Meyer locomotive on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Meyer
A Meyer
 The Meyer was in fact invented by Austrian engineer Wenzel Günther of the
The Meyer was in fact invented by Austrian engineer Wenzel Günther of the  The
The
 The Kitson Meyer is most closely associated with Kitson & Co. of
The Kitson Meyer is most closely associated with Kitson & Co. of  One Kitson-Meyer
One Kitson-Meyer 
 A Meyer
A Meyer locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
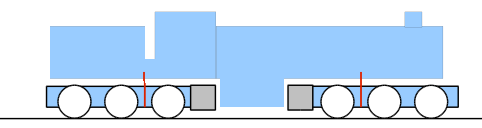
is a type of articulated locomotive
An articulated locomotive is a steam locomotive (rarely, an electric locomotive) with one or more engine units that can move independent of the main frame. Articulation allows the operation of locomotives that would otherwise be too large to neg ...
. The design was never as popular as the Garratt
A Garratt (often referred to as a Beyer Garratt) is a type of steam locomotive invented by British engineer Herbert William Garratt that is articulated into three parts. Its boiler, firebox, and cab are mounted on a centre frame or "bridge ...
or Mallet
A mallet is a tool used for imparting force on another object, often made of rubber or sometimes wood, that is smaller than a maul or beetle, and usually has a relatively large head. The term is descriptive of the overall size and proport ...
locomotives. It can be best regarded as 19th Century competition for the early compound Mallet and also the Fairlie articulated designs. Most single cab modern trains are of a similar design such as power cars, freight diesel locomotives, and some passenger locomotives.
Development and design
 The Meyer was in fact invented by Austrian engineer Wenzel Günther of the
The Meyer was in fact invented by Austrian engineer Wenzel Günther of the Wiener Neustädter Lokomotivfabrik
The ''Wiener Neustädter Lokomotivfabrik'' (Wiener Neustadt locomotive factory) was the largest locomotive and engineering factory in the Austro-Hungarian Empire. During World War II the company produced armaments as part of Rax-Werk Ges.m ...
for the Semmering Trials of 1851. However, the technology wasn't yet developed for the steam to be reliably transported to the bogies with reasonable amount of leaks, and despite generally good performance of the design on the trials the company abandoned the idea.
It was reinvigorated by Frenchman Jean-Jacques Meyer
Jean-Jacques Meyer (1805–1877) was a French engineer, noted for his work with steam engines and steam locomotives.
Innovations
Background
He was trained at the engineering school Arts et Métiers ParisTech.
Expansion valve
His first major inv ...
(1804-1877), who took out a patent on the design in 1861. The first locomotive, an named ''L'Avenir'' (Future), was built by in 1868 with the support of a state subsidy.
No wheels are rigidly affixed to the boiler; all are mounted on bogies placed directly under the boiler/cab unit (comparable with a modern diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
or electric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas ...
). This compares with a Mallet, where the rear set of wheels are attached to the frame, and only the front set swivels as a bogie. Therefore, boiler overhang is less than that of the Mallet locomotive on a curve of the same radius. Meyers are usually set up as a tank engine
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locomo ...
, with the boiler/cab unit carrying the water and fuel supplies.
A disadvantage of the design is that the firebox is directly above the rear power unit, which limits its size. With two power bogies, flexible steam pipes must be provided to all cylinders. This was difficult to achieve with 19th Century technology. Early Mallet locomotives had compound cylinders, so high pressure steam was provided to the rigid power unit, while the front cylinders (requiring flexible steam pipes) received low pressure steam.
Meyer locomotives were most common in continental Europe, particularly Germany. A number of Meyer locos can still be found on the narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
railways in Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
. The most common locomotive is the Saxon IV K
The Saxon IV K were narrow gauge, Günther-Meyer type steam engines built for the Royal Saxon State Railways with a track gauge of . A total of 96 were built between 1892 and 1921, making the Saxon IV K the most numerous narrow gauge locomotive ...
.
 The
The Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
Bernina Railway
The Bernina Railway (german: Berninalinie; it, Linea del Bernina; rm, Lingia dal Bernina) is a single-track railway line forming part of the Rhaetian Railway (RhB). It links the spa resort of St. Moritz, in the canton of Graubünden, Switze ...
had two rotary snowplow
A rotary snowplow (American English) or rotary snowplough is a piece of railroad snow removal equipment with a large circular set of blades on its front end that rotate to cut through the snow on the track ahead of it. The precursor to the rotary ...
s built by Schweizerische Lokomotiv- und Maschinenfabrik in 1910 and 1912. To work on the tight curves of the meter gauge
Metre-gauge railways are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
The metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires. In Europe, la ...
mountain railway they had to be selfpropelled, the two snow blower
A snow blower or snow thrower is a machine for removing snow from an area where it is problematic, such as a driveway, sidewalk, roadway, railroad track, ice rink, or runway. The commonly used term "snow blower" is a misnomer, as the snow is ...
s were thus built with a Meyer drive system.Alfred Leuenberger: ''Rauch, Dampf und Pulverschnee. Die Dampfschneeschleudern der Schweizer Bahnen'' (Swiss Steam Snowploughs). Orell Füssli Verlag, Zürich 1967, no ISBN Both have been preserved, Xrot d 9213 is still in working condition on the Rhaetian Railway
The Rhaetian Railway (german: Rhätische Bahn; it, Ferrovia retica; rm, Viafier retica), abbreviated RhB, is a Swiss transport company that owns the largest network of all private railway operators in Switzerland. Headquartered in Chur, the RhB ...
, based in Pontresina
Pontresina ( rm, Puntraschigna) is a municipality in the Maloja Region in the canton of Graubünden in Switzerland.
History and name
Pontresina was first mentioned in medieval Latin documents as ''ad Pontem Sarisinam'' in 1137 and ''de Ponte Sa ...
, as of 2010.
Kitson Meyer

 The Kitson Meyer is most closely associated with Kitson & Co. of
The Kitson Meyer is most closely associated with Kitson & Co. of Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
, but was also built by other locomotive builders. The design originated from an idea by Robert Stirling, Locomotive Superintendent of the Anglo-Chilian Nitrate & Railway Company. After placing an order with Kitsons for some conventional locos, he approached them with his ideas for an articulated loco. Kitsons further developed the idea, the first loco being constructed in 1894.
The Meyer design was modified by moving the rear power unit further back and allowed the firebox to be between the two power units (as in a Garratt
A Garratt (often referred to as a Beyer Garratt) is a type of steam locomotive invented by British engineer Herbert William Garratt that is articulated into three parts. Its boiler, firebox, and cab are mounted on a centre frame or "bridge ...
), thus allowing a larger firebox. The length of engine was increased, with the extra length behind the cab being used for additional water tanks. Some designs had an auxiliary chimney at the rear to avoid the need for an exhaust steam pipe running the length of the engine.
Kitson Meyers were widely used in South America, particularly on the Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
n and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
an railways. It was regarded as the best performing of all articulated designs for railway lines that constantly curved. Four 2-6-0+0-6-2 tank locomotives also had a brief service in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, serving the Manila Railway and the Manila Railroad Companies between 1914 and 1925. However, fewer than 100 Kitson Meyers were ever built and it was generally thought that the design suffered from competition with the Garratt
A Garratt (often referred to as a Beyer Garratt) is a type of steam locomotive invented by British engineer Herbert William Garratt that is articulated into three parts. Its boiler, firebox, and cab are mounted on a centre frame or "bridge ...
.
 One Kitson-Meyer
One Kitson-Meyer locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
known to survive sits in a rather poor state of preservation in Taltal
Taltal is a Chilean commune and city in Antofagasta Province, Antofagasta Region. According to the 2012 census, the commune has a population of 11,132 and has an area of .
The commune is home to Paranal Observatory and includes the northern por ...
, an old nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
port town in the Antofagasta Region
The Antofagasta Region ( es, Región de Antofagasta, ) is one of Chile's sixteen first-order administrative divisions. The second-largest region of Chile in area, it comprises three provinces, Antofagasta, El Loa and Tocopilla. It is bordered t ...
of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. It is parked in front of two old passenger coaches from the nitrate railway at coordinates . Three Kitson Meyers of the Transandine Railways also have survived, one in Argentina (Tafi Viejo; as of 2013 in derelict condition) and two in Chile (#3348 at Los Andes station workshop, seen under restoration on 8-Sep-2013 and Serial #4664 Operating #3349 at the Museo Ferroviario de Santiago, Parque Quinta Normal, Santiago de Chile, in cosmetically restored condition). There are also six very derelict locos in the "Locomotive Graveyard" at Uyuni
Uyuni (Aymara, ''uyu'' pen (enclosure), yard, cemetery, ''-ni'' a suffix to indicate ownership, "the one that has got a pen", "the one with a pen") is a city in the southwest of Bolivia.
Uyuni primarily serves as a gateway for tourists visiting t ...
, Bolivia (October 2013).

Bagnall Modified Meyer
A number of largenarrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
industrial
Industrial may refer to:
Industry
* Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry
* Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems
* Industrial city, a city dominate ...
locomotives were built in the U.K. by W. G. Bagnall
W. G. Bagnall was a locomotive manufacturer from Stafford, England which was founded in 1875 and operated
until it was taken over in 1962 by English Electric.
History
The company was founded in 1875 by William Gordon Bagnall. The majority ...
of Stafford. Generally, these were constructed on the ''Meyer'' principle as s, but were fitted with a circular firebox that did not project below the footplate. A number were built for sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
railways in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
one of which was imported into the USA and resides on the Cripple Creek and Victor Railway in Colorado where it can be seen in pieces today. The last example, maker's number 3024, named ''Monarch'', was built in 1953 for Bowater's Railway at Sittingbourne in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
and now resides on the Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway
The Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway (W&LLR) ( cy, Rheilffordd y Trallwng a Llanfair Caereinion) is a narrow gauge heritage railway in Powys, Wales. The line is around long and runs westwards from the town of Welshpool ( cy, Y Trallwng) ...
.
Sources
* Binns, Donald (2003) ''Kitson Meyer Articulated Locomotives'' Trackside Publications, Skipton, UK. {{ISBN, 0-907941-37-0