" is a novelty Christmas song with 12-year-old Augie Ríos was a record hit in 1959 which featured the Mark Jeffrey Orchestra. "Feliz Navidad (song), Feliz Navidad"(1970) by José Feliciano is another famous Latin song.
 The single largest niche industry is based on Latin music. Latin music has long influenced American popular music, and was an especially crucial part of the development of jazz. Modern pop Latin styles include a wide array of genres imported from across Latin America, including Colombian cumbia, Puerto Rican reggaeton, and Mexican
The single largest niche industry is based on Latin music. Latin music has long influenced American popular music, and was an especially crucial part of the development of jazz. Modern pop Latin styles include a wide array of genres imported from across Latin America, including Colombian cumbia, Puerto Rican reggaeton, and Mexican corrido
The corrido () is a popular narrative metrical tale and poetry that forms a ballad. The songs are often about oppression, history, daily life for criminals, the vaquero lifestyle, and other socially relevant topics. Corridos were widely popular ...
. Latin popular music in the United States began with a wave of dance bands in the 1930s and 1950s. The most popular styles included the conga, Cuban Rumba, rumba, and mambo (music), mambo. In the 1950s Perez Prado made the cha-cha-cha (music), cha-cha-cha famous, and the rise of Afro-Cuban jazz opened many ears to the harmonic, melodic, and rhythmic possibilities of Latin music. The most famous American form of Latin music, however, is salsa
Salsa most often refers to:
* Salsa (Mexican cuisine), a variety of sauces used as condiments
* Salsa music, a popular style of Latin American music
* Salsa (dance), a Latin dance associated with Salsa music
Salsa or SALSA may also refer to:
A ...
. Salsa incorporates many styles and variations; the term can be used to describe most forms of popular Cuban-derived genres. Most specifically, however, ''salsa'' refers to a particular style that was developed by mid-1970s groups of New York City-area Cuban and Puerto Rican immigrants, and stylistic descendants like 1980s salsa romantica. Salsa rhythms are complicated, with several patterns played simultaneously. The clave (rhythm), clave rhythm forms the basis of salsa songs and is used by the performers as a common rhythmic ground for their own phrase (music), phrases.
Latin American music has long influenced American popular music, jazz, rhythm and blues, and even country music. This includes music from Spanish, Portuguese, and (sometimes) French-speaking countries and territories of Latin America.
Today, the American record industry defines Latin music as any type of release with lyrics mostly in Spanish. Mainstream artists and producers tend to feature more on songs from Latin artists and it's also become more likely that English language songs crossover to Spanish radio and vice versa.
The United States played a significant role in the development of electronic dance music, specifically house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
and techno, which originated in Chicago and Detroit, respectively.
Today Latin American music has become a term for music performed by Latinos regardless of whether it has a Latin element or not. Acts such as Shakira, Jennifer Lopez, Enrique Iglesias, Pitbull (rapper), Pitbull, Selena Gomez, Christina Aguilera, Gloria Estefan, Demi Lovato, Mariah Carey
Mariah Carey (; born March 27, 1969) is an American singer, songwriter, actress, and record producer. Referred to as the " Songbird Supreme", she is noted for her five-octave vocal range, melismatic singing style and signature use of the whi ...
, Becky G, Paulina Rubio, and Camila Cabello are prominent on the pop charts. Iglesias who holds the record for most #1s on Billboard's Hot Latin Tracks released a bilingual album, inspired by urban acts he releases two completely different songs to Latin and pop formats at the same time.
