|
Cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. Choline also prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into cells. The parasympathetic nervous system, which uses acetylcholine almost exclusively to send its messages, is said to be almost entirely cholinergic. Neuromuscular junctions, preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, the basal forebrain, and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic, as are the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands. In neuroscience and related fields, the term cholinergic is used in these related contexts: * A substance (or ligand) is cholinergic if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system. These agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system by selectively blocking the binding of ACh to its receptor in nerve cells. The nerve fibers of the parasympathetic system are responsible for the involuntary movement of Smooth muscle tissue, smooth muscles present in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, lungs, sweat glands, and many other parts of the body. In broad terms, anticholinergics are divided into two categories in accordance with their specific targets in the central and peripheral nervous system and at the neuromuscular junction: antimuscarinic agents and antinicotinic agents (ganglionic blockers, neuromuscular blockers). The term "anticholinergic" is typically used to refer to antimuscarinics that competitively inhibit the binding of ACh to muscarinic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
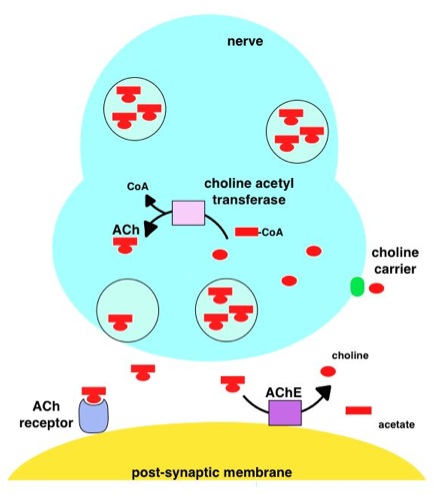
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction. In other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for both the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system, and as the final product released by the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. Some neurotransmitters are also stored in large dense core vesicles. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds to. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include Glutamate (neurotransmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate cholinergic neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 5,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoscine Hydrobromide
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin after about 20 minutes and last for up to 8 hours. It may also be used orally and as a transdermal patch since it has been long known to have transdermal bioavailability. Scopolamine is in the antimuscarinic family of drugs and works by blocking some of the effects of acetylcholine within the nervous system. Scopolamine was first written about in 1881 and started to be used for anesthesia around 1900. Scopolamine is also the main active component produced by certain plants of the nightshade family, which historically have been used as psychoactive drugs, known as '' deliriants'', due to their antimuscarinic-induced hallucinogenic effects in higher doses. In these contexts, its mind-altering effects have been utilized for re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathomimetic Drug
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors (thus mimicking acetylcholine), or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, Sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder. Some chemical weapons such as sarin or VX, non-lethal riot control agents such as tear gas, and insecticides such as diazinon fall into this category. Structure activity relationships for parasympathomimetic drugs For a cholinergic agent, the following criteria describe the structure activity relationship: # Ing's Rule of 5: there should be no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Forebrain
Part of the human brain, the basal forebrain structures are located in the forebrain to the front of and below the striatum. They include the ventral basal ganglia (including nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum), nucleus basalis, diagonal band of Broca, substantia innominata, and the medial septal nucleus. These structures are important in the production of acetylcholine, which is then distributed widely throughout the brain. The basal forebrain is considered to be the major cholinergic output of the central nervous system (CNS) centred on the output of the nucleus basalis. The presence of non-cholinergic neurons projecting to the cortex have been found to act with the cholinergic neurons to dynamically modulate activity in the cortex. Function Acetylcholine is known to promote wakefulness in the basal forebrain. Stimulating the basal forebrain gives rise to acetylcholine release, which induces wakefulness and REM sleep, whereas inhibition of acetylcholine release in the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physostigmine
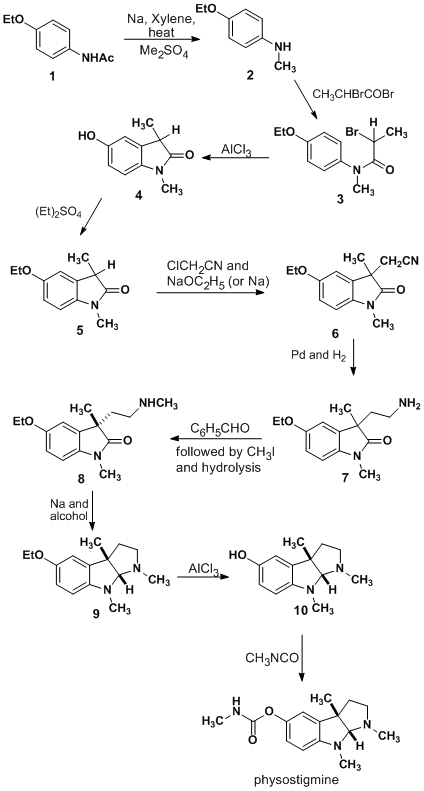
Physostigmine (also known as eserine from ''éséré'', the West African name for the Calabar bean) is a highly toxic parasympathomimetic alkaloid, specifically, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. It occurs naturally in the Calabar bean and the fruit of the Manchineel tree. The chemical was synthesized for the first time in 1935 by Percy Lavon Julian and Josef Pikl. It is available in the U.S. under the trade names Antilirium and Isopto Eserine, and as eserine salicylate and eserine sulfate. Today, physostigmine is most commonly used for its medicinal value. However, before its discovery by Robert Christison, Sir Robert Christison in 1846, it was much more prevalent as an ordeal poison. The positive medical applications of the drug were first suggested in the gold medal-winning final thesis of Thomas Richard Fraser at the University of Edinburgh in 1862. Medical uses Physostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, can be used to treat glaucoma and delayed gastric emptyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine Receptor
An acetylcholine receptor (abbreviated AChR) or a cholinergic receptor is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Classification Like other transmembrane receptors, acetylcholine receptors are classified according to their "pharmacology," or according to their relative affinities and sensitivities to different molecules. Although all acetylcholine receptors, by definition, respond to acetylcholine, they respond to other molecules as well. * Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (''nAChR'', also known as " ionotropic" acetylcholine receptors) are particularly responsive to nicotine. The nicotine ACh receptor is also a Na+, K+ and Ca2+ ion channel. * Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (''mAChR'', also known as " metabotropic" acetylcholine receptors) are particularly responsive to muscarine. Nicotinic and muscarinic are two main kinds of "cholinergic" receptors. Receptor types Molecular biology has shown that the nicotinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from Hydrolysis, breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, Autonomic ganglion, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being Butyrylcholinesterase#Inhibitors, butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase, cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP, tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |