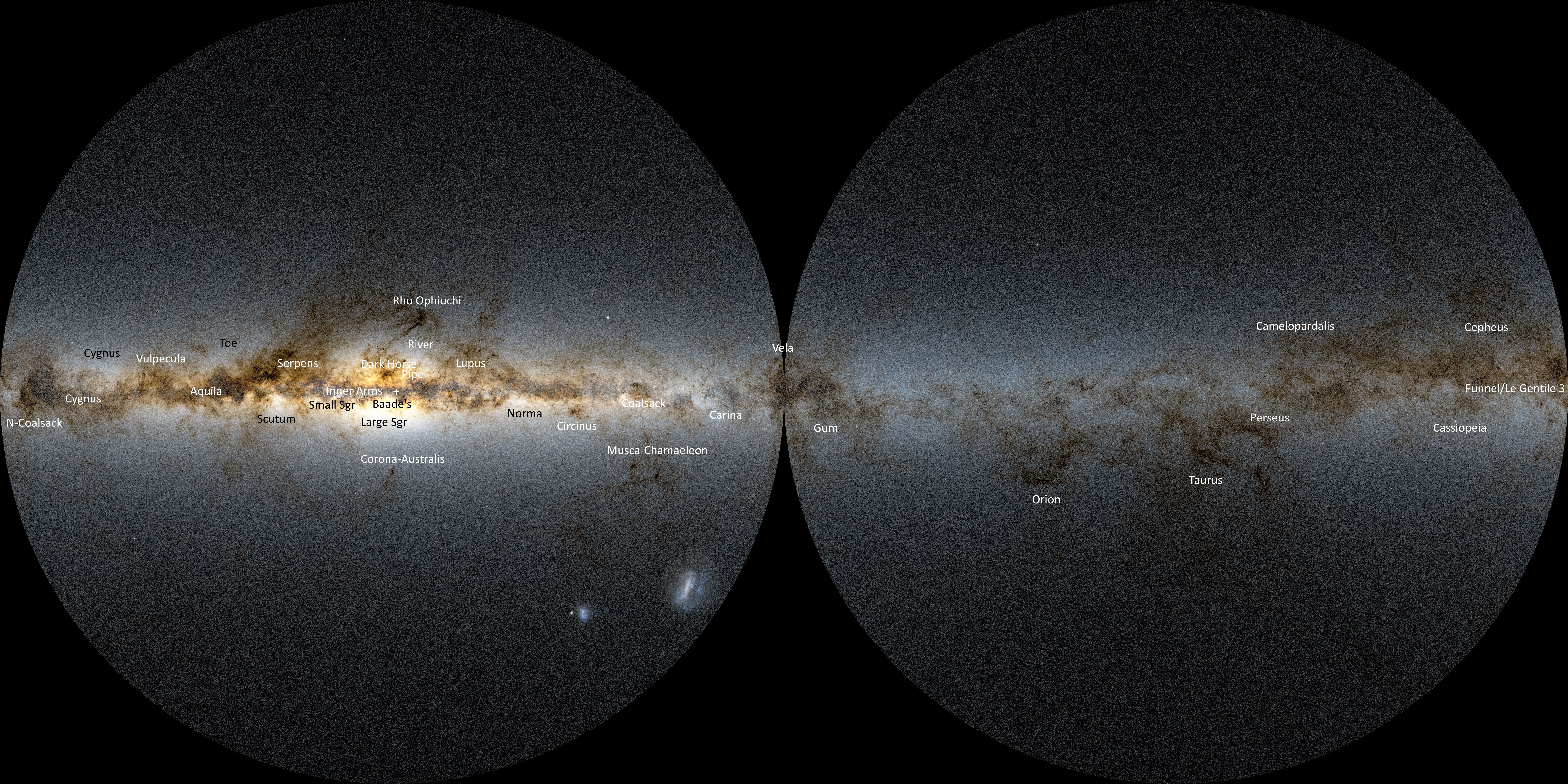
|
L1014
L1014 is a dark nebula in the Cygnus constellation. It may be among the most centrally condensed small dark clouds known, perhaps indicative of the earliest stages of star formation processes. This cloud harbors at its core a very young low-mass star named L1014 IRS; some astronomers have suggested that this object may be a brown dwarf Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen ( 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most ... or even a rogue planet at the earliest stage of its lifetime. References External links The Starless Core That Isn't// Spitzer Image, Release Date: 11/09/04 // NASA 11.09.04 Cygnus (constellation) Dark nebulae {{nebula-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions", collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function. Most stars do not form in isolation but as part of a group of stars referred as star clusters or stellar associations. Stellar nurseries Interstellar clouds A spiral galaxy like the Milky Way contains stars, stellar remnants, and a diffuse interstellar medium (ISM) of gas and dust. The inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Core
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witness The Birth Of A Star
In law, a witness is someone who has knowledge about a matter, whether they have sensed it or are testifying on another witnesses' behalf. In law a witness is someone who, either voluntarily or under compulsion, provides testimonial evidence, either oral or written, of what they know or claim to know. In law a witness might be compelled to provide testimony in court, before a grand jury, before an administrative tribunal, before a deposition officer, or in a variety of other legal proceedings. A subpoena is a legal document that commands a person to appear at a proceeding. It is used to compel the testimony of a witness in a trial. Usually, it can be issued by a judge or by the lawyer representing the plaintiff or the defendant in a civil trial or by the prosecutor or the defense attorney in a criminal proceeding, or by a government agency. In many jurisdictions, it is compulsory to comply with the subpoena and either take an oath or solemnly affirm to testify truthfully unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus (constellation)
Cygnus is a northern constellation on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Cygnus contains Deneb (ذنب, translit. ''ḏanab,'' tail)one of the brightest stars in the night sky and the most distant first-magnitude staras its "tail star" and one corner of the Summer Triangle. It also has some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. Cygnus is also known as the Northern Cross. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection nebulae. The extinction of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains located in the coldest, densest parts of molecular clouds. Clusters and large complexes of dark nebulae are associated with Giant Molecular Clouds. Isolated small dark nebulae are called Bok globules. Like other interstellar dust or material, things it obscures are only visible using radio waves in radio astronomy or infrared in infrared astronomy. Dark clouds appear so because of sub-micrometre-sized dust particles, coated with frozen carbon monoxide and nitrogen, which effectively block the passage of light at visible wavelengths. Also present are molecular hydrogen, atomic helium, C18O (CO with oxygen as the 18O isotope), CS, NH3 (ammonia), H2CO (formaldehyde), c-C3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellations in the far southern sky were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L1014 IRS
L1, L01, L.1, L 1 or L-1 may refer to: Mathematics, science and technology Math *L1 distance in mathematics, used in taxicab geometry * L1, the space of Lebesgue integrable functions * ℓ1, the space of absolutely convergent sequences Science *L1 family, a protein family of cell adhesion molecules *L1 (protein), a cell adhesion molecule *, Lagrangian point 1, the most intuitive position for an object to be gravitationally stationary relative to two larger objects (such as a satellite with respect to the Earth and Moon) *Anthranilic acid, also called vitamin L1 *The first lumbar vertebra of the vertebral column in human anatomy * The first larval stage in the ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' worm development Technology *L1, one of the frequencies used by GPS systems (see GPS frequencies) *L1, the common name for the Soviet space effort known formally as Soyuz 7K-L1, designed to launch men from the Earth to circle the Moon without going into lunar orbit *ISO/IEC 8859-1 (Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen (hydrogen-1, 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main sequence, main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most massive gas giant planets and the least massive stars, approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter (). However, they can deuterium burning, fuse deuterium (deuterium, 2H), and the most massive ones (> ) can lithium burning, fuse lithium (lithium-7, 7Li). Astronomers classify self-luminous objects by spectral classification, spectral class, a distinction intimately tied to the surface temperature, and brown dwarfs occupy types M, L, T, and Y. As brown dwarfs do not undergo stable hydrogen fusion, they cool down over time, progressively passing through later spectral types as they age. Despite their name, to the naked eye, brown dwarfs would appear in different colors depending on their temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogue Planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a host planetary system. Such objects have been ejected from the planetary system in which they formed or have never been gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf. The Milky Way alone may have billions to trillions of rogue planets, a range the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will likely be able to narrow down. Some planetary-mass objects may have formed in a similar way to stars, and the International Astronomical Union has proposed that such objects be called sub-brown dwarfs. A possible example is Cha 110913−773444, which may have been ejected and become a rogue planet, or formed on its own to become a sub-brown dwarf. Astronomers have used the Herschel Space Observatory and the Very Large Telescope to observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |