McKenzie And Holland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several iron foundries in both England and the United States during the
Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several iron foundries in both England and the United States during the
 The Vulcan Iron Works at Osmaston Road,
The Vulcan Iron Works at Osmaston Road,
 The Vulcan Iron Works at Cromwell Street,
The Vulcan Iron Works at Cromwell Street,
Retrieved 16 February 2012. The machines made by the firm included: The ironworks was reported in 1884 to have grindstones of 7 ft (2 metre) diameter; "two cupolas blown by fans, one of which is capable of melting twenty tons of metal per day"; cranes and hoists; a brass moulding shop; a sand mill (for the mouldings); and a machine for grinding coal to dust. The buildings included a draughtsmen's office; a pattern makers' and joiners' shop; a packing room; an erecting and turning shop; and a smithy. All the machines were driven by rope from a single large wheel; two horizontal steam engines powered the entire ironworks. The journalist noted that "The death rate among grinders is very high indeed, which it is almost impossible to prevent."
 Vulcan Iron Works, based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, manufactured
Vulcan Iron Works, based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, manufactured
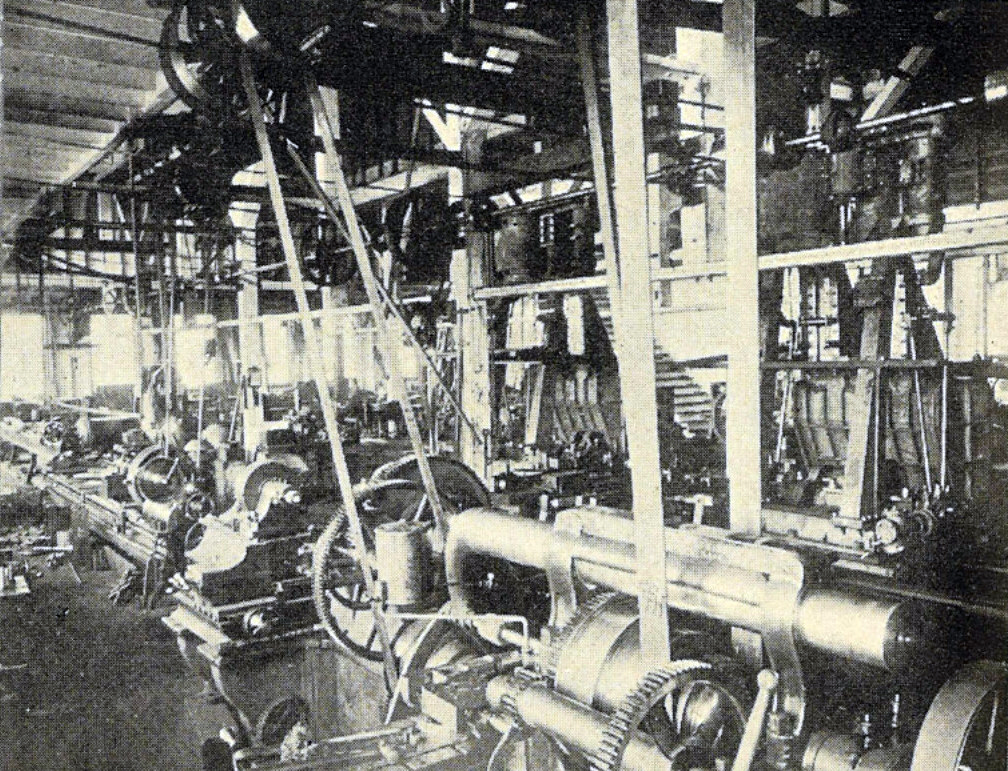 The Vulcan Iron Works in
The Vulcan Iron Works in
Preserved Vulcan Iron Works steam locomotive list
* ttp://www.prestonhistoricalsociety.org.uk/phs_display.php?mnImage=BH0971 Photograph of Gregson and Monk Engineers, Salter Street, Preston
Photograph of a Gregson and Monk power loom
Photograph of James Gregson's Highgate Park mansion, Preston in 1900
Photograph of a grate, cast by Vulcan Iron Works San Francisco
Finding Aid for Vulcan Iron Works collection at Hagley Library
Industrial machine manufacturers History of Worcester, England Foundries in the United States Defunct locomotive manufacturers of the United States Ironworks and steel mills in the United States Industrial buildings in England Foundries in the United Kingdom Buildings and structures destroyed in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
 Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several iron foundries in both England and the United States during the
Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several iron foundries in both England and the United States during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
and, in one case, lasting until the mid-20th century. Vulcan
Vulcan may refer to:
Mythology
* Vulcan (mythology), the god of fire, volcanoes, metalworking, and the forge in Roman mythology
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* Vulcan (''Star Trek''), name of a fictional race and their home p ...
, the Roman god of fire and smithery, was a popular namesake for these foundries.
England
During theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, numerous entrepreneurs independently founded factories named Vulcan Iron Works in England, notably that of Robinson Thwaites and Edward Carbutt at Bradford, and that of Thomas Clunes at Worcester,McKenzie and Holland Ltd, Vulcan Iron Works, Worcester http://www.miac.org.uk/mckenzie.htm Retrieved 12 October 2011 England. The largest of all the ironworks of Victorian England, the Cleveland Works of Bolckow Vaughan
Bolckow, Vaughan & Co., Ltd was an English steelmaking, ironmaking and mining company founded in 1864, based on the partnership since 1840 of its two founders, Henry Bolckow and John Vaughan (ironmaster), John Vaughan. The firm drove the dramat ...
in Middlesbrough, were on Vulcan Street.
Thwaites & Carbutt, Bradford
The Vulcan Works at Thornton Road,Bradford
Bradford is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 ...
was a spacious and handsome factory. It was described in Industries of Yorkshire as
Ley's, Derby
 The Vulcan Iron Works at Osmaston Road,
The Vulcan Iron Works at Osmaston Road, Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby gai ...
was founded in 1874 by Francis Ley
Sir Francis Ley, 1st Baronet (3 January 1846 – 27 January 1916) was an English industrialist. He founded Ley's Malleable Castings Vulcan Ironworks in Derby. He (re-)introduced baseball into the United Kingdom town of Derby with the Ley's Re ...
(1846-1916). On a site occupying 11 acres by the Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway, he manufactured castings for motor cars. The company became the Ley's Malleable Castings Company Ltd. In the London Gazette of April 14, 1876, Ley was granted a patent for "improvements in apparatus for locking and fastening nuts on fish plate and other bolts". The iron foundry was closed and demolished in 1986.
McKenzie, Clunes & Holland, Worcester
 The Vulcan Iron Works at Cromwell Street,
The Vulcan Iron Works at Cromwell Street, Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Englan ...
was founded in 1857 by Thomas Clunes (b. 1818, d. 28 September 1879). The firm started out as "Engineers, Millwrights, Iron & Brass Founders, Plumbers etc", according to the listing in '' Kelly's Directory''. The works had a single tall tapering square chimney, a covered area with open sides, and a handsome main building on a largely open site on the west side of the Worcester and Birmingham Canal
The Worcester and Birmingham Canal is a canal linking Birmingham and Worcester in England. It starts in Worcester, as an 'offshoot' of the River Severn (just after the river lock) and ends in Gas Street Basin in Birmingham. It is long.
There ar ...
.
By 1861, Clunes, a former "Plumber and Brass Founder" from Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
living in St Martin's, Worcester, with nine children, was a "Master Engineer employing 104 men and 10 boys"; his son Robert at age 11 was an "Apprentice to Engineer".The National Archives. 1861 England Census Record. Worcester, St Martin. RG 9/2092. District 11. Page 2. In 1861, Clunes was joined by two former railwaymen, McKenzie and Holland, and the firm moved into railway signalling
Railway signalling (), also called railroad signaling (), is a system used to control the movement of railway traffic. Trains move on fixed rails, making them uniquely susceptible to collision. This susceptibility is exacerbated by the enormou ...
equipment. Clunes retired to Fowey, Cornwall, and his name was dropped from the company's name in the 1870s. The entry in the Worcestershire Post Office Directory for 1876 is simply "RAILWAY SIGNAL MANFRS. McKenzie & Holland, Vulcan Iron Works, Worcester."
Vulcan Foundry, Newton-le-Willows
The Vulcan Foundry at Newton-le-Willows produced ironwork for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, as well as locomotives.Vulcan Iron Works, Langley Mill
The G R Turner company's Vulcan Iron Works atLangley Mill
Langley Mill is a large village in the Amber Valley district of Derbyshire, England.
History
Originally named ''Long Lea'', the village of Langley Mill was a major employer throughout the mid 1900s with many companies including The Flour Mi ...
, Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the nor ...
was built in 1874. GR Turner produced railway rolling stock until the 1960s; at its peak it employed 350 men. According to Grace's Guide, G R Turner was established in 1863; it became a Limited Company in 1902, and was registered on 29 January 1903 as acquiring T N Turner's business of "engineer, wheel and wagon maker"; in 1914 it was described as "Colliery Engineers" as well as making rolling stock, with 800 engineers.
Vulcan Ironworks, Preston
In 1857 the firm of Baxendale and Gregson was founded in Shepherd Street,Preston
Preston is a place name, surname and given name that may refer to:
Places
England
*Preston, Lancashire, an urban settlement
**The City of Preston, Lancashire, a borough and non-metropolitan district which contains the settlement
**County Boro ...
, Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancashi ...
. When the works there became too small, the business moved to a new Vulcan Ironworks, built at Salter Street, just off North Road, Preston, under the name Gregson and Monk.
In 1873, James Gregson bought 82 acres of land at Fulwood; in 1876 he built Highgate Park mansion with the land as its extensive gardens. He owned much property in Preston and was a councillor of Fulwood District. His son George Frederick Gregson ran the firm after him.
When Monk retired in March 1874, James Gregson became sole proprietor. He employed about 400 men, making up to 100 weaving looms per week. Over 25,000 looms made by Gregson were claimed to be at work in or near Preston in 1884.Our Local Industries. The Iron Trade. Messrs. Gregson and Monks, Vulcan Ironworks. (No. 9). Preston Chronicle, 30 August 1884. (Preston Digital Archive)Retrieved 16 February 2012. The machines made by the firm included: The ironworks was reported in 1884 to have grindstones of 7 ft (2 metre) diameter; "two cupolas blown by fans, one of which is capable of melting twenty tons of metal per day"; cranes and hoists; a brass moulding shop; a sand mill (for the mouldings); and a machine for grinding coal to dust. The buildings included a draughtsmen's office; a pattern makers' and joiners' shop; a packing room; an erecting and turning shop; and a smithy. All the machines were driven by rope from a single large wheel; two horizontal steam engines powered the entire ironworks. The journalist noted that "The death rate among grinders is very high indeed, which it is almost impossible to prevent."
United States
Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
 Vulcan Iron Works, based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, manufactured
Vulcan Iron Works, based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, manufactured railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s such as those shown in the illustration. The company was established in 1849 by Richard Jones. It built locomotives such as the preserved Berlin Mills Railway 7
Berlin Mills Railway 7 is a steam locomotive at Steamtown National Historic Site in Scranton, Pennsylvania. It was built in 1911 by the Vulcan Iron Works for the Berlin Mills Railway, an industrial line in Berlin, New Hampshire, Berlin, New Hamps ...
(1911), and by 1944 was constructing both steam and diesel locomotives, as illustrated (right). The company ceased operation in 1954, and its assets were acquired by General Industrial Locomotive Corp.
War-time service
In February 1944, before the 'D-Day'Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
, the company claimed
Today, hundreds of Vulcan locomotives are rendering vitally important war-time service, both at home and overseas, and our shops are working at top speed to complete urgent orders for Army, Navy and defense plant requirements. Tomorrow, more and larger Vulcan locomotives will be available to help rebuild a war-torn world. Our manufacturing facilities are being enlarged and improved ....
Locomotives
Vulcan produced a wide variety ofsteam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s, mostly small but some with up to eight driving wheels. With the advent of internal combustion technology, the firm began producing small locomotives fueled not only with gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
, but also benzine
Petroleum benzine is a hydrocarbon-based solvent mixture that is classified by its physical properties (e.g. boiling point, vapor pressure) rather than a specific chemical composition. This complicates distinction within the long list of petroleu ...
, alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
, kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
and naptha. Vulcan produced its first diesel locomotives in the 1920s; a total of 54 diesel-electric switcher
A switcher, shunter, yard pilot, switch engine, yard goat, or shifter is a small railroad locomotive used for manoeuvring railroad cars inside a rail yard in a process known as ''switching'' (US) or ''shunting'' (UK). Switchers are not inten ...
units (each weighing or more) came out of Vulcan's shops between 1938 and 1954. Its largest unit was a B-B unit built for Carnegie Steel Company in 1944. It also constructed the TCDD 56301 Class for the Turkish State Railways in 1947.
Vulcan built a large number of gasoline-powered locomotives with a mechanical drive, such as the Maumelle Ordnance Works Locomotive 1, built in 1942.
Seattle
 The Vulcan Iron Works in
The Vulcan Iron Works in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
had Jacob Furth
Jacob Furth (November 15, 1840 – June 2, 1914) was an Austrian Empire-born United States, American entrepreneur and prominent Seattle banker. He played a key role in consolidating Seattle's electric power and public transportation infrastructure ...
as its president. Furth ran the Vulcan Iron Works along with the Puget Sound Electric Railway and street railways on the Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected ma ...
.Clarence Bagley, ''History of Seattle from the earliest settlement to the present time'', Volume 2, The S.J. Clarke Publishing Company, 1916. p 732-738. This work is now in the public domain.
San Francisco
A Vulcan Iron Works was established at 135 Fremont Street,San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
in 1850 during the California gold rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
. The factory occupied the block bounded by Fremont, Mission, Howard, and First Streets. The factory maintained the name through a number of owners building boilers, steam engines, mining machinery, sawmills, and some relatively primitive steam locomotives for 19th century California railroads. It built the Oregon Pony in 1861.Other Geared Steam Locomotives — Page STUV. Geared Steam Locomotive Works. 2010-05-30. URL:http://www.gearedsteam.com/other/other_stuv.htm. The factory was destroyed by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
, but steel fabrication activities resumed on the site after the quake.
Charleston
There was a Vulcan Iron Works on Cumberland Street,Charleston
Charleston most commonly refers to:
* Charleston, South Carolina
* Charleston, West Virginia, the state capital
* Charleston (dance)
Charleston may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Charleston, South Australia
Canada
* Charleston, Newfoundlan ...
, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
in 1865.
See also
* Vulcan (motor vehicles)References
{{reflist, 32emExternal links
Preserved Vulcan Iron Works steam locomotive list
* ttp://www.prestonhistoricalsociety.org.uk/phs_display.php?mnImage=BH0971 Photograph of Gregson and Monk Engineers, Salter Street, Preston
Photograph of a Gregson and Monk power loom
Photograph of James Gregson's Highgate Park mansion, Preston in 1900
Photograph of a grate, cast by Vulcan Iron Works San Francisco
Finding Aid for Vulcan Iron Works collection at Hagley Library
Industrial machine manufacturers History of Worcester, England Foundries in the United States Defunct locomotive manufacturers of the United States Ironworks and steel mills in the United States Industrial buildings in England Foundries in the United Kingdom Buildings and structures destroyed in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake