|
American Astronomical Society
The American Astronomical Society (AAS, sometimes spoken as "double-A-S") is an American society of professional astronomers and other interested individuals, headquartered in Washington, DC. The primary objective of the AAS is to promote the advancement of astronomy and closely related branches of science, while the secondary purpose includes enhancing astronomy education and providing a political voice for its members through lobbying and grassroots activities. Its current mission is to enhance and share humanity's scientific understanding of the universe as a diverse and inclusive astronomical community. History The society was founded in 1899 through the efforts of George Ellery Hale. The constitution of the group was written by Hale, George Comstock, Edward Morley, Simon Newcomb and Edward Charles Pickering. These men, plus four others, were the first Executive Council of the society; Newcomb was the first president. The initial membership was 114. The AAS name of the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-governmental Organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in humanitarianism or the social sciences; they can also include clubs and associations that provide services to their members and others. Surveys indicate that NGOs have a high degree of public trust, which can make them a useful proxy for the concerns of society and stakeholders. However, NGOs can also be lobby groups for corporations, such as the World Economic Forum. NGOs are distinguished from international and intergovernmental organizations (''IOs'') in that the latter are more directly involved with sovereign states and their governments. The term as it is used today was first introduced in Article 71 of the newly-formed United Nations' Charter in 1945. While there is no fixed or formal definition for what NGOs are, they are genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
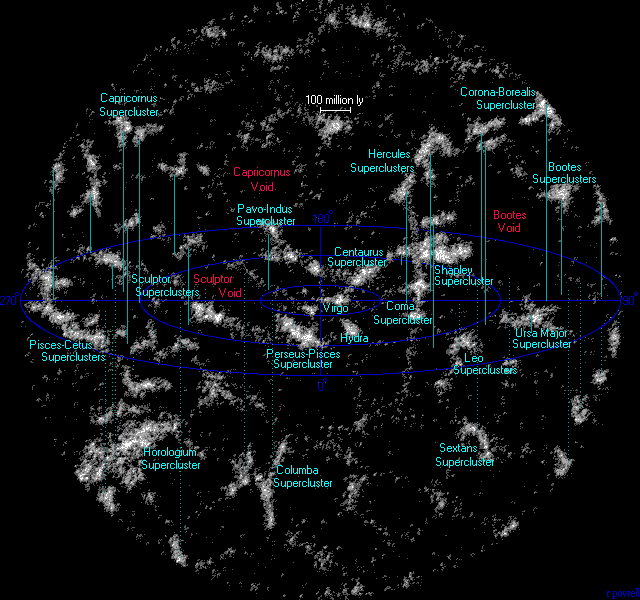
Superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea '''' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Journal
''The Astronomical Journal'' (often abbreviated ''AJ'' in scientific papers and references) is a peer-reviewed monthly scientific journal owned by the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and currently published by IOP Publishing. It is one of the premier journals for astronomy in the world. Until 2008, the journal was published by the University of Chicago Press on behalf of the AAS. The reasons for the change to the IOP were given by the society as the desire of the University of Chicago Press to revise its financial arrangement and their plans to change from the particular software that had been developed in-house. The other two publications of the society, the ''Astrophysical Journal'' and its supplement series, followed in January 2009. The journal was established in 1849 by Benjamin A. Gould. It ceased publication in 1861 due to the American Civil War, but resumed in 1885. Between 1909 and 1941 the journal was edited in Albany, New York. In 1941, editor Benjamin Boss arranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Physics
Solar physics is the branch of astrophysics that specializes in the study of the Sun. It deals with detailed measurements that are possible only for our closest star. It intersects with many disciplines of pure physics, astrophysics, and computer science, including fluid dynamics, plasma physics including magnetohydrodynamics, seismology, particle physics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, stellar evolution, space physics, spectroscopy, radiative transfer, applied optics, signal processing, computer vision, computational physics, stellar physics and solar astronomy. Because the Sun is uniquely situated for close-range observing (other stars cannot be resolved with anything like the spatial or temporal resolution that the Sun can), there is a split between the related discipline of observational astrophysics (of distant stars) and observational solar physics. The study of solar physics is also important as it provides a "physical laboratory" for the study of plasma physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Astronomy
Historical astronomy is the science of analysing historic astronomical data. The American Astronomical Society (AAS), established 1899, states that its Historical Astronomy Division "...shall exist for the purpose of advancing interest in topics relating to the historical nature of astronomy. By historical astronomy we include the history of astronomy; what has come to be known as archaeoastronomy; and the application of historical records to modern astrophysical problems.Historical and ancient observations are used to track theoretically long term trends, such as eclipse patterns and the velocity of nebular cloudsConversely, utilizing known and well documented phenomenological activity, historical astronomers apply computer models to verify the validity of ancient observations, as well as Astronomical chronology, dating such observations and documents which would otherwise be unknown. Examples * One example of such study would be the Crab Nebula, which is the remains of a supern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Astronomy
Astronomy is the oldest of the natural sciences, dating back to antiquity, with its origins in the religious, mythological, cosmological, calendrical, and astrological beliefs and practices of prehistory: vestiges of these are still found in astrology, a discipline long interwoven with public and governmental astronomy. It was not completely separated in Europe (see astrology and astronomy) during the Copernican Revolution starting in 1543. In some cultures, astronomical data was used for astrological prognostication. Early history Early cultures identified celestial objects with gods and spirits. They related these objects (and their movements) to phenomena such as rain, drought, seasons, and tides. It is generally believed that the first astronomers were priests, and that they understood celestial objects and events to be manifestations of the divine, hence early astronomy's connection to what is now called astrology. A 32,500-year-old carved ivory mammoth tusk could cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Field
In physics, a gravitational field is a model used to explain the influences that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body. Thus, a gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, and is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg). Equivalently, it is measured in meters per second squared (m/s2). In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses. Following Isaac Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace attempted to model gravity as some kind of radiation field or fluid, and since the 19th century, explanations for gravity have usually been taught in terms of a field model, rather than a point attraction. In a field model, rather than two particles attracting each other, the particles distort spacetime via their mass, and this distortion is what is perceived and measured as a "force". In such a model one states that matter moves in certain ways in response to the curvature of spacetime, and that there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gravitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. (Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom.) Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact (quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing nature. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photons) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this. Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)