Multiband Imaging Photometer For Spitzer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder.
The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission.
During the warm mission, the two short wavelength channels of IRAC operated at 28.7 K and were predicted to experience little to no degradation at this temperature compared to the nominal mission. The Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).
In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named by a board of scientists, typically after famous deceased astronomers, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.
The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder.
The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission.
During the warm mission, the two short wavelength channels of IRAC operated at 28.7 K and were predicted to experience little to no degradation at this temperature compared to the nominal mission. The Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).
In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named by a board of scientists, typically after famous deceased astronomers, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.
The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for
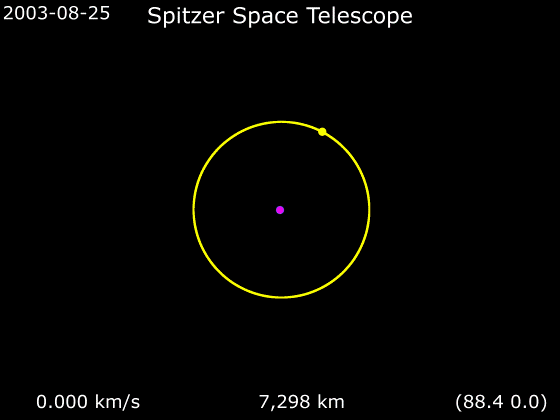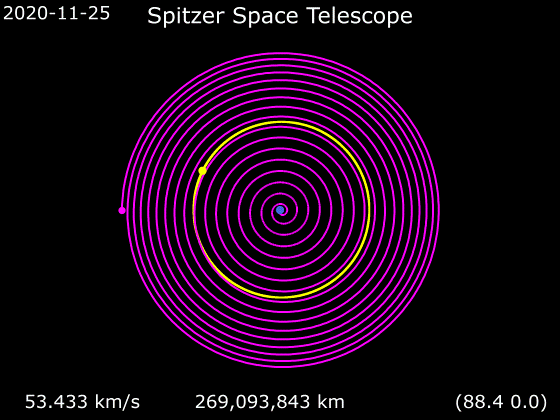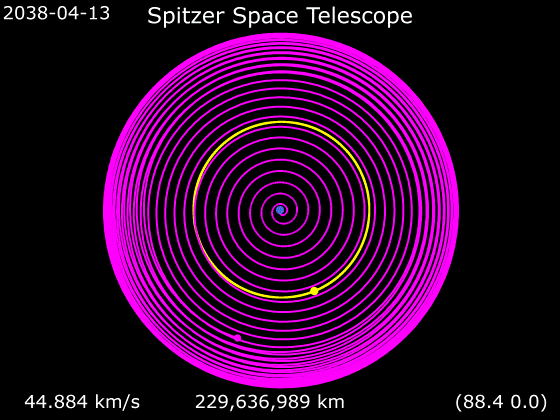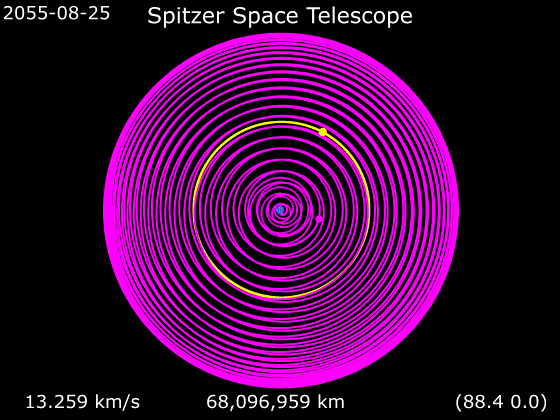 One of the most important advances of this redesign was an Earth-trailing orbit. Cryogenic satellites that require liquid helium (LHe, T ≈ 4 K) temperatures in near-Earth orbit are typically exposed to a large heat load from Earth, and consequently require large amounts of LHe coolant, which then tends to dominate the total payload mass and limits mission life. Placing the satellite in solar orbit far from Earth allowed innovative passive cooling. The sun shield protected the rest of the spacecraft from the Sun's heat, the far side of the spacecraft was painted black to enhance passive radiation of heat, and the spacecraft bus was thermally isolated from the telescope. All of these design choices combined to drastically reduce the total mass of helium needed, resulting in an overall smaller and lighter payload, resulting in major cost savings, but with a mirror the same diameter as originally designed. This orbit also simplified telescope pointing, but did require the NASA Deep Space Network for communications.
The primary instrument package (telescope and cryogenic chamber) was developed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies, in
One of the most important advances of this redesign was an Earth-trailing orbit. Cryogenic satellites that require liquid helium (LHe, T ≈ 4 K) temperatures in near-Earth orbit are typically exposed to a large heat load from Earth, and consequently require large amounts of LHe coolant, which then tends to dominate the total payload mass and limits mission life. Placing the satellite in solar orbit far from Earth allowed innovative passive cooling. The sun shield protected the rest of the spacecraft from the Sun's heat, the far side of the spacecraft was painted black to enhance passive radiation of heat, and the spacecraft bus was thermally isolated from the telescope. All of these design choices combined to drastically reduce the total mass of helium needed, resulting in an overall smaller and lighter payload, resulting in major cost savings, but with a mirror the same diameter as originally designed. This orbit also simplified telescope pointing, but did require the NASA Deep Space Network for communications.
The primary instrument package (telescope and cryogenic chamber) was developed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies, in
Jonathan O'Callaghan. '' Scientific American''. June 4, 2019. when NASA sent a shutdown signal to the telescope from the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex (GDSCC) instructing the telescope to go into safe mode. After receiving confirmation that the command was successful, Spitzer Project Manager Joseph Hunt officially declared that the mission had ended.
 Spitzer carries three instruments on board:
; Infrared Array Camera (IRAC)
: An infrared camera which operated simultaneously on four wavelengths (3.6 μm, 4.5 μm, 5.8 μm and 8 μm). Each module used a 256×256-pixel detector—the short-wavelength pair used indium antimonide technology, the long-wavelength pair used arsenic-doped silicon impurity band conduction technology.SSC IRAC (Mid IR camera) science users information page
Spitzer carries three instruments on board:
; Infrared Array Camera (IRAC)
: An infrared camera which operated simultaneously on four wavelengths (3.6 μm, 4.5 μm, 5.8 μm and 8 μm). Each module used a 256×256-pixel detector—the short-wavelength pair used indium antimonide technology, the long-wavelength pair used arsenic-doped silicon impurity band conduction technology.SSC IRAC (Mid IR camera) science users information page
4 October 2009. The principal investigator was
4 October 2009. The principal investigator was
(long wavelength 24um, 70um, & 160um) imaging photometer and spectrometer science users' information page, 4 October 2009. The principal investigator was George H. Rieke of the University of Arizona; the flight hardware was built by Ball Aerospace. All three instruments used liquid helium for cooling the sensors. Once the helium was exhausted, only the two shorter wavelengths in IRAC were used in the "warm mission".
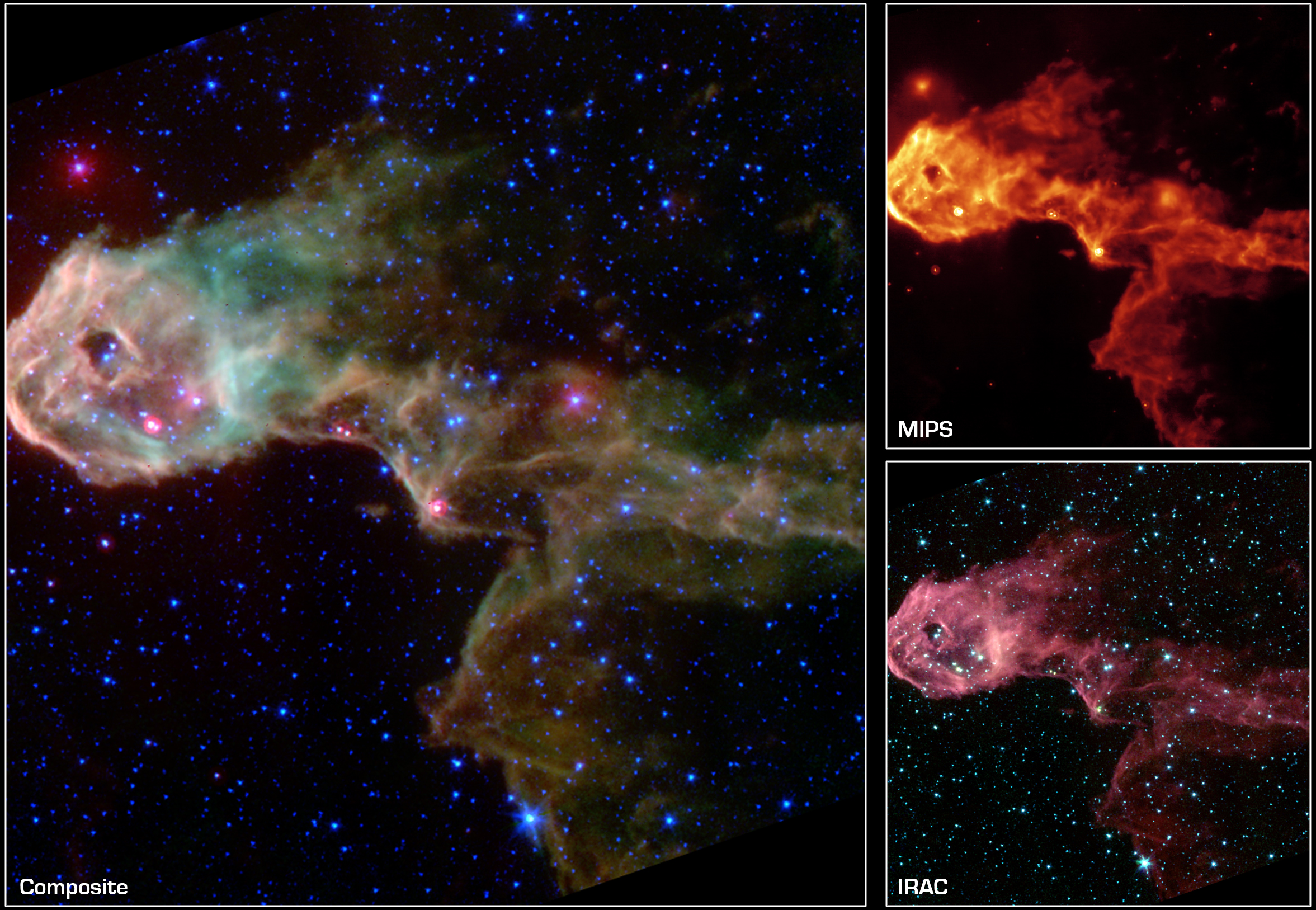
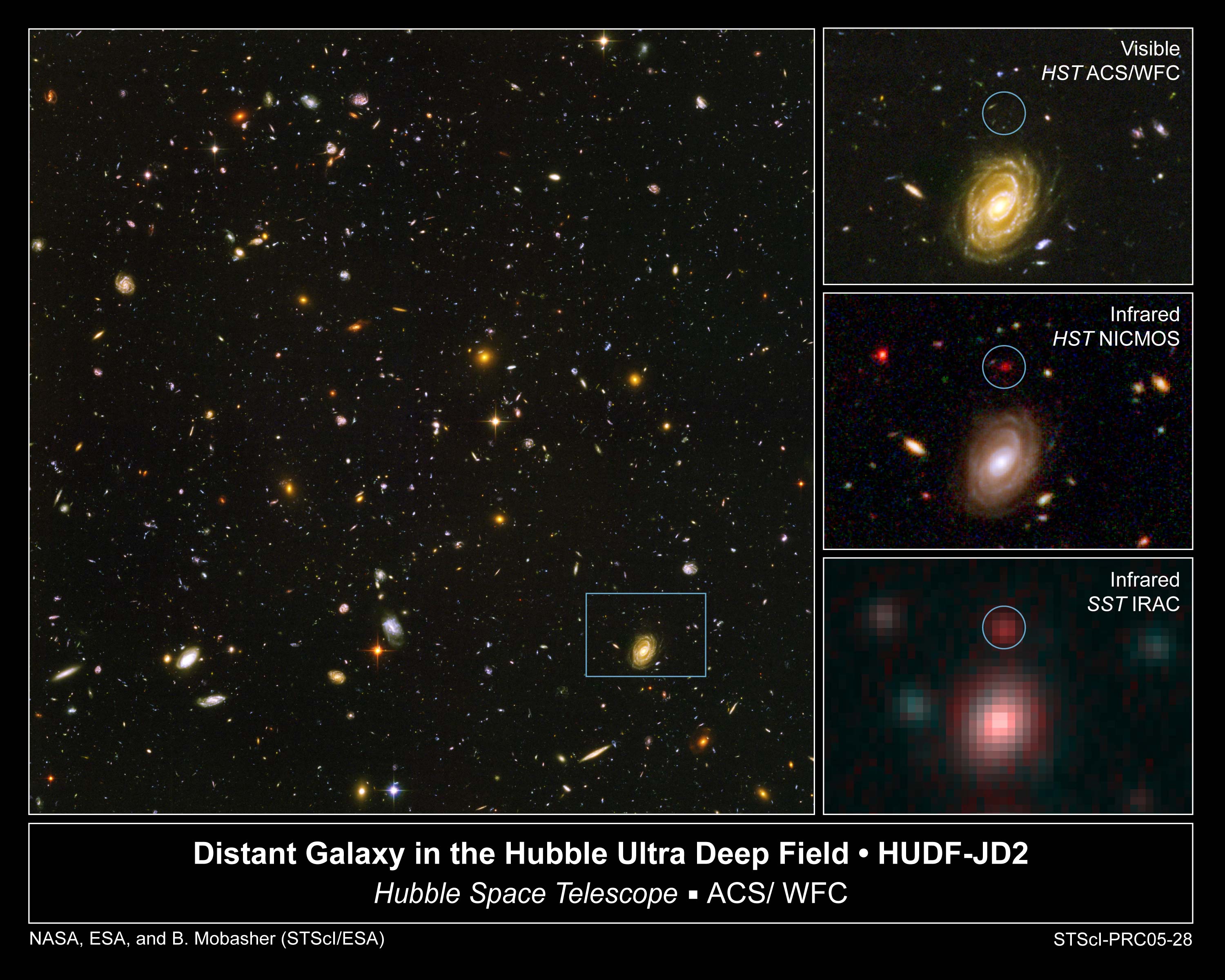
 The first released images from Spitzer were designed to show off the abilities of the telescope and showed a glowing stellar nursery, a big swirling, dusty
The first released images from Spitzer were designed to show off the abilities of the telescope and showed a glowing stellar nursery, a big swirling, dusty  In 2004, it was reported that Spitzer had spotted a faintly glowing body that may be the youngest star ever seen. The telescope was trained on a core of gas and dust known as
In 2004, it was reported that Spitzer had spotted a faintly glowing body that may be the youngest star ever seen. The telescope was trained on a core of gas and dust known as  Also in 2005, astronomers
Also in 2005, astronomers  Scientists have long wondered how tiny silicate crystals, which need high temperatures to form, have found their way into frozen comets, born in the very cold environment of the Solar System's outer edges. The crystals would have begun as non-crystallized, amorphous silicate particles, part of the mix of gas and dust from which the Solar System developed. This mystery has deepened with the results of the ''
Scientists have long wondered how tiny silicate crystals, which need high temperatures to form, have found their way into frozen comets, born in the very cold environment of the Solar System's outer edges. The crystals would have begun as non-crystallized, amorphous silicate particles, part of the mix of gas and dust from which the Solar System developed. This mystery has deepened with the results of the ''
, University of Wisconsin–Madison Department of Astronomy The images were taken over a 10-year period beginning in 2003 when Spitzer launched. MIPSGAL, a similar survey that complements GLIMPSE, covers 248° of the galactic disk using the 24 and 70 μm channels of the MIPS instrument. On 3 June 2008, scientists unveiled the largest, most detailed infrared portrait of the Milky Way, created by stitching together more than 800,000 snapshots, at the 212th meeting of the
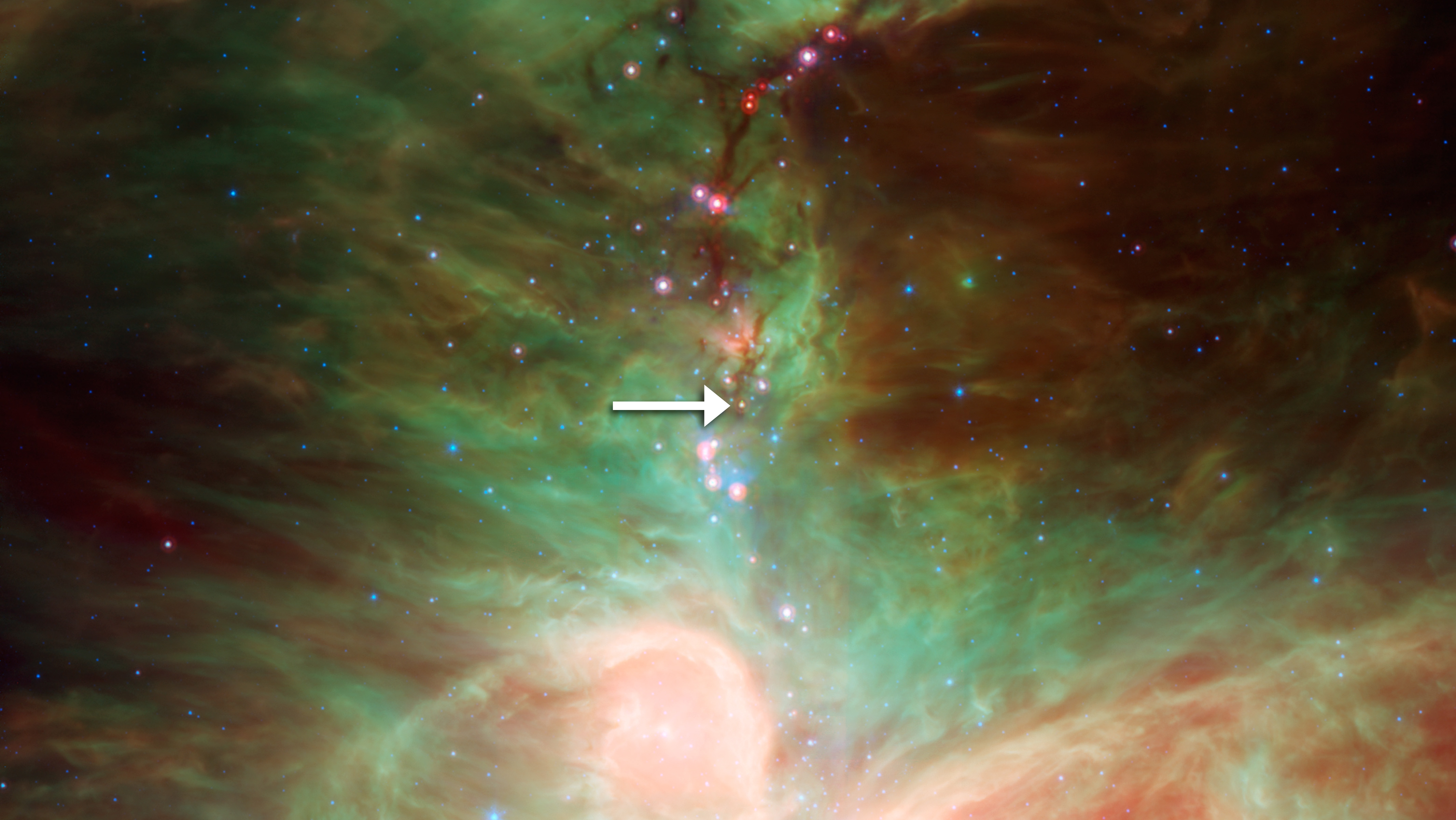 Spitzer observations, announced in May 2011, indicate that tiny forsterite crystals might be falling down like rain on to the protostar HOPS-68. The discovery of the forsterite crystals in the outer collapsing cloud of the protostar is surprising because the crystals form at lava-like high temperatures, yet they are found in the molecular cloud where the temperatures are about . This led the team of astronomers to speculate that the bipolar outflow from the young star may be transporting the forsterite crystals from near the star's surface to the chilly outer cloud.
