Muhammad Ibn Abd Al-Wahhab on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab ibn Sulayman al-Tamimi ( ar, محمد بن عبد الوهاب بن سليمان , translit=Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb ibn Sulaymān al-Tamīmī; 1703–1792) was an Arabian
 As a gifted communicator with a talent for breaking down his ideas into shorter units, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab entitled his treatises with terms such as ''qawāʿid'' ("principles"), ''masāʾil'' ("matters"), ''kalimāt'' ("phrases"), or ''uṣūl'' ("foundations"), simplifying his texts point by point for mass reading. Calling upon the people to follow his call for religious revival ('' tajdid'' ) based on following the founding texts and the authoritative practices of the first generations of
As a gifted communicator with a talent for breaking down his ideas into shorter units, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab entitled his treatises with terms such as ''qawāʿid'' ("principles"), ''masāʾil'' ("matters"), ''kalimāt'' ("phrases"), or ''uṣūl'' ("foundations"), simplifying his texts point by point for mass reading. Calling upon the people to follow his call for religious revival ('' tajdid'' ) based on following the founding texts and the authoritative practices of the first generations of
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's call gradually began to attract followers, including the ruler of 'Uyayna, Uthman ibn Mu'ammar. Upon returning to Huraymila, where his father had settled, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab wrote his first work on the Unity of God. With Ibn Mu'ammar, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab agreed to support Ibn Mu'ammar's political ambitions to expand his rule "over Najd and possibly beyond", in exchange for the ruler's support for Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's religious teachings. During the early years of preaching, he criticised various folk practices and superstitions peacefully through sermons. Starting from 1742, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab would shift towards an activist stance; and began to implement his reformist ideas. First, he persuaded Ibn Mu'ammar to help him level the tomb of Zayd ibn al-Khattab, a
 Upon his expulsion from ' Uyayna, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab was invited to settle in neighboring Diriyah by its ruler Muhammad ibn Saud Al Muqrin. After some time in Diriyah, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab concluded his second and more successful agreement with a ruler. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and Muhammad bin Saud agreed that, together, they would bring the
Upon his expulsion from ' Uyayna, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab was invited to settle in neighboring Diriyah by its ruler Muhammad ibn Saud Al Muqrin. After some time in Diriyah, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab concluded his second and more successful agreement with a ruler. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and Muhammad bin Saud agreed that, together, they would bring the
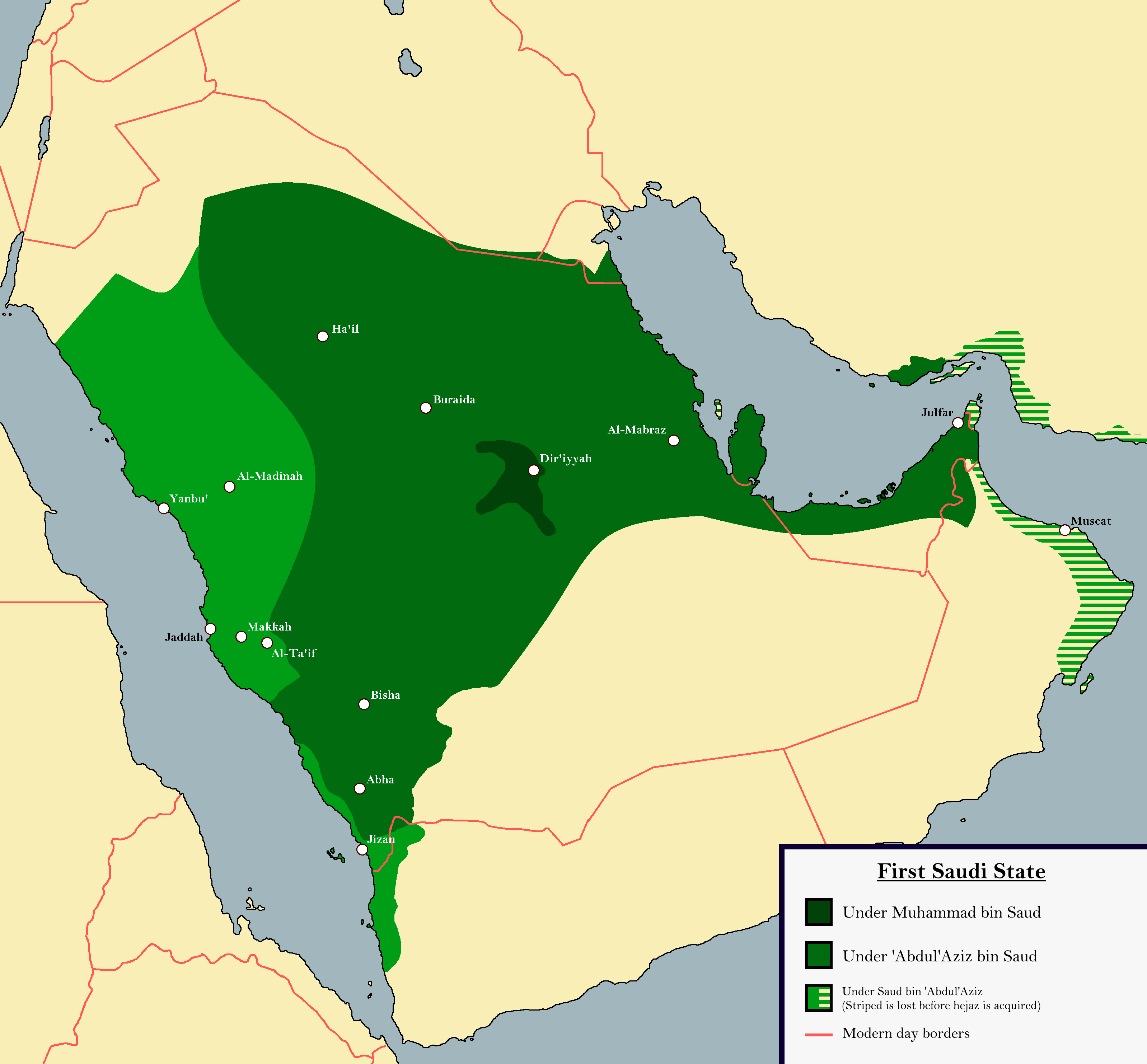 The 1744 pact between Muhammad ibn Saud and Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab marked the rise of the First Saudi state, the Emirate of Diriyah, which was established in 1727. By offering the
The 1744 pact between Muhammad ibn Saud and Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab marked the rise of the First Saudi state, the Emirate of Diriyah, which was established in 1727. By offering the
 The last point of serious threat to the Saudi state was in 1764-1765. During this period, the Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa of Najrān alongside their allied tribe of
The last point of serious threat to the Saudi state was in 1764-1765. During this period, the Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa of Najrān alongside their allied tribe of
 Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab sought to
Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab sought to
Throughout his epsitles like ''Arbaʿ qawāʿid tadūruʾl-aḥkām ʿalayhā'' (Four rules on which rulings revolve), Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab fiercely attacked the prevalent Hanbali Fiqh opinions; with a broader view of re-orienting the Fiqh tradition. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab challenged the ''
In calling for a direct return to the Scriptures, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was not a literalist and often strongly objected to literalist approaches and ritualism of religion that came with it. He believed that pure intentions ('' Niyyah'') constituted the essence of all virtous actions and upheld its superiority over dull ritualism. As a deferential and accomplished jurist with the experience of religious training under numerous masters in his travels, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab opposed the rigid, hardline views of the tradition-bound ''
According to Vahid Hussein Ranjbar, "Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab saw it as his mission to restore a more purer and original form of the faith of Islam". In accordance with the his own theology, which upheld a strict doctrine of ''
British diplomat
Meanwhile, contemporary Western historians and researchers have taken a more nuanced approach on the history and evolution of the ''
 Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's thoughts would greatly influence the pan-Islamic movement of the 19th century. The national mosque of
Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's thoughts would greatly influence the pan-Islamic movement of the 19th century. The national mosque of
 Two of the earliest sources for the biography of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab and early history of the
Two of the earliest sources for the biography of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab and early history of the
Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb: Muslim theologian
in ''Encyclopædia Britannica Online'', by The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica, Parul Jain, Satyavrat Nirala and Adam Zeidan
Biodata at MuslimScholars.info
{{DEFAULTSORT:Abd Al Wahhab, Muhammad Ibn 1703 births 1792 deaths 18th-century Arabs 18th-century Muslim scholars of Islam Muslim reformers Anti-Ottomanism Arab Sunni Muslim scholars of Islam Critics of Shia Islam Islamic religious leaders Sunni imams Proto-Salafists Hanbalis Mujaddid Chief Qadis of Emirate of Dir'iyah 18th-century Muslim theologians Atharis Wahhabists
Islamic scholar
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
, theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing th ...
, preacher
A preacher is a person who delivers sermons or homilies on religious topics to an assembly of people. Less common are preachers who preach on the street, or those whose message is not necessarily religious, but who preach components such as a ...
, activist
Activism (or Advocacy) consists of efforts to promote, impede, direct or intervene in social, political, economic or environmental reform with the desire to make changes in society toward a perceived greater good. Forms of activism range fr ...
, religious leader, and reformer from Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
in central Arabia, considered as the eponymous founder of the Wahhabi movement. His prominent students included his sons Ḥusayn, Abdullāh, ʿAlī, and Ibrāhīm, his grandson ʿAbdur-Raḥman ibn Ḥasan, his son-in-law ʿAbdul-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Saʿūd, Ḥamād ibn Nāṣir ibn Muʿammar, and Ḥusayn āl-Ghannām.
The label "Wahhabi" is not claimed by his followers but rather employed by Western scholars as well as his critics. Born to a family of jurists, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's early education consisted of learning a fairly standard curriculum of orthodox jurisprudence according to the Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
school of Islamic law, which was the school most prevalent in his area of birth. He promoted strict adherence to traditional Islamic law, proclaiming the necessity of returning directly to the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
and ''ḥadīth'' literature rather than relying on medieval interpretations, and insisted that every Muslim male and female personally read and study the Quran. He opposed ''taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
'' (following) and called for the use of ''ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
'' (independent legal reasoning through research of scripture). Being given initial rudimentary training in classical Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
tradition, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab gradually became opposed to many popular, yet contested, religious practices such as the visitation to and veneration
Veneration ( la, veneratio; el, τιμάω ), or veneration of saints, is the act of honoring a saint, a person who has been identified as having a high degree of sanctity or holiness. Angels are shown similar veneration in many religions. Etym ...
of the shrines and tombs of Muslim saints, which he felt amounted to heretical religious innovation or even idolatry. His call for social reform
A reform movement or reformism is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social or also a political system closer to the community's ideal. A reform movement is distinguished from more radical social movements such as revolutionary m ...
in society was based on the key doctrine of ''tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' (oneness of God), and was greatly inspired by the treatises of classical scholars Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
(d. 728 A.H/ 1328 C.E) and Ibn Qayyim (d. 751 A.H/ 1350 C.E).
Despite his teachings being rejected and opposed by many of the most notable Sunni Muslim scholars of the period, including his own father and brother
A brother is a man or boy who shares one or more parents with another; a male sibling. The female counterpart is a sister. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to non-famil ...
, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab charted a religio-political pact with Muhammad bin Saud to help him to establish the Emirate of Diriyah
The Emirate of Diriyah (), also known as the First Saudi State, was established in February 1727 (1139 AH). In 1744, the emir of Najdi town called Diriyah Muhammad bin Saud and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab formed an allianc ...
, the first Saudi state, and began a dynastic alliance and power-sharing arrangement between their families which continues to the present day in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
. The Al ash-Sheikh
The Al ash-Sheikh ( ar, آل الشيخ, '),Using the term ''the Al ash-Sheikh family'' is a pleonasm as the word ''Al'' already means ''family''. See Etymology. It would, in theory, be correct to use the term ''Family of the Sheikh'', but, unlik ...
, Saudi Arabia's leading religious family, are the descendants of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab, and have historically led the ''ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
'' in the Saudi state, Abir 1987: 4, 5, 7 dominating the state's clerical institutions. Metz 1992
Early years
Background
Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab is generally acknowledged to have been born in 1703 Philby 1930: 8 into the sedentary and impoverished Arab clan ofBanu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
in 'Uyayna
Al-'Uyayna or al-'Uyaynah ( ar, العيينة) is a village in central Saudi Arabia, located some northwest of the Saudi capital Riyadh. Al-Uyaynah was the birthplace of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. Today, Uyaynah is a small village and forms t ...
, a village in the Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
region of central Arabia. Before the emergence of the Wahhabi movement, there was a very limited history of Islamic education Islamic education may refer to:
* Islamic studies, the academic study of Islam and Islamic culture
*Madrasah, the Arabic word for any type of educational institution
*Islamic Education Society, an Islamic organization in India
*Education in Islam
...
in the area. For this reason, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab had modest access to Islamic education during his youth. Despite this, ibn Ghannam: 75–76 EI2: 677–78 the area had nevertheless produced several notable jurists of the Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
school of orthodox Sunni jurisprudence, which was the school of law most prominently practiced in the area. In fact, Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab's own family "had produced several doctors of the school," with his father, ʿAbd al-Wahhāb, having been the Hanbali jurisconsult of the Najd and his grandfather, Sulaymān, having been a judge of Hanbali law.
Early studies
Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab's early education was taught by his father, and consisted of learning theQuran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
by heart and studying a rudimentary level of Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning ...
and Islamic theology
Schools of Islamic theology are various Islamic schools and branches in different schools of thought regarding '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). The main schools of Islamic Theology include the Qadariyah, Falasifa, Jahmiyya, Murji'ah, Muʿtazila, Bat ...
as outlined in the works of Ibn Qudamah
Ibn Qudāmah al-Maqdisī Muwaffaq al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh b. Aḥmad b. Muḥammad ( ar, ابن قدامة المقدسي موفق الدين ابو محمد عبد الله بن احمد بن محمد ; 1147 - 7 July 1223), often re ...
(d. 1223), one of the most influential medieval representatives of the Hanbali school, whose works were regarded "as having great authority" in the Najd. The affirmation of Islamic sainthood and the ability of saints to perform miracles ('' karamat'') by the grace of God had become a major aspect of Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
belief throughout the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
, being agreed-upon by majority of the classical Islamic scholars. Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab had encountered various excessive beliefs and practices associated with saint-veneration and saint-cults which were prevalent in his area. During that era, various supernatural rituals and beliefs associated with magic, superstitions, occultism
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism a ...
, numerology
Numerology (also known as arithmancy) is the belief in an occult, divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value, via an alphanumeric system, of the letters in ...
, etc. had become predominant across numerous towns and villages of Arabian Peninsula. He probably chose to leave Najd and look elsewhere for studies to see if such beliefs and rituals were as popular in the neighboring places of the Muslim world or the possibility that his home town offered inadequate educational resources. Even today, the reasoning for why he left Najd is unclear.
Travels
Pilgrimage to Mecca
After leaving 'Uyayna around the age of twenty, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab performed the Greater Pilgrimage inMecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
, where the scholars appear to have held opinions and espoused teachings that were unpalatable to him. After this, he went to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, the stay at which seems to have been "decisive in shaping the later direction of his thought." In Medina, he met a Hanbali theologian from Najd named ʿAbd Allāh ibn Ibrāhīm al-Najdī, who had been a supporter of the works of Ibn Taymiyyah
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
(d. 1328), the controversial medieval scholar whose teachings had been considered heterodox and misguided on several important points by the vast majority of Sunni Muslim scholars up to that point in history.
Tutelage under Al-Sindhi
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's teacher, 'Abdallah ibn Ibrahim ibn Sayf, introduced the relatively young man toMohammad Hayya Al-Sindhi
Muhammad Hayyat al-Sindhi ( sd, محمد حيات سنڌي) (died 3 February 1750) was an Islamic scholar who lived during the period of the Ottoman Empire.
He belonged to the Naqshbandi order of Sufism.
Education and scholarship
Al-Sindhi wa ...
in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, who belonged to the Naqshbandi
The Naqshbandi ( fa, نقشبندی)), Neqshebendi ( ku, نهقشهبهندی), and Nakşibendi (in Turkish) is a major Sunni order of Sufism. Its name is derived from Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari. Naqshbandi masters trace their ...
order (''tariqa
A tariqa (or ''tariqah''; ar, طريقة ') is a school or order of Sufism, or specifically a concept for the mystical teaching and spiritual practices of such an order with the aim of seeking '' haqiqa'', which translates as "ultimate truth".
...
'') of Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
, and recommended him as a student. Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab and al-Sindhi became very close, and Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab stayed with him for some time. Voll 1975: 32–39 "Scholars have described Muhammad Hayya as having an important influence on Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, encouraging him in his developing determination to denounce rigid imitation of medieval commentaries and to utilize informed individual analysis (ijtihad). Muhammad Hayya also taught Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab a rejection of popular religious practices associated with 'saints' and their tombs that is similar to later Wahhdbi teachings." Muhammad Hayya taught Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab to reject popular religious practices associated with wali
A wali (''wali'' ar, وَلِيّ, '; plural , '), the Arabic word which has been variously translated "master", "authority", "custodian", "protector", is most commonly used by Muslims to indicate an Islamic saint, otherwise referred to by t ...
s and their tombs. He also encouraged him to reject rigid imitation (''Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
'') of medieval legal commentaries and develop individual research of scriptures (''Ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
''). Influenced by Al-Sindi's teachings, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab became critical of the established ''Madh'hab
A ( ar, مذهب ', , "way to act". pl. مَذَاهِب , ) is a school of thought within '' fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence).
The major Sunni Mathhab are Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i and Hanbali.
They emerged in the ninth and tenth centuries ...
'' system, prompting him to disregard the instruments of '' Usul al-Fiqh'' in his intellectual approach. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab rarely made use of ''Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
'' (Islamic jurisprudence) and various legal opinions in his writings, by and large forming views based on his direct understanding of Scriptures.
Apart from his emphasis on hadith studies
Hadith studies ( ar, علم الحديث ''ʻilm al-ḥadīth'' "science of hadith", also science of hadith, or science of hadith criticism or hadith criticism)
consists of several religious scholarly disciplines used by Muslim scholars in th ...
, aversion for the ''madhhab'' system and disregard for technical juristic discussions involving legal principles, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhāb's views on '' ziyārah'' (visitations to the shrines of '' Awliyaa'') were also shaped by Al-Sindhi. Sindi encouraged his student to reject folk practices associated with graves and saints. Various themes in Al-Sindi's writings, such as his opposition to erecting tombs and drawing human images, would be revived later by the Wahhabi
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, ...
movement. Sindi instilled in Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab the belief that practices like beseeching the dead saints constituted apostasy
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that i ...
and resembled the customs of the people of '' Jahiliyya'' (pre-Islamic era). In a significant encounter between a young Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab and Al-Sindhi reported by the Najdi historian 'Uthman Ibn Bishr (d. 1288 A.H./ 1871/2 C.E.):"... one day Shaykh Muḥammadbn 'Abdi'l-Wahhāb BN, Bn or bn may refer to: Businesses and organizations * RTV BN, a Bosnian Serb TV network * Bangladesh Navy * Barisan Nasional (also known as "National Front"), a political coalition in Malaysia * Barnes & Noble, an American specialty retailer ...stood by the chamber of the Prophet where people were calling pon him or supplicatingand seeking help by the Prophet's chamber, blessings and peace be upon him. He then saw Muḥammad Ḥayātl Sindī L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''el'' (pronounced ), plural ''els''. History Lamedh ...and came to him. The shaykhbn 'Abdi'l-Wahhāb BN, Bn or bn may refer to: Businesses and organizations * RTV BN, a Bosnian Serb TV network * Bangladesh Navy * Barisan Nasional (also known as "National Front"), a political coalition in Malaysia * Barnes & Noble, an American specialty retailer ...asked, "What do you say about them?" He l-Sindīsaid, "Verily that in which they are engaged shall be destroyed and their acts are invalid.""
Journey to Basra
Following his early education in Medina, Ibn ʿAbd-al-Wahhab traveled outside of the Arabian Peninsula, venturing first toBasra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
which was still an active center of Islamic culture. During his stay in Basra, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab studied Hadith and Fiqh under the Islamic scholar Muhammad al-Majmu'i. In Basra, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab came into contact with Shi'is
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
and would write a treatise repudiating the theological doctrines of '' Rafidah'', an extreme sect of Shiism. He also became influenced by the writings of Hanbali theologian Ibn Rajab (d. 1393 C.E/ 795 A.H) such as "''Kalimat al-Ikhlas''" which inspired Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's seminal treatise "''Kitab al-Tawhid''".
Return to 'Uyaynah
Early preaching
His leave fromBasra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
marked the end of his education and by the time of his return to 'Uyayna
Al-'Uyayna or al-'Uyaynah ( ar, العيينة) is a village in central Saudi Arabia, located some northwest of the Saudi capital Riyadh. Al-Uyaynah was the birthplace of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. Today, Uyaynah is a small village and forms t ...
, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab had mastered various religious disciplines such as Islamic ''Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
'' (jurisprudence), theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing th ...
, hadith sciences and '' Tasawwuf''. His exposure to various practices centered around the cult of saints and grave veneration would eventually propel Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab to grow critical of Sufi superstitious accretions and practices. Rather than targeting "Sufism" as a phenomenon or a group, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab denounced particular practices which he considered sinful. He fashioned his reformist campaign in a manner that appealed to the socio-cultural dynamics of 18th century Arabia. Many of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's scholarly treatises, pamphlets and speeches appropriated idioms of local Arab dialects, monologues of vernacular poetry and catchphrases of folk culture into his religious discourse.
 As a gifted communicator with a talent for breaking down his ideas into shorter units, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab entitled his treatises with terms such as ''qawāʿid'' ("principles"), ''masāʾil'' ("matters"), ''kalimāt'' ("phrases"), or ''uṣūl'' ("foundations"), simplifying his texts point by point for mass reading. Calling upon the people to follow his call for religious revival ('' tajdid'' ) based on following the founding texts and the authoritative practices of the first generations of
As a gifted communicator with a talent for breaking down his ideas into shorter units, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab entitled his treatises with terms such as ''qawāʿid'' ("principles"), ''masāʾil'' ("matters"), ''kalimāt'' ("phrases"), or ''uṣūl'' ("foundations"), simplifying his texts point by point for mass reading. Calling upon the people to follow his call for religious revival ('' tajdid'' ) based on following the founding texts and the authoritative practices of the first generations of Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab declared: "I do not - God be blessed - conform to any particular sufiorder Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...or '' faqih'', nor follow the course of any speculative theologian (''mutakalim'') or any other Imam for that matter, not even such dignitaries as ibn al-Qayyim,al-Dhahabi Shams ad-Dīn adh-Dhahabī (), also known as Shams ad-Dīn Abū ʿAbdillāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn ʿUthmān ibn Qāymāẓ ibn ʿAbdillāh at-Turkumānī al-Fāriqī ad-Dimashqī (5 October 1274 – 3 February 1348) was an Islamic historia ..., or ibn Kathir, I summon you only to God, and Only Him as well as observe the path laid by HisProphet In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ..., God's messenger."
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's call gradually began to attract followers, including the ruler of 'Uyayna, Uthman ibn Mu'ammar. Upon returning to Huraymila, where his father had settled, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab wrote his first work on the Unity of God. With Ibn Mu'ammar, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab agreed to support Ibn Mu'ammar's political ambitions to expand his rule "over Najd and possibly beyond", in exchange for the ruler's support for Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's religious teachings. During the early years of preaching, he criticised various folk practices and superstitions peacefully through sermons. Starting from 1742, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab would shift towards an activist stance; and began to implement his reformist ideas. First, he persuaded Ibn Mu'ammar to help him level the tomb of Zayd ibn al-Khattab, a
companion of Muhammad
The Companions of the Prophet ( ar, اَلصَّحَابَةُ; ''aṣ-ṣaḥāba'' meaning "the companions", from the verb meaning "accompany", "keep company with", "associate with") were the disciples and followers of Muhammad who saw or ...
, whose shrine was revered by locals. Secondly, he ordered the cutting down of trees considered sacred by locals, cutting down "the most glorified of all of the trees" himself. Third, he organized the stoning
Stoning, or lapidation, is a method of capital punishment where a group throws stones at a person until the subject dies from blunt trauma. It has been attested as a form of punishment for grave misdeeds since ancient times.
The Torah and T ...
of a woman who confessed to having committed adultery. Lacey 1983: 56
These actions gained the attention of Sulaiman ibn Muhammad ibn Ghurayr of the tribe of Bani Khalid, the chief of Al-Hasa and Qatif
Qatif or Al-Qatif ( ar, ٱلْقَطِيف ''Al-Qaṭīf'') is a governorate and urban area located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It extends from Ras Tanura and Jubail in the north to Dammam in the south, and from the Persian Gulf in t ...
, who held substantial influence in Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. Ibn Ghurayr threatened Ibn Mu'ammar by denying him the ability to collect a land tax for some properties that Ibn Mu'ammar owned in Al-Hasa if he did not kill or drive away from Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab. Consequently, Ibn Mu'ammar forced Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab to leave.
The early Wahhabis had been protected by Ibn Mu'ammar in 'Uyayna, despite being persecuted in other settlements. As soon as Ibn Mu'ammar disowned them, Wahhabis were subject to excommunication ('' Takfir''); exposing themselves to loss of lives and property. This experience of suffering reminded them of the '' Mihna'' against Ahmad Ibn Hanbal
Ahmad ibn Hanbal al-Dhuhli ( ar, أَحْمَد بْن حَنْبَل الذهلي, translit=Aḥmad ibn Ḥanbal al-Dhuhlī; November 780 – 2 August 855 CE/164–241 AH), was a Muslim jurist, theologian, ascetic, hadith traditionist, and ...
and his followers, and shaped the collective Wahhabi memory. As late as 1749, the sharif of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca ( ar, شريف مكة, Sharīf Makkah) or Hejaz ( ar, شريف الحجاز, Sharīf al-Ḥijāz, links=no) was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina and ...
imprisoned those Wahhabis who went to Mecca to perform the '' Hajj'' (annual pilgrimage).
Pact with Muhammad bin Saud
 Upon his expulsion from ' Uyayna, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab was invited to settle in neighboring Diriyah by its ruler Muhammad ibn Saud Al Muqrin. After some time in Diriyah, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab concluded his second and more successful agreement with a ruler. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and Muhammad bin Saud agreed that, together, they would bring the
Upon his expulsion from ' Uyayna, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab was invited to settle in neighboring Diriyah by its ruler Muhammad ibn Saud Al Muqrin. After some time in Diriyah, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab concluded his second and more successful agreement with a ruler. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and Muhammad bin Saud agreed that, together, they would bring the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
of the peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on al ...
back to the "true" principles of Islam as they saw it. According to the anonymous author of ''Lam al-Shihab'' (Brilliance of the Meteor), when they first met, Ibn Saud declared:"This oasis is yours, do not fear your enemies. By the name of God, if all Nejd was summoned to throw you out, we will never agree to expel you."Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab replied:
"You are the settlement's chief and wise man. I want you to grant me an oath that you will perform jihad against the unbelievers. In return, you will be imam, leader of the Muslim community and I will be leader in religious matters."The agreement was confirmed with a mutual oath of loyalty ('' bay'ah'') in 1744. Once Al-Sa'ud made Dir'iyya a safe haven, Wahhabis from other towns took refuge. These included dissenters from Ibn Mu'ammar clan who had sworn allegiance to Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab. The nucleus of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's supporters all across
Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
retreated to Dir'iyyah and formed the vanguard of the insurgency launched by Al-Saud against other towns.
From a person who started his career as a lone activist, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab would become the spiritual guide of the nascent Emirate of Muhammad ibn Saud Al-Muqrin. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab would be responsible for religious matters and Ibn Saud in charge of political and military issues. This agreement became a "mutual support pact" and power-sharing arrangement between the Aal Saud family, and the '' Aal ash-Sheikh'' and followers of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab, which had remained in place for nearly 300 years, providing the ideological impetus to Saudi expansion. Reviving the teachings of Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
, the ''Muwaḥḥidūn'' (Unitarian) movement emphasized strict adherence to ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'' and ''Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
''; while simultaneously championing the conception of an Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
based on the model of early Muslim community in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. Meanwhile, it's Muslim and Western opponents derogatorily labelled the movement as the "''Wahhābiyyah''" ( anglicised as "Wahhabism" ).
Rise of Emirate of Dir'iyyah
 The 1744 pact between Muhammad ibn Saud and Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab marked the rise of the First Saudi state, the Emirate of Diriyah, which was established in 1727. By offering the
The 1744 pact between Muhammad ibn Saud and Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab marked the rise of the First Saudi state, the Emirate of Diriyah, which was established in 1727. By offering the Al-Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), a ...
a clearly defined religious mission, the alliance provided the ideological impetus to Saudi expansion. Deducing from his bitter experiences in 'Uyaynah, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab had understood the necessity of political backing from a strong Islamic political entity to transform the local socio-religious status quo and also safeguard Wahhabism's territorial base from external pressure. After consolidating his position in Diriyah, he wrote to the rulers and clerics of other towns; appealing them to embrace his doctrines. While some heeded his calls, others rejected it; accusing him of ignorance or sorcery.
War with Riyadh (1746–1773)
Realising the significance of efficient religious preaching ('' da'wa''), Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab called upon his students to master the path of reasoning and proselytising over warfare to convince other Muslims of theirreformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
endeavour. Between 1744 and 1746, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's preaching continued in the same non-violent manner as before and spread widely across the people of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. Rulers of various towns across Najd pledged their allegiance to Ibn Suʿūd. This situation changed drastically around 1158/1746; when the powerful anti-Wahhabi chieftain of Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, Literal translation, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi Arabic, Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyad ...
, Dahhām ibn Dawwās (fl. 1187/1773), attacked the town of Manfuha which had pledged allegiance to Diriyah. This would spark a nearly 30-year long between Diriyah and Riyadh, which lasted until 1187/1773, barring some interruptions. First conquering Najd, Muhammad ibn Saud's forces expanded the Wahhabi influence to most of the present-day territory of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, eradicating various popular practices they viewed as akin to polytheism and propagating the doctrines of ʿAbd al-Wahhab.
Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb maintained that the military campaigns of the Emirate of Dirʿiyya were strictly defensive and rebuked his opponents as being the first to initiate '' Takfir'' (excommunication). Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab had defined jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
as an activity that must have a valid religious justification and which can only be declared by an ''Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, se ...
'' whose purpose must be strictly defensive in nature. Justifying the Wahhabi military campaigns as defensive operations against their enemies, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab asserts:"As for warfare, until today, we did not fight anyone, except in defense of our lives and honor. They came to us in our area and did not spare any effort in fighting us. We only initiated fighting against some of them in retaliation for their continued aggression, he recompense for an evil is an evil like thereof(42:40)... they are the ones who started declaring us to be unbelievers and fighting us"
Rebellion in Huraymila (1752–1755)
In 1753–4, the Wahhabis were confronted by an alarming number of towns renouncing allegiance and aligning with their opponents. Most prominent amongst these was the town of Huraymila, which had pledged allegiance to Dir'iyah in 1747. However, by 1752, a group of rebels encouraged by Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb's brother, Sulaymān, had initiated a coup in Huraymila and installed a new ruler that threatened to topple the Wahhābī order. A fierce war between Diriyah and Huraymila began in a magnitude that was unprecedented. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab held a convocation of Wahhabis from all the settlements across Najd. Reviewing the recent desertions and defeats, he encouraged them to hold fast to their faith and recommit to the struggle. The ensuing battles and the re-capture of Huraymila in 1168/1755, constituted a significant development in Wahhabi expansionist stage. Abd al-Azeez, the son of Muhammad ibn Saud, had emerged as the principal leader of the Wahhabi military operations. Alongside a force of 800 men, accompanied by an additional 200 under the command of the deposed ruler of Huraymila, Abd al Azeez was able to subdue the rebels. More significantly, the rationale behind the campaign was based on Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb's newly written epistle ''Mufīd al-mustafīd'', which marked a shift from the earlier posture of defensiveJihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
to justify a more aggressive one. In the treatise, compiled to justify Jihad pursued by Dir'iyyah and its allies, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab excommunicated the inhabitants of Huraymila and declared it as a duty of Wahhabi soldiers to fight them as apostates. He also quoted several '' Qur'anic'' verses indicative of offensive forms of jihād.
Capture of Riyadh and Retirement (1773)
 The last point of serious threat to the Saudi state was in 1764-1765. During this period, the Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa of Najrān alongside their allied tribe of
The last point of serious threat to the Saudi state was in 1764-1765. During this period, the Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa of Najrān alongside their allied tribe of 'Ujman
Al-Ajman or al-'Ijman ( ar, العُجمان, singular Ajmi ar, العجمي) is an Arabian tribal confederation in the Arabian Peninsula, with Ajman spread across Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait.
Origin
Al-Ajman is a ...
, combined forces to inflict a major defeat on the Saudis at the Battle of Hair in October 1764, killing around 500 men. The anti-Wahhabi forces allied with the invaders and participated in the combined siege of Dirʿiyya. However, the defenders were able to hold onto their town due to the unexpected departure of the Najranis after a truce concluded with the Saudis. A decade later in 1773-'4, 'Abd al-Azeez had conquered Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, Literal translation, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi Arabic, Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyad ...
and secured the entirety of al-ʿĀriḍ, after its chieftain Dahham ibn Dawwas fled. By 1776/7, Sulayman ibn Abd al-Wahhab had surrendered. The capture of Riyadh marked the point at which Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab delegated all affairs of governing to 'Abd al-Azeez, withdrew from public life and devoted himself to teaching, preaching and worshipping. Meanwhile, 'Abd al-Azeez would proceed with his military campaigns, conquering towns like Sudayr (1196/1781), al-Kharj (1199/1784), etc. Opposition in towns to the North like al-Qaṣīm was stamped out by 1196/1781, and the rebels in ʿUnayza were subdued by 1202/1787. Further north, the town of Ḥāʾil, was captured in 1201/1786 and by the 1780s; Wahhābīs were able to establish their jurisdiction over most of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
.
Death
After his departure from public affairs, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab would remain a consultant to 'Abd al-Azeez, who followed his recommendations. However, he withdrew from any active military and political activities of the Emirate of Diriyah and devoted himself to educational endeavours, preaching, and worship. His last major activity in state affairs was in 1202/1787; when he called on the people to give '' bay'ah'' (allegiance) to Suʿūd, ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz's son, as heir apparent. Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab fell ill and died in June 1792 C.E or 1206 A.H in the lunar month of Dhul-Qa'dah, at the age of eighty-nine. He would be buried in an unmarked grave at al-Turayf in al- Dir'iyya. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab left behind four daughters and six sons, many of whom became clerics of greater or lesser distinction. A clear separation of roles between the Saudi family and the Wahhabi clerics had begun to emerge during the interval between Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's retirement from front-line politics in 1773 and his death in 1792. Although the Aal Ash-Shaykhs did not engage in politics, they comprised a significant part of the designating group of notables who gave allegiance (''bay'ah'') to a new ruler and acclaimed his accession. After Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, his son 'Abd Allah, recognised by his critics as moderate and fair-minded, would succeed him as the dominant Wahhabi cleric. The Wahhabi cause would flourish for more than two decades after Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's death; until the defeat of the First Saudi State in theOttoman-Saudi war
The Ottoman-Saudi War ( ar, الحرب العثمانية-السعودية, translit=al-ḥarb al-ʿUthmānīyah-al-Saʿūdīyah, ) also known as the Ottoman/Egyptian-Saudi War (1811–1818) was fought from early 1811 to 1818, between the Ot ...
. 'Abd Allah would spend his last days as an exile in Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
, having witnessed the destruction of Dirʿiyya and the execution of his talented son Sulayman ibn 'Abd Allah in 1818.
Family
According to academic publications such as the ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The ( Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various ...
'', Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab married an affluent
Wealth is the abundance of valuable financial assets or physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the originating Old English word , which is from an ...
woman during his studies in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesipho ...
. When she died, he inherited her property and wealth. EBO ''Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb'' 2011 Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab had six sons; Hussain (died 1809), 'Abdallah (1751–1829), Hassan, Ali (died 1829), Ibrahim and 'Abdulazeez who died in his youth. Four of his sons, Hussain, Abdullah, Ali and Ibrahim, established religious schools close to their home in Dir'iyah and taught the young students from Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
, Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
, Najd and other parts of Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
at their ''majlis
( ar, المجلس, pl. ') is an Arabic term meaning "sitting room", used to describe various types of special gatherings among common interest groups of administrative, social or religious nature in countries with linguistic or cultural conne ...
'' (study circle). One of their pupils was Husayn Ibn Abu Bakr Ibn Ghannam, a well-known Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
scholar and chronicler. (Although Islamic scholar ibn 'Uthaymin writes about Ibn Ghannam that he was a Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as primar ...
scholar from al-Ahsa.)
Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab also had a daughter named Fatimah, who was a revered Islamic scholar
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
known for her piety, valour and beauty. She was a committed adherent to her father's reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
ideals and taught numerous men and women. Fatimah travelled a lot and remained unmarried throughout her life inorder to research hadith sciences and concentrate on her scholarly endeavours. She witnessed the Fall of Dir'iyah and fled to Ras al-Khaimah in 1818; which was captured by the British the following year. As a result, she was again forced to emigrate along with her nephew; this time to Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
, wherein she became a major proponent of reformist teachings of the ''Muwahhidun'' and campaigned against various superstitions. Fatimah returned to Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, Literal translation, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi Arabic, Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyad ...
after the establishment of Emirate of Nejd
The Emirate of Nejd or Imamate of Nejd was the Second Saudi State, existing between 1824 and 1891 in Nejd, the regions of Riyadh and Ha'il of what is now Saudi Arabia. Saudi rule was restored to central and eastern Arabia after the Emirate of D ...
in 1824. Due to her travels, she was often referred to by her appellation "Lady of the Two Migrations". As the daughter of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, Fatimah became a role model for Arabian women active in educational efforts and various social undertakings.
The descendants of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab, the Al ash-Sheikh
The Al ash-Sheikh ( ar, آل الشيخ, '),Using the term ''the Al ash-Sheikh family'' is a pleonasm as the word ''Al'' already means ''family''. See Etymology. It would, in theory, be correct to use the term ''Family of the Sheikh'', but, unlik ...
, have historically led the ''ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
'' (clerical establishment) of the Saudi state, dominating the state's religious institutions. Within Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, the family is held in prestige similar to the Saudi royal family, with whom they share power, and has included several religious scholars and officials. Ottaway 2008: 176 The arrangement between the two families is based on the Al Saud maintaining the Al ash-Sheikh's authority in religious matters and upholding and propagating the Salafi doctrine. In return, the Al ash-Sheikh support the Al Saud's political authority thereby using its religious-moral authority Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive, laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change, the princi ...
to legitimize the royal family's rule.
Views
On ''Tawhid''
revive
Revive or Revived may refer to:
* Revival, especially bringing back to life
* Revive (video gaming), resurrecting a defeated character.
Music
* Revive (band), a Christian rock band
* ''Revive'', classical album by Elīna Garanča 2016
* ''Revive' ...
and purify Islam from what he perceived as non-Islamic popular religious beliefs and practices by returning to what, he believed, were the fundamental principles of the Islamic religion. His works were generally short, full of quotations from the ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'' and ''Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
'', such as his main and foremost theological treatise, ''Kitāb at-Tawḥīd'' ( ar, كتاب التوحيد; "The Book of Oneness"). He taught that the primary doctrine of Islam was the uniqueness and oneness of God (''tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
''), and denounced those religious beliefs and practices widespread amongst the people of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. Following Ibn Taymiyya's teachings on ''Tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'', Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab believed that much of Najd had descended into superstitious folk religion akin to the period of '' Jahiliyya'' (pre-Islamic era) and denounced much of their beliefs as polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, ...
(''shirk''). He associated such practices with the culture of ''Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
'' (imitation to established customs) adored by pagan-cults of ''Jahiliyya'' era. Based on the doctrine of ''Tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' espoused in ''Kitab al-Tawhid'', the followers of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab referred themselves by the designation "''Al-Muwahhidun''" (Unitarians).
The "core" of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's teaching is found in ''Kitāb at-Tawḥīd'', a theological treatise which draws from material in the ''Qur'an'' and the recorded doings and sayings of the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets a ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
in the Hadith literature. It preaches that worship in Islam includes conventional acts of worship such as the five daily prayers ('' Salat''); fasting ('' Sawm''); supplication ('' Dua''); seeking protection or refuge (''Istia'dha''); seeking help (''Ist'ana'' and ''Istigatha'') of Allah.Ibn Abd al-Wahhab, ''Kitab al-Tawhid''
Traditionally, many Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
throughout history had held the view that declaring the testimony of faith is sufficient in becoming a Muslim. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab did not agree with this. He asserted that an individual who believed in the existence of intercessors or intermediaries alongside God was guilty of '' shirk'' (polytheism or idolatry). This was the major difference between him and his opponents, and led him to accuse his adversaries who engaged in these religious practices to be apostates (a practice known in Islamic jurisprudence as '' takfir'') and idolaters (''mushrikin'').
Another major doctrine of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was the concept known as ''Al-'Udhr bil Jahl'' ( excuse of ignorance), wherein any ignorant person unaware of core Islamic teachings is excused by default until clarification. As per this doctrine, those who fell into beliefs of ''shirk'' (polytheism) or '' kufr'' (disbelief) cannot be excommunicated until they have direct access to Scriptural evidences and get the opportunity to understand their mistakes and retract. If not, their affairs are to be delegated only to God. Hence, he believed that education and dialogue was the only effective path for the successful implementation of reforms. Explaining this concept in various pamphlets addressed to the masses and other scholars, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab declared:"What has been mentioned to you about me, that I make generalised ''Rejecting the allegations of his detractors who accused him of ex-communicating whoever didn't follow his doctrines, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab maintained that he only advocated orthodox Sunni doctrines. In a letter addressed to thetakfīr ''Takfir'' or ''takfīr'' ( ar, تكفير, takfīr) is an Arabic and Islamic term which denotes excommunication from Islam of one Muslim by another, i.e. accusing another Muslim to be an apostate. The word is found neither in the Quran nor in ...'', this is from the slanders of the enemies.. atherwe make ''takfīr'' of the one who affirms the religion ofAllāh Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", an ...and HisMessenger ''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoch ...but then showed enmity towards it and hindered people from it; as well as the one who worshipped idols after he came to know that this is the religion of the polytheists and beautified it for the people nviting them to it. nfacteveryscholar A scholar is a person who pursues academic and intellectual activities, particularly academics who apply their intellectualism into expertise in an area of study. A scholar can also be an academic, who works as a professor, teacher, or research ...on the face of the Earth makes ''takfīr'' of them, save an obstinate or ignorant... But we nlymake ''takfīr'' of the one who associates partners with Allāh in His sole right of worship (ilāhiyyah), after we have made clear to him the proof for the futility of '' shirk''."
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
i scholar Abdul Rahman Al-Suwaidi who had sought clarification over the rumours spread against his mission, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab explains:"I am a man of social standing in my village and the people respect my word. This led some chieftains to reject my call, because I called them to what contradicts the traditions they were raised to uphold.... the chieftains directed their criticism and enmity towards our enjoining ''Tawheed'' and forbidding ''Shirk''... Among the false accusations they propagated, ... is the claim that I accuse all Muslims, except my followers, of being Kuffar (Unbelievers)... This is truly incredible. How can any sane person accept such accusations? Would a Muslim say these things? I declare that I renounce, before Allah, these statements that only a mad person would utter. In short, what I was accused of calling to, other than enjoining Tawheed and forbidding Shirk, is all false."
On ''Taqlid''
Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was highly critical of the practice of ''Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
'' ( blind-following), which in his view, deviated people away from ''Qur'an'' and ''Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
''. He also advocated for ''Ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
'' of qualified scholars
A scholar is a person who pursues academic and intellectual activities, particularly academics who apply their intellectualism into expertise in an area of study. A scholar can also be an academic, who works as a professor, teacher, or researche ...
in accordance with the teachings of ''Qur'an'' and ''Hadith''. In his legal writings, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab referred to a number of sources- ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'', ''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
'' , opinions of companions, ''Salaf
Salaf ( ar, سلف, "ancestors" or "predecessors"), also often referred to with the honorific expression of "al-salaf al-ṣāliḥ" (, "the pious predecessors") are often taken to be the first three generations of Muslims. This comprises Muhamm ...
'' as well as the treatises of the 4 schools of thought. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab argued that Qur'an condemned blind emulation of forefathers and nowhere did it stipulate scholarly credentials for a person to refer to it directly. His advocacy of ''Ijtihad'' and harsh denunciation of ''Taqlid'' arose widespread condemnation from Sufi orthodoxy in Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
and beyond, compelling him to express many of his legal verdicts ( ''fatwa
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist ...
s'' ) discreetly, using convincing juristic terms. He differed from Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
school in various points of law and in some cases, also departed from the positions of the 4 schools. In his treatise ''Usul al-Sittah'' (Six Foundations), Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab vehemently rebuked his detractors for raising the description of '' Mujtahids'' to what he viewed as humanely unattainable levels. He condemned the establishment clergy as a class of oppressors who ran a "tyranny of wordly possessions" by exploiting the masses to make money out of their religious activities. The teachings of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
n hadith scholar Muhammad Hayat as Sindi highly influenced the anti-taqlid views of Ibn 'Abd al Wahhab.
Muhammad Ibn Abd al-Wahhab opposed partisanship to '' madhabs'' (legal schools) and didn't consider it obligatory to follow a particular madhab. Rather, in his view, the obligation is to follow ''Qur'an'' and the ''Sunnah''. Referring to the classical scholars Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
and Ibn Qayyim, ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab condemned the popular practice prevalent amongst his contemporary scholars to blindfollow latter-day legal works and urged Muslims to take directly from Qur'an and Sunnah. He viewed it as a duty upon every Muslim, laymen and scholar, male & female, to seek knowledge directly from the sources. Radically departing from both Ibn Taymiyya and Ibn Qayyim, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab viewed the entirety of the prevalent ''mad'hab'' system of jurisprudence (''Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
'') as a fundamentally corrupt institution, seeking a radical reform of scholarly institutions and preached the obligation of all Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
to directly refer to the foundational texts of revelation. He advocated a form of scholarly authority based upon the revival of the practice of ''ittiba'', i.e., laymen following the scholars only after seeking evidences. The prevalent legal system was, in his view, a "factory for the production of slavish emulators" symbolic of Muslim decline.
On the nature of ''Nubuwwah'' (Prophethood)
Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab elucidated his concept on the nature of Prophethood in his book ''Mukhtaṣar sīrat al-Rasūl'' ("Abridgement of the life of the Prophet"), an extensive biographical work on the Islamic prophetMuhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
. ''Mukhtaṣar'' was written with the purpose of explaining Muhammad's role in universal history by undermining certain prophetologic conceptions that had come to prominence among Sunnī religious circles during the twelfth Islamic century. These included negating those concepts and beliefs that bestowed the Prophet with mystical attributes that elevated Muhammad beyond the status of ordinary humans. In his introduction to ''Mukhtasar'', Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab asserts that every Prophet came with the mission of upholding ''Tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' and prohibiting '' shirk''. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab further tries to undermine the belief in the pre-existence of Muḥammad as a divine light preceding all other creation, a salient concept that served as an aspect of Prophetic devotion during the eleventh Islamic century. Additionally, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb omitted mentioning other episodes narrated in various '' sirah'' (Prophetic biography) works such as trees and stones allegedly expressing veneration for Muḥammad, purification of Muhammad's heart by angels, etc. which suggested that Muḥammad possessed characteristics that transcend those of ordinary humans.
Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab adhered to Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
's understanding of the concept of '' Isma'' (infallibility) which insisted that ''ʿiṣma'' does not prevent prophets from committing minor sins or speaking false things. This differed from the alternative understanding of Sunni theologians like Fakhr al-Dīn al-Rāzi, Qāḍī ʿIyāḍ, etc. who had emphasised the complete independence of the Prophet from any form of error or sin. Following Ibn Taymiyya, Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab affirmed the incident of '' qiṣṣat al-gharānīq'' (the "story of cranes" or "Satanic Verses") which demonstrated that Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
was afflicted by "Satan
Satan,, ; grc, ὁ σατανᾶς or , ; ar, شيطانالخَنَّاس , also known as the Devil, and sometimes also called Lucifer in Christianity, is an entity in the Abrahamic religions that seduces humans into sin or falsehoo ...
ic interference". This idea of Ibn Taymiyya had been recently revived in the circles of Kurdish hadith scholar Ibrāhīm al-Kūrānī (1025/1616–1101/1686); whose son Abūl-Ṭāhir al-Kūrānī was the teacher of Muḥammad Ḥayāt al-Sindi, the master of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab. Using this concept to explain ''Tawhid al-ulūhiyya'' (Oneness of Worship), Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab rejected the idea that anybody could act as intercessor between God and man by employing the Qurʾānic verses related to the event. He also used these and other similar incidents to undermine the belief regarding prophets being completely free from sin, error, or Satanic afflictions.
Furthermore, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab had given little importance to Prophetic miracles in his ''Mukhtaṣar''. Although he hadn't denied miracles as an expression of Divine Omnipotence so long as they are attested by ''Qur'an'' or authentic ''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
'', ''Al-Mukhtasar'' represented an open protest against the exuberance of miracles that characterised later biographies of Muḥammad. In Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's view, miracles are of little significance in the life of Muḥammad in comparison to that of the previous prophets, since central to his prophethood were the institutionalisation of '' Jihād'' and the '' ḥudud'' punishments. Contrary to prevalent religious beliefs, Muḥammad was not portrayed as the central purpose of creation in the historical conception of ''Mukhtaṣar''. Instead, he has a function within creation and for the created beings. Rather than being viewed as an extraordinary performer of miracles, Muhammad should instead be upheld as a model of emulation. By depriving the person of Muḥammad of all supernatural aspects not related to '' Wahy'' (revelation) and Divine intervention, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab also re-inforced his rejection of beliefs and practices related to cult of saints and veneration of graves. Thus, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb's conception of history emphasised the necessity to follow the role-model of Muḥammad and re-establish the Islamic order.
Influence on Salafism
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's movement is known today asWahhabism
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic Islamic revival, revivalist and Islamic fundamentalism, fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabians, ...
( ar, الوهابية, translit=Wahhābiyyah). The designation of his doctrine as ''Wahhābiyyah'' actually derives from his father's name, ʿAbd al-Wahhab. Many adherents consider the label "Wahhabism" as a derogatory term coined by his opponents, and prefer it to be known as the Salafi movement
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a Islah, reform branch movement within Sunni Islam that originated during the nineteenth century. The name refers to advocacy of a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three g ...
. Modern scholars of Islamic studies
Islamic studies refers to the academic study of Islam, and generally to academic multidisciplinary "studies" programs—programs similar to others that focus on the history, texts and theologies of other religious traditions, such as Easter ...
point out that "Salafism" is a term applied to several forms of puritanical Islam in various parts of the world, while Wahhabism refers to the specific Saudi school, which is seen as a more strict form of Salafism. However, modern scholars remark that Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's followers adopted the term "Salafi" as a self-designation much later. His early followers denominated themselves as ''Ahl al-Tawhid'' and ''al-Muwahhidun'' ("Unitarians" or "those who affirm/defend the unity of God"), and were labeled "Wahhabis" by their opponents.
The '' Salafiyya'' movement was not directly connected to Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's movement in Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. According to professor Abdullah Saeed, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab should rather be considered as one of the "precursors" of the modern ''Salafiyya'' movement since he called for a return to the pristine purity of the early eras of Islam by adhering to the ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'' and the ''Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
'', rejection of the blind following (''Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
'') of earlier scholars and advocating for ''Ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
''. Scholars like Adam J. Silverstein consider Wahhabi movement as "the most influential expression of Salafism of the Islamist sort, both for its role in shaping (some might say: 'creating') modern Islamism, and for disseminating ''salafi'' ideas widely across the Muslim world."
On ''Fiqh''
Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's approach to ''Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
'' (Islamic jurisprudence) was based on four major principles:
* Prohibition on speaking about God without '' halal
''Halal'' (; ar, حلال, ) is an Arabic word that translates to "permissible" in English. In the Quran, the word ''halal'' is contrasted with '' haram'' (forbidden). This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification k ...
'' (allowance) and ''haram
''Haram'' (; ar, حَرَام, , ) is an Arabic term meaning 'Forbidden'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowle ...
'' (prohibition) are clear in the Scriptures and those issues which are unclear should be left as ambiguous
According to Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, the clear meaning of authentic '' hadiths'' takes precedence over the opinions of any other scholar, even if it went against the agreement of the eponyms of the four '' madhabs''. In line with these principles, he encouraged all believers to engage directly with the Scriptures while respecting '' Ikhtilaf'' (scholarly differences), writing:"The companions of the Messenger of God, may God bless him and grant him peace, differed on various issues without denunciation, so long as the text was not clear. It is upon the believer to place his concern and intent to know the command of God and His Messenger in those matters of disagreement, and to act accordingly whilst respecting the people of knowledge, and respect them, even if they erred, but he does not take them as lords besides God; This is the way of those who are blessed. As for those who throw away their speech and do not respect, then this is the path of those who have incurred God's wrath."
Throughout his epsitles like ''Arbaʿ qawāʿid tadūruʾl-aḥkām ʿalayhā'' (Four rules on which rulings revolve), Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab fiercely attacked the prevalent Hanbali Fiqh opinions; with a broader view of re-orienting the Fiqh tradition. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab challenged the ''
madhhab
A ( ar, مذهب ', , "way to act". pl. مَذَاهِب , ) is a school of thought within ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence).
The major Sunni Mathhab are Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i and Hanbali.
They emerged in the ninth and tenth centuries CE ...
'' system, by advocating for a direct understanding of the Scriptures. Rather than rejecting ''madhabs'' outright, he sought a reformation of the system by condemning prevalent trends within the ''madhabs''. He criticised the ''madhhab'' partisans for adhering solely to medieval ''Fiqh'' manuals of later scholars and ignoring ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'', ''Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
'' and opinions of early Imams. He rebuked the contemporary Shafi'i scholars for being partisans of Ibn Hajar al Haytami (d. 1566) and relying solely on his 16th-century manual ''Tuhfat al Muhtaj''. Similarly, he critiqued the Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as primar ...
s for being dependent on the '' Mukhtasar'' of the Egyptian jurist Khalil ibn Ishaq (d. 1365) rather than acting upon authentic traditions (''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
''). In addition to criticising the Madhab partisans, he berated the advocates of ''Taqlid'' for discouraging the practice of ''Ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
'' and called on the laity to follow scholars only after asking for Scriptural evidences. Most noticeably, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab rejected the authority of ''Al-Iqna'' and ''Al-Muntaha'' - two of the most important medieval Hanbali works for the regional clerics of Arabia - asserting:"The Hanbalis are the least prone of all people to innovation. etmost of the ''Iqna'' and the ''Muntahā'' wo late Hanbali authoritative worksconflicts with the view ofAhmad Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet. Etymology The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the v ...and his explicit statements, not to mention thehadith Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...of the Messenger of God"
In calling for a direct return to the Scriptures, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was not a literalist and often strongly objected to literalist approaches and ritualism of religion that came with it. He believed that pure intentions ('' Niyyah'') constituted the essence of all virtous actions and upheld its superiority over dull ritualism. As a deferential and accomplished jurist with the experience of religious training under numerous masters in his travels, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab opposed the rigid, hardline views of the tradition-bound ''
ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
'' who had excommunicated sinful, unrepenting Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
; thereby making their blood forfeit based on their reading of the reports of Muhammad and Companions. On the other hand, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab contextualised those reports; arguing that they must be understood in recognition of historical circumstances. According to his view, sincerity and purity of intent (''Ikhlas'') could expiate the evil of sins committed in mistakes. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's legal approach began with ''hadith'' authentication, followed by contextualised intrapolation in consideration of Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
legal principles such as ''Maslaha
Maslaha or maslahah ( ar, مصلحة, lit=public interest) is a concept in shari'ah (Islamic divine law) regarded as a basis of law.I. Doi, Abdul Rahman. (1995). "Mașlahah". In John L. Esposito. ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic Wor ...
'' (public welfate). Other legal criteria involved upholding the spirit of the law, ''Maqasid al-Sharia
''Maqasid'' ( ar, مقاصد, lit. goals, purposes) or ''maqāṣid al-sharīʿa'' (goals or objectives of ''sharia'') is an Islamic legal doctrine. Together with another related classical doctrine, '' maṣlaḥa'' (welfare or public interest), i ...
'', and intent behind pronouncing legal verdicts which addressed various themes such as societal justice and safeguarding women. He also believed in a holistic legal understanding of ''Qur'anic'' verses and ''hadith'', distinguishing between general rules applicable for all Muslims and rulings unique to various life-time situations.On Islamic revival
As a young scholar inMedina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was profoundly influenced by the revivalist doctrines taught by his teachers Muhammad Hayyat ibn Ibrahim al-Sindhi and Abdullah Ibn Ibrahim Ibn Sayf. Much of the Wahhabi teachings such as opposition to saint-cults, radical denunciation of blind-following medieval commentaries, adherence to Scriptures and other revivalist thoughts came from Muhammad Hayyat. Ibn Abd al-Wahhab's revivalist efforts were based on a strong belief in ''Tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' (Oneness of Allah) and a firm adherence to the Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
. His reformative efforts left exemplary marks on contemporary Islamic scholarship. Viewing Blind adherence ( ''Taqlid'' ) as an obstacle to the progress of Muslims, he dedicated himself to educating the masses for them to be vanguards of Islam. According to Ibn Abd al-Wahhab, the degradation and lagging behind of Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
was due to their neglect of the teachings of Islam, emphasizing that progress could be achieved only by firmly adhering to Islam. He also campaigned against popular Sufi practices associated with ''istigatha'', myths and superstitions.
On Sufism
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab praised Tasawwuf. He stated the popular saying: "From among the wonders is to find a Sufi who is a '' faqih'' and a scholar who is anascetic
Asceticism (; from the el, ἄσκησις, áskesis, exercise', 'training) is a lifestyle characterized by abstinence from sensual pleasures, often for the purpose of pursuing spiritual goals. Ascetics may withdraw from the world for their p ...
(''zahid'')". He described Tasawwuf as "the science of the deeds of the heart, which is known as the science of ''Suluk''", and considered it as an important branch of Islamic religious sciences.
At the end of his treatise, ''Al-Hadiyyah al-Suniyyah'', Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's son 'Abd Allah speaks positively on the practice of '' tazkiah'' (purification of the inner self). 'Abd Allah Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab ends his treatise saying:
We do not negate the way of the Sufis and the purification of the inner self from the vices of those sins connected to the heart and the limbs as long as the individual firmly adheres to the rules of Shari'ah and the correct and observed way. However, we will not take it on ourselves to allegorically interpret (''ta'wil'') his speech and his actions. We only place our reliance on, seek help from, beseech aid from and place our confidence in all our dealings in Allah Most High. He is enough for us, the best trustee, the best ''mawla'' and the best helper. May Allah send peace on our master Muhammad, his family and companions.
On social reforms
Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab concerned himself with the social reformation of his people. As an 18th-century reformer, Muhammad ibn 'Abd al Wahhab called for the re-opening of ''Ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a l ...
'' by qualified persons through strict adherence to Scriptures in reforming society. His thoughts reflected the major trends apparent in the 18th-century Islamic reform movements. Unlike other reform movements which were restricted to ''da'wa'', Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was also able to transform his movement into a successful Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
. Thus, his teachings had a profound influence on majority of Islamic reform
Reform ( lat, reformo) means the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The use of the word in this way emerges in the late 18th century and is believed to originate from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement ...
- revivalist movements since the 18th century. Numerous significant socio-economic reforms would be advocated by the ''Imam'' during his lifetime. His reforms touched over various fields such as '' aqeeda'', '' ibaadat'' (ritual acts of worship), '' muamalaat'' (social interactions), etc. In the affairs of ''mu'amalat'', he harshly rebuked the practice of leaving endowments to prevent the rightful heirs (particularly the females) from receiving their deserved inheritance. He also objected to various forms of ''riba
The Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) is a professional body for architects primarily in the United Kingdom, but also internationally, founded for the advancement of architecture under its royal charter granted in 1837, three suppl ...
'' (usury) as well as the practice of presenting judges with gifts, which according to him, was nothing more than bribing. He also opposed and brought an end to numerous un-Islamic taxes that were forced upon the people.
On women
The legal writings of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab reflected a general concern of female welfare and gender justice. In line with this approach, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab denounced the practice of instant '' triple talaq'', counting it as only a single ''talaq'' (regardless of the number of pronouncements). The outlawing of ''triple talaq'' is considered to be one of the most significant reforms across theIslamic World
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
in the 20th and 21st centuries. Following a balanced approach in issues of gender, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab advocated moderation between men and women in social interactions as well as spirituality. According to Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, women has a place in society with both rights and responsibility, with the society being obliged to respect her status and protect her. He also condemned forced marriages and declared any marriage contracted without the consent of a woman (be it minor, virgin or non-virgin) to be "invalid". This too was a significant reform as well as a break from the four Sunni schools which allowed the ''wali
A wali (''wali'' ar, وَلِيّ, '; plural , '), the Arabic word which has been variously translated "master", "authority", "custodian", "protector", is most commonly used by Muslims to indicate an Islamic saint, otherwise referred to by t ...
'' (ward/guardian) to compel minor daughters into marriage without consent. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab also stipulated the permission of the guardian as a condition in marriage (in line with traditional Hanbali, Shafi'i and Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as primar ...
schools). Nevertheless, as a practical jurist, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab allowed guardians to delegate the right to contract marriages to women herself, after which his permission cannot be denied. He also allowed women the right to stipulate favourable conditions for her in the marriage contract. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab also defended the woman's right to divorce through '' Khul''' for various reasons, including in cases wherein she despised her husband. He also prohibited the killing of women, children and various non-combatants such as monks, elderly, blind, ''shaykhs'', slaves and peasants in warfare.
Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab believed in social participation of women for communal solidarity; as per Islamic codes of modesty (''Haya
Haya may refer to:
Biology
* ''Haya'' (dinosaur), a genus of basal ornithopod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous from Mongolia
* ''Haya'' (plant), a genus of plants in the family Caryophyllaceae
* Haya de Herguijuela (Spanish: beech ...
'') that was inclusive to all sections of society, especially the poor. He also campaigned for improving female literacy and asserted women's education as part of their religious rights and duties. Educated elite women played an important role in the Wahhabi movement through social activism and in some instances also weld significant political influence. Many women were trained in various religious disciplines, memorising ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'' and being proficient in hadith sciences; which gained them civic respect as well as a source of income by teaching. As a result, the townsfolk of 19th-century Central Arabia had noticeably higher rates of literacy as observed by foreign travellers. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab also encouraged educated women to be active in various communal activities so as to bolster the reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
campaigns of the ''Muwahhidun'', educating other women, generating awareness of superstitions as well as other cultural activities such as reciting poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek '' poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings ...
, playing tambourine
The tambourine is a musical instrument in the percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingles, called " zills". Classically the term tambourine denotes an instrument with a drumhead, thou ...
during feasts, weddings and various social gatherings. Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's own daughter, Fatima was an influential Islamic scholar
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
active in social and communal affairs and would influence subsequent generations of Arabian women.
On Muslim saints
Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab strongly condemned the veneration of Muslim saints (Which he described as worship) or associating divinity to beings other than God, labeling it as '' shirk''. Despite his great aversion to venerating the saints after their earthly passing and seeking their intercession, it should nevertheless be noted that Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab did not deny the existence of saints as such; on the contrary, he acknowledged that "the miracles of saints (''karāmāt al-awliyāʾ'') are not to be denied, and their right guidance by God is acknowledged" when they acted properly during their life. Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab opposing the practice of the pilgrimage of the saint's tombs as it is considered asBidʻah
In Islam, bid'ah ( ar, بدعة; en, innovation) refers to innovation in religious matters. Linguistically, the term means "innovation, novelty, heretical doctrine, heresy".
In classical Arabic literature (''Adab (literature), adab''), it has ...
(heresy), such as the practice of the pilgrimage towards a tomb believed belong to a companion of the Prophet named Dhiraar ibn al-Azwar in the valley of Ghobaira.
On non-Muslims
According to thepolitical scientist
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
Dore Gold, Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab presented a strong anti-Christian and anti-Judaic stance in his main theological treatise ''Kitāb at-Tawḥīd'', describing the followers of both Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
and Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
faiths as sorcerers who believe in devil-worship, and by citing a hadith attributed to the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets a ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
he stated that capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that ...
for the sorcerer is "that he be struck with the sword". Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab asserted that both the Christian and Jewish religions had improperly made the graves of their prophet into places of worship and warned Muslims not to imitate this practice. Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab concluded that "The ways of the People of the Book are condemned as those of polytheists."
However, Western scholar Natana J. DeLong-Bas defended the position of Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab, stating that
despite his at times vehement denunciations of other religious groups for their supposedly heretical beliefs, Ibn Abd al Wahhab never called for their destruction or death ... he assumed that these people would be punished in the Afterlife ..."
According to Vahid Hussein Ranjbar, "Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab saw it as his mission to restore a more purer and original form of the faith of Islam". In accordance with the his own theology, which upheld a strict doctrine of ''
tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' (oneness of God), Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab condemned the veneration of any personality other than God and sought the demolition of the tombs of Muslim saints (''awliya''). Those who didn't adhere to his interpretation of monotheism were considered disbelieving polytheists
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, ...
(including Sufi and Shia Muslims
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
), Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
, and other Non-Muslims. He also advocated for a literalist interpretation of the Quran and its laws.
Reception
By contemporaries
The doctrines of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab were criticized by a number of Islamic scholars during his lifetime, accusing him of disregarding Islamic history, monuments, traditions and the sanctity of Muslim life. His critics were mainly ''ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
'' from his homeland, the Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
region of central Arabia, which was directly affected by the growth of the Wahhabi movement, based in the cities of Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
, and Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. The early opponents of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab classified his doctrine as a "Kharijite
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the ...
sectarian
Sectarianism is a political or cultural conflict between two groups which are often related to the form of government which they live under. Prejudice, discrimination, or hatred can arise in these conflicts, depending on the political status quo ...
heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
".
On the other hand, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb and his supporters held that they were the victims of aggressive warfare; accusing their opponents of starting the pronouncements of '' Takfir'' (excommunication) and maintained that the military operations of Emirate of Dirʿiyya were strictly defensive. The memory of the unprovoked military offensive launched by Dahhām ibn Dawwās (fl. 1187/1773), the powerful chieftain of Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, Literal translation, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi Arabic, Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyad ...
, on Diriyya in 1746 was deeply engrained in the Wahhabi tradition. Early Wahhabi chronicler Ibn Ghannām states in his book ''Tarikh an-Najd'' (History of Najd) that Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb did not order the use of violence until his enemies excommunicated him and deemed his blood licit:"He gave no order to spill blood or to fight against the majority of the heretics and the misguided until they started ruling that he and his followers were to be killed and excommunicated."By 1802, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
had officially begun to wage religious campaigns against the Wahhabis, issuing tracts condemning them as ''Kharijites''. In contrast, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab profoundly despised the "decorous, arty tobacco-smoking, music happy, drum pounding, Egyptian and Ottoman nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
who traveled across Arabia to pray at Mecca each year", and intended to either subjugate them to his doctrine or overthrow them. A handful of Arabian Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
s participated on the Ottoman side of the controversy. Muhammad ibn 'Abdullah ibn Humayd's 19th century biographical dictionary sheds light on those Hanbali scholars. However, the reliability of his biography itself is disputed for its inherent biases, which portrays Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and his followers as heretics. It also misrepresents many Najdi Hanbali scholars as on the side of Ottoman Hanbalis.
Ibn Humayd's maternal lineage, Al-Turki, was of some local renown for its religious scholars, including two men who opposed the Wahhabi movement. One of them, named Ibn Muhammad, compared Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab with Musaylimah. He also accused Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab of wrongly declaring fellow Muslims to be infidels based on a misguided reading of Quranic passages and prophetic traditions (''Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
''), and of wrongly declaring all scholars as infidels who did not agree with his "deviant innovation". In contrast to this anti-Wahhabi family tradition, Ibn Humayd's early education included extensive studies under two Wahhabi Shaykhs, both praised in his biographical dictionary. He then travelled to Damascus and Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
, wherein he attended lessons of men known for strong anti-Wahhabi convictions. Ibn Humayd's compatibility with Ottoman religious outlook made him eligible for the post of Ottoman Mufti
A Mufti (; ar, مفتي) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion ('' fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatwas'' played an important rol ...
in Mecca.
Another Hanbali scholar whom Ibn Humayd portrays as a central figure in rejecting Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's doctrine was Ibn Fayruz Al-Tamimi al-Ahsai (1729/30 – 1801/02). Ibn Fayruz publicly repudiated Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's teachings when he sent an envoy to him. Ibn Fayruz then wrote to Sultan Abdul Hamid I and requested Ottoman assistance to subjugate Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's followers, whom he referred to as the "seditious Kharijites
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the ...
" of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. The Wahhabis, in turn, came to view him as one of their worst enemies and an exemplar of idolatry.
According to Ibn Humayd, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's father criticized his son for his unwillingness to specialize in jurisprudence and disagreed with his doctrine and declared that he would be the cause of wickedness. Similarly his brother, Sulayman ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab
Sulaymān ibn ‘Abd al-Wahhāb at-Tamīmī ( ar, سُليمان بن عبدالوهّاب التميمي) was an Islamic scholar, Hanbali jurist, and theologian from the Najd region in central Arabia. He was the old brother of Muhammad ibn Abd al- ...
, wrote one of the first treatises refuting the Wahhabi doctrine, ''The Divine Thunderbolts in Refutation of Wahhabism'' (''Al-Šawā'iq Al-Ilāhiyya fī Al-radd 'alā Al-Wahhābiyya''), alleging that Muhammad was ill-educated and intolerant, and classing his views as fringe and fanatical. Sulayman's first anti-Wahhabi treatise was followed by a second book, ''The Unmistakable Judgment in the Refutation of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab'' (''Faṣl al-Ḫiṭāb fī Al-radd 'alā Muḥammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhāb''). Later ''Muwahhidun'' scholarly figures like Abdullah ibn Abd al-Latif Aal al-Shaykh (d. 1921 C.E) would respond to these accusations by asserting that Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab refrained from making ''Takfir'': " Shaykh Muhammad (May God have Mercy on him) never made takfeer of the people in the beginning; except via establishing the proofs and the da'wah, because at that time there was a dearth of knowledge of the message (of Islām) and for that reason he said 'due to their ignorance and the lack of anyone who makes them aware'. However, as for those on whom the proofs are established, then there is nothing to prevent ''takfeer'' being made on such people"Both Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's father and brother disagreed with him and didn't share his doctrinal statements because they considered his doctrine, and the way he intended to impose it in Arabia, too extreme and intolerant. The Arabian historian Ahmad ibn al-Zayni Dahlan, Shaykh al-Islām and Grand Mufti of the Shafi'i madhab in Mecca, recorded the account of the dispute between Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and his brother Sulayman, reporting that: According to various historical records, Sulayman repented and joined the religious mission of his brother. However, there is a disagreement regarding his repentance. While earlier Najdi chroniclers like Ibn Ghannam reported he repented and embraced Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's cause in Diriyah, later historians like Ibn Bishr simply mentions his departure to Diriyah with his family and his last years under the protection of Diriyah, while being allowed by state-allotted stipend. A letter attributed to Sulayman also mentions his public repentance. The Ottoman Grand Mufti of Mecca, Ahmad Zayni Dahlan (d. 1886), wrote an anti-Wahhabi treatise, in which he listed the religious practices that the Najdi Hanbalis considered idolatrous: visiting the
tomb of Muhammad
Al-Masjid an-Nabawi (), known in English as the Prophet's Mosque, is a mosque built by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the city of Medina in the Al Madinah Province of Saudi Arabia. It was the second mosque built by Muhammad in Medina, after Qub ...
, seeking the intercession of saints, venerating Muhammad and obtaining the blessings of saints. He also accused Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab of not adhering to the Hanbali school and that he was deficient in learning. However, Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab had believed that visiting the tomb of Muhammad was a righteous deed, referring to it as "among the best of deeds" while condemning its excesses. The medieval theologians Ibn Taymiyyah
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
and Ibn Qayyim, who inspired Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, had issued ''Fatwa
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist ...
s'' declaring the visitations to the tomb of Muhammad to be ''haram
''Haram'' (; ar, حَرَام, , ) is an Arabic term meaning 'Forbidden'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowle ...
'' (forbidden); which would lead to their imprisonment.
In response, the British Indian ''Ahl-i Hadith
Ahl-i Hadith or Ahl-e-Hadith ( bn, আহলে হাদীছ, hi, एहले हदीस, ur, اہلِ حدیث, ''people of hadith'') is a Salafi reform movement that emerged in North India in the mid-nineteenth century from the teach ...
'' scholar Muhammad Bashir Sahsawani (1834-1908 C.E) wrote the treatise ''Sayaanah al-Insaan an Waswaswah al-Shaikh Dahlaan'' in order to refute Dahlan. Sahsawani asserted that after his correspondence with various scholars of the ''Muwahhidun'' movement and study of their creedal works; he came to the conclusion that the allegation that they excommunicated "non-Wahhabis" were false and slanderous.
The Islamic scholar Muhammad Rashid Rida (d. 1935 C.E/ 1354 A.H) in his introduction to al-Sahsawani's refutation of Dahlan, described Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab as a '' mujaddid'' repelling the innovations and deviations in Muslim life. Through his '' Al-Manar'' magazine, Rashid Rida greatly contributed to the spread of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's teachings in the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
. He was a strong supporter of Ibn Taymiyyah and scholars of Najd, publishing works in his magazine entitled ''Majmooah al-Rasaail wa al-Masaail al-Najdiyyah'' and ''al-Wahhaabiyoon wa al-Hijaaz.'' Rida notes that given Dahlan's position in Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
, and availability there of the works of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab, he must have simply chosen to write otherwise. Rida also argued that Dahlan simply wrote what he heard from people, and criticised him for not verifying reports and seeking out the writings of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab. He condemned Dahlan for his ignorance and his sanctioning of acts of ''kufr'' and ''shirk''; based on his reinterpretation of Islamic texts.
Rashid Rida contended that Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was a victim of persecution by the combined oppression of three forces: i) the power of state and its rulers ii) power of hypocritical scholars and iii) power of tyrannical commoners. Fiercely rebuking his opponents, Rashid Rida declared:"The best weapon they brandished against him was that he contradicted the majority of Muslims. Who were the majority of Muslims Muhammad Ibn Abdul Wahhab contradicted in his ''Da'wah''? They were Bedouins of the desert, worse than the people of '' Jahiliyyah'', intent on looting and theft. They allowed shedding the blood of Muslims and non-Muslims, just to earn a living. They took their tyrants as judges in every matter and denied many aspects of Islam on which there is consensus specially among scholars matters in which no Muslim can claim ignorance."
Ali Bey el Abbassi
Domingo Francisco Jorge Badía y Leblich; 1767–1818), better known by his pseudonym Ali Bey el Abbassi ( ar, علي باي العباسي, ''Alī Bay al-Abasī''), was a Spanish explorer, soldier, and spy in the early 19th century. He supported ...
, a Spanish explorer who was in Mecca in 1803, shortly after the Wahhabi conquest of Hejaz, presented a starkly different view of the Wahhabis. He was surprised to find that they were fairly "moderate, reasonable and civilized". He further observed that, rather than engaging in rampant violence and destruction, the Wahhabis were pleasant and well-organized. According to Ali Bey, there were major differences in the political approach of Muhammad ibn Saud Al Muqrin, and that of his son, Abdulaziz bin Muhammad Al Saud, during whose reign
A reign is the period of a person's or dynasty's occupation of the office of monarch of a nation (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Belgium, Andorra), of a people (e.g., the Franks, the Zulus) or of a spiritual community (e.g., Catholicism, Tibetan Budd ...
Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was retired from active public life. Ali Bey asserts that unlike the fair-minded Muhammad Ibn Saud; his son 'Abd Al-Azeez began employing a "convert or die" approach for the acquirment of wealth and stabilising the state. Ali Bey writes in his ''Travels'': "I discovered much reason and moderation among the Wehhabites to whom I spoke, and from whom I obtained the greater part of the information which I have given concerning their nation..... The reformer Abdoulwehhab did not invest himself with any honour or public character: he was only the chief of the sect, and did not require any personal distinction. After his death, his son, who succeeded him, preserved the same simplicity."
British diplomat
Harford Jones-Brydges
Sir Harford Jones-Brydges, 1st Baronet, DL (12 January 1764 – 17 March 1847), born Harford Jones, was a British diplomat and author.
Life
Born on 12 January 1764, Sir Harford Jones-Brydges was the son of Harford Jones of Presteign, Radn ...
, who was stationed in Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
in 1784 attributed the popular hysteria about the Wahhabis to a different cause. Unlike Ottoman depictions, Brydges believed that Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's doctrine was in keeping with the teachings of Quran, was "perfectly orthodox", "consonant to the purest and best interpretations of that volume", and that Ottomans feared its spread precisely on that basis.
The Egyptian historian and Azhari
, image = جامعة_الأزهر_بالقاهرة.jpg
, image_size = 250
, caption = Al-Azhar University portal
, motto =
, established =
*970/972 first foundat ...
Islamic scholar Abd al-Rahman al-Jabarti (1753–1825 C.E) was a great admirer of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab and his movement. He defended his doctrines in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
and held the movement in high regard, viewing its doctrines as having a great prospective to spearhead future Islamic revival
Islamic revival ( ar, تجديد'' '', lit., "regeneration, renewal"; also ', "Islamic awakening") refers to a revival of the Islamic religion. The revivers are known in Islam as '' mujaddids''.
Within the Islamic tradition, ''tajdid'' has be ...
. Al-Jabarti had the chance to personally meet with various Wahhabi scholars in Egypt in 1814. Finding them to be friendly and knowledgeable, Al-Jabarti stated that the Wahhabis were "modest men of good morals, well trained in oratory, in the principles of religion, the branches of fiqh, and the disagreements of the Schools of Law. In all this they were extraordinary." He described Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab as a man who "summoned men to ''Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
'' and the Prophet's '' Sunna'', bidding them to abandon innovations in worship". Through his writings, Al-Jabarti repeatedly stressed that the beliefs and doctrines championed by Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab were nothing other than orthodox Sunni Islam.
Moroccan military leader 'Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi (1882-1963 C.E) praised Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's reform endeavour as a "promising voice" that sparked spiritual and intellectual Awakening across the Islamic World
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
.
Prominent Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indig ...
Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
scholar 'Abd al-Qadir ibn Badran (1864-1927 C.E/ 1280-1346 A.H) praised the efforts of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab in his treatise ''Al-Madkhal ila Madhhab il-Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal'' (An Introduction to the Madhab of Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal), writing: "When he .e, Ibn 'Abd al Wahhablearned the narrations and the ''Sunnah In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...'' and became expertised in the '' madhab'' ofAhmad Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet. Etymology The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the v ...; he began supporting the Truth, fighting '' bid'ah'' and resisting what illiterates have made part of this monotheistic religion and '' Sharia'' of moderation''.'' Some people supported him and made their worship solely to The One God following his path, which was to establish pure ''Tawhid'', call sincerely to monotheism and direct worship in all of its forms solely to The Creator of creation alone. Some people resisted him; they were used to rigidity in following what their forefathers did and they armoured themselves with laziness instead of seeking the truth."
Modern reception
Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab is often compared to the 15th-centuryGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
pastor
A pastor (abbreviated as "Pr" or "Ptr" , or "Ps" ) is the leader of a Christian congregation who also gives advice and counsel to people from the community or congregation. In Lutheranism, Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy and ...
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
, for their efforts in launching religious movements that challenged the authority of the dominant clerical and political hierarchy of their societies. Despite being of different religious persuasions; both of them were inspired by an idealised vision of the past and shared similar themes such as the social and economic upliftment of their societies empowered through mass-education enabled by calls for open access to Scriptures. He is honoured by many scholars of the Salafi
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a reform branch movement within Sunni Islam that originated during the nineteenth century. The name refers to advocacy of a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generat ...
tradition as a juristic authority and source of reference. Salafi scholars Rashid Rida
Muḥammad Rashīd ibn ʿAlī Riḍā ibn Muḥammad Shams al-Dīn ibn Muḥammad Bahāʾ al-Dīn ibn Munlā ʿAlī Khalīfa (23 September 1865 or 18 October 1865 – 22 August 1935 CE/ 1282 - 1354 AH), widely known as Sayyid Rashid Rida ( ar, � ...
and ' Abd al-Aziz ibn Baz considered him a '' mujaddid''. The Albanian Salafi revivalist Al-Albani (d. 1999) believed that Ibn Abd al-Wahhab was not a mujtahid in fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
, as he 'blindlly' followed the Hanbali school. Al-Albani also questioned Ibn Abd al-Wahhab's knowledge of hadith.
According to the 20th-century Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
scholar Muhammad Asad
Muhammad Asad, ( ar, محمد أسد , ur, , born Leopold Weiss; 2 July 1900 – 20 February 1992) was an Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian-born Pakistani journalist, traveler, writer, Linguistics, linguist, List of political theorists, polit ...
, all modern Islamic Renaissance movements took inspiration from the spiritual impetus set in motion in the 18th century by Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab. Crediting Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab for his contributions to Islamic Renaissance and spread of revolutionary ideals across the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
, Tunisian Islamist intellectual Rached Gannouchi writes:"Just as in theWest West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...in the age of Renaissance, the Muslim world was stirred by a great awakening. Muhammad bin Abd al-Wahhab’s message of ''jihad'' and ''ijtihad'' inspired an unbroken movement... to push theumma Umma ( sux, ; in modern Dhi Qar Province in Iraq, formerly also called Gishban) was an ancient city in Sumer. There is some scholarly debate about the Sumerian and Akkadian names for this site. Traditionally, Umma was identified with Tell ...towards ''jihad'' against its enemies, to abandon the guise of tradition (''taqlid'') and to unite its divisions around the mystical origins of Islam and Islamic thought."
Rashid Ahmad Gangohi
Rashīd Aḥmad ibn Hidāyat Aḥmad Ayyūbī Anṣārī Gangohī (182611 August 1905) ( ur, ) was an Indian Deobandi Islamic scholar, a leading figure of the Deobandi jurist and scholar of hadith. His lineage reaches back to Abu Ayyub al-A ...
, one of the founders of the Deobandi school
Deobandi is a revivalist movement within Sunni Islam, adhering to the Hanafi school of law,
formed in the late 19th century around the Darul Uloom Madrassa in Deoband, India, from which the name derives,
by Muhammad Qasim Nanautavi, R ...
praised Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab as a virtuous scholar who upheld the Sunnah and campaigned against polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, th ...
and superstitious
A superstition is any belief or practice considered by non-practitioners to be irrational or supernatural, attributed to fate or magic, perceived supernatural influence, or fear of that which is unknown. It is commonly applied to beliefs and pr ...
beliefs and practices. Hence, the contemporary ''ulema'' of Deoband mostly respect him while being critical of the Salafi movement. Major scholars of Tabligh Jamaat -a Deobandi-inspired missionary movement- such as Muhammad Zakariya, Muhammad Ilyas Kandhlawi, Yusuf Kandhalawi, etc. were supportive of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's ideals. Senior Deobandi scholar Manzur Numani penned the treatise "''Sheikh Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab ke Khilaf Propaganda''" (The Propaganda against Sheikh Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab) in defense of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab. Thus, many activists of Deobandi persuasion view Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's movement as an example for establishing an Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
in contemporary Muslim societies.
Islamic scholar Yusuf Al-Qārādawī praised Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab as a '' Mujaddid'' (religious reviver) of the Arabian Peninsula who defended the purity of ''Tawhid
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single ...
'' from various superstitions and polytheistic beliefs. Praising Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's efforts, Muhammad Rashīd Ridá wrote:"Muhammad bin Abd al-Wahhab al-Najdi was one of those ''Mujaddids'', hocalled for the upholding of ''Tawhid'' and the sincerity of worship to God alone with what He legislated in His Book and on the tongue of His Messenger, the Seal of the Prophets; ... abandoning heresies and sins, establishing the abandoned rituals of Islam, and venerating its violated sanctities."In his book "''Saviours of the Islamic Spirit''", Islamic scholar Abul Hasan Ali Nadwi (1913-1999 C.E) acclaimed Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab as a "great reformer" who called his people to ''Tawhid'', revived injunctions based on ''Qur'an'' and ''
Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
'' and eradicated superstitious rites prevalent amongst the illiterate masses of Central Arabia. Nadwi compared his movement to that of the contemporary South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
n Islamic revivalist Shah Waliullah Dehlawi
Quṭb-ud-Dīn Aḥmad Walīullāh Ibn ʿAbd-ur-Raḥīm Ibn Wajīh-ud-Dīn Ibn Muʿaẓẓam Ibn Manṣūr Al-ʿUmarī Ad-Dehlawī ( ar, ; 1703–1762), commonly known as Shāh Walīullāh Dehlawī (also Shah Wali Allah), was an Islami ...
(1703-1762 C.E/ 1114-1176 A.H) who had expounded similar ideas such as differentiating between ''Tawhid-i-Uluhiyyat'' (Oneness of Worship) and ''Tawhid-i-Rububiyat'' (Oneness of Lordship) and promotion of strict adherence to ''Qur'an'' and ''Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
''. In Nadwi's opinion, Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab was able to make outstanding efforts with far-reaching impact compared to other contemporary reformers since he played the role of a revolutionary reformer whose initiatives were implemented through a newly established Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
and thus his movement was highly pertinent for the people of his time.
In 2010, Prince Salman bin Abdulaziz, at the time serving as the governor of Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, Literal translation, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi Arabic, Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyad ...
, said that the doctrine of Muhammad Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab was pure Islam, and said regarding his works:"I dare anyone to bring a single alphabetical letter from the Sheikh's books that goes against the book of Allah and the teachings of his prophet, Muhammad."
Western Reception
In the 21st century Western security discourse, Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's movement, Wahhabism, is often associated with variousJihadi
Jihadism is a neologism which is used in reference to "militant Islamic movements that are perceived as existentially threatening to the West" and "rooted in political Islam."Compare: Appearing earlier in the Pakistani and Indian media, We ...
movements across the Islamic World
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
. According to various Western analysts, the Islamist terrorist organization Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
has been influenced by the Wahhabi doctrine. Other scholars note that the ideology of Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military targets in various countri ...
is Salafi jihadism
Salafi jihadism or jihadist-Salafism is a transnational, hybrid religious-political ideology based on the Sunni sect of Islamism, seeking to establish a global caliphate, characterized by the advocacy for "physical" (military) jihadist and ...
that emerged as a synthesis of the Qutbist doctrine with Salafism. The Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pas ...
in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
was often conflated with Wahhabis in the early 2000s; however, the Taliban emerged from the Deobandi
Deobandi is a revivalist movement within Sunni Islam, adhering to the Hanafi school of law,
formed in the late 19th century around the Darul Uloom Madrassa in Deoband, India, from which the name derives,
by Muhammad Qasim Nanau ...
school rather than the Wahhabi movement. According to other sources, Salafis are fundamentally opposed to the ideology of Al-Qaeda. According to various scholars, the ideology of Islamic State, another Islamic terrorist organization, has also been inspired by Wahhabi doctrines, alongside Salafism, Qutbism
Qutbism ( ar, ٱلْقُطْبِيَّةِ, al-Quṭbīyah) is an Islamist ideology which was developed by Sayyid Qutb, a leading member of the Muslim Brotherhood who was executed by the Egyptian government in 1966. It has been described as ad ...
, and Salafi jihadism
Salafi jihadism or jihadist-Salafism is a transnational, hybrid religious-political ideology based on the Sunni sect of Islamism, seeking to establish a global caliphate, characterized by the advocacy for "physical" (military) jihadist and ...
.
During the Post-9/11 period, when the FBI listed al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
as "the number one terrorist threat to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
", American neo-conservative journalist Lulu Schwartz
Lulu Schwartz (born Stephen Suleyman Schwartz, September 9, 1948) is an American Sufi journalist, columnist, and author. She has been published in a variety of media, including ''The Wall Street Journal''. She served as the director of the "Is ...
, and former U.S. Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
and Republican politician Jon Kyl
Jon Llewellyn Kyl ( ; born April 25, 1942) is an American politician and lobbyist who served as a United States Senator for Arizona from 1995 to 2013 and again in 2018. A Republican, he held both of Arizona's Senate seats at different times, ...
asserted during the hearing before the Subcommittee on Terrorism, Technology, and Homeland Security of the U.S. Senate in June 2003 that "Wahhabism is the source of the overwhelming majority of terrorist atrocities in today's world". Their recommendations would become influential in the 21st century US foreign policy
The officially stated goals of the foreign policy of the United States of America, including all the bureaus and offices in the United States Department of State, as mentioned in the ''Foreign Policy Agenda'' of the Department of State, are ...
:
Meanwhile, contemporary Western historians and researchers have taken a more nuanced approach on the history and evolution of the ''
Muwahhidun The People of Monotheism may translate several Arabic terms:
* ( ar, أهل التوحيد), a name the Druze use for themselves. Literally, "The People of the Unity" or "The Unitarians", from '' '', unity (of God).
* ( ar, الموحدون) is ...
'' movement; pointing out the discrepancy between the Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's teachings, some of his later followers and the actions of contemporary militant Jihadist groups. Various scholars assert that many writings of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab were revised during the 19th century by authorities of the Second Saudi State; transforming them away from a poetic-vernacular style of communication with mass appeal to a more rigid and purist understanding that aligned with the interests of the ruling class and the clerical establishment. David E. Long believes that modern Jihadist movements are more influenced by the ideological worldview of Egyptian Islamist extremism of the 20th century, rather than Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's socio-religious reformism. Although many Salafi-Jihadists maybe inspired by Wahhabi ideals, it doesn't credibly explain their inclinations towards lethal violence.
Western scholars like Michael Ryan assert that Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
teachings were a rationalist enterprise that sought to eradicate superstitions widespread in the context of tribal rivalry within the Arabian Peninsula. Moreover, the regional background of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's intellectual efforts in the chaotic context of the 18th-century Arabian Peninsula had been distinct from the 21st century global Jihad ideology of organisations like Al-Qaeda or IS. Consequently, his scholarly heirs, including the prestigious Aal al-Shaykhs constitute the primary ideological nemesis of groups such as Al-Qaeda. Since the Saudi population overwhelmingly prefers their traditional religious institutions and scholars to Bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden (10 March 1957 – 2 May 2011) was a Saudi-born extremist militant who founded al-Qaeda and served as its leader from 1988 until his death in 2011. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, his group is designated ...
's claims to revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective, to refer to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor. ...
Jihadi-Salafism; Al-Qaeda harshly attacks these mainstream Saudi clerics with much theological vitriol.
Various scholars have also contested Orientalist portrayals of Wahhabi movement as "ultra-conservative" or "stagnant". Asserting the dynamic nature of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's call and its capability of multiple interpretations; Professor
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an academic rank at universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professor ...
of Philosophy at the University of Kentucky
The University of Kentucky (UK, UKY, or U of K) is a public land-grant research university in Lexington, Kentucky. Founded in 1865 by John Bryan Bowman as the Agricultural and Mechanical College of Kentucky, the university is one of the state's ...
, Oliver Leaman states: "the development of thehadith Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ..., whose importance cannot be over-emphasized, incorporated dynamism into the very heart of Islam. When Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab criticized local customs in Arabia on the basis of their incongruence with the past he was indeed trying to get back to a former golden age, but that is a very modern thing to do... What the Wahhabis were doing was to criticize current society and seek to undermine the existing order, something that the earlierIbn Taymiyya Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...fell foul of when for having similar views he was tortured and threatened with death."
Contemporary recognition
 Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's thoughts would greatly influence the pan-Islamic movement of the 19th century. The national mosque of
Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's thoughts would greatly influence the pan-Islamic movement of the 19th century. The national mosque of Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it ...
is named after him. The " Imam Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab Mosque" was opened in 2011, with the Emir of Qatar presiding over the occasion. The mosque has the capacity to host a congregation of 30,000 people. In 2017, there was a request published in the Saudi Arabian newspaper '' Okaz'' signed by 200 descendants of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab that the name of the mosque be changed, because according to their statement "it does not carry its true Salafi path", even though most Qataris adhere to Wahhabism.
The Turaif district in Diriyah, the capital of the First Saudi state, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
in 2010. In 2011, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
announced its plans for large-scale development of Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab's domain Diriyah; to establish a national cultural site in Diriyah and turn it into a major tourist attraction. Other features in the area include the ''Sheikh Muhammad bin Abdul Wahab Foundation'', which is planned to include a light and sound presentation located near the ''Mosque of Sheikh Mohammad bin Abdulwahab''.
Works
Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab has been described as a "prolific writer" whose scholarly treatises are collected into fourteen large volumes; which consists of various legal books, Qur'anic commentaries, creedal works, and compilation of '' fatwas''. Some of his major works include:See also
*Ibn Taymiyyah
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
* Wahhabi Movement
* Emirate of Diriyah
The Emirate of Diriyah (), also known as the First Saudi State, was established in February 1727 (1139 AH). In 1744, the emir of Najdi town called Diriyah Muhammad bin Saud and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab formed an allianc ...
* International propagation of Salafism and Wahhabism
Sources
 Two of the earliest sources for the biography of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab and early history of the
Two of the earliest sources for the biography of Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab and early history of the Wahhabi
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, ...
movement have been documented by its followers:
* Wahhabi chronicler and scholar Ibn Ghannam's ''Rawdhat al-Afkar wal-Afham'' or ''Tarikh Najd'' (History of Najd) and Husain ibn Ghannam (d. 1811), an alim from al-Hasa was the only historian to have observed the beginnings of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's movement first-hand. His chronicle ends at the year 1797. Vasilʹev 1998: 13
* Najdi Historian Ibn Bishr's ''Unwan al-Majd fi Tarikh Najd'' (The Glorious History of Najd). Ibn Bishr's chronicle, which stops at the year 1854, was written a generation later than Ibn Ghannam's but is considered valuable partly because Ibn Bishr was a native of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
and because he adds many details to Ibn Ghannam's account.
A third account, covering Arabian history between the 1730s to 1817 is ''Lam' al-Shihab'' (The Brilliance of the Meteor) written by an anonymous author who respectfully disapproved of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's movement, regarding it as a '' bid'ah'' (heresy).
It is also commonly cited in Orientalist circles because it is considered to be a relatively objective and unofficial treatment of the subject. However, unlike Ibn Ghannam and Ibn Bishr, its author did not live in Najd and his work contains various tales, apocryphal and legendary materials concerning the details of Ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab's life. Vasilʹev 1998: 14
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Valentine, S. R., "Force & Fanaticism: Wahhabism in Saudi Arabia and Beyond", Hurst & Co, London, 2015, * * *Online
Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb: Muslim theologian
in ''Encyclopædia Britannica Online'', by The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica, Parul Jain, Satyavrat Nirala and Adam Zeidan
External links
*Biodata at MuslimScholars.info
{{DEFAULTSORT:Abd Al Wahhab, Muhammad Ibn 1703 births 1792 deaths 18th-century Arabs 18th-century Muslim scholars of Islam Muslim reformers Anti-Ottomanism Arab Sunni Muslim scholars of Islam Critics of Shia Islam Islamic religious leaders Sunni imams Proto-Salafists Hanbalis Mujaddid Chief Qadis of Emirate of Dir'iyah 18th-century Muslim theologians Atharis Wahhabists