|
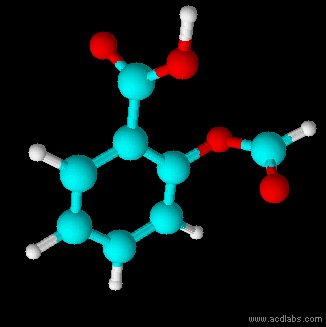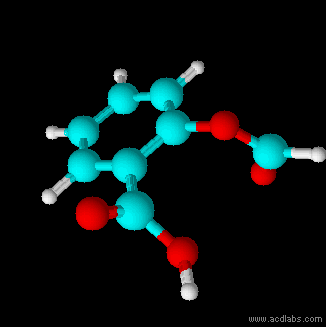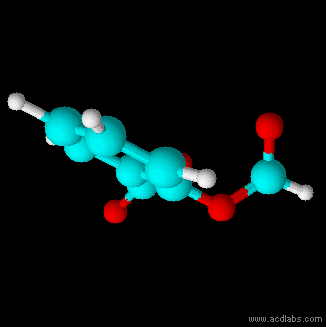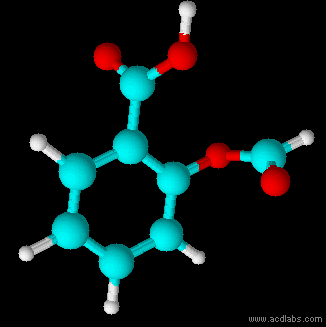
Structural Formula
The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure (determined by structural chemistry methods), showing how the atoms are connected to one another. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. Unlike other chemical formula types, which have a limited number of symbols and are capable of only limited descriptive power, structural formulas provide a more complete geometric representation of the molecular structure. For example, many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different enantiomeric structures but the same molecular formula. There are multiple types of ways to draw these structural formulas such as: Lewis structures, condensed formulas, skeletal formulas, Newman projections, Cyclohexane conformations, Haworth projections, and Fischer projections. Several systematic chemical naming formats, as in chemical databases, are used that are equivalent to, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalamin Skeletal
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Chemical Identifier
The International Chemical Identifier (InChI, pronounced ) is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary. Since May 2009, it has been developed by the InChI Trust, a nonprofit charity from the United Kingdom which works to implement and promote the use of InChI. The identifiers describe chemical substances in terms of ''layers'' of information — the atoms and their bond connectivity, tautomeric information, isotope information, stereochemistry, and electronic charge information. Not all layers have to be provided; for instance, the tautomer layer can be omitted if that type of information is not relevant to the particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ (potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− (chloride ion) and OH− (hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connection Of Bonds
Connection may refer to: Mathematics *Connection (algebraic framework) *Connection (mathematics), a way of specifying a derivative of a geometrical object along a vector field on a manifold * Connection (affine bundle) *Connection (composite bundle) *Connection (fibred manifold) *Connection (principal bundle), gives the derivative of a section of a principal bundle *Connection (vector bundle), differentiates a section of a vector bundle along a vector field *Cartan connection, achieved by identifying tangent spaces with the tangent space of a certain model Klein geometry *Ehresmann connection, gives a manner for differentiating sections of a general fibre bundle *Electrical connection, allows the flow of electrons *Galois connection, a type of correspondence between two partially ordered sets *Affine connection, a geometric object on a smooth manifold which connects nearby tangent spaces *Levi-Civita connection, used in differential geometry and general relativity; differentiates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonds And Electron Sharing
Bond or bonds may refer to: Common meanings * Bond (finance), a type of debt security * Bail bond, a commercial third-party guarantor of surety bonds in the United States * Fidelity bond, a type of insurance policy for employers * Chemical bond, the attraction of atoms, ions or molecules to form chemical compounds * Emotional bond, an emotional attachment between one or more individuals. People * Bond (surname) * Bonds (surname) * Mr. Bond (musician), Austrian rapper Arts and entertainment * James Bond, a series of works about the eponymous fictional character * James Bond (literary character), a British secret agent in a series of novels and films * Bond (string quartet), an Australian/British string quartet ** ''Bond: Video Clip Collection'', a video collection from the band * Bond (Canadian band), a Canadian rock band in the 1970s * The Bond (2007 book), ''The Bond'' (2007 book), an American autobiography written by The Three Doctors * ''The Bond'', a 1918 film by Charlie Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six Electron pair bond, bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent bond, covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent covalent bond, single bonds or double bond, double bonds, with a bond order of three. The most common triple bond is in a nitrogen N2 molecule; the second most common is that between two carbon atoms, which can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as diphosphorus and carbon monoxide, are also triple bonded. In skeletal formula, skeletal formulae the triple bond is drawn as three parallel lines (≡) between the two connected atoms. Bonding Triple bonding can be explained in terms of orbital hybridization. In the case of acetylene, each carbon atom has two sp orbital, sp-orbitals and two p-orbitals. The two sp-orbitals are linear, with 180° bond angles, and occupy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist between two different elements: for example, in a carbonyl group between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom. Other common double bonds are found in azo compounds (N=N), imines (C=N), and sulfoxides (S=O). In a skeletal formula, a double bond is drawn as two parallel lines (=) between the two connected atoms; typographically, the equals sign is used for this. Double bonds were introduced in chemical notation by Russian chemist Alexander Butlerov. Double bonds involving carbon are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The bond order is two. Double bonds are also electron-rich, which makes them potentially more reactive in the presence of a strong electron acceptor (as in addition reactions of the halogens). File:Ethene structural.svg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Bond
In chemistry, a single bond is a chemical bond between two atoms involving two valence electrons. That is, the atoms share one pair of electrons where the bond forms. Therefore, a single bond is a type of covalent bond. When shared, each of the two electrons involved is no longer in the sole possession of the Atomic orbital, orbital in which it originated. Rather, both of the two electrons spend time in either of the orbitals which overlap in the bonding process. As a Lewis structure, a single bond is denoted as AːA or A-A, for which A represents an element. In the first rendition, each dot represents a shared electron, and in the second rendition, the bar represents both of the electrons shared in the single bond. A covalent bond can also be a double bond or a triple bond. A single bond is weaker than either a double bond or a triple bond. This difference in strength can be explained by examining the component bonds of which each of these types of covalent bonds consists (Moo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds, or some combination of these effects. Chemical bonds are described as having different strengths: there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. Electrons shared between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them. "Constructive quantum mechanical wavefunction interference" stabilizes the paired nuclei (see Theories of chemical bonding). Bonded nuclei maintain an optima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChemDraw
ChemDraw™ is a molecule editor and communication suite, for the management, reporting, and presentation of chemistry research and discoveries. ChemDraw was originally conceived in 1985 by Selena "Sally" Evans, her husband David A. Evans, and Stewart Rubenstein. In July 1985, ChemDraw was demonstrated at the Gordon Research Conference on Reactions & Processes in New Hampshire, USA, an event remembered by many chemists, such was the breakthrough provided by the software. Later that same year, Stewart’s younger brother, Michael, began developing Chem3D, a companion program to ChemDraw that allows users to draw three-dimensional chemical structures. ChemDraw’s popularity led to the launch of cheminformatics company Cambridge Scientific Computing, later renamed CambridgeSoft, to further develop the program. CambridgeSoft was sold to PerkinElmer in 2011. In 2022, PerkinElmer split their businesses, and the Life Science and Diagnostics divisions became Revvity, Inc. Today, ChemD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemsketch
ACD/ChemSketch is a molecular modeling program used to create and modify images of chemical structures. The software allows for the importation and display of molecules and molecular models displayed in two and three dimensions. Features ACD/ChemSketch allows for both basic structure drawing and importation of 3D and 2D .MDL files from other molecular modelling programs. ChemSketch has been favorably compared to other molecular modelling software, especially ChemDraw, based on its ability to display a wide range of structural components and the ease of creating complex structures quickly. The program offers some advanced features that allows the molecules rotate and apply color to improve visualization. It has several templates with ions and functional groups with the possibility to add text and use other tools to optimize productions created by the software. Applications Using ACD/ChemSketch is primarily for educational use. With this program it is possible to write and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |