Mandala (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A mandala ( sa, मण्डल, maṇḍala, circle, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for establishing a
 In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a ''
In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a ''
''Vajrabhairava mandala''
a silk tapestry woven with gilded paper depicting lavish elements like crowns and jewelry, which gives a three-dimensional effect to the piece.
''Cosmological Mandala with Mount Meru''
a

 A "mandala offering" in
A "mandala offering" in
 The mandala in
The mandala in
 Mandalas have sometimes been used in
Mandalas have sometimes been used in

https://video.alexanderstreet.com/watch/sand-painting-sacred-art-of-tibet . These sand mandalas are made to be destroyed to symbolize impermanence, the Buddhist belief that death is not the end, and that one's essence will always return to the elements. It is also related to the belief that one should not become attached to anything. To create these mandalas, the monks first create a sketch, then take colorful sand traditionally made from powdered stones and gems into copper funnels called Cornetts and gently tap sand out of them to create the sand mandala. Each color represents attributes of deities. While making the mandalas the monks will pray and meditate, each grain of sand represents a blessing. Monks will travel to demonstrate this art form to people, often in museums.
 The Sun Stone is thought to be a ceremonial representation of the entire universe as seen by the Aztec religious class, in some ways resembling a mandala.
The earliest interpretations of the stone relate to its use as a calendar. In 1792, two years after the stone's unearthing, Mexican anthropologist
The Sun Stone is thought to be a ceremonial representation of the entire universe as seen by the Aztec religious class, in some ways resembling a mandala.
The earliest interpretations of the stone relate to its use as a calendar. In 1792, two years after the stone's unearthing, Mexican anthropologist
''getty.edu'', accessed 22 August 2018 Yet another characteristic of the stone is its possible geographic significance. The four points may relate to the four corners of the earth or the cardinal points. The inner circles may express space as well as time. Lastly, there is the political aspect of the stone. It may have been intended to show
 The
The 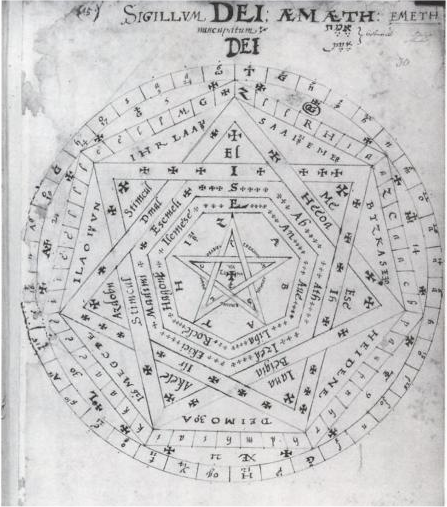

File:元 緙絲 須彌山曼陀羅-Cosmological Mandala with Mount Meru MET DP276037.jp
Cosmological mandala with Mount Meru
silk tapestry, China via The Metropolitan Museum of Art File:元 緙絲大威德金剛曼陀羅-Vajrabhairava Mandala MET DT841.jp
Vajrabhairava mandala
silk tapestry, China via The Metropolitan Museum of Art File:Sri Yantra 256bw.gif, A diagramic drawing of the
Introduction to Mandalas
{{Authority control Buddhist philosophical concepts Buddhist art Buddhist meditation Ceremonies Hindu philosophical concepts Indian iconography Meditation Religious objects Religious symbols Tibetan Buddhist practices Tibetan Buddhist ritual implements
sacred space
Sacred space, sacred ground, sacred place, sacred temple, holy ground, or holy place refers to a location which is deemed to be sacred or hallowed. The sacredness of a natural feature may accrue through tradition or be granted through a bless ...
and as an aid to meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
and trance
Trance is a state of semi-consciousness in which a person is not self-aware and is either altogether unresponsive to external stimuli (but nevertheless capable of pursuing and realizing an aim) or is selectively responsive in following the dir ...
induction. In the Eastern religions
The Eastern religions are the religions which originated in East, South and Southeast Asia and thus have dissimilarities with Western, African and Iranian religions. This includes the East Asian religions such as Confucianism, Taoism, Chinese fol ...
of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
and Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
it is used as a map representing deities, or especially in the case of Shinto, paradises, kami
are the deities, divinities, spirits, phenomena or "holy powers", that are venerated in the Shinto religion. They can be elements of the landscape, forces of nature, or beings and the qualities that these beings express; they can also be the sp ...
or actual shrines. A mandala generally represents the spiritual journey, starting from outside to the inner core, through layers.
Hinduism
 In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a ''
In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a ''yantra
Yantra () (literally "machine, contraption") is a geometrical diagram, mainly from the Tantric traditions of the Indian religions. Yantras are used for the worship of deities in temples or at home; as an aid in meditation; used for the benefits ...
'', takes the form of a square with four gates containing a circle with a center point. Each gate is in the general shape of a T. Mandalas often have radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric)
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) ...
balance
Balance or balancing may refer to:
Common meanings
* Balance (ability) in biomechanics
* Balance (accounting)
* Balance or weighing scale
* Balance as in equality or equilibrium
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgarian ...
.
A ''yantra
Yantra () (literally "machine, contraption") is a geometrical diagram, mainly from the Tantric traditions of the Indian religions. Yantras are used for the worship of deities in temples or at home; as an aid in meditation; used for the benefits ...
'' is similar to a mandala, usually smaller and using a more limited colour palette. It may be a two- or three-dimensional geometric composition used in '' sadhanas'', puja or meditative rituals, and may incorporate a mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
into its design. It is considered to represent the abode of the deity. Each ''yantra'' is unique and calls the deity into the presence of the practitioner through the elaborate symbolic geometric designs. According to one scholar, "Yantras function as revelatory symbols of cosmic truths and as instructional charts of the spiritual aspect of human experience"
Many situate ''yantras'' as central focus points for Hindu tantric practice. ''Yantras'' are not representations, but are lived, experiential, nondual
Nondualism, also called nonduality and nondual awareness, is a fuzzy concept originating in Indian philosophy and religion for which many definitions can be found, including: nondual awareness, the nonduality of seer and seen or nondiffer ...
realities. As Khanna describes:
The term 'mandala' appears in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
as the name of the sections of the work, and Vedic rituals
The historical Vedic religion (also known as Vedicism, Vedism or ancient Hinduism and subsequently Brahmanism (also spelled as Brahminism)), constituted the religious ideas and practices among some Indo-Aryan peoples of northwest Indian Subco ...
use mandalas such as the Navagraha
Navagraha are nine heavenly bodies and deities that influence human life on Earth according to Hinduism and Hindu astrology. The term is derived from ''nava'' ( sa, नव "nine") and ''graha'' ( sa, ग्रह "planet, seizing, laying hold of, ...
mandala to this day.
Buddhism
Vajrayana
InVajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
Buddhism, mandalas have been developed also into sandpainting
Sandpainting is the art of pouring coloured sands, and powdered pigments from minerals or crystals, or pigments from other natural or synthetic sources onto a surface to make a fixed or unfixed sand painting. Unfixed sand paintings have a long es ...
. They are also a key part of Anuttarayoga Tantra
Classes of Tantra in Tibetan Buddhism refers to the categorization of Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist tantric scriptures in Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism. Tibetan Buddhism inherited numerous tantras and forms of Tantra, tantric practice from ...
meditation practices.
Visualisation of Vajrayana teachings
The man mandala can be shown to represent in visual form the core essence of theVajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
teachings. The mandala represents the nature of the Pure Land, Enlightened mind.
An example of this type of mandala i''Vajrabhairava mandala''
a silk tapestry woven with gilded paper depicting lavish elements like crowns and jewelry, which gives a three-dimensional effect to the piece.
=Mount Meru
= A mandala can also represent the entire universe, which is traditionally depicted withMount Meru
Mount Meru (Sanskrit/Pali: मेरु), also known as Sumeru, Sineru or Mahāmeru, is the sacred five-peaked mountain of Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist cosmology and is considered to be the centre of all the physical, metaphysical and spiritu ...
as the axis mundi
In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles.
In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere.
Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the '' ...
in the center, surrounded by the continents. One example is th''Cosmological Mandala with Mount Meru''
a
silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven by hand on a loom. Tapestry is weft-faced weaving, in which all the warp threads are hidden in the completed work, unlike most woven textiles, where both the warp and the weft threads may ...
from the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
that serves as a diagram of the Tibetan cosmology, which was given to China from Nepal and Tibet.
=Wisdom and impermanence
= In the mandala, the outer circle of fire usually symbolises wisdom. The ring of eightcharnel ground
A charnel ground (Sanakrit: श्मशान; IAST: śmaśāna; Tibetan pronunciation: durtrö; )Rigpa Shedra (July 2009). 'Charnel ground'. Source(accessed: Saturday December 19, 2009) is an above-ground site for the putrefaction of bodies, g ...
s represents the Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
exhortation to be always mindful of death, and the impermanence with which '' samsara'' is suffused: "such locations were utilized in order to confront and to realize the transient nature of life". Described elsewhere: "within a flaming rainbow nimbus and encircled by a black ring of dorje
The Vajra () is a legendary and ritual weapon, symbolising the properties of a diamond (indestructibility) and a thunderbolt (irresistible force).
The vajra is a type of club with a ribbed spherical head. The ribs may meet in a ball-shape ...
s, the major outer ring depicts the eight great charnel grounds, to emphasize the dangerous nature of human life". Inside these rings lie the walls of the mandala palace itself, specifically a place populated by deities and Buddhas.
=Five Buddhas
= One well-known type of mandala is the mandala of the "Five Buddhas", archetypal Buddha forms embodying various aspects of enlightenment. Such Buddhas are depicted depending on the school ofBuddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, and even the specific purpose of the mandala. A common mandala of this type is that of the Five Wisdom Buddhas
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
5, five or number 5 may also refer to:
* AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era
* 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era
Literature
* ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram
* ''5'' (comics), an awa ...
(a.k.a. Five ''Jinas
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (Sanskrit: '; English: literally a ' ford-maker') is a saviour and spiritual teacher of the ''dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a '' tirtha'', which is a fordable passa ...
''), the Buddhas Vairocana
Vairocana (also Mahāvairocana, sa, वैरोचन) is a cosmic buddha from Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism. Vairocana is often interpreted, in texts like the ''Avatamsaka Sutra'', as the dharmakāya of the historical Gautama Buddha. In East ...
, Aksobhya
Akshobhya ( sa, अक्षोभ्य, ''Akṣobhya'', "Immovable One"; ) is one of the Five Wisdom Buddhas, a product of the Adibuddha, who represents consciousness as an aspect of reality. By convention he is located in the east of the Di ...
, Ratnasambhava
Ratnasambhava ( sa, रत्नसम्भव, lit. "Jewel-Born") is one of the Five Dhyani Buddhas (or "Five Meditation Buddhas") of Mahayana and Vajrayana or Tantric Buddhism. Ratnasambhava's mandalas and mantras focus on developing equanimity ...
, Amitabha and Amoghasiddhi
Amoghasiddhi (Devanagari: अमोघसिद्धि}) is one of the Five Wisdom Buddhas of the Mahayana and Vajrayana tradition of Buddhism. He is associated with the accomplishment of the Buddhist path and of the destruction of the poison o ...
. When paired with another mandala depicting the Five Wisdom Kings
A Wisdom King (Sanskrit: विद्याराज; IAST: ''Vidyārāja'', ) is a type of wrathful deity in East Asian Buddhism.
Whereas the Sanskrit name is translated literally as "wisdom / knowledge king(s)," the term '' vidyā'' in Vajra ...
, this forms the Mandala of the Two Realms
The Mandala of the Two Realms (Traditional Chinese: 両界曼荼羅; Pinyin: ''Liǎngjiè màntúluó''; Romanji: ''Ryōkai mandara''), also known as the Mandala of the Two Divisions (Traditional Chinese: 両部曼荼羅; Pinyin: ''Liǎngbù màn ...
.
Practice
Mandalas are commonly used by tantric Buddhists as an aid to meditation. The mandala is "a support for the meditating person", something to be repeatedly contemplated to the point of saturation, such that the image of the mandala becomes fully internalised in even the minutest detail and can then be summoned and contemplated at will as a clear and vivid visualized image. With every mandala comes what Tucci calls "its associated liturgy ... contained in texts known astantras
Tantras ("''doctrine''" or "''framework''" or "''system''" ) refers to numerous and varied scriptures pertaining to any of several esoteric traditions rooted in Hindu and Buddhist philosophy. The religious culture of the Tantras is essentially ...
", instructing practitioners on how the mandala should be drawn, built and visualised, and indicating the mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
s to be recited during its ritual use.
By visualizing "pure lands", one learns to understand experience ''itself'' as pure, and as the abode of enlightenment. The protection that we need, in this view, is from our own minds, as much as from external sources of confusion. In many tantric mandalas, this aspect of separation and protection from the outer samsaric world is depicted by "the four outer circles: the purifying fire of wisdom, the vajra
The Vajra () is a legendary and ritual weapon, symbolising the properties of a diamond (indestructibility) and a thunderbolt (irresistible force).
The vajra is a type of club with a ribbed spherical head. The ribs may meet in a ball-shape ...
circle, the circle with the eight tombs, the lotus circle". The ring of ''vajras'' forms a connected fence-like arrangement running around the perimeter of the outer mandala circle.
As a meditation on impermanence (a central teaching of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
), after days or weeks of creating the intricate pattern of a sand mandala
Sand mandala (; ) is a Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist tradition involving the creation and destruction of mandalas made from colored sand. Once complete, the sand mandala's ritualistic Art destruction, dismantling is accompanied by ceremo ...
, the sand is brushed together into a pile and spilled into a body of running water to spread the blessings of the mandala.
Kværne in his extended discussion of sahaja
Sahaja ( pra, সহজ sa, सहज ) means spontaneous enlightenment in Indian and Tibetan Buddhist spirituality. Sahaja practices first arose in Bengal during the 8th century among yogis called Sahajiya siddhas.
Ananda Coomaraswamy describe ...
, discusses the relationship of sadhana interiority and exteriority in relation to mandala thus:

Offerings
 A "mandala offering" in
A "mandala offering" in Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
is a symbolic offering of the entire universe. Every intricate detail of these mandalas is fixed in the tradition and has specific symbolic meanings, often on more than one level.
Whereas the above mandala represents the pure surroundings of a Buddha, this mandala represents the universe. This type of mandala is used for the mandala-offerings, during which one symbolically offers the universe to the Buddhas or to one's teacher. Within Vajrayana practice, 100,000 of these mandala offerings (to create merit) can be part of the preliminary practices before a student even begins actual tantric practices. This mandala is generally structured according to the model of the universe as taught in a Buddhist classic text the '' Abhidharma-kośa'', with Mount Meru
Mount Meru (Sanskrit/Pali: मेरु), also known as Sumeru, Sineru or Mahāmeru, is the sacred five-peaked mountain of Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist cosmology and is considered to be the centre of all the physical, metaphysical and spiritu ...
at the centre, surrounded by the continents, oceans and mountains, etc.
Theravada Buddhism
Various Mandalas are described in many Pali Buddhist texts. Some of the examples of theTheravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
Buddhist Mandalas are:
* Mandala of Eight Disciples of Buddha describing the Shakyamuni Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was ...
at center and Eight great disciple in eight major directions.
* Mandala of Buddhas is the mandala consisting of nine major Buddhas of the past and the present Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lu ...
occupying the ten directions.
* Mandala of Eight Devis includes the eight Devis occupying and protecting the eight corners of the Universe.
In Sigālovāda Sutta
Sigalovada Sutta is the 31st Sutta described in the Digha Nikaya ("Long Discourses of Buddha"). It is also known as the Sīgāla Sutta, the Sīgālaka Sutta, the Sigālovāda Sutta, and the Sigālovāda Suttanta ("The Sigāla Homily").
Buddhagh ...
, Buddha describes the relationships of a common lay persons in Mandala style.
Shingon Buddhism
One Japanese branch of Mahayana Buddhism –Shingon
file:Koyasan (Mount Koya) monks.jpg, Shingon monks at Mount Koya
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks suc ...
Buddhism – makes frequent use of mandalas in its rituals as well, though the actual mandalas differ. When Shingon's founder, Kukai, returned from his training in China, he brought back two mandalas that became central to Shingon ritual: the Mandala of the Womb Realm and the Mandala of the Diamond Realm.
These two mandalas are engaged in the '' abhiseka'' initiation rituals for new Shingon students, more commonly known as the (). A common feature of this ritual is to blindfold the new initiate and to have them throw a flower upon either mandala. Where the flower lands assists in the determination of which tutelary deity
A tutelary () (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety and ...
the initiate should follow.
Sand mandala
Sand mandala (; ) is a Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist tradition involving the creation and destruction of mandalas made from colored sand. Once complete, the sand mandala's ritualistic Art destruction, dismantling is accompanied by ceremo ...
s, as found in Tibetan Buddhism, are not practiced in Shingon Buddhism.
Nichiren Buddhism
 The mandala in
The mandala in Nichiren Buddhism
Nichiren Buddhism ( ja, 日蓮仏教), also known as Hokkeshū ( ja, 法華宗, meaning ''Lotus Sect'') is a branch of Mahayana Buddhism based on the teachings of the 13th-century Japanese Buddhist priest Nichiren (1222–1282) and is one of ...
is a (), which is a paper hanging scroll
A hanging scroll is one of the many traditional ways to display and exhibit East Asian painting and calligraphy. The hanging scroll was displayed in a room for appreciation; it is to be distinguished from the handscroll, which was narrower and ...
or wooden tablet whose inscription consists of Chinese characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
and medieval-Sanskrit script representing elements of the Buddha's enlightenment, protective Buddhist deities, and certain Buddhist concepts. Called the ''Gohonzon
is a generic term for a venerated religious object in Japanese Buddhism. It may take the form of a scroll or statuary. The term typically refers to the mainstream use of venerated objects within Nichiren Buddhism, referring to the calligr ...
'', it was originally inscribed by Nichiren
Nichiren (16 February 1222 – 13 October 1282) was a Japanese Buddhist priest and philosopher of the Kamakura period.
Nichiren declared that the Lotus Sutra alone contains the highest truth of Buddhist teachings suited for the Third Age of B ...
, the founder of this branch of Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had a ...
, during the late 13th Century. The ''Gohonzon'' is the primary object of veneration in some Nichiren schools and the only one in others, which consider it to be the supreme object of worship as the embodiment of the supreme Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for '' ...
and Nichiren's inner enlightenment. The seven characters Namu Myōhō Renge Kyō
''Namu Myōhō Renge Kyō'' () are Japanese words chanted within all forms of Nichiren Buddhism. In English, they mean "Devotion to the Mystic Law of the Lotus Sutra" or "Glory to the Dharma of the Lotus Sutra".
The words refer to the Japanese ...
, considered to be the name of the supreme Dharma, as well as the invocation
An invocation (from the Latin verb ''invocare'' "to call on, invoke, to give") may take the form of:
*Supplication, prayer or spell.
*A form of possession.
*Command or conjuration.
*Self-identification with certain spirits.
These forms are ...
that believers chant, are written down the center of all Nichiren-sect ''Gohonzons'', whose appearance may otherwise vary depending on the particular school and other factors.
Pure Land Buddhism
 Mandalas have sometimes been used in
Mandalas have sometimes been used in Pure Land Buddhism
Pure Land Buddhism (; ja, 浄土仏教, translit=Jōdo bukkyō; , also referred to as Amidism in English,) is a broad branch of Mahayana Buddhism focused on achieving rebirth in a Buddha's Buddha-field or Pure Land. It is one of the most wid ...
to graphically represent Pure Land
A pure land is the celestial realm of a buddha or bodhisattva in Mahayana Buddhism. The term "pure land" is particular to East Asian Buddhism () and related traditions; in Sanskrit the equivalent concept is called a buddha-field (Sanskrit ). Th ...
s, based on descriptions found in the '' Larger Sutra'' and the ''Contemplation Sutra
The ''Amitāyurdhyāna Sūtra'' (Sanskrit; , ''Guan-wuliangshou-jing;'' Vietnamese: Phật Thuyết Kinh Quán Vô Lượng Thọ Phật; English: ''Sutra on the Visualization of he BuddhaImmeasurable Life'') is a Mahayana sutra in Pure Land Bu ...
''. The most famous mandala in Japan is the Taima mandala
The Taima Mandala (當麻曼荼羅,綴織当麻曼荼羅図) is an 8th century mandala in Japanese Pure Land Buddhism. It depicts Sukhavati, the western Pure Land, with the Buddha Amitābha (Japanese: Amida) in the center. The original copy was ...
, dated to about 763 CE. The Taima mandala is based on the ''Contemplation Sutra'', but other similar mandalas have been made subsequently. Unlike mandalas used in Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
Buddhism, it is not used as an object of meditation or for esoteric ritual. Instead, it provides a visual representation of the Pure Land texts, and is used as a teaching aid.
Also in Jodo Shinshu Buddhism, Shinran
''Popular Buddhism in Japan: Shin Buddhist Religion & Culture'' by Esben Andreasen, pp. 13, 14, 15, 17. University of Hawaii Press 1998, was a Japanese Buddhist monk, who was born in Hino (now a part of Fushimi, Kyoto) at the turbulent close of ...
and his descendant, Rennyo
Rennyo (, 1415–1499) was the 8th Monshu (head priest) of the Hongan-ji Temple of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, and descendant of founder Shinran. Jodo Shinshu Buddhists often referred to as the restorer of the sect ( in Japanese). He w ...
, sought a way to create easily accessible objects of reverence for the lower-classes of Japanese society. Shinran designed a mandala using a hanging scroll, and the words of the ''nembutsu
Nianfo (, Japanese: , , vi, niệm Phật) is a term commonly seen in Pure Land Buddhism. In the context of Pure Land practice, it generally refers to the repetition of the name of Amitābha. It is a translation of Sanskrit '' '' (or, "recolle ...
'' () written vertically. This style of mandala is still used by some Jodo Shinshu Buddhists in home altars, or ''butsudan
A , sometimes spelled Butudan, is a shrine commonly found in temples and homes in Japanese Buddhist cultures. A ''butsudan'' is either a defined, often ornate platform or simply a wooden cabinet sometimes crafted with doors that enclose and pr ...
''.
Bodhimandala
Bodhimaṇḍala is a term inBuddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
that means "circle of awakening".
Sand mandalas

Sand mandala
Sand mandala (; ) is a Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist tradition involving the creation and destruction of mandalas made from colored sand. Once complete, the sand mandala's ritualistic Art destruction, dismantling is accompanied by ceremo ...
s are colorful mandalas made from sand that are ritualistically destroyed. They originated in India in the 8th-12th century but are now practiced in Tibetan Buddhism. Each mandala is dedicated to specific deities. In Buddhism Deities represent states of the mind to be obtained on the path to enlightenment, the mandala itself is representative of the deities palace which also represents the mind of the deity. Each mandala is a pictorial representation of a tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the Indian ...
. for the process of making Sand mandalas they are created by monks that have trained for 3-5 years in a monastery."Sand Painting: Sacred Art of Tibet." , directed by Sheri Brenner. , produced by Sheri Brenner. , Berkeley Media, 2002. Alexander Street, Mesoamerican civilizations
Mayan ''Tzolk'in''
TheMaya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a populat ...
civilization tended to present calendars in a form similar to a mandala. It is similar in form and function to the ''Kalachakra
''Kālacakra'' () is a polysemic term in Vajrayana Buddhism that means "wheel of time" or "time cycles". "''Kālacakra''" is also the name of a series of Buddhist texts and a major practice lineage in Indian Buddhism and Tibetan Buddhism. The ta ...
'' (Wheel of Time) sand paintings of Tibetan Buddhists. Maya symbolism was later used in the Dreamspell
The Dreamspell is an esoteric calendar in part inspired by the Maya calendar by New Age spiritualist, Mayanist philosopher, and author José Argüelles and Lloydine Burris Argüelles. The Dreamspell calendar was initiated in 1987 and released ...
calendar, developed by José Argüelles
José Argüelles (; born Joseph Anthony Argüelles; January 24, 1939 – March 23, 2011) was an American New Age author and artist. He was the co-founder, along with Lloydine Argüelles, of the Planet Art Network and the Foundation for the Law of ...
. Sometimes described as an authentic Mayan mandala, it is "inspired by" elements of the 260-day Tzolk'in calendar (as opposed to the 365-day Haabʼ
The Haabʼ () is part of the Maya calendric system. It was a 365-day calendar used by many of the pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica.
Description
The Haabʼ comprises eighteen months of twenty days each, plus an additional period of five day ...
calendar).
Aztec Sun Stone
 The Sun Stone is thought to be a ceremonial representation of the entire universe as seen by the Aztec religious class, in some ways resembling a mandala.
The earliest interpretations of the stone relate to its use as a calendar. In 1792, two years after the stone's unearthing, Mexican anthropologist
The Sun Stone is thought to be a ceremonial representation of the entire universe as seen by the Aztec religious class, in some ways resembling a mandala.
The earliest interpretations of the stone relate to its use as a calendar. In 1792, two years after the stone's unearthing, Mexican anthropologist Antonio de León y Gama
Antonio de León y Gama (1735–1802) was a Mexican astronomer, anthropologist and writer. When in 1790 the Aztec calendar stone (also called sun stone) was discovered buried under the main square of Mexico City, he published an essay about it ...
wrote a treatise on the Aztec calendar using the stone as its basis. Some of the circles of glyph
A glyph () is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A g ...
s are the glyphs for the days of the month.K. Mills, W. B. Taylor & S. L. Graham (eds), ''Colonial Latin America: A Documentary History'', 'The Aztec Stone of the Five Eras', p. 23 The four symbols included in the Ollin glyph represent the four past suns that the Mexica believed the earth had passed through.
Another aspect of the stone is its religious significance. One theory is that the face at the center of the stone represents Tonatiuh, the Aztec deity of the sun; it is for this reason that the stone became known as the "Sun Stone." Richard Townsend proposed a different theory, claiming that the figure at the center of the stone represents Tlaltecuhtli
Tlaltecuhtli (Classical Nahuatl ''Tlāltēuctli'', ) is a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican deity worshipped primarily by the Mexica (Aztec) people. Sometimes referred to as the "earth monster," Tlaltecuhtli's dismembered body was the basis for the worl ...
, the Mexica earth deity who features in Mexica creation myths. Modern archaeologists, such as those at the National Anthropology Museum
The National Museum of Anthropology ( es, Museo Nacional de Antropología, MNA) is a national museum of Mexico. It is the largest and most visited museum in Mexico. Located in the area between Paseo de la Reforma and Mahatma Gandhi Street within ...
in Mexico City, believe it is more likely to have been used primarily as a ceremonial basin or ritual altar for gladiatorial sacrifices than as an astrological or astronomical reference.Getty Museum, "Aztec Calendar Stone"''getty.edu'', accessed 22 August 2018 Yet another characteristic of the stone is its possible geographic significance. The four points may relate to the four corners of the earth or the cardinal points. The inner circles may express space as well as time. Lastly, there is the political aspect of the stone. It may have been intended to show
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
as the center of the world and therefore, as the center of authority. Townsend argues in favor of this idea, claiming that the small glyphs of additional dates amongst the four previous suns - 1 Flint (''Tecpatl''), 1 Rain (''Atl''), and 7 Monkey (''Ozomahtli'') – represent matters of historical importance to the Mexica state. He posits, for example, that 7 Monkey represents the significant day for the cult of a community within ''Tenochtitlan''. His claim is further supported by the presence of Mexica ruler Moctezuma II
Moctezuma Xocoyotzin ( – 29 June 1520; oteːkˈsoːmaḁ ʃoːkoˈjoːt͡sĩn̥), nci-IPA, Motēuczōmah Xōcoyōtzin, moteːkʷˈsoːma ʃoːkoˈjoːtsin variant spellings include Motewksomah, Motecuhzomatzin, Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecu ...
's name on the work.
Christianity
 The
The Cosmati
The Cosmati were a Roman family, seven members of which, for four generations, were skilful architects, sculptors and workers in decorative geometric mosaic, mostly for church floors. Their name is commemorated in the genre of Cosmatesque work, ...
pavements, including that at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
, are geometric supposedly mandala-like mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
designs from thirteenth century Italy. The Great Pavement at Westminster Abbey is believed to embody divine and cosmic geometries as the seat of enthronement of the monarchs of England.
Similarly, many of the Illuminations of Hildegard von Bingen
Hildegard of Bingen (german: Hildegard von Bingen; la, Hildegardis Bingensis; 17 September 1179), also known as Saint Hildegard and the Sibyl of the Rhine, was a German Benedictine abbess and polymath active as a writer, composer, philosopher ...
can be used as mandalas, as well as many of the images of esoteric Christianity
Esoteric Christianity is an approach to Christianity which features "secret traditions" that require an initiation to learn or understand.Guy G. Stroumsa (2005). Hidden Wisdom: Esoteric Traditions and the Roots of Christian Mysticism. Leiden: Br ...
, as in Christian Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical system that is primarily based on the purported teachings of Hermes Trismegistus (a legendary Hellenistic combination of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth). These teachings are containe ...
, Christian Alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
, and Rosicrucianism
Rosicrucianism is a spiritual and cultural movement that arose in Europe in the early 17th century after the publication of several texts purported to announce the existence of a hitherto unknown esoteric order to the world and made seeking its ...
.
Alchemist, mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
and astrologer
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, teacher, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divinatio ...
developed a geometric symbol which he called the ''Sigillum Dei
The Sigillum Dei (seal of God, or signum dei vivi, symbol of the living God, called by John Dee the Sigillum Dei Aemeth) is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the name ...
'' (Seal of God) manifesting a universal geometric order which incorporated the names of the archangels
Archangels () are the second lowest rank of angel in the hierarchy of angels. The word ''archangel'' itself is usually associated with the Abrahamic religions, but beings that are very similar to archangels are found in a number of other relig ...
, derived from earlier forms of the ''clavicula salomonis'' or key of Solomon
The ''Key of Solomon'' ( la, Clavicula Salomonis; he, מפתח שלמה []) (Also known as "The Greater Key of Solomon") is a pseudepigraphical grimoire (also known as a book of spells) attributed to Solomon, King Solomon. It probably dates ba ...
.

The Layer Monument
The Layer monument is an early 17th-century polychrome marble mural monument (320 × 350 cm) erected in the memory of the lawyer Christopher Layer (1531–1600), and located in the Church of Saint John the Baptist, Norwich.
Inscription
Its ...
, an early 17th-century marble mural funerary monument at the Church of Saint John the Baptist, Maddermarket, Norwich
The Church of St John the Baptist, Maddermarket, is a redundant Anglican church in the city of Norwich, Norfolk, England. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building, and is in the care ...
, is a rare example of Christian iconography absorbing alchemical symbolism to create a mandala in Western funerary art.
Western psychological interpretations
The re-introduction of mandalas into modern Western thought is largely credited to psychologistCarl Gustav Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philo ...
. In his exploration of the unconscious through art, Jung observed the common appearance of a circle motif across religions and cultures. He hypothesized that the circle drawings reflected the mind's inner state at the moment of creation and were a kind of symbolic archetype in the universal subconscious. Familiarity with the philosophical writings of India prompted Jung to adopt the word "mandala" to describe these drawings created by himself and his patients. In his autobiography, Jung wrote:
Jung claimed that the urge to make mandalas emerges during moments of intense personal growth. He further hypothesized their appearance indicated a "profound re-balancing process" is underway in the psyche; the result of the process would be a more complex and better integrated personality.
American art therapist Joan Kellogg later created the MARI card test, a free response measure, based on Jung's work.
Transpersonal psychologist David Fontana
David G. J. Fontana FBPsS (1 November 1934 – 18 October 2010) was a British psychologist, parapsychologist and author. He was Professor of Psychology at Cardiff University. He was also visiting professor at Liverpool John Moores University and ...
proposed that the symbolic nature of a mandala may help one "to access progressively deeper levels of the unconscious, ultimately assisting the meditator to experience a mystical sense of oneness with the ultimate unity from which the cosmos in all its manifold forms arises."
In architecture
Buddhist architecture
Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries ( viharas), places to venerate relics (stupas), and shrines or prayer ha ...
often applied mandala as the blueprint or plan to design Buddhist structures, including temple complex and stupas. A notable example of mandala in architecture is the 9th century Borobudur
Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur ( id, Candi Borobudur, jv, ꦕꦤ꧀ꦝꦶꦧꦫꦧꦸꦝꦸꦂ, Candhi Barabudhur) is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, not far from the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indone ...
in Central Java, Indonesia. It is built as a large stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circumamb ...
surrounded by smaller ones arranged on terraces formed as a stepped pyramid
A step pyramid or stepped pyramid is an architectural structure that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed shape similar to a geometric pyramid. Step pyramids are structures which characterized several ...
, and when viewed from above, takes the form of a giant tantric Buddhist
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
mandala, simultaneously representing the Buddhist cosmology and the nature of mind. Other temples from the same period that also have mandala plans include Sewu
Sewu ( jv, ꦱꦺꦮꦸ, Sèwu) is an eighth century Mahayana Buddhist temple located 800 metres north of Prambanan in Central Java, Indonesia. The word for a Hindu or Buddhist temple in Indonesian is "candi," hence the common name is "Candi Sew ...
, Plaosan
Candi Plaosan, also known as the 'Plaosan Complex', is one of the Buddhist temples located in Bugisan village, Prambanan district, Klaten Regency, Central Java, Indonesia, about to the northeast of the renowned Hindu Prambanan Temple.
Candi Pla ...
and Prambanan
Prambanan ( id, Candi Prambanan, jv, ꦫꦫꦗꦺꦴꦁꦒꦿꦁ, Rara Jonggrang) is a 9th-century Hindu temple compound in Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia, dedicated to the Trimūrti, the expression of God as the Creator (Brahma), the P ...
. Similar mandala designs are also observable in Cambodia, Thailand and Myanmar.
In science
Circular diagrams are often used inphylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek language, Greek wikt:φυλή, φυλή/wikt:φῦλον, φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary his ...
, especially for the graphical representation of phylogenetic relationships. Evolutionary trees often encompass numerous species that are conveniently shown on a circular tree, with images of the species shown on the periphery of a tree. Such diagrams have been called phylogenetic mandalas.
In art
Mandala as an art form first appeared in Buddhist art that were produced in India during the first century B.C.E. These can also be seen inRangoli
Rangoli is an art form that originates from in the Indian subcontinent, in which patterns are created on the floor or a tabletop using materials such as powdered lime stone, red ochre, dry rice flour, coloured sand, quartz powder, flower petal ...
designs in Indian households.
In New Age
New Age is a range of spiritual or religious practices and beliefs which rapidly grew in Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars conside ...
, the mandala is a diagram, chart or geometric pattern that represents the cosmos
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in ...
metaphysically or symbolically; a time-microcosm of the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
, but it originally meant to represent wholeness and a model for the organizational structure of life itself, a cosmic diagram that shows the relation to the infinite and the world that extends beyond and within various minds & bodies.
In archaeology
One of the most intense archaeological discoveries in recent years that could redefine the history of eastern thought and tradition of mandala is the discovery of five giant mandalas in the valley ofManipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanm ...
, India, made with Google Earth imagery. Located in the paddy field in the west of Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the fo ...
, the capital of Manipur, the Maklang geoglyph is perhaps the world's largest mandala built entirely of mud. The site wasn't discovered until 2013 as its whole structure could only be visible via Google Earth satellite imagery. The whole paddy field, locally known as Bihu Loukon
Bihu is a set of three important Assamese festivals in the Indian state of Assam – 'Rongali' or 'Bohag Bihu' observed in April, 'Kongali' or 'Kati Bihu' observed in October, and 'Bhogali' or 'Magh Bihu' observed in January. The Rongali Bihu i ...
, is now protected and announced as historical monument and site by the government of Manipur in the same year. The site is situated 12 km aerial distance from Kangla
The Kangla Palace ( mni, /kəŋ.la/), popularly as well as officially known as the Kangla Fort, is an old fortified palace at Imphal in the Manipur state of India. It was formerly situated on both sides (western and eastern) of the bank of the ...
with the GPS coordinates of 24° 48' N and 93° 49' E. It covers a total area of around 224,161.45 square meters. This square mandala has four similar protruding rectangular ‘gates’ in the cardinal directions guarded each by similar but smaller rectangular ‘gates’ on the left and right. Within the square there is an eight petalled flower or rayed-star, recently called as Maklang ‘Star fort’ by the locals, in the centre covering a total area of around 50,836.66 square meters. The discovery of other five giant mandalas in the valley of Manipur is also made with Google Earth. The five giant mandalas, viz., Sekmai mandala, Heikakmapal mandala, Phurju twin mandalas and Sangolmang mandala are located on the western bank of the Iril River. Another two fairly large mandala shaped geoglyph at Nongren and Keinou are also reported from Manipur valley, India, in 2019. They are named as Nongren mandala and Keinou mandala.
In politics
The ''Rajamandala
The Rajamandala (or ''Raja-mandala'' meaning "circle of kings"; , ''mandala'' is a Sanskrit word that means "circle") was formulated by the Indian author Chanakya (Kautilya) in his work on politics, the ''Arthashastra'' (written between 4th century ...
'' (or ''Raja-mandala''; circle of states) was formulated by the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n author Kautilya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya o ...
in his work on politics, the ''Arthashastra
The ''Arthashastra'' ( sa, अर्थशास्त्रम्, ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, political science, economic policy and military strategy. Kautilya, also identified as Vishnugupta and Chanakya, is ...
'' (written between 4th century BCE and 2nd century BCE). It describes circles of friendly and enemy states surrounding the king's state.
In historical, social and political sense, the term "mandala" is also employed to denote traditional Southeast Asian political formations (such as federation of kingdoms or vassalized states). It was adopted by 20th century Western historians from ancient Indian political discourse as a means of avoiding the term 'state' in the conventional sense. Not only did Southeast Asian polities not conform to Chinese and European views of a territorially defined state with fixed borders and a bureaucratic apparatus, but they diverged considerably in the opposite direction: the polity was defined by its centre rather than its boundaries, and it could be composed of numerous other tributary polities without undergoing administrative integration. Empires such as Bagan
Bagan (, ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Bagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that wou ...
, Ayutthaya Ayutthaya, Ayudhya, or Ayuthia may refer to:
* Ayutthaya Kingdom, a Thai kingdom that existed from 1350 to 1767
** Ayutthaya Historical Park, the ruins of the old capital city of the Ayutthaya Kingdom
* Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province (locally ...
, Champa
Champa (Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd cen ...
, Khmer, Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
and Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
are known as "mandala" in this sense.
In contemporary use
Fashion designer Mandali Mendrilla designed an interactive art installation called Mandala of Desires (Blue Lotus Wish Tree) made in peace silk and eco friendly textile ink, displayed at theChina Art Museum
The China Art Museum, also called the China Art Palace (; Shanghainese: ''Zongwu Nyizeh Ghon'') or its original name, Shanghai Art Museum, is a museum of modern Chinese art located in Pudong, Shanghai. The museum is housed in the former China Pav ...
in Shanghai in November 2015. The pattern of the dress was based on the Goloka Yantra mandala, shaped as a lotus with eight petals. Visitors were invited to place a wish on the sculpture dress, which will be taken to India and offered to a genuine living Wish Tree
A wish tree is a tree, usually distinguished by species, location or appearance, which is used as an object of wishes and offerings. Such trees are identified as possessing a special religious or spiritual value. Postulants make votive offering ...
.
Gallery
Cosmological mandala with Mount Meru
silk tapestry, China via The Metropolitan Museum of Art File:元 緙絲大威德金剛曼陀羅-Vajrabhairava Mandala MET DT841.jp
Vajrabhairava mandala
silk tapestry, China via The Metropolitan Museum of Art File:Sri Yantra 256bw.gif, A diagramic drawing of the
Sri Yantra
The Sri Yantra, Shri Yantra, or Shri Chakra is a form of mystical diagram (''yantra'') used in the Shri Vidya school of Hinduism. It consists of nine interlocking triangles - four upward ones which represent Shiva, and five downward ones represen ...
, showing the outside square, with four T-shaped gates, and the central circle
File:Vishnu Mandala.jpg, Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
Mandala(Traditionally found in Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
)
File:Painted 19th century Tibetan mandala of the Naropa tradition, Vajrayogini stands in the center of two crossed red triangles, Rubin Museum of Art.jpg, Painted 19th century Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
an mandala of the Naropa
Nāropā (Prakrit; sa, Nāropāda, Naḍapāda or Abhayakirti) or Abhayakirti was an Indian Buddhist Mahasiddha. He was the disciple of Tilopa and brother, or some sources say partner and pupil, of Niguma. As an Indian Mahasiddha, Naropa's ...
tradition, Vajrayogini
Vajrayoginī ( sa, italic=yes, Vajrayoginī वज्रयोगिनी; , Dorjé Neljorma; mn, Огторгуйд Одогч, Нархажид, ) is a Tantric Buddhist female Buddha and a . The ''Vajrayogini'' cult dates back to the tenth a ...
stands in the center of two crossed red triangles, Rubin Museum of Art
The Rubin Museum of Art, also known as the Rubin Museum is a museum dedicated to the collection, display, and preservation of the art and cultures of the Himalayas, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia and other regions within Eurasia, with a per ...
File:Medicine Buddha painted mandala with goddess Prajnaparamita in center, 19th century, Rubin.jpg, Painted Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
ese Medicine Buddha
Bhaiṣajyaguru ( sa, भैषज्यगुरु, zh, t= , ja, 薬師仏, ko, 약사불, bo, སངས་རྒྱས་སྨན་བླ), or ''Bhaishajyaguru'', formally Bhaiṣajya-guru-vaiḍūrya-prabhā-rāja ("Medicine Master ...
mandala with the goddess Prajnaparamita in center, 19th century, Rubin Museum of Art
The Rubin Museum of Art, also known as the Rubin Museum is a museum dedicated to the collection, display, and preservation of the art and cultures of the Himalayas, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia and other regions within Eurasia, with a per ...
File:Mandala of the Six Chakravartins.JPG, Mandala of the Six Chakravartin
A ''chakravarti'' ( sa, चक्रवर्तिन्, ''cakravartin''; pi, cakkavatti; zh, 轉輪王, ''Zhuǎnlúnwáng'', "Wheel-Turning King"; , ''Zhuǎnlún Shèngwáng'', "Wheel-Turning Sacred King"; ja, 転輪王, ''Tenrin'ō'' ...
s
File:Vajravarahi Mandala.jpg, Vajravarahi mandala
File:Sankhitta Sangheyani Cosmography.jpg, Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
cosmological diagrams and text.
File:Mandala Golden Flower Jung.JPG, Mandala painted by a patient of Carl Jung
File:Mahavra 1900 art.jpg, Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
picture of Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
File:Kalachakra mandala in a special glass pavilion.jpg, Kalachakra mandala in a special glass pavilion. Buddhist pilgrims bypass the pavilion in a clockwise direction three times.Buryatiya, July 16, 2019
File:Maitighar Mandala.jpg, Mandala in Maitighar, Kathmandu, Nepal
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Citations
General sources
* Brauen, M. (1997). ''The Mandala, Sacred circle in Tibetan Buddhism'' Serindia Press, London. * Bucknell, Roderick & Stuart-Fox, Martin (1986). ''The Twilight Language: Explorations in Buddhist Meditation and Symbolism''. Curzon Press: London. * Cammann, S. (1950). ''Suggested Origin of the Tibetan Mandala Paintings'' The Art Quarterly, Vol. 8, Detroit. * Cowen, Painton (2005). ''The Rose Window'', London and New York, (offers the most complete overview of the evolution and meaning of the form, accompanied by hundreds of colour illustrations.) * Crossman, Sylvie and Barou, Jean-Pierre (1995). ''Tibetan Mandala, Art & Practice'' The Wheel of Time, Konecky and Konecky. * Fontana, David (2005). "Meditating with Mandalas", Duncan Baird Publishers, London. * Rochester, Vermont: Inner Traditions International. * Mipham, Sakyong Jamgön (2002) ''2000 Seminary Transcripts Book 1'' Vajradhatu Publications * Somorjit, Wangam (2018). "World's Largest Mandalas from Manipur and Carl Jung's Archetype of the Self", neScholar, vol.04, Issue 01, ed.Dr. R.K. Nimai Singh * Tucci, Giuseppe (1973). ''The Theory and Practice of the Mandala'' trans. Alan Houghton Brodrick, New York, Samuel Weisner. * Vitali, Roberto (1990). ''Early Temples of Central Tibet'' London, Serindia Publications. * Wayman, Alex (1973). ''"Symbolism of the Mandala Palace"'' in ''The Buddhist Tantras'' Delhi, Motilal Banarsidass.Further reading
* Grotenhuis, Elizabeth Ten (1999). Japanese mandalas: representations of sacred geography, Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press * (see index)External links
Introduction to Mandalas
{{Authority control Buddhist philosophical concepts Buddhist art Buddhist meditation Ceremonies Hindu philosophical concepts Indian iconography Meditation Religious objects Religious symbols Tibetan Buddhist practices Tibetan Buddhist ritual implements