Mucormycosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are
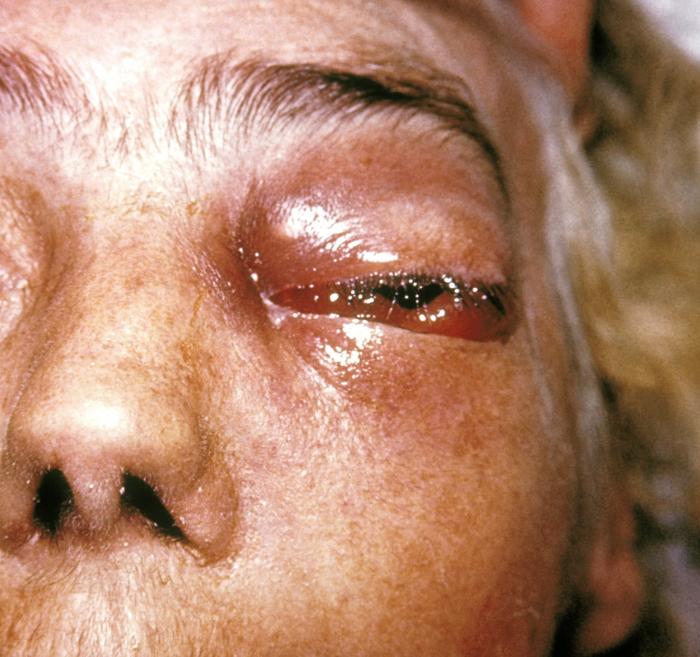 Signs and symptoms of mucormycosis depend on the location in the body of the infection. Infection usually begins in the mouth or nose and enters the central nervous system via the eyes.
If the fungal infection begins in the nose or sinus and extends to brain, symptoms and signs may include one-sided eye pain or
Signs and symptoms of mucormycosis depend on the location in the body of the infection. Infection usually begins in the mouth or nose and enters the central nervous system via the eyes.
If the fungal infection begins in the nose or sinus and extends to brain, symptoms and signs may include one-sided eye pain or
File:Zygomycosis, mucormycosis 2.jpg, Ribbon-like hyphae which branch at 90°
File:Zygomycosis Mucormycosis (13430751363).jpg, Hyphae in blood vessel
File:Mature sporangium of a Mucor sp. fungus.jpg, Mature sporangium of a Mucor
 During the
During the
immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the infection occurs. It most commonly infects the nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes th ...
, sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
, eye, and brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
resulting in a runny nose
Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies ( hay fever) or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COVI ...
, one-sided facial swelling and pain, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, blurred vision, bulging or displacement of the eye (proptosis), and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of th ...
, stomach and intestines, and skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
.
It is spread by spores of molds of the order Mucorales
The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.
Systematics ...
, most often through inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
, contaminated food, or contamination of open wounds
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epider ...
. These fungi are common in soils, decomposing organic matter (such as rotting fruit and vegetables), and animal manure, but usually do not affect people. It is not transmitted between people. Risk factors include diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
with persistently high blood sugar levels or diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of ...
, low white blood cells
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of leukocytes (WBC). Found in the blood, they are the white blood cells, and are the body's primary defense against an infection. Thus the condition of leukopenia places individuals at increased risk of inf ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpo ...
, iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatosi ...
, kidney problems
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
, long-term steroids or use of immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
s, and to a lesser extent in HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
.
Diagnosis is by biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, with medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
to help determine the extent of disease. It may appear similar to aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung di ...
. Treatment is generally with amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious mycosis, fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candida infections, candidiasis, coccidioidomy ...
and surgical debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
. Preventive measures include wearing a face mask in dusty areas, avoiding contact with water-damaged buildings, and protecting the skin from exposure to soil such as when gardening or certain outdoor work. It tends to progress rapidly and is fatal in about half of sinus cases and almost all cases of the widespread type.
Mucormycosis is usually rare, affecting fewer than 2 people per million people each year in San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
, but is now ~80 times more common in India. People of any age may be affected, including premature infants. The first known case of mucormycosis was possibly the one described by Friedrich Küchenmeister
Gottlieb Heinrich Friedrich Küchenmeister (22 January 1821, Buchheim (now Bad Lausick) – 13 April 1890 Dresden) was a German physician.
Life
Küchenmeister studied medicine in Leipzig and Prague, and in 1846 he became a general practitioner i ...
in 1855. The disease has been reported in natural disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some econ ...
s; 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami and the 2011 Missouri tornado. During the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
, an association between mucormycosis and COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
has been reported. This association is thought to relate to reduced immune function during the course of the illness and may also be related to glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
therapy for COVID-19. A rise in cases was particularly noted in India.
Classification
Generally, mucormycosis is classified into five main types according to the part of the body affected. A sixth type has been described as mucormycosis of the kidney, or miscellaneous, i.e., mucormycosis at other sites, although less commonly affected. *Sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
(rhinocerebral); most common in people with poorly controlled diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
and in people who have had a kidney transplant
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantati ...
.
* Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of th ...
(pulmonary); the most common type of mucormycosis in people with cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and in people who have had an organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpo ...
or a stem cell transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produc ...
.
* Stomach and intestine (gastrointestinal); more common among young, premature, and low birth weight infants, who have had antibiotics, surgery, or medications that lower the body's ability to fight infection.
* Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
(cutaneous); after a burn, or other skin injury, in people with leukaemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ' ...
, poorly controlled diabetes, graft-versus-host disease, HIV and intravenous drug use
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or subcutaneous location). Intravenou ...
.
* Widespread (disseminated); when the infection spreads to other organs via the blood.
Signs and symptoms
 Signs and symptoms of mucormycosis depend on the location in the body of the infection. Infection usually begins in the mouth or nose and enters the central nervous system via the eyes.
If the fungal infection begins in the nose or sinus and extends to brain, symptoms and signs may include one-sided eye pain or
Signs and symptoms of mucormycosis depend on the location in the body of the infection. Infection usually begins in the mouth or nose and enters the central nervous system via the eyes.
If the fungal infection begins in the nose or sinus and extends to brain, symptoms and signs may include one-sided eye pain or headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, and may be accompanied by pain in the face, numbness, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, loss of smell, a blocked nose
Nasal congestion is the blockage of nasal breathing usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflamed blood vessels.
Background
In about 85% of cases, nasal congestion leads to mouth breathing rather than nasal breathing. ...
or runny nose
Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies ( hay fever) or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COVI ...
. The person may appear to have sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
. The face may look swollen on one side, with rapidly progressing "black lesions" across the nose or upper inside of mouth. One eye may look swollen
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
and bulging, and vision may be blurred.
Fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
, or coughing up blood, can occur when the lungs are involved. A stomach ache
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, nausea, vomiting and bleeding can occur when the gastrointestinal tract is involved. Affected skin may appear as a dusky reddish tender patch with a darkening centre due to tissue death. There may be an ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o ...
, and it can be very painful.
Invasion of the blood vessels
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
can result in thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thro ...
and subsequent death of surrounding tissue due to a loss of blood supply. Widespread (disseminated) mucormycosis typically occurs in people who are already sick from other medical conditions, so it can be difficult to know which symptoms are related to mucormycosis. People with disseminated infection in the brain can develop changes in mental status or lapse into a coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
.
Cause
Mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused byfungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
in the order Mucorales
The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.
Systematics ...
. In most cases it is due to an invasion of the genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
''Rhizopus
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and ...
'' and ''Mucor
''Mucor'' is a microbial genus of approximately 40 species of molds in the family Mucoraceae. Species are commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, some cheeses like Tomme de Savoie, rotten vegetable matter and iron oxide re ...
'', common bread molds. Most fatal infections are caused by ''Rhizopus oryzae
''Rhizopus oryzae'' is a filamentous heterothallic microfungus that occurs as a saprotroph in soil, dung, and rotting vegetation. This species is very similar to ''Rhizopus stolonifer'', but it can be distinguished by its smaller sporangia and a ...
''. It is less likely due to ''Lichtheimia
''Lichtheimia'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Lichtheimiaceae
''Lichtheimiaceae'' is a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. The family was circumscribed in 2013 after a molecular phylogenetic analysis helped delineate a new ...
'', and rarely due to ''Apophysomyces
''Apophysomyces'' is a genus of filamentous fungi that are commonly found in soil and decaying vegetation. Species normally grow in tropical to subtropical regions.
The genus ''Apophysomyces'' historically was monospecific, containing only the t ...
''. Others include ''Cunninghamella
Cunninghamella is a genus of fungi in the order Mucorales, and the family Cunninghamellaceae. The genus was circumscribed by French mycologist Alphonse Louis Paul Matruchot in Ann. Mycol. Vol.1 on page 47 in 1903.
The genus name of ''Cunning ...
'', ''Mortierella
''Mortierella'' species are soil fungi belonging to the order Mortierellales within the subphylum Mortierellomycotina (phylum: Mucoromycota). The widespread genus contains about 85 species.
Taxonomy
The genus name of ''Mortierella'' is in hon ...
'', and ''Saksenaea
''Saksenaea'' is a genus of fungi in the Saksenaeaceae family. First described in 1953, the genus contains two pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is ...
''.
The fungal spores are present in the environment, can be found on items such as moldy bread and fruit, and are breathed in frequently, but cause disease only in some people. In addition to being breathed in and deposited in the nose, sinuses, and lungs, the spores can also enter the skin via blood or directly through a cut or open wound, and can also grow in the intestine if eaten. Once deposited, the fungus grows branch-like filaments which invade blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s, causing clots to form and surrounding tissues to die. Other reported causes include contaminated wound dressings. Mucormycosis has been reported following the use of elastoplast
Elastoplast is a brand of adhesive bandages (also called ''sticking plasters'') and medical dressings made by Beiersdorf.
Background
In 1928 Smith & Nephew of the UK acquired the licence to market and produce the Elastoplast range of bandages.
...
and the use of tongue depressor
A tongue depressor (sometimes called spatula) is a tool used in medical practice to depress the tongue to allow for examination of the mouth and throat. The most common modern tongue depressors are flat, thin, wooden blades, smoothed and rounded ...
s for holding in place intravenous catheters. Outbreaks have also been linked to hospital bed sheets, negative-pressure rooms, water leaks, poor ventilation, contaminated medical equipment, and building works.
Risk factors
Predisposing factors for mucormycosis includeimmune deficiencies
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
, a low neutrophil count, and metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys ...
. Risk factors include poorly controlled diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
(particularly DKA
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of ...
), organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpo ...
, iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatosi ...
, such cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s as lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlar ...
s, kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
, liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the sig ...
, severe malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, and long term corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
and immunosuppressive therapy
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
. Other risk factors include tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
(TB), deferoxamine
Deferoxamine (DFOA), also known as desferrioxamine and sold under the brand name Desferal, is a medication that binds iron and aluminium. It is specifically used in iron overdose, hemochromatosis either due to multiple blood transfusions or an un ...
and to a lesser extent HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
. Cases of mucormycosis in fit and healthy people are less common.
Corticosteroids are commonly used in the treatment of COVID-19 and reduce damage caused by the body's own immune response to the virus. They are immunosuppressant and increase blood sugar levels in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients. It is thought that both these effects may contribute to cases of mucormycosis.
Mechanism
Most people are frequently exposed to Mucorales without developing the disease. Mucormycosis is generally spread by breathing in, eating food contaminated by, or getting spores of molds of theMucorales
The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.
Systematics ...
type in an open wound
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves laceration, lacerated or puncture wound, punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a bruise, contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force physical trauma, trauma or compression. In pathology, a '' ...
. It is not transmitted between people.
The precise mechanism by which diabetics become susceptible is unclear. ''In vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'', a high sugar level alone does not permit the growth of the fungus, but acidosis
Acidosis is a process causing increased acidity in the blood and other body tissues (i.e., an increase in hydrogen ion concentration). If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma.
The term ''acidemia'' describes t ...
alone does. People with high sugar levels frequently have high iron levels, also known to be a risk factor for developing mucormycosis. In people taking deferoxamine, the iron removed is captured by siderophore
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron- chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is n ...
s on ''Rhizopus'' species, which then use the iron to grow.
Diagnosis
There is no blood test that can confirm the diagnosis. Diagnosis requires identifying the mold in the affected tissue bybiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
and confirming it with a fungal culture. Because the causative fungi occur all around and may therefore contaminate cultures underway, a culture alone is not decisive. Tests may also include culture and direct detection of the fungus in lung fluid, blood, serum, plasma and urine. Blood tests include a complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
to look specifically for neutropenia. Other blood tests include iron levels
Iron tests are groups of clinical chemistry laboratory blood tests that are used to evaluate body iron stores or the iron level in blood serum.
Other terms used for the same tests are iron panel, iron profile, iron indices, iron status or iron ...
, blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
, bicarbonate, and electrolytes
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon di ...
. Endoscopic examination of the nasal passages may be needed.
Imaging
Imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
is often performed, such as CT scan of lungs and sinuses. Signs on chest CT scans, such as nodules, cavities, halo signs, pleural effusion and wedge-shaped shadows, showing invasion of blood vessels, may suggest a fungal infection, but do not confirm mucormycosis. A reverse halo sign in a person with a blood cancer and low neutrophil count is highly suggestive of mucormycosis. CT scan images of mucormycosis can be useful to distinguish mucormycosis of the orbit and cellulitis of the orbit, but images may appear identical to those of aspergillosis. MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
may also be useful. Currently, MRI with gadolinium contrast is the investigation of choice in rhinoorbito-cerebral mucormycosis.
Culture and biopsy
To confirm the diagnosis,biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
samples can be cultured. Culture from biopsy samples does not always give a result as the organism is very fragile. To precisely identify the species requires an expert. The appearance
Appearance may refer to:
* Visual appearance, the way in which objects reflect and transmit light
* Human physical appearance, what someone looks like
* ''Appearances'' (film), a 1921 film directed by Donald Crisp
* Appearance (philosophy), or p ...
of the fungus under the microscope will determine the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
and species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
. The appearances can vary but generally show wide, ribbon-like filaments that generally do not have septa and that—unlike in aspergillosis—branch at right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s, resembling antlers of a moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, which may be seen to be invading blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s.
Other
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of ...
may be used to identify the species. A blood sample from an artery may be useful to assess for metabolic acidosis.
Differential diagnosis
Other filamentous fungi may however look similar. It may be difficult to differentiate fromaspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung di ...
. Other possible diagnoses include anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The sk ...
, cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
, bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or Ileus, functional obstruction of the Gastrointestinal tract#Lower gastrointestinal tract, intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Eith ...
, ecthyma gangrenosum
Ecthyma gangrenosum is a type of skin lesion characterized by vesicles or blisters which rapidly evolve into pustules and necrotic ulcers with undermined tender erythematous border. "Ecthyma" means a pus forming infection of the skin with an ulcer ...
, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from tran ...
, clot in lungs, sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
and fusariosis
Fusariosis is an infection seen in people with low neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights infection. It is a significant opportunistic pathogen in people with blood cancer.
It is associated with infections with ''Fusarium
''Fusari ...
.
Prevention
Preventive measures include wearing a face mask in dusty areas, washing hands, avoiding direct contact with water-damaged buildings, and protecting skin, feet, and hands where there is exposure to soil or manure, such as gardening or certain outdoor work. In high risk groups, such as organ transplant patients,antifungal drug
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryp ...
s may be given as a preventative.
Treatment
Treatment involves a combination of antifungal drugs, surgically removing infecting tissue and correcting underlying medical problems, such as diabetic ketoacidosis.Medication
Once mucormycosis is suspected,amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious mycosis, fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candida infections, candidiasis, coccidioidomy ...
at an initial dose of 1 mg is initially given slowly over 10–15 minutes into a vein, then given as a once daily dose according to body weight for the next 14 days. It may need to be continued for longer. Isavuconazole
Isavuconazonium sulfate, sold under the brand name Cresemba, is a systemic antifungal medication of the triazole class which is used to treat invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis.
The most common side effects include abnormal liver tests, ...
and Posaconazole
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.
It was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2006, and is available as a generic medication.
Medical uses
Posaconazole is u ...
are alternatives.
Surgery
Surgery can be very drastic, and, in some cases of disease involving the nasal cavity and the brain, removal of infected brain tissue may be required. Removal of thepalate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sepa ...
, nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
, or eye structures can be very disfiguring. Sometimes more than one operation is required.
Other considerations
The disease must be monitored carefully for any signs of reemergence. Treatment also requires correcting sugar levels and improving neutrophil counts.Hyperbaric oxygen
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure ...
may be considered as an adjunctive therapy, because higher oxygen pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
increases the ability of neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
to kill the fungus. The efficacy of this therapy is uncertain.
Prognosis
It tends to progress rapidly and is fatal in about half of sinus cases, two thirds of lung cases, and almost all cases of the widespread type. Skin involvement carries the lowest mortality rate of around 15%. Possible complications of mucormycosis include the partial loss of neurological function,blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
, and clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
of blood vessels in the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
or lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
.
As treatment usually requires extensive and often disfiguring facial surgery, the effect on life after surviving, particularly sinus and brain involvement, is significant.
Epidemiology
The true incidence and prevalence of mucormycosis may be higher than appears. Mucormycosis is rare, affecting fewer than 1.7 people per million population each year in San Francisco. It is around 80 times more prevalent in India, where it is estimated that there are around 0.14 cases per 1000 population, and where its incidence has been rising. Causative fungi are highly dependent on location. ''Apophysomyces variabilis
''Apophysomyces variabilis'' is an emerging fungal pathogen that can cause serious and sometimes fatal infection in humans. This fungus is a soil-dwelling Saprotrophic nutrition, saprobe with tropical to subtropical distribution. It is a zygomyc ...
'' has its highest prevalence in Asia and '' Lichtheimia spp.'' in Europe. It is the third most common serious fungal infection to infect people, after aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung di ...
and candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth ...
.
Diabetes is the main underlying disease in low and middle-income countries, whereas, blood cancers and organ transplantation are the more common underlying problems in developed countries. As new immunomodulating drugs and diagnostic tests are developed, the statistics for mucormycosis have been changing. In addition, the figures change as new genera and species are identified, and new risk factors reported such as tuberculosis and kidney problems.
COVID-19–associated mucormycosis
 During the
During the COVID-19 pandemic in India
The COVID-19 pandemic in India is a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 () caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (). As of , according to Indian government figures, India has the second-highest n ...
, the Indian government reported that more than 11,700 people were receiving care for mucormycosis as of 25 May 2021. Many Indian media outlets called it "black fungus" because of the black discoloration of dead and dying tissue the fungus causes. Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, rates of mucormycosis in India were estimated to be about 70 times higher than in the rest of the world. Due to its rapidly growing number of cases some Indian state governments have declared it an epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
. One treatment was a daily injection for eight weeks of anti-fungal intravenous injection of amphotericin B which was in short supply. The injection could be standard amphotericin B deoxycholate
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. ...
or the liposomal form. The liposomal form cost more but it was considered "safer, more effective and ith
The Ith () is a ridge in Germany's Central Uplands which is up to 439 m high. It lies about 40 km southwest of Hanover and, at 22 kilometres, is the longest line of crags in North Germany.
Geography
Location
The Ith is immediatel ...
lesser side effects".§ The major obstacle of using antifungal drugs in black fungus is the lack of clinical trials.
Recurrence of mucormycosis during COVID-19 second wave in India
Pre-COVID mucormycosis was a very rare infection, even in India. It is so rare that an ENT (ear, nose, throat) doctor would not witness often a case during their university time. So, the documentation available on the treatment of mucormycosis is limited. In fact, there used to be a couple of mucormycosis expert ENT surgeons for millions of people pre-pandemic. The sudden rise in mucormycosis cases has left a majority of the ENT doctors with no option but to accept mucormycosis cases, as the expert doctors were very much occupied and the patient would die if left untreated. The majority of the ENT doctors had to manage with minimal or no experience on mucormycosis, this has led to the recurrence of mucormycosis in the patients they treated. When a highly experienced doctor in mucormycosis treats a patient even he cannot guarantee that the individual is completely cured and will not have a relapse of mucormycosis; an inexperienced ENT surgeon will definitely have a high number of patients with recurrence due to which there were many recurrent cases of mucormycosis although it did not get the limelight of media or the Indian Government.History
The first case of mucormycosis was possibly one described byFriedrich Küchenmeister
Gottlieb Heinrich Friedrich Küchenmeister (22 January 1821, Buchheim (now Bad Lausick) – 13 April 1890 Dresden) was a German physician.
Life
Küchenmeister studied medicine in Leipzig and Prague, and in 1846 he became a general practitioner i ...
in 1855. Fürbringer first described the disease in the lungs in 1876. In 1884, Lichtheim established the development of the disease in rabbits and described two species; '' Mucor corymbifera'' and '' Mucor rhizopodiformis'', later known as ''Lichtheimia'' and ''Rhizopus
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and ...
'', respectively. In 1943, its association with poorly controlled diabetes was reported in three cases with severe sinus, brain and eye involvement.
In 1953, ''Saksenaea vasiformis
''Saksenaea vasiformis'' is an infectious fungus associated with cutaneous or subcutaneous lesions following trauma. It causes opportunistic infections as the entry of the fungus is through open spaces of cutaneous barrier ranging in severity fr ...
'', found to cause several cases, was isolated from Indian forest soil, and in 1979, P. C. Misra examined soil from an Indian mango orchard, from where they isolated ''Apophysomyces'', later found to be a major cause of mucormycosis. Several species of mucorales have since been described. When cases were reported in the United States in the mid-1950s, the author thought it to be a new disease resulting from the use of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s, ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important c ...
and steroids. Until the latter half of the 20th century, the only available treatment was potassium iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are u ...
. In a review of cases involving the lungs diagnosed following flexible bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopy, endoscopic medical procedure, technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, o ...
between 1970 and 2000, survival was found to be better in those who received combined surgery and medical treatment, mostly with amphotericin B.
Naming
Arnold Paltauf coined the term "''Mycosis Mucorina''" in 1885, after describing a case with systemic symptoms involving the sinus, brain and gastrointestinal tract, following which the term "mucormycosis" became popular. "Mucormycosis" is often used interchangeably with "zygomycosis
Zygomycosis is the broadest term to refer to infections caused by ''bread mold fungi'' of the zygomycota phylum. However, because zygomycota has been identified as polyphyletic, and is not included in modern fungal classification systems, the dise ...
", a term made obsolete following changes in classification of the kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
. The former phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature f ...
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living i ...
included Mucorales, Entomophthorales
The Entomophthorales are an order of fungi that were previously classified in the class Zygomycetes. A new subdivision, Entomophthoromycotina, has recently been circumscribed for them.
Most species of the Entomophthorales are pathogens of ins ...
, and others. Mucormycosis describes infections caused by fungi of the order Mucorales. (several authors)
COVID-19–associated mucormycosis
COVID-19 associated mucormycosis cases were reported during first and second(delta) wave, with maximum number of cases in delta wave. There were no cases reported during the Omicron wave. A number of cases of mucormycosis,aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung di ...
, and candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth ...
, linked to immunosuppressive treatment for COVID-19 were reported during the COVID-19 pandemic in India in 2020 and 2021. One review in early 2021 relating to the association of mucormycosis and COVID-19 reported eight cases of mucormycosis; three from the U.S., two from India, and one case each from Brazil, Italy, and the UK. The most common underlying medical condition was diabetes. Most had been in hospital with severe breathing problems due to COVID-19, had recovered, and developed mucormycosis 10–14 days following treatment for COVID-19. Five had abnormal kidney function tests, three involved the sinus, eye and brain, three the lungs, one the gastrointestinal tract, and in one the disease was widespread. In two of the seven deaths, the diagnosis of mucormycosis was made at postmortem. That three had no traditional risk factors led the authors to question the use of steroids and immunosuppressive drugs. Although, there were cases without diabetes or use of immunosuppressive drugs. There were cases reported even in children. In May 2021, the BBC reported increased cases in India. In a review of COVID-19-related eye problems, mucormycosis affecting the eyes was reported to occur up to several weeks following recovery from COVID-19. It was observed that people with COVID-19 were recovering from mucormycosis a bit easily when compared to non-COVID-19 patients. This is because unlike non-COVID-19 patients with severe diabetes, cancer or HIV, the recovery time required for the main cause of immune suppression is temporary.
Other countries affected included Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Russia, Uruguay, Paraguay, Chile, Egypt, Iran, Brazil, Iraq, Mexico, Honduras, Argentina Oman, and Afghanistan. One explanation for why the association has surfaced remarkably in India is high rates of COVID-19 infection and high rates of diabetes. In May 2021, the Indian Council of Medical Research
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research, is one of the oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world.
The ICMR is funded by the Gove ...
issued guidelines for recognising and treating COVID-19–associated mucormycosis. In India, as of 28 June 2021, over 40,845 people have been confirmed to have mucormycosis, and 3,129 have died. From these cases, 85.5% (34,940) had a history of being infected with SARS-CoV-2 and 52.69% (21,523) were on steroids, also 64.11% (26,187) had diabetes.
Society and culture
The disease has been reported in natural disasters and catastrophes; 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami and the 2011 Missouri tornado. The first international congress on mucormycosis was held in Chicago in 2010, set up by the Hank Schueuler 41 & 9 Foundation, which was established in 2008 for the research of children with leukaemia and fungal infections. A cluster of infections occurred in the wake of the 2011 Joplin tornado. By July 19, 2011, a total of 18 suspected cases of mucormycosis of the skin had been identified, of which 13 were confirmed. A confirmed case was defined as 1)necrotizing
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
soft-tissue infection requiring antifungal treatment or surgical debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
in a person injured in the tornado, 2) with illness onset on or after May 22 and 3) positive fungal culture or histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
and genetic sequencing consistent with a mucormycete. No additional cases related to that outbreak were reported after June 17. Ten people required admission to an intensive-care unit, and five died.
In 2014, details of a lethal mucormycosis outbreak that occurred in 2008 emerged after television and newspaper reports responded to an article in a pediatric medical journal. Contaminated hospital linen was found to be spreading the infection. A 2018 study found many freshly laundered hospital linens delivered to U.S. transplant hospitals were contaminated with Mucorales. Another study attributed an outbreak of hospital-acquired mucormycosis to a laundry facility supplying linens contaminated with Mucorales. The outbreak stopped when major changes were made at the laundry facility. The authors raised concerns on the regulation of healthcare linens.
Other animals
Mucormycosis in other animals is similar, in terms of frequency and types, to that in people. Cases have been described in cats, dogs, cows, horses, dolphins, bison, and seals.References
Further reading
*External links
{{Authority control Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions Rare diseases Rare infectious diseases Fungal diseases