Malta GHI Mid-size-map 156x188mm-300dpi V20200616 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an
– Qatar Financial Centre, 2015. or metropolitan areas. Malta became a British colony in 1813, serving as a way station for ships and the headquarters for the British Mediterranean Fleet. It was besieged by the Axis powers during World War II and was an important Allied base for operations in North Africa and the Mediterranean. The
 After a probable sack by the
After a probable sack by the

 Pottery from the Għar Dalam phase is similar to pottery found in
Pottery from the Għar Dalam phase is similar to pottery found in
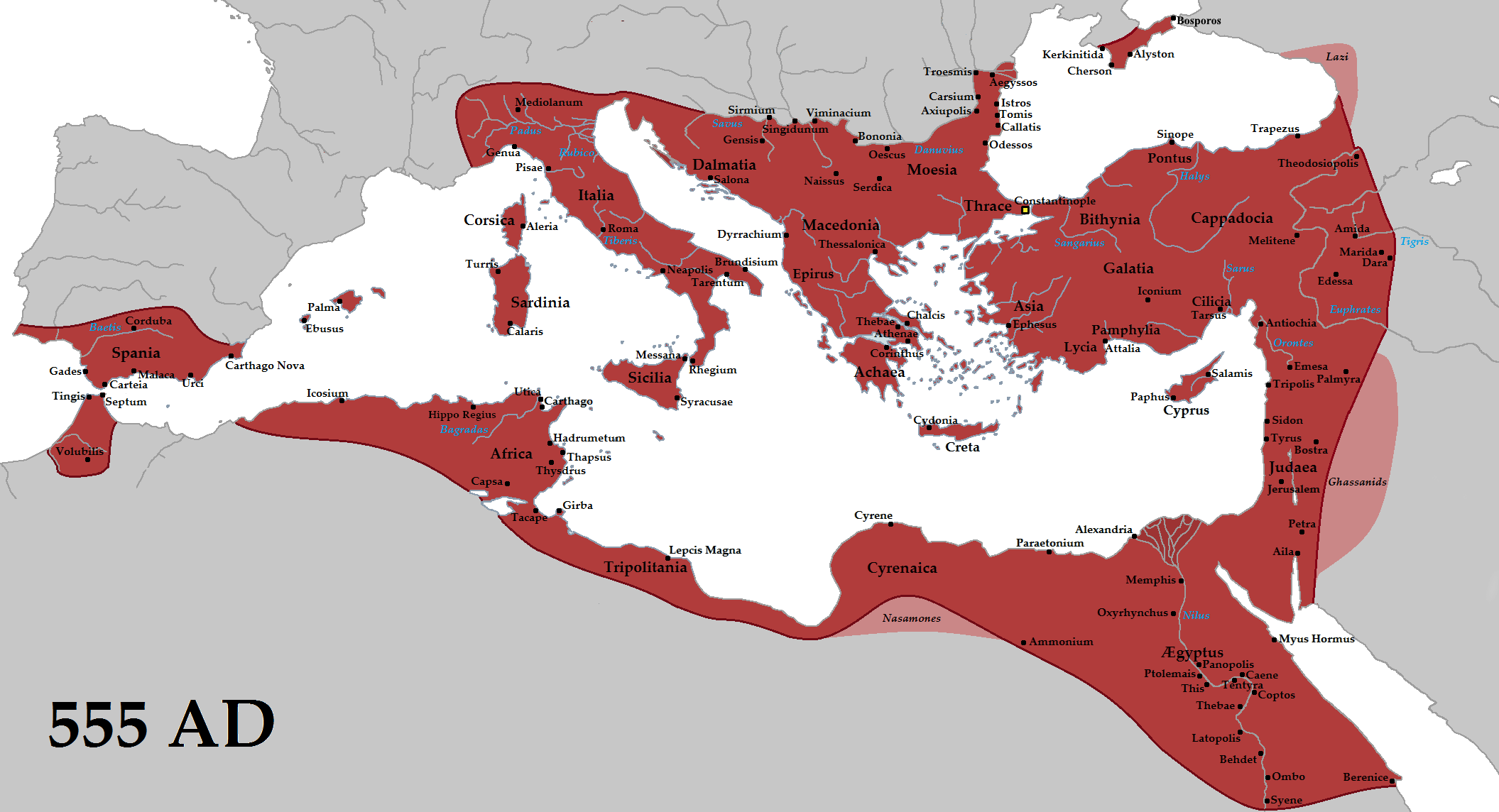 Phoenician traders colonised the islands sometime after 1000 BC as a stop on their trade routes from the eastern
Phoenician traders colonised the islands sometime after 1000 BC as a stop on their trade routes from the eastern  After the fall of Phoenicia in 332 BC, the area came under the control of
After the fall of Phoenicia in 332 BC, the area came under the control of
 The
The
 Malta was ruled by the
Malta was ruled by the
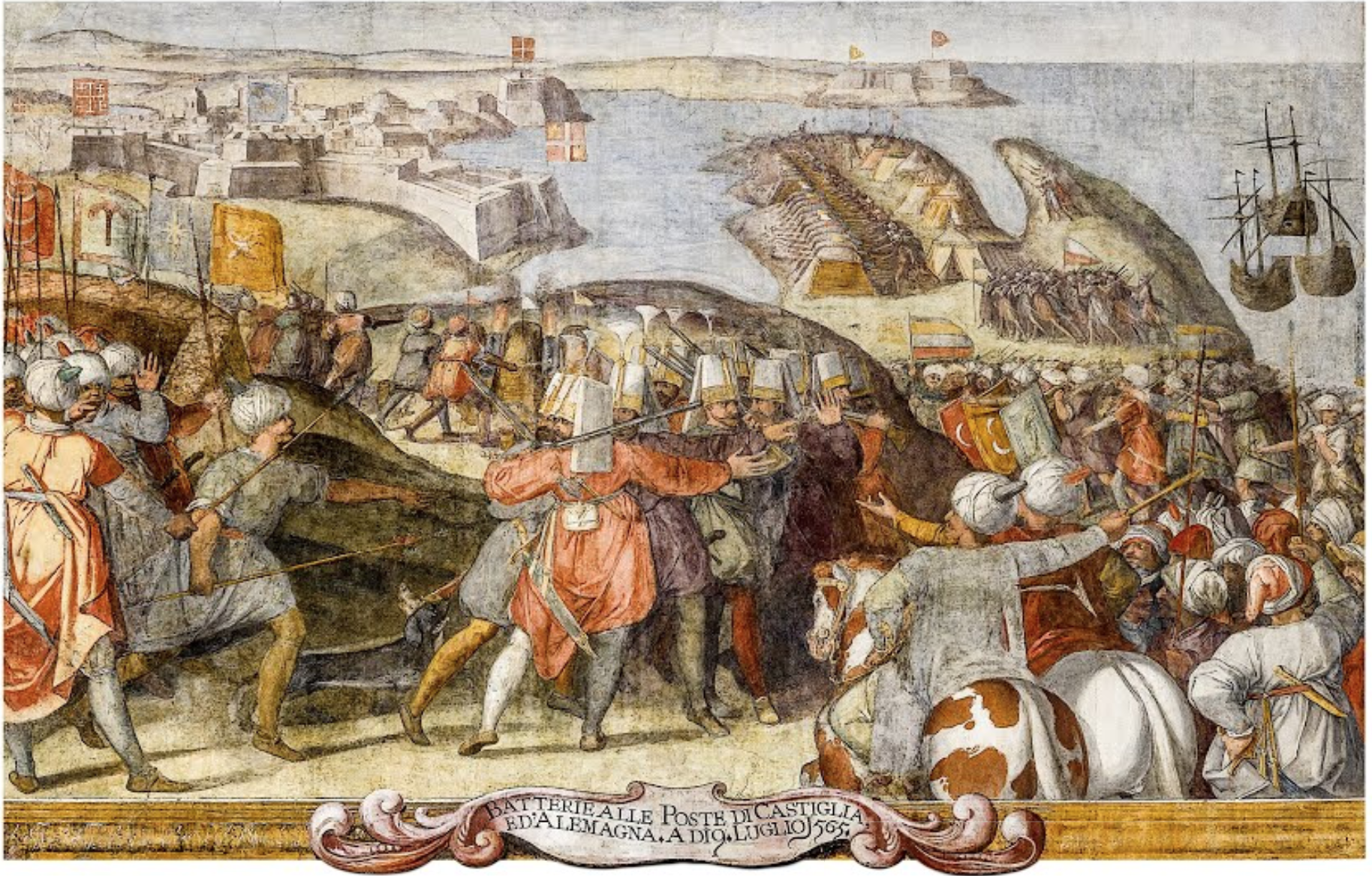
. ''El Pais'' (14 August 2005). Retrieved 1 May 2017. These knights, a military religious order also known as the Order of St John and later as the Knights of Malta, had been driven out of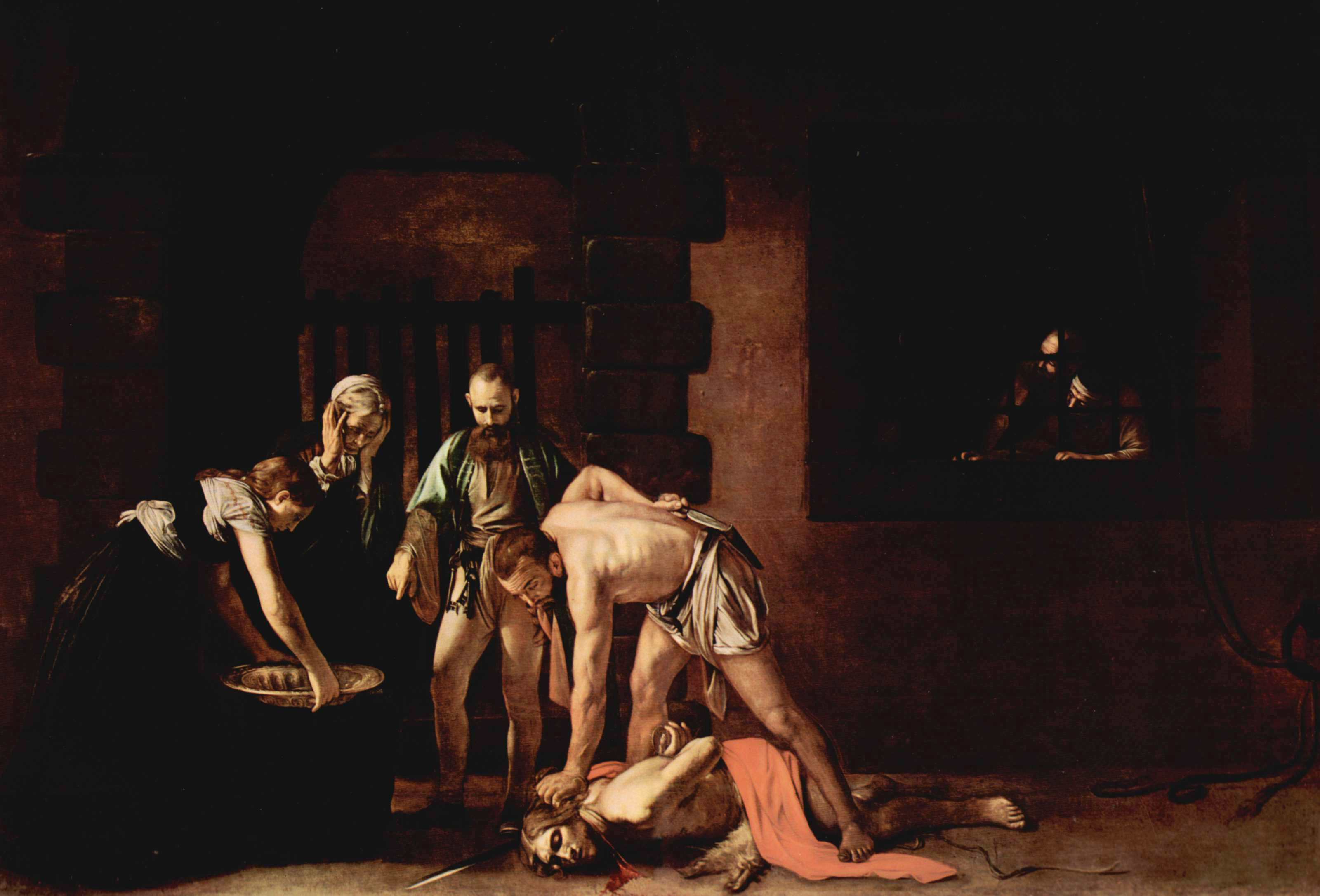 The knights, led by Frenchman
The knights, led by Frenchman
 During 12–18 June 1798, Napoleon resided at the Palazzo Parisio in Valletta. He reformed national administration with the creation of a Government Commission, twelve municipalities, a public finance administration, the abolition of all feudal rights and privileges, the
During 12–18 June 1798, Napoleon resided at the Palazzo Parisio in Valletta. He reformed national administration with the creation of a Government Commission, twelve municipalities, a public finance administration, the abolition of all feudal rights and privileges, the
