Museums In Santa Fe, New Mexico on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Santa Fe ( ; , Spanish for 'Holy Faith'; tew, Oghá P'o'oge, Tewa for 'white shell water place'; tiw, Hulp'ó'ona, label=
 Lack of Native American representation within the province of
Lack of Native American representation within the province of

 In 1846, the United States declared war on Mexico. Brigadier General
In 1846, the United States declared war on Mexico. Brigadier General  On October 21, 1887,
On October 21, 1887,  Neither was sufficient to offset the negative effects of Santa Fe's having been bypassed by the main railroad route. It suffered gradual economic decline into the early 20th century. Activists created a number of resources for the arts and
Neither was sufficient to offset the negative effects of Santa Fe's having been bypassed by the main railroad route. It suffered gradual economic decline into the early 20th century. Activists created a number of resources for the arts and
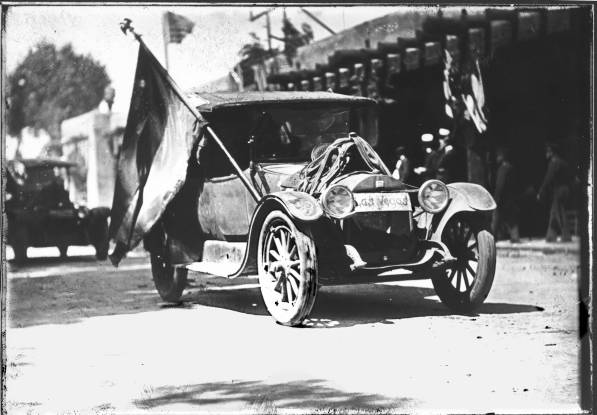 After the mainline of the railroad bypassed Santa Fe, it lost population. However, artists and writers, as well as retirees, were attracted to the cultural richness of the area, the beauty of the landscapes, and its dry climate. Local leaders began promoting the city as a tourist attraction. The city sponsored architectural restoration projects and erected new buildings according to traditional techniques and styles, thus creating the Santa Fe Style.
Edgar L. Hewett, founder and first director of the
After the mainline of the railroad bypassed Santa Fe, it lost population. However, artists and writers, as well as retirees, were attracted to the cultural richness of the area, the beauty of the landscapes, and its dry climate. Local leaders began promoting the city as a tourist attraction. The city sponsored architectural restoration projects and erected new buildings according to traditional techniques and styles, thus creating the Santa Fe Style.
Edgar L. Hewett, founder and first director of the
 According to the
According to the
 The Spanish laid out the city according to the "
The Spanish laid out the city according to the " To achieve that goal, the city created the idea of imposing a unified building style – the Spanish Pueblo Revival look, which was based on work done restoring the Palace of the Governors. The sources for this style came from the many defining features of local architecture: (rough, exposed beams that extrude through supporting walls, and are thus visible outside as well as inside the building) and (rain spouts cut into short parapet walls around flat roofs), features borrowed from many old adobe homes and churches built many years before and found in the Pueblos, along with the earth-toned look (reproduced in
To achieve that goal, the city created the idea of imposing a unified building style – the Spanish Pueblo Revival look, which was based on work done restoring the Palace of the Governors. The sources for this style came from the many defining features of local architecture: (rough, exposed beams that extrude through supporting walls, and are thus visible outside as well as inside the building) and (rain spouts cut into short parapet walls around flat roofs), features borrowed from many old adobe homes and churches built many years before and found in the Pueblos, along with the earth-toned look (reproduced in  In a September 2003 report by Angelou Economics, it was determined that Santa Fe should focus its economic development efforts in the following seven industries: Arts and Culture, Design, Hospitality, Conservation Technologies, Software Development, Publishing and New Media, and Outdoor Gear and Apparel. Three secondary targeted industries for Santa Fe to focus development in are health care, retiree services, and food & beverage. Angelou Economics recognized three economic signs that Santa Fe's economy was at risk of long-term deterioration. These signs were; a lack of business diversity which tied the city too closely to fluctuations in tourism and the government sector; the beginnings of urban sprawl, as a result of Santa Fe County growing faster than the city, meaning people will move farther outside the city to find land and lower costs for housing; and an aging population coupled with a rapidly shrinking population of individuals under 45 years old, making Santa Fe less attractive to business recruits. The seven industries recommended by the report "represent a good mix for short-, mid-, and long-term economic cultivation."
In a September 2003 report by Angelou Economics, it was determined that Santa Fe should focus its economic development efforts in the following seven industries: Arts and Culture, Design, Hospitality, Conservation Technologies, Software Development, Publishing and New Media, and Outdoor Gear and Apparel. Three secondary targeted industries for Santa Fe to focus development in are health care, retiree services, and food & beverage. Angelou Economics recognized three economic signs that Santa Fe's economy was at risk of long-term deterioration. These signs were; a lack of business diversity which tied the city too closely to fluctuations in tourism and the government sector; the beginnings of urban sprawl, as a result of Santa Fe County growing faster than the city, meaning people will move farther outside the city to find land and lower costs for housing; and an aging population coupled with a rapidly shrinking population of individuals under 45 years old, making Santa Fe less attractive to business recruits. The seven industries recommended by the report "represent a good mix for short-, mid-, and long-term economic cultivation."
 *
*
 The city is well known as a center for arts that reflect the multicultural character of the city; it has been designated as a UNESCO Creative City in Design, Crafts and Folk Art.
In 2012, the city was listed among the 10 best places to retire in the U.S. by ''
The city is well known as a center for arts that reflect the multicultural character of the city; it has been designated as a UNESCO Creative City in Design, Crafts and Folk Art.
In 2012, the city was listed among the 10 best places to retire in the U.S. by ''

 Canyon Road, east of the Plaza, has the highest concentration of art galleries in the city, and is a major destination for international collectors, tourists and locals. The Canyon Road galleries showcase a wide array of contemporary,
Canyon Road, east of the Plaza, has the highest concentration of art galleries in the city, and is a major destination for international collectors, tourists and locals. The Canyon Road galleries showcase a wide array of contemporary,
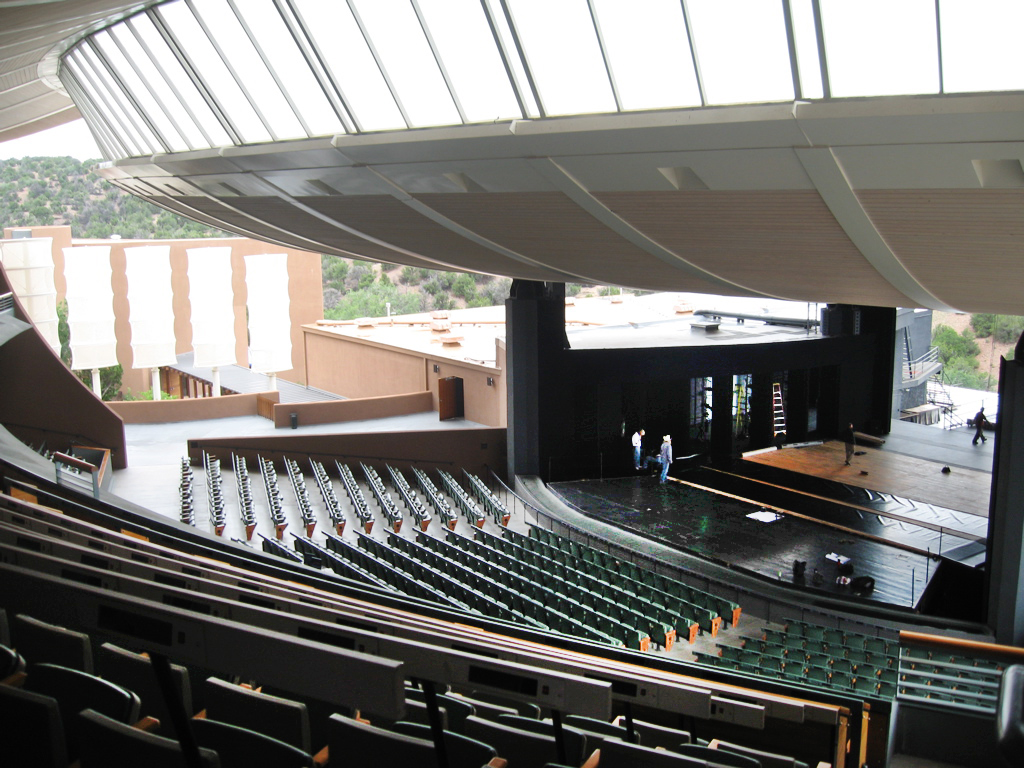 Performance Santa Fe, formerly the Santa Fe Concert Association, is the oldest presenting organization in Santa Fe. Founded in 1937, Performance Santa Fe brings celebrated and legendary musicians as well as some of the world's greatest dancers and actors to the city year-round. The
Performance Santa Fe, formerly the Santa Fe Concert Association, is the oldest presenting organization in Santa Fe. Founded in 1937, Performance Santa Fe brings celebrated and legendary musicians as well as some of the world's greatest dancers and actors to the city year-round. The
 Tourism is a major element of the Santa Fe economy, with visitors attracted year-round by the climate and related outdoor activities (such as skiing in years of adequate snowfall; hiking in other seasons) plus cultural activities of the city and the region. Tourism information is provided by the
Tourism is a major element of the Santa Fe economy, with visitors attracted year-round by the climate and related outdoor activities (such as skiing in years of adequate snowfall; hiking in other seasons) plus cultural activities of the city and the region. Tourism information is provided by the
 Santa Fe has three public high schools:
* Santa Fe High School (1,500 students)
* Capital High School (1,300 students)
* New Mexico School for the Arts (200 students)
Public schools in Santa Fe are operated by
Santa Fe has three public high schools:
* Santa Fe High School (1,500 students)
* Capital High School (1,300 students)
* New Mexico School for the Arts (200 students)
Public schools in Santa Fe are operated by
 Santa Fe Trails, run by the city, operates a number of bus routes within the city during business hours and also provides connections to regional transit.
The
Santa Fe Trails, run by the city, operates a number of bus routes within the city during business hours and also provides connections to regional transit.
The
 *
*  *
*  *
*
Santa Fe Convention & Visitors Bureau official tourism website
Santa Fe Chamber of Commerce
* {{Authority control Santa Fe Cities in New Mexico Cities in Santa Fe County, New Mexico County seats in New Mexico Populated places established in 1610 1610 establishments in New Spain
Northern Tiwa
The Taos language of the Tiwa languages, Northern Tiwa branch of the Tanoan language family is spoken in Taos Pueblo, New Mexico.
Sociolinguistics
In data collected in 1935 and 1937, George L. Trager (1946) notes that Taos was spoken by all mem ...
; nv, Yootó, Navajo for 'bead + water place') is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
. The name “Santa Fe” means 'Holy Faith' in Spanish, and the city's full name as founded remains ('The Royal Town of the Holy Faith of Saint Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a Mysticism, mystic Italian Catholic Church, Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most vener ...
').
With a population of 87,505 at the 2020 census, it is the fourth-largest city in New Mexico. It is also the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
of Santa Fe County
Santa Fe County ( es, Condado de Santa Fe; meaning ''Holy faith'' in Spanish) is located in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 144,170, making it New Mexico's third-most populous county, after Bernalillo Cou ...
. Its metropolitan area is part of the Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
–Santa Fe–Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
combined statistical area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
, which had a population of 1,162,523 in 2020. Human settlement dates back thousands of years in the region, the placita was founded in 1610 as the capital of . It replaced the previous capital, , near modern Española, at San Gabriel de Yungue-Ouinge, which makes it the oldest state capital in the United States. It is also at the highest altitude of any of the U.S. state capitals, with an elevation of 7,199 feet (2,194 m).
Santa Fe is widely considered one of the world's great art cities, due to its many art galleries and installations, and it is recognized by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's Creative Cities Network
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a project of UNESCO launched in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities which recognized creativity as a major factor in their urban development.Santa Fe Plaza
The Santa Fe Plaza is a National Historic Landmark in downtown Santa Fe, New Mexico in the style of traditional Spanish-American colonial cities. The plaza, or city square is a gathering place for locals and also a tourist attraction. It is home ...
, the Palace of the Governors
The Palace of the Governors ( es, Palacio de los Gobernadores) is an adobe structure built in the Territorial Style of Pueblo architecture on Palace Avenue in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Located within the Santa Fe Historic District along the Santa Fe ...
, the Fiesta de Santa Fe, numerous restaurants featuring distinctive New Mexican cuisine
New Mexican cuisine is the cuisine of the Southwestern US state of New Mexico. The region is primarily known for its fusion of Pueblo Native American cuisine with Hispano Spanish and Mexican cuisine originating in Nuevo México.
This cuisi ...
, and performances of New Mexico music
New Mexico music ( es, música nuevo mexicana) is a genre of music that originated in the US state of New Mexico, it derives from Pueblo music in the 13th century, and with the folk music of Hispanos during the 16th to 19th centuries in Santa ...
. Among its many art galleries and installations are the Georgia O'Keeffe Museum
The Georgia O'Keeffe Museum is dedicated to the artistic legacy of Georgia O'Keeffe, her life, American modernism, and public engagement. It opened on July 17, 1997, eleven years after the artist's death. It comprises multiple sites in two locat ...
, a gallery by cartoonist Chuck Jones
Charles Martin Jones (September 21, 1912 – February 22, 2002) was an American animator, director, and painter, best known for his work with Warner Bros. Cartoons on the ''Looney Tunes'' and ''Merrie Melodies'' series of shorts. He wrote, produ ...
, and newer art collectives such as Meow Wolf
Meow Wolf is an American arts and entertainment company that creates large-scale interactive and immersive art installations. Founded in 2008, its flagship attraction, ''House of Eternal Return'' in Santa Fe, New Mexico, is a facility, which i ...
. The cityscape is known for its adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
-style Pueblo Revival
The Pueblo Revival style or Santa Fe style is a regional architectural style of the Southwestern United States, which draws its inspiration from Santa Fe de Nuevo México's traditional Pueblo architecture, the Spanish missions, and Territorial ...
and Territorial Revival architecture
Territorial Revival architecture describes the style of architecture developed in the U.S. state of New Mexico in the 1930s. It derived from Territorial Style, an original style which had developed in the 19th century and before, in the wider regi ...
.
Etymology
BeforeEuropean colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short ter ...
, the area Santa Fe occupied between 900 CE and the 1500s was known to the Tewa
The Tewa are a linguistic group of Pueblo Native Americans who speak the Tewa language and share the Pueblo culture. Their homelands are on or near the Rio Grande in New Mexico north of Santa Fe. They comprise the following communities:
* ...
peoples as ('white shell water place') and by the Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
people as ('bead' + 'water place'). In 1610, Juan de Oñate
Juan de Oñate y Salazar (; 1550–1626) was a Spanish conquistador from New Spain, explorer, and colonial governor of the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in the viceroyalty of New Spain. He led early Spanish expeditions to the Great Pla ...
established the area as , a province of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
. Formal Spanish settlements were developed leading the colonial governor Pedro de Peralta
Pedro de Peralta (c. 1584 – 1666) was Governor of New Mexico between 1610 and 1613 at a time when it was a province of New Spain.
He formally founded the city of Santa Fe, New Mexico in 1610. In August 1613 he was arrested and jailed for almo ...
to rename the area ('the Royal Town of the Holy Faith of Saint Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
'). The Spanish phrase is translated as 'holy faith' in English. Although more commonly known as Santa Fe, the city's full, legal name remains to this day as . The full name of the city is in both the seal and the flag of the city, although, as pointed out by Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. newspa ...
in 2020, Assisi
Assisi (, also , ; from la, Asisium) is a town and ''comune'' of Italy in the Province of Perugia in the Umbria region, on the western flank of Monte Subasio.
It is generally regarded as the birthplace of the Latin poet Propertius, born aroun ...
in Spanish is misspelled, reading ''Aśis'' instead of .
The standard Spanish pronunciation of the city's name is , as contextualized within the city's full Spanish name . However, due to the large amounts of tourism and immigration into Santa Fe, an English pronunciation of is also commonly used.
History
Spain and Mexico
The area of Santa Fe was originally occupied by indigenousTanoan
Tanoan , also Kiowa–Tanoan or Tanoan–Kiowa, is a family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples in present-day New Mexico, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Most of the languages – Tiwa (Taos, Picuris, Southern Tiwa), Tewa, and Towa – a ...
peoples, who lived in numerous Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
villages along the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
. One of the earliest known settlements in what today is downtown Santa Fe came sometime after 900 CE. A group of native Tewa
The Tewa are a linguistic group of Pueblo Native Americans who speak the Tewa language and share the Pueblo culture. Their homelands are on or near the Rio Grande in New Mexico north of Santa Fe. They comprise the following communities:
* ...
built a cluster of homes that centered around the site of today's Plaza and spread for half a mile to the south and west; the village was called ''Oghá P'o'oge'' in Tewa
The Tewa are a linguistic group of Pueblo Native Americans who speak the Tewa language and share the Pueblo culture. Their homelands are on or near the Rio Grande in New Mexico north of Santa Fe. They comprise the following communities:
* ...
. The Tanoans and other Pueblo peoples settled along the Santa Fe River for its water and transportation.
The river had a year-round flow until the 1700s. By the 20th century the Santa Fe River was a seasonal waterway. , the river was recognized as the most endangered river in the United States, according to the conservation group American Rivers.
Don Juan de Oñate
Juan de Oñate y Salazar (; 1550–1626) was a Spanish conquistador from New Spain, explorer, and colonial governor of the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in the viceroyalty of New Spain. He led early Spanish expeditions to the Great Pla ...
led the first Spanish effort to colonize the region in 1598, establishing Santa Fe de Nuevo México
Santa Fe de Nuevo México ( en, Holy Faith of New Mexico; shortened as Nuevo México or Nuevo Méjico, and translated as New Mexico in English) was a Kingdom of the Spanish Empire and New Spain, and later a territory of independent Mexico. The ...
as a province of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
. Under Juan de Oñate and his son, the capital of the province was the settlement of San Juan de los Caballeros
Ohkay Owingeh (Tewa: Ohkwee Ówîngeh ), known by its Spanish name as San Juan de los Caballeros from 1589 to 2005, is a pueblo and census-designated place (CDP) in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico. Ohkay Owingeh is also a federally recognized tribe ...
north of Santa Fe near modern Ohkay Owingeh Pueblo
Ohkay Owingeh ( Tewa: Ohkwee Ówîngeh ), known by its Spanish name as San Juan de los Caballeros from 1589 to 2005, is a pueblo and census-designated place (CDP) in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico. Ohkay Owingeh is also a federally recognized tribe ...
. Juan de Oñate was banished and exiled from New Mexico by the Spanish, after his rule was deemed cruel towards the indigenous population. New Mexico's second Spanish governor, Don Pedro de Peralta
Pedro de Peralta (c. 1584 – 1666) was Governor of New Mexico between 1610 and 1613 at a time when it was a province of New Spain.
He formally founded the city of Santa Fe, New Mexico in 1610. In August 1613 he was arrested and jailed for almo ...
, however, founded a new city at the foot of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains
)
, country= United States
, subdivision1_type= States
, subdivision1=
, parent= Rocky Mountains
, geology=
, orogeny=
, area_mi2= 17193
, range_coordinates=
, length_mi= 242
, length_orientation= north-south
, width_mi= 120
, w ...
in 1607, which he called ''La Villa Real de la Santa Fe de San Francisco de Asís'', the Royal Town of the Holy Faith of Saint Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
. In 1610, he designated it as the capital of the province, which it has almost constantly remained, making it the oldest state capital in the United States.
 Lack of Native American representation within the province of
Lack of Native American representation within the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México
Santa Fe de Nuevo México ( en, Holy Faith of New Mexico; shortened as Nuevo México or Nuevo Méjico, and translated as New Mexico in English) was a Kingdom of the Spanish Empire and New Spain, and later a territory of independent Mexico. The ...
, New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
(current New Mexico's early government) led to the 1680 Pueblo Revolt
The Pueblo Revolt of 1680, also known as Popé's Rebellion or Popay's Rebellion, was an uprising of most of the indigenous Pueblo people against the Spanish empire, Spanish colonizers in the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, larger than prese ...
, when groups of different Native Pueblo people
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zun ...
s were successful in driving the Spaniards out of New Mexico to El Paso, the Pueblo continued running New Mexico proper from the Palace of the Governors in Santa Fe from 1680 to 1692. The territory was reconquered in 1692 by Don Diego de Vargas
Diego de Vargas Zapata y Luján Ponce de León y Contreras (1643–1704), commonly known as Don Diego de Vargas, was a Spanish Governor of the New Spain territory of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, to the US states of New Mexico and Arizona, titular ...
through the war campaign called the "Bloodless Reconquest" which was criticized as violent even at the time, it was actually the following governor that truly started to broker peace, such as the founding of Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
, to guarantee better representation and trade access for Pueblos in New Mexico's government. Other governors of New Mexico, such as , continued to be better known for their more forward thinking work with the indigenous population of New Mexico. Santa Fe was Spain's provincial seat at outbreak of the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
in 1810. It was considered important to fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
rs based in present-day Saint Louis, Missouri
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which ...
. When the area was still under Spanish rule, the Chouteau brothers of Saint Louis gained a monopoly on the fur trade, before the United States acquired Missouri under the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
of 1803. The fur trade contributed to the wealth of Saint Louis. The city's status as the capital of the Mexican territory of was formalized in the 1824 Constitution after Mexico achieved independence from Spain.
When the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
seceded from Mexico in 1836, it attempted to claim Santa Fe and other parts of as part of the western portion of Texas along the . In 1841, a small military and trading expedition set out from Austin
Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the seat and largest city of Travis County, with portions extending into Hays and Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the 11th-most-populous city ...
, intending to take control of the Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
. Known as the Texan Santa Fe Expedition
The Texan Santa Fe Expedition was a commercial and military expedition to secure the Republic of Texas's claims to parts of Northern New Mexico for Texas in 1841. The expedition was unofficially initiated by the then-President of Texas, Mirabeau B ...
, the force was poorly prepared and was easily captured by the New Mexican military.
United States

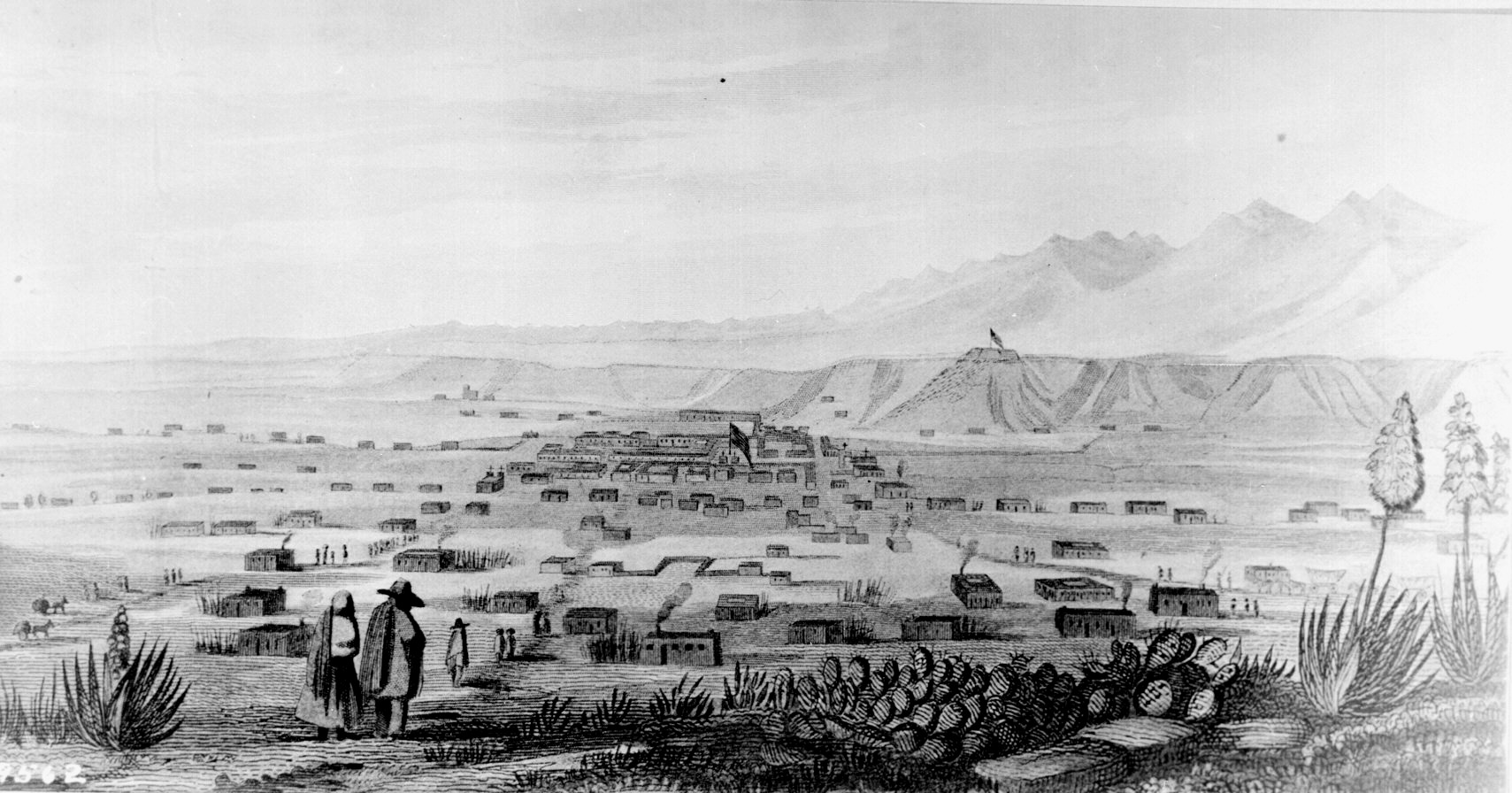
 In 1846, the United States declared war on Mexico. Brigadier General
In 1846, the United States declared war on Mexico. Brigadier General Stephen W. Kearny
Stephen Watts Kearny (sometimes spelled Kearney) ( ) (August 30, 1794October 31, 1848) was one of the foremost History of the United States (1789–1849), antebellum frontier officers of the United States Army. He is remembered for his significan ...
led the main body of his Army of the West of some 1,700 soldiers into Santa Fe to claim it and the whole New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of ''Santa Fe de Nuevo México ...
for the United States. By 1848 the U.S. officially gained New Mexico through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
.
Colonel Alexander William Doniphan
Alexander William Doniphan (July 9, 1808 – August 8, 1887) was a 19th-century American attorney, soldier and politician from Missouri who is best known today as the man who prevented the summary execution of Joseph Smith, founder of the Church ...
, under the command of Kearny, recovered ammunition from Santa Fe labeled "Spain 1776" showing both the lack of communications and quality of military support New Mexico received under Mexican rule.
After its annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
claimed Santa Fe along with other territory in eastern New Mexico. Texas Governor Peter H. Bell
Peter Hansborough Bell (May 11, 1810Various sources give multiple dates in May 1810 and May 1812 for Bell's birth. Bell's gravestone uses a May 1812 date.March 8, 1898) was an American military officer and politician who served as the third Gove ...
sent a letter to President Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader who served as the 12th president of the United States from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to th ...
, who died before he could read it, demanding that the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
stop defending New Mexico. In response, Taylor's successor Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
stationed additional troops to the area to halt any incursion by the Texas Militia
The Texas Militia are the militia forces of the State of Texas. It currently consists of the Texas Army National Guard, Texas Air National Guard, and Texas State Guard. It is administered by the Texas Military Department under command of the Te ...
. The territorial dispute was finally resolved by the Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Ame ...
, which designated the 103rd meridian west
The meridian 103° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole.
In the United States, the border betwe ...
as Texas's western border.
Some American visitors at first saw little promise in the remote town. One traveller in 1849 wrote:
In 1851, Jean Baptiste Lamy
Jean-Baptiste Lamy (October 11, 1814 – February 13, 1888), was a French-American Roman Catholic prelate who served as the first Archbishop of Santa Fe, New Mexico. Willa Cather's novel '' Death Comes for the Archbishop'' is based on his life ...
arrived, becoming bishop of New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Colorado in 1853. During his leadership, he traveled to France, Rome, Tucson, Los Angeles, St. Louis, New Orleans, and Mexico City. He built the Santa Fe Saint Francis Cathedral
The Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi ( es, Catedral basílica de San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Saint Francis Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in downtown Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is the mother church of the Arc ...
and shaped Catholicism in the region until his death in 1888.
As part of the New Mexico Campaign of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, General Henry Sibley occupied the city, flying the Confederate flag
The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and ...
over Santa Fe for a few days in March 1862. Sibley was forced to withdraw after Union troops destroyed his logistical trains following the Battle of Glorieta Pass
The Battle of Glorieta Pass (March 26–28, 1862) in the northern New Mexico Territory, was the decisive battle of the New Mexico campaign during the American Civil War. Dubbed the " Gettysburg of the West" by some authors (a term described ...
. The Santa Fe National Cemetery
Santa Fe National Cemetery is a United States National Cemetery in the city of Santa Fe, in Santa Fe County, New Mexico. It encompasses , and as of 2021, had 68,000 interments. Administered by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, it ...
was created by the federal government after the war in 1870 to inter the Union soldiers who died fighting there.
 On October 21, 1887,
On October 21, 1887, Anton Docher
Anton Docher (1852–1928), born Antonin Jean Baptiste Docher (pronounced ɑ̃tɔnɛ̃ ʒɑ̃ batist dɔʃe), was a French Franciscan Roman Catholic priest, who served as a missionary to Native Americans in New Mexico, in the Southwest of t ...
, "The Padre of Isleta", went to New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
where he was ordained as a priest in the St Francis Cathedral of Santa Fe by Bishop Jean-Baptiste Salpointe
Jean-Baptiste Salpointe (February 22, 1825 – July 15, 1898) was the first Bishop of Arizona and the second Archbishop of Santa Fe.
Early life and education
Salpointe was born in Saint-Maurice-près-Pionsat, Puy-de-Dôme, to Jean and Jeanne (n ...
. After a few years serving in Santa Fe, Bernalillo
Bernalillo () is a town in Sandoval County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 8,320. It is the county seat of Sandoval County.
Bernalillo is part of the Albuquerque Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Histor ...
and Taos
Taos or TAOS may refer to:
Places
* Taos, Missouri, a city in Cole County, Missouri, United States
* Taos County, New Mexico, United States
** Taos, New Mexico, a city, the county seat of Taos County, New Mexico
*** Taos art colony, an art colo ...
, he moved to Isleta
Pueblo of Isleta ( tix, Shiewhibak , kjq, Dîiw'a'ane ; nv, Naatoohó ) is an unincorporated community and Tanoan pueblo in Bernalillo County, New Mexico, United States, originally established in the . The Southern Tiwa name of the pueblo ...
on December 28, 1891. He wrote an ethnological article published in '' The Santa Fé Magazine'' in June 1913, in which he describes early 20th century life in the Pueblos.
As railroads were extended into the West, Santa Fe was originally envisioned as an important stop on the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison, Kansas, Atchison and Top ...
. But as the tracks were constructed into New Mexico, the civil engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing ...
s decided that it was more practical to go through Lamy
Lamy is a German pen manufacturing company. Josef Lamy, who was a sales representative for Parker Pen in Germany, founded the business in 1930 by purchasing the Orthos pen manufacturer. Lamy was a pioneer in the use of moulded synthetic plast ...
, a town in Santa Fe County
Santa Fe County ( es, Condado de Santa Fe; meaning ''Holy faith'' in Spanish) is located in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 144,170, making it New Mexico's third-most populous county, after Bernalillo Cou ...
to the south of Santa Fe. A branch line was completed from Lamy to Santa Fe in 1880. The Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad
The Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad , often shortened to ''Rio Grande'', D&RG or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, was an American Class I railroad company. The railroad started as a narrow-gauge line running south from De ...
extended the narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
Chili Line
The Chili Line, officially known as the Santa Fe Branch, was a narrow-gauge branch of the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW). It ran from Antonito, Colorado, to Santa Fe, New Mexico. The Denver and Rio Grande Railway (D&RG) began co ...
from the nearby city of Española to Santa Fe in 1886.
 Neither was sufficient to offset the negative effects of Santa Fe's having been bypassed by the main railroad route. It suffered gradual economic decline into the early 20th century. Activists created a number of resources for the arts and
Neither was sufficient to offset the negative effects of Santa Fe's having been bypassed by the main railroad route. It suffered gradual economic decline into the early 20th century. Activists created a number of resources for the arts and archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
, notably the School of American Research
The School for Advanced Research (SAR), until 2007 known as the School of American Research and founded in 1907 as the School for American Archaeology (SAA), is an advanced research center located in Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. Since 1967, the s ...
, created in 1907 under the leadership of the prominent archaeologist Edgar Lee Hewett
Edgar Lee Hewett (November 23, 1865 – December 31, 1946) was an American archaeologist and anthropologist whose focus was the Native American communities of New Mexico and the southwestern United States. He is best known for his role in ...
. In the early 20th century, Santa Fe became a base for numerous writers and artists. The first airplane to fly over Santa Fe was piloted by Rose Dugan, carrying Vera von Blumenthal as passenger. Together the two women started the development of the Pueblo Indian pottery industry, helping native women to market their wares. They contributed to the founding of the annual Santa Fe Indian Market
The Santa Fe Indian Market is an annual art market held in Santa Fe, New Mexico on the weekend following the third Thursday in August. The event draws an estimated 150,000 people to the city from around the world. The Southwestern Association for ...
.
In 1912, New Mexico was admitted as the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
's 47th state, with Santa Fe as its capital.
20th century
1912 plan
In 1912, when the town's population was approximately 5,000 people, the city's civic leaders designed and enacted a sophisticated city plan that incorporated elements of the contemporaryCity Beautiful
The City Beautiful Movement was a reform philosophy of North American architecture and urban planning that flourished during the 1890s and 1900s with the intent of introducing beautification and monumental grandeur in cities. It was a part of the ...
movement, city planning, and historic preservation. The latter was particularly influenced by similar movements in Germany. The plan anticipated limited future growth, considered the scarcity of water, and recognized the future prospects of suburban development on the outskirts. The planners foresaw that its development must be in harmony with the city's character.
Artists and tourists
 After the mainline of the railroad bypassed Santa Fe, it lost population. However, artists and writers, as well as retirees, were attracted to the cultural richness of the area, the beauty of the landscapes, and its dry climate. Local leaders began promoting the city as a tourist attraction. The city sponsored architectural restoration projects and erected new buildings according to traditional techniques and styles, thus creating the Santa Fe Style.
Edgar L. Hewett, founder and first director of the
After the mainline of the railroad bypassed Santa Fe, it lost population. However, artists and writers, as well as retirees, were attracted to the cultural richness of the area, the beauty of the landscapes, and its dry climate. Local leaders began promoting the city as a tourist attraction. The city sponsored architectural restoration projects and erected new buildings according to traditional techniques and styles, thus creating the Santa Fe Style.
Edgar L. Hewett, founder and first director of the School of American Research
The School for Advanced Research (SAR), until 2007 known as the School of American Research and founded in 1907 as the School for American Archaeology (SAA), is an advanced research center located in Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. Since 1967, the s ...
and the Museum of New Mexico The Museum of New Mexico is a collection of museums, historic sites, and archaeological services governed by the State of New Mexico. It currently consists of six divisions : the Palace of the Governors state history museum, the New Mexico Museum of ...
in Santa Fe, was a leading promoter. He began the Santa Fe Fiesta in 1919 and the Southwest Indian Fair in 1922 (now known as the Indian Market
The Santa Fe Indian Market is an annual art market held in Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe, New Mexico on the weekend following the third Thursday in August. The event draws an estimated 150,000 people to the city from around the world. The Southwe ...
). When Hewett tried to attract a summer program for Texas women, many artists rebelled, saying the city should not promote artificial tourism at the expense of its artistic culture. The writers and artists formed the Old Santa Fe Association and defeated the plan.
Japanese-American internment camp
New Mexico voted against interring any of its citizens of Japanese heritage, so none of the Japanese New Mexicans were interred during World War II. DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the federal government ordered a Japanese-American internment camp
are Americans of Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 census, they have declined in number to constitute the sixth largest Asi ...
to be established. Beginning in June 1942, the Department of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a v ...
arrested 826 Japanese-American men after the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
; they held them near Santa Fe, in a former Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) was a voluntary government work relief program that ran from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men ages 18–25 and eventually expanded to ages 17–28. The CCC was a major part of ...
site that had been acquired and expanded for the purpose. Although there was a lack of evidence and no due process
Due process of law is application by state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to the case so all legal rights that are owed to the person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual pers ...
, the men were held on suspicion of fifth column
A fifth column is any group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. According to Harris Mylonas and Scott Radnitz, "fifth columns" are “domestic actors who work to un ...
activity. Security at Santa Fe was similar to a military prison, with twelve-foot barbed wire fences, guard towers equipped with searchlights, and guards carrying rifles, side arms and tear gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymator agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the early commercial aerosol, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the eye to produce tears. In ad ...
. By September, the internees had been transferred to other facilities—523 to War Relocation Authority
The War Relocation Authority (WRA) was a United States government agency established to handle the internment of Japanese Americans during World War II. It also operated the Fort Ontario Emergency Refugee Shelter in Oswego, New York, which was t ...
concentration camps in the interior of the West, and 302 to Army internment camps.
The Santa Fe site was used next to hold German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
nationals, who were considered enemy aliens after the outbreak of war. In February 1943, these civilian detainees were transferred to Department of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a v ...
custody.
The camp was expanded at that time to take in 2,100 men segregated from the general population of Japanese-American inmates. These were mostly and who renounced their U.S. citizenship rather than sign an oath to "give up loyalty to the Japanese emperor" (offending them, since they had no identification with the emperor & were being asked to enlist in fighting him while their Japanese-born parents were interned) and other "troublemakers" from the Tule Lake Segregation Center. In 1945, four internees were seriously injured when violence broke out between the internees and guards in an event known as the Santa Fe Riot. The camp remained open past the end of the war; the last detainees were released in mid 1946. The facility was closed and sold as surplus soon after. The camp was located in what is now the Casa Solana neighborhood.
Geography
 According to the
According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, the city has a total area of , of which are land and (0.21%) is covered by water.
Santa Fe is located at above sea level, making it the highest state capital in the United States.United States Geological Survey
The Santa Fe River and the arroyos of Santa Fe
The arroyos of Santa Fe, along with the Santa Fe River (New Mexico), Santa Fe River, make up the drainage network of the city and region of Santa Fe, New Mexico. Besides drainage, the arroyos provide a network of pathways for recreation and exerc ...
drain the region to the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
.
