
In the
history of Europe
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first earl ...
, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the
post-classical period of
global history
World history may refer to:
* Human history, the history of human beings
* History of Earth, the history of planet Earth
* World history (field), a field of historical study that takes a global perspective
* ''World History'' (album), a 1998 albu ...
. It began with the
fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
and transitioned into the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
and the
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history:
classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
, the medieval period, and the
modern period
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is appli ...
. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the
Early
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
,
High, and
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
.
Population decline
A population decline (also sometimes called underpopulation, depopulation, or population collapse) in humans is a reduction in a human population size. Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth's total human population ...
,
counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of
tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confl ...
s, which had begun in
late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the
Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
, including various
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century,
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
and the Middle East—most recently part of the
Eastern Roman (or Byzantine) Empire—came under the rule of the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
, an Islamic empire, after conquest by
Muhammad's successors. Although there were substantial changes in society and political structures, the break with classical antiquity was not complete. The still-sizeable Byzantine Empire,
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
's direct continuation, survived in the Eastern Mediterranean and remained a major power. Secular law was advanced greatly by the ''
Code of Justinian''. In the West, most kingdoms incorporated extant Roman institutions, while new bishoprics and monasteries were founded as Christianity expanded in Europe. The
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, under the
Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pi ...
, briefly established the
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
during the later 8th and early 9th centuries. It covered much of Western Europe but later succumbed to the pressures of internal civil wars combined with external invasions:
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
from the north,
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ural ...
from the east, and
Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia P ...
s from the south.
During the High Middle Ages, which began after 1000, the population of Europe increased greatly as technological and
agricultural innovations allowed trade to flourish and the
Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP), also known as the Medieval Climate Optimum or the Medieval Climatic Anomaly, was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region that lasted from to . Climate proxy records show peak warmth occurred at diffe ...
climate change allowed crop yields to increase.
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or " tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fort ...
, the organisation of
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasan ...
s into villages that owed rent and labour services to the
nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteri ...
, and
feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
, the political structure whereby
knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the G ...
s and lower-status nobles owed military service to their
overlord
An overlord in the English feudal system was a lord of a manor who had subinfeudated a particular manor, estate or fee, to a tenant. The tenant thenceforth owed to the overlord one of a variety of services, usually military service or s ...
s in return for the right to rent from lands and manors, were two of the ways society was organised in the High Middle Ages. This period also saw the formal division of the
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
and
Orthodox churches, with the
East–West Schism of 1054. The
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
, which began in 1095, were military attempts by Western European Christians to regain control of the
Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Ho ...
from
Muslims, and also contributed to the expansion of Latin Christendom in the
Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
and the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. Kings became the heads of centralised
nation states
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
, reducing crime and violence but making the ideal of a unified
Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
more distant. In the West, intellectual life was marked by
scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translat ...
, a philosophy that emphasised joining faith to reason, and by the founding of
universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which ...
. The theology of
Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
, the paintings of
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/ Proto-Renaissance period. ...
, the poetry of
Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His '' Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ...
and
Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for '' The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
, the travels of
Marco Polo, and the
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. I ...
of cathedrals such as
Chartres mark the end of this period.
The Late Middle Ages was marked by difficulties and calamities including famine, plague, and war, which significantly diminished the population of Europe; between 1347 and 1350, the
Black Death killed about a third of Europeans. Controversy,
heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
, and the
Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Vatican Standoff, the Great Occidental Schism, or the Schism of 1378 (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 1378 to 1417 in which bishops residing in Rome and Avignon bo ...
within the Catholic Church paralleled the interstate conflict, civil strife, and
peasant revolts that occurred in the kingdoms. Cultural and technological developments transformed European society, concluding the Late Middle Ages and beginning the
early modern period.
Terminology and periodisation
The Middle Ages is one of the three major periods in the most enduring scheme for analysing
European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first earl ...
:
Antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, the Middle Ages and the
Modern Period
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is appli ...
.
[Power ''Central Middle Ages'' p. 3] A similar term first appears in Latin in 1469 as or "middle season". In early usage, there were many variants, including , or "middle age", first recorded in 1604, and , or "middle centuries", first recorded in 1625.
[Murray "Should the Middle Ages Be Abolished?" ''Essays in Medieval Studies'' p. 4] The adjective "medieval" (or sometimes "mediaeval"
[Flexner (ed.) ''Random House Dictionary'' p. 1194] or "mediæval"), meaning pertaining to the Middle Ages, derives from .
[
Medieval writers divided history into periods such as the " Six Ages" or the " Four Empires", and considered their time to be the last before the end of the world. The concept of living in a "middle age" was alien to them, and they referred to themselves as "", or "we modern people". In their concept, their age began when Christ had brought light to mankind, and contrasted the light of their age with the spiritual darkness of previous periods. The Italian humanist and poet ]Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credite ...
(d. 1374) was the first to revise the metaphor. He was convinced that a period of decline had begun when emperors of non-Italian origin assumed power in the Roman Empire, and described it as an age of "darkness". His concept was further developed by humanists like Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was som ...
(d. 1375) and Filippo Villani who emphasized the "rebirth" of culture in their age after a long period of cultural darkness. Leonardo Bruni was the first historian to use tripartite periodisation in his ''History of the Florentine People'' (1442), with a middle period "between the fall of the Roman Empire and the revival of city life sometime in late eleventh and twelfth centuries".[Hankins ''Introduction to History of the Florentine people by Leonardo Bruni'' pp. xvii–xviii] Tripartite periodisation became standard after the 17th-century German historian Christoph Cellarius
Christoph (Keller) Cellarius (22 November 1638 – 4 June 1707) was a German classical scholar from Schmalkalden who held positions in Weimar and Halle Halle may refer to:
Places Germany
* Halle (Saale), also called Halle an der Saale, a c ...
divided history into three periods: ancient, medieval, and modern.[
The most commonly given starting point for the Middle Ages is around 500, with the date of 476—the year the last Western Roman Emperor was deposed—first used by Bruni.][ Later starting dates are sometimes used in the outer parts of Europe. For Europe as a whole, 1500 is often considered to be the end of the Middle Ages, but there is no universally agreed upon end date. Depending on the context, events such as the ]conquest of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
by the Turks in 1453, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
's first voyage to the Americas in 1492, or the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in 1517 are sometimes used.[ English historians often use the ]Battle of Bosworth Field
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 ...
in 1485 to mark the end of the period. For Spain, dates commonly used are the death of King Ferdinand II in 1516, the death of Queen Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...
in 1504, or the conquest of Granada
The Granada War ( es, Guerra de Granada) was a series of military campaigns between 1482 and 1491 during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, against the Nasrid dynasty's Emirate of Granada. It ...
in 1492.
Historians from Romance-speaking countries tend to divide the Middle Ages into two parts: an earlier "High" and later "Low" period. English-speaking historians, following their German counterparts, generally subdivide the Middle Ages into three intervals: "Early", "High", and "Late".[ In the 19th century, the entire Middle Ages were often referred to as the " Dark Ages", but with the adoption of these subdivisions, use of this term was restricted to the Early Middle Ages in the early 20th century.][Mommsen "Petrarch's Conception of the 'Dark Ages'" ''Speculum'' p. 226]
Later Roman Empire
The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
reached its greatest territorial extent during the 2nd century AD; the following two centuries witnessed the slow decline of Roman control over its outlying territories. Runaway inflation, external pressure on the frontiers, and outbreaks of plague combined to create the Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensi ...
, with emperors coming to the throne only to be rapidly replaced by new usurpers. Military expenses increased steadily during the 3rd century, mainly in response to the war with the newly established Sasanian Empire.[Heather ''Fall of the Roman Empire'' p. 111] The army doubled in size, and cavalry and smaller units replaced the Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of t ...
as the main tactical unit.[Brown ''World of Late Antiquity'' pp. 24–25] The need for revenue led to increased taxes and a decline in numbers of the curial, or landowning, class, and decreasing numbers of them willing to shoulder the burdens of holding office in their native towns.[ More bureaucrats were needed in the central administration to deal with the needs of the army, which led to complaints from civilians that there were more tax-collectors in the empire than tax-payers.][
The Emperor Diocletian (r. 284–305) split the empire into separately administered eastern and western halves in 286. This system, which eventually encompassed two senior and two junior co-emperors (hence known as the ]Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
) stabilised the imperial government for about two decades. Diocletian's further reforms strengthened the governmental bureaucracy, reformed taxation, and strengthened the army, which bought the empire time but did not resolve the problems it was facing: excessive taxation, a declining birthrate, and pressures on its frontiers, among others. In 330, after a period of civil war, Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
(r. 306–337) refounded the city of Byzantium as the newly renamed eastern capital, Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. For much of the 4th century, Roman society stabilised in a new form that differed from the earlier classical period, with a widening gulf between the rich and poor, and a decline in the vitality of the smaller towns. Another change was the Christianisation
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
, or conversion of the empire to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
. The process was stimulated by the 3rd-century crisis, accelerated by the conversion of Constantine the Great, and by the end of the century Christianity emerged as the empire's dominant religion. Debates about Christian theology, customs and ethics intensified. Mainstream Christianity developed under imperial patronage, and those who persisted with theological views condemned at the Church leaders' general assemblies known as ecumenical councils had to endure official persecution. Heretic views could survive by popular support, or through intensive proselytizing activities. Examples include the uncompromisingly Monophysite Syrians and Egyptians, and the spread of Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by G ...
among the Germanic peoples. Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
remained a tolerated religion although legislation limited the Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
' rights, hindering conversion of Christians to Judaism.
Civil war between rival emperors became common in the middle of the 4th century, diverting soldiers from the empire's frontier forces and allowing invaders
''InVader'' is the fourth album by Finnish glam metal band Reckless Love, released on 4 March 2016 through Spinefarm Records.
Track listing
All songs written by Olli Herman, Pepe Reckless, and Ikka Wirtanen, unless otherwise noted.
Reception
Wr ...
to encroach. Although the movements of peoples during this period are usually described as "invasions", they were not just military expeditions but migrations of entire peoples into the empire.[Brown, ''World of Late Antiquity'', pp. 122–124] In 376, the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
, fleeing from the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, received permission from Emperor Valens
Valens ( grc-gre, Ουάλης, Ouálēs; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half o ...
(r. 364–378) to settle in Roman territory in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The settlement did not go smoothly, and when Roman officials mishandled the situation, the Goths began to raid and plunder. Valens, attempting to put down the disorder, was killed fighting the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople
The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Greutungs, non-Gothic ...
on 9 August 378. In 401, the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, a Gothic group, invaded the Western Roman Empire and, although briefly forced back from Italy, in 410 sacked the city of Rome. In 406 the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
, and Suevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names ...
crossed into Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
; over the next three years they spread across Gaul and in 409 crossed the Pyrenees Mountains into modern-day Spain. The Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, Alemanni, and the Burgundians all ended up in Gaul while the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
, and Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
settled in Britain,[Cunliffe ''Europe Between the Oceans'' p. 417] and the Vandals went on to cross the strait of Gibraltar after which they conquered the province of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The Hunnic king Attila
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and ...
(r. 434–453) led invasions into the Balkans in 442 and 447, Gaul in 451, and Italy in 452. The Hunnic threat remained until Attila's death in 453, when the Hunnic confederation he led fell apart.
When dealing with the migrations, the eastern and western elites applied different methods. The Eastern Romans combined the deployment of armed forces with gifts and grants of offices to the tribal leaders. The Western aristocrats failed to support the army but refused to pay tribute to prevent invasions by the tribes.[ These invasions completely changed the political and demographic nature of the western section of the empire.][ By the end of the 5th century it was divided into smaller political units, ruled by the tribes that had invaded in the early part of the century. The emperors of the 5th century were often controlled by military strongmen such as ]Stilicho
Flavius Stilicho (; c. 359 – 22 August 408) was a military commander in the Roman army who, for a time, became the most powerful man in the Western Roman Empire. He was of Vandal origins and married to Serena, the niece of emperor Theodosi ...
(d. 408), Aetius (d. 454), Aspar
Flavius Ardabur Aspar (Greek: Άσπαρ, fl. 400471) was an Eastern Roman patrician and ''magister militum'' ("master of soldiers") of Alanic-Gothic descent. As the general of a Germanic army in Roman service, Aspar exerted great influence on ...
(d. 471), Ricimer
Flavius Ricimer ( , ; – 18/19 August 472) was a Romanized Germanic general who effectively ruled the remaining territory of the Western Roman Empire from 461 until his death in 472, with a brief interlude in which he contested power with An ...
(d. 472), or Gundobad
Gundobad ( la, Flavius Gundobadus; french: Gondebaud, Gondovald; 452 – 516 AD) was King of the Burgundians (473 – 516), succeeding his father Gundioc of Burgundy. Previous to this, he had been a patrician of the moribund Western Roman Empi ...
(d. 516), who were partly or fully of non-Roman ancestry. The deposition of the last emperor of the west, Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus ( 465 – after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne by his father, the ''magister militum'' Orestes, and, at that time ...
, in 476 has traditionally marked the end of the Western Roman Empire.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 86] The Eastern Roman Empire, often referred to as the Byzantine Empire after the fall of its western counterpart, had little ability to assert control over the lost western territories. The Byzantine emperors
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, to Fall of Constantinople, its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. On ...
maintained a claim over the territory, but while none of the new kings in the west dared to elevate himself to the position of emperor of the west, Byzantine control of most of the Western Empire could not be sustained.
Early Middle Ages
New realms
 In the post-Roman world ethnic identities were flexible, often determined by loyalty to a successful military leader or by religion instead of ancestry or language. Ethnic markers quickly changed—by around 500, Arianism, originally a genuine Roman heresy, was associated with Germanic peoples, and the Goths rarely used their Germanic language outside their churches. The fusion of Roman culture with the customs of the invading tribes is well documented. Popular assemblies that allowed free male tribal members more say in political matters than had been common in the Roman state developed into legislative and judicial bodies.
In the post-Roman world ethnic identities were flexible, often determined by loyalty to a successful military leader or by religion instead of ancestry or language. Ethnic markers quickly changed—by around 500, Arianism, originally a genuine Roman heresy, was associated with Germanic peoples, and the Goths rarely used their Germanic language outside their churches. The fusion of Roman culture with the customs of the invading tribes is well documented. Popular assemblies that allowed free male tribal members more say in political matters than had been common in the Roman state developed into legislative and judicial bodies.[Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 98–101] Material artefacts left by the Romans and the invaders are often similar, and tribal items were often modelled on Roman objects.[Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', p. 100] Much of the scholarly and written culture of the new kingdoms was also based on Roman intellectual traditions.[Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', pp. 96–97] An important difference was the gradual loss of tax revenue by the new polities. Many of the new political entities no longer supported their armies through taxes, instead relying on granting them land or rents. This meant there was less need for large tax revenues and so the taxation systems decayed.[Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 102–103]
 Among the new peoples filling the political void left by Roman centralised government, the first Germanic groups now collectively known as
Among the new peoples filling the political void left by Roman centralised government, the first Germanic groups now collectively known as Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
settled in Britain before the middle of the 5th century. The local culture had little impact on their way of life, but the linguistic assimilation of masses of the local Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
to the newcomers is evident. By around 600, new political centres emerged, some local leaders accumulated considerable wealth, and a number of small kingdoms were formed. From among these realms, the kingdoms of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
, Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era= Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ...
, Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, and East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
emerged as dominant powers by the end of the 7th century. Smaller kingdoms in present-day Wales and Scotland were still under the control of the native Britons and Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 156–159] Ireland was divided into even smaller political units, usually known as tribal kingdoms, under the control of kings. There were perhaps as many as 150 local kings in Ireland, of varying importance.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 164–165]
The Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
, a Gothic tribe moved to Italy from the Balkans in the late 5th century under Theoderic the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
(r. 493–526). He set up a kingdom marked by its co-operation between the Italians and the Ostrogoths, at least until the last years of his reign. Power struggles between Romanized and traditionalist Ostrogothic groups followed his death, providing the opportunity for the Byzantines to reconquer Italy in the middle of 6th century.[James ''Europe's Barbarians'' pp. 82–94] The Burgundians settled in Gaul, and after an earlier realm was destroyed by the Huns in 436, formed a new kingdom in the 440s. Between today's Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situ ...
and Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
, it grew to become the realm of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
in the late 5th and early 6th centuries.[James ''Europe's Barbarians'' pp. 77–78] Elsewhere in Gaul, the Franks and Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
set up stable polities. Francia
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
was centred in northern Gaul, and the first king of whom much is known is Childeric I
Childeric I (; french: Childéric; la, Childericus; reconstructed Frankish: ''*Hildirīk''; – 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin '' ...
(d. 481). Under Childeric's son Clovis I (r. 509–511), the founder of the Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
, the Frankish kingdom expanded and converted to Christianity.[James ''Europe's Barbarians'' pp. 79–81] Unlike other Germanic peoples, the Franks accepted Catholicism which facilitated their cooperation with the native Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
aristocracy. Britons fleeing from – modern-day Great Britain – settled in what is now Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
.[
Other monarchies were established by the Visigoths in the ]Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, the Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
in northwestern Iberia, and the Vandals in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
.[ The ]Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
settled in Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
, but the influx of the nomadic Avars from the Asian steppes to Central Europe forced them to move on to Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
in 568. Here they conquered the lands once held by the Ostrogoths from the Byzantines, and established a new kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
composed of town-based duchies.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 196–208] By the end of the 6th century, the Avars conquered most Slavic, Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
and Germanic tribes in the lowlands along the Lower and Middle Danube, and they were routinely able to force the Eastern emperors to pay tribute.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 51–59] Around 670, another steppe people, the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
settled at the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta ( ro, Delta Dunării, ; uk, Дельта Дунаю, Deľta Dunaju, ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies i ...
. In 681, they defeated a Byzantine imperial army, and established a new empire on the Lower Danube, subjugating the local Slavic tribes.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 71–77]
During the invasions, some regions received a larger influx of new peoples than others. In Gaul for instance, the invaders settled much more extensively in the north-east than in the south-west. Slavs settled in Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
and the Balkan Peninsula. The settlement of peoples was accompanied by changes in languages. Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
, the literary language of the Western Roman Empire, was gradually replaced by vernacular languages which evolved from Latin, but were distinct from it, collectively known as Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language f ...
. These changes from Latin to the new languages took many centuries. Greek remained the language of the Byzantine Empire, but the migrations of the Slavs expanded the area of Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavs, Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic language, Proto ...
in Eastern Europe.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 235–238]
Byzantine survival
 As Western Europe witnessed the formation of new kingdoms, the Eastern Roman Empire remained intact and experienced an economic revival that lasted into the early 7th century. There were fewer invasions of the eastern section of the empire; most occurred in the Balkans. Peace with the Sasanian Empire, the traditional enemy of Rome, lasted throughout most of the 5th century. The Eastern Empire was marked by closer relations between the political state and Christian Church, with doctrinal matters assuming an importance in Eastern politics that they did not have in Western Europe. Legal developments included the codification of
As Western Europe witnessed the formation of new kingdoms, the Eastern Roman Empire remained intact and experienced an economic revival that lasted into the early 7th century. There were fewer invasions of the eastern section of the empire; most occurred in the Balkans. Peace with the Sasanian Empire, the traditional enemy of Rome, lasted throughout most of the 5th century. The Eastern Empire was marked by closer relations between the political state and Christian Church, with doctrinal matters assuming an importance in Eastern politics that they did not have in Western Europe. Legal developments included the codification of Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Jus ...
; the first effort—the ''Codex Theodosianus
The ''Codex Theodosianus'' (Eng. Theodosian Code) was a compilation of the laws of the Roman Empire under the Christian emperors since 312. A commission was established by Emperor Theodosius II and his co-emperor Valentinian III on 26 March 429 ...
''—was completed in 438.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 81–83] Under Emperor Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized '' renova ...
(r. 527–565), a more comprehensive compilation took place—the ''Corpus Juris Civilis
The ''Corpus Juris'' (or ''Iuris'') ''Civilis'' ("Body of Civil Law") is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Byzantine Emperor. It is also sometimes referr ...
''.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', pp. 130–131]
Justinian almost lost his throne during the Nika riots, a popular revolt of elementary force that destroyed half of Constantinople in 532. After crushing the revolt, he reinforced the autocratic elements of the imperial government and mobilized his troops against the heretic western realms. The general Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean ter ...
(d. 565) conquered North Africa from the Vandals, and attacked the Ostrogoths, but the Italian campaign was interrupted due to an unexpected Sasanian invasion from the east. For the movement of troops from the Balkan provinces left the region virtually unprotected, the neighboring Slavic and Turkic tribes intensified their plundering raids across the Danube. Between 541 and 543, a deadly outbreak of plague decimated the empire's population, and the epidemic swept through the Mediterranean several times during the following decades. Justinian was to apply new methods to counterbalance its negative effects. He covered the lack of military personnel by developing an extensive system of border forts. To reduce fiscal deficit, he nationalized the silk industry and ceased to finance the maintenance of public roads. In a decade, he resumed expansionism, completing the conquest of the Ostrogothic kingdom, and seizing much of southern Spain from the Visigoths.[Brown ''World of Late Antiquity'' pp. 150–156]
Justinian's reconquests and excessive building program have been criticised by historians for bringing his realm to the brink of bankruptcy, but many of the difficulties faced by Justinian's successors were probably due to other factors, including the epidemic. An additional problem to face the empire came as a result of the massive expansion of the Avars and their Slav allies. They conquered the Balkans and Greece with the exception of a few coastal cities before their assault on Constantinople was repulsed in 626.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 8–10] In the east, border defences collapsed during a new war with the Sasanian Empire and the Persians seized large chunks of the empire, including Egypt, Syria, and much of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
. A Persian army approached Constantinople to join the Avars and Slavs during the siege but a Byzantine fleet prevented them from crossing the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern T ...
in 626. Two years later, Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
(r. 610–641) launched an unexpected counterattack against the heart of the Sassanian Empire bypassing the Persian army in the mountainous regions of Anatolia. He triumphed and the empire recovered all of its lost territories in the east in a new peace treaty.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 140–143]
Western society
In Western Europe, some of the older Roman elite families died out while others became more involved with ecclesiastical than secular affairs. Values attached to Latin scholarship and education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. ...
mostly disappeared, and while literacy remained important, it became a practical skill rather than a sign of elite status. In the 4th century, Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
(d. 420) dreamed that God rebuked him for spending more time reading Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the est ...
than the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts o ...
. By the 6th century, Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Florent ...
(d. 594) had a similar dream, but instead of being chastised for reading Cicero, he was chastised for learning shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek ''st ...
.[Brown ''World of Late Antiquity'' pp. 174–175] By the late 6th century, the principal means of religious instruction in the Church had become music and art rather than the book.[Brown ''World of Late Antiquity'' p. 181] Most intellectual efforts went towards imitating classical scholarship, but some original works were created, along with now-lost oral compositions. The writings of Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November of an unknown year, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Sidonius is "the single most important surviving author from 5th-century Gaul ...
(d. 489), Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator' ...
(d. ), and Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, '' magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the t ...
(d. ) were typical of the age.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 45–49]
Changes also took place among laymen, as aristocratic culture focused on great feasts held in halls rather than on literary pursuits. Clothing for the elites was richly embellished with jewels and gold. Lords and kings supported entourages of fighters who formed the backbone of the military forces. Family ties within the elites were important, as were the virtues of loyalty, courage, and honour. These ties led to the prevalence of the feud in aristocratic society, examples of which included those related by Gregory of Tours that took place in Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
Gaul. Most feuds seem to have ended quickly with the payment of some sort of compensation.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 189–193]
Women took part in aristocratic society mainly in their roles as wives and mothers of men, with the role of mother of a ruler being especially prominent in Merovingian Gaul. In Anglo-Saxon society the lack of many child rulers meant a lesser role for women as queen mothers, but this was compensated for by the increased role played by abbess
An abbess (Latin: ''abbatissa''), also known as a mother superior, is the female superior of a community of Catholic nuns in an abbey.
Description
In the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and Eastern Catholic), Eastern Orthodox, Coptic ...
es of monasteries. In contrast, in medieval Italy women were always considered under the protection and control of a male relative.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 195–199] Women's influence on politics was particularly fragile, and early medieval authors tended to depict powerful women in a bad light. Examples include the Arian queen Goiswintha (d. 589), a vehement but unsuccessful opponent of the Visigoth's conversion to Catholicism, and the Frankish queen Brunhilda of Austrasia
Brunhilda (c. 543–613) was queen consort of Austrasia, part of Francia, by marriage to the Merovingian king Sigebert I of Austrasia, and regent for her son, grandson and great-grandson.
In her long and complicated career she ruled the easte ...
(d. 613) who was torn to pieces by horses after her enemies captured her at the age of 70.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 116, 195–197] Women usually died at considerably younger age than men, primarily due to infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose is the prevention of resou ...
and complacations at childbirth. Infanticide was not an unusual practice in times of famine, and daughters fell victim to it more frequently than their brothers who could potentially do harder works. The disparity between the numbers of marriageable women and grown men led to the detailed regulation of legal institutions protecting women's interests, including the , or "morning gift", a compensation for the loss of virginity.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', p. 120] Early medieval laws acknowledged a man's right to have long-term sexual relationships with women other than his wife, such as concubines
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive.
Concubin ...
and those who were bound to him by a special contract known as , but women were expected to remain faithful to their life partners. Clerics censured sexual unions outside marriage, and monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time ( serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., polyg ...
became also the norm of secular law in the 9th century.[Bitel, ''Women in Early Medieval Europe'', p. 180–182]
 Peasant society is much less documented than the nobility. Most of the surviving information available to historians comes from
Peasant society is much less documented than the nobility. Most of the surviving information available to historians comes from archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
; few detailed written records documenting peasant life remain from before the 9th century. Most of the descriptions of the lower classes come from either law codes or writers from the upper classes.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 204] Landholding patterns were not uniform; some areas had greatly fragmented landholding patterns, but in other areas large contiguous blocks of land were the norm. These differences allowed for a wide variety of peasant societies, some dominated by aristocratic landholders and others having a great deal of autonomy.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 205–210] Land settlement also varied greatly. Some peasants lived in large settlements that numbered as many as 700 inhabitants. Others lived in small groups of a few families and still others lived on isolated farms spread over the countryside. There were also areas where the pattern was a mix of two or more of those systems.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 211–212] Legislation made a clear distinction between free and unfree, but there was no sharp break between the legal status of the free peasant and the aristocrat, and it was possible for a free peasant's family to rise into the aristocracy over several generations through military service.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 215] Demand for slaves was covered through warring and raids. Initially, the Franks' expansion and conflicts between the Anglo-Saxon realms supplied the slave market with prisoners of war and captives. After the Anglo-Saxons' conversion to Christianity, slave hunters mainly targeted the pagan Slav tribes—hence the English word "slave" from , the Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used f ...
term for Slavs. Christian ethics brought about significant changes in the position of slaves in the 7th and 8th centuries. They were no more regarded as their lords' property, and their right to a decent treatment was enacted.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', pp. 119–120]
Roman city life and culture changed greatly in the early Middle Ages. Although Italian cities remained inhabited, they contracted significantly in size. Rome, for instance, shrank from a population of hundreds of thousands to around 30,000 by the end of the 6th century. Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete state. Today they remain "the most obvious symbol of R ...
s were converted into Christian churches
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for ...
and city walls remained in use.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 24–26] In Northern Europe, cities also shrank, while civic monuments and other public buildings were raided for building materials. The establishment of new kingdoms often meant some growth for the towns chosen as capitals.[Gies and Gies ''Life in a Medieval City'' pp. 3–4] The Jewish communities survived the fall of the Western Roman Empire in Spain, southern Gaul and Italy. The Visigothic kings made concentrated efforts to convert the Hispanic Jews
The history of the Jews in Latin America began with conversos who joined the Spanish and Portuguese expeditions to the continents. The Alhambra Decree of 1492 led to the mass conversion of Spain's Jews to Catholicism and the expulsion of thos ...
to Christianity in the 7th century but the Jewish community quickly regenerated after the Muslim conquest. Under Muslim rule, the Jews' activities were less limited, and the Muslim rulers regularly employed them in their courts. In contrast, Christian legislation forbade the Jews' appointment to government positions.
Rise of Islam
 Religious beliefs were in flux in the lands along the Eastern Roman and Persian frontiers during the late 6th and early 7th centuries. State-sponsored Christian missionaries proselytised among the pagan steppe peoples, and the Persians made attempts to enforce their
Religious beliefs were in flux in the lands along the Eastern Roman and Persian frontiers during the late 6th and early 7th centuries. State-sponsored Christian missionaries proselytised among the pagan steppe peoples, and the Persians made attempts to enforce their Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
on the Christian Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
. Judaism was an active proselytising faith, and at least one Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
political leader—Dhu Nuwas
Dhū Nuwās, ( ar, ذُو نُوَاس), real name "Yūsuf Asʾar Yathʾar" ( Musnad: 𐩺𐩥𐩪𐩰 𐩱𐩪𐩱𐩧 𐩺𐩻𐩱𐩧, ''Yws¹f ʾs¹ʾr Yṯʾr''), "Yosef Nu'as" ( he, יוסף נואס), or "Yūsuf ibn Sharhabīl" ( ar, يُ� ...
, ruler of what is today Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
—converted to it.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 136, 141–142] The emergence of Islam in Arabia during the lifetime of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
(d. 632) brought about more radical changes. After his death, Islamic forces conquered much of the Near East, starting with Syria in 634–35, continuing with Persia between 637 and 642, and reaching Egypt in 640–41. In the eastern Mediterranean, the Muslim expansion was halted at Constantinople. The Eastern Romans used the Greek Fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Eastern Roman Empire beginning . Used to set fire to enemy ships, it consisted of a combustible compound emitted by a flame-throwing weapon. Some historians believe it could be ignited on contact ...
, a highly combustible liquid, to defend their capital in 674–78 and 717–18. In the west, the advance of Islamic troops continued. They conquered North Africa by the early 8th century
The 8th century is the period from 701 ( DCCI) through 800 ( DCCC) in accordance with the Julian Calendar. The coast of North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula quickly came under Islamic Arab domination. The westward expansion of the Umayyad E ...
, annihilated the Visigothic Kingdom in 711, and invaded southern France from 713.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 142–143, 150, 160][Cunliffe ''Europe Between the Oceans'' pp. 421–423]
The Muslim conquerors bypassed the mountainous northwestern region of the Iberian Peninsula. Here a small kingdom, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensi ...
emerged as the centre of local resistance.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 376–377] The defeat of Muslim forces at the Battle of Tours in 732 led to the reconquest of southern France by the Franks, but the main reason for the halt of Islamic growth in Europe was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and its replacement by the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
. The Abbasids moved their capital to Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesipho ...
and were more concerned with the Middle East than Europe, losing control of sections of the Muslim lands. Umayyad descendants took over Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
(or Muslim Spain), the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about ...
controlled North Africa, and the Tulunids became rulers of Egypt.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 15]
Trade and economy
The migrations and invasions of the 4th and 5th centuries disrupted trade networks around the Mediterranean. African goods stopped being imported into Europe, first disappearing from the interior and by the 7th century found only in a few cities such as Rome or Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
. By the end of the 7th century, under the impact of the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, African products were no longer found in Western Europe. The replacement of goods from long-range trade with local products was a trend throughout the old Roman lands that happened in the Early Middle Ages. This was especially marked in the lands that did not lie on the Mediterranean, such as northern Gaul or Britain. Non-local goods appearing in the archaeological record are usually luxury goods or metalworks.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 218–219] In the 7th and 8th centuries, new commercial networks were developing in northern Europe. Goods like furs, walrus ivory
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fa ...
and amber were delivered from the Baltic region to western Europe, contributing to the development of new trade centers in East Anglia, northern Francia and Scandinavia. Conflicts over the control of trade routes and toll stations were common, and those who failed turned to raiding or settled in foreign lands.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 347–348]
The flourishing Islamic economies' constant demand for fresh labour force and raw materials opened up a new market for Europe around 750. Europe emerged as a major supplier of house slaves and slave soldiers for Al-Andalus, northern Africa and the Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
. Located in the vicinity of the Central European slave hunting areas, Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
developed into the most important European center of slave trade. In addition, timber, fur and arms were delivered from Europe to the Mediterranean, while Europe imported spices, medicine, incense, and silk from the Levant. The demand for exotic merchandise was reinforced primarily by internal factors, like population growth, and improved agricultural productivity. The large rivers connecting distant regions facilitated the expansion of transcontinental trade. Contemporaneous reports indicate that Anglo-Saxon merchants visited fairs at Paris, pirates preyed on tradesman travelling on the Danube, and Eastern Frankish merchants reached as far as Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tribut ...
in Al-Andalus.
The various Germanic states in the west all had coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in orde ...
ages that imitated existing Roman and Byzantine forms. Gold continued to be minted until the end of the 7th century in 693-94 when it was replaced by silver in the Merovingian kingdom. The basic Frankish silver coin was the denarius
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
or denier, while the Anglo-Saxon version was called a penny
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is t ...
. From these areas, the denier or penny spread throughout Europe from 700 to 1000 AD. Copper or bronze coins were not struck, nor were gold except in Southern Europe. No silver coins denominated in multiple units were minted.[Grierson "Coinage and currency" ''Middle Ages'']
Church and monasticism
 The idea of Christian unity endured although differences in ideology and practice between the Eastern and Western Churches became apparent by the 6th century. The formation of new realms reinforced the traditional Christian concept of the
The idea of Christian unity endured although differences in ideology and practice between the Eastern and Western Churches became apparent by the 6th century. The formation of new realms reinforced the traditional Christian concept of the separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular sta ...
in the west, whereas this notion was alien to eastern clergymen who regarded the Roman state as an instrument of divine providence. In the Eastern Christians' view, an individual could be saved from sin through direct mystical communication with God, but western clerics tended to regard themselves as unavoidable intercessors.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 41] In the late 7th century, clerical marriage emerged as a permanent focus of controversy: the Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Jo ...
promoted complete celibacy while the eastern clergy insisted on the more tolerant traditional approach. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant, the Byzantine emperors could less effectively intervene in the west. When Leo III Leo III, Leon III, or Levon III may refer to:
; People
* Leo III the Isaurian (685-741), Byzantine emperor 717-741
* Pope Leo III (d. 816), Pope 795-816
* Leon III of Abkhazia, King of Abkhazia 960–969
* Leo II, King of Armenia (c. 1236–1289), ...
(r. 717–741) prohibited the display of paintings representing human figures in places of worship, the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
openly censured the emperor's iconoclast doctrine and his claim to declare new dogmas by imperial edicts.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 218–233] Although the Byzantine Church condemned iconoclasm in 843, further issues such as fierce rivalry for ecclesiastic jurisdiction over newly converted peoples, and the unilateral modification of the Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is ...
in the west widened to the extent that the differences were greater than the similarities. The decisive break, known as the East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, ...
, came in 1054, when the papacy and the patriarchy of Constantinople clashed over papal supremacy and excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose ...
each other, which led to the division of Christianity into two Churches—the Western branch became the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Eastern branch the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
.[Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 45–46]
The ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Empire survived the movements and invasions in the west mostly intact, but the papacy was little regarded, and few of the Western bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
s looked to the bishop of Rome for religious or political leadership. Many of the popes prior to 750 were more concerned with Byzantine affairs and Eastern theological controversies. The register, or archived copies of the letters, of Pope Gregory the Great
Pope Gregory I ( la, Gregorius I; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instigating the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregori ...
(pope 590–604) survived, and of those more than 850 letters, the vast majority were concerned with affairs in Italy or Constantinople. The only part of Western Europe where the papacy had influence was Britain, where Gregory had sent the Gregorian mission in 597 to convert the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 170–172] Irish missionaries were most active in Western Europe between the 5th and the 7th centuries, going first to England and Scotland and then on to the continent. Under such monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s as Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is tod ...
(d. 597) and Columbanus
Columbanus ( ga, Columbán; 543 – 21 November 615) was an Irish missionary notable for founding a number of monasteries after 590 in the Frankish and Lombard kingdoms, most notably Luxeuil Abbey in present-day France and Bobbio Abbey in pr ...
(d. 615), they founded monasteries, taught in Latin and Greek, and authored secular and religious works.[Colish ''Medieval Foundations'' pp. 62–63] Early medieval people did not visit churches regularly. Instead, meetings with itinerant clergy and pilgrimages to popular saints' shrine
A shrine ( la, scrinium "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred or holy space dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, daemon, or similar figure of respect, wherein they ...
s were instrumental in the spread of Christian teaching. From the 6th century, Irish and British clerics developed special handbooks to determine the appropriate acts of penance
Penance is any act or a set of actions done out of repentance for sins committed, as well as an alternate name for the Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession. It also plays a pa ...
—typically prayers, and fasts—for sinners. These penitentials were introduced in Continental Europe by missionaries from the British Isles. They covered several aspects of everyday life but placed a special emphasis on sexuality. To defend monogamous marriage, they prescribed severe penances for adulterers, fornicators and those engaged in non-reproductive sexual acts, such as homosexuals.[Bitel, ''Women in Early Medieval Europe'', p. 127–133]
The Early Middle Ages witnessed the rise of Christian monasticism
Christian monasticism is the devotional practice of Christians who live ascetic and typically cloistered lives that are dedicated to Christian worship. It began to develop early in the history of the Christian Church, modeled upon scriptural e ...
. The shape of European monasticism was determined by traditions and ideas that originated with the Desert Fathers
The Desert Fathers or Desert Monks were early Christian hermits and ascetics, who lived primarily in the Scetes desert of the Roman province of Egypt, beginning around the third century AD. The is a collection of the wisdom of some of the earl ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
. Monastic ideals spread through hagiographical literature such as the '' Life of Anthony''. Most European monasteries were of the type that focuses on community experience of the spiritual life, called cenobitism, which was pioneered by the Egyptian hermit Pachomius
Pachomius (; el, Παχώμιος ''Pakhomios''; ; c. 292 – 9 May 348 AD), also known as Saint Pachomius the Great, is generally recognized as the founder of Christian cenobitic monasticism. Coptic churches celebrate his feast day on 9 May ...
(d. ).[Lawrence ''Medieval Monasticism'' pp. 10–13][Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 75–76] Bishop Basil of Caesarea (d. 379) wrote a monastic rule for a community of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
n ascetics which served as a highly esteemed template for similar regulations in the Mediterranean. These mainly covered the spiritual aspects of monasticism. In contrast, the Italian monk Benedict of Nursia
Benedict of Nursia ( la, Benedictus Nursiae; it, Benedetto da Norcia; 2 March AD 480 – 21 March AD 548) was an Italian Christian monk, writer, and theologian who is venerated in the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Ori ...
(d. 547) adopted a more practical approach, regulating both the administrative and spiritual responsibilities of a community of monks led by an abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. Th ...
. The Benedictine Rule became widely used in western monasteries already before it was decreed the norm for Frankish monastic communities in 817.[Lawrence ''Medieval Monasticism'' pp. 18–24][Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 237–240, 323] In the east, the monastic rules compiled by Theodore the Studite
Theodore the Studite ( grc-x-medieval, Θεόδωρος ό Στουδίτης; 759–826), also known as Theodorus Studita and Saint Theodore of Stoudios/Studium, was a Byzantine Greek monk and abbot of the Stoudios Monastery in Constantinople. H ...
(d. 826) gained popularity after they were adopted in the Great Lavra
The Monastery of Great Lavra ( el, Μονή Μεγίστης Λαύρας) is the first monastery built on Mount Athos. It is located on the southeastern foot of the Mount at an elevation of . The founding of the monastery in AD 963 by Athanasi ...
, a newly established imperial monastery on Mount Athos
Mount Athos (; el, Ἄθως, ) is a mountain in the distal part of the eponymous Athos peninsula and site of an important centre of Eastern Orthodox monasticism in northeastern Greece. The mountain along with the respective part of the peni ...
in the 960s. The Great Lavra set a precedent for the founding of further Athonite monasteries, turning the mount into the most important centre of Orthodox monasticism.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 322, 495]
Monks and monasteries had a deep effect on the religious and political life of the Early Middle Ages, in various cases acting as land trust
Land trusts are nonprofit organizations which own and manage land, and sometimes waters. There are three common types of land trust, distinguished from one another by the ways in which they are legally structured and by the purposes for which th ...
s for powerful families and important centres of political authority.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 185–187] They were the main and sometimes only outposts of education and literacy in a region. Many of the surviving manuscripts of the Latin classics were copied in monasteries in the Early Middle Ages.[Hamilton ''Religion in the Medieval West'' pp. 43–44] Monks were also the authors of new works, including history, theology, and other subjects, written by authors such as Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
(d. 735), a native of northern England.[Colish ''Medieval Foundations'' pp. 64–65] The Byzantine missionary Constantine (d. 869) developed Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic literary language.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with standardizing the language and using it in translating the Bible and other ...
as a new liturgical language
A sacred language, holy language or liturgical language is any language that is cultivated and used primarily in church service or for other religious reasons by people who speak another, primary language in their daily lives.
Concept
A sac ...
enriching Slavic vocabulary with Greek religious terms. He also created an alphabet, likely the Glagolitic script
The Glagolitic script (, , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed to have been created in the 9th century by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzan ...
, for it. These innovations established the basis for a flourishing Slavic religious literature. Constantine died as the monk Cyril in a Roman monastery. His work was continued by his brother Methodius (d. 885) and their pupils.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 183–191] A version of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
uncial script
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th ...
now known as Cyrillic replaced Glagolitic after around 900.
Carolingian Europe
 Royal authority was substantially weak in Francia. The Merovingian kings customarily distributed the kingdom among their sons and destroyed their own power base by extensive land grants. In the northeastern Frankish realm
Royal authority was substantially weak in Francia. The Merovingian kings customarily distributed the kingdom among their sons and destroyed their own power base by extensive land grants. In the northeastern Frankish realm Austrasia
Austrasia was a territory which formed the north-eastern section of the Merovingian Kingdom of the Franks during the 6th to 8th centuries. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of th ...
, the Arnulfings
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vo ...
were the most prominent beneficiaries of royal favour. As hereditary Mayors of the Palace, they were the power behind the Austrasian throne from the mid-7th century. The Arnulfings consolidated their authority by keeping their patrimony undivided through generations, and one of them, Pepin of Herstal
Pepin II (c. 635 – 16 December 714), commonly known as Pepin of Herstal, was a Frankish statesman and military leader who de facto ruled Francia as the Mayor of the Palace from 680 until his death. He took the title Duke and Prince of the ...
(d. 714) also assumed power in the central Frankish realm Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks.
Neustria included the land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, approximately the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities. It la ...
. His successor Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish state ...
(d. 741) took advantage of the permanent Muslim threat to confiscate church property and raise new troops by parcelling it out among the recruits. His victory over an expeditionary force from Al-Andalus in the Battle of Tours brought him enormous prestige.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', pp. 150–154]
The Carolingians
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
, as Charles Martel's descendants are known, succeeded the Merovingians as the new royal dynasty of Francia in 751. This year the last Merovingian king Childeric III
Childeric III ( 717 – 754) was King of Francia from 743 until he was deposed by Pope Zachary in March 751 at the instigation of Pepin the Short. Although his parentage is uncertain, he is considered the last Frankish king from the Merovingia ...
(r. 743–751) was deposed, and Charles Martel's son Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
(r. 751–768) was crowned king with the consent of the papacy and the Frankish leaders. Two or three years later Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II ( la, Stephanus II; 714 – 26 April 757) was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzant ...
(pope 752–757) personally sanctioned the coup by anointing
Anointing is the ritual act of pouring aromatic oil over a person's head or entire body.
By extension, the term is also applied to related acts of sprinkling, dousing, or smearing a person or object with any perfumed oil, milk, butter, or o ...
Pepin and his two sons with chrism
Chrism, also called myrrh, ''myron'', holy anointing oil, and consecrated oil, is a consecrated oil used in the Anglican, Assyrian, Catholic, Nordic Lutheran, Old Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Latter Day Saint churche ...
during his visit to Francia. He came to persuade Pepin to attack the Lombards whose expansion menaced the city of Rome. Pepin defeated the Lombards and enforced their promise to respect the possessions of the papacy. His subsequent donation of Central Italian territories to the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
marked the beginnings of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct Sovereignty, sovereign rule of ...
.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 276–278][Brown "Transformation of the Roman Mediterranean" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 97–99] At the time of his death in 768, Pepin left his kingdom in the hands of his two sons, Charles (r. 768–814) and Carloman (r. 768–771). When Carloman died of natural causes, Charles blocked the succession of Carloman's young son and installed himself as the king of the reunited Francia. Charles, more often known as Charles the Great or Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
, embarked upon a programme of systematic expansion in 772. In the wars that lasted beyond 800, he rewarded allies with war booty and command over parcels of land. Charlemagne subjugated the Saxons, conquered the Lombards, and created a new border province in northern Spain.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 280–288] Between 791 and 803, Frankish troops annihilated the Avars' empire which facilitated the development of small Slavic principalities, mainly ruled by ambitious warlords under Frankish suzerainty.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 103–110.]
 The coronation of Charlemagne as emperor on Christmas Day 800 is regarded as a turning point in medieval history, marking a return of the Western Roman Empire, since the new emperor ruled over much of the area previously controlled by the Western emperors. It also marks a change in Charlemagne's relationship with the Byzantine Empire, as the assumption of the imperial title by the Carolingians asserted their equivalence to the Byzantine state. In 812, as a result of careful and protracted negotiations, the Byzantines acknowledged Charlemagne's title of "emperor" but without recognizing him as a second "emperor of the Romans", or accepting his successors' claim to use his new title.
The coronation of Charlemagne as emperor on Christmas Day 800 is regarded as a turning point in medieval history, marking a return of the Western Roman Empire, since the new emperor ruled over much of the area previously controlled by the Western emperors. It also marks a change in Charlemagne's relationship with the Byzantine Empire, as the assumption of the imperial title by the Carolingians asserted their equivalence to the Byzantine state. In 812, as a result of careful and protracted negotiations, the Byzantines acknowledged Charlemagne's title of "emperor" but without recognizing him as a second "emperor of the Romans", or accepting his successors' claim to use his new title.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 109–111] The empire was administered by an itinerant court that travelled with the emperor, as well as approximately 300 imperial officials called count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New Yor ...
s, who administered the counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
the empire had been divided into.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 302] The central administration supervised the counts through imperial emissaries called '' missi dominici'', who served as roving inspectors and troubleshooters. The clerics of the royal chapel were responsible for recording important royal grants and decisions.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' p. 306]
Carolingian Renaissance
Charlemagne's court in Aachen was the centre of the cultural revival sometimes referred to as the "Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the Christian Roman Empire of t ...
". Literacy increased, as did development in the arts, architecture and jurisprudence, as well as liturgical and scriptural studies. The English monk Alcuin
Alcuin of York (; la, Flaccus Albinus Alcuinus; 735 – 19 May 804) – also called Ealhwine, Alhwin, or Alchoin – was a scholar, clergyman, poet, and teacher from York, Northumbria. He was born around 735 and became the student o ...
(d. 804) was invited to Aachen and brought the education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. ...
available in the monasteries of Northumbria. Charlemagne's chancery
Chancery may refer to:
Offices and administration
* Chancery (diplomacy), the principal office that houses a diplomatic mission or an embassy
* Chancery (medieval office), responsible for the production of official documents
* Chancery (Scotlan ...
—or writing office—made use of a new script
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of ha ...
today known as Carolingian minuscule
Carolingian minuscule or Caroline minuscule is a script which developed as a calligraphic standard in the medieval European period so that the Latin alphabet of Jerome's Vulgate Bible could be easily recognized by the literate class from on ...
, allowing a common writing style that advanced communication across much of Europe. Charlemagne sponsored changes in Christian liturgy, church liturgy, imposing the Roman form of church service on his domains, as well as the Gregorian chant in liturgical music for the churches. An important activity for scholars during this period was the copying, correcting, and dissemination of basic works on religious and secular topics, with the aim of encouraging learning. New works on religious topics and schoolbooks were also produced.[Colish ''Medieval Foundations'' pp. 66–70] Linguistics, Grammarians of the period modified the Latin language, changing it from the Classical Latin of the Roman Empire into a more flexible form to fit the needs of the Church and government. By the reign of Charlemagne, the language had so diverged from the classical Latin that it was later called Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used f ...
.[Loyn "Language and dialect" ''Middle Ages'' p. 204]
Breakup of the Carolingian Empire
Charlemagne continued the Frankish tradition of dividing his empire between all his sons, but only one son, Louis the Pious (r. 814–840), was still alive by 813. Just before Charlemagne died in 814, he made Louis co-emperor. Louis's reign of 26 years was marked by numerous divisions of the empire among his sons. Initially, Louis promised the bulk of his empire to his eldest son (d. 855) and invested him as co-emperor. He granted two marginal provinces, Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine and Duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria to his younger sons Pepin I of Aquitaine, Pepin (d. 838) and Louis the German (d. 876), while Lothair received the Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), Kingdom of Italy from him. When his second wife Judith of Bavaria (died 843), Judith (d. 843) gave birth to a fourth son Charles the Bald (d. 877), Louis decided to revise his previous plans about the division of the empire. This led to civil wars between various alliances of father and sons over the control of various parts of the empire. When Pepin died, Louis forged an alliance between Lothair and Charles by proposing to divide the empire into two nearly equal parts between them, and leaving only Bavaria to the middle child, Louis, but Lothair's claim to suzerainty over his younger brothers caused a new civil war after their father's death.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 318–330]
By the Treaty of Verdun (843), a kingdom between the Rhine and Rhone rivers was created for Lothair to go with his lands in Italy, and his imperial title was recognised. Louis the German was in control of Bavaria and the eastern lands in modern-day Germany. Charles the Bald received the western Frankish lands, comprising most of modern-day France.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. xxvi–xxvii, 396] Charlemagne's grandsons and great-grandsons divided their kingdoms between their descendants, eventually causing all internal cohesion to be lost.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' p. 139] There was a brief re-uniting of the empire by Charles the Fat in 884, although the actual units of the empire were not merged and retained their separate administrations. Charles was deposed in 887 and died in January 888.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 356–358] By that time, the Carolingians were close to extinction, and non-dynastic claimants assumed power in most of the successor states, such as Odo of France, Odo of Paris (r. 888–898) in West Francia, and the rival kings Berengar I of Italy, Berengar of Friuli (r. 888–924) and Guy III of Spoleto, Guy of Spoleto (r. 889–894) in Italy.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 401–403] In the eastern lands the dynasty died out with the death of Louis the Child (r. 899–911), and the selection of the Duchy of Franconia, Franconian duke Conrad I of Germany, Conrad I (r. 911–918) as king.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', p. 254] In West Francia the dynasty was restored first in 898, then in 936, but the last Carolingian kings were unable to keep the powerful aristocracy under control. In 987 the dynasty was replaced, with the crowning of Hugh Capet (r. 987–996) as king.[
Frankish culture and the Carolingian methods of state administration had a significant impact on the neighboring peoples, and Frankish threat triggered the formation of new states along the empire's eastern frontier—Duchy of Bohemia, Bohemia in the shelter of the Bohemian Forest, Great Moravia, Moravia along the Middle Danube, and Duchy of Croatia, Croatia on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic coast.][Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 488–489] The breakup of the Carolingian Empire was accompanied by invasions, migrations, and raids by external foes. The Atlantic and northern shores were harassed by the Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
, who also raided the British Isles and settled there. In 911, the Viking chieftain Rollo (d. c. 931) received permission from the Frankish king Charles the Simple (r. 898–922) to settle in what became Normandy. The eastern parts of the Frankish kingdoms, especially Germany and Italy, were under continual Hungarian invasions of Europe, Magyar assault until the invaders' defeat at the Battle of Lechfeld in 955.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 191–199] The breakup of the Abbasid dynasty meant that the Islamic world fragmented into smaller political states, some of which began expanding. The Aghlabids Muslim conquest of Sicily, conquered Sicily, the Umayyads of Al-Andalus annexed the Balearic Islands, and Arab pirates launched regular raids against Italy and southern France.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 394–395]
New kingdoms and Byzantine revival
 The Vikings' settlement in the British Isles led to the formation of new political entities, including the small but militant Kingdom of Dublin in Ireland.
The Vikings' settlement in the British Isles led to the formation of new political entities, including the small but militant Kingdom of Dublin in Ireland.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 350, 365] In Anglo-Saxon England, King Alfred the Great (r. 871–899) came to an agreement with the Great Heathen Army, Danish invaders in 879, acknowledging the existence of an independent Danelaw, Viking realm in Northumbria, East Anglia and eastern Mercia.[Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', p. 196][Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 362–363] By the middle of the 10th century, Alfred's successors had conquered the territory, and restored English control over most of the southern part of Great Britain.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' p. 387] In northern Britain, Kenneth MacAlpin (d. c. 860) united the Picts and the Scottish people, Scots into the Kingdom of Alba.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 169] In the early 10th century, the Ottonian dynasty established itself in Kingdom of Germany, Germany, and was engaged in driving back the Magyars and fighting the Stem duchy, disobedient dukes. After an appeal by the widowed Queen Adelaide of Italy (d. 999) for protection, the German king (r. 936–973) crossed the Alps into Italy, married the young widow and had himself crowned king in Pavia in 951. He demonstrated his claim to Charlemagne's legacy with his coronation as Holy Roman Emperor in Rome in 962.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 394–411] Otto's successors remained keenly interested in Italian affairs but the absent German kings were unable to assert permanent authority over the local aristocracy. France in the Middle Ages, France was more fragmented, and although the Capetian dynasty, Capetian kings remained nominally in charge, much of the political power devolved to the local lords.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 439–444] In the Iberian Peninsula, Asturias expanded slowly south in the 8th and 9th centuries, and continued as the Kingdom of León when the royal centre was moved from the northern Oviedo to León, Spain, León in the 910s.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 376–386]
The Eastern European trade routes towards Central Asia and the Near East were controlled by the Khazars. Their multiethnic empire Arab–Khazar wars, resisted the Muslim expansion, and the Khazar leaders converted to Judaism by the 830s. The Khazars were nominally ruled by a sacred king, the khagan, but the commander-in-chief of his army, the Bey, beg, was the power behind the throne.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 131–134, 141–142] At the end of the 9th century, a new trade route developed, bypassing Khazar territory and connecting Central Asia with Europe across Volga Bulgaria. Here the local elite, and by around 985 the masses of the local population converted to Islam.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 143–151] In Scandinavia, contacts with Francia paved the way for missionary efforts by Christian clergy, and Christianization of Scandinavia, Christianization was closely associated with the growth of centralised kingdoms in History of Denmark, Denmark, History of Norway, Norway, and History of Sweden (800–1521), Sweden. Besides the settlements in the British Isles, and Normandy, Scandinavians also expanded and colonised in eastern and northern Europe. Swedish traders and slave hunters ranged down the rivers of the East European Plain, captured Kyiv from the Khazars, and even attempted to seize Constantinople in Rus'–Byzantine War (860), 860 and Rus'–Byzantine War (907), 907.[Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 366–370] Norse colonists Settlement of Iceland, settled in Iceland, and created a Icelandic Commonwealth, political system that hindered the accumulation of power by ambitious Gothi, chieftains.[Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 476–477]
Byzantium revived its fortunes under Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886) and his successors Leo VI the Wise, Leo VI (r. 886–912) and Constantine VII (r. 913–959), members of the Macedonian dynasty. Commerce revived and the emperors oversaw the extension of a uniform administration to all the provinces. The imperial court was the centre of a revival of classical learning, a process known as the Macedonian Renaissance. Writers such as John Geometres (floruit, fl. early 10th century) composed new hymns, poems, and other works. The military was reorganised, which allowed the emperors John I Tzimiskes, John I (r. 969–976) and Basil II (r. 976–1025) to expand the frontiers of the empire on all fronts.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 318–320] Missionary efforts by both Eastern and Western clergy resulted in the conversion of the Moravians (tribe), Moravians, Danubian Bulgars, Czechs, Poles, Magyars, and the inhabitants of the Kievan Rus'.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 321–326] Moravia fell victim to Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, Magyar invasions around 900, Bulgaria to Byzantine expansionism between Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria, 971 and 1018.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 239–248] After the fall of Moravia, dukes of the Czech Přemyslid dynasty consolidated authority in Bohemia although they had to acknowledge the German kings' suzerainty.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 391–400] In History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Poland, the destruction of old power centres and construction of new strongholds accompanied the formation of state under the Piast dynasty, Piast dukes in the second half of the 10th century.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 343–347] During the same period, the princes of the Árpád dynasty applied extensive violence to crush opposition by rival Magyar chieftains in Principality of Hungary, Hungary.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 334] The Rurik dynasty, Rurikid princes of Kievan Rus' replaced the Khazars as the hegemon power of East Europe's vast forest zones after Rus' people, Rus' raiders sacked the Khazar capital Atil in 965.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 289–300]
Architecture and art
 After the Edict of Milan legalized Christianity, new public places of worship were built in quick succession in Rome, Constantinople and the Holy Land under Constantine the Great. Basilica, Basilicas, large halls that had previously been used for administrative and commercial purposes, were adapted for Christian worship. During his successors' reign, new basilicas were built in the major cities of the Roman world, and even in the post-Roman tribal kingdoms until the mid-6th century. In the late 6th century, Byzantine church architecture adopted an alternative model imitating the rectangular plan and the dome of Justinian's Hagia Sophia. Built in Constantinople after the Nika riots, the Hagia Sophia was the largest single roofed structure of the Roman world. As the spacious basilicas became of little use with the decline of urban centres in the west, they gave way to smaller churches, mainly divided into little chambers. By the beginning of the 8th century, the Carolingian Empire revived the basilica form of architecture. One new standard feature of Carolingian basilicas is the use of a transept, or the "arms" of a T-shaped building that are perpendicular to the long nave. Other new features of religious architecture include the Crossing (architecture), crossing tower and a monumental westwork, entrance to the church, usually at the west end of the building.
Magnificent halls built of timber or stone were the centres of political and social life all over the early Middle Ages. Their design often adopted elements of Late Roman architecture like pilasters (on the exterior walls of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen, palace at Aachen), columns (in the Carolingian Aula regia, royal palace at Ingelheim), and sculptured discs (in the Asturian Santa María del Naranco, kings' palace at Oviedo). In Bulgaria, two splendid palace complexes were built at the royal capital Preslav—one for the tsar (or emperor), and one likely for the Patriarch of All Bulgaria, patriarch. In northern Europe, rural community leaders lived in large, sometimes 40-meter-long wooden houses, but most peasants shared a small wooden or wattle and daub hut with four or five other people. The leaders' houses were divided into multiple rooms, and often included a stable, whereas the peasants' huts had one or two rooms. After the disintegration of the Carolingian Empire, the spread of aristocratic castles indicates a transition from communal fortifications to private defence in western Europe. In this period, most castles were wooden structures but the wealthiest lords could afford the building of stone fortresses. One or more towers, now known as keeps, were the most characteristic features of a medieval fortress. Castles often developed into multifunctional compounds with their drawbridges, fortified courtyards, cisterns or wells, halls, chapels, stables and workshops.
Carolingian art was produced for a small group of figures around the court, and the monasteries and churches they supported. It was dominated by efforts to regain the dignity and classicism of imperial Roman and Byzantine art, but was also influenced by the Insular art of the British Isles. Insular art integrated the energy of Celtic art, Irish Celtic and Anglo-Saxon art, Anglo-Saxon Germanic styles of ornament with Mediterranean forms such as the book, and established many characteristics of art for the rest of the medieval period. Surviving religious works from the Early Middle Ages are mostly illuminated manuscripts and carved Ivory carving#Antiquity and the Early Medieval period, ivories, originally made for metalwork that has since been melted down.
After the Edict of Milan legalized Christianity, new public places of worship were built in quick succession in Rome, Constantinople and the Holy Land under Constantine the Great. Basilica, Basilicas, large halls that had previously been used for administrative and commercial purposes, were adapted for Christian worship. During his successors' reign, new basilicas were built in the major cities of the Roman world, and even in the post-Roman tribal kingdoms until the mid-6th century. In the late 6th century, Byzantine church architecture adopted an alternative model imitating the rectangular plan and the dome of Justinian's Hagia Sophia. Built in Constantinople after the Nika riots, the Hagia Sophia was the largest single roofed structure of the Roman world. As the spacious basilicas became of little use with the decline of urban centres in the west, they gave way to smaller churches, mainly divided into little chambers. By the beginning of the 8th century, the Carolingian Empire revived the basilica form of architecture. One new standard feature of Carolingian basilicas is the use of a transept, or the "arms" of a T-shaped building that are perpendicular to the long nave. Other new features of religious architecture include the Crossing (architecture), crossing tower and a monumental westwork, entrance to the church, usually at the west end of the building.
Magnificent halls built of timber or stone were the centres of political and social life all over the early Middle Ages. Their design often adopted elements of Late Roman architecture like pilasters (on the exterior walls of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen, palace at Aachen), columns (in the Carolingian Aula regia, royal palace at Ingelheim), and sculptured discs (in the Asturian Santa María del Naranco, kings' palace at Oviedo). In Bulgaria, two splendid palace complexes were built at the royal capital Preslav—one for the tsar (or emperor), and one likely for the Patriarch of All Bulgaria, patriarch. In northern Europe, rural community leaders lived in large, sometimes 40-meter-long wooden houses, but most peasants shared a small wooden or wattle and daub hut with four or five other people. The leaders' houses were divided into multiple rooms, and often included a stable, whereas the peasants' huts had one or two rooms. After the disintegration of the Carolingian Empire, the spread of aristocratic castles indicates a transition from communal fortifications to private defence in western Europe. In this period, most castles were wooden structures but the wealthiest lords could afford the building of stone fortresses. One or more towers, now known as keeps, were the most characteristic features of a medieval fortress. Castles often developed into multifunctional compounds with their drawbridges, fortified courtyards, cisterns or wells, halls, chapels, stables and workshops.
Carolingian art was produced for a small group of figures around the court, and the monasteries and churches they supported. It was dominated by efforts to regain the dignity and classicism of imperial Roman and Byzantine art, but was also influenced by the Insular art of the British Isles. Insular art integrated the energy of Celtic art, Irish Celtic and Anglo-Saxon art, Anglo-Saxon Germanic styles of ornament with Mediterranean forms such as the book, and established many characteristics of art for the rest of the medieval period. Surviving religious works from the Early Middle Ages are mostly illuminated manuscripts and carved Ivory carving#Antiquity and the Early Medieval period, ivories, originally made for metalwork that has since been melted down.[Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 18–21, 63–71] Objects in precious metals were the most prestigious form of art, but almost all are lost except for a few crosses such as the Cross of Lothair, several Reliquary, reliquaries, and finds such as the Anglo-Saxon burial at Sutton Hoo and the hoards of Treasure of Gourdon, Gourdon from Merovingian France, Treasure of Guarrazar, Guarrazar from Visigothic Spain and Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós, Nagyszentmiklós near Byzantine territory. There are survivals from the large brooches in Fibula (brooch), fibula or Celtic brooch, penannular form that were a key piece of personal adornment for elites, including the Irish Tara Brooch.[Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 36–42, 49–55, 103, 143, 204–208] Highly decorated books were mostly Gospel Books and these have survived in List of illuminated manuscripts, larger numbers, including the Insular Book of Kells, the Lindisfarne Gospels, Book of Lindisfarne, and the imperial Codex Aureus of St. Emmeram, which is one of the few to retain its "treasure binding" of gold encrusted with jewels. Charlemagne's court seems to have been responsible for the acceptance of figurative monumental sculpture in Christian art, and by the end of the period near life-sized figures such as the Gero Cross were common in important churches.
Military and technology
During the later Roman Empire, the principal military developments were attempts to create an effective cavalry force as well as the continued development of highly specialised types of troops. The creation of heavily armoured cataphract-type soldiers as cavalry was an important feature of the Late Roman military. The various invading tribes had differing emphases on types of soldiers—ranging from the primarily infantry Anglo-Saxon invaders of Britain to the Vandals and Visigoths who had a high proportion of cavalry in their armies. The greatest change in military affairs during the invasion period was the adoption of the Hunnic composite bow in place of the earlier, and weaker, Scythian composite bow. The Avar heavy cavalry introduced the use of stirrups in Europe, and it was adopted by Byzantine cavalrymen before the end of the 6th century. Another development was the increasing use of longswords and the progressive replacement of scale armour by Mail (armour), mail armour and lamellar armour.
The importance of infantry and light cavalry began to decline during the early Carolingian period, with a growing dominance of elite heavy cavalry. Although much of the Carolingian armies were mounted, a large proportion during the early period appear to have been mounted infantry, rather than true cavalry. The use of Conscription, militia-type levies of the free population declined over the Carolingian period. One exception was Anglo-Saxon England, where the armies were still composed of regional levies, known as the ''fyrd'', which were led by the local elites. In military technology, one of the main changes was the return of the crossbow, which had been known in Roman times and reappeared as a military weapon during the last part of the Early Middle Ages.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 80] Stirrups spread in Carolingian Europe from the 9th century, enhancing the effectiveness of the use of weapons by cavalrymen. A technological advance that had implications beyond the military was the horseshoe, which allowed horses to be used in rocky terrain.
High Middle Ages
Society and economy
 The High Middle Ages was a period of tremendous Medieval demography, expansion of population. The estimated population of Europe grew from 35 to 80 million between 1000 and 1347, although the exact causes remain unclear: improved agricultural techniques, assarting (or bringing new lands into production), a Medieval Warm Period, more clement climate and the lack of invasion have all been suggested. Among the agricultural innovations, a more advanced crop rotation system replaced the traditional two-field agriculture in many regions, leaving only one third of the arable land without sowing in each season.
The High Middle Ages was a period of tremendous Medieval demography, expansion of population. The estimated population of Europe grew from 35 to 80 million between 1000 and 1347, although the exact causes remain unclear: improved agricultural techniques, assarting (or bringing new lands into production), a Medieval Warm Period, more clement climate and the lack of invasion have all been suggested. Among the agricultural innovations, a more advanced crop rotation system replaced the traditional two-field agriculture in many regions, leaving only one third of the arable land without sowing in each season.[Jordan ''Europe in the High Middle Ages'' pp. 5–10] Most medieval western thinkers divided the society of their own age into three social class, fundamental classes. These were the clergy, the nobility, and the peasantry (or commoners). In their view, adherence to mainstream Christianity secured social cohesion.
As much as 90 percent of the European population remained rural peasants. Many were no longer settled in isolated farms but had gathered into more defensible small communities, usually known as Manorialism, manors or villages.[ In the system of manorialism, a manor was the basic unit of landholding, and it comprised smaller components, such as parcels held by peasant tenants, and the lord's demesne. Most peasants living in a manor were subject to the manor lord. Slaveholding was declining as churchmen prohibited the enslavement of co-religionists and promoted manumission, but a new form of dependency serfdom supplanted slavery by the late 11th century. Unlike slaves, serfs had legal capacity, and their hereditary status was regulated by agreements with their lords. Restrictions on their activities varied but their freedom of movement was customarily limited, and they usually owed , or labor services, to their lords. Freemen often chose serfdom by submitting themselves to a local strongman's jurisdiction for various reasons, such as protection or the remission of a debt, but there remained free peasants throughout this period and beyond. Serfs and slaves could enhance their status by bringing new lands into cultivation because the lords of uncultivated lands rewarded colonists doing the burdensome work of assarting with freedom.
A special contractual framework, known as ]feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
in modern historiography, regulated fundamental social relations between people of higher status in many parts of Europe. In this system, one party granted property, typically land to the other in return for services, mostly of military nature that the recipient, or vassal, had to render to the grantor, or lord. Although the vassals were not the owners of the land they held in fief from their lords, they could grant parts of it to their own vassals. Not all lands were held in fief. In Germany, inalienable allods remained the dominant forms of landholding. Their owners owed homage (feudal), homage to a higher-ranking aristocrat or the king but their landholding was free of feudal obligations. With the development of heavy cavalry, the previously more or less uniform class of free warriors split into two groups. Those who could equip themselves as mounted knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the G ...
s were integrated into the traditional aristocracy, but others were assimilated into the peasantry. The position of the new aristocracy was stabilized through the adoption of strict inheritance customs. In many areas, lands were no longer divisible between all the heirs as had been the case in the early medieval period. Instead, most lands went to the eldest son in accordance with the newly introduced principle of primogeniture. The dominance of the nobility was built upon its landholding, military service, control of castles, and various immunities from taxes or other impositions. Control of castles provided protection from invaders or rivals, and allowed the aristocrats to defy kings or other overlords. Nobles were stratified. Kings and the highest-ranking nobility controlled large numbers of commoners and large tracts of land, as well as other nobles. Beneath them, lesser aristocrats had authority over smaller areas of land and fewer people, often only commoners. The lowest-ranking nobles did not hold land, and had to serve wealthier aristocrats. Although constituting only about one percent of the population, the nobility was never a closed group: kings could raise commoners to the aristocracy, wealthy commoners could marry into noble families, and impoverished aristocrats sometimes had to give up their privileged status.
The clergy was divided into two types: the secular clergy, who cared for the believers' spiritual needs mainly serving in the parish churches, and the regular clergy, who lived under a religious rule as monks, Canon (clergy), canons or friars. Throughout the period clerics remained a very small proportion of the population, usually about one percent. Although high-ranking clerics, like bishops and canons were mainly appointed from among the aristocracy, church career was a channel for social advancement as clerics were not born into their class but Holy orders, ordained to their office. Church courts had exclusive jurisdiction over marriage affairs, and churchmen supervised several aspects of everyday life. Church authorities supported popular Peace and Truce of God, peace movements forbidding armed conflicts during the holiest seasons of the liturgical year, and offering spiritual protection for serfs, pilgrims, women and children during wartime.
The expansion of population, greater agricultural productivity and relative political stability laid the foundations for the medieval "Commercial Revolution" in the 11th century.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 58] People with surplus cash began investing in commodities like salt, pepper and silk at faraway markets. Rising trade brought new methods of dealing with money, and gold coinage was again minted in Europe, first in Italy and later in France. Accounting methods improved, partly through the use of Double-entry bookkeeping system, double-entry bookkeeping. New forms of commercial contracts emerged, allowing risk to be shared within the framework of partnerships known as or . Bill of exchange, Bills of exchange also appeared, enabling easy transmission of money. As many types of coins were in circulation, money changers facilitated transactions between local and foreign merchants. Loans could also be negotiated with them which gave rise to the development of credit institutions called banks for the money changers' , or benches. As new towns were developing from local commercial centres near fortresses, bridges or harbours, the economic growth brought about a new wave of urbanisation. Kings and aristocrats mainly supported the process in the hope of increased tax revenues. Most urban communities received privileges acknowledging their autonomy but few cities could get rid of all elements of royal or aristocratic control. Townsmen were in a somewhat unusual position, as they did not fit into the traditional three-fold division of society.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 48–49] Throughout the Middle Ages the population of the towns probably never exceeded 10 percent of the total population.[Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 171]
 The Italian maritime republics such as Duchy of Amalfi, Amalfi, Venice, Republic of Genoa, Genoa, and Republic of Pisa, Pisa were the first to profit from the revival of commerce in the Mediterranean. In the north, German merchants established associations known as and took control of the trade routes connecting the British Islands and the Low Countries with Scandinavia and Eastern Europe. Great Fair, trading fairs were established and flourished Champagne fairs, in northern France, allowing Italian and German merchants to trade with each other as well as local merchants. In the late 13th century new land and sea routes to the Far East were pioneered, famously described in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' written by one of the traders, Marco Polo (d. 1324). Economic growth provided opportunities to Jewish merchants to spread all over Europe, mainly with the active support of kings, bishops or aristocrats. Although the Christian rulers appreciated the Jews' contribution to the local economy, many commoners regarded the non-Christian newcomers as an imminent threat to social cohesion. As they could not engage in prestigious trades outside their communities, they often took despised jobs such as ragmen or tax collectors. They were especially active in moneylendering for they could ignore the Christian clerics' condemnation on loan interest. The Jewish moneylenders and pawn brokers reinforced antisemitism, which led to accusations of blasphemy, blood libels, and pogroms. Church authorities' growing concerns about Jewish influence on Christian life inspired segregationist laws, and even their expulsion Edict of Expulsion, from England in 1290.
Women in the Middle Ages were officially required to be subordinate to some male, whether their father, husband, or other kinsman. Women's work generally consisted of household or other domestically inclined tasks such as child-care. Peasant women could supplement the household income by spinning or brewing at home, and they were also expected to help with field-work at harvest-time. Townswomen could engage in trade but often only by right of their husband, and unlike their male competitors, they were not always allowed to train apprentices. Noblewomen could inherit land in the absence of a male heir but their potential to give birth to children was regarded as their principal virtue. The only role open to women in the Church was that of nuns, as they were unable to become priests.
The Italian maritime republics such as Duchy of Amalfi, Amalfi, Venice, Republic of Genoa, Genoa, and Republic of Pisa, Pisa were the first to profit from the revival of commerce in the Mediterranean. In the north, German merchants established associations known as and took control of the trade routes connecting the British Islands and the Low Countries with Scandinavia and Eastern Europe. Great Fair, trading fairs were established and flourished Champagne fairs, in northern France, allowing Italian and German merchants to trade with each other as well as local merchants. In the late 13th century new land and sea routes to the Far East were pioneered, famously described in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' written by one of the traders, Marco Polo (d. 1324). Economic growth provided opportunities to Jewish merchants to spread all over Europe, mainly with the active support of kings, bishops or aristocrats. Although the Christian rulers appreciated the Jews' contribution to the local economy, many commoners regarded the non-Christian newcomers as an imminent threat to social cohesion. As they could not engage in prestigious trades outside their communities, they often took despised jobs such as ragmen or tax collectors. They were especially active in moneylendering for they could ignore the Christian clerics' condemnation on loan interest. The Jewish moneylenders and pawn brokers reinforced antisemitism, which led to accusations of blasphemy, blood libels, and pogroms. Church authorities' growing concerns about Jewish influence on Christian life inspired segregationist laws, and even their expulsion Edict of Expulsion, from England in 1290.
Women in the Middle Ages were officially required to be subordinate to some male, whether their father, husband, or other kinsman. Women's work generally consisted of household or other domestically inclined tasks such as child-care. Peasant women could supplement the household income by spinning or brewing at home, and they were also expected to help with field-work at harvest-time. Townswomen could engage in trade but often only by right of their husband, and unlike their male competitors, they were not always allowed to train apprentices. Noblewomen could inherit land in the absence of a male heir but their potential to give birth to children was regarded as their principal virtue. The only role open to women in the Church was that of nuns, as they were unable to become priests.
Rise of state power
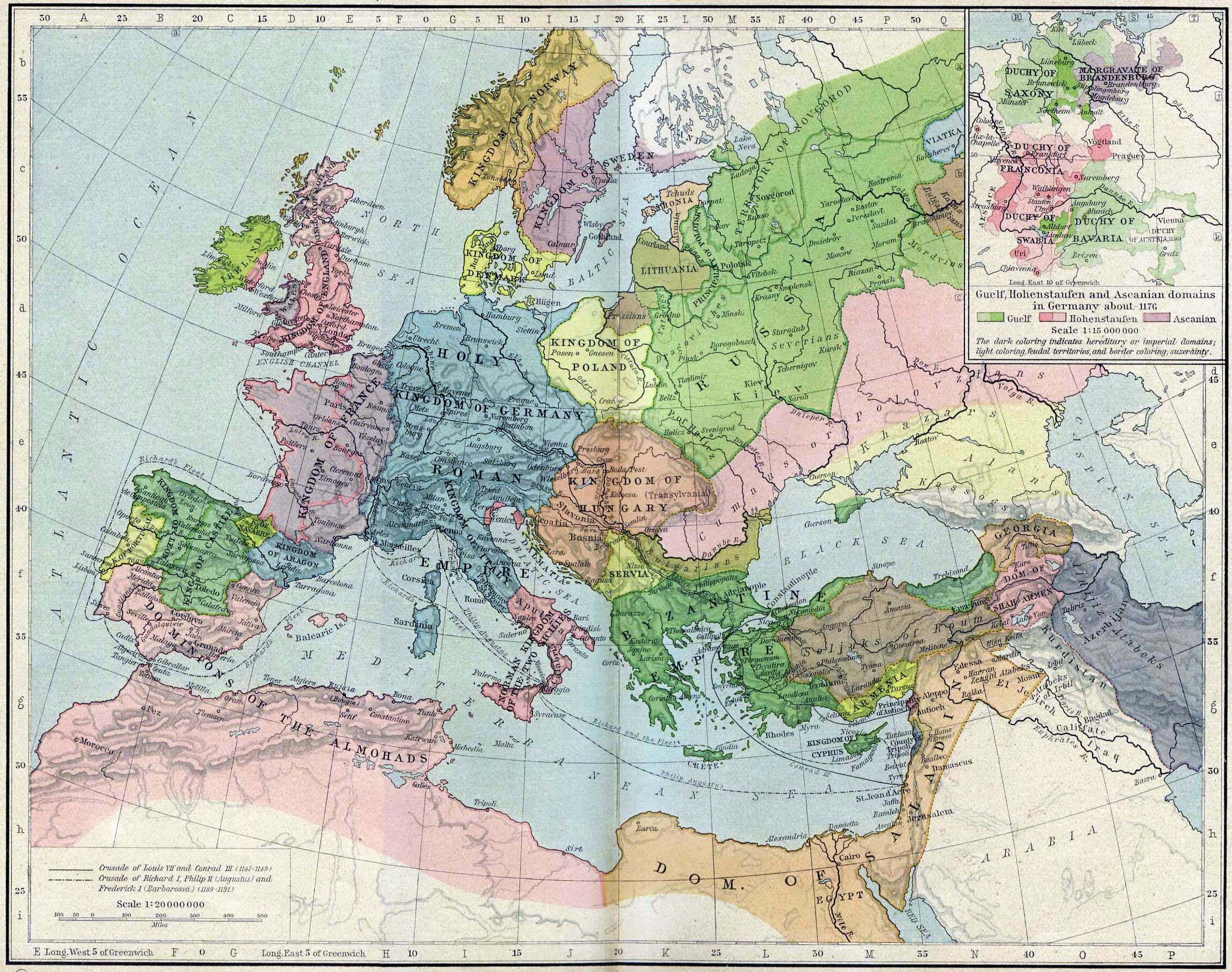 The High Middle Ages saw the development of institutions and traditions that would dominate the European political life till the late 18th century. By the end of the period, representative assemblies came into being in most countries, in kingdoms and city-states alike, that exerted influence on state administration primarily through their control of taxation. The concept of hereditary monarchy was strengthening in parallel with the development of laws governing the inheritance of land. As female succession was recognised, initially mainly in the Mediterranean kingdoms, the first Queen regnant, reigning queens assumed power in this period. The queen mother's claim to assume the regency for her underage son was also widely acknowledged by the end of the 12th century.
The papacy, long attached to an ideology of independence from secular influence, first asserted its claim to temporal authority over the entire Christian world; the Temporal power (papal), Papal Monarchy reached its apogee under the pontificate of (pope 1198–1216). In the Holy Roman Empire, the Ottonians were replaced by the Salian dynasty in 1024, who famously clashed with the papacy under (r. 1056–1105) over Church appointments as part of the Investiture Controversy.
The High Middle Ages saw the development of institutions and traditions that would dominate the European political life till the late 18th century. By the end of the period, representative assemblies came into being in most countries, in kingdoms and city-states alike, that exerted influence on state administration primarily through their control of taxation. The concept of hereditary monarchy was strengthening in parallel with the development of laws governing the inheritance of land. As female succession was recognised, initially mainly in the Mediterranean kingdoms, the first Queen regnant, reigning queens assumed power in this period. The queen mother's claim to assume the regency for her underage son was also widely acknowledged by the end of the 12th century.
The papacy, long attached to an ideology of independence from secular influence, first asserted its claim to temporal authority over the entire Christian world; the Temporal power (papal), Papal Monarchy reached its apogee under the pontificate of (pope 1198–1216). In the Holy Roman Empire, the Ottonians were replaced by the Salian dynasty in 1024, who famously clashed with the papacy under (r. 1056–1105) over Church appointments as part of the Investiture Controversy.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 181–186] During the following centuries, the conflict renewed several times, allowing the northern Italian cities and the German Imperial Estate, ecclesiastic and secular princes to extort considerable concessions from the emperors. Peace of Constance, In 1183, the first emperor from the Hohenstaufen dynasty Frederick I Barbarossa, Barbarossa (r. 1155–90) sanctioned the right of the Italian cities united in the Lombard League to elect their leaders and to regulate a wide spectrum of internal affairs. The German princes' judicial and economic privileges Statutum in favorem principum, were confirmed during the reign of his grandson (r. 1220–50). Frederick, who had grown up in his mother's multicultural Sicilian kingdom, was famed for his erudition and unconventional life style, and associated with the Antichrist by papalist writers. A period of interregnum, or rather civil war, followed the Hohenstaufens' fall in Germany. The tradition of elective monarchy revived, and the right of seven prince-electors to elect the German king was reaffirmed. Rudolf of Habsburg (r. 1273–91), the first king to be elected after the interregnum, realised that he was unable to control the whole empire. Instead, he established a basis for the Habsburgs' future dominance in Central Europe by granting the Duchy of Austria to his sons in 1282.
 Under the Capetian dynasty the French monarchy slowly began to expand its authority over the nobility, growing out of the Île-de-France to exert control over more of the country in the 11th and 12th centuries. They faced a powerful rival in the Duke of Normandy, Dukes of Normandy, who in 1066 under William the Conqueror (r. 1035–87), conquered England and created a cross-Channel empire that lasted, in various forms, throughout the rest of the Middle Ages. Italo-Normans, Norman warbands Norman conquest of southern Italy, seized southern Italy and Sicily from the local Lombard, Byzantine and Muslim rulers. Their hold of the territory Treaty of Melfi, was recognised by the papacy in 1059, and Roger II of Sicily, Roger II (r. 1105–54) united these lands into the Kingdom of Sicily. Under the Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasty of (r. 1154–89) and his son Richard I of England, Richard I (r. 1189–99), the kings of England ruled over Angevin Empire, England and large areas of France. Richard's younger brother John, King of England, John (r. 1199–1216) lost Normandy and the rest of the northern French possessions in 1204 to the French King Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus (r. 1180–1223). This led to dissension among the English nobility, while John's financial exactions to pay for his unsuccessful attempts to regain Normandy led in 1215 to Magna Carta, a charter that confirmed the rights and privileges of free men in England. Under (r. 1216–72), John's son, further concessions were made to the nobility, and royal power was diminished. The French monarchy continued to make gains against the nobility during the late 12th and 13th centuries, bringing more territories within the kingdom under the king's personal rule and centralising the royal administration. Under Louis IX of France, Louis IX (r. 1226–70), royal prestige rose to new heights as Louis served as a mediator for most of Europe.
In Iberia, the Christian states, which had been confined to the northern part of the peninsula, began to push back against the Islamic states in the south, a period known as the ''Reconquista''.
Under the Capetian dynasty the French monarchy slowly began to expand its authority over the nobility, growing out of the Île-de-France to exert control over more of the country in the 11th and 12th centuries. They faced a powerful rival in the Duke of Normandy, Dukes of Normandy, who in 1066 under William the Conqueror (r. 1035–87), conquered England and created a cross-Channel empire that lasted, in various forms, throughout the rest of the Middle Ages. Italo-Normans, Norman warbands Norman conquest of southern Italy, seized southern Italy and Sicily from the local Lombard, Byzantine and Muslim rulers. Their hold of the territory Treaty of Melfi, was recognised by the papacy in 1059, and Roger II of Sicily, Roger II (r. 1105–54) united these lands into the Kingdom of Sicily. Under the Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasty of (r. 1154–89) and his son Richard I of England, Richard I (r. 1189–99), the kings of England ruled over Angevin Empire, England and large areas of France. Richard's younger brother John, King of England, John (r. 1199–1216) lost Normandy and the rest of the northern French possessions in 1204 to the French King Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus (r. 1180–1223). This led to dissension among the English nobility, while John's financial exactions to pay for his unsuccessful attempts to regain Normandy led in 1215 to Magna Carta, a charter that confirmed the rights and privileges of free men in England. Under (r. 1216–72), John's son, further concessions were made to the nobility, and royal power was diminished. The French monarchy continued to make gains against the nobility during the late 12th and 13th centuries, bringing more territories within the kingdom under the king's personal rule and centralising the royal administration. Under Louis IX of France, Louis IX (r. 1226–70), royal prestige rose to new heights as Louis served as a mediator for most of Europe.
In Iberia, the Christian states, which had been confined to the northern part of the peninsula, began to push back against the Islamic states in the south, a period known as the ''Reconquista''.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 345] By about 1150, the Christian north had coalesced into the five major kingdoms of Kingdom of León, León, Kingdom of Castile, Castile, Kingdom of Aragon, Aragon, Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 341] Southern Iberia remained under control of Islamic states, initially under the Caliphate of Córdoba, which broke up in 1031 into a shifting number of petty states known as ''taifas''.[ Although the Almoravid dynasty, Almoravids and the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads, two dynasties from the Maghreb, established centralised rule over Southern Iberia in the 1110s and 1170s respectively, their empires quickly disintegrated. Christian forces advanced again in the early 13th century, culminating in the capture of Seville in 1248.][Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 350–355] New kingdoms such as Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary and Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland, after their conversion to Christianity, became Central European powers.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 365–380] Northern Crusades and the advance of Christian kingdoms and military orders into previously paganism, pagan regions in the Baltic and Finland, Finnic north-east brought the forced assimilation of numerous native peoples into European culture.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 371–372]
With the rise of the Mongol Empire in the Eurasian steppes under Genghis Khan (r. 1206–27), a new expansionist power reached Europe's eastern borderlands. Convinced of their heavenly sanctioned mission to conquer the world, the Mongols used extreme violence to overcome all resistance.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 458–460] Mongol invasion of Europe, Between 1236 and 1242, they conquered Volga Bulgaria, shattered the Kievan Rus' principalities, and laid waste to large regions in Poland, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia and Bulgaria. Their commander-in-chief Batu Khan (r. 1241–56)—a grandson of Genghis Khan—set up his capital at Sarai (city), Sarai on the Volga, establishing the Golden Horde, a Mongol state nominally under the distant Great Khan's authority. The Mongols extracted heavy tribute from the Rus' principalities, and the Rus' princes had to ingratiate themselves with the Mongol khans for economic and political concessions. The Mongol conquest was followed by a peaceful period in Eastern Europe. This facilitated the development of direct trade contacts between Europe and China through newly established Genoese colonies in the Black Sea region.[Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 703–717]
Crusades
 In the 11th century, the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuk Turks took over much of the Middle East, occupying Persia during the 1040s, Armenia in the 1060s, and Jerusalem in 1070. In 1071, the Turkish army defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert and captured the Byzantine Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes, Romanus IV (r. 1068–71). The Turks were then free to invade Asia Minor, which dealt a dangerous blow to the Byzantine Empire by seizing a large part of its population and its economic heartland. Although the Byzantines regrouped and recovered somewhat, they never fully regained Asia Minor and were often on the defensive. The Turks also had difficulties, losing control of Jerusalem to the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimids of Egypt and suffering from a series of internal civil wars.
In the 11th century, the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuk Turks took over much of the Middle East, occupying Persia during the 1040s, Armenia in the 1060s, and Jerusalem in 1070. In 1071, the Turkish army defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert and captured the Byzantine Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes, Romanus IV (r. 1068–71). The Turks were then free to invade Asia Minor, which dealt a dangerous blow to the Byzantine Empire by seizing a large part of its population and its economic heartland. Although the Byzantines regrouped and recovered somewhat, they never fully regained Asia Minor and were often on the defensive. The Turks also had difficulties, losing control of Jerusalem to the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimids of Egypt and suffering from a series of internal civil wars.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 332–333] The Byzantines also faced a revived Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, which in the late 12th and 13th centuries spread throughout the Balkans.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 386–387]
The crusades were intended to seize Jerusalem from Muslim control. The First Crusade was proclaimed by Pope Pope Urban II, Urban II (pope 1088–99) at the Council of Clermont in 1095 in response to a request from the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118) for aid against further Muslim advances. Urban promised indulgence to anyone who took part. Tens of thousands of people from all levels of society mobilised across Europe and captured Jerusalem in 1099.[ One feature of the crusades was the pogroms against local Jews that often took place as the crusaders left their countries for the East. These were especially brutal during the First Crusade,][Loyn "Jews" ''Middle Ages'' p. 191] when the Jewish communities in Cologne, Mainz, and Worms, Germany, Worms were destroyed, as well as other communities in cities between the rivers Seine and the Rhine.[Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 397–399] Another outgrowth of the crusades was the foundation of a new type of monastic order, the Military order (society), military orders of the Knights Templar, Templars and Knights Hospitaller, Hospitallers, which fused monastic life with military service.[
The crusaders consolidated their conquests into crusader states. During the 12th and 13th centuries, there were a series of conflicts between them and the surrounding Islamic states. Appeals from the crusader states to the papacy led to further crusades,][Riley-Smith "Crusades" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 106–107] such as the Third Crusade, called to try to regain Jerusalem, which had been captured by Saladin (d. 1193) in 1187.[Payne ''Dream and the Tomb'' pp. 204–205] In 1203, the Fourth Crusade was diverted from the Holy Land to Constantinople, and captured the city in 1204, setting up a Latin Empire, Latin Empire of Constantinople[Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 156–161] and greatly weakening the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines recaptured the city in 1261, but never regained their former strength.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 299–300] By 1291 all the crusader states had been captured.[Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' p. 122]
Popes called for crusades to take place elsewhere besides the Holy Land: in Spain, southern France, and along the Baltic.[ The Spanish crusades became fused with the ''Reconquista'' of Spain from the Muslims. Although the Templars and Hospitallers took part in the Spanish crusades, similar Spanish military religious orders were founded, most of which had become part of the two main orders of Order of Calatrava, Calatrava and Order of Santiago, Santiago by the beginning of the 12th century.][Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 205–213] Northern Europe also remained outside Christian influence until the 11th century or later, and became a crusading venue as part of the Northern Crusades of the 12th to 14th centuries. These crusades also spawned a military order, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword, Order of the Sword Brothers. Another order, the Teutonic Knights, although founded in the crusader states, focused much of its activity in the Baltic after 1225, and in 1309 moved its headquarters to Malbork Castle, Marienburg in Prussia.[Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 213–224]
Intellectual life
During the 11th century, developments in philosophy and theology led to increased intellectual activity. There was debate between the Philosophical realism, realists and the Nominalism, nominalists over the concept of "Universal (metaphysics), universals". Philosophical discourse was stimulated by the rediscovery of Aristotle and his emphasis on empiricism and rationalism. Scholars such as Peter Abelard (d. 1142) and Peter Lombard (d. 1164) introduced Term logic, Aristotelian logic into theology. In the late 11th and early 12th centuries cathedral schools spread throughout Western Europe, signalling the shift of learning from monasteries to cathedrals and towns.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 232–237] Cathedral schools were in turn replaced by the medieval university, universities established in major European cities.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 247–252] Philosophy and theology fused in scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translat ...
, an attempt by 12th- and 13th-century scholars to reconcile authoritative texts, most notably Aristotle and the Bible. This movement tried to employ a systemic approach to truth and reason[Loyn "Scholasticism" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 293–294] and culminated in the thought of Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
(d. 1274), who wrote the ''Summa Theologica'', or ''Summary of Theology''.[Colish ''Medieval Foundations'' pp. 295–301]
 Chivalry and the ethos of courtly love developed in royal and noble courts. This culture was expressed in the Vernacular, vernacular languages rather than Latin, and comprised poems, stories, legends, and popular songs spread by troubadours, or wandering minstrels. Often the stories were written down in the ''Chanson de geste, chansons de geste'', or "songs of great deeds", such as ''The Song of Roland'' or ''Hildebrand, The Song of Hildebrand''.
Chivalry and the ethos of courtly love developed in royal and noble courts. This culture was expressed in the Vernacular, vernacular languages rather than Latin, and comprised poems, stories, legends, and popular songs spread by troubadours, or wandering minstrels. Often the stories were written down in the ''Chanson de geste, chansons de geste'', or "songs of great deeds", such as ''The Song of Roland'' or ''Hildebrand, The Song of Hildebrand''.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 252–260] Secular and religious histories were also produced.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 349] Geoffrey of Monmouth (d. c. 1155) composed his ''Historia Regum Britanniae'', a collection of stories and legends about King Arthur, Arthur.[Saul ''Companion to Medieval England'' pp. 113–114] Other works were more clearly history, such as Otto of Freising, Otto von Freising's (d. 1158) ''Gesta Friderici Imperatoris'' detailing the deeds of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, or William of Malmesbury's (d. c. 1143) ''Gesta Regum'' on the kings of England.[
Legal studies advanced during the 12th century. Both secular law and canon law, or ecclesiastical law, were studied in the High Middle Ages. Secular law, or Roman law, was advanced greatly by the discovery of the '']Corpus Juris Civilis
The ''Corpus Juris'' (or ''Iuris'') ''Civilis'' ("Body of Civil Law") is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Byzantine Emperor. It is also sometimes referr ...
'' in the 11th century, and by 1100 Roman law was being taught at University of Bologna, Bologna. This led to the recording and standardisation of legal codes throughout Western Europe. Canon law was also studied, and around 1140 a monk named Decretum Gratiani, Gratian (fl. 12th century), a teacher at Bologna, wrote what became the standard text of canon law—the ''Decretum Gratiani, Decretum''.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 237–241]
Among the results of the Greek and Islamic influence on this period in European history was the replacement of Roman numerals with the decimal Positional notation, positional number system and the invention of algebra, which allowed more advanced mathematics. Astronomy advanced following the translation of Ptolemy's ''Almagest'' from Greek into Latin in the late 12th century. Medicine was also studied, especially in southern Italy, where Islamic medicine influenced the Schola Medica Salernitana, school at Salerno.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 241–246]
Technology and military
 In the 12th and 13th centuries, Europe experienced economic growth and innovations in methods of production. Major technological advances included the invention of the windmill, the first mechanical clocks, the manufacture of distilled spirits, and the use of the astrolabe.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, Europe experienced economic growth and innovations in methods of production. Major technological advances included the invention of the windmill, the first mechanical clocks, the manufacture of distilled spirits, and the use of the astrolabe.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' p. 246] Concave spectacles were invented around 1286 by an unknown Italian artisan, probably working in or near Pisa.
The development of a three-field Crop rotation, rotation system for planting crops increased the usage of land from one half in use each year under the old two-field system to two-thirds under the new system, with a consequent increase in production.[ The development of the Plough, heavy plough allowed heavier soils to be farmed more efficiently, aided by the spread of the horse collar, which led to the use of Working animal, draught horses in place of oxen. Horses are faster than oxen and require less pasture, factors that aided the implementation of the three-field system.][Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 156–159] Legumes – such as peas, beans, or lentils – were grown more widely as crops, in addition to the usual cereal crops of wheat, oats, barley, and rye.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 80]
The construction of cathedrals and castles advanced building technology, leading to the development of large stone buildings. Ancillary structures included new town halls, houses, bridges, and tithe barns.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 68] Shipbuilding improved with the use of the Boat building, rib and plank method rather than the old Roman system of mortise and tenon. Other improvements to ships included the use of lateen sails and the rudder#Medieval Europe, stern-post rudder, both of which increased the speed at which ships could be sailed.[Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 73]
In military affairs, the use of infantry with specialised roles increased. Along with the still-dominant heavy cavalry, armies often included mounted and infantry crossbowmen, as well as sappers and engineers.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 125] Crossbows, which had been known in Late Antiquity, increased in use partly because of the increase in siege warfare in the 10th and 11th centuries.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 130] Gunpowder was known in Europe by the mid-13th century with a recorded use in European warfare by the English against the Scots in 1304, although it was merely used as an explosive and not as a weapon. Cannon were being used for sieges in the 1320s, and hand-held guns were in use by the 1360s.[
]
Architecture, art, and music
 In the 10th century the establishment of churches and monasteries led to the development of stone architecture that elaborated vernacular Roman forms, from which the term "Romanesque" is derived. Where available, Roman brick and stone buildings were recycled for their materials. From the tentative beginnings known as the First Romanesque, the style flourished and spread across Europe in a remarkably homogeneous form. Just before 1000 there was a great wave of building stone churches all over Europe.
In the 10th century the establishment of churches and monasteries led to the development of stone architecture that elaborated vernacular Roman forms, from which the term "Romanesque" is derived. Where available, Roman brick and stone buildings were recycled for their materials. From the tentative beginnings known as the First Romanesque, the style flourished and spread across Europe in a remarkably homogeneous form. Just before 1000 there was a great wave of building stone churches all over Europe.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 55] Romanesque architecture, Romanesque buildings have massive stone walls, openings topped by semi-circular arches, small windows, and, particularly in France, arched stone vaults.[Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 181–189] The large Portal (architecture), portal with coloured sculpture in Relief, high relief became a central feature of façades, especially in France, and the Capital (architecture), capitals of columns were often carved with narrative scenes of imaginative monsters and animals.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 58–60, 65–66, 73–75] According to art historian Charles Reginald Dodwell, C. R. Dodwell, "virtually all the churches in the West were decorated with wall-paintings", of which few survive.[Dodwell ''Pictorial Arts of the West'' p. 37] Simultaneous with the development in church architecture, the distinctive European form of the castle was developed and became crucial to politics and warfare.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 295–299]
Romanesque art, especially metalwork, was at its most sophisticated in Mosan art, in which distinct artistic personalities including Nicholas of Verdun (d. 1205) become apparent, and an almost Ancient Greek art, classical style is seen in works such as a Baptismal font at St Bartholomew's Church, Liège, font at Liège,[Lasko ''Ars Sacra'' pp. 240–250] contrasting with the writhing animals of the exactly contemporary Gloucester Candlestick. Large illuminated bibles and psalters were the typical forms of luxury manuscripts, and wall-painting flourished in churches, often following a scheme with a ''Last Judgment, Last Judgement'' on the west wall, a Christ in Majesty at the east end, and narrative biblical scenes down the nave, or in the best surviving example, at Abbey Church of Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, on the Barrel vault, barrel-vaulted roof.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 91–92]
 From the early 12th century, French builders developed the Gothic architecture, Gothic style, marked by the use of rib vaults, Ogive, pointed arches, flying buttresses, and large stained glass windows. It was used mainly in churches and cathedrals and continued in use until the 16th century in much of Europe. Classic examples of Gothic architecture include Chartres Cathedral and Reims Cathedral in France as well as Salisbury Cathedral in England.
From the early 12th century, French builders developed the Gothic architecture, Gothic style, marked by the use of rib vaults, Ogive, pointed arches, flying buttresses, and large stained glass windows. It was used mainly in churches and cathedrals and continued in use until the 16th century in much of Europe. Classic examples of Gothic architecture include Chartres Cathedral and Reims Cathedral in France as well as Salisbury Cathedral in England.[Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 195–216] Stained glass became a crucial element in the design of churches, which continued to use extensive wall-paintings, now almost all lost.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 185–190; 269–271]
During this period the practice of manuscript illumination gradually passed from monasteries to lay workshops, so that according to Janetta Benton "by 1300 most monks bought their books in shops",[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 250] and the book of hours developed as a form of devotional book for lay-people. Metalwork continued to be the most prestigious form of art, with Limoges enamel a popular and relatively affordable option for objects such as reliquaries and crosses.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 135–139, 245–247] In Italy the innovations of Cimabue and Duccio, followed by the Trecento master Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/ Proto-Renaissance period. ...
(d. 1337), greatly increased the sophistication and status of panel painting and fresco.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 264–278] Increasing prosperity during the 12th century resulted in greater production of secular art; many ivory carving, carved ivory objects such as gaming-pieces, combs, and small religious figures have survived.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 248–250]
Church life
 Monastic reform became an important issue during the 11th century, as elites began to worry that monks were not adhering to the rules binding them to a strictly religious life. Cluny Abbey, founded in the Mâcon region of France in 909, was established as part of the Cluniac Reforms, a larger movement of monastic reform in response to this fear.
Monastic reform became an important issue during the 11th century, as elites began to worry that monks were not adhering to the rules binding them to a strictly religious life. Cluny Abbey, founded in the Mâcon region of France in 909, was established as part of the Cluniac Reforms, a larger movement of monastic reform in response to this fear.[Rosenwein ''Rhinoceros Bound'' pp. 40–41] Cluny quickly established a reputation for austerity and rigour. It sought to maintain a high quality of spiritual life by placing itself under the protection of the papacy and by electing its own abbot without interference from laymen, thus maintaining economic and political independence from local lords.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 143–144]
Monastic reform inspired change in the secular Church. The ideals upon which it was based were brought to the papacy by Pope Pope Leo IX, Leo IX (pope 1049–1054), and provided the ideology of clerical independence that led to the Investiture Controversy in the late 11th century. This involved Pope Pope Gregory VII, Gregory VII (pope 1073–85) and Emperor Henry IV, who initially clashed over episcopal appointments, a dispute that turned into a battle over the ideas of investiture, clerical marriage, and simony. The emperor saw the protection of the Church as one of his responsibilities as well as wanting to preserve the right to appoint his own choices as bishops within his lands, but the papacy insisted on the Church's independence from secular lords. These issues remained unresolved after the compromise of 1122 known as the Concordat of Worms. The dispute represents a significant stage in the creation of a papal monarchy separate from and equal to laity, lay authorities. It also had the permanent consequence of empowering German princes at the expense of the German emperors.[
] The High Middle Ages was a period of great religious movements. Besides the Crusades and monastic reforms, people sought to participate in new forms of religious life. New monastic orders were founded, including the Carthusians and the Cistercians. The latter, in particular, expanded rapidly in their early years under the guidance of Bernard of Clairvaux (d. 1153). These new orders were formed in response to the feeling of the laity that Benedictine monasticism no longer met the needs of the laymen, who along with those wishing to enter the religious life wanted a return to the simpler hermit, hermetical monasticism of early Christianity, or to live an Apostles in the New Testament, Apostolic life.
The High Middle Ages was a period of great religious movements. Besides the Crusades and monastic reforms, people sought to participate in new forms of religious life. New monastic orders were founded, including the Carthusians and the Cistercians. The latter, in particular, expanded rapidly in their early years under the guidance of Bernard of Clairvaux (d. 1153). These new orders were formed in response to the feeling of the laity that Benedictine monasticism no longer met the needs of the laymen, who along with those wishing to enter the religious life wanted a return to the simpler hermit, hermetical monasticism of early Christianity, or to live an Apostles in the New Testament, Apostolic life.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 145–149] Christian pilgrimage, Religious pilgrimages were also encouraged. Old pilgrimage sites such as Rome, Jerusalem, and Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, Compostela received increasing numbers of visitors, and new sites such as Sanctuary of Monte Sant'Angelo, Monte Gargano and Basilica di San Nicola, Bari rose to prominence.[Morris "Northern Europe" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 199]
In the 13th century mendicant orders—the Franciscans and the Dominican Order, Dominicans—who swore vows of poverty and earned their living by begging, were approved by the papacy.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 155–167] Religious groups such as the Waldensians and the Humiliati also attempted to return to the life of early Christianity in the middle 12th and early 13th centuries, another heretical movement condemned by the papacy. Others joined the Catharism, Cathars, another movement condemned as heretical by the papacy. In 1209, a crusade was preached against the Cathars, the Albigensian Crusade, which in combination with the medieval Inquisition, eliminated them.[Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 185–192]
Late Middle Ages
War, famine, and plague
The first years of the 14th century were marked by famines, culminating in the Great Famine of 1315–1317, Great Famine of 1315–17.[Loyn "Famine" ''Middle Ages'' p. 128] The causes of the Great Famine included the slow transition from the Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP), also known as the Medieval Climate Optimum or the Medieval Climatic Anomaly, was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region that lasted from to . Climate proxy records show peak warmth occurred at diffe ...
to the Little Ice Age, which left the population vulnerable when bad weather caused agricultural crises.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 373–374] The years 1313–14 and 1317–21 were excessively rainy throughout Europe, resulting in widespread crop failures.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' p. 41] The climate change—which resulted in a declining average annual temperature for Europe during the 14th century—was accompanied by an economic downturn.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' p. 370]
 These troubles were followed in 1347 by the Black Death, a pandemic that spread throughout Europe during the following three years.
These troubles were followed in 1347 by the Black Death, a pandemic that spread throughout Europe during the following three years.[Schove "Plague" ''Middle Ages'' p. 269] The death toll was probably about 35 million people in Europe, about one-third of the population. Towns were especially hard-hit because of their crowded conditions. Large areas of land were left sparsely inhabited, and in some places fields were left unworked. Wages rose as landlords sought to entice the reduced number of available workers to their fields. Further problems were lower rents and lower demand for food, both of which cut into agricultural income. Urban workers also felt that they had a right to greater earnings, and Popular revolt in late-medieval Europe, popular uprisings broke out across Europe.[Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 374–380] Among the uprisings were the ''jacquerie'' in France, the Peasants' Revolt in England, and revolts in the cities of Florence in Italy and Ghent and Bruges in Flanders. The trauma of the plague led to an increased piety throughout Europe, manifested by the foundation of new charities, the self-mortification of the flagellants, and the Black Death Jewish persecutions, scapegoating of Jews.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 412–413] Conditions were further unsettled by the return of the plague throughout the rest of the 14th century; it continued to strike Europe periodically during the rest of the Middle Ages.[
These dire conditions resulted in an increase of interpersonal violence in most parts of Europe. Population increase, religious intolerance, famine and disease led to an increase in violent acts in vast parts of the medieval society. One exception to this was Northeastern Europe, North-Eastern Europe, whose population managed to maintain low levels of violence due to a more organized society resulting from extensive and successful trade.
]
Society and economy
Society throughout Europe was disturbed by the dislocations caused by the Black Death. Lands that had been marginally productive were abandoned, as the survivors were able to acquire more fertile areas.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 184–185] Although serfdom declined in Western Europe it became more common in Eastern Europe, as landlords imposed it on those of their tenants who had previously been free.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 246–247] Most peasants in Western Europe managed to change the work they had previously owed to their landlords into cash rents.[ The percentage of serfs amongst the peasantry declined from a high of 90 to closer to 50 percent by the end of the period.][Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 8] Landlords also became more conscious of common interests with other landholders, and they joined to extort privileges from their governments. Partly at the urging of landlords, governments attempted to legislate a return to the economic conditions that existed before the Black Death.[Keen ''Pelican History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 234–237] Non-clergy became increasingly literate, and urban populations began to imitate the nobility's interest in chivalry.[Vale "Civilization of Courts and Cities" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 346–349]
Jewish communities were Edict of Expulsion, expelled from England in 1290 and from History of the Jews in France#The Great Exile of 1306, France in 1306. Although some were allowed back into France, most were not, and many Jews emigrated eastwards, History of the Jews in Poland#Early history: 966–1385, settling in Poland and Hungary.[Loyn "Jews" ''Middle Ages'' p. 192] The Jews were expelled from Alhambra Decree, Spain in 1492, and dispersed to Turkey, France, Italy, and Holland.[ The History of banking#Medieval Europe, rise of banking in Italy during the 13th century continued throughout the 14th century, fuelled partly by the increasing warfare of the period and the needs of the papacy to move money between kingdoms. Many banking firms loaned money to royalty, at great risk, as some were bankrupted when kings defaulted on their loans.][Keen ''Pelican History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 237–239]
State resurgence
 Strong, royalty-based nation states rose throughout Europe in the Late Middle Ages, particularly in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of France, France, and the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula: Crown of Aragon, Aragon, Crown of Castile, Castile, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal. The long conflicts of the period strengthened royal control over their kingdoms and were extremely hard on the peasantry. Kings profited from warfare that extended royal legislation and increased the lands they directly controlled.
Strong, royalty-based nation states rose throughout Europe in the Late Middle Ages, particularly in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of France, France, and the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula: Crown of Aragon, Aragon, Crown of Castile, Castile, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal. The long conflicts of the period strengthened royal control over their kingdoms and were extremely hard on the peasantry. Kings profited from warfare that extended royal legislation and increased the lands they directly controlled.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 201–219] Paying for the wars required that methods of taxation become more effective and efficient, and the rate of taxation often increased.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 224–233] The requirement to obtain the consent of taxpayers allowed representative bodies such as the Parliament of England, English Parliament and the Estates General (France), French Estates General to gain power and authority.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 233–238]
 Throughout the 14th century, French kings sought to expand their influence at the expense of the territorial holdings of the nobility.
Throughout the 14th century, French kings sought to expand their influence at the expense of the territorial holdings of the nobility.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 166] They ran into difficulties when attempting to confiscate the holdings of the English kings in southern France, leading to the Hundred Years' War,[Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 169] waged from 1337 to 1453.[Loyn "Hundred Years' War" ''Middle Ages'' p. 176] Early in the war the English under Edward III of England, Edward III (r. 1327–77) and his son Edward, the Black Prince (d. 1376), won the battles of Battle of Crécy, Crécy and Battle of Poitiers, Poitiers, captured the city of Calais, and won control of much of France. The resulting stresses almost caused the disintegration of the French kingdom during the early years of the war.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 180–181] In the early 15th century, France again came close to dissolving, but in the late 1420s the military successes of Joan of Arc (d. 1431) led to the victory of the French and the capture of the last English possessions in southern France in 1453.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 317–322] The price was high, as the population of France at the end of the Wars was likely half what it had been at the start of the conflict. Conversely, the Wars had a positive effect on English national identity, doing much to fuse the various local identities into a national English ideal. The conflict with France also helped create a national culture in England separate from French culture, which had previously been the dominant influence.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 423] The dominance of the English longbow began during early stages of the Hundred Years' War,[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 186] and cannon appeared on the battlefield at Crécy in 1346.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' pp. 296–298]
In modern-day Germany, the Holy Roman Empire continued to rule, but the elective nature of the imperial crown meant there was no enduring dynasty around which a strong state could form.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 170–171] Further east, the kingdoms of Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Poland, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia grew powerful.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 173–175] In Iberia, the Christian kingdoms continued to gain land from the Muslim kingdoms of the peninsula;[Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 173] Portugal concentrated on expanding overseas during the 15th century, while the other kingdoms were riven by difficulties over royal succession and other concerns.[Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 327–332][Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 340] After losing the Hundred Years' War, England went on to suffer a long civil war known as the Wars of the Roses, which lasted into the 1490s[ and only ended when Henry VII of England, Henry Tudor (r. 1485–1509 as Henry VII) became king and consolidated power with his victory over Richard III of England, Richard III (r. 1483–85) at Battle of Bosworth Field, Bosworth in 1485.][Davies ''Europe'' pp. 425–426] In Scandinavia, Margaret I of Denmark (r. in Denmark 1387–1412) consolidated Norway, Denmark, and Sweden in the Kalmar Union, Union of Kalmar, which continued until 1523. The major power around the Baltic Sea was the Hanseatic League, a commercial confederation of city-states that traded from Western Europe to Russia.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 431] Scotland emerged from English domination under Robert the Bruce (r. 1306–29), who secured papal recognition of his kingship in 1328.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 408–409]
Collapse of Byzantium and rise of the Ottomans
Although the Palaiologos emperors recaptured Constantinople from the Western Europeans in 1261, they were never able to regain control of much of the former imperial lands. They usually controlled only a small section of the Balkan Peninsula near Constantinople, the city itself, and some coastal lands on the Black Sea and around the Aegean Sea. The former Byzantine lands in the Balkans were divided between the new Kingdom of Serbia (medieval), Kingdom of Serbia, the Second Bulgarian Empire and the city-state of Republic of Venice, Venice. The power of the Byzantine emperors was threatened by a new Turkish tribe, the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, who established themselves in Anatolia in the 13th century and Byzantine–Ottoman Wars, steadily expanded throughout the 14th century. The Ottomans expanded into Europe, reducing Bulgaria to a vassal state by 1366 and taking over Serbia after its defeat at the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. Western Europeans rallied to the plight of the Christians in the Balkans and declared a new crusade in 1396; a great army was sent to the Balkans, where it was defeated at the Battle of Nicopolis.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 385–389] Constantinople was finally Fall of Constantinople, captured by the Ottomans in 1453.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 446] The Ottoman Empire's ever more aggressive policy of conquest became a horror for the Christendom, Christian world.
Controversy within the Church
 During the tumultuous 14th century, disputes within the leadership of the Church led to the Avignon Papacy of 1309–76,
During the tumultuous 14th century, disputes within the leadership of the Church led to the Avignon Papacy of 1309–76,[Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 170–171] also called the "Babylonian Captivity of the Papacy" (a reference to the Babylonian captivity of the Jews),[Loyn "Avignon" ''Middle Ages'' p. 45] and then to the Western Schism, Great Schism, lasting from 1378 to 1418, when there were two and later three rival popes, each supported by several states.[Loyn "Great Schism" ''Middle Ages'' p. 153] Ecclesiastical officials convened at the Council of Constance in 1414, and in the following year the council deposed one of the rival popes, leaving only two claimants. Further depositions followed, and in November 1417, the council elected Pope Martin V, Martin V (pope 1417–31) as pope.[Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 184–187]
Besides the schism, the Western Church was riven by theological controversies, some of which turned into heresies. John Wycliffe (d. 1384), an English theologian, was condemned as a heretic in 1415 for teaching that the laity should have access to the text of the Bible as well as for holding views on the Eucharist that were contrary to Church doctrine.[Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 197–199] Wycliffe's teachings influenced two of the major heretical movements of the later Middle Ages: Lollardy in England and Hussites, Hussitism in Bohemia.[Thomson ''Western Church'' p. 218] The Bohemian movement initiated with the teaching of Jan Hus, who was burned at the stake in 1415, after being condemned as a heretic by the Council of Constance. The Hussite Church, although the target of a crusade, survived beyond the Middle Ages.[Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 213–217] Other heresies were manufactured, such as the accusations against the Knights Templar that resulted in their suppression in 1312, and the division of their great wealth between the French King Philip IV of France, Philip IV (r. 1285–1314) and the Hospitallers.[Loyn "Knights of the Temple (Templars)" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 201–202]
The papacy further refined the practice in the Mass (liturgy), Mass in the Late Middle Ages, holding that the clergy alone was allowed to partake of the wine in the Eucharist. This further distanced the secular laity from the clergy. The laity continued the practices of pilgrimages, veneration of relics, and belief in the power of the Devil. Mystics such as Meister Eckhart (d. 1327) and Thomas à Kempis (d. 1471) wrote works that taught the laity to focus on their inner spiritual life, which laid the groundwork for the Protestant Reformation. Besides mysticism, belief in witches and witchcraft became widespread, and by the late 15th century the Church had begun to lend credence to populist fears of witchcraft with its condemnation of witches in 1484, and the publication in 1486 of the ''Malleus Maleficarum'', the most popular handbook for witch-hunters.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 436–437]
Scholars, intellectuals, and exploration
During the Later Middle Ages, theologians such as Duns Scotus, John Duns Scotus (d. 1308) and William of Ockham (d. c. 1348)[ led a reaction against intellectualist scholasticism, objecting to the application of reason to faith. Their efforts undermined the prevailing Platonic idealism, Platonic idea of universals. Ockham's insistence that reason operates independently of faith allowed science to be separated from theology and philosophy.][Davies ''Europe'' pp. 433–434] Legal studies were marked by the steady advance of Roman law into areas of jurisprudence previously governed by Custom (law), customary law. The lone exception to this trend was in England, where the common law remained pre-eminent. Other countries codified their laws; legal codes were promulgated in Castile, Poland, and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 438–439]
 Education remained mostly focused on the training of future clergy. The basic learning of the letters and numbers remained the province of the family or a village priest, but the secondary subjects of the trivium—grammar, rhetoric, logic—were studied in cathedral schools or in schools provided by cities. Commercial secondary schools spread, and some Italian towns had more than one such enterprise. Universities also spread throughout Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries. Lay literacy rates rose, but were still low; one estimate gave a literacy rate of ten percent of males and one percent of females in 1500.
Education remained mostly focused on the training of future clergy. The basic learning of the letters and numbers remained the province of the family or a village priest, but the secondary subjects of the trivium—grammar, rhetoric, logic—were studied in cathedral schools or in schools provided by cities. Commercial secondary schools spread, and some Italian towns had more than one such enterprise. Universities also spread throughout Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries. Lay literacy rates rose, but were still low; one estimate gave a literacy rate of ten percent of males and one percent of females in 1500.[Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 224]
The publication of vernacular literature increased, with Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His '' Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ...
(d. 1321), Petrarch and Boccaccio in 14th-century Italy, Geoffrey Chaucer (d. 1400) and William Langland (d. c. 1386) in England, and François Villon (d. 1464) and Christine de Pizan (d. c. 1430) in France. Much literature remained religious in character, and although a great deal of it continued to be written in Latin, a new demand developed for saints' lives and other devotional tracts in the vernacular languages.[ This was fed by the growth of the ''Devotio Moderna'' movement, most prominently in the formation of the Brethren of the Common Life, but also in the works of German mystics such as Meister Eckhart and Johannes Tauler (d. 1361).][Keen ''Pelican History of Medieval Europe'' pp. 282–283] Theatre also developed in the guise of Mystery play, miracle plays put on by the Church.[ At the end of the period, the development of the printing press in about 1450 led to the establishment of publishing houses throughout Europe by 1500.][Davies ''Europe'' p. 445]
In the early 15th century, the countries of the Iberian Peninsula began to sponsor exploration beyond the boundaries of Europe. Prince Henry the Navigator of Portugal (d. 1460) sent expeditions that discovered the Canary Islands, the Azores, and Cape Verde during his lifetime. After his death, exploration continued; Bartolomeu Dias (d. 1500) went around the Cape of Good Hope in 1486, and Vasco da Gama (d. 1524) sailed around Africa to India in 1498.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 451] The combined Spanish monarchies of Castile and Aragon sponsored the voyage of exploration by Christopher Columbus (d. 1506) in 1492 that led to his discovery of the Americas.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 454–455] The English crown under Henry VII of England, Henry VII sponsored the voyage of John Cabot (d. 1498) in 1497, which landed on Cape Breton Island.[Davies ''Europe'' p. 511]
Technological and military developments
 One of the major developments in the military sphere during the Late Middle Ages was the increased use of infantry and light cavalry.
One of the major developments in the military sphere during the Late Middle Ages was the increased use of infantry and light cavalry.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 180] The English also employed longbowmen, but other countries were unable to create similar forces with the same success.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 183] Armour continued to advance, spurred by the increasing power of crossbows, and plate armour was developed to protect soldiers from crossbows as well as the hand-held guns that were developed.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 188] Pole weapon, Pole arms reached new prominence with the development of the Flemish and Swiss infantry armed with pikes and other long spears.[Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 185]
In agriculture, the increased usage of sheep with long-fibred wool allowed a stronger thread to be spun. In addition, the spinning wheel replaced the traditional distaff for spinning wool, tripling production.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 193–194] A less technological refinement that still greatly affected daily life was the use of buttons as closures for garments, which allowed for better fitting without having to lace clothing on the wearer.[Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 38] Windmills were refined with the creation of the tower mill, allowing the upper part of the windmill to be spun around to face the direction from which the wind was blowing.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 200–201] The blast furnace appeared around 1350 in Sweden, increasing the quantity of iron produced and improving its quality.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 203–204] The first Patent, patent law in 1447 in Venice protected the rights of inventors to their inventions.[Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' p. 213]
Late medieval art and architecture
 The Late Middle Ages in Europe as a whole correspond to the Trecento and Renaissance, Early Renaissance cultural periods in Italy. Northern Europe and Spain continued to use Gothic styles, which became increasingly elaborate in the 15th century, until almost the end of the period. International Gothic was a courtly style that reached much of Europe in the decades around 1400, producing masterpieces such as the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry.
The Late Middle Ages in Europe as a whole correspond to the Trecento and Renaissance, Early Renaissance cultural periods in Italy. Northern Europe and Spain continued to use Gothic styles, which became increasingly elaborate in the 15th century, until almost the end of the period. International Gothic was a courtly style that reached much of Europe in the decades around 1400, producing masterpieces such as the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 253–256] All over Europe secular art continued to increase in quantity and quality, and in the 15th century the mercantile classes of Italy and Flanders became important patrons, commissioning small portraits of themselves in oils as well as a growing range of luxury items such as jewellery, Casket with Scenes of Romances (Walters 71264), ivory caskets, cassone chests, and maiolica pottery. These objects also included the Hispano-Moresque ware produced by mostly Mudéjar potters in Spain. Although royalty owned huge collections of plate, little survives except for the Royal Gold Cup. Italian silk manufacture developed, so that Western churches and elites no longer needed to rely on imports from Byzantium or the Islamic world. In France and Flanders tapestry weaving of sets like ''The Lady and the Unicorn'' became a major luxury industry.[Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 257–262]
The large external sculptural schemes of Early Gothic churches gave way to more sculpture inside the building, as tombs became more elaborate and other features such as pulpits were sometimes lavishly carved, as in the Pulpit of Sant' Andrea, Pistoia (Giovanni Pisano), Pulpit by Giovanni Pisano in Sant'Andrea. Painted or carved wooden relief altarpieces became common, especially as churches created many Chapel, side-chapels. Early Netherlandish painting by artists such as Jan van Eyck (d. 1441) and Rogier van der Weyden (d. 1464) rivalled that of Italy, as did northern illuminated manuscripts, which in the 15th century began to be collected on a large scale by secular elites, who also commissioned secular books, especially histories. From about 1450 printed books rapidly became popular, though still expensive. There were around 30,000 different editions of Incunable, incunabula, or works printed before 1500,[British Library Staff]
Incunabula Short Title Catalogue
''British Library'' by which time illuminated manuscripts were commissioned only by royalty and a few others. Very small woodcuts, nearly all religious, were affordable even by peasants in parts of Northern Europe from the middle of the 15th century. More expensive engravings supplied a wealthier market with a variety of images.[Griffiths ''Prints and Printmaking'' pp. 17–18; 39–46]
Modern perceptions
 The medieval period is frequently caricatured as a "time of ignorance and superstition" that placed "the word of religious authorities over personal experience and rational activity." This is a legacy from both the
The medieval period is frequently caricatured as a "time of ignorance and superstition" that placed "the word of religious authorities over personal experience and rational activity." This is a legacy from both the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
and Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment when scholars favourably contrasted their intellectual cultures with those of the medieval period. Renaissance scholars saw the Middle Ages as a period of decline from the high culture and civilisation of the Classical world. Enlightenment scholars saw reason as superior to faith, and thus viewed the Middle Ages as a time of ignorance and superstition.[Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293]
Others argue that reason was generally held in high regard during the Middle Ages. Science historian Edward Grant writes, "If revolutionary rational thoughts were expressed [in the 18th century], they were only made possible because of the long medieval tradition that established the use of reason as one of the most important of human activities".[Grant ''God and Reason'' p. 9] Also, contrary to common belief, David C. Lindberg, David Lindberg writes, "the late medieval scholar rarely experienced the coercive power of the Church and would have regarded himself as free (particularly in the natural sciences) to follow reason and observation wherever they led".[Quoted in Peters "Science and Religion" ''Encyclopedia of Religion'' p. 8182]
The caricature of the period is also reflected in some more specific notions. One misconception, first propagated in the 19th century[Russell ''Inventing the Flat Earth'' pp. 49–58] and still very common, is that all people in the Middle Ages believed that the Myth of the flat Earth, Earth was flat.[ This is untrue, as lecturers in the medieval universities commonly argued that evidence showed the Earth was a sphere. Lindberg and Ronald Numbers, another scholar of the period, state that there "was scarcely a Christian scholar of the Middle Ages who did not acknowledge [Earth's] sphericity and even know its approximate circumference".][Lindberg and Numbers "Beyond War and Peace" ''Church History'' p. 342] Other misconceptions such as "the Church prohibited autopsies and dissections during the Middle Ages", "the rise of Christianity killed off ancient science", or "the medieval Christian Church suppressed the growth of natural philosophy", are all cited by Numbers as examples of widely popular myths that still pass as historical truth, although they are not supported by historical research.[Numbers]
Myths and Truths in Science and Religion: A historical perspective
''Lecture archive'' Archived 11 October 2017
Notes
Citations
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
De Re Militari: The Society for Medieval Military History
Learning resources from the British Library including studies of beautiful medieval manuscripts.
Medievalists.net
News and articles about the period.
Medieval History Database (MHDB)
* Medieval worlds, Medieval Worlds
Official website
– Comparative and interdisciplinary articles about the period.
The Labyrinth
Resources for Medieval Studies.
{{Subject bar , portal1=Middle Ages , portal2=History , portal3=Europe , portal5=War , commons=y , q=y , s=y
5th century
6th century in Europe
7th century in Europe
8th century in Europe
9th century in Europe
10th century in Europe
11th century in Europe
12th century in Europe
13th century in Europe
14th century in Europe
15th century in Europe
Christianization
Dark ages
Featured articles
Historical eras
History of Europe by period
Middle Ages,
Wikipedia pages semi-protected against vandalism
 In the
In the  In the post-Roman world ethnic identities were flexible, often determined by loyalty to a successful military leader or by religion instead of ancestry or language. Ethnic markers quickly changed—by around 500, Arianism, originally a genuine Roman heresy, was associated with Germanic peoples, and the Goths rarely used their Germanic language outside their churches. The fusion of Roman culture with the customs of the invading tribes is well documented. Popular assemblies that allowed free male tribal members more say in political matters than had been common in the Roman state developed into legislative and judicial bodies.Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 98–101 Material artefacts left by the Romans and the invaders are often similar, and tribal items were often modelled on Roman objects.Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', p. 100 Much of the scholarly and written culture of the new kingdoms was also based on Roman intellectual traditions.Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', pp. 96–97 An important difference was the gradual loss of tax revenue by the new polities. Many of the new political entities no longer supported their armies through taxes, instead relying on granting them land or rents. This meant there was less need for large tax revenues and so the taxation systems decayed.Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 102–103
In the post-Roman world ethnic identities were flexible, often determined by loyalty to a successful military leader or by religion instead of ancestry or language. Ethnic markers quickly changed—by around 500, Arianism, originally a genuine Roman heresy, was associated with Germanic peoples, and the Goths rarely used their Germanic language outside their churches. The fusion of Roman culture with the customs of the invading tribes is well documented. Popular assemblies that allowed free male tribal members more say in political matters than had been common in the Roman state developed into legislative and judicial bodies.Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 98–101 Material artefacts left by the Romans and the invaders are often similar, and tribal items were often modelled on Roman objects.Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', p. 100 Much of the scholarly and written culture of the new kingdoms was also based on Roman intellectual traditions.Collins, ''Early Medieval Europe'', pp. 96–97 An important difference was the gradual loss of tax revenue by the new polities. Many of the new political entities no longer supported their armies through taxes, instead relying on granting them land or rents. This meant there was less need for large tax revenues and so the taxation systems decayed.Wickham, ''Inheritance of Rome'', pp. 102–103
 Among the new peoples filling the political void left by Roman centralised government, the first Germanic groups now collectively known as
Among the new peoples filling the political void left by Roman centralised government, the first Germanic groups now collectively known as  As Western Europe witnessed the formation of new kingdoms, the Eastern Roman Empire remained intact and experienced an economic revival that lasted into the early 7th century. There were fewer invasions of the eastern section of the empire; most occurred in the Balkans. Peace with the Sasanian Empire, the traditional enemy of Rome, lasted throughout most of the 5th century. The Eastern Empire was marked by closer relations between the political state and Christian Church, with doctrinal matters assuming an importance in Eastern politics that they did not have in Western Europe. Legal developments included the codification of
As Western Europe witnessed the formation of new kingdoms, the Eastern Roman Empire remained intact and experienced an economic revival that lasted into the early 7th century. There were fewer invasions of the eastern section of the empire; most occurred in the Balkans. Peace with the Sasanian Empire, the traditional enemy of Rome, lasted throughout most of the 5th century. The Eastern Empire was marked by closer relations between the political state and Christian Church, with doctrinal matters assuming an importance in Eastern politics that they did not have in Western Europe. Legal developments included the codification of  Peasant society is much less documented than the nobility. Most of the surviving information available to historians comes from
Peasant society is much less documented than the nobility. Most of the surviving information available to historians comes from  The idea of Christian unity endured although differences in ideology and practice between the Eastern and Western Churches became apparent by the 6th century. The formation of new realms reinforced the traditional Christian concept of the
The idea of Christian unity endured although differences in ideology and practice between the Eastern and Western Churches became apparent by the 6th century. The formation of new realms reinforced the traditional Christian concept of the  The coronation of Charlemagne as emperor on Christmas Day 800 is regarded as a turning point in medieval history, marking a return of the Western Roman Empire, since the new emperor ruled over much of the area previously controlled by the Western emperors. It also marks a change in Charlemagne's relationship with the Byzantine Empire, as the assumption of the imperial title by the Carolingians asserted their equivalence to the Byzantine state. In 812, as a result of careful and protracted negotiations, the Byzantines acknowledged Charlemagne's title of "emperor" but without recognizing him as a second "emperor of the Romans", or accepting his successors' claim to use his new title.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 109–111 The empire was administered by an itinerant court that travelled with the emperor, as well as approximately 300 imperial officials called
The coronation of Charlemagne as emperor on Christmas Day 800 is regarded as a turning point in medieval history, marking a return of the Western Roman Empire, since the new emperor ruled over much of the area previously controlled by the Western emperors. It also marks a change in Charlemagne's relationship with the Byzantine Empire, as the assumption of the imperial title by the Carolingians asserted their equivalence to the Byzantine state. In 812, as a result of careful and protracted negotiations, the Byzantines acknowledged Charlemagne's title of "emperor" but without recognizing him as a second "emperor of the Romans", or accepting his successors' claim to use his new title.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 109–111 The empire was administered by an itinerant court that travelled with the emperor, as well as approximately 300 imperial officials called  The Vikings' settlement in the British Isles led to the formation of new political entities, including the small but militant Kingdom of Dublin in Ireland.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 350, 365 In Anglo-Saxon England, King Alfred the Great (r. 871–899) came to an agreement with the Great Heathen Army, Danish invaders in 879, acknowledging the existence of an independent Danelaw, Viking realm in Northumbria, East Anglia and eastern Mercia.Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', p. 196Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 362–363 By the middle of the 10th century, Alfred's successors had conquered the territory, and restored English control over most of the southern part of Great Britain.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' p. 387 In northern Britain, Kenneth MacAlpin (d. c. 860) united the Picts and the Scottish people, Scots into the Kingdom of Alba.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 169 In the early 10th century, the Ottonian dynasty established itself in Kingdom of Germany, Germany, and was engaged in driving back the Magyars and fighting the Stem duchy, disobedient dukes. After an appeal by the widowed Queen Adelaide of Italy (d. 999) for protection, the German king (r. 936–973) crossed the Alps into Italy, married the young widow and had himself crowned king in Pavia in 951. He demonstrated his claim to Charlemagne's legacy with his coronation as Holy Roman Emperor in Rome in 962.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 394–411 Otto's successors remained keenly interested in Italian affairs but the absent German kings were unable to assert permanent authority over the local aristocracy. France in the Middle Ages, France was more fragmented, and although the Capetian dynasty, Capetian kings remained nominally in charge, much of the political power devolved to the local lords.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 439–444 In the Iberian Peninsula, Asturias expanded slowly south in the 8th and 9th centuries, and continued as the Kingdom of León when the royal centre was moved from the northern Oviedo to León, Spain, León in the 910s.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 376–386
The Eastern European trade routes towards Central Asia and the Near East were controlled by the Khazars. Their multiethnic empire Arab–Khazar wars, resisted the Muslim expansion, and the Khazar leaders converted to Judaism by the 830s. The Khazars were nominally ruled by a sacred king, the khagan, but the commander-in-chief of his army, the Bey, beg, was the power behind the throne.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 131–134, 141–142 At the end of the 9th century, a new trade route developed, bypassing Khazar territory and connecting Central Asia with Europe across Volga Bulgaria. Here the local elite, and by around 985 the masses of the local population converted to Islam.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 143–151 In Scandinavia, contacts with Francia paved the way for missionary efforts by Christian clergy, and Christianization of Scandinavia, Christianization was closely associated with the growth of centralised kingdoms in History of Denmark, Denmark, History of Norway, Norway, and History of Sweden (800–1521), Sweden. Besides the settlements in the British Isles, and Normandy, Scandinavians also expanded and colonised in eastern and northern Europe. Swedish traders and slave hunters ranged down the rivers of the East European Plain, captured Kyiv from the Khazars, and even attempted to seize Constantinople in Rus'–Byzantine War (860), 860 and Rus'–Byzantine War (907), 907.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 366–370 Norse colonists Settlement of Iceland, settled in Iceland, and created a Icelandic Commonwealth, political system that hindered the accumulation of power by ambitious Gothi, chieftains.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 476–477
Byzantium revived its fortunes under Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886) and his successors Leo VI the Wise, Leo VI (r. 886–912) and Constantine VII (r. 913–959), members of the Macedonian dynasty. Commerce revived and the emperors oversaw the extension of a uniform administration to all the provinces. The imperial court was the centre of a revival of classical learning, a process known as the Macedonian Renaissance. Writers such as John Geometres (floruit, fl. early 10th century) composed new hymns, poems, and other works. The military was reorganised, which allowed the emperors John I Tzimiskes, John I (r. 969–976) and Basil II (r. 976–1025) to expand the frontiers of the empire on all fronts.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 318–320 Missionary efforts by both Eastern and Western clergy resulted in the conversion of the Moravians (tribe), Moravians, Danubian Bulgars, Czechs, Poles, Magyars, and the inhabitants of the Kievan Rus'.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 321–326 Moravia fell victim to Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, Magyar invasions around 900, Bulgaria to Byzantine expansionism between Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria, 971 and 1018.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 239–248 After the fall of Moravia, dukes of the Czech Přemyslid dynasty consolidated authority in Bohemia although they had to acknowledge the German kings' suzerainty.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 391–400 In History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Poland, the destruction of old power centres and construction of new strongholds accompanied the formation of state under the Piast dynasty, Piast dukes in the second half of the 10th century.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 343–347 During the same period, the princes of the Árpád dynasty applied extensive violence to crush opposition by rival Magyar chieftains in Principality of Hungary, Hungary.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 334 The Rurik dynasty, Rurikid princes of Kievan Rus' replaced the Khazars as the hegemon power of East Europe's vast forest zones after Rus' people, Rus' raiders sacked the Khazar capital Atil in 965.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 289–300
The Vikings' settlement in the British Isles led to the formation of new political entities, including the small but militant Kingdom of Dublin in Ireland.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 350, 365 In Anglo-Saxon England, King Alfred the Great (r. 871–899) came to an agreement with the Great Heathen Army, Danish invaders in 879, acknowledging the existence of an independent Danelaw, Viking realm in Northumbria, East Anglia and eastern Mercia.Backman, ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'', p. 196Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 362–363 By the middle of the 10th century, Alfred's successors had conquered the territory, and restored English control over most of the southern part of Great Britain.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' p. 387 In northern Britain, Kenneth MacAlpin (d. c. 860) united the Picts and the Scottish people, Scots into the Kingdom of Alba.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' p. 169 In the early 10th century, the Ottonian dynasty established itself in Kingdom of Germany, Germany, and was engaged in driving back the Magyars and fighting the Stem duchy, disobedient dukes. After an appeal by the widowed Queen Adelaide of Italy (d. 999) for protection, the German king (r. 936–973) crossed the Alps into Italy, married the young widow and had himself crowned king in Pavia in 951. He demonstrated his claim to Charlemagne's legacy with his coronation as Holy Roman Emperor in Rome in 962.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 394–411 Otto's successors remained keenly interested in Italian affairs but the absent German kings were unable to assert permanent authority over the local aristocracy. France in the Middle Ages, France was more fragmented, and although the Capetian dynasty, Capetian kings remained nominally in charge, much of the political power devolved to the local lords.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 439–444 In the Iberian Peninsula, Asturias expanded slowly south in the 8th and 9th centuries, and continued as the Kingdom of León when the royal centre was moved from the northern Oviedo to León, Spain, León in the 910s.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 376–386
The Eastern European trade routes towards Central Asia and the Near East were controlled by the Khazars. Their multiethnic empire Arab–Khazar wars, resisted the Muslim expansion, and the Khazar leaders converted to Judaism by the 830s. The Khazars were nominally ruled by a sacred king, the khagan, but the commander-in-chief of his army, the Bey, beg, was the power behind the throne.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 131–134, 141–142 At the end of the 9th century, a new trade route developed, bypassing Khazar territory and connecting Central Asia with Europe across Volga Bulgaria. Here the local elite, and by around 985 the masses of the local population converted to Islam.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 143–151 In Scandinavia, contacts with Francia paved the way for missionary efforts by Christian clergy, and Christianization of Scandinavia, Christianization was closely associated with the growth of centralised kingdoms in History of Denmark, Denmark, History of Norway, Norway, and History of Sweden (800–1521), Sweden. Besides the settlements in the British Isles, and Normandy, Scandinavians also expanded and colonised in eastern and northern Europe. Swedish traders and slave hunters ranged down the rivers of the East European Plain, captured Kyiv from the Khazars, and even attempted to seize Constantinople in Rus'–Byzantine War (860), 860 and Rus'–Byzantine War (907), 907.Collins ''Early Medieval Europe'' pp. 366–370 Norse colonists Settlement of Iceland, settled in Iceland, and created a Icelandic Commonwealth, political system that hindered the accumulation of power by ambitious Gothi, chieftains.Wickham ''Inheritance of Rome'' pp. 476–477
Byzantium revived its fortunes under Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886) and his successors Leo VI the Wise, Leo VI (r. 886–912) and Constantine VII (r. 913–959), members of the Macedonian dynasty. Commerce revived and the emperors oversaw the extension of a uniform administration to all the provinces. The imperial court was the centre of a revival of classical learning, a process known as the Macedonian Renaissance. Writers such as John Geometres (floruit, fl. early 10th century) composed new hymns, poems, and other works. The military was reorganised, which allowed the emperors John I Tzimiskes, John I (r. 969–976) and Basil II (r. 976–1025) to expand the frontiers of the empire on all fronts.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 318–320 Missionary efforts by both Eastern and Western clergy resulted in the conversion of the Moravians (tribe), Moravians, Danubian Bulgars, Czechs, Poles, Magyars, and the inhabitants of the Kievan Rus'.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 321–326 Moravia fell victim to Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, Magyar invasions around 900, Bulgaria to Byzantine expansionism between Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria, 971 and 1018.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 239–248 After the fall of Moravia, dukes of the Czech Přemyslid dynasty consolidated authority in Bohemia although they had to acknowledge the German kings' suzerainty.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 391–400 In History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Poland, the destruction of old power centres and construction of new strongholds accompanied the formation of state under the Piast dynasty, Piast dukes in the second half of the 10th century.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 343–347 During the same period, the princes of the Árpád dynasty applied extensive violence to crush opposition by rival Magyar chieftains in Principality of Hungary, Hungary.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 334 The Rurik dynasty, Rurikid princes of Kievan Rus' replaced the Khazars as the hegemon power of East Europe's vast forest zones after Rus' people, Rus' raiders sacked the Khazar capital Atil in 965.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 289–300
 After the Edict of Milan legalized Christianity, new public places of worship were built in quick succession in Rome, Constantinople and the Holy Land under Constantine the Great. Basilica, Basilicas, large halls that had previously been used for administrative and commercial purposes, were adapted for Christian worship. During his successors' reign, new basilicas were built in the major cities of the Roman world, and even in the post-Roman tribal kingdoms until the mid-6th century. In the late 6th century, Byzantine church architecture adopted an alternative model imitating the rectangular plan and the dome of Justinian's Hagia Sophia. Built in Constantinople after the Nika riots, the Hagia Sophia was the largest single roofed structure of the Roman world. As the spacious basilicas became of little use with the decline of urban centres in the west, they gave way to smaller churches, mainly divided into little chambers. By the beginning of the 8th century, the Carolingian Empire revived the basilica form of architecture. One new standard feature of Carolingian basilicas is the use of a transept, or the "arms" of a T-shaped building that are perpendicular to the long nave. Other new features of religious architecture include the Crossing (architecture), crossing tower and a monumental westwork, entrance to the church, usually at the west end of the building.
Magnificent halls built of timber or stone were the centres of political and social life all over the early Middle Ages. Their design often adopted elements of Late Roman architecture like pilasters (on the exterior walls of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen, palace at Aachen), columns (in the Carolingian Aula regia, royal palace at Ingelheim), and sculptured discs (in the Asturian Santa María del Naranco, kings' palace at Oviedo). In Bulgaria, two splendid palace complexes were built at the royal capital Preslav—one for the tsar (or emperor), and one likely for the Patriarch of All Bulgaria, patriarch. In northern Europe, rural community leaders lived in large, sometimes 40-meter-long wooden houses, but most peasants shared a small wooden or wattle and daub hut with four or five other people. The leaders' houses were divided into multiple rooms, and often included a stable, whereas the peasants' huts had one or two rooms. After the disintegration of the Carolingian Empire, the spread of aristocratic castles indicates a transition from communal fortifications to private defence in western Europe. In this period, most castles were wooden structures but the wealthiest lords could afford the building of stone fortresses. One or more towers, now known as keeps, were the most characteristic features of a medieval fortress. Castles often developed into multifunctional compounds with their drawbridges, fortified courtyards, cisterns or wells, halls, chapels, stables and workshops.
Carolingian art was produced for a small group of figures around the court, and the monasteries and churches they supported. It was dominated by efforts to regain the dignity and classicism of imperial Roman and Byzantine art, but was also influenced by the Insular art of the British Isles. Insular art integrated the energy of Celtic art, Irish Celtic and Anglo-Saxon art, Anglo-Saxon Germanic styles of ornament with Mediterranean forms such as the book, and established many characteristics of art for the rest of the medieval period. Surviving religious works from the Early Middle Ages are mostly illuminated manuscripts and carved Ivory carving#Antiquity and the Early Medieval period, ivories, originally made for metalwork that has since been melted down.Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 18–21, 63–71 Objects in precious metals were the most prestigious form of art, but almost all are lost except for a few crosses such as the Cross of Lothair, several Reliquary, reliquaries, and finds such as the Anglo-Saxon burial at Sutton Hoo and the hoards of Treasure of Gourdon, Gourdon from Merovingian France, Treasure of Guarrazar, Guarrazar from Visigothic Spain and Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós, Nagyszentmiklós near Byzantine territory. There are survivals from the large brooches in Fibula (brooch), fibula or Celtic brooch, penannular form that were a key piece of personal adornment for elites, including the Irish Tara Brooch.Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 36–42, 49–55, 103, 143, 204–208 Highly decorated books were mostly Gospel Books and these have survived in List of illuminated manuscripts, larger numbers, including the Insular Book of Kells, the Lindisfarne Gospels, Book of Lindisfarne, and the imperial Codex Aureus of St. Emmeram, which is one of the few to retain its "treasure binding" of gold encrusted with jewels. Charlemagne's court seems to have been responsible for the acceptance of figurative monumental sculpture in Christian art, and by the end of the period near life-sized figures such as the Gero Cross were common in important churches.
After the Edict of Milan legalized Christianity, new public places of worship were built in quick succession in Rome, Constantinople and the Holy Land under Constantine the Great. Basilica, Basilicas, large halls that had previously been used for administrative and commercial purposes, were adapted for Christian worship. During his successors' reign, new basilicas were built in the major cities of the Roman world, and even in the post-Roman tribal kingdoms until the mid-6th century. In the late 6th century, Byzantine church architecture adopted an alternative model imitating the rectangular plan and the dome of Justinian's Hagia Sophia. Built in Constantinople after the Nika riots, the Hagia Sophia was the largest single roofed structure of the Roman world. As the spacious basilicas became of little use with the decline of urban centres in the west, they gave way to smaller churches, mainly divided into little chambers. By the beginning of the 8th century, the Carolingian Empire revived the basilica form of architecture. One new standard feature of Carolingian basilicas is the use of a transept, or the "arms" of a T-shaped building that are perpendicular to the long nave. Other new features of religious architecture include the Crossing (architecture), crossing tower and a monumental westwork, entrance to the church, usually at the west end of the building.
Magnificent halls built of timber or stone were the centres of political and social life all over the early Middle Ages. Their design often adopted elements of Late Roman architecture like pilasters (on the exterior walls of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen, palace at Aachen), columns (in the Carolingian Aula regia, royal palace at Ingelheim), and sculptured discs (in the Asturian Santa María del Naranco, kings' palace at Oviedo). In Bulgaria, two splendid palace complexes were built at the royal capital Preslav—one for the tsar (or emperor), and one likely for the Patriarch of All Bulgaria, patriarch. In northern Europe, rural community leaders lived in large, sometimes 40-meter-long wooden houses, but most peasants shared a small wooden or wattle and daub hut with four or five other people. The leaders' houses were divided into multiple rooms, and often included a stable, whereas the peasants' huts had one or two rooms. After the disintegration of the Carolingian Empire, the spread of aristocratic castles indicates a transition from communal fortifications to private defence in western Europe. In this period, most castles were wooden structures but the wealthiest lords could afford the building of stone fortresses. One or more towers, now known as keeps, were the most characteristic features of a medieval fortress. Castles often developed into multifunctional compounds with their drawbridges, fortified courtyards, cisterns or wells, halls, chapels, stables and workshops.
Carolingian art was produced for a small group of figures around the court, and the monasteries and churches they supported. It was dominated by efforts to regain the dignity and classicism of imperial Roman and Byzantine art, but was also influenced by the Insular art of the British Isles. Insular art integrated the energy of Celtic art, Irish Celtic and Anglo-Saxon art, Anglo-Saxon Germanic styles of ornament with Mediterranean forms such as the book, and established many characteristics of art for the rest of the medieval period. Surviving religious works from the Early Middle Ages are mostly illuminated manuscripts and carved Ivory carving#Antiquity and the Early Medieval period, ivories, originally made for metalwork that has since been melted down.Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 18–21, 63–71 Objects in precious metals were the most prestigious form of art, but almost all are lost except for a few crosses such as the Cross of Lothair, several Reliquary, reliquaries, and finds such as the Anglo-Saxon burial at Sutton Hoo and the hoards of Treasure of Gourdon, Gourdon from Merovingian France, Treasure of Guarrazar, Guarrazar from Visigothic Spain and Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós, Nagyszentmiklós near Byzantine territory. There are survivals from the large brooches in Fibula (brooch), fibula or Celtic brooch, penannular form that were a key piece of personal adornment for elites, including the Irish Tara Brooch.Henderson ''Early Medieval'' pp. 36–42, 49–55, 103, 143, 204–208 Highly decorated books were mostly Gospel Books and these have survived in List of illuminated manuscripts, larger numbers, including the Insular Book of Kells, the Lindisfarne Gospels, Book of Lindisfarne, and the imperial Codex Aureus of St. Emmeram, which is one of the few to retain its "treasure binding" of gold encrusted with jewels. Charlemagne's court seems to have been responsible for the acceptance of figurative monumental sculpture in Christian art, and by the end of the period near life-sized figures such as the Gero Cross were common in important churches.
 The High Middle Ages was a period of tremendous Medieval demography, expansion of population. The estimated population of Europe grew from 35 to 80 million between 1000 and 1347, although the exact causes remain unclear: improved agricultural techniques, assarting (or bringing new lands into production), a Medieval Warm Period, more clement climate and the lack of invasion have all been suggested. Among the agricultural innovations, a more advanced crop rotation system replaced the traditional two-field agriculture in many regions, leaving only one third of the arable land without sowing in each season.Jordan ''Europe in the High Middle Ages'' pp. 5–10 Most medieval western thinkers divided the society of their own age into three social class, fundamental classes. These were the clergy, the nobility, and the peasantry (or commoners). In their view, adherence to mainstream Christianity secured social cohesion.
As much as 90 percent of the European population remained rural peasants. Many were no longer settled in isolated farms but had gathered into more defensible small communities, usually known as Manorialism, manors or villages. In the system of manorialism, a manor was the basic unit of landholding, and it comprised smaller components, such as parcels held by peasant tenants, and the lord's demesne. Most peasants living in a manor were subject to the manor lord. Slaveholding was declining as churchmen prohibited the enslavement of co-religionists and promoted manumission, but a new form of dependency serfdom supplanted slavery by the late 11th century. Unlike slaves, serfs had legal capacity, and their hereditary status was regulated by agreements with their lords. Restrictions on their activities varied but their freedom of movement was customarily limited, and they usually owed , or labor services, to their lords. Freemen often chose serfdom by submitting themselves to a local strongman's jurisdiction for various reasons, such as protection or the remission of a debt, but there remained free peasants throughout this period and beyond. Serfs and slaves could enhance their status by bringing new lands into cultivation because the lords of uncultivated lands rewarded colonists doing the burdensome work of assarting with freedom.
A special contractual framework, known as
The High Middle Ages was a period of tremendous Medieval demography, expansion of population. The estimated population of Europe grew from 35 to 80 million between 1000 and 1347, although the exact causes remain unclear: improved agricultural techniques, assarting (or bringing new lands into production), a Medieval Warm Period, more clement climate and the lack of invasion have all been suggested. Among the agricultural innovations, a more advanced crop rotation system replaced the traditional two-field agriculture in many regions, leaving only one third of the arable land without sowing in each season.Jordan ''Europe in the High Middle Ages'' pp. 5–10 Most medieval western thinkers divided the society of their own age into three social class, fundamental classes. These were the clergy, the nobility, and the peasantry (or commoners). In their view, adherence to mainstream Christianity secured social cohesion.
As much as 90 percent of the European population remained rural peasants. Many were no longer settled in isolated farms but had gathered into more defensible small communities, usually known as Manorialism, manors or villages. In the system of manorialism, a manor was the basic unit of landholding, and it comprised smaller components, such as parcels held by peasant tenants, and the lord's demesne. Most peasants living in a manor were subject to the manor lord. Slaveholding was declining as churchmen prohibited the enslavement of co-religionists and promoted manumission, but a new form of dependency serfdom supplanted slavery by the late 11th century. Unlike slaves, serfs had legal capacity, and their hereditary status was regulated by agreements with their lords. Restrictions on their activities varied but their freedom of movement was customarily limited, and they usually owed , or labor services, to their lords. Freemen often chose serfdom by submitting themselves to a local strongman's jurisdiction for various reasons, such as protection or the remission of a debt, but there remained free peasants throughout this period and beyond. Serfs and slaves could enhance their status by bringing new lands into cultivation because the lords of uncultivated lands rewarded colonists doing the burdensome work of assarting with freedom.
A special contractual framework, known as  The Italian maritime republics such as Duchy of Amalfi, Amalfi, Venice, Republic of Genoa, Genoa, and Republic of Pisa, Pisa were the first to profit from the revival of commerce in the Mediterranean. In the north, German merchants established associations known as and took control of the trade routes connecting the British Islands and the Low Countries with Scandinavia and Eastern Europe. Great Fair, trading fairs were established and flourished Champagne fairs, in northern France, allowing Italian and German merchants to trade with each other as well as local merchants. In the late 13th century new land and sea routes to the Far East were pioneered, famously described in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' written by one of the traders, Marco Polo (d. 1324). Economic growth provided opportunities to Jewish merchants to spread all over Europe, mainly with the active support of kings, bishops or aristocrats. Although the Christian rulers appreciated the Jews' contribution to the local economy, many commoners regarded the non-Christian newcomers as an imminent threat to social cohesion. As they could not engage in prestigious trades outside their communities, they often took despised jobs such as ragmen or tax collectors. They were especially active in moneylendering for they could ignore the Christian clerics' condemnation on loan interest. The Jewish moneylenders and pawn brokers reinforced antisemitism, which led to accusations of blasphemy, blood libels, and pogroms. Church authorities' growing concerns about Jewish influence on Christian life inspired segregationist laws, and even their expulsion Edict of Expulsion, from England in 1290.
Women in the Middle Ages were officially required to be subordinate to some male, whether their father, husband, or other kinsman. Women's work generally consisted of household or other domestically inclined tasks such as child-care. Peasant women could supplement the household income by spinning or brewing at home, and they were also expected to help with field-work at harvest-time. Townswomen could engage in trade but often only by right of their husband, and unlike their male competitors, they were not always allowed to train apprentices. Noblewomen could inherit land in the absence of a male heir but their potential to give birth to children was regarded as their principal virtue. The only role open to women in the Church was that of nuns, as they were unable to become priests.
The Italian maritime republics such as Duchy of Amalfi, Amalfi, Venice, Republic of Genoa, Genoa, and Republic of Pisa, Pisa were the first to profit from the revival of commerce in the Mediterranean. In the north, German merchants established associations known as and took control of the trade routes connecting the British Islands and the Low Countries with Scandinavia and Eastern Europe. Great Fair, trading fairs were established and flourished Champagne fairs, in northern France, allowing Italian and German merchants to trade with each other as well as local merchants. In the late 13th century new land and sea routes to the Far East were pioneered, famously described in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' written by one of the traders, Marco Polo (d. 1324). Economic growth provided opportunities to Jewish merchants to spread all over Europe, mainly with the active support of kings, bishops or aristocrats. Although the Christian rulers appreciated the Jews' contribution to the local economy, many commoners regarded the non-Christian newcomers as an imminent threat to social cohesion. As they could not engage in prestigious trades outside their communities, they often took despised jobs such as ragmen or tax collectors. They were especially active in moneylendering for they could ignore the Christian clerics' condemnation on loan interest. The Jewish moneylenders and pawn brokers reinforced antisemitism, which led to accusations of blasphemy, blood libels, and pogroms. Church authorities' growing concerns about Jewish influence on Christian life inspired segregationist laws, and even their expulsion Edict of Expulsion, from England in 1290.
Women in the Middle Ages were officially required to be subordinate to some male, whether their father, husband, or other kinsman. Women's work generally consisted of household or other domestically inclined tasks such as child-care. Peasant women could supplement the household income by spinning or brewing at home, and they were also expected to help with field-work at harvest-time. Townswomen could engage in trade but often only by right of their husband, and unlike their male competitors, they were not always allowed to train apprentices. Noblewomen could inherit land in the absence of a male heir but their potential to give birth to children was regarded as their principal virtue. The only role open to women in the Church was that of nuns, as they were unable to become priests.
 The High Middle Ages saw the development of institutions and traditions that would dominate the European political life till the late 18th century. By the end of the period, representative assemblies came into being in most countries, in kingdoms and city-states alike, that exerted influence on state administration primarily through their control of taxation. The concept of hereditary monarchy was strengthening in parallel with the development of laws governing the inheritance of land. As female succession was recognised, initially mainly in the Mediterranean kingdoms, the first Queen regnant, reigning queens assumed power in this period. The queen mother's claim to assume the regency for her underage son was also widely acknowledged by the end of the 12th century.
The papacy, long attached to an ideology of independence from secular influence, first asserted its claim to temporal authority over the entire Christian world; the Temporal power (papal), Papal Monarchy reached its apogee under the pontificate of (pope 1198–1216). In the Holy Roman Empire, the Ottonians were replaced by the Salian dynasty in 1024, who famously clashed with the papacy under (r. 1056–1105) over Church appointments as part of the Investiture Controversy.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 181–186 During the following centuries, the conflict renewed several times, allowing the northern Italian cities and the German Imperial Estate, ecclesiastic and secular princes to extort considerable concessions from the emperors. Peace of Constance, In 1183, the first emperor from the Hohenstaufen dynasty Frederick I Barbarossa, Barbarossa (r. 1155–90) sanctioned the right of the Italian cities united in the Lombard League to elect their leaders and to regulate a wide spectrum of internal affairs. The German princes' judicial and economic privileges Statutum in favorem principum, were confirmed during the reign of his grandson (r. 1220–50). Frederick, who had grown up in his mother's multicultural Sicilian kingdom, was famed for his erudition and unconventional life style, and associated with the Antichrist by papalist writers. A period of interregnum, or rather civil war, followed the Hohenstaufens' fall in Germany. The tradition of elective monarchy revived, and the right of seven prince-electors to elect the German king was reaffirmed. Rudolf of Habsburg (r. 1273–91), the first king to be elected after the interregnum, realised that he was unable to control the whole empire. Instead, he established a basis for the Habsburgs' future dominance in Central Europe by granting the Duchy of Austria to his sons in 1282.
The High Middle Ages saw the development of institutions and traditions that would dominate the European political life till the late 18th century. By the end of the period, representative assemblies came into being in most countries, in kingdoms and city-states alike, that exerted influence on state administration primarily through their control of taxation. The concept of hereditary monarchy was strengthening in parallel with the development of laws governing the inheritance of land. As female succession was recognised, initially mainly in the Mediterranean kingdoms, the first Queen regnant, reigning queens assumed power in this period. The queen mother's claim to assume the regency for her underage son was also widely acknowledged by the end of the 12th century.
The papacy, long attached to an ideology of independence from secular influence, first asserted its claim to temporal authority over the entire Christian world; the Temporal power (papal), Papal Monarchy reached its apogee under the pontificate of (pope 1198–1216). In the Holy Roman Empire, the Ottonians were replaced by the Salian dynasty in 1024, who famously clashed with the papacy under (r. 1056–1105) over Church appointments as part of the Investiture Controversy.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 181–186 During the following centuries, the conflict renewed several times, allowing the northern Italian cities and the German Imperial Estate, ecclesiastic and secular princes to extort considerable concessions from the emperors. Peace of Constance, In 1183, the first emperor from the Hohenstaufen dynasty Frederick I Barbarossa, Barbarossa (r. 1155–90) sanctioned the right of the Italian cities united in the Lombard League to elect their leaders and to regulate a wide spectrum of internal affairs. The German princes' judicial and economic privileges Statutum in favorem principum, were confirmed during the reign of his grandson (r. 1220–50). Frederick, who had grown up in his mother's multicultural Sicilian kingdom, was famed for his erudition and unconventional life style, and associated with the Antichrist by papalist writers. A period of interregnum, or rather civil war, followed the Hohenstaufens' fall in Germany. The tradition of elective monarchy revived, and the right of seven prince-electors to elect the German king was reaffirmed. Rudolf of Habsburg (r. 1273–91), the first king to be elected after the interregnum, realised that he was unable to control the whole empire. Instead, he established a basis for the Habsburgs' future dominance in Central Europe by granting the Duchy of Austria to his sons in 1282.
 Under the Capetian dynasty the French monarchy slowly began to expand its authority over the nobility, growing out of the Île-de-France to exert control over more of the country in the 11th and 12th centuries. They faced a powerful rival in the Duke of Normandy, Dukes of Normandy, who in 1066 under William the Conqueror (r. 1035–87), conquered England and created a cross-Channel empire that lasted, in various forms, throughout the rest of the Middle Ages. Italo-Normans, Norman warbands Norman conquest of southern Italy, seized southern Italy and Sicily from the local Lombard, Byzantine and Muslim rulers. Their hold of the territory Treaty of Melfi, was recognised by the papacy in 1059, and Roger II of Sicily, Roger II (r. 1105–54) united these lands into the Kingdom of Sicily. Under the Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasty of (r. 1154–89) and his son Richard I of England, Richard I (r. 1189–99), the kings of England ruled over Angevin Empire, England and large areas of France. Richard's younger brother John, King of England, John (r. 1199–1216) lost Normandy and the rest of the northern French possessions in 1204 to the French King Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus (r. 1180–1223). This led to dissension among the English nobility, while John's financial exactions to pay for his unsuccessful attempts to regain Normandy led in 1215 to Magna Carta, a charter that confirmed the rights and privileges of free men in England. Under (r. 1216–72), John's son, further concessions were made to the nobility, and royal power was diminished. The French monarchy continued to make gains against the nobility during the late 12th and 13th centuries, bringing more territories within the kingdom under the king's personal rule and centralising the royal administration. Under Louis IX of France, Louis IX (r. 1226–70), royal prestige rose to new heights as Louis served as a mediator for most of Europe.
In Iberia, the Christian states, which had been confined to the northern part of the peninsula, began to push back against the Islamic states in the south, a period known as the ''Reconquista''.Davies ''Europe'' p. 345 By about 1150, the Christian north had coalesced into the five major kingdoms of Kingdom of León, León, Kingdom of Castile, Castile, Kingdom of Aragon, Aragon, Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 341 Southern Iberia remained under control of Islamic states, initially under the Caliphate of Córdoba, which broke up in 1031 into a shifting number of petty states known as ''taifas''. Although the Almoravid dynasty, Almoravids and the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads, two dynasties from the Maghreb, established centralised rule over Southern Iberia in the 1110s and 1170s respectively, their empires quickly disintegrated. Christian forces advanced again in the early 13th century, culminating in the capture of Seville in 1248.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 350–355 New kingdoms such as Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary and Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland, after their conversion to Christianity, became Central European powers.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 365–380 Northern Crusades and the advance of Christian kingdoms and military orders into previously paganism, pagan regions in the Baltic and Finland, Finnic north-east brought the forced assimilation of numerous native peoples into European culture.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 371–372
With the rise of the Mongol Empire in the Eurasian steppes under Genghis Khan (r. 1206–27), a new expansionist power reached Europe's eastern borderlands. Convinced of their heavenly sanctioned mission to conquer the world, the Mongols used extreme violence to overcome all resistance.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 458–460 Mongol invasion of Europe, Between 1236 and 1242, they conquered Volga Bulgaria, shattered the Kievan Rus' principalities, and laid waste to large regions in Poland, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia and Bulgaria. Their commander-in-chief Batu Khan (r. 1241–56)—a grandson of Genghis Khan—set up his capital at Sarai (city), Sarai on the Volga, establishing the Golden Horde, a Mongol state nominally under the distant Great Khan's authority. The Mongols extracted heavy tribute from the Rus' principalities, and the Rus' princes had to ingratiate themselves with the Mongol khans for economic and political concessions. The Mongol conquest was followed by a peaceful period in Eastern Europe. This facilitated the development of direct trade contacts between Europe and China through newly established Genoese colonies in the Black Sea region.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 703–717
Under the Capetian dynasty the French monarchy slowly began to expand its authority over the nobility, growing out of the Île-de-France to exert control over more of the country in the 11th and 12th centuries. They faced a powerful rival in the Duke of Normandy, Dukes of Normandy, who in 1066 under William the Conqueror (r. 1035–87), conquered England and created a cross-Channel empire that lasted, in various forms, throughout the rest of the Middle Ages. Italo-Normans, Norman warbands Norman conquest of southern Italy, seized southern Italy and Sicily from the local Lombard, Byzantine and Muslim rulers. Their hold of the territory Treaty of Melfi, was recognised by the papacy in 1059, and Roger II of Sicily, Roger II (r. 1105–54) united these lands into the Kingdom of Sicily. Under the Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasty of (r. 1154–89) and his son Richard I of England, Richard I (r. 1189–99), the kings of England ruled over Angevin Empire, England and large areas of France. Richard's younger brother John, King of England, John (r. 1199–1216) lost Normandy and the rest of the northern French possessions in 1204 to the French King Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus (r. 1180–1223). This led to dissension among the English nobility, while John's financial exactions to pay for his unsuccessful attempts to regain Normandy led in 1215 to Magna Carta, a charter that confirmed the rights and privileges of free men in England. Under (r. 1216–72), John's son, further concessions were made to the nobility, and royal power was diminished. The French monarchy continued to make gains against the nobility during the late 12th and 13th centuries, bringing more territories within the kingdom under the king's personal rule and centralising the royal administration. Under Louis IX of France, Louis IX (r. 1226–70), royal prestige rose to new heights as Louis served as a mediator for most of Europe.
In Iberia, the Christian states, which had been confined to the northern part of the peninsula, began to push back against the Islamic states in the south, a period known as the ''Reconquista''.Davies ''Europe'' p. 345 By about 1150, the Christian north had coalesced into the five major kingdoms of Kingdom of León, León, Kingdom of Castile, Castile, Kingdom of Aragon, Aragon, Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 341 Southern Iberia remained under control of Islamic states, initially under the Caliphate of Córdoba, which broke up in 1031 into a shifting number of petty states known as ''taifas''. Although the Almoravid dynasty, Almoravids and the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads, two dynasties from the Maghreb, established centralised rule over Southern Iberia in the 1110s and 1170s respectively, their empires quickly disintegrated. Christian forces advanced again in the early 13th century, culminating in the capture of Seville in 1248.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 350–355 New kingdoms such as Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary and Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland, after their conversion to Christianity, became Central European powers.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 365–380 Northern Crusades and the advance of Christian kingdoms and military orders into previously paganism, pagan regions in the Baltic and Finland, Finnic north-east brought the forced assimilation of numerous native peoples into European culture.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 371–372
With the rise of the Mongol Empire in the Eurasian steppes under Genghis Khan (r. 1206–27), a new expansionist power reached Europe's eastern borderlands. Convinced of their heavenly sanctioned mission to conquer the world, the Mongols used extreme violence to overcome all resistance.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 458–460 Mongol invasion of Europe, Between 1236 and 1242, they conquered Volga Bulgaria, shattered the Kievan Rus' principalities, and laid waste to large regions in Poland, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia and Bulgaria. Their commander-in-chief Batu Khan (r. 1241–56)—a grandson of Genghis Khan—set up his capital at Sarai (city), Sarai on the Volga, establishing the Golden Horde, a Mongol state nominally under the distant Great Khan's authority. The Mongols extracted heavy tribute from the Rus' principalities, and the Rus' princes had to ingratiate themselves with the Mongol khans for economic and political concessions. The Mongol conquest was followed by a peaceful period in Eastern Europe. This facilitated the development of direct trade contacts between Europe and China through newly established Genoese colonies in the Black Sea region.Curta ''Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages'' pp. 703–717
 In the 11th century, the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuk Turks took over much of the Middle East, occupying Persia during the 1040s, Armenia in the 1060s, and Jerusalem in 1070. In 1071, the Turkish army defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert and captured the Byzantine Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes, Romanus IV (r. 1068–71). The Turks were then free to invade Asia Minor, which dealt a dangerous blow to the Byzantine Empire by seizing a large part of its population and its economic heartland. Although the Byzantines regrouped and recovered somewhat, they never fully regained Asia Minor and were often on the defensive. The Turks also had difficulties, losing control of Jerusalem to the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimids of Egypt and suffering from a series of internal civil wars.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 332–333 The Byzantines also faced a revived Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, which in the late 12th and 13th centuries spread throughout the Balkans.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 386–387
The crusades were intended to seize Jerusalem from Muslim control. The First Crusade was proclaimed by Pope Pope Urban II, Urban II (pope 1088–99) at the Council of Clermont in 1095 in response to a request from the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118) for aid against further Muslim advances. Urban promised indulgence to anyone who took part. Tens of thousands of people from all levels of society mobilised across Europe and captured Jerusalem in 1099. One feature of the crusades was the pogroms against local Jews that often took place as the crusaders left their countries for the East. These were especially brutal during the First Crusade,Loyn "Jews" ''Middle Ages'' p. 191 when the Jewish communities in Cologne, Mainz, and Worms, Germany, Worms were destroyed, as well as other communities in cities between the rivers Seine and the Rhine.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 397–399 Another outgrowth of the crusades was the foundation of a new type of monastic order, the Military order (society), military orders of the Knights Templar, Templars and Knights Hospitaller, Hospitallers, which fused monastic life with military service.
The crusaders consolidated their conquests into crusader states. During the 12th and 13th centuries, there were a series of conflicts between them and the surrounding Islamic states. Appeals from the crusader states to the papacy led to further crusades,Riley-Smith "Crusades" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 106–107 such as the Third Crusade, called to try to regain Jerusalem, which had been captured by Saladin (d. 1193) in 1187.Payne ''Dream and the Tomb'' pp. 204–205 In 1203, the Fourth Crusade was diverted from the Holy Land to Constantinople, and captured the city in 1204, setting up a Latin Empire, Latin Empire of ConstantinopleLock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 156–161 and greatly weakening the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines recaptured the city in 1261, but never regained their former strength.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 299–300 By 1291 all the crusader states had been captured.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' p. 122
Popes called for crusades to take place elsewhere besides the Holy Land: in Spain, southern France, and along the Baltic. The Spanish crusades became fused with the ''Reconquista'' of Spain from the Muslims. Although the Templars and Hospitallers took part in the Spanish crusades, similar Spanish military religious orders were founded, most of which had become part of the two main orders of Order of Calatrava, Calatrava and Order of Santiago, Santiago by the beginning of the 12th century.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 205–213 Northern Europe also remained outside Christian influence until the 11th century or later, and became a crusading venue as part of the Northern Crusades of the 12th to 14th centuries. These crusades also spawned a military order, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword, Order of the Sword Brothers. Another order, the Teutonic Knights, although founded in the crusader states, focused much of its activity in the Baltic after 1225, and in 1309 moved its headquarters to Malbork Castle, Marienburg in Prussia.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 213–224
In the 11th century, the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuk Turks took over much of the Middle East, occupying Persia during the 1040s, Armenia in the 1060s, and Jerusalem in 1070. In 1071, the Turkish army defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert and captured the Byzantine Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes, Romanus IV (r. 1068–71). The Turks were then free to invade Asia Minor, which dealt a dangerous blow to the Byzantine Empire by seizing a large part of its population and its economic heartland. Although the Byzantines regrouped and recovered somewhat, they never fully regained Asia Minor and were often on the defensive. The Turks also had difficulties, losing control of Jerusalem to the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimids of Egypt and suffering from a series of internal civil wars.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 332–333 The Byzantines also faced a revived Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, which in the late 12th and 13th centuries spread throughout the Balkans.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 386–387
The crusades were intended to seize Jerusalem from Muslim control. The First Crusade was proclaimed by Pope Pope Urban II, Urban II (pope 1088–99) at the Council of Clermont in 1095 in response to a request from the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118) for aid against further Muslim advances. Urban promised indulgence to anyone who took part. Tens of thousands of people from all levels of society mobilised across Europe and captured Jerusalem in 1099. One feature of the crusades was the pogroms against local Jews that often took place as the crusaders left their countries for the East. These were especially brutal during the First Crusade,Loyn "Jews" ''Middle Ages'' p. 191 when the Jewish communities in Cologne, Mainz, and Worms, Germany, Worms were destroyed, as well as other communities in cities between the rivers Seine and the Rhine.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 397–399 Another outgrowth of the crusades was the foundation of a new type of monastic order, the Military order (society), military orders of the Knights Templar, Templars and Knights Hospitaller, Hospitallers, which fused monastic life with military service.
The crusaders consolidated their conquests into crusader states. During the 12th and 13th centuries, there were a series of conflicts between them and the surrounding Islamic states. Appeals from the crusader states to the papacy led to further crusades,Riley-Smith "Crusades" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 106–107 such as the Third Crusade, called to try to regain Jerusalem, which had been captured by Saladin (d. 1193) in 1187.Payne ''Dream and the Tomb'' pp. 204–205 In 1203, the Fourth Crusade was diverted from the Holy Land to Constantinople, and captured the city in 1204, setting up a Latin Empire, Latin Empire of ConstantinopleLock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 156–161 and greatly weakening the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines recaptured the city in 1261, but never regained their former strength.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 299–300 By 1291 all the crusader states had been captured.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' p. 122
Popes called for crusades to take place elsewhere besides the Holy Land: in Spain, southern France, and along the Baltic. The Spanish crusades became fused with the ''Reconquista'' of Spain from the Muslims. Although the Templars and Hospitallers took part in the Spanish crusades, similar Spanish military religious orders were founded, most of which had become part of the two main orders of Order of Calatrava, Calatrava and Order of Santiago, Santiago by the beginning of the 12th century.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 205–213 Northern Europe also remained outside Christian influence until the 11th century or later, and became a crusading venue as part of the Northern Crusades of the 12th to 14th centuries. These crusades also spawned a military order, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword, Order of the Sword Brothers. Another order, the Teutonic Knights, although founded in the crusader states, focused much of its activity in the Baltic after 1225, and in 1309 moved its headquarters to Malbork Castle, Marienburg in Prussia.Lock ''Routledge Companion to the Crusades'' pp. 213–224
 Chivalry and the ethos of courtly love developed in royal and noble courts. This culture was expressed in the Vernacular, vernacular languages rather than Latin, and comprised poems, stories, legends, and popular songs spread by troubadours, or wandering minstrels. Often the stories were written down in the ''Chanson de geste, chansons de geste'', or "songs of great deeds", such as ''The Song of Roland'' or ''Hildebrand, The Song of Hildebrand''.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 252–260 Secular and religious histories were also produced.Davies ''Europe'' p. 349 Geoffrey of Monmouth (d. c. 1155) composed his ''Historia Regum Britanniae'', a collection of stories and legends about King Arthur, Arthur.Saul ''Companion to Medieval England'' pp. 113–114 Other works were more clearly history, such as Otto of Freising, Otto von Freising's (d. 1158) ''Gesta Friderici Imperatoris'' detailing the deeds of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, or William of Malmesbury's (d. c. 1143) ''Gesta Regum'' on the kings of England.
Legal studies advanced during the 12th century. Both secular law and canon law, or ecclesiastical law, were studied in the High Middle Ages. Secular law, or Roman law, was advanced greatly by the discovery of the ''
Chivalry and the ethos of courtly love developed in royal and noble courts. This culture was expressed in the Vernacular, vernacular languages rather than Latin, and comprised poems, stories, legends, and popular songs spread by troubadours, or wandering minstrels. Often the stories were written down in the ''Chanson de geste, chansons de geste'', or "songs of great deeds", such as ''The Song of Roland'' or ''Hildebrand, The Song of Hildebrand''.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 252–260 Secular and religious histories were also produced.Davies ''Europe'' p. 349 Geoffrey of Monmouth (d. c. 1155) composed his ''Historia Regum Britanniae'', a collection of stories and legends about King Arthur, Arthur.Saul ''Companion to Medieval England'' pp. 113–114 Other works were more clearly history, such as Otto of Freising, Otto von Freising's (d. 1158) ''Gesta Friderici Imperatoris'' detailing the deeds of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, or William of Malmesbury's (d. c. 1143) ''Gesta Regum'' on the kings of England.
Legal studies advanced during the 12th century. Both secular law and canon law, or ecclesiastical law, were studied in the High Middle Ages. Secular law, or Roman law, was advanced greatly by the discovery of the '' In the 12th and 13th centuries, Europe experienced economic growth and innovations in methods of production. Major technological advances included the invention of the windmill, the first mechanical clocks, the manufacture of distilled spirits, and the use of the astrolabe.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' p. 246 Concave spectacles were invented around 1286 by an unknown Italian artisan, probably working in or near Pisa.
The development of a three-field Crop rotation, rotation system for planting crops increased the usage of land from one half in use each year under the old two-field system to two-thirds under the new system, with a consequent increase in production. The development of the Plough, heavy plough allowed heavier soils to be farmed more efficiently, aided by the spread of the horse collar, which led to the use of Working animal, draught horses in place of oxen. Horses are faster than oxen and require less pasture, factors that aided the implementation of the three-field system.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 156–159 Legumes – such as peas, beans, or lentils – were grown more widely as crops, in addition to the usual cereal crops of wheat, oats, barley, and rye.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 80
The construction of cathedrals and castles advanced building technology, leading to the development of large stone buildings. Ancillary structures included new town halls, houses, bridges, and tithe barns.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 68 Shipbuilding improved with the use of the Boat building, rib and plank method rather than the old Roman system of mortise and tenon. Other improvements to ships included the use of lateen sails and the rudder#Medieval Europe, stern-post rudder, both of which increased the speed at which ships could be sailed.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 73
In military affairs, the use of infantry with specialised roles increased. Along with the still-dominant heavy cavalry, armies often included mounted and infantry crossbowmen, as well as sappers and engineers.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 125 Crossbows, which had been known in Late Antiquity, increased in use partly because of the increase in siege warfare in the 10th and 11th centuries. The increasing use of crossbows during the 12th and 13th centuries led to the use of closed-face Combat helmet, helmets, heavy body armour, as well as Barding, horse armour.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 130 Gunpowder was known in Europe by the mid-13th century with a recorded use in European warfare by the English against the Scots in 1304, although it was merely used as an explosive and not as a weapon. Cannon were being used for sieges in the 1320s, and hand-held guns were in use by the 1360s.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, Europe experienced economic growth and innovations in methods of production. Major technological advances included the invention of the windmill, the first mechanical clocks, the manufacture of distilled spirits, and the use of the astrolabe.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' p. 246 Concave spectacles were invented around 1286 by an unknown Italian artisan, probably working in or near Pisa.
The development of a three-field Crop rotation, rotation system for planting crops increased the usage of land from one half in use each year under the old two-field system to two-thirds under the new system, with a consequent increase in production. The development of the Plough, heavy plough allowed heavier soils to be farmed more efficiently, aided by the spread of the horse collar, which led to the use of Working animal, draught horses in place of oxen. Horses are faster than oxen and require less pasture, factors that aided the implementation of the three-field system.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 156–159 Legumes – such as peas, beans, or lentils – were grown more widely as crops, in addition to the usual cereal crops of wheat, oats, barley, and rye.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 80
The construction of cathedrals and castles advanced building technology, leading to the development of large stone buildings. Ancillary structures included new town halls, houses, bridges, and tithe barns.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 68 Shipbuilding improved with the use of the Boat building, rib and plank method rather than the old Roman system of mortise and tenon. Other improvements to ships included the use of lateen sails and the rudder#Medieval Europe, stern-post rudder, both of which increased the speed at which ships could be sailed.Barber ''Two Cities'' p. 73
In military affairs, the use of infantry with specialised roles increased. Along with the still-dominant heavy cavalry, armies often included mounted and infantry crossbowmen, as well as sappers and engineers.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 125 Crossbows, which had been known in Late Antiquity, increased in use partly because of the increase in siege warfare in the 10th and 11th centuries. The increasing use of crossbows during the 12th and 13th centuries led to the use of closed-face Combat helmet, helmets, heavy body armour, as well as Barding, horse armour.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 130 Gunpowder was known in Europe by the mid-13th century with a recorded use in European warfare by the English against the Scots in 1304, although it was merely used as an explosive and not as a weapon. Cannon were being used for sieges in the 1320s, and hand-held guns were in use by the 1360s.
 In the 10th century the establishment of churches and monasteries led to the development of stone architecture that elaborated vernacular Roman forms, from which the term "Romanesque" is derived. Where available, Roman brick and stone buildings were recycled for their materials. From the tentative beginnings known as the First Romanesque, the style flourished and spread across Europe in a remarkably homogeneous form. Just before 1000 there was a great wave of building stone churches all over Europe.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 55 Romanesque architecture, Romanesque buildings have massive stone walls, openings topped by semi-circular arches, small windows, and, particularly in France, arched stone vaults.Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 181–189 The large Portal (architecture), portal with coloured sculpture in Relief, high relief became a central feature of façades, especially in France, and the Capital (architecture), capitals of columns were often carved with narrative scenes of imaginative monsters and animals.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 58–60, 65–66, 73–75 According to art historian Charles Reginald Dodwell, C. R. Dodwell, "virtually all the churches in the West were decorated with wall-paintings", of which few survive.Dodwell ''Pictorial Arts of the West'' p. 37 Simultaneous with the development in church architecture, the distinctive European form of the castle was developed and became crucial to politics and warfare.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 295–299
Romanesque art, especially metalwork, was at its most sophisticated in Mosan art, in which distinct artistic personalities including Nicholas of Verdun (d. 1205) become apparent, and an almost Ancient Greek art, classical style is seen in works such as a Baptismal font at St Bartholomew's Church, Liège, font at Liège,Lasko ''Ars Sacra'' pp. 240–250 contrasting with the writhing animals of the exactly contemporary Gloucester Candlestick. Large illuminated bibles and psalters were the typical forms of luxury manuscripts, and wall-painting flourished in churches, often following a scheme with a ''Last Judgment, Last Judgement'' on the west wall, a Christ in Majesty at the east end, and narrative biblical scenes down the nave, or in the best surviving example, at Abbey Church of Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, on the Barrel vault, barrel-vaulted roof.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 91–92
In the 10th century the establishment of churches and monasteries led to the development of stone architecture that elaborated vernacular Roman forms, from which the term "Romanesque" is derived. Where available, Roman brick and stone buildings were recycled for their materials. From the tentative beginnings known as the First Romanesque, the style flourished and spread across Europe in a remarkably homogeneous form. Just before 1000 there was a great wave of building stone churches all over Europe.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 55 Romanesque architecture, Romanesque buildings have massive stone walls, openings topped by semi-circular arches, small windows, and, particularly in France, arched stone vaults.Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 181–189 The large Portal (architecture), portal with coloured sculpture in Relief, high relief became a central feature of façades, especially in France, and the Capital (architecture), capitals of columns were often carved with narrative scenes of imaginative monsters and animals.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 58–60, 65–66, 73–75 According to art historian Charles Reginald Dodwell, C. R. Dodwell, "virtually all the churches in the West were decorated with wall-paintings", of which few survive.Dodwell ''Pictorial Arts of the West'' p. 37 Simultaneous with the development in church architecture, the distinctive European form of the castle was developed and became crucial to politics and warfare.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 295–299
Romanesque art, especially metalwork, was at its most sophisticated in Mosan art, in which distinct artistic personalities including Nicholas of Verdun (d. 1205) become apparent, and an almost Ancient Greek art, classical style is seen in works such as a Baptismal font at St Bartholomew's Church, Liège, font at Liège,Lasko ''Ars Sacra'' pp. 240–250 contrasting with the writhing animals of the exactly contemporary Gloucester Candlestick. Large illuminated bibles and psalters were the typical forms of luxury manuscripts, and wall-painting flourished in churches, often following a scheme with a ''Last Judgment, Last Judgement'' on the west wall, a Christ in Majesty at the east end, and narrative biblical scenes down the nave, or in the best surviving example, at Abbey Church of Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, Saint-Savin-sur-Gartempe, on the Barrel vault, barrel-vaulted roof.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 91–92
 From the early 12th century, French builders developed the Gothic architecture, Gothic style, marked by the use of rib vaults, Ogive, pointed arches, flying buttresses, and large stained glass windows. It was used mainly in churches and cathedrals and continued in use until the 16th century in much of Europe. Classic examples of Gothic architecture include Chartres Cathedral and Reims Cathedral in France as well as Salisbury Cathedral in England.Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 195–216 Stained glass became a crucial element in the design of churches, which continued to use extensive wall-paintings, now almost all lost.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 185–190; 269–271
During this period the practice of manuscript illumination gradually passed from monasteries to lay workshops, so that according to Janetta Benton "by 1300 most monks bought their books in shops",Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 250 and the book of hours developed as a form of devotional book for lay-people. Metalwork continued to be the most prestigious form of art, with Limoges enamel a popular and relatively affordable option for objects such as reliquaries and crosses.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 135–139, 245–247 In Italy the innovations of Cimabue and Duccio, followed by the Trecento master
From the early 12th century, French builders developed the Gothic architecture, Gothic style, marked by the use of rib vaults, Ogive, pointed arches, flying buttresses, and large stained glass windows. It was used mainly in churches and cathedrals and continued in use until the 16th century in much of Europe. Classic examples of Gothic architecture include Chartres Cathedral and Reims Cathedral in France as well as Salisbury Cathedral in England.Adams ''History of Western Art'' pp. 195–216 Stained glass became a crucial element in the design of churches, which continued to use extensive wall-paintings, now almost all lost.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 185–190; 269–271
During this period the practice of manuscript illumination gradually passed from monasteries to lay workshops, so that according to Janetta Benton "by 1300 most monks bought their books in shops",Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' p. 250 and the book of hours developed as a form of devotional book for lay-people. Metalwork continued to be the most prestigious form of art, with Limoges enamel a popular and relatively affordable option for objects such as reliquaries and crosses.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 135–139, 245–247 In Italy the innovations of Cimabue and Duccio, followed by the Trecento master  Monastic reform became an important issue during the 11th century, as elites began to worry that monks were not adhering to the rules binding them to a strictly religious life. Cluny Abbey, founded in the Mâcon region of France in 909, was established as part of the Cluniac Reforms, a larger movement of monastic reform in response to this fear.Rosenwein ''Rhinoceros Bound'' pp. 40–41 Cluny quickly established a reputation for austerity and rigour. It sought to maintain a high quality of spiritual life by placing itself under the protection of the papacy and by electing its own abbot without interference from laymen, thus maintaining economic and political independence from local lords.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 143–144
Monastic reform inspired change in the secular Church. The ideals upon which it was based were brought to the papacy by Pope Pope Leo IX, Leo IX (pope 1049–1054), and provided the ideology of clerical independence that led to the Investiture Controversy in the late 11th century. This involved Pope Pope Gregory VII, Gregory VII (pope 1073–85) and Emperor Henry IV, who initially clashed over episcopal appointments, a dispute that turned into a battle over the ideas of investiture, clerical marriage, and simony. The emperor saw the protection of the Church as one of his responsibilities as well as wanting to preserve the right to appoint his own choices as bishops within his lands, but the papacy insisted on the Church's independence from secular lords. These issues remained unresolved after the compromise of 1122 known as the Concordat of Worms. The dispute represents a significant stage in the creation of a papal monarchy separate from and equal to laity, lay authorities. It also had the permanent consequence of empowering German princes at the expense of the German emperors.
Monastic reform became an important issue during the 11th century, as elites began to worry that monks were not adhering to the rules binding them to a strictly religious life. Cluny Abbey, founded in the Mâcon region of France in 909, was established as part of the Cluniac Reforms, a larger movement of monastic reform in response to this fear.Rosenwein ''Rhinoceros Bound'' pp. 40–41 Cluny quickly established a reputation for austerity and rigour. It sought to maintain a high quality of spiritual life by placing itself under the protection of the papacy and by electing its own abbot without interference from laymen, thus maintaining economic and political independence from local lords.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 143–144
Monastic reform inspired change in the secular Church. The ideals upon which it was based were brought to the papacy by Pope Pope Leo IX, Leo IX (pope 1049–1054), and provided the ideology of clerical independence that led to the Investiture Controversy in the late 11th century. This involved Pope Pope Gregory VII, Gregory VII (pope 1073–85) and Emperor Henry IV, who initially clashed over episcopal appointments, a dispute that turned into a battle over the ideas of investiture, clerical marriage, and simony. The emperor saw the protection of the Church as one of his responsibilities as well as wanting to preserve the right to appoint his own choices as bishops within his lands, but the papacy insisted on the Church's independence from secular lords. These issues remained unresolved after the compromise of 1122 known as the Concordat of Worms. The dispute represents a significant stage in the creation of a papal monarchy separate from and equal to laity, lay authorities. It also had the permanent consequence of empowering German princes at the expense of the German emperors.
 The High Middle Ages was a period of great religious movements. Besides the Crusades and monastic reforms, people sought to participate in new forms of religious life. New monastic orders were founded, including the Carthusians and the Cistercians. The latter, in particular, expanded rapidly in their early years under the guidance of Bernard of Clairvaux (d. 1153). These new orders were formed in response to the feeling of the laity that Benedictine monasticism no longer met the needs of the laymen, who along with those wishing to enter the religious life wanted a return to the simpler hermit, hermetical monasticism of early Christianity, or to live an Apostles in the New Testament, Apostolic life.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 145–149 Christian pilgrimage, Religious pilgrimages were also encouraged. Old pilgrimage sites such as Rome, Jerusalem, and Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, Compostela received increasing numbers of visitors, and new sites such as Sanctuary of Monte Sant'Angelo, Monte Gargano and Basilica di San Nicola, Bari rose to prominence.Morris "Northern Europe" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 199
In the 13th century mendicant orders—the Franciscans and the Dominican Order, Dominicans—who swore vows of poverty and earned their living by begging, were approved by the papacy.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 155–167 Religious groups such as the Waldensians and the Humiliati also attempted to return to the life of early Christianity in the middle 12th and early 13th centuries, another heretical movement condemned by the papacy. Others joined the Catharism, Cathars, another movement condemned as heretical by the papacy. In 1209, a crusade was preached against the Cathars, the Albigensian Crusade, which in combination with the medieval Inquisition, eliminated them.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 185–192
The High Middle Ages was a period of great religious movements. Besides the Crusades and monastic reforms, people sought to participate in new forms of religious life. New monastic orders were founded, including the Carthusians and the Cistercians. The latter, in particular, expanded rapidly in their early years under the guidance of Bernard of Clairvaux (d. 1153). These new orders were formed in response to the feeling of the laity that Benedictine monasticism no longer met the needs of the laymen, who along with those wishing to enter the religious life wanted a return to the simpler hermit, hermetical monasticism of early Christianity, or to live an Apostles in the New Testament, Apostolic life.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 145–149 Christian pilgrimage, Religious pilgrimages were also encouraged. Old pilgrimage sites such as Rome, Jerusalem, and Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, Compostela received increasing numbers of visitors, and new sites such as Sanctuary of Monte Sant'Angelo, Monte Gargano and Basilica di San Nicola, Bari rose to prominence.Morris "Northern Europe" ''Oxford Illustrated History of Medieval Europe'' p. 199
In the 13th century mendicant orders—the Franciscans and the Dominican Order, Dominicans—who swore vows of poverty and earned their living by begging, were approved by the papacy.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 155–167 Religious groups such as the Waldensians and the Humiliati also attempted to return to the life of early Christianity in the middle 12th and early 13th centuries, another heretical movement condemned by the papacy. Others joined the Catharism, Cathars, another movement condemned as heretical by the papacy. In 1209, a crusade was preached against the Cathars, the Albigensian Crusade, which in combination with the medieval Inquisition, eliminated them.Barber ''Two Cities'' pp. 185–192
 These troubles were followed in 1347 by the Black Death, a pandemic that spread throughout Europe during the following three years.Schove "Plague" ''Middle Ages'' p. 269 The death toll was probably about 35 million people in Europe, about one-third of the population. Towns were especially hard-hit because of their crowded conditions. Large areas of land were left sparsely inhabited, and in some places fields were left unworked. Wages rose as landlords sought to entice the reduced number of available workers to their fields. Further problems were lower rents and lower demand for food, both of which cut into agricultural income. Urban workers also felt that they had a right to greater earnings, and Popular revolt in late-medieval Europe, popular uprisings broke out across Europe.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 374–380 Among the uprisings were the ''jacquerie'' in France, the Peasants' Revolt in England, and revolts in the cities of Florence in Italy and Ghent and Bruges in Flanders. The trauma of the plague led to an increased piety throughout Europe, manifested by the foundation of new charities, the self-mortification of the flagellants, and the Black Death Jewish persecutions, scapegoating of Jews.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 412–413 Conditions were further unsettled by the return of the plague throughout the rest of the 14th century; it continued to strike Europe periodically during the rest of the Middle Ages.
These dire conditions resulted in an increase of interpersonal violence in most parts of Europe. Population increase, religious intolerance, famine and disease led to an increase in violent acts in vast parts of the medieval society. One exception to this was Northeastern Europe, North-Eastern Europe, whose population managed to maintain low levels of violence due to a more organized society resulting from extensive and successful trade.
These troubles were followed in 1347 by the Black Death, a pandemic that spread throughout Europe during the following three years.Schove "Plague" ''Middle Ages'' p. 269 The death toll was probably about 35 million people in Europe, about one-third of the population. Towns were especially hard-hit because of their crowded conditions. Large areas of land were left sparsely inhabited, and in some places fields were left unworked. Wages rose as landlords sought to entice the reduced number of available workers to their fields. Further problems were lower rents and lower demand for food, both of which cut into agricultural income. Urban workers also felt that they had a right to greater earnings, and Popular revolt in late-medieval Europe, popular uprisings broke out across Europe.Backman ''Worlds of Medieval Europe'' pp. 374–380 Among the uprisings were the ''jacquerie'' in France, the Peasants' Revolt in England, and revolts in the cities of Florence in Italy and Ghent and Bruges in Flanders. The trauma of the plague led to an increased piety throughout Europe, manifested by the foundation of new charities, the self-mortification of the flagellants, and the Black Death Jewish persecutions, scapegoating of Jews.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 412–413 Conditions were further unsettled by the return of the plague throughout the rest of the 14th century; it continued to strike Europe periodically during the rest of the Middle Ages.
These dire conditions resulted in an increase of interpersonal violence in most parts of Europe. Population increase, religious intolerance, famine and disease led to an increase in violent acts in vast parts of the medieval society. One exception to this was Northeastern Europe, North-Eastern Europe, whose population managed to maintain low levels of violence due to a more organized society resulting from extensive and successful trade.
 Strong, royalty-based nation states rose throughout Europe in the Late Middle Ages, particularly in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of France, France, and the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula: Crown of Aragon, Aragon, Crown of Castile, Castile, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal. The long conflicts of the period strengthened royal control over their kingdoms and were extremely hard on the peasantry. Kings profited from warfare that extended royal legislation and increased the lands they directly controlled.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 201–219 Paying for the wars required that methods of taxation become more effective and efficient, and the rate of taxation often increased.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 224–233 The requirement to obtain the consent of taxpayers allowed representative bodies such as the Parliament of England, English Parliament and the Estates General (France), French Estates General to gain power and authority.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 233–238
Strong, royalty-based nation states rose throughout Europe in the Late Middle Ages, particularly in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of France, France, and the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula: Crown of Aragon, Aragon, Crown of Castile, Castile, and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal. The long conflicts of the period strengthened royal control over their kingdoms and were extremely hard on the peasantry. Kings profited from warfare that extended royal legislation and increased the lands they directly controlled.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 201–219 Paying for the wars required that methods of taxation become more effective and efficient, and the rate of taxation often increased.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 224–233 The requirement to obtain the consent of taxpayers allowed representative bodies such as the Parliament of England, English Parliament and the Estates General (France), French Estates General to gain power and authority.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 233–238
 Throughout the 14th century, French kings sought to expand their influence at the expense of the territorial holdings of the nobility.Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 166 They ran into difficulties when attempting to confiscate the holdings of the English kings in southern France, leading to the Hundred Years' War,Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 169 waged from 1337 to 1453.Loyn "Hundred Years' War" ''Middle Ages'' p. 176 Early in the war the English under Edward III of England, Edward III (r. 1327–77) and his son Edward, the Black Prince (d. 1376), won the battles of Battle of Crécy, Crécy and Battle of Poitiers, Poitiers, captured the city of Calais, and won control of much of France. The resulting stresses almost caused the disintegration of the French kingdom during the early years of the war.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 180–181 In the early 15th century, France again came close to dissolving, but in the late 1420s the military successes of Joan of Arc (d. 1431) led to the victory of the French and the capture of the last English possessions in southern France in 1453.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 317–322 The price was high, as the population of France at the end of the Wars was likely half what it had been at the start of the conflict. Conversely, the Wars had a positive effect on English national identity, doing much to fuse the various local identities into a national English ideal. The conflict with France also helped create a national culture in England separate from French culture, which had previously been the dominant influence.Davies ''Europe'' p. 423 The dominance of the English longbow began during early stages of the Hundred Years' War,Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 186 and cannon appeared on the battlefield at Crécy in 1346.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' pp. 296–298
In modern-day Germany, the Holy Roman Empire continued to rule, but the elective nature of the imperial crown meant there was no enduring dynasty around which a strong state could form.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 170–171 Further east, the kingdoms of Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Poland, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia grew powerful.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 173–175 In Iberia, the Christian kingdoms continued to gain land from the Muslim kingdoms of the peninsula;Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 173 Portugal concentrated on expanding overseas during the 15th century, while the other kingdoms were riven by difficulties over royal succession and other concerns.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 327–332Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 340 After losing the Hundred Years' War, England went on to suffer a long civil war known as the Wars of the Roses, which lasted into the 1490s and only ended when Henry VII of England, Henry Tudor (r. 1485–1509 as Henry VII) became king and consolidated power with his victory over Richard III of England, Richard III (r. 1483–85) at Battle of Bosworth Field, Bosworth in 1485.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 425–426 In Scandinavia, Margaret I of Denmark (r. in Denmark 1387–1412) consolidated Norway, Denmark, and Sweden in the Kalmar Union, Union of Kalmar, which continued until 1523. The major power around the Baltic Sea was the Hanseatic League, a commercial confederation of city-states that traded from Western Europe to Russia.Davies ''Europe'' p. 431 Scotland emerged from English domination under Robert the Bruce (r. 1306–29), who secured papal recognition of his kingship in 1328.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 408–409
Throughout the 14th century, French kings sought to expand their influence at the expense of the territorial holdings of the nobility.Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 166 They ran into difficulties when attempting to confiscate the holdings of the English kings in southern France, leading to the Hundred Years' War,Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 169 waged from 1337 to 1453.Loyn "Hundred Years' War" ''Middle Ages'' p. 176 Early in the war the English under Edward III of England, Edward III (r. 1327–77) and his son Edward, the Black Prince (d. 1376), won the battles of Battle of Crécy, Crécy and Battle of Poitiers, Poitiers, captured the city of Calais, and won control of much of France. The resulting stresses almost caused the disintegration of the French kingdom during the early years of the war.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 180–181 In the early 15th century, France again came close to dissolving, but in the late 1420s the military successes of Joan of Arc (d. 1431) led to the victory of the French and the capture of the last English possessions in southern France in 1453.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 317–322 The price was high, as the population of France at the end of the Wars was likely half what it had been at the start of the conflict. Conversely, the Wars had a positive effect on English national identity, doing much to fuse the various local identities into a national English ideal. The conflict with France also helped create a national culture in England separate from French culture, which had previously been the dominant influence.Davies ''Europe'' p. 423 The dominance of the English longbow began during early stages of the Hundred Years' War,Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 186 and cannon appeared on the battlefield at Crécy in 1346.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' pp. 296–298
In modern-day Germany, the Holy Roman Empire continued to rule, but the elective nature of the imperial crown meant there was no enduring dynasty around which a strong state could form.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 170–171 Further east, the kingdoms of Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Poland, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, and Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia grew powerful.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 173–175 In Iberia, the Christian kingdoms continued to gain land from the Muslim kingdoms of the peninsula;Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 173 Portugal concentrated on expanding overseas during the 15th century, while the other kingdoms were riven by difficulties over royal succession and other concerns.Watts ''Making of Polities'' pp. 327–332Watts ''Making of Polities'' p. 340 After losing the Hundred Years' War, England went on to suffer a long civil war known as the Wars of the Roses, which lasted into the 1490s and only ended when Henry VII of England, Henry Tudor (r. 1485–1509 as Henry VII) became king and consolidated power with his victory over Richard III of England, Richard III (r. 1483–85) at Battle of Bosworth Field, Bosworth in 1485.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 425–426 In Scandinavia, Margaret I of Denmark (r. in Denmark 1387–1412) consolidated Norway, Denmark, and Sweden in the Kalmar Union, Union of Kalmar, which continued until 1523. The major power around the Baltic Sea was the Hanseatic League, a commercial confederation of city-states that traded from Western Europe to Russia.Davies ''Europe'' p. 431 Scotland emerged from English domination under Robert the Bruce (r. 1306–29), who secured papal recognition of his kingship in 1328.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 408–409
 During the tumultuous 14th century, disputes within the leadership of the Church led to the Avignon Papacy of 1309–76,Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 170–171 also called the "Babylonian Captivity of the Papacy" (a reference to the Babylonian captivity of the Jews),Loyn "Avignon" ''Middle Ages'' p. 45 and then to the Western Schism, Great Schism, lasting from 1378 to 1418, when there were two and later three rival popes, each supported by several states.Loyn "Great Schism" ''Middle Ages'' p. 153 Ecclesiastical officials convened at the Council of Constance in 1414, and in the following year the council deposed one of the rival popes, leaving only two claimants. Further depositions followed, and in November 1417, the council elected Pope Martin V, Martin V (pope 1417–31) as pope.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 184–187
Besides the schism, the Western Church was riven by theological controversies, some of which turned into heresies. John Wycliffe (d. 1384), an English theologian, was condemned as a heretic in 1415 for teaching that the laity should have access to the text of the Bible as well as for holding views on the Eucharist that were contrary to Church doctrine.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 197–199 Wycliffe's teachings influenced two of the major heretical movements of the later Middle Ages: Lollardy in England and Hussites, Hussitism in Bohemia.Thomson ''Western Church'' p. 218 The Bohemian movement initiated with the teaching of Jan Hus, who was burned at the stake in 1415, after being condemned as a heretic by the Council of Constance. The Hussite Church, although the target of a crusade, survived beyond the Middle Ages.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 213–217 Other heresies were manufactured, such as the accusations against the Knights Templar that resulted in their suppression in 1312, and the division of their great wealth between the French King Philip IV of France, Philip IV (r. 1285–1314) and the Hospitallers.Loyn "Knights of the Temple (Templars)" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 201–202
The papacy further refined the practice in the Mass (liturgy), Mass in the Late Middle Ages, holding that the clergy alone was allowed to partake of the wine in the Eucharist. This further distanced the secular laity from the clergy. The laity continued the practices of pilgrimages, veneration of relics, and belief in the power of the Devil. Mystics such as Meister Eckhart (d. 1327) and Thomas à Kempis (d. 1471) wrote works that taught the laity to focus on their inner spiritual life, which laid the groundwork for the Protestant Reformation. Besides mysticism, belief in witches and witchcraft became widespread, and by the late 15th century the Church had begun to lend credence to populist fears of witchcraft with its condemnation of witches in 1484, and the publication in 1486 of the ''Malleus Maleficarum'', the most popular handbook for witch-hunters.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 436–437
During the tumultuous 14th century, disputes within the leadership of the Church led to the Avignon Papacy of 1309–76,Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 170–171 also called the "Babylonian Captivity of the Papacy" (a reference to the Babylonian captivity of the Jews),Loyn "Avignon" ''Middle Ages'' p. 45 and then to the Western Schism, Great Schism, lasting from 1378 to 1418, when there were two and later three rival popes, each supported by several states.Loyn "Great Schism" ''Middle Ages'' p. 153 Ecclesiastical officials convened at the Council of Constance in 1414, and in the following year the council deposed one of the rival popes, leaving only two claimants. Further depositions followed, and in November 1417, the council elected Pope Martin V, Martin V (pope 1417–31) as pope.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 184–187
Besides the schism, the Western Church was riven by theological controversies, some of which turned into heresies. John Wycliffe (d. 1384), an English theologian, was condemned as a heretic in 1415 for teaching that the laity should have access to the text of the Bible as well as for holding views on the Eucharist that were contrary to Church doctrine.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 197–199 Wycliffe's teachings influenced two of the major heretical movements of the later Middle Ages: Lollardy in England and Hussites, Hussitism in Bohemia.Thomson ''Western Church'' p. 218 The Bohemian movement initiated with the teaching of Jan Hus, who was burned at the stake in 1415, after being condemned as a heretic by the Council of Constance. The Hussite Church, although the target of a crusade, survived beyond the Middle Ages.Thomson ''Western Church'' pp. 213–217 Other heresies were manufactured, such as the accusations against the Knights Templar that resulted in their suppression in 1312, and the division of their great wealth between the French King Philip IV of France, Philip IV (r. 1285–1314) and the Hospitallers.Loyn "Knights of the Temple (Templars)" ''Middle Ages'' pp. 201–202
The papacy further refined the practice in the Mass (liturgy), Mass in the Late Middle Ages, holding that the clergy alone was allowed to partake of the wine in the Eucharist. This further distanced the secular laity from the clergy. The laity continued the practices of pilgrimages, veneration of relics, and belief in the power of the Devil. Mystics such as Meister Eckhart (d. 1327) and Thomas à Kempis (d. 1471) wrote works that taught the laity to focus on their inner spiritual life, which laid the groundwork for the Protestant Reformation. Besides mysticism, belief in witches and witchcraft became widespread, and by the late 15th century the Church had begun to lend credence to populist fears of witchcraft with its condemnation of witches in 1484, and the publication in 1486 of the ''Malleus Maleficarum'', the most popular handbook for witch-hunters.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 436–437
 Education remained mostly focused on the training of future clergy. The basic learning of the letters and numbers remained the province of the family or a village priest, but the secondary subjects of the trivium—grammar, rhetoric, logic—were studied in cathedral schools or in schools provided by cities. Commercial secondary schools spread, and some Italian towns had more than one such enterprise. Universities also spread throughout Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries. Lay literacy rates rose, but were still low; one estimate gave a literacy rate of ten percent of males and one percent of females in 1500.Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 224
The publication of vernacular literature increased, with
Education remained mostly focused on the training of future clergy. The basic learning of the letters and numbers remained the province of the family or a village priest, but the secondary subjects of the trivium—grammar, rhetoric, logic—were studied in cathedral schools or in schools provided by cities. Commercial secondary schools spread, and some Italian towns had more than one such enterprise. Universities also spread throughout Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries. Lay literacy rates rose, but were still low; one estimate gave a literacy rate of ten percent of males and one percent of females in 1500.Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 224
The publication of vernacular literature increased, with  One of the major developments in the military sphere during the Late Middle Ages was the increased use of infantry and light cavalry.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 180 The English also employed longbowmen, but other countries were unable to create similar forces with the same success.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 183 Armour continued to advance, spurred by the increasing power of crossbows, and plate armour was developed to protect soldiers from crossbows as well as the hand-held guns that were developed.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 188 Pole weapon, Pole arms reached new prominence with the development of the Flemish and Swiss infantry armed with pikes and other long spears.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 185
In agriculture, the increased usage of sheep with long-fibred wool allowed a stronger thread to be spun. In addition, the spinning wheel replaced the traditional distaff for spinning wool, tripling production.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 193–194 A less technological refinement that still greatly affected daily life was the use of buttons as closures for garments, which allowed for better fitting without having to lace clothing on the wearer.Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 38 Windmills were refined with the creation of the tower mill, allowing the upper part of the windmill to be spun around to face the direction from which the wind was blowing.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 200–201 The blast furnace appeared around 1350 in Sweden, increasing the quantity of iron produced and improving its quality.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 203–204 The first Patent, patent law in 1447 in Venice protected the rights of inventors to their inventions.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' p. 213
One of the major developments in the military sphere during the Late Middle Ages was the increased use of infantry and light cavalry.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 180 The English also employed longbowmen, but other countries were unable to create similar forces with the same success.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 183 Armour continued to advance, spurred by the increasing power of crossbows, and plate armour was developed to protect soldiers from crossbows as well as the hand-held guns that were developed.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 188 Pole weapon, Pole arms reached new prominence with the development of the Flemish and Swiss infantry armed with pikes and other long spears.Nicolle ''Medieval Warfare Source Book: Warfare in Western Christendom'' p. 185
In agriculture, the increased usage of sheep with long-fibred wool allowed a stronger thread to be spun. In addition, the spinning wheel replaced the traditional distaff for spinning wool, tripling production.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 193–194 A less technological refinement that still greatly affected daily life was the use of buttons as closures for garments, which allowed for better fitting without having to lace clothing on the wearer.Singman ''Daily Life'' p. 38 Windmills were refined with the creation of the tower mill, allowing the upper part of the windmill to be spun around to face the direction from which the wind was blowing.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 200–201 The blast furnace appeared around 1350 in Sweden, increasing the quantity of iron produced and improving its quality.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' pp. 203–204 The first Patent, patent law in 1447 in Venice protected the rights of inventors to their inventions.Epstein ''Economic and Social History'' p. 213
 The Late Middle Ages in Europe as a whole correspond to the Trecento and Renaissance, Early Renaissance cultural periods in Italy. Northern Europe and Spain continued to use Gothic styles, which became increasingly elaborate in the 15th century, until almost the end of the period. International Gothic was a courtly style that reached much of Europe in the decades around 1400, producing masterpieces such as the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 253–256 All over Europe secular art continued to increase in quantity and quality, and in the 15th century the mercantile classes of Italy and Flanders became important patrons, commissioning small portraits of themselves in oils as well as a growing range of luxury items such as jewellery, Casket with Scenes of Romances (Walters 71264), ivory caskets, cassone chests, and maiolica pottery. These objects also included the Hispano-Moresque ware produced by mostly Mudéjar potters in Spain. Although royalty owned huge collections of plate, little survives except for the Royal Gold Cup. Italian silk manufacture developed, so that Western churches and elites no longer needed to rely on imports from Byzantium or the Islamic world. In France and Flanders tapestry weaving of sets like ''The Lady and the Unicorn'' became a major luxury industry.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 257–262
The large external sculptural schemes of Early Gothic churches gave way to more sculpture inside the building, as tombs became more elaborate and other features such as pulpits were sometimes lavishly carved, as in the Pulpit of Sant' Andrea, Pistoia (Giovanni Pisano), Pulpit by Giovanni Pisano in Sant'Andrea. Painted or carved wooden relief altarpieces became common, especially as churches created many Chapel, side-chapels. Early Netherlandish painting by artists such as Jan van Eyck (d. 1441) and Rogier van der Weyden (d. 1464) rivalled that of Italy, as did northern illuminated manuscripts, which in the 15th century began to be collected on a large scale by secular elites, who also commissioned secular books, especially histories. From about 1450 printed books rapidly became popular, though still expensive. There were around 30,000 different editions of Incunable, incunabula, or works printed before 1500,British Library Staff
The Late Middle Ages in Europe as a whole correspond to the Trecento and Renaissance, Early Renaissance cultural periods in Italy. Northern Europe and Spain continued to use Gothic styles, which became increasingly elaborate in the 15th century, until almost the end of the period. International Gothic was a courtly style that reached much of Europe in the decades around 1400, producing masterpieces such as the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 253–256 All over Europe secular art continued to increase in quantity and quality, and in the 15th century the mercantile classes of Italy and Flanders became important patrons, commissioning small portraits of themselves in oils as well as a growing range of luxury items such as jewellery, Casket with Scenes of Romances (Walters 71264), ivory caskets, cassone chests, and maiolica pottery. These objects also included the Hispano-Moresque ware produced by mostly Mudéjar potters in Spain. Although royalty owned huge collections of plate, little survives except for the Royal Gold Cup. Italian silk manufacture developed, so that Western churches and elites no longer needed to rely on imports from Byzantium or the Islamic world. In France and Flanders tapestry weaving of sets like ''The Lady and the Unicorn'' became a major luxury industry.Benton ''Art of the Middle Ages'' pp. 257–262
The large external sculptural schemes of Early Gothic churches gave way to more sculpture inside the building, as tombs became more elaborate and other features such as pulpits were sometimes lavishly carved, as in the Pulpit of Sant' Andrea, Pistoia (Giovanni Pisano), Pulpit by Giovanni Pisano in Sant'Andrea. Painted or carved wooden relief altarpieces became common, especially as churches created many Chapel, side-chapels. Early Netherlandish painting by artists such as Jan van Eyck (d. 1441) and Rogier van der Weyden (d. 1464) rivalled that of Italy, as did northern illuminated manuscripts, which in the 15th century began to be collected on a large scale by secular elites, who also commissioned secular books, especially histories. From about 1450 printed books rapidly became popular, though still expensive. There were around 30,000 different editions of Incunable, incunabula, or works printed before 1500,British Library Staff The medieval period is frequently caricatured as a "time of ignorance and superstition" that placed "the word of religious authorities over personal experience and rational activity." This is a legacy from both the
The medieval period is frequently caricatured as a "time of ignorance and superstition" that placed "the word of religious authorities over personal experience and rational activity." This is a legacy from both the