In January 2012, it was reported that further analysis of the Spitzer observations of EX Lupi can be understood if the forsterite crystalline dust was moving away from the protostar at a remarkable average speed of . It would appear that such high speeds can arise only if the dust grains had been ejected by a bipolar outflow close to the star. Such observations are consistent with an astrophysical theory, developed in the early 1990s, where it was suggested that bipolar outflows garden or transform the disks of gas and dust that surround protostars by continually ejecting reprocessed, highly heated material from the inner disk, adjacent to the protostar, to regions of the accretion disk further away from the protostar.
In April 2015, Spitzer and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment were reported as co-discovering one of the most distant planets ever identified: a gas giant about away from Earth.
Spitzer observations, announced in May 2011, indicate that tiny forsterite crystals might be falling down like rain on to the protostar HOPS-68. The discovery of the forsterite crystals in the outer collapsing cloud of the protostar is surprising because the crystals form at lava-like high temperatures, yet they are found in the molecular cloud where the temperatures are about . This led the team of astronomers to speculate that the bipolar outflow from the young star may be transporting the forsterite crystals from near the star's surface to the chilly outer cloud.
In January 2012, it was reported that further analysis of the Spitzer observations of EX Lupi can be understood if the forsterite crystalline dust was moving away from the protostar at a remarkable average speed of . It would appear that such high speeds can arise only if the dust grains had been ejected by a bipolar outflow close to the star. Such observations are consistent with an astrophysical theory, developed in the early 1990s, where it was suggested that bipolar outflows garden or transform the disks of gas and dust that surround protostars by continually ejecting reprocessed, highly heated material from the inner disk, adjacent to the protostar, to regions of the accretion disk further away from the protostar.
In April 2015, Spitzer and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment were reported as co-discovering one of the most distant planets ever identified: a gas giant about away from Earth.
 In June and July 2015, the brown dwarf was discovered using the gravitational microlensing detection method in a joint effort between Swift, Spitzer, and the ground-based Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment, the first time two space telescopes have observed the same microlensing event. This method was possible because of the large separation between the two spacecraft: Swift is in low-Earth orbit while Spitzer is more than one AU distant in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. This separation provided significantly different perspectives of the brown dwarf, allowing for constraints to be placed on some of the object's physical characteristics.
Reported in March 2016, Spitzer and Hubble were used to discover the most distant-known galaxy, GN-z11. This object was seen as it appeared 13.4 billion years ago.
In June and July 2015, the brown dwarf was discovered using the gravitational microlensing detection method in a joint effort between Swift, Spitzer, and the ground-based Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment, the first time two space telescopes have observed the same microlensing event. This method was possible because of the large separation between the two spacecraft: Swift is in low-Earth orbit while Spitzer is more than one AU distant in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. This separation provided significantly different perspectives of the brown dwarf, allowing for constraints to be placed on some of the object's physical characteristics.
Reported in March 2016, Spitzer and Hubble were used to discover the most distant-known galaxy, GN-z11. This object was seen as it appeared 13.4 billion years ago.
 Spitzer was also put to work studying exoplanets thanks to creatively tweaking its hardware. This included doubling its stability by modifying its heating cycle, finding a new use for the "peak-up" camera, and analyzing the sensor at a sub-pixel level. Although in its "warm" mission, the spacecraft's passive cooling system kept the sensors at . Spitzer used the transit photometry and gravitational microlensing techniques to perform these observations. According to NASA's Sean Carey, "We never even considered using Spitzer for studying exoplanets when it launched. ... It would have seemed ludicrous back then, but now it's an important part of what Spitzer does."
Examples of exoplanets discovered using Spitzer include
Spitzer was also put to work studying exoplanets thanks to creatively tweaking its hardware. This included doubling its stability by modifying its heating cycle, finding a new use for the "peak-up" camera, and analyzing the sensor at a sub-pixel level. Although in its "warm" mission, the spacecraft's passive cooling system kept the sensors at . Spitzer used the transit photometry and gravitational microlensing techniques to perform these observations. According to NASA's Sean Carey, "We never even considered using Spitzer for studying exoplanets when it launched. ... It would have seemed ludicrous back then, but now it's an important part of what Spitzer does."
Examples of exoplanets discovered using Spitzer include
Spitzer Space Telescope
at NASA.gov
Spitzer Space Telescope
at Caltech.edu
Spitzer Space Telescope
by NASA's Solar System Exploration
GLIMPSE/MIPSGAL image viewer
at Alienearths.org
" Spitzer Space Telescope: Discovering "More Things in the Heavens" with NASA's Spitzer Project Scientist Michael Werner"
'Bridging the Gaps: A Portal for Curious Minds', 2019 {{authority control Great Observatories program Space telescopes Infrared telescopes Jet Propulsion Laboratory Lockheed Martin satellites and probes Derelict satellites in heliocentric orbit Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets Space probes launched in 2003 2003 establishments in Florida
 The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder.
The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission.
During the warm mission, the two short wavelength channels of IRAC operated at 28.7 K and were predicted to experience little to no degradation at this temperature compared to the nominal mission. The Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).
In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named by a board of scientists, typically after famous deceased astronomers, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.
The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder.
The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission.
During the warm mission, the two short wavelength channels of IRAC operated at 28.7 K and were predicted to experience little to no degradation at this temperature compared to the nominal mission. The Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).
In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named by a board of scientists, typically after famous deceased astronomers, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.
The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is financed ...
describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as "his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program."
The Spitzer was launched on 25 August 2003 at 05:35:39 UTC from Cape Canaveral
, image = cape canaveral.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = View of Cape Canaveral from space in 1991
, map = Florida#USA
, map_width = 300
, type =Cape
, map_caption = Location in Florida
, location ...
SLC-17B aboard a Delta II 7920H rocket. It was placed into a heliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at ...
(as opposed to a geocentric) orbit trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical units per year (an "Earth-trailing" orbit).
The primary mirror is in diameter, , made of beryllium and was cooled to . The satellite contains three instruments that allowed it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3.6 to 160 micrometers, spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
from 5.2 to 38 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 55 to 95 micrometers.
History
By the early 1970s, astronomers began to consider the possibility of placing an infrared telescope above the obscuring effects of Earth's atmosphere. In 1979, a report from the National Research Council of theNational Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, ''A Strategy for Space Astronomy and Astrophysics for the 1980s'', identified a Shuttle Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) as "one of two major astrophysics facilities o be developed
O, or o, is the fifteenth letter and the fourth vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''o'' (pronounced ), plu ...
for Spacelab", a shuttle-borne platform. Anticipating the major results from an upcoming Explorer satellite and from the Shuttle mission, the report also favored the "study and development of ... long-duration spaceflights of infrared telescopes cooled to cryogenic temperatures."
The launch in January 1983 of the Infrared Astronomical Satellite, jointly developed by the United States, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom, to conduct the first infrared survey of the sky, whetted the appetites of scientists worldwide for follow-up space missions capitalizing on the rapid improvements in infrared detector technology.
Earlier infrared observations had been made by both space-based and ground-based observatories. Ground-based observatories have the drawback that at infrared wavelengths or frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
, both the Earth's atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
and the telescope itself will radiate (glow) brightly. Additionally, the atmosphere is opaque at most infrared wavelengths. This necessitates lengthy exposure times and greatly decreases the ability to detect faint objects. It could be compared to trying to observe the stars in the optical at noon from a telescope built out of light bulbs. Previous space observatories (such as IRAS, the Infrared Astronomical Satellite, and ISO, the Infrared Space Observatory) were launched during the 1980s and 1990s and great advances in astronomical technology have been made since then.
Most of the early concepts envisioned repeated flights aboard the NASA Space Shuttle. This approach was developed in an era when the Shuttle program was expected to support weekly flights of up to 30 days duration. A May 1983 NASA proposal described SIRTF as a Shuttle-attached mission, with an evolving scientific instrument payload. Several flights were anticipated with a probable transition into a more extended mode of operation, possibly in association with a future space platform or space station. SIRTF would be a 1-meter class, cryogenically cooled, multi-user facility consisting of a telescope and associated focal plane instruments. It would be launched on the Space Shuttle and remain attached to the Shuttle as a Spacelab payload during astronomical observations, after which it would be returned to Earth for refurbishment prior to re-flight. The first flight was expected to occur about 1990, with the succeeding flights anticipated beginning approximately one year later. However, the Spacelab-2 flight aboard STS-51-F showed that the Shuttle environment was poorly suited to an onboard infrared telescope due to contamination from the relatively "dirty" vacuum associated with the orbiters. By September 1983, NASA was considering the "possibility of a long duration ree-flyerSIRTF mission".
Spitzer is the only one of the Great Observatories
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electrom ...
not launched by the Space Shuttle, as was originally intended. However, after the 1986 Challenger disaster, the Shuttle-Centaur upper stage, which would have been required to place it into its final orbit, was abandoned. The mission underwent a series of redesigns during the 1990s, primarily due to budget considerations. This resulted in a much smaller but still fully capable mission that could use the smaller Delta II expendable launch vehicle.
 One of the most important advances of this redesign was an Earth-trailing orbit. Cryogenic satellites that require liquid helium (LHe, T ≈ 4 K) temperatures in near-Earth orbit are typically exposed to a large heat load from Earth, and consequently require large amounts of LHe coolant, which then tends to dominate the total payload mass and limits mission life. Placing the satellite in solar orbit far from Earth allowed innovative passive cooling. The sun shield protected the rest of the spacecraft from the Sun's heat, the far side of the spacecraft was painted black to enhance passive radiation of heat, and the spacecraft bus was thermally isolated from the telescope. All of these design choices combined to drastically reduce the total mass of helium needed, resulting in an overall smaller and lighter payload, resulting in major cost savings, but with a mirror the same diameter as originally designed. This orbit also simplified telescope pointing, but did require the NASA Deep Space Network for communications.
The primary instrument package (telescope and cryogenic chamber) was developed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies, in
One of the most important advances of this redesign was an Earth-trailing orbit. Cryogenic satellites that require liquid helium (LHe, T ≈ 4 K) temperatures in near-Earth orbit are typically exposed to a large heat load from Earth, and consequently require large amounts of LHe coolant, which then tends to dominate the total payload mass and limits mission life. Placing the satellite in solar orbit far from Earth allowed innovative passive cooling. The sun shield protected the rest of the spacecraft from the Sun's heat, the far side of the spacecraft was painted black to enhance passive radiation of heat, and the spacecraft bus was thermally isolated from the telescope. All of these design choices combined to drastically reduce the total mass of helium needed, resulting in an overall smaller and lighter payload, resulting in major cost savings, but with a mirror the same diameter as originally designed. This orbit also simplified telescope pointing, but did require the NASA Deep Space Network for communications.
The primary instrument package (telescope and cryogenic chamber) was developed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies, in Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a home rule city that is the county seat and most populous municipality of Boulder County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, making it the 12th most populous city in Color ...
. The individual instruments were developed jointly by industrial, academic, and government institutions, the principals being Cornell, the University of Arizona, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on astrophysical studies including galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, solar, earth and planetary sciences, the ...
, Ball Aerospace, and Goddard Spaceflight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
. The shorter-wavelength infrared detectors were developed by Raytheon in Goleta, California. Raytheon used indium antimonide and a doped silicon detector in the creation of the infrared detectors. These detectors are 100 times more sensitive than what was available at the beginning of the project during the 1980s. The far-infrared detectors (70–160 micrometers) were developed jointly by the University of Arizona and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), commonly referred to as the Berkeley Lab, is a United States Department of Energy National Labs, United States national laboratory that is owned by, and conducts scientific research on behalf of, t ...
using gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminiu ...
-doped germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors s ...
. The spacecraft was built by Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
. The mission was operated and managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the ''Spitzer Science Center'', located on the Caltech campus in Pasadena, California.
Launch and commissioning
Warm mission and end of mission
Spitzer ran out of liquid helium coolant on 15 May 2009, which stopped far-IR observations. Only the IRAC instrument remained in use, and only at the two shorter wavelength bands (3.6 μm and 4.5 μm). The telescope equilibrium temperature was then around , and IRAC continued to produce valuable images at those wavelengths as the "Spitzer Warm Mission". Late in the mission, ~2016, Spitzer's distance to Earth and the shape of its orbit meant the spacecraft had to pitch over at an extreme angle to aim its antenna at Earth. The solar panels were not fully illuminated at this angle, and this limited those communications to 2.5 hours due to the battery drain. The telescope was retired on 30 January 2020Ending in 2020, NASA's Infrared Spitzer Mission Leaves a Gap in Astronomy.Jonathan O'Callaghan. '' Scientific American''. June 4, 2019. when NASA sent a shutdown signal to the telescope from the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex (GDSCC) instructing the telescope to go into safe mode. After receiving confirmation that the command was successful, Spitzer Project Manager Joseph Hunt officially declared that the mission had ended.
Instruments
 Spitzer carries three instruments on board:
; Infrared Array Camera (IRAC)
: An infrared camera which operated simultaneously on four wavelengths (3.6 μm, 4.5 μm, 5.8 μm and 8 μm). Each module used a 256×256-pixel detector—the short-wavelength pair used indium antimonide technology, the long-wavelength pair used arsenic-doped silicon impurity band conduction technology.SSC IRAC (Mid IR camera) science users information page
Spitzer carries three instruments on board:
; Infrared Array Camera (IRAC)
: An infrared camera which operated simultaneously on four wavelengths (3.6 μm, 4.5 μm, 5.8 μm and 8 μm). Each module used a 256×256-pixel detector—the short-wavelength pair used indium antimonide technology, the long-wavelength pair used arsenic-doped silicon impurity band conduction technology.SSC IRAC (Mid IR camera) science users information page4 October 2009. The principal investigator was
Giovanni Fazio
Giovanni Fazio is an American physicist at Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian. He is an astrophysicist who has initiated and participated in multiple observation programs.
Career
In 1962 he joined the Smithsonian Astrophysical Obs ...
of Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian; the flight hardware was built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
.
; Infrared Spectrograph (IRS)
: An infrared spectrometer with four sub-modules which operate at the wavelengths 5.3–14 μm (low resolution), 10–19.5 μm (high resolution), 14–40 μm (low resolution), and 19–37 μm (high resolution). Each module used a 128×128-pixel detector—the short-wavelength pair used arsenic-doped silicon blocked impurity band technology, the long-wavelength pair used antimony-doped silicon blocked impurity band technology.SSC IRS (spectrometer) science users' information page4 October 2009. The principal investigator was
James R. Houck
James Richard Houck (October 5, 1940 – September 18, 2015) was the Kenneth A. Wallace Professor of Astronomy at Cornell University.
Houck pioneered infrared observational astronomy, designing detectors and spectrographs that were flown on sound ...
of Cornell University; the flight hardware was built by Ball Aerospace.
; Multiband Imaging Photometer for Spitzer (MIPS)
: Three detector arrays in the mid- to far-infrared (128 × 128 pixels at 24 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
, 32 × 32 pixels at 70 μm, 2 × 20 pixels at 160 μm). The 24 μm detector is identical to one of the IRS short-wavelength modules. The 70 μm detector used gallium-doped germanium technology, and the 160 μm detector also used gallium-doped germanium, but with mechanical stress added to each pixel to lower the bandgap and extend sensitivity to this long-wavelength.SSC MIPS(long wavelength 24um, 70um, & 160um) imaging photometer and spectrometer science users' information page, 4 October 2009. The principal investigator was George H. Rieke of the University of Arizona; the flight hardware was built by Ball Aerospace. All three instruments used liquid helium for cooling the sensors. Once the helium was exhausted, only the two shorter wavelengths in IRAC were used in the "warm mission".
Results
While some time on the telescope was reserved for participating institutions and crucial projects, astronomers around the world also had the opportunity to submit proposals for observing time. Prior to launch, there was a proposal call for large, coherent investigations using Spitzer. If the telescope failed early and/or ran out of cryogen very quickly, these so-called Legacy Projects would ensure the best possible science could be obtained quickly in the early months of the mission. As a requirement tied to the funding these Legacy teams received, the teams had to deliver high-level data products back to the Spitzer Science Center (and the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive) for use by the community, again ensuring the rapid scientific return of the mission. The international scientific community quickly realized the value of delivering products for others to use, and even though Legacy projects were no longer explicitly solicited in subsequent proposal calls, teams continued to deliver products to the community. The Spitzer Science Center later reinstated named "Legacy" projects (and later still "Exploration Science" projects) in response to this community-driven effort. Important targets included forming stars ( young stellar objects, or YSOs), planets, and other galaxies. Images are freely available for educational and journalistic purposes.
 The first released images from Spitzer were designed to show off the abilities of the telescope and showed a glowing stellar nursery, a big swirling, dusty
The first released images from Spitzer were designed to show off the abilities of the telescope and showed a glowing stellar nursery, a big swirling, dusty galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
, a disc of planet-forming debris, and organic material in the distant universe. Since then, many monthly press releases have highlighted Spitzer capabilities, as the NASA and ESA images do for the Hubble Space Telescope.
As one of its most noteworthy observations, in 2005, Spitzer became the first telescope to directly capture light from exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s, namely the "hot Jupiters" HD 209458 b and TrES-1b
TrES-1b is an extrasolar planet approximately 523 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra (the Lyre). The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a Jovian planet with a similar bulk composition to Jupiter. Unlike Jupiter, but similar ...
, although it did not resolve that light into actual images. This was the first time the light from extrasolar planets had been directly detected; earlier observations had been indirectly made by drawing conclusions from behaviors of the stars the planets were orbiting. The telescope also discovered in April 2005 that Cohen-kuhi Tau/4 had a planetary disk that was vastly younger and contained less mass than previously theorized, leading to new understandings of how planets are formed.
 In 2004, it was reported that Spitzer had spotted a faintly glowing body that may be the youngest star ever seen. The telescope was trained on a core of gas and dust known as
In 2004, it was reported that Spitzer had spotted a faintly glowing body that may be the youngest star ever seen. The telescope was trained on a core of gas and dust known as L1014
L1014 is a dark nebula in the Cygnus (constellation), Cygnus constellation. It may be among the most centrally condensed small dark clouds known, perhaps indicative of the earliest stages of star formation processes. This cloud harbors at its core ...
which had previously appeared completely dark to ground-based observatories and to ISO ( Infrared Space Observatory), a predecessor to Spitzer. The advanced technology of Spitzer revealed a bright red hot spot in the middle of L1014.
Scientists from the University of Texas at Austin, who discovered the object, believe the hot spot to be an example of early star development, with the young star collecting gas and dust from the cloud around it. Early speculation about the hot spot was that it might have been the faint light of another core that lies 10 times further from Earth but along the same line of sight as L1014. Follow-up observation from ground-based near-infrared observatories detected a faint fan-shaped glow in the same location as the object found by Spitzer. That glow is too feeble to have come from the more distant core, leading to the conclusion that the object is located within L1014. (Young ''et al.'', 2004)
In 2005, astronomers from the University of Wisconsin at Madison and Whitewater determined, on the basis of 400 hours of observation on the Spitzer Space Telescope, that the Milky Way galaxy has a more substantial bar structure across its core than previously recognized.
 Also in 2005, astronomers
Also in 2005, astronomers Alexander Kashlinsky
Alexander (Sasha) Kashlinsky (born 1957 in Riga) is an astronomer and cosmologist working at NASA Goddard-Space-Flight-Center, known for work on dark flow Also,
and the cosmic infrared background.
Kashlinsky has been interviewed by Morgan Freem ...
and John Mather of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
reported that one of Spitzer earliest images may have captured the light of the first stars in the universe. An image of a quasar
A quasar is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a m ...
in the Draco constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
, intended only to help calibrate the telescope, was found to contain an infrared glow after the light of known objects was removed. Kashlinsky and Mather are convinced that the numerous blobs in this glow are the light of stars that formed as early as 100 million years after the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
, redshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in f ...
ed by cosmic expansion.
In March 2006, astronomers reported an nebula near the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, the Double Helix Nebula, which is, as the name implies, twisted into a double spiral shape. This is thought to be evidence of massive magnetic fields generated by the gas disc orbiting the supermassive black hole at the galaxy's center, from the nebula and from Earth. This nebula was discovered by Spitzer and published in the magazine '' Nature'' on 16 March 2006.
In May 2007, astronomers successfully mapped the atmospheric temperature of HD 189733 b, thus obtaining the first map of some kind of an extrasolar planet.
Starting in September 2006, the telescope participated in a series of surveys called the Gould Belt Survey
The Gould Belt Survey is an astronomical research project led by the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian, with the participation of several other institutions.
The astronomers use observations and data captured by the Spitzer Space Tel ...
, observing the Gould's Belt
The Gould Belt is a local, partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3,000 light-years long, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, amounting to the nearest star-forming regi ...
region in multiple wavelengths. The first set of observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope was completed from 21 September 2006 through 27 September. Resulting from these observations, the team of astronomers led by Dr. Robert Gutermuth, of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian reported the discovery of Serpens South, a cluster of 50 young stars in the Serpens constellation.
 Scientists have long wondered how tiny silicate crystals, which need high temperatures to form, have found their way into frozen comets, born in the very cold environment of the Solar System's outer edges. The crystals would have begun as non-crystallized, amorphous silicate particles, part of the mix of gas and dust from which the Solar System developed. This mystery has deepened with the results of the ''
Scientists have long wondered how tiny silicate crystals, which need high temperatures to form, have found their way into frozen comets, born in the very cold environment of the Solar System's outer edges. The crystals would have begun as non-crystallized, amorphous silicate particles, part of the mix of gas and dust from which the Solar System developed. This mystery has deepened with the results of the ''Stardust
Stardust may refer to:
* A type of cosmic dust, composed of particles in space
Entertainment Songs
* “Stardust” (1927 song), by Hoagy Carmichael
* “Stardust” (David Essex song), 1974
* “Stardust” (Lena Meyer-Landrut song), 2012
* ...
'' sample return mission, which captured particles from Comet Wild 2. Many of the Stardust particles were found to have formed at temperatures in excess of 1,000 K.
In May 2009, Spitzer researchers from Germany, Hungary, and the Netherlands found that amorphous silicate appears to have been transformed into crystalline form by an outburst from a star. They detected the infrared signature of forsterite silicate crystals on the disk of dust and gas surrounding the star EX Lupi during one of its frequent flare-ups, or outbursts, seen by Spitzer in April 2008. These crystals were not present in Spitzer previous observations of the star's disk during one of its quiet periods. These crystals appear to have formed by radiative heating of the dust within 0.5 AU of EX Lupi.
In August 2009, the telescope found evidence of a high-speed collision between two burgeoning planets orbiting a young star.
In October 2009, astronomers Anne J. Verbiscer, Michael F. Skrutskie, and Douglas P. Hamilton published findings of the " Phoebe ring" of Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, which was found with the telescope; the ring is a huge, tenuous disc of material extending from 128 to 207 times the radius of Saturn.
GLIMPSE and MIPSGAL surveys
GLIMPSE, the ''Galactic Legacy Infrared Mid-Plane Survey Extraordinaire'', was a series of surveys that spanned 360° of the inner region of the Milky Way galaxy, which provided the first large-scale mapping of the galaxy. It consists of more than 2 million snapshots taken in four separate wavelengths using the Infrared Array Camera.Galactic Legacy Infrared Mid-Plane Survey Extraordinaire, University of Wisconsin–Madison Department of Astronomy The images were taken over a 10-year period beginning in 2003 when Spitzer launched. MIPSGAL, a similar survey that complements GLIMPSE, covers 248° of the galactic disk using the 24 and 70 μm channels of the MIPS instrument. On 3 June 2008, scientists unveiled the largest, most detailed infrared portrait of the Milky Way, created by stitching together more than 800,000 snapshots, at the 212th meeting of the
American Astronomical Society
The American Astronomical Society (AAS, sometimes spoken as "double-A-S") is an American society of professional astronomers and other interested individuals, headquartered in Washington, DC. The primary objective of the AAS is to promote the adv ...
in St. Louis, Missouri. This composite survey is now viewable with the GLIMPSE/MIPSGAL Viewer.
2010s
 Spitzer observations, announced in May 2011, indicate that tiny forsterite crystals might be falling down like rain on to the protostar HOPS-68. The discovery of the forsterite crystals in the outer collapsing cloud of the protostar is surprising because the crystals form at lava-like high temperatures, yet they are found in the molecular cloud where the temperatures are about . This led the team of astronomers to speculate that the bipolar outflow from the young star may be transporting the forsterite crystals from near the star's surface to the chilly outer cloud.
In January 2012, it was reported that further analysis of the Spitzer observations of EX Lupi can be understood if the forsterite crystalline dust was moving away from the protostar at a remarkable average speed of . It would appear that such high speeds can arise only if the dust grains had been ejected by a bipolar outflow close to the star. Such observations are consistent with an astrophysical theory, developed in the early 1990s, where it was suggested that bipolar outflows garden or transform the disks of gas and dust that surround protostars by continually ejecting reprocessed, highly heated material from the inner disk, adjacent to the protostar, to regions of the accretion disk further away from the protostar.
In April 2015, Spitzer and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment were reported as co-discovering one of the most distant planets ever identified: a gas giant about away from Earth.
Spitzer observations, announced in May 2011, indicate that tiny forsterite crystals might be falling down like rain on to the protostar HOPS-68. The discovery of the forsterite crystals in the outer collapsing cloud of the protostar is surprising because the crystals form at lava-like high temperatures, yet they are found in the molecular cloud where the temperatures are about . This led the team of astronomers to speculate that the bipolar outflow from the young star may be transporting the forsterite crystals from near the star's surface to the chilly outer cloud.
In January 2012, it was reported that further analysis of the Spitzer observations of EX Lupi can be understood if the forsterite crystalline dust was moving away from the protostar at a remarkable average speed of . It would appear that such high speeds can arise only if the dust grains had been ejected by a bipolar outflow close to the star. Such observations are consistent with an astrophysical theory, developed in the early 1990s, where it was suggested that bipolar outflows garden or transform the disks of gas and dust that surround protostars by continually ejecting reprocessed, highly heated material from the inner disk, adjacent to the protostar, to regions of the accretion disk further away from the protostar.
In April 2015, Spitzer and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment were reported as co-discovering one of the most distant planets ever identified: a gas giant about away from Earth.
 In June and July 2015, the brown dwarf was discovered using the gravitational microlensing detection method in a joint effort between Swift, Spitzer, and the ground-based Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment, the first time two space telescopes have observed the same microlensing event. This method was possible because of the large separation between the two spacecraft: Swift is in low-Earth orbit while Spitzer is more than one AU distant in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. This separation provided significantly different perspectives of the brown dwarf, allowing for constraints to be placed on some of the object's physical characteristics.
Reported in March 2016, Spitzer and Hubble were used to discover the most distant-known galaxy, GN-z11. This object was seen as it appeared 13.4 billion years ago.
In June and July 2015, the brown dwarf was discovered using the gravitational microlensing detection method in a joint effort between Swift, Spitzer, and the ground-based Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment, the first time two space telescopes have observed the same microlensing event. This method was possible because of the large separation between the two spacecraft: Swift is in low-Earth orbit while Spitzer is more than one AU distant in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. This separation provided significantly different perspectives of the brown dwarf, allowing for constraints to be placed on some of the object's physical characteristics.
Reported in March 2016, Spitzer and Hubble were used to discover the most distant-known galaxy, GN-z11. This object was seen as it appeared 13.4 billion years ago.
''Spitzer Beyond''
On 1 October 2016, Spitzer began its Observation Cycle 13, a year extended mission nicknamed ''Beyond''. One of the goals of this extended mission was to help prepare for theJames Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
, also an infrared telescope, by identifying candidates for more detailed observations.
Another aspect of the ''Beyond'' mission was the engineering challenges of operating Spitzer in its progressing orbital phase. As the spacecraft moved farther from Earth on the same orbital path from the Sun, its antenna had to point at increasingly higher angles to communicate with ground stations; this change in angle imparted more and more solar heating on the vehicle while its solar panels received less sunlight.
Planet hunter
 Spitzer was also put to work studying exoplanets thanks to creatively tweaking its hardware. This included doubling its stability by modifying its heating cycle, finding a new use for the "peak-up" camera, and analyzing the sensor at a sub-pixel level. Although in its "warm" mission, the spacecraft's passive cooling system kept the sensors at . Spitzer used the transit photometry and gravitational microlensing techniques to perform these observations. According to NASA's Sean Carey, "We never even considered using Spitzer for studying exoplanets when it launched. ... It would have seemed ludicrous back then, but now it's an important part of what Spitzer does."
Examples of exoplanets discovered using Spitzer include
Spitzer was also put to work studying exoplanets thanks to creatively tweaking its hardware. This included doubling its stability by modifying its heating cycle, finding a new use for the "peak-up" camera, and analyzing the sensor at a sub-pixel level. Although in its "warm" mission, the spacecraft's passive cooling system kept the sensors at . Spitzer used the transit photometry and gravitational microlensing techniques to perform these observations. According to NASA's Sean Carey, "We never even considered using Spitzer for studying exoplanets when it launched. ... It would have seemed ludicrous back then, but now it's an important part of what Spitzer does."
Examples of exoplanets discovered using Spitzer include HD 219134 b
HD 219134 b (or HR 8832 b) is one of at least five exoplanets orbiting HD 219134, a main-sequence star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. HD 219134 b has a size of about 1.6 , and a density of 6.4 g/cm3 and orbits at 21.25 light-years away. ...
in 2015, which was shown to be a rocky planet about 1.5 times as large as Earth in a three-day orbit around its star; and an unnamed planet found using microlensing located about from Earth.
In September–October 2016, Spitzer was used to discover five of a total of seven known planets around the star TRAPPIST-1, all of which are approximately Earth-sized and likely rocky. Three of the discovered planets are located in the habitable zone, which means they are capable of supporting liquid water given sufficient parameters. Using the transit method, Spitzer helped measure the sizes of the seven planets and estimate the mass and density of the inner six. Further observations will help determine if there is liquid water on any of the planets.
See also
*Herschel Space Observatory
The Herschel Space Observatory was a space observatory built and operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was active from 2009 to 2013, and was the largest infrared telescope ever launched until the launch of the James Webb Space Telesc ...
(2009–2013)
* Infrared astronomy
* List of deep fields
* List of space telescopes
* List of largest infrared telescopes
References
External links
*Spitzer Space Telescope
at NASA.gov
Spitzer Space Telescope
at Caltech.edu
Spitzer Space Telescope
by NASA's Solar System Exploration
GLIMPSE/MIPSGAL image viewer
at Alienearths.org
" Spitzer Space Telescope: Discovering "More Things in the Heavens" with NASA's Spitzer Project Scientist Michael Werner"
'Bridging the Gaps: A Portal for Curious Minds', 2019 {{authority control Great Observatories program Space telescopes Infrared telescopes Jet Propulsion Laboratory Lockheed Martin satellites and probes Derelict satellites in heliocentric orbit Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets Space probes launched in 2003 2003 establishments in Florida