Climate
Santa Fe's climate is characterized by cool, dry winters, hot summers, and relatively low precipitation. According to theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, depending on which variant of the system is used, the city has either a subtropical highland climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(''Cfb'') or a warm-summer humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(''Dfb''), somewhat unusual at 35°N. With low precipitation, though, it is more similar to the climates of Turkey that fall into this category. The 24-hour average temperature in the city ranges from in December to in July. Due to the relative aridity
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
and elevation, average diurnal temperature variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day.
Temperature lag
Temperature lag is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation: peak d ...
exceeds in every month, and much of the year. The city usually receives six to eight snowfalls a year between November and April. The heaviest rainfall occurs in July and August, with the arrival of the North American Monsoon
The North American monsoon, variously known as the Southwest monsoon, the Mexican monsoon, the New Mexican monsoon, or the Arizona monsoon is a pattern of pronounced increase in thunderstorms and rainfall over large areas of the southwestern Uni ...
.
Spanish and Pueblo influences
 The Spanish laid out the city according to the "
The Spanish laid out the city according to the "Laws of the Indies
The Laws of the Indies ( es, Leyes de las Indias) are the entire body of laws issued by the Spanish Crown for the American and the Asian possessions of its empire. They regulated social, political, religious, and economic life in these areas. Th ...
", town planning rules and ordinances which had been established in 1573 by King Philip II. The fundamental principle was that the town be laid out around a central plaza. On its north side was the Palace of the Governors
The Palace of the Governors ( es, Palacio de los Gobernadores) is an adobe structure built in the Territorial Style of Pueblo architecture on Palace Avenue in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Located within the Santa Fe Historic District along the Santa Fe ...
, while on the east was the church that later became the Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi
The Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi ( es, Catedral basílica de San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Saint Francis Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in downtown Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is the mother church of the Arc ...
.
An important style implemented in planning the city was the radiating grid of streets centered on the central Plaza. Many were narrow and included small alley-ways, but each gradually merged into the more casual byways of the agricultural perimeter areas. As the city grew throughout the 19th century, the building styles evolved too, so that by statehood in 1912, the eclectic nature of the buildings caused it to look like "Anywhere USA". The city government realized that the economic decline, which had started more than twenty years before with the railway moving west and the federal government closing down Fort Marcy, might be reversed by the promotion of tourism.
 To achieve that goal, the city created the idea of imposing a unified building style – the Spanish Pueblo Revival look, which was based on work done restoring the Palace of the Governors. The sources for this style came from the many defining features of local architecture: (rough, exposed beams that extrude through supporting walls, and are thus visible outside as well as inside the building) and (rain spouts cut into short parapet walls around flat roofs), features borrowed from many old adobe homes and churches built many years before and found in the Pueblos, along with the earth-toned look (reproduced in
To achieve that goal, the city created the idea of imposing a unified building style – the Spanish Pueblo Revival look, which was based on work done restoring the Palace of the Governors. The sources for this style came from the many defining features of local architecture: (rough, exposed beams that extrude through supporting walls, and are thus visible outside as well as inside the building) and (rain spouts cut into short parapet walls around flat roofs), features borrowed from many old adobe homes and churches built many years before and found in the Pueblos, along with the earth-toned look (reproduced in stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
) of the old adobe exteriors.
After 1912 this style became official: all buildings were to be built using these elements. By 1930 there was a broadening to include the "Territorial", a style of the pre-statehood period which included the addition of (large, covered porches) and white-painted window and door pediments (and also sometimes terra cotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta ...
tiles on sloped roofs, but with flat roofs still dominating). The city had become "different". However, "in the rush to pueblofy" Santa Fe, the city lost a great deal of its architectural history and eclecticism. Among the architects most closely associated with this new style are T. Charles Gaastra and John Gaw Meem
John Gaw Meem IV (November 17, 1894 – August 4, 1983) was an American architect based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. He is best known for his instrumental role in the development and popularization of the Pueblo Revival Style and as a proponent of ar ...
.
By an ordinance passed in 1957, new and rebuilt buildings, especially those in designated historic districts, must exhibit a Spanish Territorial or Pueblo style of architecture, with flat roofs and other features suggestive of the area's traditional adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
construction. However, many contemporary houses in the city are built from lumber, concrete blocks, and other common building materials, but with stucco surfaces (sometimes referred to as "faux-dobe", pronounced as one word: "foe-dough-bee") reflecting the historic style.
Architectural highlights
 *
* New Mexico State Capitol
The New Mexico State Capitol, located in Santa Fe at 490 Old Santa Fe Trail, is the seat of government of the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is the only round state capitol in the United States and is known informally as "the Roundhouse".
Desig ...
* Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi
The Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi ( es, Catedral basílica de San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Saint Francis Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in downtown Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is the mother church of the Arc ...
, the mother church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Santa Fe
The Archdiocese of Santa Fe ( la, Archidioecesis Sanctae Fidei in America Septentrionali, link=no, es, Arquidiócesis de Santa Fe, link=no) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the southwestern region of the United States in ...
* Loretto Chapel
The Loretto Chapel in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States, is a former Roman Catholic church that is now used as a museum and a wedding chapel.
It is known for its unusual helix-shaped spiral staircase (the "Miraculous Stair"). The Sisters of L ...
* Palace of the Governors
The Palace of the Governors ( es, Palacio de los Gobernadores) is an adobe structure built in the Territorial Style of Pueblo architecture on Palace Avenue in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Located within the Santa Fe Historic District along the Santa Fe ...
* San Miguel Mission
San Miguel Chapel, is a Spanish colonial mission church in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Originally built around 1610, it is often referred to as the oldest church in the United States (excluding Puerto Rico). The church was rebuilt twice, once in ...
and the rest of the Barrio De Analco Historic District
The Barrio de Analco Historic District is a National Historic Landmark District centered at the junction of East De Vargas Street and Old Santa Fe Trail in Santa Fe, New Mexico. The seven buildings of the district represent one of the oldest clu ...
* Santuario de Guadalupe
* De Vargas Street House
* New Mexico Governor's Mansion
The New Mexico Governor's Residence is the official residence of the governor of New Mexico and their family. The current structure, located at 1 Mansion Drive in Santa Fe, New Mexico, has served as the Governor's official residence since 1954. ...
Districts
*Barrio De Analco Historic District
The Barrio de Analco Historic District is a National Historic Landmark District centered at the junction of East De Vargas Street and Old Santa Fe Trail in Santa Fe, New Mexico. The seven buildings of the district represent one of the oldest clu ...
* Don Gaspar Historic District
The Don Gaspar Historic District is a historic district in Santa Fe, New Mexico. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. The listing included 278 contributing buildings.
History
The district is primarily residenti ...
* Santa Fe Historic District
Santa Fe Historic District is a historic district in Santa Fe, New Mexico that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. It includes two sites that are individually named U.S. National Historic Landmarks:
*Santa Fe Plaza
...
* Santa Fe Railyard arts district
Demographics
As of the 2020 census, there were 87,505 people living in the city, up from 67,947 in 2010, equating to an annual growth of close to 3%. As per the 2010 census, the racial makeup of the city residents was 78.9%White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, 2.1% Native American; 1.4% Black, 1.4% Asian; and 3.7% from two or more races. A total of 48.7% of the population were Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to Vic ...
or Latino of any race. Non-Hispanic Whites
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as " ...
were 46.2% of the population.
As of the census of 2000, there were 62,203 people, 27,569 households, and 14,969 families living in the city. The population density was 1,666.1 people per square mile (643.4/km2). There were 30,533 housing units at an average density of 817.8 per square mile (315.8/km2). According to the Census Bureau's 2006 American Community Survey, the racial makeup of the city was 75% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, 2.5% Native American, 1.9% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 0.4% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.3% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific Islands. As an ethnic group, ethnic/race (human categorization), racial term, it is used to describe the original p ...
, 16.9% from other races
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
, and 3.1% from two or more races. Hispanics or Latinos of any race were 44.5% of the population.
There were 27,569 households, out of which 24.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.6% were married couples living together, 12.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 45.7% were non-families. 36.4% of all households were made up of individuals living alone, and 10.2% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.20 and the average family size was 2.90.
The age distribution was 20.3% under 18, 8.9% from 18 to 24, 29.0% from 25 to 44, 28.0% from 45 to 64, and 13.9% who were 65 or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females, there were 91.7 males. For every 100 women age 18 and over, there were 89.0 men.
The median income for a household in the city was $40,392, and the median income for a family was $49,705. Men had a median income of $32,373 versus $27,431 for women. The per capita income for the city was $25,454. About 9.5% of families and 12.3% of the population were below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for t ...
, including 17.2% of those under age 18 and 9.2% of those age 65 or over.
Arts and culture
 The city is well known as a center for arts that reflect the multicultural character of the city; it has been designated as a UNESCO Creative City in Design, Crafts and Folk Art.
In 2012, the city was listed among the 10 best places to retire in the U.S. by ''
The city is well known as a center for arts that reflect the multicultural character of the city; it has been designated as a UNESCO Creative City in Design, Crafts and Folk Art.
In 2012, the city was listed among the 10 best places to retire in the U.S. by ''CBS MoneyWatch
''CBS MoneyWatch'', a division of CBS News and a property of Paramount Global, is a personal finance website that provides advice on retirement, investing, money, work and real estate. Launched in April 2009, the site was originally an extensi ...
'' and '' U.S. News & World Report''.
Visual arts

 Canyon Road, east of the Plaza, has the highest concentration of art galleries in the city, and is a major destination for international collectors, tourists and locals. The Canyon Road galleries showcase a wide array of contemporary,
Canyon Road, east of the Plaza, has the highest concentration of art galleries in the city, and is a major destination for international collectors, tourists and locals. The Canyon Road galleries showcase a wide array of contemporary, Southwestern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, indigenous American, and experimental art, in addition to Russian, Taos Masters, and Native American pieces.
Since its opening in 1995, SITE Santa Fe
SITE Santa Fe (often referred to simply as SITE) is a nonprofit contemporary arts organization based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Since its founding in 1995, SITE Santa Fe has presented 11 biennials, more than 90 contemporary art exhibitions, and wor ...
has been committed to supporting new developments in contemporary art, encouraging artistic exploration, and expanding traditional museum experiences. Launched in 1995 to organize the only international biennial of contemporary art in the United States, SITE Santa Fe has drawn global attention. The biennials are on par with such renowned exhibitions as the Whitney Biennial
The Whitney Biennial is a biennial exhibition of contemporary American art, typically by young and lesser known artists, on display at the Whitney Museum of American Art in New York City, United States. The event began as an annual exhibition in ...
and the Venice Biennale
The Venice Biennale (; it, La Biennale di Venezia) is an international cultural exhibition hosted annually in Venice, Italy by the Biennale Foundation. The biennale has been organised every year since 1895, which makes it the oldest of ...
.
Santa Fe contains a lively contemporary art scene, with Meow Wolf
Meow Wolf is an American arts and entertainment company that creates large-scale interactive and immersive art installations. Founded in 2008, its flagship attraction, ''House of Eternal Return'' in Santa Fe, New Mexico, is a facility, which i ...
as its main art collective. Backed by author George R. R. Martin
George Raymond Richard Martin (born George Raymond Martin; September 20, 1948), also known as GRRM, is an American novelist, screenwriter, television producer and short story writer. He is the author of the series of epic fantasy novels ''A Song ...
, Meow Wolf opened an elaborate art installation space, called House of Eternal Return, in 2016.
There are many outdoor sculptures, including many statues of Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
, and several other holy figures, such as Kateri Tekakwitha
Kateri Tekakwitha ( in Mohawk), given the name Tekakwitha, baptized as Catherine and informally known as Lily of the Mohawks (1656 – April 17, 1680), is a Catholic saint and virgin who was an Algonquin–Mohawk. Born in the Mohawk village of O ...
. The styles run the whole spectrum from Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
to Post-modern
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by skepticism toward the " grand narratives" of moderni ...
.
Literature
Numerous authors followed the influx of specialists in thevisual arts
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile arts al ...
. Well-known writers like D. H. Lawrence
David Herbert Lawrence (11 September 1885 – 2 March 1930) was an English writer, novelist, poet and essayist. His works reflect on modernity, industrialization, sexuality, emotional health, vitality, spontaneity and instinct. His best-k ...
, Cormac McCarthy
Cormac McCarthy (born Charles Joseph McCarthy Jr., July 20, 1933) is an American writer who has written twelve novels, two plays, five screenplays and three short stories, spanning the Western and post-apocalyptic genres. He is known for his gr ...
, Michael Tobias
Michael Charles Tobias (born June 27, 1951) is an American author, environmentalist, mountaineer, and filmmaker. In 1991, Tobias produced a ten-hour dramatic television series, ''Voice of the Planet'', for Turner Broadcasting; the series starre ...
, Kate Braverman
Kate Braverman (February 5, 1949 – October 12, 2019) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and poet. Los Angeles is the focus for much of her writing.
Biography
Kate Braverman was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on February 5, 1949. ...
, Douglas Adams
Douglas Noel Adams (11 March 1952 – 11 May 2001) was an English author and screenwriter, best known for ''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy''. Originally a 1978 BBC radio comedy, ''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy'' developed into a " ...
, Tony Hillerman
Anthony Grove Hillerman (May 27, 1925 – October 26, 2008) was an American author of detective novels and nonfiction works, best known for his mystery novels featuring Navajo Nation Police officers Joe Leaphorn and Jim Chee. Several of his work ...