 In 1814, as part of the
In 1814, as part of the

 Malta achieved its independence as the State of Malta on 21 September 1964 ( Independence Day) after intense negotiations with the United Kingdom, led by Maltese Prime Minister George Borġ Olivier. Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Elizabeth II as Queen of Malta and thus
Malta achieved its independence as the State of Malta on 21 September 1964 ( Independence Day) after intense negotiations with the United Kingdom, led by Maltese Prime Minister George Borġ Olivier. Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Elizabeth II as Queen of Malta and thus
 The House of Representatives has 65 members, elected for a five-year term in 13 five-seat electoral divisions, called ''distretti elettorali'', with constitutional amendments that allow for mechanisms to establish strict proportionality amongst seats and votes of political parliamentary groups.
Members of the House of Representatives are elected by direct universal suffrage through single transferable vote every five years, unless the House is dissolved earlier by the president either on the advice of the Prime Minister of Malta, prime minister or through the adoption of a motion of no confidence carried within the House of Representatives and not overturned within three days. In either of these cases, the president may alternatively choose to invite another Member of Parliament who invariably should command the majority of the House of Representatives to form an alternative government for the remainder of the legislature.
The House of Representatives is nominally made up of 65 members of parliament whereby 5 members of parliament are elected from each of the thirteen electoral districts. However, where a party wins an absolute majority of votes but does not have a majority of seats, that party is given additional seats to ensure a parliamentary majority. The 80th article of the Constitution of Malta provides that the president appoint as prime minister "... the member of the House of Representatives who, in his judgment, is best able to command the support of a majority of the members of that House".
The House of Representatives has 65 members, elected for a five-year term in 13 five-seat electoral divisions, called ''distretti elettorali'', with constitutional amendments that allow for mechanisms to establish strict proportionality amongst seats and votes of political parliamentary groups.
Members of the House of Representatives are elected by direct universal suffrage through single transferable vote every five years, unless the House is dissolved earlier by the president either on the advice of the Prime Minister of Malta, prime minister or through the adoption of a motion of no confidence carried within the House of Representatives and not overturned within three days. In either of these cases, the president may alternatively choose to invite another Member of Parliament who invariably should command the majority of the House of Representatives to form an alternative government for the remainder of the legislature.
The House of Representatives is nominally made up of 65 members of parliament whereby 5 members of parliament are elected from each of the thirteen electoral districts. However, where a party wins an absolute majority of votes but does not have a majority of seats, that party is given additional seats to ensure a parliamentary majority. The 80th article of the Constitution of Malta provides that the president appoint as prime minister "... the member of the House of Representatives who, in his judgment, is best able to command the support of a majority of the members of that House".
 Maltese politics is a two-party system dominated by the Labour Party (Malta), Labour Party ( mt, Partit Laburista), a centre-left social democracy, social democratic party, and the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist Party ( mt, Partit Nazzjonalista), a centre-right Christian democracy, Christian democratic party. The Labour Party has been the governing party since 2013 and is currently led by Prime Minister Robert Abela, who has been in office since 13 January 2020. The Nationalist Party, with Bernard Grech as its leader, is currently in opposition. There are a number of small political parties in Malta which have no parliamentary representation.
Until the
Maltese politics is a two-party system dominated by the Labour Party (Malta), Labour Party ( mt, Partit Laburista), a centre-left social democracy, social democratic party, and the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist Party ( mt, Partit Nazzjonalista), a centre-right Christian democracy, Christian democratic party. The Labour Party has been the governing party since 2013 and is currently led by Prime Minister Robert Abela, who has been in office since 13 January 2020. The Nationalist Party, with Bernard Grech as its leader, is currently in opposition. There are a number of small political parties in Malta which have no parliamentary representation.
Until the
 Malta has had a system of local government since 1993, based on the European Charter of Local Self-Government. The country is divided into Regions of Malta, five regions (one of them being Gozo), with each region having its own Regional Committee, serving as the intermediate level between local government and national government. The regions are divided into Local councils of Malta, local councils, of which there are currently 68 (54 in Malta and 14 in Gozo). The Districts of Malta, six districts (five on Malta and the sixth being Gozo) serve primarily statistical purposes.
Each council is made up of a number of councillors (from 5 to 13, depending on and relative to the population they represent). A mayor and a deputy mayor are elected by and from the councillors. The executive secretary, who is appointed by the council, is the executive, administrative and financial head of the council. Councillors are elected every four years through the single transferable vote. People who are eligible to vote in the election of the Maltese House of Representatives of Malta, House of Representatives as well as a resident Citizenship of the European Union, citizens of the EU are eligible to vote. Due to system reforms, no elections were held before 2012. Since then, elections have been held every two years for an alternating half of the councils.
Local councils are responsible for the general upkeep and embellishment of the locality (including repairs to non-arterial roads), allocation of local wardens, and refuse collection; they also carry out general administrative duties for the central government such as the collection of government rents and funds and answer government-related public inquiries. Additionally, a number of individual towns and villages in the Republic of Malta have List of twin towns and sister cities in Malta, sister cities.
Malta has had a system of local government since 1993, based on the European Charter of Local Self-Government. The country is divided into Regions of Malta, five regions (one of them being Gozo), with each region having its own Regional Committee, serving as the intermediate level between local government and national government. The regions are divided into Local councils of Malta, local councils, of which there are currently 68 (54 in Malta and 14 in Gozo). The Districts of Malta, six districts (five on Malta and the sixth being Gozo) serve primarily statistical purposes.
Each council is made up of a number of councillors (from 5 to 13, depending on and relative to the population they represent). A mayor and a deputy mayor are elected by and from the councillors. The executive secretary, who is appointed by the council, is the executive, administrative and financial head of the council. Councillors are elected every four years through the single transferable vote. People who are eligible to vote in the election of the Maltese House of Representatives of Malta, House of Representatives as well as a resident Citizenship of the European Union, citizens of the EU are eligible to vote. Due to system reforms, no elections were held before 2012. Since then, elections have been held every two years for an alternating half of the councils.
Local councils are responsible for the general upkeep and embellishment of the locality (including repairs to non-arterial roads), allocation of local wardens, and refuse collection; they also carry out general administrative duties for the central government such as the collection of government rents and funds and answer government-related public inquiries. Additionally, a number of individual towns and villages in the Republic of Malta have List of twin towns and sister cities in Malta, sister cities.
 Malta is an
Malta is an  The following uninhabited minor islands are part of the archipelago:
* Barbaġanni Rock ( Gozo)
* Cominotto (''Kemmunett'')
* Dellimara Island (Marsaxlokk)
* Filfla (Żurrieq)/(Siġġiewi)
* Fessej Rock
* Fungus Rock (''Il-Ġebla tal-Ġeneral''), ( Gozo)
* Għallis Rock (Naxxar)
* Ħalfa Rock ( Gozo)
* Large Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Islands of St. Paul/Selmunett Island (Mellieħa)
* Manoel Island, which connects to the town of Gżira, on the mainland via a bridge
* Mistra Rocks (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Taċ-Ċawl Rock ( Gozo)
* Qawra Point/Ta' Fraben Island (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Small Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Sala Rock (Żabbar)
* Xrobb l-Għaġin Rock (Marsaxlokk)
* Ta' taħt il-Mazz Rock
The following uninhabited minor islands are part of the archipelago:
* Barbaġanni Rock ( Gozo)
* Cominotto (''Kemmunett'')
* Dellimara Island (Marsaxlokk)
* Filfla (Żurrieq)/(Siġġiewi)
* Fessej Rock
* Fungus Rock (''Il-Ġebla tal-Ġeneral''), ( Gozo)
* Għallis Rock (Naxxar)
* Ħalfa Rock ( Gozo)
* Large Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Islands of St. Paul/Selmunett Island (Mellieħa)
* Manoel Island, which connects to the town of Gżira, on the mainland via a bridge
* Mistra Rocks (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Taċ-Ċawl Rock ( Gozo)
* Qawra Point/Ta' Fraben Island (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Small Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Sala Rock (Żabbar)
* Xrobb l-Għaġin Rock (Marsaxlokk)
* Ta' taħt il-Mazz Rock
– MET Office in Malta International Airport Large fluctuations in temperature are rare. Snow is very rare on the island, although various snowfalls have been recorded in the last century, the last one reported in various locations across Malta in 2014. The average annual sea temperature is , from in February to in August. In the 6 months – from June to November – the average sea temperature exceeds . The annual average relative humidity is high, averaging 75%, ranging from 65% in July (morning: 78% evening: 53%) to 80% in December (morning: 83% evening: 73%). Sunshine duration hours total around 3,000 per year, from an average 5.2 hours of sunshine duration per day in December to an average above 12 hours in July. This is about double that of cities in the northern half of Europe, for comparison: London – 1,461; however, in winter it has up to four times more sunshine; for comparison: in December, London has 37 hours of sunshine whereas Malta has above 160.
 According to Eurostat, Malta is composed of two larger urban zones nominally referred to as "Valletta" (the main island of Malta) and "Gozo". The main urban area covers the entire main island, with a population of around 400,000. The core of the urban area, the ''greater city'' of Valletta, has a population of 205,768."Population on 1 January by age groups and sex – cities and greater cities"
According to Eurostat, Malta is composed of two larger urban zones nominally referred to as "Valletta" (the main island of Malta) and "Gozo". The main urban area covers the entire main island, with a population of around 400,000. The core of the urban area, the ''greater city'' of Valletta, has a population of 205,768."Population on 1 January by age groups and sex – cities and greater cities"
Eurostat, 2015. According to the data from 2020 by Eurostat, the Functional Urban Area and metropolitan region covered the whole island and has a population of 480 134. According to the United Nations, about 95 percent of the area of Malta is urban and the number grows every year."World Urbanization Prospects"
– Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division, United Nations (Table A.2; page 79) Also, according to the results of ESPON and EU Commission studies, "''the whole territory of Malta constitutes a single urban region''"."Interim Territorial Cohesion Report"
– Preliminary results of ESPON and EU Commission studies Occasionally in books, government publications and documents, and in some international institutions, Malta is referred to as a
– Federal Institute for Research on Building, Urban Affairs and Spatial Development, 2011. Also, the Maltese coat-of-arms bears a mural crown described as "representing the fortifications of Malta and denoting a City State". Malta, with area of and population of over 0.5 million, is one of the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, most densely populated countries worldwide. World Health Organization, WHO reassigned the Islands and Small States Institute in Malta on 29 April 2022 as a collaborating center that included heavy work on topics like the development of policy recommendations on building health-system resilience in small states, the interrelationship between tourism, health systems and sustainability, with a focus on islands and small countries, through a planetary health and equity approach and the development of a toolkit on health information, digital health and evidence generation in small states.
 Malta is classified as an advanced economy together with 32 other countries according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Until 1800, Malta depended on cotton, tobacco and its shipyards for exports. Once under British control, they came to depend on Malta Dockyard for support of the
Malta is classified as an advanced economy together with 32 other countries according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Until 1800, Malta depended on cotton, tobacco and its shipyards for exports. Once under British control, they came to depend on Malta Dockyard for support of the  Currently, Malta's major resources are limestone, a favourable geographic location and a productive labour force. Malta produces only about 20 percent of its food needs, has limited fresh water supplies because of the drought in the summer, and has no domestic energy sources, aside from the potential for solar energy from its plentiful sunlight. The economy is dependent on foreign trade (serving as a freight trans-shipment point), manufacturing (especially electronics and textiles), and tourism.
Access to biocapacity in Malta is below the world average. In 2016, Malta had 0.6 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, contrasted with a global average of 1.6 hectares per person. Additionally, residents of Malta exhibited an ecological footprint of consumption of 5.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person, resulting in a sizable biocapacity deficit.
Films shot in Malta, Film production has contributed to the Maltese economy. The film ''Sons of the Sea'' was the first shot in Malta, in 1925; by 2016, over 100 feature films had been entirely or partially filmed in the country since. Malta has served as a "double" for a wide variety of locations and historic periods including Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Ancient and modern Rome, Iraq, the Middle East and many more. The Maltese government introduced financial incentives for filmmakers in 2005. The current financial incentives to foreign productions as of 2015 stand at 25 per cent with an additional 2 per cent if Malta stands in as Malta; meaning a production can get up to 27 per cent back on their eligible spending incurred in Malta.
Currently, Malta's major resources are limestone, a favourable geographic location and a productive labour force. Malta produces only about 20 percent of its food needs, has limited fresh water supplies because of the drought in the summer, and has no domestic energy sources, aside from the potential for solar energy from its plentiful sunlight. The economy is dependent on foreign trade (serving as a freight trans-shipment point), manufacturing (especially electronics and textiles), and tourism.
Access to biocapacity in Malta is below the world average. In 2016, Malta had 0.6 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, contrasted with a global average of 1.6 hectares per person. Additionally, residents of Malta exhibited an ecological footprint of consumption of 5.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person, resulting in a sizable biocapacity deficit.
