|
China Art Museum
The China Art Museum, also called the China Art Palace (; Shanghainese: ''Zongwu Nyizeh Ghon'') or its original name, Shanghai Art Museum, is a museum of modern Chinese art located in Pudong, Shanghai. The museum is housed in the former China Pavilion of Expo 2010. It is one of the largest art museums in Asia. History The predecessor of the China Art Museum was the Shanghai Art Museum, which was established in 1956 in a former restaurant on West Nanjing Road, and completely rebuilt in 1986. On 18 March 2000, the Shanghai Art Museum was moved to the former Shanghai Race Club building on the People's Square, which had housed the Shanghai Library until 1997. With the move its exhibition space increased from 2,200 to 5,800 square meters. Shanghai hosted Expo 2010 from 1 May to 31 October 2010, and the China Pavilion received close to 17 million visitors. Due to its popularity, the China Pavilion was reopened for six extra months after the end of the Shanghai Expo. On 13 No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Art Museum Logo
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Station Of Art
The Power Station of Art is a contemporary art museum in Shanghai. Housed in a former power station, it is China's first state-run contemporary art museum. Converting the building cost $64 million which was paid for by the Shanghai government. The museum is on the site of the Expo 2010 and on the left bank of the Huangpu River. It opened in 2012 with an exhibition of contemporary art from Centre Pompidou, Paris's best-known contemporary art museum, entitled Electric Fields, Surrealism and Beyond. The director is Li Xu. The deputy director is Gong Yan, who was formerly the editor in chief of the Chinese-language magazine ''Art World.'' See also * 50 Moganshan Road * West Bund Art & Design * Long Museum * China Art Museum * Museum of Contemporary Art Shanghai * Shanghai Museum * Tianzifang * Xintiandi Xintiandi (, Shanghainese: ''Shinthidi'' lit. "New Heaven and Earth",Warr, Anne: ''Shanghai Architecture'', The Watermark Press, 2007, fig. "New World") is an affluent ped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
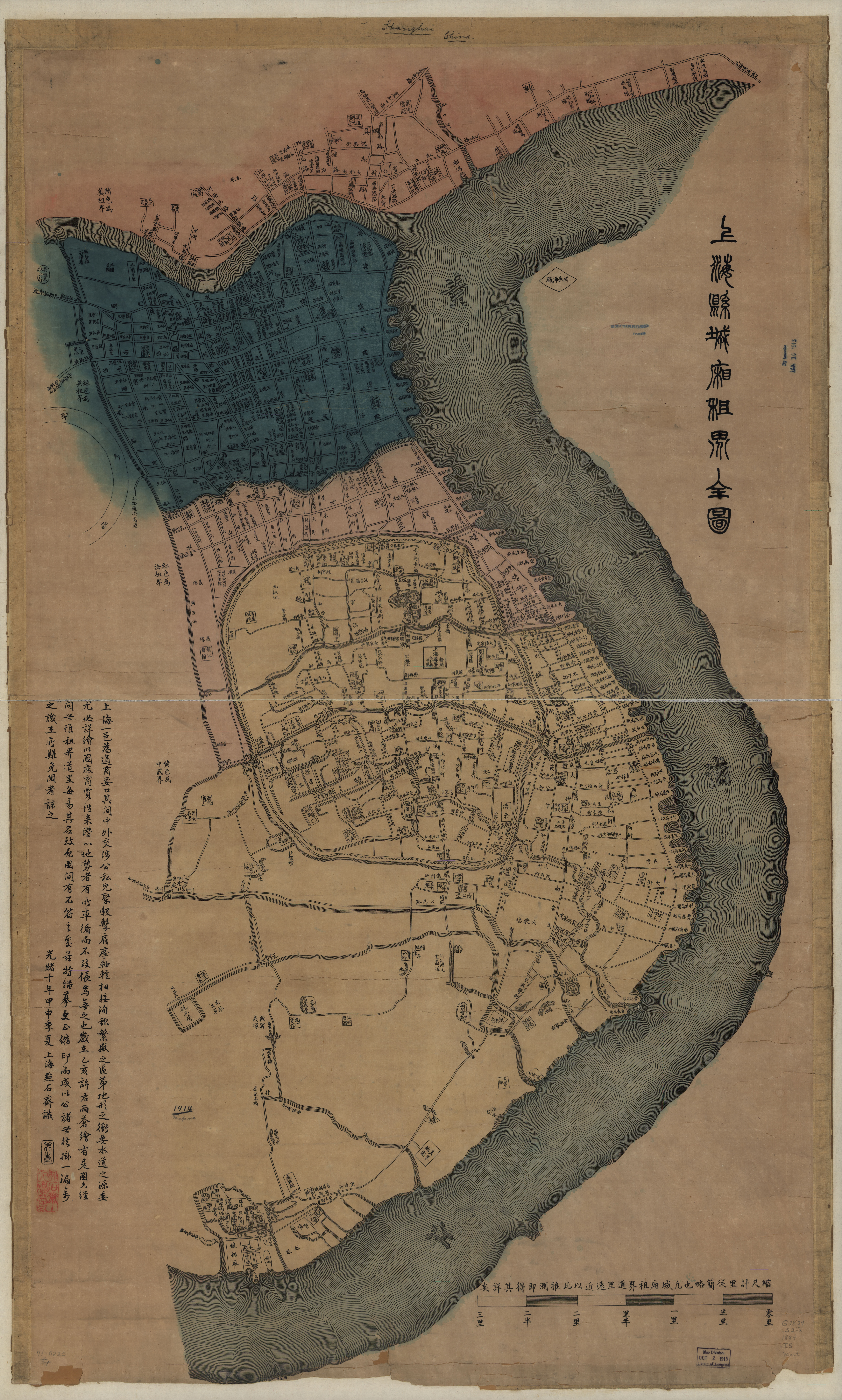
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai School
''Haipai'' (, Shanghainese: ''hepha'', ; literally " hangai style") refers to the avant-garde but unique "East Meets West" culture from Shanghai in the 20th and 21st centuries. It is a part of the culture of Shanghai. Etymology The term was coined by a group of Beijing writers in 1920 to criticize some Shanghai scholars and the styles of embracing or admiring western capitalism and western culture. The name ''Haipai'' originally came from painting and drama. According to ''History of Chinese Painting'', which was published in 1937, "During Emperor Tongzhi's and Guangxu's reign in the Qing Dynasty, most Chinese painters lived in Shanghai and made a living by selling paintings. In order to make profits, painters catered to vulgar public taste. Their paintings gradually demonstrated ''Haipai'' style." In addition, performers of Peking opera regarded Beijing as the authority of China and they referred to cities outside Beijing as ''Haipai''. At that time ''Haipai'' was used by schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Art
Modern art includes artistic work produced during the period extending roughly from the 1860s to the 1970s, and denotes the styles and philosophies of the art produced during that era. The term is usually associated with art in which the traditions of the past have been thrown aside in a spirit of experimentation. Modern artists experimented with new ways of seeing and with fresh ideas about the nature of materials and functions of art. A tendency away from the narrative, which was characteristic for the traditional arts, toward abstraction is characteristic of much modern art. More recent artistic production is often called contemporary art or postmodern art. Modern art begins with the heritage of painters like Vincent van Gogh, Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec all of whom were essential for the development of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century Henri Matisse and several other young artists including the Proto-Cubism, pre-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Art Museum, Shanghai Interior
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dynastie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ding (vessel)