, Roger Zelazny
Roger Joseph Zelazny (May 13, 1937 – June 14, 1995) was an American poet and writer of fantasy and science fiction short stories and novels, best known for ''The Chronicles of Amber''. He won the Nebula Award three times (out of 14 nomin ...
, Alice Corbin Henderson
Alice Corbin Henderson (April 16, 1881 – July 18, 1949) was an American poet, author and poetry editor.
Early life and education
Alice Corbin was born in St. Louis, Missouri. Her mother died in 1884 and she was briefly sent to live with her f ...
, Mary Austin, Witter Bynner
Harold Witter Bynner (August 10, 1881 – June 1, 1968), also known by the pen name Emanuel Morgan, was an American poet and translator. He was known for his long residence in Santa Fe, New Mexico, and association with other literary figures ther ...
, Dan Flores
Dan Louie Flores (born October 19, 1948) is an American writer and historian who specializes in cultural and environmental studies of the American West. He held the A.B. Hammond Chair in Western History at the University of Montana in Missoula, ...
, Paul Horgan
Paul George Vincent O'Shaughnessy Horgan (August 1, 1903 – March 8, 1995) was an American writer of historical fiction and non-fiction who mainly wrote about the Southwestern United States. He was the recipient of two Pulitzer Prizes for Histor ...
, Rudolfo Anaya
Rudolfo Anaya (October 30, 1937June 28, 2020) was an American author. Noted for his 1972 novel ''Bless Me, Ultima'', Anaya was considered one of the founders of the canon of contemporary Chicano literature. The themes and cultural references of ...
, George R. R. Martin
George Raymond Richard Martin (born George Raymond Martin; September 20, 1948), also known as GRRM, is an American novelist, screenwriter, television producer and short story writer. He is the author of the series of epic fantasy novels ''A Song ...
, Mitch Cullin
Mitch Cullin (born March 23, 1968) is an American writer. He is the author of seven novels, and one short story collection. He currently resides in Arcadia, California and Tokyo, Japan with his partner and frequent collaborator Peter I. Chang. Hi ...
, David Morrell
David Morrell (born April 24, 1943) is a Canadian-American novelist whose debut 1972 novel ''First Blood'', later adapted as the 1982 film of the same name, went on to spawn the successful ''Rambo'' franchise starring Sylvester Stallone. He h ...
, Evan S. Connell, Richard Bradford, John Masters
Lieutenant Colonel John Masters, DSO, OBE (26 October 1914 – 7 May 1983) was a British novelist and regular officer of the Indian Army.
In World War II, he served with the Chindits behind enemy lines in Burma, and became the GSO1 (chief st ...
, Jack Schaefer
Jack Warner Schaefer (November 19, 1907 – 24 January 1991) was an American writer known for his Westerns. His best-known works are the 1949 novel ''Shane'', voted the greatest western novel, and the 1964 children's book ''Stubby Pringle's C ...
, Hampton Sides
Wade Hampton Sides (born 1962) is an American historian, author and journalist. He is the author of '' Hellhound on His Trail,'' ''Ghost Soldiers,'' '' Blood and Thunder'', ''On Desperate Ground'', and other bestselling works of narrative histor ...
, Ariel Gore and Michael McGarrity are or were residents of Santa Fe. Walker Percy
Walker Percy, OSB (May 28, 1916 – May 10, 1990) was an American writer whose interests included philosophy and semiotics. Percy is noted for his philosophical novels set in and around New Orleans; his first, ''The Moviegoer'', won the Nat ...
lived on a dude ranch
A guest ranch, also known as a dude ranch, is a type of ranch oriented towards visitors or tourism. It is considered a form of agritourism.
History
Guest ranches arose in response to the romanticization of the American West that began to occur ...
outside of Santa Fe before returning to Louisiana to begin his literary career.
Media
Santa Fe's daily newspaper is the ''Santa Fe New Mexican
''The Santa Fe New Mexican'' or simply ''The New Mexican'' is a daily newspaper published in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Dubbed "the West's oldest newspaper," its first issue was printed on November 28, 1849.
Background
The downtown offices for ''T ...
'' and each Friday, it publishes ''Pasatiempo'', its long-running calendar and commentary on arts and events. ''The Magazine'' has been the arts magazine of Santa Fe since its founding by Guy Cross in 1992. It publishes critical reviews and profiles New Mexico based artists monthly. Each Wednesday the alternative weekly
An alternative newspaper is a type of newspaper that eschews comprehensive coverage of general news in favor of stylized reporting, opinionated reviews and columns, investigations into edgy topics and magazine-style feature stories highlighting l ...
newspaper, the ''Santa Fe Reporter
The ''Santa Fe Reporter'' (''SFR'') is an alternative weekly newspaper published in Santa Fe, New Mexico. First published in 1974, the ''Santa Fe Reporter'' features reports on local news, politics, art and culture, and is published once a week o ...
'', publishes information on the arts and culture of Santa Fe.
Video games
The 2006 racing video game '' Need For Speed: Carbon'' has an unused part of its Palmont City setting called San Juan, which you briefly play in, in the tutorial for the game's career mode. The San Juan setting is very loosely based on Santa Fe. It has New Mexico flags all over the roads. * The Crew *The Crew 2
''The Crew 2'' is a 2018 open world racing video game developed by Ivory Tower and published by Ubisoft for Microsoft Windows, PlayStation 4, Xbox One and Stadia. It is the sequel to 2014's '' The Crew''. It features a persistent open world ...
Music, dance, and opera
 Performance Santa Fe, formerly the Santa Fe Concert Association, is the oldest presenting organization in Santa Fe. Founded in 1937, Performance Santa Fe brings celebrated and legendary musicians as well as some of the world's greatest dancers and actors to the city year-round. The
Performance Santa Fe, formerly the Santa Fe Concert Association, is the oldest presenting organization in Santa Fe. Founded in 1937, Performance Santa Fe brings celebrated and legendary musicians as well as some of the world's greatest dancers and actors to the city year-round. The Santa Fe Opera
Santa Fe Opera (SFO) is an American opera company, located north of Santa Fe, New Mexico. After creating the ''Opera Association of New Mexico'' in 1956, its founding director, John Crosby (conductor), John Crosby, oversaw the building of the fir ...
stages its productions between late June and late August each year. The city also hosts the Santa Fe Chamber Music Festival
The Santa Fe Chamber Music Festival is a six-week-long summer Festival of chamber music held annually in July and August and located in Santa Fe, New Mexico. It was founded in 1972 and presented its first series of concerts in 1973. Well-known mu ...
which is held at about the same time, mostly in the St. Francis Auditorium and in the Lensic Theater
The Lensic Theater, located at 211 West San Francisco Street in Santa Fe, New Mexico, is an 821-seat theater designed by Boller Brothers of Kansas City, well-known movie-theater and vaudeville-house architects who designed almost one hundred theat ...
. Also in July and August, the Santa Fe Desert Chorale holds its summer festival. Santa Fe has its own professional ballet company, Aspen Santa Fe Ballet
Aspen Santa Fe Ballet (ASFB) is an American contemporary dance company. It comprises eleven classically trained dancers.
In addition to its domestic and international performances, the organization has a presentation program called "Aspen Santa ...
, which performs in both cities and tours nationally and internationally. Santa Fe is also home to internationally acclaimed Flamenco dancer's María Benítez
María Benítez is an American dancer, choreographer and director in Spanish dance and flamenco. Born of a mother of Chippewa, Algonquian, Oneida and Iroquois parentage and a Puerto Rican father, Benítez is best known for the work of the company ...
Institute for Spanish Arts which offers programs and performance in Flamenco, Spanish Guitar and similar arts year round. Other notable local figures include the National Dance Institute of New Mexico
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
and German New Age musician Deuter
Deuter (born Georg Deuter, 1945) is a German new-age music, new age instrumentalist and recording artist known for his meditative style that blends Eastern and Western musical elements.
Discography
* 1971 - ''D (Deuter album), D''
* 1972 - ''Au ...
.
Museums
Santa Fe has many museums located near the downtown Plaza: *New Mexico Museum of Art
The New Mexico Museum of Art is an art museum in Santa Fe governed by the state of New Mexico. It is one of four state-run museums in Santa Fe that are part of the Museum of New Mexico. It is located at 107 West Palace Avenue, one block off the ...
– collections of modern and contemporary Southwestern art
* Museum of Contemporary Native Arts
The Institute of American Indian Arts (IAIA) is a public tribal land-grant college in Santa Fe, New Mexico. The college focuses on Native American art. It operates the Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA), which is housed in the historic ...
– contemporary Native American arts with political aspects
* Georgia O'Keeffe Museum
The Georgia O'Keeffe Museum is dedicated to the artistic legacy of Georgia O'Keeffe, her life, American modernism, and public engagement. It opened on July 17, 1997, eleven years after the artist's death. It comprises multiple sites in two locat ...
– devoted to the work of O'Keeffe and others whom she influenced
* New Mexico History Museum
The New Mexico History Museum is a history museum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or s ...
– located behind the Palace of the Governors
The Palace of the Governors ( es, Palacio de los Gobernadores) is an adobe structure built in the Territorial Style of Pueblo architecture on Palace Avenue in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Located within the Santa Fe Historic District along the Santa Fe ...
* Site Santa Fe
SITE Santa Fe (often referred to simply as SITE) is a nonprofit contemporary arts organization based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Since its founding in 1995, SITE Santa Fe has presented 11 biennials, more than 90 contemporary art exhibitions, and wor ...
– a contemporary art space
Several other museums are located in the area known as Museum Hill:
* Museum of International Folk Art
The Museum of International Folk Art is a state-run institution in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States. It is one of many cultural institutions operated by the New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs.
History
The museum was founded by Floren ...
– folk art from around the world
* Museum of Indian Arts and Culture
The Museum of Indian Arts and Culture is a museum of Native American art and culture located in Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is one of eight museums in the state operated by the New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs and is accredited by the Ameri ...
– Native American art
Visual arts by indigenous peoples of the Americas encompasses the visual artistic practices of the indigenous peoples of the Americas from ancient times to the present. These include works from South America and North America, which includes C ...
s
* Wheelwright Museum of the American Indian
The Wheelwright Museum of the American Indian is a museum devoted to Native American arts. It is located in Santa Fe, New Mexico and was founded in 1937 by Mary Cabot Wheelwright, who came from Boston, and Hastiin Klah, a Navajo singer and medici ...
– Native American art and history
* Museum of Spanish Colonial Art – Tradition arts from the Spanish-colonial era to contemporary times.
Sports
The New Mexico Style were anAmerican Basketball Association
The American Basketball Association (ABA) was a major men's professional basketball league from 1967 to 1976. The ABA ceased to exist with the ABA–NBA merger, American Basketball Association–National Basketball Association merger in 1976, ...
franchise founded in 2005, but reformed in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
for the 2007–08 season as the El Paso S'ol (which folded without playing an ABA game in their new city). The Santa Fe Roadrunners
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnight ...
were a North American Hockey League
The North American Hockey League (NAHL) is one of the top junior hockey leagues in the United States and is in its 48th season of operation in 2022–23. It is the only Tier II junior league sanctioned by USA Hockey, and acts as an alternati ...
team, but moved to Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
to become the Topeka Roadrunners
The Amarillo Wranglers are a junior ice hockey#Tier II, Tier II junior ice hockey team in the North American Hockey League's South Division. The team's home arena is the Amarillo Civic Center in Amarillo, Texas.
History
Lone Star Cavalry
The Lon ...
. Santa Fe's rodeo
Rodeo () is a competitive equestrian sport that arose out of the working practices of cattle herding in Spain and Mexico, expanding throughout the Americas and to other nations. It was originally based on the skills required of the working va ...
, the Rodeo De Santa Fe, is held annually the last week of June.
In May 2012, Santa Fe became the home of the Santa Fe Fuego
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnight ...
of the Pecos League of Professional Baseball Clubs. They play their home games at Fort Marcy Ballfield
Fort Marcy Ballfield or Fort Marcy Ballpark is an approximately 1,100-seat baseball stadium in Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. The ballpark is part of the City of Santa Fe's Fort Marcy Recreation Complex, located on the former United States military r ...
. Horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
events were held at The Downs at Santa Fe from 1971 until 1997.
Government
The city of Santa Fe is acharter city
In the United States, a charter city is a city in which the governing system is defined by the city's own charter document rather than solely by general law. In states where city charters are allowed by law, a city can adopt or modify its organ ...
. It is governed by a mayor-council system. The city is divided into four electoral district
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
s, each represented by two councilors. Councilors are elected to staggered four-year terms and one councilor from each district is elected every two years.
The municipal judgeship is an elected position and a requirement of the holder is that they be a member of the state bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
. The judge is elected to four-year terms.
The mayor is the chief executive officer of the city and is a member of the governing body. The mayor has numerous powers and duties, and while previously the mayor could only vote when there was a tie among the city council, the city charter was amended by referendum in 2014 to allow the mayor to vote on all matters in front of the council. Starting in 2018, the position of mayor will be a full-time professional paid position within city government. Day-to-day operations of the municipality are undertaken by the city manager's office.
Federal operations
The Joseph M. Montoya Federal Building and Post Office serves as an office for U.S. federal government operations. It also contains the primaryUnited States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
post office in the city. Other post offices in the Santa Fe city limits include Coronado, De Vargas Mall, and Santa Fe Place Mall. The U.S. Courthouse building, constructed in 1889, was added to the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
in 1973.
Tourism
 Tourism is a major element of the Santa Fe economy, with visitors attracted year-round by the climate and related outdoor activities (such as skiing in years of adequate snowfall; hiking in other seasons) plus cultural activities of the city and the region. Tourism information is provided by the
Tourism is a major element of the Santa Fe economy, with visitors attracted year-round by the climate and related outdoor activities (such as skiing in years of adequate snowfall; hiking in other seasons) plus cultural activities of the city and the region. Tourism information is provided by the convention and visitor bureau
A destination marketing organization (DMO) is an Organization, organisation which promotes a location as an attractive travel destination. DMOs are known as tourist boards, tourism authorities or "Convention and Visitors Bureaux". They primarily ex ...
and the chamber of commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to ad ...
.
Most tourist activity takes place in the historic downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business distric ...
, especially on and around the Plaza
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
, a one-block square adjacent to the Palace of the Governors
The Palace of the Governors ( es, Palacio de los Gobernadores) is an adobe structure built in the Territorial Style of Pueblo architecture on Palace Avenue in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Located within the Santa Fe Historic District along the Santa Fe ...
, the original seat of New Mexico's territorial government since the time of Spanish colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
. Other areas include "Museum Hill", the site of the major art museums of the city as well as the Santa Fe International Folk Art Market Since 2004, thInternational Folk Art Markethas hosted more than 1000 master folk artists from 100 countries in the world's largest exhibition and sale of works by master folk artists. Artist earnings have exceeded $34 million and impacted more than ...
, which takes place each year during the second full weekend of July. The Canyon Road arts area with its galleries is also a major attraction for locals and visitors alike.
Some visitors find Santa Fe particularly attractive around the second week of September when the aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the ''Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China ...
s in the Sangre de Cristo Mountains
)
, country= United States
, subdivision1_type= States
, subdivision1=
, parent= Rocky Mountains
, geology=
, orogeny=
, area_mi2= 17193
, range_coordinates=
, length_mi= 242
, length_orientation= north-south
, width_mi= 120
, w ...
turn yellow and the skies are clear and blue. This is also the time of the annual Fiestas de Santa Fe
Fiestas de Santa Fe is a festival held every autumn in Santa Fe, New Mexico, usually during the second week of September.
History
On September 16, 1712 the first Fiesta council signed a proclamation declaring there should be a celebration to co ...
, celebrating the "reconquering" of Santa Fe by Don Diego de Vargas
Diego de Vargas Zapata y Luján Ponce de León y Contreras (1643–1704), commonly known as Don Diego de Vargas, was a Spanish Governor of the New Spain territory of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, to the US states of New Mexico and Arizona, titula ...
, a highlight of which is the burning Zozobra
The Zozobra (also known as "Old Man Gloom") is a giant marionette effigy constructed of wood, wire and cotton cloth that is built and burned prior to the annual Fiestas de Santa Fe in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States. It stands high.
As i ...
("Old Man Gloom"), a marionette
A marionette (; french: marionnette, ) is a puppet controlled from above using wires or strings depending on regional variations. A marionette's puppeteer is called a marionettist. Marionettes are operated with the puppeteer hidden or reveale ...
.
Popular day trips in the Santa Fe area include locations such as the town of Taos
Taos or TAOS may refer to:
Places
* Taos, Missouri, a city in Cole County, Missouri, United States
* Taos County, New Mexico, United States
** Taos, New Mexico, a city, the county seat of Taos County, New Mexico
*** Taos art colony, an art colo ...
, about north of Santa Fe. The historic Bandelier National Monument
Bandelier National Monument is a United States National Monument near Los Alamos in Sandoval and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico. The monument preserves the homes and territory of the Ancestral Puebloans of a later era in the Southwest. Most ...
and the Valles Caldera
Valles Caldera (or Jemez Caldera) is a wide volcanic caldera in the Jemez Mountains of northern New Mexico. Hot springs, streams, fumaroles, natural gas seeps and volcanic domes dot the caldera floor landscape. The highest point in the caldera i ...
can be found about away. Santa Fe's ski resort
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area – a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In North ...
, Ski Santa Fe
Ski Santa Fe or Santa Fe Ski Basin is a medium-sized ski resort located in the Sangre de Cristo Mountains in Santa Fe County, New Mexico, Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States, 16 miles east of the state capital of Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa ...
, is about northeast of the city. Chimayo is also nearby and many locals complete the annual pilgrimage to the Santuario de Chimayo
El Santuario de Chimayó is a Roman Catholic church in Chimayó, New Mexico, United States. (''Santuario'' is Spanish for "sanctuary".) This shrine, a National Historic Landmark, is famous for the story of its founding and as a contemporary pil ...
.
Science and technology
Santa Fe has had an association with science and technology since 1943 when the town served as the gateway toLos Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
(LANL), a 45-minute drive from the city. In 1984, the Santa Fe Institute
The Santa Fe Institute (SFI) is an independent, nonprofit theoretical research institute located in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States and dedicated to the multidisciplinary study of the fundamental principles of complex adaptive systems, includ ...
(SFI) was founded to research complex systems
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication s ...
in the physical, biological, economic, and political sciences. It has hosted such Nobel laureates as Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann (; September 15, 1929 – May 24, 2019) was an American physicist who received the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles. He was the Robert Andrews Millikan Professor of Theoretical ...
(physics), Philip Warren Anderson
Philip Warren Anderson (December 13, 1923 – March 29, 2020) was an American theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate. Anderson made contributions to the theories of localization, antiferromagnetism, symmetry breaking (including a paper in 19 ...
(physics), and Kenneth Arrow
Kenneth Joseph Arrow (23 August 1921 – 21 February 2017) was an American economist, mathematician, writer, and political theorist. He was the joint winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with John Hicks in 1972.
In economics ...
(economics). The National Center for Genome Resources
The National Center for Genome Resources (NCGR) is a not-for-profit research institute that innovates, collaborates, and educates in the field of genomic data science.
References
{{authority control
Genetics or genomics research institutions ...
(NCGR) was founded in 1994 to focus on research at the intersection among bioscience
''BioScience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Institute of Biological Sciences. It was established in 1964 and was preceded by the ''AIBS Bulletin'' (1951–19 ...
, computing, and mathematics. In the 1990s and 2000s several technology companies formed to commercialize technologies from LANL, SFI and NCGR.
Due to the presence of Los Alamos National Laboratory, Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Ba ...
and the Santa Fe Institute, and because of its attractiveness for visitors and an established tourist industry, Santa Fe routinely serves as a host to a variety of scientific meetings, summer schools, and public lectures, such as International q-bio Conference on Cellular Information Processing, Santa Fe Institute's Complex Systems Summer School, and LANL's Center For Nonlinear Studies Annual Conference.
Education
Santa Fe Public Schools
Santa Fe Public Schools (SFPS) is a school district based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Santa Fe Public Schools serves the city of Santa Fe, the communities of Tesuque and Eldorado, and the historic neighborhood of Agua Fria, and other communities ...
, with the exception of the New Mexico School for the Arts, which is a public/private partnership comprising the NMSA-Art Institute, a nonprofit art educational institution, and NMSA-Charter School, an accredited New Mexico state charter high school.
The city's institutions of higher education include St. John's College, a liberal arts college
A liberal arts college or liberal arts institution of higher education is a college with an emphasis on undergraduate study in liberal arts and sciences. Such colleges aim to impart a broad general knowledge and develop general intellectual capac ...
; the Institute of American Indian Arts
The Institute of American Indian Arts (IAIA) is a public tribal land-grant college in Santa Fe, New Mexico. The college focuses on Native American art. It operates the Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA), which is housed in the historic S ...
, a tribal college for Native American arts; Southwestern College, a graduate school for counseling and art therapy; and Santa Fe Community College
Santa Fe Community College (SFCC) is a public community college in Santa Fe, New Mexico. It has an undergraduate population of about 4,027 students, as well as approximately 4,706 contract training and continuing education students. The college ...
.
The city has six private college preparatory high schools: Santa Fe Waldorf School, St. Michael's High School, Desert Academy, New Mexico School for the Deaf
The New Mexico School for the Deaf (NMSD) is a state-run school in Santa Fe, New Mexico, providing education for deaf and hard-of-hearing students from preschool through grade 12. Established in 1887 by the New Mexico Legislature, New Mexico legis ...
, Santa Fe Secondary School, Santa Fe Preparatory School
Santa Fe Preparatory School is a private school located in Santa Fe, New Mexico The school provides grades 7-12 with an enrollment of 340 students. It was founded in February 1961.
History
The school was founded in February 1961. The school op ...
, and the Mandela International Magnet School. The Santa Fe Indian School
The Federal Government established the Santa Fe Indian School (SFIS) in 1890 to educate Native American children from tribes throughout the Southwestern United States. The purpose of creating SFIS was an attempt to assimilate the Native American c ...
is an off-reservation school for Native Americans. Santa Fe is also the location of the New Mexico School for the Arts, a public-private partnership, arts-focused high school. The city has many private elementary schools as well, including Little Earth School, Santa Fe International Elementary School, Rio Grande School, Desert Montessori School, La Mariposa Montessori, The Tara School, Fayette Street Academy, The Santa Fe Girls' School, The Academy for the Love of Learning, and Santa Fe School for the Arts and Sciences.
Transportation
Air
Santa Fe is served by theSanta Fe Municipal Airport
Santa Fe Regional Airport is a public use airport in Santa Fe, in Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States, southwest of the city center. The airport serves the greater Santa Fe and Los Alamos areas.
Santa Fe's is the second busiest commer ...
. American Airlines
American Airlines is a major airlines of the United States, major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the Largest airlines in the world, largest airline in the world when measured ...
provides regional jet service to Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport , also known as DFW Airport, is the primary international airport serving the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex and the North Texas Region in the U.S. state of Texas.
It is the largest hub for American Air ...
and Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport
Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport is a civil–military public airport east of downtown Phoenix, in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. It is Arizona's largest and busiest airport, and among the largest commercial airports in th ...
. United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
has regional jet service to Denver International Airport
Denver International Airport , locally known as DIA, is an international airport in the Western United States, primarily serving metropolitan Denver, Colorado, as well as the greater Front Range Urban Corridor. At , it is the largest airport in ...
.
Road
Santa Fe is located onI-25
Interstate 25 (I-25) is a major Interstate Highway in the western United States. It is primarily a north–south highway, serving as the main route through New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming. I-25 stretches from I-10 at Las Cruces, New Mexic ...
. In addition, U.S. Routes 84 and 285
The year 285 ( CCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the "Year of the Consulship of Carinus and Aurelius" (or, less frequently, "year ...
pass through the city, along St. Francis Drive. NM-599 forms a limited-access road
A limited-access road, known by various terms worldwide, including limited-access highway, dual-carriageway, expressway, limited access freeway, and partial controlled access highway, is a highway or arterial road for high-speed traffic which ...
bypass around the northwestern part of the city.
In its earliest alignment (1926–1937), U.S. Route 66
U.S. Route 66 or U.S. Highway 66 (US 66 or Route 66) was one of the original highways in the United States Numbered Highway System. It was established on November 11, 1926, with road signs erected the following year. The h ...
ran through Santa Fe.
Public transportation
 Santa Fe Trails, run by the city, operates a number of bus routes within the city during business hours and also provides connections to regional transit.
The
Santa Fe Trails, run by the city, operates a number of bus routes within the city during business hours and also provides connections to regional transit.
The New Mexico Rail Runner Express
The New Mexico Rail Runner Express ( AAR reporting mark NMRX) is a commuter rail system serving the metropolitan areas of Albuquerque and Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is administered by the New Mexico Department of Transportation (NMDOT) and the Ri ...
is a commuter rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are con ...
service operating in Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, Valencia and the Municipalities of Spain, third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is ...
, Bernalillo
Bernalillo () is a town in Sandoval County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 8,320. It is the county seat of Sandoval County.
Bernalillo is part of the Albuquerque Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Histor ...
(including Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
), Sandoval
Sandoval is a habitational surname of Spanish origin. It primarily originates from Sandoval de la Reina, Spain, earlier called ''Sannoval'', which is a blend word of Latin ''saltus'' (meaning 'grove' or 'wood') and Latin ''novalis'' (meaning 'newl ...
, and Santa Fe Counties. In Santa Fe County, the service uses of new right-of-way connecting the BNSF Railway
BNSF Railway is one of the largest freight railroads in North America. One of seven North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that ...
's old transcontinental mainline to existing right-of-way in Santa Fe used by the Santa Fe Southern Railway
The Santa Fe Southern Railway is a short line railroad in New Mexico, United States. In addition to carrying freight on occasion, it also operates as a tourist railroad called Sky Railway that carries passengers between Lamy and Santa Fe: a di ...
. Santa Fe is currently served by four stations, Santa Fe Depot, South Capitol, Zia Road, and Santa Fe County/NM 599.
New Mexico Park and Ride
NMDOT Park and Ride is the name given to a network of intercity buses in New Mexico and Texas, operated by the New Mexico Department of Transportation. The network is composed of eleven routes, including eight intercity routes and three local shut ...
, a division of the New Mexico Department of Transportation
The New Mexico Department of Transportation (NMDOT; es, Departamento de Transporte de Nuevo México) is a state government organization which oversees transportation in New Mexico, State of New Mexico in the southwestern United States. The agency ...
, and the North Central Regional Transit District
The North Central Regional Transit District operates a network of several local and intercity bus routes in northern New Mexico, serving Santa Fe, Española, Taos, and many smaller communities along a network of 25 fixed routes and one demand-resp ...
operate primarily weekday commuter coach
Coach may refer to:
Guidance/instruction
* Coach (sport), a director of athletes' training and activities
* Coaching, the practice of guiding an individual through a process
** Acting coach, a teacher who trains performers
Transportation
* Co ...
/bus service to Santa Fe from Torrance, Rio Arriba
Rio Arriba County is a List of counties in New Mexico, county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population was 40,246. Its county seat is Tierra Amarilla, New Mexico, Tierra Amarilla. Its nort ...
, Taos
Taos or TAOS may refer to:
Places
* Taos, Missouri, a city in Cole County, Missouri, United States
* Taos County, New Mexico, United States
** Taos, New Mexico, a city, the county seat of Taos County, New Mexico
*** Taos art colony, an art colo ...
, San Miguel and Los Alamos Counties in addition to shuttle services within Santa Fe connecting major government activity centers. Prior to the Rail Runner's extension to Santa Fe, Park and Ride operated commuter coach service between Albuquerque and Santa Fe.
Greyhound Lines
Greyhound Lines, Inc. (commonly known as simply Greyhound) operates the largest intercity bus service in North America, including Greyhound Mexico. It also operates charter bus services, Amtrak Thruway services, commuter bus services, and pac ...
serves Santa Fe on its route from Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
to El Paso, Texas
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the county seat, seat of El Paso County, Texas, El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau w ...
. Groome Transportation provides shuttles between Santa Fe and the Albuquerque International Sunport
Albuquerque International Sunport is the primary international airport serving the U.S. state of New Mexico, the Albuquerque metropolitan area, and the larger Albuquerque– Santa Fe–Las Vegas combined statistical area. It handles around 5. ...
.
Rail
Along with theNew Mexico Rail Runner Express
The New Mexico Rail Runner Express ( AAR reporting mark NMRX) is a commuter rail system serving the metropolitan areas of Albuquerque and Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is administered by the New Mexico Department of Transportation (NMDOT) and the Ri ...
, a commuter rail line serving the metropolitan areas of Albuquerque and Santa Fe, the city or its environs are served by two other railroads. The Santa Fe Southern Railway
The Santa Fe Southern Railway is a short line railroad in New Mexico, United States. In addition to carrying freight on occasion, it also operates as a tourist railroad called Sky Railway that carries passengers between Lamy and Santa Fe: a di ...
, now mostly a tourist rail experience but also carrying freight, operates excursion services out of Santa Fe as far as Lamy, to the southeast. The Santa Fe Southern line is one of the United States' few rails with trails
Rails with trails (RWT) are a small subset of rail trails in which a railway right-of-way remains in use by trains yet also has a parallel recreational trail. Hundreds of kilometers of RWTs exist in Canada, Europe, the United States, and Wester ...
. Lamy is also served by Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
's daily ''Southwest Chief
The ''Southwest Chief'' (formerly the ''Southwest Limited'' and ''Super Chief'') is a passenger train operated by Amtrak on a route between Chicago and Los Angeles through the Midwest and Southwest via Kansas City, Albuquerque, and Flagstaff ...
'' for train service to Chicago, Los Angeles, and intermediate points. Passengers transiting Lamy may use a special connecting coach/van service to reach Santa Fe.
Trails
Multi-use bicycle, pedestrian, and equestrian trails are increasingly popular in Santa Fe, for both recreation and commuting. These include the Dale Ball Trails, a network starting within two miles () of the Santa Fe Plaza; the longSanta Fe Rail Trail
The Santa Fe Rail Trail is a multi-use trail, part of the trail system in the city of Santa Fe, New Mexico. The trail begins at the Santa Fe Depot, in the Railyard arts district, and ends at U.S. Route 285, near Lamy, New Mexico and the Lam ...
to Lamy
Lamy is a German pen manufacturing company. Josef Lamy, who was a sales representative for Parker Pen in Germany, founded the business in 1930 by purchasing the Orthos pen manufacturer. Lamy was a pioneer in the use of moulded synthetic plast ...
; the Atalaya Trail up Atalaya Mountain; and the Santa Fe River Trail. Santa Fe is the terminus of three National Historic Trail
The National Trails System is a series of trails in the United States designated "to promote the preservation of, public access to, travel within, and enjoyment and appreciation of the open-air, outdoor areas and historic resources of the Nati ...
s: El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro National Historic Trail
The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro ( en, Royal Road of the Interior Land), also known as the Silver Route, was a Spanish road between Mexico City and San Juan Pueblo (''Ohkay Owingeh''), New Mexico, USA, that was used from 1598 to 1882. It was ...
, the Old Spanish National Historic Trail
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Mai ...
, and the Santa Fe National Historic Trail
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a Legend, legendary figure originating in Western Christianity, Western Christian culture who is said to Christmas gift-bringer, bring ...
.
Sister cities and twin towns
Santa Fe'ssister cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
are:
* Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, Bukhara Region
Bukhara Region (Buxoro Region) ( uz, Buxoro viloyati/Бухоро вилояти, بۇحارا ۋىلايەتى, russian: Бухарская область) is a region of Uzbekistan located in the southwest of the country. The Kyzyl Kum desert ...
, Uzbekistan (1988)
* Hidalgo del Parral
Hidalgo del Parral is a city and seat of the municipality of Hidalgo del Parral in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It is located in the southern part of the state, from the state capital, the city of Chihuahua, Chihuahua. As of 2015, the city ...
, Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
*Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mun ...
, Mexico (1984)
* Holguín
Holguín () is a municipality and city in Cuba, and the capital of Province of Holguín. After Havana, Santiago de Cuba, and Camagüey, it is the fourth largest city in Cuba.
History
Before Columbus, the Taino people settled in huts made fro ...
, Holguín Province
Holguín () is one of the provinces of Cuba, the third most populous after Havana and Santiago de Cuba. It lies in the southeast of the country. Its major cities include Holguín (the capital), Banes, Antilla, Mayarí, and Moa.
The province ha ...
, Cuba (2001)
* Icheon
Icheon () is a city in Gyeonggi Province, South Korea.
Together with Yeoju, Icheon is known as a center of South Korean ceramic manufacturing and is a UNESCO City of Crafts and Folk Art. Other famous local products include peaches and rice. Loc ...
, Gyeonggi-do
Gyeonggi-do (, ) is the most populous province in South Korea. Its name, ''Gyeonggi'', means "京 (the capital) and 畿 (the surrounding area)". Thus, ''Gyeonggi-do'' can be translated as "Seoul and the surrounding areas of Seoul". Seoul, the na ...
, South Korea (2013)
* Livingstone, Southern Province, Zambia (2012)
* San Miguel de Allende
San Miguel de Allende () is the principal city in the municipality of San Miguel de Allende, located in the far eastern part of Guanajuato, Mexico. A part of the Bajío region, the city lies from Mexico City, 86 km (53 mi) from Queré ...
, Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city i ...
, Mexico (1992)
* Santa Fe, Granada Province
Granada is a province of southern Spain, in the eastern part of the autonomous community of Andalusia. It is bordered by the provinces of Albacete, Murcia, Almería, Jaén, Córdoba, Málaga, and the Mediterranean Sea (along the Costa Tropical). ...
, Spain (1983)
* Sorrento
Sorrento (, ; nap, Surriento ; la, Surrentum) is a town overlooking the Bay of Naples in Southern Italy. A popular tourist destination, Sorrento is located on the Sorrentine Peninsula at the south-eastern terminus of the Circumvesuviana rail ...
, Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
, Italy (1995)
* Tsuyama
is a city in Okayama Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 102,294 and a population density of 200 persons per km². The total area was 185.73 km². The area increased in 2005 as the result of a merger with adjacent to ...
, Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
, Japan (1992)
* Zhangjiajie
Zhangjiajie (), also known in Tujia language as ''Zhangx jif avlar'' /dzaŋ˩ ji˥ a˩.la˥/, is a prefecture-level city in the northwestern part of Hunan Province, China. It comprises the district of Yongding, Wulingyuan and counties of Cili a ...
, Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to ...
, China (2009)
Notable people
 *
* David W. Alexander
David W. Alexander (June 22, 1812 – April 29, 1886) was an early California politician and pioneer in Los Angeles County, California. He was on the Board of Supervisors in 1853 and 1854, and in 1855 he was elected the third sheriff for the count ...
(1812–1886), Los Angeles politician and sheriff
* Antonio Armijo
Antonio Mariano Armijo (1804–1850) was a Spanish explorer and merchant who is famous for leading the first commercial caravan party between Abiquiú, Nuevo México and San Gabriel Mission, Alta California in 1829–1830. His route, the southe ...
(1804–1850), explorer and merchant who led the first commercial caravan between Santa Fe, and Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, in 1829–1830
* Mary Hunter Austin
Mary Hunter Austin (September 9, 1868 – August 13, 1934) was an American writer. One of the early nature writers of the American Southwest, her classic '' The Land of Little Rain'' (1903) describes the fauna, flora, and people – as well as e ...
(1868–1934), writer
* Gustave Baumann
Gustave Baumann (June 27, 1881 – October 8, 1971) was an American printmaker and painter, and one of the leading figures of the color woodcut revival in America. His works have been shown at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art, The C ...
(1881–1971), print-maker, marionette-maker and painter; resident artist for more than fifty years; died in Santa Fe
* William Berra (born 1952), painter
* Florence Birdwell
Florence Gillam Birdwell (December 31, 1924 – February 15, 2021), sometimes referred to as Flo Birdwell, was an American educator, musician, and singer. She taught musical theater and opera singing for more than six decades. She served as a pro ...
(1924–2021), musician, teacher
* Ned Bittinger
Edmund Stuart Bittinger (born July 4, 1951), better known by Ned Bittinger, is an American portrait painter and illustrator whose work includes the official Congressional portraits of Abraham Lincoln and Lindy Boggs for the US Capitol, as well a ...
(born 1951), portrait painter and illustrator
* Merrill Brockway
Merrill La Monte Brockway (February 28, 1923 – May 2, 2013) was an American television producer known for producing the PBS television series ''Dance in America''.
Biography
Brockway was born on February 28, 1923, in New Carlisle, Indiana. He ...
(1923–2013), Emmy Award
The Emmy Awards, or Emmys, are an extensive range of awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international television industry. A number of annual Emmy Award ceremonies are held throughout the calendar year, each with the ...
-winning producer, director
* Dana Tai Soon Burgess (born 1968), dancer, choreographer
* Paul Burlin
Paul Burlin (September 10, 1886 – March 13, 1969) was an American modern and abstract expressionist painter.
Childhood
Paul Burlin was born Isadore Berlin to Jacob and Julia Berlin in 1886 in New York. The family name was originally Berlins ...
(1886–1969), modern and abstract expressionist painter
* Witter Bynner
Harold Witter Bynner (August 10, 1881 – June 1, 1968), also known by the pen name Emanuel Morgan, was an American poet and translator. He was known for his long residence in Santa Fe, New Mexico, and association with other literary figures ther ...
(1881–1968), poet
* Julia Cameron
Julia B. Cameron (born March 4, 1948Floor Sample, by Julia Cameron, (Tarcher, 2006; ), a memoir) is an American teacher, author, artist, poet, playwright, novelist, filmmaker, pigeon fancier, composer, and journalist. She is best known for her ...
(1948), author of ''The Artist's Way
''The Artist's Way: A Spiritual Path to Higher Creativity'' is a 1992 self-help book by American author Julia Cameron. The book was written to help people with artistic creative recovery, which teaches techniques and exercises to assist people ...
''
* Dana B. Chase (1848–1897), photographer
* Zach Condon
Beirut is an American band that was originally the solo musical project of Zach Condon. Beirut's music combines elements of indie rock and world music. The band's first performance with the full brass section was in New York, in May 2006, in sup ...
(born 1986), lead singer and songwriter of band Beirut
* Bronson M. Cutting
Bronson Murray Cutting (June 23, 1888May 6, 1935) was a United States senator from New Mexico. A prominent progressive Republican, he had also been a newspaper publisher and military attaché.
Biography
Bronson Cutting was born in Great River, ...
(1888–1935), politician, newspaper publisher and military attaché
* Chris Eyre
Chris Eyre (born 1968), an enrolled member of the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes, is an American film director and producer who as of 2012 is chairman of the film department at the Santa Fe University of Art and Design.
Films
In 1998, Chris Eyre ...
(born 1968), actor, director
* Jane Fonda
Jane Seymour Fonda (born December 21, 1937) is an American actress, activist, and former fashion model. Recognized as a film icon, Fonda is the recipient of various accolades including two Academy Awards, two British Academy Film Awards, sev ...
(born 1937), actress; owner of Forked Lightning Ranch
* Tom Ford
Thomas Carlyle Ford (born August 27, 1961) is an American fashion designer and filmmaker. He launched his eponymous luxury brand in 2005, having previously served as the creative director at Gucci and Yves Saint Laurent. Ford wrote and directe ...
(born 1961), fashion designer
 *
* Garance Franke-Ruta
Garance Franke-Ruta is the executive editor of GEN by Medium. She has worked as Washington editor of Yahoo News and editor in chief of Yahoo Politics, Voices columnist and politics editor of ''The Atlantic'' Online, national web politics editor ...
(born 1972), journalist
* T. Charles Gaastra (1879–1947), architect in the Pueblo Revival Style
* Greer Garson
Eileen Evelyn Greer Garson (29 September 1904 – 6 April 1996) was an English-American actress and singer. She was a major star at Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer who became popular during the Second World War for her portrayal of strong women on the hom ...
(1904–1996), actress and philanthropist
* Laura Gilpin
Laura Gilpin (April 22, 1891 – November 30, 1979) was an American photographer.
Gilpin is known for her photographs of Native Americans, particularly the Navajo and Pueblo, and Southwestern landscapes. Gilpin began taking photographs as a ch ...
, (1891–1979), photographer and author
* John Grubesic (born 1965), New Mexico State Senator, representing the 25th District as a Democrat
* Anna Gunn
Anna Gunn (born August 11, 1968) is an American actress. She is best known for her role as Skyler White on the AMC drama series ''Breaking Bad'' (2008–2013), for which she won the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actress in a D ...
(born 1968), Emmy-winning actress
* Gene Hackman
Eugene Allen Hackman (born January 30, 1930) is an American retired actor and former novelist. In a career that has spanned more than six decades, Hackman has won two Academy Awards, four Golden Globes, one Screen Actors Guild Award, two BAFTAs ...
(born 1930), Oscar-winning actor
* Edgar Lee Hewett
Edgar Lee Hewett (November 23, 1865 – December 31, 1946) was an American archaeologist and anthropologist whose focus was the Native American communities of New Mexico and the southwestern United States. He is best known for his role in ...
(1865–1946), archaeologist and anthropologist
* Dorothy B. Hughes
Dorothy B. Hughes (August 10, 1904 May 6, 1993) was an American crime writer, literary critic, and historian. Hughes wrote fourteen crime and detective novels, primarily in the hardboiled and noir styles, and is best known for the novels ''In ...
(1904–1993), novelist and literary critic
* John Brinckerhoff Jackson (1909–1996), landscape architect
* Jeffe Kennedy
Jeffe Kennedy is a fantasy and erotic romance author who has published dozens of novels, including the fantasy romance series ''The Twelve Kingdoms, The Uncharted Realms'' and ''The Chroniclles of Dasnaria'' from Kensington Books. Her novel ''The P ...
, author
* Matt King Matthew or Matt King may refer to:
Matthew
* Matthew King (composer) (born 1967), British composer and pianist
* Matthew King (cricketer) (born 1977), Australian cricketer
* Matthew Yang King (born 1974), American actor, voice actor, director, prod ...
, artist, co-founder of Meow Wolf
* Jean Kraft
Jean Kraft (January 9, 1927 – July 15, 2021) was an American operatic mezzo-soprano. She began her career singing with the New York City Opera (NYCO) during the early 1960s, after which she embarked on a partnership with The Santa Fe Opera fro ...
(1927–2021), operatic singer (mezzo-soprano)
 *
* Oliver La Farge
Oliver Hazard Perry La Farge II (December 19, 1901 – August 2, 1963) was an American writer and anthropologist. In 1925 he explored early Olmec sites in Mexico, and later studied additional sites in Central America and the American Southw ...
(1901–1963), writer
* Jean Baptiste LeLande (1778–1821), merchant
* Jean-Baptiste Lamy
Jean-Baptiste Lamy (October 11, 1814 – February 13, 1888), was a French-American Roman Catholic prelate who served as the first Archbishop of Santa Fe, New Mexico. Willa Cather's novel ''Death Comes for the Archbishop'' is based on his life ...
(1814–1888), first Archbishop of Santa Fe
* Marjorie Herrera Lewis
Marjorie Herrera Lewis (born 1957) is a sports journalist best known for her 2018 novel ''When the Men Were Gone''. In 2018, the book was selected by ''Sports Illustrated'' as one of the best sports books in its year-in-review issue. In 2017, at ag ...
(born 1957), author
* Ali MacGraw
Elizabeth Alice MacGraw (born April 1, 1939) is an American actress and activist. She gained attention with her role in the film ''Goodbye, Columbus'' (1969), for which she won the Golden Globe Award for Most Promising Newcomer. She gained an ...
(born 1939), actress
* Shirley MacLaine
Shirley MacLaine (born Shirley MacLean Beaty, April 24, 1934) is an American actress, author, and former dancer. Known for her portrayals of quirky, strong-willed and eccentric women, MacLaine has received numerous accolades over her seven-dec ...
(born 1934), actress
* George R. R. Martin
George Raymond Richard Martin (born George Raymond Martin; September 20, 1948), also known as GRRM, is an American novelist, screenwriter, television producer and short story writer. He is the author of the series of epic fantasy novels ''A Song ...
(born 1948), author and screenwriter, ''Game of Thrones''
* Cormac McCarthy
Cormac McCarthy (born Charles Joseph McCarthy Jr., July 20, 1933) is an American writer who has written twelve novels, two plays, five screenplays and three short stories, spanning the Western and post-apocalyptic genres. He is known for his gr ...
(born 1933), author, winner of Pulitzer Prize for Fiction
* Christine McHorse
Christine McHorse (December 21, 1948 – February 17, 2021), also known as Christine Nofchissey McHorse, was a Navajo Pottery, ceramic artist from Santa Fe, New Mexico.
Early life and education
Born Christine Nofchissey on December 21, 1949, in ...
(1948–2021), ceramic artist
* Dorothy McKibbin
Dorothy McKibbin (December 12, 1897 – December 17, 1985) worked on the Manhattan Project during World War II. She ran the project's office at 109 East Palace in Santa Fe, through which staff moving to the Los Alamos Laboratory passed. She was ...
(1897–1985), gatekeeper and point-of-contact for personnel at the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
* John Gaw Meem
John Gaw Meem IV (November 17, 1894 – August 4, 1983) was an American architect based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. He is best known for his instrumental role in the development and popularization of the Pueblo Revival Style and as a proponent of ar ...
(1894–1983) Architect who popularized the Pueblo Revival
The Pueblo Revival style or Santa Fe style is a regional architectural style of the Southwestern United States, which draws its inspiration from Santa Fe de Nuevo México's traditional Pueblo architecture, the Spanish missions, and Territorial ...
style
* Sylvanus Morley
Sylvanus Griswold Morley (June 7, 1883September 2, 1948) was an American archaeology, archaeologist and epigraphy, epigrapher who studied the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in the early 20th century. Morley led extensive excavations of the Ma ...
(1883–1948), archaeologist and Mayanist
A Mayanist ( es, mayista) is a scholar specialising in research and study of the Mesoamerican pre-Columbian Maya civilisation. This discipline should not be confused with Mayanism, a collection of New Age beliefs about the ancient Maya.
Mayan ...
* John Nieto
John Nieto (1936–2018) was an American contemporary artist who concentrated on Native American themes including Native American tribal representatives as well as indigenous wildlife. He was a longtime resident of Santa Fe, New Mexico.
Biogr ...
(1936–2018), contemporary artist
* Jesse L. Nusbaum Jesse L. Nusbaum (1887–1975), was an American archaeologist, anthropologist, photographer and National Park Service Superintendent who lived in the American Southwest, where he made significant achievements in the identification, documentation, r ...
(1887–1975), archaeologist, anthropologist, photographer and National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
Superintendent
* Georgia O'Keeffe
Georgia Totto O'Keeffe (November 15, 1887 – March 6, 1986) was an American modernist artist. She was known for her paintings of enlarged flowers, New York skyscrapers, and New Mexico landscapes. O'Keeffe has been called the "Mother of Amer ...
(1887–1986), artist, winner of National Medal of Arts
* Elliot Porter (1901–1990), photographer
* Robert Redford
Charles Robert Redford Jr. (born August 18, 1936) is an American actor and filmmaker. He is the List of awards and nominations received by Robert Redford, recipient of various accolades, including an Academy Awards, Academy Award from four nomi ...
(born 1936), actor, director
* Wendy Rule (born 1966) Australian-born musician
* Hib Sabin (born 1935), indigenous-style sculptor
* Manuel de Sandoval
Manuel de Sandoval was a prominent Neomexican soldier who served as governor of Coahuila (1729–1733 ) and Texas (1734–1736). During his administration in Texas, he lived in and worked on the problems of Bexar, but he neglected Los Adaes, wh ...
, colonial governor of Texas. He was the only native of New Mexico that governed Spanish Texas
* Brad Sherwood
Bradley Sherwood is an American actor, singer, comedian, game show host and writer.
Career
His first acting job was a recurring role on ''L.A. Law'' as Ned Barron, which lasted for six episodes from 1991 to 1992.
Sherwood was introduced to im ...
(born 1964), actor and comedian
* Wes Studi
Wesley Studi ( chr, ᏪᏌ ᏍᏚᏗ; born December 17, 1947) is a Native American (Cherokee Nation) actor and film producer. He has garnered critical acclaim and awards throughout his career, particularly for his portrayal of Native Americans ...
(born 1947), actor and musician
* Teal Swan
Teal Swan (born Mary Teal Bosworth; June 16, 1984) is an American author who writes primarily on spiritual topics. A number of publications, including Eonline, The Guardian and BBC, the BBC noted that some of Swan’s teaching methods on how to m ...
(born 1984), spiritual guru and author
* Sheri S. Tepper (1929–2016), writer
* Charlene Teters
Charlene Teters (born April 25, 1952, Spokane, Washington) is a Native American artist, educator, and lecturer.Mai, Uyen"Culture Infused" Art Exhibit Presented by Cal Poly Pomona's La Bounty Chair of Interdisciplinary Applied Knowledge.''Califor ...
(born 1952), artist, activist
* Michael Charles Tobias (born 1951), author and global ecologist
* Stanislaw Ulam
Stanisław Marcin Ulam (; 13 April 1909 – 13 May 1984) was a Polish-American scientist in the fields of mathematics and nuclear physics. He participated in the Manhattan Project, originated the Teller–Ulam design of thermonuclear weapon ...
(1909–1984), mathematician associated with the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
* Jeremy Ray Valdez
Jeremy Ray Valdez (born July 10, 1980) is an American actor and musician. He won the 2010 Imagen Award for Best Supporting Actor in a Feature Film for his role in '' La Mission''.
Early life
Valdez was born in Santa Fe, New Mexico in 1980. His ...
(born 1980), actor
* Lew Wallace
Lewis Wallace (April 10, 1827February 15, 1905) was an American lawyer, Union general in the American Civil War, governor of the New Mexico Territory, politician, diplomat, and author from Indiana. Among his novels and biographies, Wallace is ...
(1827–1905), territorial governor 1878–1881, and author of Ben-Hur
* Tuesday Weld
Tuesday Weld (born Susan Ker Weld; August 27, 1943) is an American actress and model. She began acting as a child and progressed to mature roles in the late 1950s. She won a Golden Globe Award for Most Promising Female Newcomer in 1960. Over t ...
(born 1943), actress
* Josh West
A. Joshua West (born 25 March 1977) is a dual citizen British-American Olympic rower and Earth Sciences professor. He is a two-time World Championship silver medalist, a World Championship bronze medalist, and a four-time Cambridge Blue, and r ...
(born 1977), Olympic medalist rower and Earth Sciences professor
* Roger Zelazny
Roger Joseph Zelazny (May 13, 1937 – June 14, 1995) was an American poet and writer of fantasy and science fiction short stories and novels, best known for ''The Chronicles of Amber''. He won the Nebula Award three times (out of 14 nomin ...
(1937–1995), writer
* Pinchas Zukerman
Pinchas Zukerman ( he, פנחס צוקרמן, born 16 July 1948) is an Israeli-American violinist, violist and conductor.
Life and career
Zukerman was born in Tel Aviv, to Jewish parents and Holocaust survivors Yehuda and Miriam Lieberman Zuk ...
(born 1948), violinist, conductor
* Marc Whitmore (born 1992), Grammy award-winning music producer and engineer
See also
* Homewise, founded in 1986 *National Old Trails Road
National Old Trails Road, also known as the Ocean-to-Ocean Highway, was established in 1912, and became part of the National Auto Trail system in the United States. It was long and stretched from Baltimore, Maryland (some old maps indicate Ne ...
* Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
*Santa Fe Convention & Visitors Bureau official tourism website
Santa Fe Chamber of Commerce
* {{Authority control Santa Fe Cities in New Mexico Cities in Santa Fe County, New Mexico County seats in New Mexico Populated places established in 1610 1610 establishments in New Spain