Films shot in Malta, Film production has contributed to the Maltese economy. The film ''Sons of the Sea'' was the first shot in Malta, in 1925; by 2016, over 100 feature films had been entirely or partially filmed in the country since. Malta has served as a "double" for a wide variety of locations and historic periods including Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Ancient and modern Rome, Iraq, the Middle East and many more. The Maltese government introduced financial incentives for filmmakers in 2005. The current financial incentives to foreign productions as of 2015 stand at 25 per cent with an additional 2 per cent if Malta stands in as Malta; meaning a production can get up to 27 per cent back on their eligible spending incurred in Malta.
 In preparation for Malta's membership in the
In preparation for Malta's membership in the
 The two largest commercial banks are Bank of Valletta and HSBC Bank Malta, both of which can trace their origins back to the 19th century. As of recently, Digital banking, digital banks such as Revolut have also increased in popularity.
The Central Bank of Malta (Bank Ċentrali ta' Malta) has two key areas of responsibility: the formulation and implementation of monetary policy and the promotion of a sound and efficient financial system. It was established by the Central Bank of Malta Act on 17 April 1968. The Maltese government entered ERM II on 4 May 2005, and adopted the euro as the country's currency on 1 January 2008.
FinanceMalta is the quasi-governmental organisation tasked with marketing and educating business leaders coming to Malta and runs seminars and events around the world highlighting the emerging strength of Malta as a jurisdiction for banking and finance and insurance.
The two largest commercial banks are Bank of Valletta and HSBC Bank Malta, both of which can trace their origins back to the 19th century. As of recently, Digital banking, digital banks such as Revolut have also increased in popularity.
The Central Bank of Malta (Bank Ċentrali ta' Malta) has two key areas of responsibility: the formulation and implementation of monetary policy and the promotion of a sound and efficient financial system. It was established by the Central Bank of Malta Act on 17 April 1968. The Maltese government entered ERM II on 4 May 2005, and adopted the euro as the country's currency on 1 January 2008.
FinanceMalta is the quasi-governmental organisation tasked with marketing and educating business leaders coming to Malta and runs seminars and events around the world highlighting the emerging strength of Malta as a jurisdiction for banking and finance and insurance.
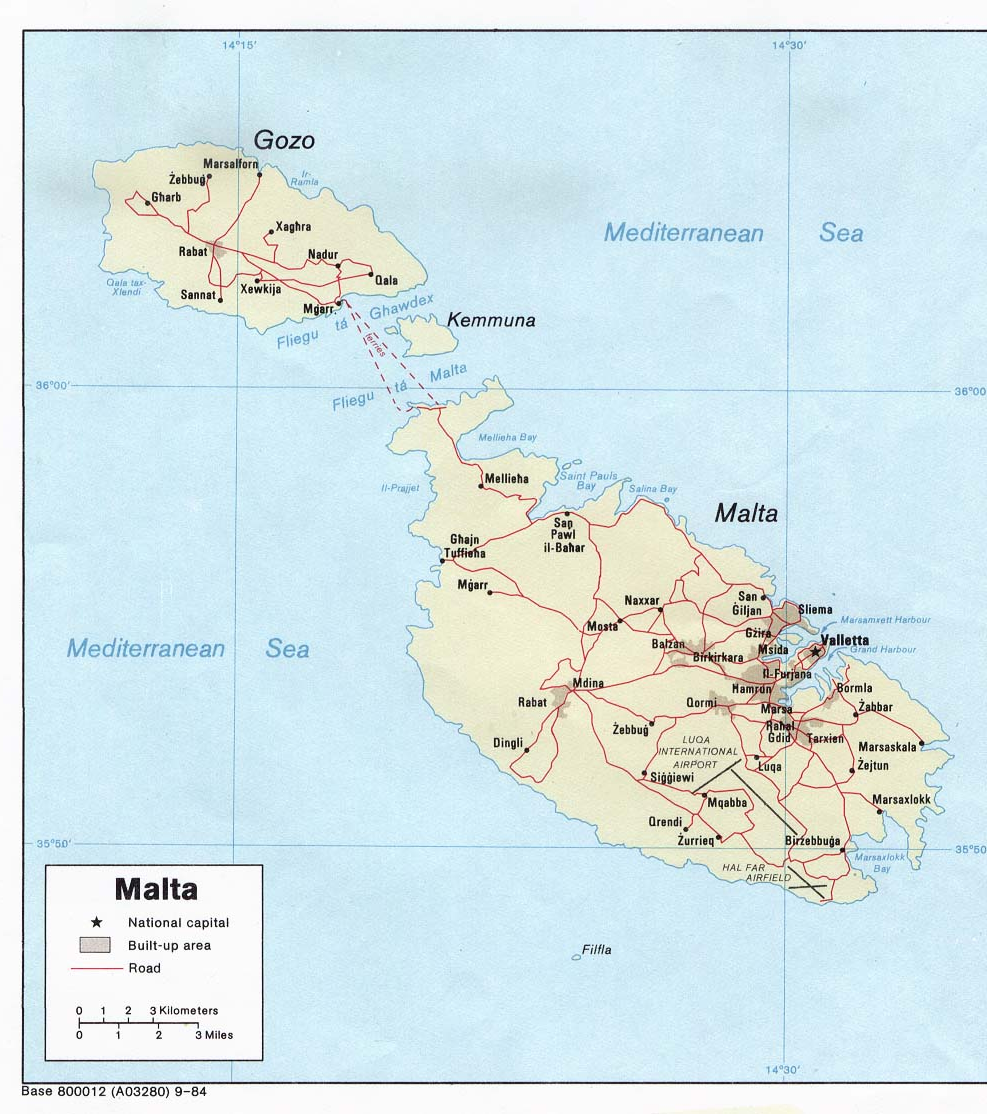 Being a former British Colony, traffic in Malta Driving on the left or drives on the left. Car ownership in Malta is exceedingly high, considering the very small size of the islands; it is the fourth-highest in the European Union. The number of registered cars in 1990 amounted to 182,254, giving an automobile density of .
Malta has of road, (87.5 per cent) of which are paved and are unpaved (as of December 2003).
The main roads of Malta from the southernmost point to the northernmost point are these: Triq Birżebbuġa in Birżebbuġa, Għar Dalam Road and Tal-Barrani Road in Żejtun, Santa Luċija Avenue in Paola, Malta, Paola, Aldo Moro Street (Trunk Road), 13 December Street and Ħamrun-Marsa Bypass in Marsa, Malta, Marsa, Regional Road in Santa Venera/Msida/Gżira/San Ġwann, St Andrew's Road in Swieqi/Pembroke, Malta, Coast Road in Baħar iċ-Ċagħaq, Salina Road, Kennedy Drive, St. Paul's Bypass and Xemxija Hill in San Pawl il-Baħar, Mistra Hill, Wettinger Street (Mellieħa Bypass) and Marfa Road in Mellieħa.
Being a former British Colony, traffic in Malta Driving on the left or drives on the left. Car ownership in Malta is exceedingly high, considering the very small size of the islands; it is the fourth-highest in the European Union. The number of registered cars in 1990 amounted to 182,254, giving an automobile density of .
Malta has of road, (87.5 per cent) of which are paved and are unpaved (as of December 2003).
The main roads of Malta from the southernmost point to the northernmost point are these: Triq Birżebbuġa in Birżebbuġa, Għar Dalam Road and Tal-Barrani Road in Żejtun, Santa Luċija Avenue in Paola, Malta, Paola, Aldo Moro Street (Trunk Road), 13 December Street and Ħamrun-Marsa Bypass in Marsa, Malta, Marsa, Regional Road in Santa Venera/Msida/Gżira/San Ġwann, St Andrew's Road in Swieqi/Pembroke, Malta, Coast Road in Baħar iċ-Ċagħaq, Salina Road, Kennedy Drive, St. Paul's Bypass and Xemxija Hill in San Pawl il-Baħar, Mistra Hill, Wettinger Street (Mellieħa Bypass) and Marfa Road in Mellieħa.
 Malta bus, Buses (''xarabank'' or ''karozza tal-linja'') are the primary method of public transport, established in 1905. Malta's vintage buses operated in the Maltese islands up to 2011 and became popular tourist attractions in their own right. To this day they are depicted on many Maltese advertisements to promote tourism as well as on gifts and merchandise for tourists.
The bus service underwent extensive reform in July 2011. The management structure changed from having self-employed drivers driving their own vehicles to a service being offered by a single company through a public tender (in Gozo, being considered a small network, the service was given through direct order). The public tender was won by Arriva Malta, a member of the Arriva group, which introduced a fleet of brand new buses, built by King Long especially for service by Arriva Malta and including a smaller fleet of articulated buses brought in from Arriva London. It also operated two smaller buses for an intra-Valletta route only and 61 nine-metre buses, which were used to ease congestion on high-density routes. Overall Arriva Malta operated 264 buses. On 1 January 2014 Arriva ceased operations in Malta due to financial difficulties, having been nationalised as ''Malta Public Transport'' by the Maltese government, with a new bus operator planned to take over their operations. The government chose Autobuses Urbanos de León (ALSA (bus company), ALSA subsidiary) as its preferred bus operator for the country in October 2014. The company took over the bus service on 8 January 2015, while retaining the name ''Malta Public Transport''. It introduced the pre-pay 'tallinja card'. With lower fares than the walk-on rate, it can be topped up online. The card was initially not well received, as reported by several local news sites. During the first week of August 2015, another 40 buses of the Turkish make ''Otokar'' arrived and were put into service.
From October 2022 the bus system will be free of charge for residents of Malta.
From 1883 to 1931 Malta had a Malta Railway, railway line that connected Valletta to the army barracks at Mtarfa via Mdina and a number of towns and villages. The railway fell into disuse and eventually closed altogether, following the introduction of electric trams and buses. At the height of the bombing of Malta during the Second World War, Benito Mussolini, Mussolini announced that his forces had destroyed the railway system, but by the time war broke out, the railway had been mothballed for more than nine years.
As of 2021, an underground Malta Metro is being planned, with a projected total cost of €6.2 billion.
Malta bus, Buses (''xarabank'' or ''karozza tal-linja'') are the primary method of public transport, established in 1905. Malta's vintage buses operated in the Maltese islands up to 2011 and became popular tourist attractions in their own right. To this day they are depicted on many Maltese advertisements to promote tourism as well as on gifts and merchandise for tourists.