''Ding'' () are prehistoric and ancient Chinese cauldrons, standing upon legs with a lid and two facing handles. They are one of the most important shapes used in Chinese ritual bronzes. They were made in two shapes: round vessels with three legs and rectangular ones with four, the latter often called ''fangding''. They were used for cooking, storage, and ritual offerings to the gods or to ancestors. The earliest recovered examples are pre-Shang ceramic ding at the Erlitou site but they are better known from the Bronze Age, particularly after the Zhou deemphasized the ritual use of wine practiced by the Shang kings. Under the Zhou, the ding and the privilege to perform the associated rituals became symbols of authority. The number of permitted ding varied according to one's rank in the Chinese nobility: the Nine Ding of the Zhou kings were a symbol of their rule over all China but were lost by the first emperor, Shi Huangdi in the late 3rd century BCE. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dougong
''Dougong'' () is a structural element of interlocking wooden brackets, one of the most important in traditional Chinese architecture. The use of dougong first appeared in buildings of the late centuries BC and evolved into a structural network that joined pillars and columns to the frame of the roof. ''Dougong'' was widely used by the ancient Chinese during the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC) and developed into a complex set of interlocking parts by its peak in the Tang and Song periods. The pieces are fitted together by joinery alone without glue or fasteners, requiring precise carpentry. After the Song Dynasty, brackets and bracket sets used in palatial structures and important religious buildings became more ornamental than structural, no longer fitting the description of traditional ''dougong''. Function Dougong is part of the network of wooden supports essential to the timber frame structure of traditional Chinese building. Because the walls in these s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the structure. A piece of timber projecting in the same way was called a "tassel" or a "bragger" in England. The technique of corbelling, where rows of corbels deeply keyed inside a wall support a projecting wall or parapet, has been used since Neolithic (New Stone Age) times. It is common in medieval architecture and in the Scottish baronial style as well as in the vocabulary of classical architecture, such as the modillions of a Corinthian cornice. The corbel arch and corbel vault use the technique systematically to make openings in walls and to form ceilings. These are found in the early architecture of most cultures, from Eurasia to Pre-Columbian architecture. A console is more specifically an "S"-shaped scroll bracket in the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
He Jingtang
He Jingtang (; born 1938 Dongguan) is a Chinese architect and the head of the architecture program at the South China University of Technology's school of architecture whose works include the wrestling and badminton venues built for the 2008 Beijing Olympics and the Chinese Pavilion sometimes referred to as the "Crown of China" for Expo 2010 which was held in Shanghai and later reopened as the China Art Museum. More recently designed the new campus of the University of Macau which was completed in 2013. In 2016 the Dachang Muslim Cultural Center designed by He opened outside Beijing. It features a colonnade of petal-shaped arches that in turn give birth to an illuminated walkway around the outline of cultural centre He participated in the 2016 Venice Biennale of Architecture Venice Biennale of Architecture (in Italian Mostra di Architettura di Venezia) is an international exhibition of architecture from nations around the world, held in Venice, Italy, every other year. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Globe And Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it falls slightly behind the ''Toronto Star'' in overall weekly circulation because the ''Star'' publishes a Sunday edition, whereas the ''Globe'' does not. ''The Globe and Mail'' is regarded by some as Canada's "newspaper of record". ''The Globe and Mail''s predecessors, '' The Globe'' and ''The Mail and Empire'' were both established in the 19th century. The former was established in 1844, while the latter was established in 1895 through a merger of '' The Toronto Mail'' and the ''Toronto Empire''. In 1936, ''The Globe'' and ''The Mail and Empire'' merged to form ''The Globe and Mail''. The newspaper was acquired by FP Publications in 1965, who later sold the paper to the Thomson Corporation in 1980. In 2001, the paper merged with broadc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Pavilion Of Expo 2010
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dynastie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_with_human_faces_02.jpg)

_2.jpg)
