Molecular Modelling Software on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

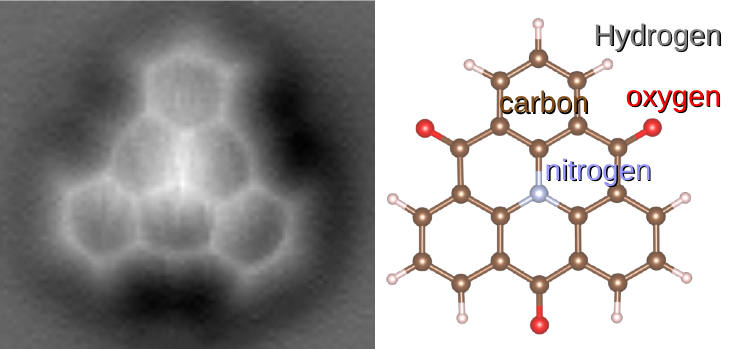 A molecule is a group of two or more
A molecule is a group of two or more
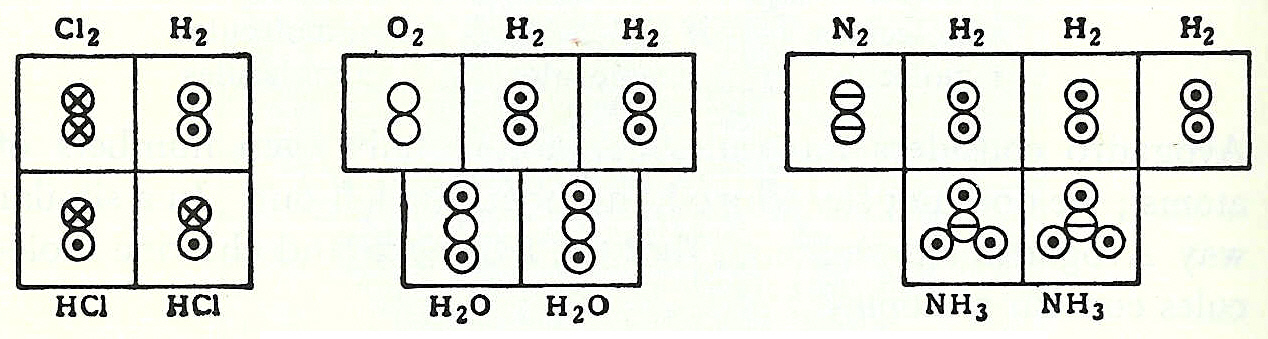 In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named
In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named 
 A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed ''shared pairs'' or ''bonding pairs'', and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed ''covalent bonding''.
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed ''shared pairs'' or ''bonding pairs'', and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed ''covalent bonding''.
 Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in
 For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such
For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such
 Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different
Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different
 Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (
Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (
Molecule of the MonthSchool of Chemistry, University of Bristol
{{Authority control Molecular physics, Molecules, Chemistry Matter

 A molecule is a group of two or more
A molecule is a group of two or more atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...
s; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
, organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, and biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special c ...
s.
A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
composed of more than one element, e.g. water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
(two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some cases, oganesson (Og) ...
are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
s or ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic ...
s, are typically not considered single molecules.
Concepts similar to molecules have been discussed since ancient times, but modern investigation into the nature of molecules and their bonds began in the 17th century. Refined over time by scientists such as Robert Boyle, Amedeo Avogadro, Jean Perrin, and Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling ( ; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist and peace activist. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 gre ...
, the study of molecules is today known as molecular physics or molecular chemistry.
Etymology
According toMerriam-Webster
Merriam-Webster, Incorporated is an list of companies of the United States by state, American company that publishes reference work, reference books and is mostly known for Webster's Dictionary, its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary pub ...
and the Online Etymology Dictionary
Etymonline, or ''Online Etymology Dictionary'', sometimes abbreviated as OED (not to be confused with the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', which the site often cites), is a free online dictionary that describes the etymology, origins of English la ...
, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
" moles" or small unit of mass. The word is derived from French ' (1678), from Neo-Latin
Neo-LatinSidwell, Keith ''Classical Latin-Medieval Latin-Neo Latin'' in ; others, throughout. (also known as New Latin and Modern Latin) is the style of written Latin used in original literary, scholarly, and scientific works, first in Italy d ...
', diminutive of Latin ' "mass, barrier". The word, which until the late 18th century was used only in Latin form, became popular after being used in works of philosophy by Descartes.
History
The definition of the molecule has evolved as knowledge of the structure of molecules has increased. Earlier definitions were less precise, defining molecules as the smallest particles of purechemical substance
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be com ...
s that still retain their composition and chemical properties. This definition often breaks down since many substances in ordinary experience, such as rocks, salts, and metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s, are composed of large crystalline networks of chemically bonded atoms or ions, but are not made of discrete molecules.
The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific and Greek philosophers such as Leucippus
Leucippus (; , ''Leúkippos''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He is traditionally credited as the founder of atomism, which he developed with his student Democritus. Leucippus divided the world into two entities: atoms, indivisible ...
and Democritus
Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an ...
who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles
Empedocles (; ; , 444–443 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is known best for originating the Cosmogony, cosmogonic theory of the four cla ...
imagined fundamental elements (fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion re ...
(), earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
(), air
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
(), and water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
()) and "forces" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact.
A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe.
In a more concrete manner, however, the concept of aggregates or units of bonded atoms, i.e. "molecules", traces its origins to Robert Boyle's 1661 hypothesis, in his famous treatise '' The Sceptical Chymist'', that matter is composed of ''clusters of particles'' and that chemical change results from the rearrangement of the clusters. Boyle argued that matter's basic elements consisted of various sorts and sizes of particles, called "corpuscles", which were capable of arranging themselves into groups. In 1789, William Higgins published views on what he called combinations of "ultimate" particles, which foreshadowed the concept of valency bonds. If, for example, according to Higgins, the force between the ultimate particle of oxygen and the ultimate particle of nitrogen were 6, then the strength of the force would be divided accordingly, and similarly for the other combinations of ultimate particles.
Amedeo Avogadro created the word "molecule". His 1811 paper "Essay on Determining the Relative Masses of the Elementary Molecules of Bodies", he essentially states, i.e. according to Partington
Partington is a town and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester, England. It is sited south-west of Manchester city centre. Within the boundaries of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Ches ...
's ''A Short History of Chemistry'', that:In coordination with these concepts, in 1833 the French chemist Marc Antoine Auguste Gaudin presented a clear account of Avogadro's hypothesis, regarding atomic weights, by making use of "volume diagrams", which clearly show both semi-correct molecular geometries, such as a linear water molecule, and correct molecular formulas, such as H2O:
 In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named
In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling ( ; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist and peace activist. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 gre ...
was learning the Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method, which was the mainstream description of bonds between atoms at the time. Pauling, however, was not satisfied with this method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method. In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating the Avogadro constant
The Avogadro constant, commonly denoted or , is an SI defining constant with an exact value of when expressed in reciprocal moles.
It defines the ratio of the number of constituent particles to the amount of substance in a sample, where th ...
using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas). The traditional mathematical formulation of Brownian motion is that of the Wiener process, which is often called Brownian motion, even in mathematical ...
, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London and Walter Heitler applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship
Guggenheim Fellowships are Grant (money), grants that have been awarded annually since by the John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation, endowed by the late Simon Guggenheim, Simon and Olga Hirsh Guggenheim. These awards are bestowed upon indiv ...
.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" in which he used quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:
Molecular science
The science of molecules is called ''molecular chemistry'' or '' molecular physics'', depending on whether the focus is on chemistry or physics. Molecular chemistry deals with the laws governing the interaction between molecules that results in the formation and breakage of chemical bonds, while molecular physics deals with the laws governing their structure and properties. In practice, however, this distinction is vague. In molecular sciences, a molecule consists of a stable system (bound state
A bound state is a composite of two or more fundamental building blocks, such as particles, atoms, or bodies, that behaves as a single object and in which energy is required to split them.
In quantum physics, a bound state is a quantum state of a ...
) composed of two or more atoms. Polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special c ...
s may sometimes be usefully thought of as electrically charged molecules. The term ''unstable molecule'' is used for very reactive species, i.e., short-lived assemblies ( resonances) of electrons and nuclei, such as radicals, molecular ions, Rydberg molecules, transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked w ...
s, van der Waals complexes, or systems of colliding atoms as in Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einste ...
.
Prevalence
Molecules as components of matter are common. They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. Most organic substances are molecules. The substances of life are molecules, e.g. proteins, the amino acids of which they are composed, the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. The nutrient minerals are generally ionic compounds, thus they are not molecules, e.g. iron sulfate. However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth are made partly or completely of crystals or ionic compounds, which are not made of molecules. These include all of the minerals that make up the substance of the Earth, sand, clay, pebbles, rocks, boulders, bedrock, the molten interior, and the core of the Earth. All of these contain many chemical bonds, but are ''not'' made of identifiable molecules. No typical molecule can be defined for salts nor for covalent crystals, although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a plane, e.g.graphene
Graphene () is a carbon allotrope consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, honeycomb planar nanostructure. The name "graphene" is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, indicating ...
; or three-dimensionally e.g. diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
. The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most metals which are condensed phases with metallic bonding. Thus solid metals are not made of molecules. In glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
es, which are solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds with no presence of any definable molecule, nor any of the regularity of repeating unit-cellular-structure that characterizes salts, covalent crystals, and metals.
Bonding
Molecules are generally held together by covalent bonding. Several non-metallic elements exist only as molecules in the environment either in compounds or as homonuclear molecules, not as free atoms: for example, hydrogen. While some people say a metallic crystal can be considered a single giant molecule held together bymetallic bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be desc ...
, others point out that metals behave very differently than molecules.
Covalent
Ionic
 Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrica ...
s. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s (termed cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s). This transfer of electrons is termed ''electrovalence'' in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4+ or SO42−. At normal temperatures and pressures, ionic bonding mostly creates solids (or occasionally liquids) without separate identifiable molecules, but the vaporization/sublimation of such materials does produce separate molecules where electrons are still transferred fully enough for the bonds to be considered ionic rather than covalent.
Molecular size
Most molecules are far too small to be seen with the naked eye, although molecules of manypolymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s can reach macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenome ...
sizes, including biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
s such as DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. Molecules commonly used as building blocks for organic synthesis have a dimension of a few angstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–18 ...
s (Å) to several dozen Å, or around one billionth of a meter. Single molecules cannot usually be observed by light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
(as noted above), but small molecules and even the outlines of individual atoms may be traced in some circumstances by use of an atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the diffr ...
. Some of the largest molecules are macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
s or supermolecules.
The smallest molecule is the diatomic
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear mol ...
hydrogen (H2), with a bond length of 0.74 Å.
Effective molecular radius is the size a molecule displays in solution.
The table of permselectivity for different substances contains examples.
Molecular formulas
Chemical formula types
Thechemical formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as pare ...
for a molecule uses one line of chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to one typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts.
A compound's empirical formula is a very simple type of chemical formula. It is the simplest integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of the chemical elements that constitute it. For example, water is always composed of a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, and ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
(ethyl alcohol) is always composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 2:6:1 ratio. However, this does not determine the kind of molecule uniquely – dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
has the same ratios as ethanol, for instance. Molecules with the same atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s in different arrangements are called isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s. Also carbohydrates, for example, have the same ratio (carbon:hydrogen:oxygen= 1:2:1) (and thus the same empirical formula) but different total numbers of atoms in the molecule.
The molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. However different isomers can have the same atomic composition while being different molecules.
The empirical formula is often the same as the molecular formula but not always. For example, the molecule acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is u ...
has molecular formula C2H2, but the simplest integer ratio of elements is CH.
The molecular mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quan ...
can be calculated from the chemical formula and is typically expressed in daltons, which are equal to 1/12 of the mass of a neutral carbon-12 (12 C isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
) atom. For network solids, the term formula unit
In chemistry, a formula unit is the smallest unit of a non-molecular substance, such as an ionic compound, covalent network solid, or metal. It can also refer to the chemical formula for that unit. Those structures do not consist of discrete mol ...
is used in stoichiometric calculations.
Structural formula
 For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such
For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic name#In chemistry, systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Appli ...
requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
Molecular geometry
 Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different
Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, ...
activities.
Molecular spectroscopy
 Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (
Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
(or frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
, according to the Planck relation
The Planck relationFrench & Taylor (1978), pp. 24, 55.Cohen-Tannoudji, Diu & Laloë (1973/1977), pp. 10–11. (referred to as Planck's energy–frequency relation,Schwinger (2001), p. 203. the Planck–Einstein relation, Planck equation, and Plan ...
). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
studies where particles such as neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Theoretical aspects
The study of molecules by molecular physics and theoretical chemistry is largely based on quantum mechanics and is essential for the understanding of the chemical bond. The simplest of molecules is the hydrogen molecule-ion, H2+, and the simplest of all the chemical bonds is the one-electron bond. H2+ is composed of two positively charged protons and one negatively chargedelectron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
, which means that the Schrödinger equation for the system can be solved more easily due to the lack of electron–electron repulsion. With the development of fast digital computers, approximate solutions for more complicated molecules became possible and are one of the main aspects of computational chemistry.
When trying to define rigorously whether an arrangement of atoms is ''sufficiently stable'' to be considered a molecule, IUPAC suggests that it "must correspond to a depression on the potential energy surface that is deep enough to confine at least one vibrational state". This definition does not depend on the nature of the interaction between the atoms, but only on the strength of the interaction. In fact, it includes weakly bound species that would not traditionally be considered molecules, such as the helium Dimer (chemistry), dimer, helium dimer, He2, which has one vibrational bound state and is so loosely bound that it is only likely to be observed at very low temperatures.
Whether or not an arrangement of atoms is ''sufficiently stable'' to be considered a molecule is inherently an operational definition. Philosophically, therefore, a molecule is not a fundamental entity (in contrast, for instance, to an elementary particle); rather, the concept of a molecule is the chemist's way of making a useful statement about the strengths of atomic-scale interactions in the world that we observe.
See also
* Atom * Chemical polarity * Chemical structure * Covalent bond * Diatomic molecule * List of compounds * List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules * Molecular biology * Molecular design software * Molecular engineering * Molecular geometry * Molecular Hamiltonian * Molecular ion * Molecular modelling * Molecular promiscuity * Molecular orbital * Non-covalent bonding * Periodic systems of small molecules * Small molecule * Comparison of software for molecular mechanics modeling * Van der Waals molecule * World Wide Molecular MatrixReferences
External links
Molecule of the MonthSchool of Chemistry, University of Bristol
{{Authority control Molecular physics, Molecules, Chemistry Matter