Miosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
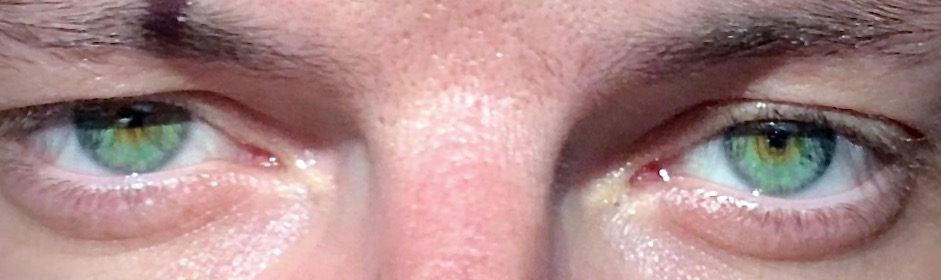
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil.Farlex medical dictionary
citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, mydriasis, is the dilation of the pupil. Anisocoria is the condition of one pupil being more dilated than the other.
FP Notebook
{{Eye pathology Medical signs Ophthalmology
citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, mydriasis, is the dilation of the pupil. Anisocoria is the condition of one pupil being more dilated than the other.
Causes
Age
* Senile miosis (a reduction in the size of a person's pupil in old age)Diseases
* Ehlers Danlos Syndrome * Horner's syndrome *Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
into pons (intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) refers to any form of Hemorrhage, bleeding Internal bleeding, within the Human skull, skull. It can result from trauma, vascular abnormalities, hypertension, or other medical conditions. ICH is broadly categorized ...
)
* Hereditary disorders
* Cluster headaches with ptosis
* Iridocyclitis
* Fatal familial insomnia
* Aphakia
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of ability to maintain focus ( accommodation), high degree of farsightedn ...

Drugs
* Opioids such asfentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
, morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
, heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
and methadone (the notable exception being pethidine)
* Products containing nicotine such as cigarettes, chewing tobacco or gum
* Imidazolines such as clonidine, naphazoline, oxymetazoline and tetrahydrozoline
* Antipsychotics, including risperidone
Risperidone, sold under the brand name Risperdal among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, as well as aggressive and self-injurious behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorder. It is t ...
, haloperidol, chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine (CPZ), marketed under the brand names Thorazine and Largactil among others, is an antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Other uses include the treatment of bipolar d ...
, olanzapine, quetiapine
* Cholinergic agents such as acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
* Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from Hydrolysis, breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both th ...
* Serotonin antagonists, such as ondansetron (an anti-emetic) known by its brand name Zofran/ Emiston in BD
* Some cancer chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
drugs, including camptothecin derivatives
* Mirtazapine
Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical antidepressant, atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat Depression (mood), depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but ca ...
, a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant ( NaSSA)
* Some MAO inhibitors
* Pilocarpine eye drops and all other parasympathomimetics
* In some rare cases, when exposed to mustard gas
* Organophosphates
Physiology of the photomotor reflex
Light entering the eye strikes three different photoreceptors in theretina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
: the familiar rods and cones used in image forming and the more newly discovered photosensitive ganglion cells. The ganglion cells give information about ambient light levels, and react sluggishly compared to the rods and cones. Signals from photosensitive ganglion cells have multiple functions including acute suppression of the hormone melatonin, entrainment of the body's circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
s and regulation of the size of the pupil.
The retinal photoceptors convert light stimuli into electric impulses. Nerves involved in the resizing of the pupil connect to the pretectal nucleus of the high midbrain, bypassing the lateral geniculate nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, Anatomical ter ...
and the primary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
. From the pretectal nucleus neurons send axons to neurons of the Edinger-Westphal nucleus whose visceromotor axons run along both the left and right oculomotor nerves. Visceromotor nerve axons (which constitute a portion of cranial nerve III, along with the somatomotor portion derived from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus) synapse on ciliary ganglion neurons, whose parasympathetic axons innervate the iris sphincter muscle, producing miosis.
See also
* Adie syndrome * Argyll Robertson pupil * Cycloplegia * Glaucoma * Marcus Gunn pupil * Parinaud's syndrome * Pupillary light reflex *Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
References
External links
FP Notebook
{{Eye pathology Medical signs Ophthalmology