|
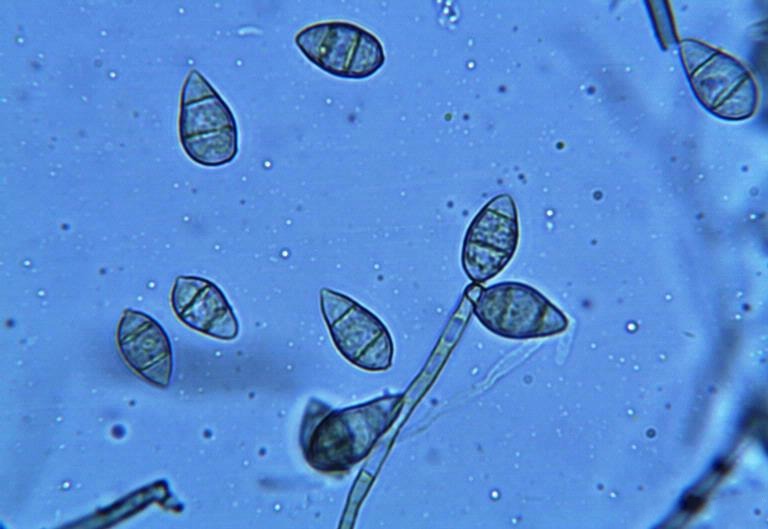
Rhizopus Microsporus
''Rhizopus microsporus '' is a fungal plant pathogen infecting maize, sunflower, and rice. A domesticated variant of this species is used in the preparation of traditional soy fermentation such as tempeh and sufu (see ''Rhizopus oligosporus''). It can also cause a nosocomial infection and necrosis to the infected area, particularly prevalent in pre-term infants. This fungus contains the bacterial endosymbiont '' Burkholderia rhizoxinica'' that produces the antitumor drug rhizoxin. Hosts and symptoms Certain strains of ''Rhizopus microsporus'' use agricultural rice as a host, causing the disease Rice Seedling Blight. This infection is first observed by the fast swelling of seedling roots, but displays no further signs of infection. The main causal agent of Rice Seedling Blight is attributed to the endosymbiotic relationship with ''Burkholderia'' sp. The production of rhizoxin by the bacteria inhibits the ability of rice plant cells to perform mitosis, dramatically weakening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
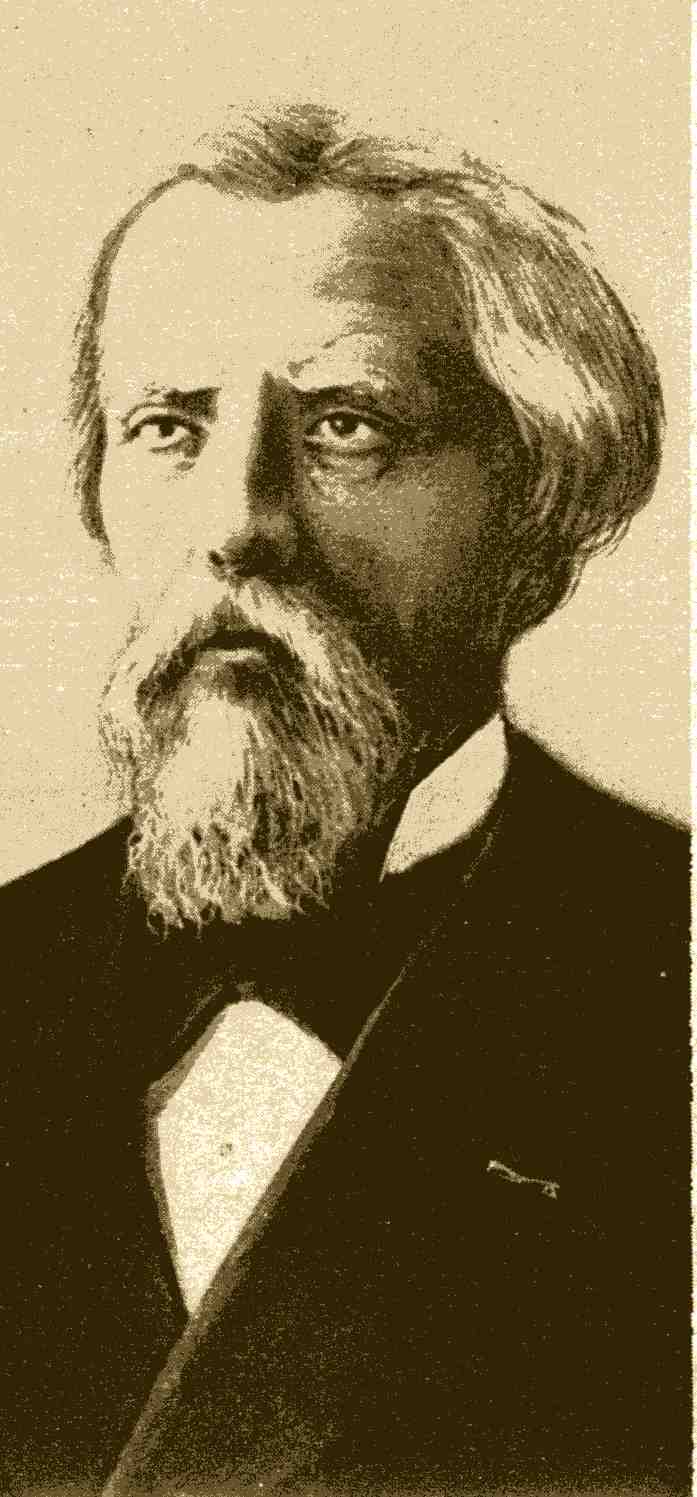
Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem
Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem (; 19 April 1839 – 28 April 1914) was a French botanist born in Baillleul in the département of Nord. He was one of the best known French botanists of the latter nineteenth century. Life Van Tieghem's father was a textile merchant who died of yellow fever in Martinique before he was born, and his mother shortly thereafter. One of five children, he obtained his ''baccalauréat'' in 1856, and continued his studies at the École Normale Supérieure, where after receiving agrégation, he worked in the laboratory of Louis Pasteur (1822–1895). Here he performed research involving the cultivation of mushrooms. He is credited with creation of the eponymous "Van Tieghem cell", a device mounted on a microscope slide that allows for observing the development of a fungus' mycelium. In 1864 he earned his doctorate in physical sciences with a thesis titled ''Recherches sur la fermentation de l'urée et de l'acide hippurique'', and two years later ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1875
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Seedling Blight
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi (Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from ''Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cereal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
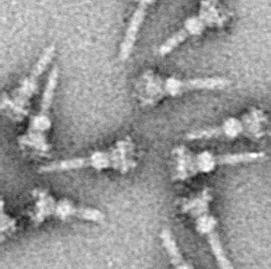
Type Three Secretion System
Type three secretion system (often written Type III secretion system and abbreviated TTSS or T3SS, also called Injectisome) is a protein appendage found in several Gram-negative bacteria. In pathogenic bacteria, the needle-like structure is used as a sensory probe to detect the presence of eukaryotic organisms and secrete proteins that help the bacteria infect them. The secreted effector proteins are secreted directly from the bacterial cell into the eukaryotic (host) cell, where they exert a number of effects that help the pathogen to survive and to escape an immune response. Overview The term Type III secretion system was coined in 1993. This secretion system is distinguished from at least five other secretion systems found in Gram-negative bacteria. Many animal and plant associated bacteria possess similar T3SSs. These T3SSs are similar as a result of divergent evolution and phylogenetic analysis supports a model in which gram-negative bacteria can transfer the T3SS gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygospore
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are formed in zygosporangia after the fusion of specialized budding structures, from mycelia of the same (in homothallic fungi) or different mating types (in heterothallic fungi), and may be chlamydospores. In many eukaryotic algae, including many species of the Chlorophyta, zygospores are formed by the fusion of unicellular gametes of different mating types. A zygospore remains dormant while it waits for environmental cues, such as light, moisture, heat, or chemicals secreted by plants. When the environment is favorable, the zygospore germinates, meiosis occurs, and haploid vegetative cells are released. In fungi, a sporangium is produced at the end of a sporangiophore that sheds spores. A fungus that forms zygospores is called a zygomycete, indicating that the class Class or The Class may refer to: Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. The S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic. Etymology The name ''Zygomycota'' refers to the zygosporangia characteristically formed by the members of this clade, in which resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. ''Zygos'' is Greek for "joining" or "a yoke", referring to the fusion of two hyphal strands which produces these spores, and ''-mycota'' is a suffix referring to a division of fungi. Spores The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia
''Burkholderia'' is a genus of Pseudomonadota whose pathogenic members include the ''Burkholderia cepacia'' complex, which attacks humans and ''Burkholderia mallei'', responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; ''Burkholderia pseudomallei'', causative agent of melioidosis; and '' Burkholderia cepacia'', an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). ''Burkholderia'' species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized ''Burkholderia cepacia'' from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. The ''Burkholderia'' (previously part of ''Pseudomonas'') genus name refers to a group of virtually ubiquitous Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that are motile by means of single or multiple polar flagella, with the exception of ''Burkholderia mallei'', which is nonmotile. Members belonging to the genus do not produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycelium
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrate (biology), substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a Monokaryon, monokaryotic mycelium, which cannot reproduce sexually; when two compatible monokaryotic mycelia join and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form sporocarp (fungi), fruiting bodies such as mushrooms. A mycelium may be minute, forming a colony that is too small to see, or may grow to span thousands of acres as in ''Armillaria''. Through the mycelium, a fungus absorbs nutrients from its environment. It does this in a two-stage process. First, the hyphae secrete enzymes onto or into the food source, which break down biopolymers, biological polymers into smaller units such as monomers. These monomers are then absorbed into the mycelium by facilitated diffusion and active transport. Mycelia are v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |