|
Steam Locomotives
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number 4468 Mallard In York
A number is a mathematical object used to counting, count, measurement, measure, and nominal number, label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called ''numerals''; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the 5, number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called numerical digit, digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a ''numeral'' is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He was an early pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport, and his most significant contributions were the development of the first high-pressure steam engine and the first working railway steam locomotive. The world's first locomotive-hauled railway journey took place on 21 February 1804, when Trevithick's unnamed steam locomotive hauled a train along the tramway of the Penydarren Ironworks, in Merthyr Tydfil, Wales. Turning his interests abroad Trevithick also worked as a mining consultant in Peru and later explored parts of Costa Rica. Throughout his professional career he went through many ups and downs and at one point faced financial ruin, also suffering from the strong rivalry of many mining and steam engineers of the day. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephenson's Rocket
Stephenson's ''Rocket'' is an early steam locomotive of 0-2-2 wheel arrangement. It was built for and won the Rainhill Trials of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), held in October 1829 to show that improved locomotives would be more efficient than stationary steam engines. ''Rocket'' was designed and built by Robert Stephenson in 1829, and built at the Forth Street Works of his company in Newcastle upon Tyne. Though ''Rocket'' was by no means the first steam locomotive, it was the first to bring together several innovations to produce the most advanced locomotive of its day. It is the most famous example of an evolving design of locomotives by Stephenson that became the template for most steam engines in the following 150 years. The locomotive was preserved and displayed in the Science Museum in London until 2018, after which it was displayed at the National Railway Museum in York. Design Overall layout The locomotive had a tall smokestack chimney at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool And Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail. Trains were hauled by company steam locomotives between the two towns, though private wagons and carriages were allowed. Cable haulage of freight trains was down the steeply-graded Wapping Tunnel to Liverpool Docks from Edge Hill junction. The railway was primarily built to provide faster transport of raw materials, finished goods and passengers between the Port of Liverpool and the cotton mills and factories of Manchester and surrounding towns. Designed and built by George Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockton And Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton-on-Tees in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833. The S&DR was involved in the building of the East Coast Main Line between York and Darlington, but its main expansion was at Middlesbrough Docks and west into Weardale and east to Redcar. It suffered severe financial difficulties at the end of the 1840s and was nearly taken over by the York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway, before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stephenson And Company
Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England. It was the first company in the world created specifically to build railway engines. Famous early locomotives were ''Locomotion'' No. 1 and ''Rocket''. By 1899, 3,000 locomotives had been built at the Forth Street site, and a new company was formed, Robert Stephenson and Company Limited, and the Darlington works was opened. In 1937, the company merged with Hawthorn Leslie to form Robert Stephenson and Hawthorns. In 1944, they became part of English Electric. Foundation and early success The company was set up in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England by George Stephenson, his son Robert, with Edward Pease and Thomas Richardson. The manager of the works between 1824 and 1825 was James Kennedy. The company's first engine was ''Locomotion No 1'', which opened the Stockton and Darlington Railway, followed by three more: ''Hope' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stephenson
Robert Stephenson Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS HFRSE FRSA Doctor of Civil Law, DCL (16 October 1803 – 12 October 1859) was an English civil engineer and designer of locomotives. The only son of George Stephenson, the "Father of Railways", he built on the achievements of his father. Robert has been called the greatest engineer of the 19th century. Life Robert was born in Willington Quay near Wallsend, Northumberland, the son of George Stephenson and his wife, Frances Henderson. The family moved to Killingworth, where Robert was taught at the local village school. Robert attended the middle-class Percy Street Academy in Newcastle and at the age of fifteen was apprenticed to the mining engineer Nicholas Wood. He left before he had completed his three years to help his father survey the Stockton and Darlington Railway. Robert spent six months at Edinburgh University before working for three years as a mining engineer in Colombia. When he returned his father was building t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. Self-help advocate Samuel Smiles particularly praised his achievements. His chosen rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway line in the world to use locomotives, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotion No
Locomotion means the act or ability of something to transport or move itself from place to place. Locomotion may refer to: Motion * Motion (physics) * Robot locomotion, of man-made devices By environment * Aquatic locomotion * Flight * Locomotion in space * Terrestrial locomotion Biological locomotion Animal locomotion * Animal locomotion ** Climbing ** Crawling ** Flight ** Fish locomotion (swimming, others) ** Gait analysis *** Horse gaits **** Trot (horse gait) ** Jumping ** Running ** Slithering, limbless terrestrial locomotion *** Snake locomotion ** Swimming ** Walking Fine and gross motor skills * Fine motor skills (smaller muscles; fine movements) * Gross motor skills (larger muscles; large movements) Microbial locomotion * Microswimmer * Protist locomotion, locomotion of unicellular eukaryotes * Bacterial motility Arts, entertainment, and media Clubs * Loco Motion (Youth Group), a film and media club based in Essex, UK Games * ''Loco-Motion'' (video game), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlyn (publisher)
Hamlyn is a UK publishing company founded by Paul Hamlyn in 1950 with an initial investment of £350. His desire was to create "fine books with the common touch" which remains the foundation of its commercial success. It is part of the Octopus Publishing Group, now owned by Hachette Livre. History Paul Hamlyn sold the company to the International Publishing Company (now Time Inc. UK) in 1964, but stayed on until 1969. In 1964 Hamlyn commenced in Australia under the management of Kevin Weldon. It owned an interest in the Australian independent paperback publisher Sun Books from 1968 until 1971 when Macmillan Australia acquired that company. Paul Hamlyn bought the company back in 1986 and added it to the holdings of his new company, Octopus Books. Octopus was sold in 1987 to Reed International. Hamlyn's children's division was sold to the Egmont Group in 1998. Hachette Livre bought Octopus in 2001. Hamlyn is an international publisher of non-fiction illustrated books. Two thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middleton Railway
The Middleton Railway is the world's oldest continuously working railway, situated in the English city of Leeds. It was founded in 1758 and is now a heritage railway, run by volunteers from The Middleton Railway Trust Ltd. since 1960. The railway operates passenger services at weekends and on public holidays over approximately of track between its headquarters at Moor Road, in Hunslet, and Park Halt, on the outskirts of Middleton Park. Origins: Middleton colliery Coal has been worked in Middleton since the 13th century, from bell pits, gin pits and later "day level" or adits. Anne Leigh, heiress to the Middleton Estates, married Ralph Brandling from Felling near Gateshead on the River Tyne. They lived in Gosforth and left running of the Middleton pits to agents. Charles Brandling was their successor. In 1754, Richard Humble, from Tyneside, was his agent. Brandling was in competition with the Fentons in Rothwell who were able to transport coal into Leeds by river, put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
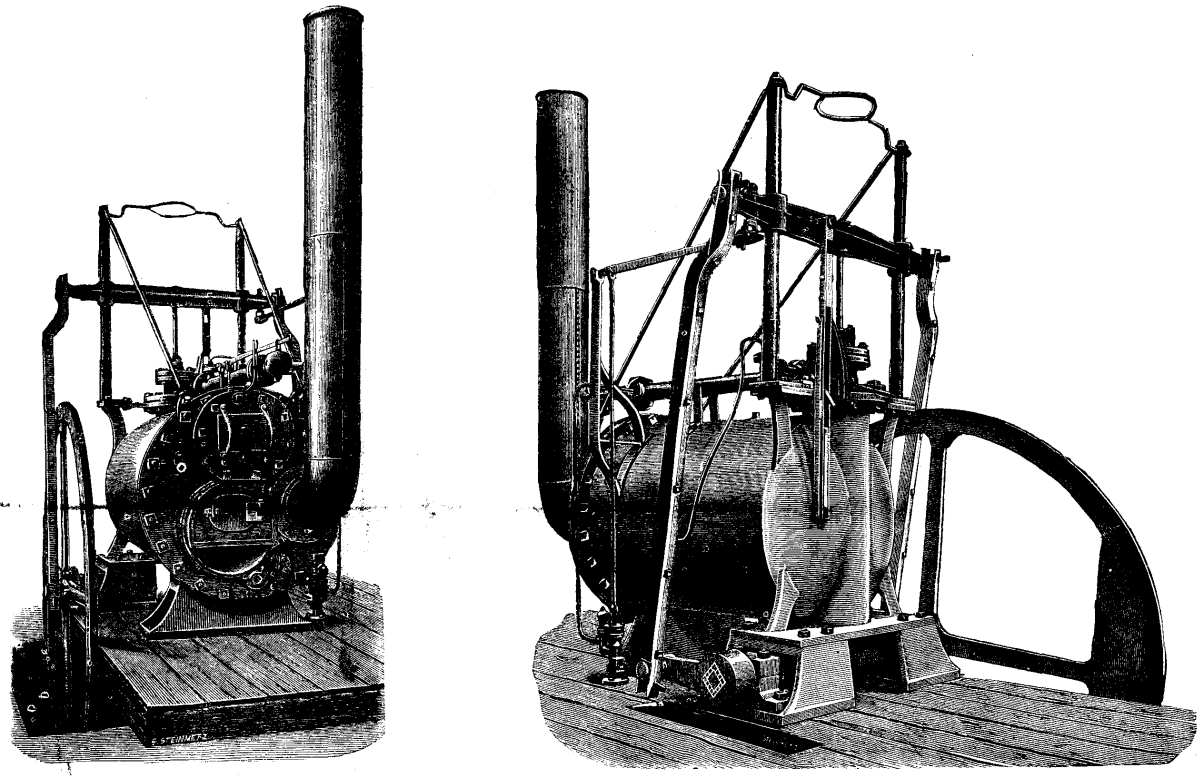
Matthew Murray
Matthew Murray (1765 – 20 February 1826) was an English steam engine and machine tool manufacturer, who designed and built the first commercially viable steam locomotive, the twin cylinder ''Salamanca'' in 1812. He was an innovative designer in many fields, including steam engines, machine tools and machinery for the textile industry. Early years Little is known about Matthew Murray's early years. He was born in Newcastle upon Tyne in 1765. He left school at fourteen and was apprenticed to be either a blacksmith or a whitesmith. In 1785, when he concluded his apprenticeship, he married Mary Thompson (1764–1836) of Whickham, County Durham. The following year he moved to Stockton and began work as a journeyman mechanic at the flax mill of John Kendrew in Darlington, where the mechanical spinning of flax had been invented.. Murray and his wife, Mary, had three daughters and a son, also called Matthew.. Leeds In 1789, due to a lack of trade in the Darlington flax mills, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

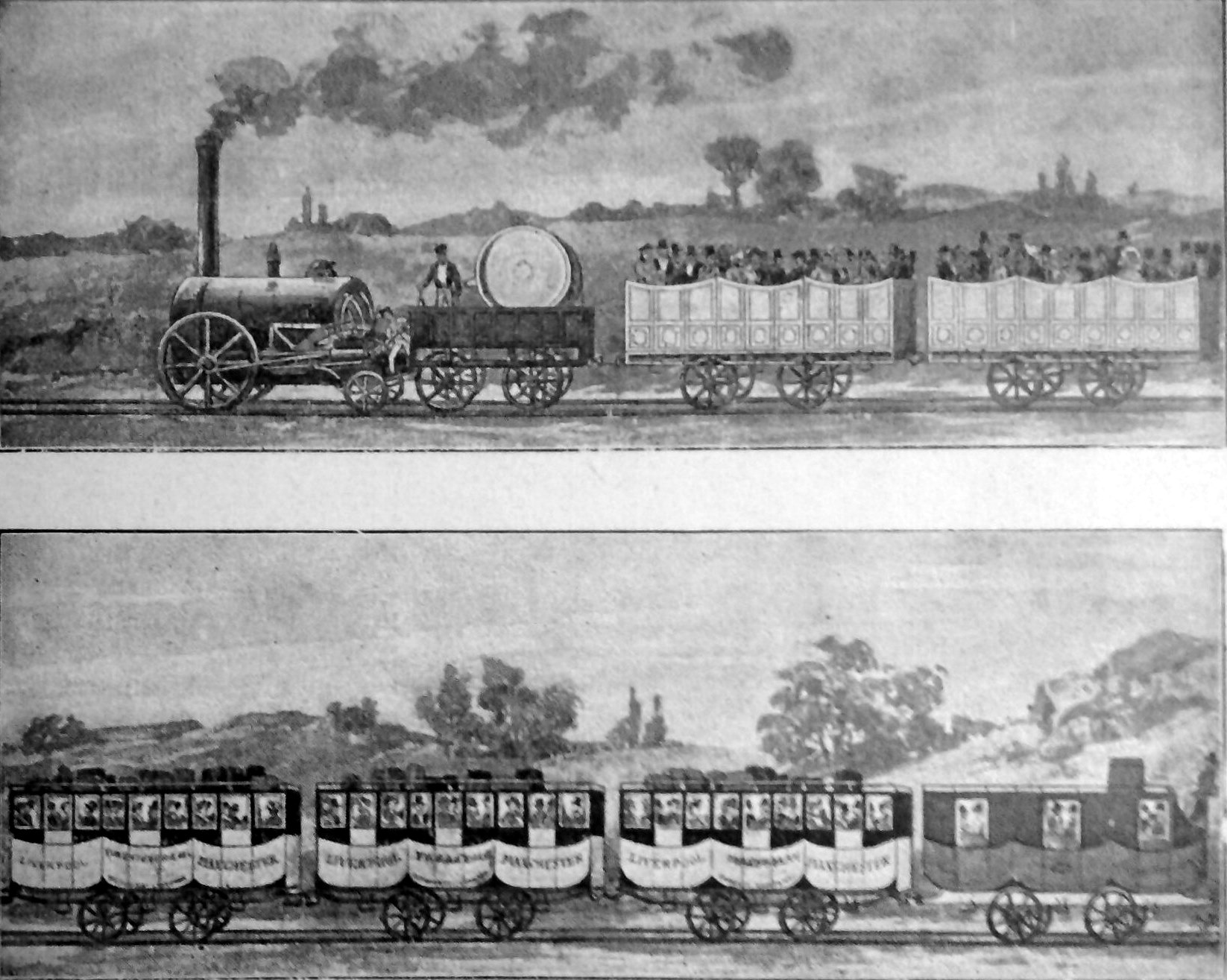
.jpg)
.jpg)