Government, politics and law
Industry and economics
 The United States has the world's global music industry market share data, largest music market with a total retail value of 4.9 billion dollars in 2014, The American music industry includes a number of fields, ranging from record companies to radio in the United States, radio stations and community orchestras. Total industry revenue is about $40 billion worldwide, and about $12 billion in the United States. Most of the world's major label, major record companies are based in the United States; they are represented by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). The major record companies produce material by artists that have signed to one of their record labels, a brand name often associated with a particular genre or record producer. Record companies may also promote and market their artists, through advertising, public performances and concerts, and television appearances. Record companies may be affiliated with other music media companies, which produce a product related to popular recorded music. These include television channels like
The United States has the world's global music industry market share data, largest music market with a total retail value of 4.9 billion dollars in 2014, The American music industry includes a number of fields, ranging from record companies to radio in the United States, radio stations and community orchestras. Total industry revenue is about $40 billion worldwide, and about $12 billion in the United States. Most of the world's major label, major record companies are based in the United States; they are represented by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). The major record companies produce material by artists that have signed to one of their record labels, a brand name often associated with a particular genre or record producer. Record companies may also promote and market their artists, through advertising, public performances and concerts, and television appearances. Record companies may be affiliated with other music media companies, which produce a product related to popular recorded music. These include television channels like MTV
MTV (Originally an initialism of Music Television) is an American cable channel that launched on August 1, 1981. Based in New York City, it serves as the flagship property of the MTV Entertainment Group, part of Paramount Media Networks, a di ...
, magazines like ''Rolling Stone'' and radio stations. In recent years the music industry has been embroiled in turmoil over the rise of the Internet downloading of copyrighted music; many musicians and the RIAA have sought to punish fans who illegally download copyrighted music.Garofalo, p. 445–446.
 Radio stations in the United States often broadcast popular music. Each music station has a radio format, format, or a category of songs to be played; these are generally similar to but not the same as ordinary generic classification. Many radio stations in the United States are locally owned and operated, and may offer an eclectic assortment of recordings; many other stations are owned by large companies like Clear Channel Communications, Clear Channel, and are generally formatted on smaller, more repetitive playlists. Commercial sales of recordings are tracked by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard'' magazine, which compiles a number of music charts for various fields of recorded music sales. The Billboard Hot 100, ''Billboard'' Hot 100 is the top pop music chart for single (music), singles, a recording consisting of a handful of songs; longer pop recordings are albums, and are tracked by the Billboard 200, ''Billboard'' 200. Though recorded music is commonplace in American homes, many of the music industry's revenue comes from a small number of devotees; for example, 62% of album sales come from less than 25% of the music-buying audience. Total CD sales in the United States topped 705 million units sold in 2005, and singles sales just under three million.
Though the major record companies dominate the American music industry, an indie music, independent music industry (''indie music'') does exist. Most indie record labels have limited, if any, retail distribution outside a small region. Artists sometimes record for an indie label and gain enough acclaim to be signed to a major label; others choose to remain at an indie label for their entire careers. Indie music may be in styles generally similar to mainstream music, but is often inaccessible, unusual, or otherwise unappealing to many people. Indie musicians often release some or all of their songs over the Internet for fans and others to download and listen. In addition to recording artists of many kinds, there are numerous fields of professional musicianship in the United States, many of whom rarely record, including community orchestras, wedding singers and bands, lounge singers, and nightclub DJs. The American Federation of Musicians is the largest American trade union, labor union for professional musicians. However, only 15% of the Federation's members have steady music employment.
Radio stations in the United States often broadcast popular music. Each music station has a radio format, format, or a category of songs to be played; these are generally similar to but not the same as ordinary generic classification. Many radio stations in the United States are locally owned and operated, and may offer an eclectic assortment of recordings; many other stations are owned by large companies like Clear Channel Communications, Clear Channel, and are generally formatted on smaller, more repetitive playlists. Commercial sales of recordings are tracked by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard'' magazine, which compiles a number of music charts for various fields of recorded music sales. The Billboard Hot 100, ''Billboard'' Hot 100 is the top pop music chart for single (music), singles, a recording consisting of a handful of songs; longer pop recordings are albums, and are tracked by the Billboard 200, ''Billboard'' 200. Though recorded music is commonplace in American homes, many of the music industry's revenue comes from a small number of devotees; for example, 62% of album sales come from less than 25% of the music-buying audience. Total CD sales in the United States topped 705 million units sold in 2005, and singles sales just under three million.
Though the major record companies dominate the American music industry, an indie music, independent music industry (''indie music'') does exist. Most indie record labels have limited, if any, retail distribution outside a small region. Artists sometimes record for an indie label and gain enough acclaim to be signed to a major label; others choose to remain at an indie label for their entire careers. Indie music may be in styles generally similar to mainstream music, but is often inaccessible, unusual, or otherwise unappealing to many people. Indie musicians often release some or all of their songs over the Internet for fans and others to download and listen. In addition to recording artists of many kinds, there are numerous fields of professional musicianship in the United States, many of whom rarely record, including community orchestras, wedding singers and bands, lounge singers, and nightclub DJs. The American Federation of Musicians is the largest American trade union, labor union for professional musicians. However, only 15% of the Federation's members have steady music employment.
Education and scholarship
 Music is an important part of education in the United States, and is a part of most or all school systems in the country. Music education is generally mandatory in public elementary schools, and is an elective in later years.
Music is an important part of education in the United States, and is a part of most or all school systems in the country. Music education is generally mandatory in public elementary schools, and is an elective in later years.
 The scholarly study of music in the United States includes work relating music to social class, racial, ethnic and religious identity, gender and sexuality, as well as studies of music history, musicology, and other topics. The academic study of American music can be traced back to the late 19th century, when researchers like Alice Fletcher and Francis La Flesche studied the music of the Omaha (tribe), Omaha peoples, working for the Bureau of American Ethnology and the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. In the 1890s and into the early 20th century, musicological recordings were made among indigenous, Hispanic, African-American and Anglo-American peoples of the United States. Many worked for the Library of Congress, first under the leadership of Oscar Sonneck, chief of the Library's Music Divisions.Blum, Stephen, "Sources, Scholarship and Historiography" in the ''Garland Encyclopedia of World Music''. These researchers included Robert W. Gordon, founder of the Archive of American Folk Song, and John Lomax, John and Alan Lomax; Alan Lomax was the most prominent of several folk song collectors who helped to inspire the 20th century roots revival of American folk culture.
The scholarly study of music in the United States includes work relating music to social class, racial, ethnic and religious identity, gender and sexuality, as well as studies of music history, musicology, and other topics. The academic study of American music can be traced back to the late 19th century, when researchers like Alice Fletcher and Francis La Flesche studied the music of the Omaha (tribe), Omaha peoples, working for the Bureau of American Ethnology and the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. In the 1890s and into the early 20th century, musicological recordings were made among indigenous, Hispanic, African-American and Anglo-American peoples of the United States. Many worked for the Library of Congress, first under the leadership of Oscar Sonneck, chief of the Library's Music Divisions.Blum, Stephen, "Sources, Scholarship and Historiography" in the ''Garland Encyclopedia of World Music''. These researchers included Robert W. Gordon, founder of the Archive of American Folk Song, and John Lomax, John and Alan Lomax; Alan Lomax was the most prominent of several folk song collectors who helped to inspire the 20th century roots revival of American folk culture.
 Early 20th scholarly analysis of American music tended to interpret European-derived classical traditions as the most worthy of study, with the folk, religious, and traditional musics of the common people denigrated as low-class and of little artistic or social worth. American music history was compared to the much longer historical record of European nations, and was found wanting, leading writers like the composer Arthur Farwell to ponder what sorts of musical traditions might arise from American culture, in his 1915 ''Music in America''. In 1930, John Tasker Howard's ''Our American Music'' became a standard analysis, focusing on largely on concert music composed in the United States.Crawford, p. x. Since the analysis of musicologist Charles Seeger in the mid-20th century, American music history has often been described as intimately related to perceptions of race and ancestry. Under this view, the diverse racial and ethnic background of the United States has both promoted a sense of musical separation between the races, while still fostering constant acculturation, as elements of European, African, and indigenous musics have shifted between fields. Gilbert Chase's ''America's Music, from the Pilgrims to the Present'', was the first major work to examine the music of the entire United States, and recognize folk traditions as more culturally significant than music for the concert hall. Chase's analysis of a diverse American musical identity has remained the dominant view among the academic establishment. Until the 1960s and 1970s, however, most musical scholars in the United States continued to study European music, limiting themselves only to certain fields of American music, especially European-derived classical and operatic styles, and sometimes African American jazz. More modern musicologists and ethnomusicologists have studied subjects ranging from the national musical identity to the individual styles and techniques of specific communities in a particular time of American history. Prominent recent studies of American music include Charles Hamm's ''Music in the New World'' from 1983 and Richard Crawford (music historian), Richard Crawford's ''America's Musical Life'' from 2001.Crawford, p. x–xi.
Early 20th scholarly analysis of American music tended to interpret European-derived classical traditions as the most worthy of study, with the folk, religious, and traditional musics of the common people denigrated as low-class and of little artistic or social worth. American music history was compared to the much longer historical record of European nations, and was found wanting, leading writers like the composer Arthur Farwell to ponder what sorts of musical traditions might arise from American culture, in his 1915 ''Music in America''. In 1930, John Tasker Howard's ''Our American Music'' became a standard analysis, focusing on largely on concert music composed in the United States.Crawford, p. x. Since the analysis of musicologist Charles Seeger in the mid-20th century, American music history has often been described as intimately related to perceptions of race and ancestry. Under this view, the diverse racial and ethnic background of the United States has both promoted a sense of musical separation between the races, while still fostering constant acculturation, as elements of European, African, and indigenous musics have shifted between fields. Gilbert Chase's ''America's Music, from the Pilgrims to the Present'', was the first major work to examine the music of the entire United States, and recognize folk traditions as more culturally significant than music for the concert hall. Chase's analysis of a diverse American musical identity has remained the dominant view among the academic establishment. Until the 1960s and 1970s, however, most musical scholars in the United States continued to study European music, limiting themselves only to certain fields of American music, especially European-derived classical and operatic styles, and sometimes African American jazz. More modern musicologists and ethnomusicologists have studied subjects ranging from the national musical identity to the individual styles and techniques of specific communities in a particular time of American history. Prominent recent studies of American music include Charles Hamm's ''Music in the New World'' from 1983 and Richard Crawford (music historian), Richard Crawford's ''America's Musical Life'' from 2001.Crawford, p. x–xi.
Holidays and festivals
Music is an important part of several American holidays, especially playing a major part in the wintertime celebration of Christmas. Christmas music, Music of the holiday includes both religious songs like "O Holy Night" and secular songs like "Jingle Bells". Patriotic songs like the national anthem, " The Star-Spangled Banner", are a major part of Independence Day (United States), Independence Day celebrations. Music also plays a role at many regional holidays that are not celebrated nationwide, most famously Mardi Gras, a music and dance parade and festival in New Orleans, Louisiana. The United States is home to numerous music festivals, which showcase styles ranging from the blues and jazz to indie rock and heavy metal. Some music festivals are strictly local in scope, including few or no performers with a national reputation, and are generally operated by local promoters. The large recording companies operate their own music festivals, such as Lollapalooza and Ozzfest, which draw huge crowds.See also
*Protest songs in the United States By region: *Music of Atlanta, Atlanta *Music of Austin, Texas, Austin *Music of Chicago, Chicago *Music of Detroit, Detroit *Music of Kentucky, Ketucky *Music of Los Angeles, Los Angeles *Music of Massachusetts, Massachusetts *Music of Miami, Miami *Minneapolis Sound, Minneapolis *Music of Missouri, Missouri *Music of Nevada, Nevada *Music of New Orleans, New Orleans *Music of New York City, New York City *Music of Ohio, Ohio *Music of Oregon, Oregon *Music of Philadelphia, Philadelphia *San Francisco Sound, San Francisco *Music of Puerto Rico, San Juan *Music of Seattle, Seattle *Music of Texas, Texas *Music of Washington, D.C., Washington, D.C.Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
Audio clips: Traditional music of the United States.
Musée d'Ethnographie de Genève. Accessed November 25, 2010.
American Guild of Music
6 Ever American Trending Music Stars
Music Publisher's Association
Music Library Association
Historic American Sheet Music
Lester S. Levy Sheet Music Collection
popular American music, 1780–1960 {{DEFAULTSORT:Music Of The United States American music, Performing arts pages with videographic documentation