The bus service underwent extensive reform in July 2011. The management structure changed from having self-employed drivers driving their own vehicles to a service being offered by a single company through a public tender (in Gozo, being considered a small network, the service was given through direct order). The public tender was won by Arriva Malta, a member of the Arriva group, which introduced a fleet of brand new buses, built by King Long especially for service by Arriva Malta and including a smaller fleet of articulated buses brought in from Arriva London. It also operated two smaller buses for an intra-Valletta route only and 61 nine-metre buses, which were used to ease congestion on high-density routes. Overall Arriva Malta operated 264 buses. On 1 January 2014 Arriva ceased operations in Malta due to financial difficulties, having been nationalised as ''Malta Public Transport'' by the Maltese government, with a new bus operator planned to take over their operations. The government chose Autobuses Urbanos de León (ALSA (bus company), ALSA subsidiary) as its preferred bus operator for the country in October 2014. The company took over the bus service on 8 January 2015, while retaining the name ''Malta Public Transport''. It introduced the pre-pay 'tallinja card'. With lower fares than the walk-on rate, it can be topped up online. The card was initially not well received, as reported by several local news sites. During the first week of August 2015, another 40 buses of the Turkish make ''Otokar'' arrived and were put into service.
From October 2022 the bus system will be free of charge for residents of Malta.
From 1883 to 1931 Malta had a Malta Railway, railway line that connected Valletta to the army barracks at Mtarfa via Mdina and a number of towns and villages. The railway fell into disuse and eventually closed altogether, following the introduction of electric trams and buses. At the height of the bombing of Malta during the Second World War, Benito Mussolini, Mussolini announced that his forces had destroyed the railway system, but by the time war broke out, the railway had been mothballed for more than nine years.
As of 2021, an underground Malta Metro is being planned, with a projected total cost of €6.2 billion.
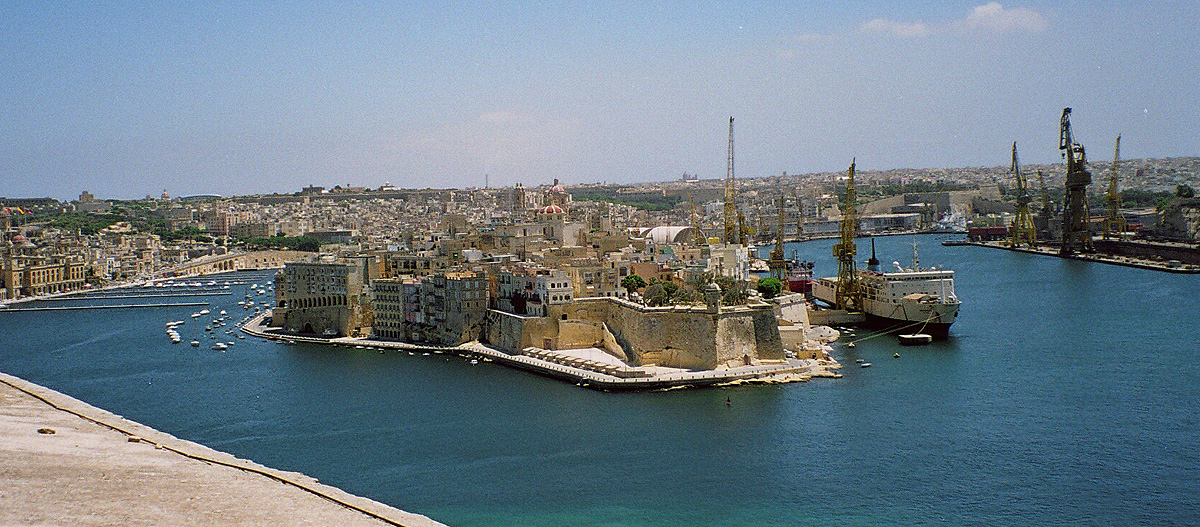

 Malta has three large natural harbours on its main island:
* The
Malta has three large natural harbours on its main island:
* The  The national airline is Air Malta, which is based at Malta International Airport and operates services to 36 destinations in Europe and North Africa. The owners of Air Malta are the Government of Malta (98 percent) and private investors (2 percent). Air Malta employs 1,547 staff along with having a 25 percent share in Medavia.
Air Malta has concluded over 191 interline ticketing agreements with other International Air Transport Association, IATA airlines. It also has a codeshare agreement with Qantas covering three routes. In September 2007, Air Malta made two agreements with Abu Dhabi-based Etihad Airways by which Air Malta wet-leased two Airbus aircraft to Etihad Airways for the winter period starting 1 September 2007, and provided operational support on another Airbus A320 aircraft which it leased to Etihad Airways.
In June 2019, Ryanair has invested into a fully-fledged airline subsidiary, called Malta Air, operating a low-cost model. The Government of Malta holds one share in the airline whereby it holds rights to the brand name.
The national airline is Air Malta, which is based at Malta International Airport and operates services to 36 destinations in Europe and North Africa. The owners of Air Malta are the Government of Malta (98 percent) and private investors (2 percent). Air Malta employs 1,547 staff along with having a 25 percent share in Medavia.
Air Malta has concluded over 191 interline ticketing agreements with other International Air Transport Association, IATA airlines. It also has a codeshare agreement with Qantas covering three routes. In September 2007, Air Malta made two agreements with Abu Dhabi-based Etihad Airways by which Air Malta wet-leased two Airbus aircraft to Etihad Airways for the winter period starting 1 September 2007, and provided operational support on another Airbus A320 aircraft which it leased to Etihad Airways.
In June 2019, Ryanair has invested into a fully-fledged airline subsidiary, called Malta Air, operating a low-cost model. The Government of Malta holds one share in the airline whereby it holds rights to the brand name.
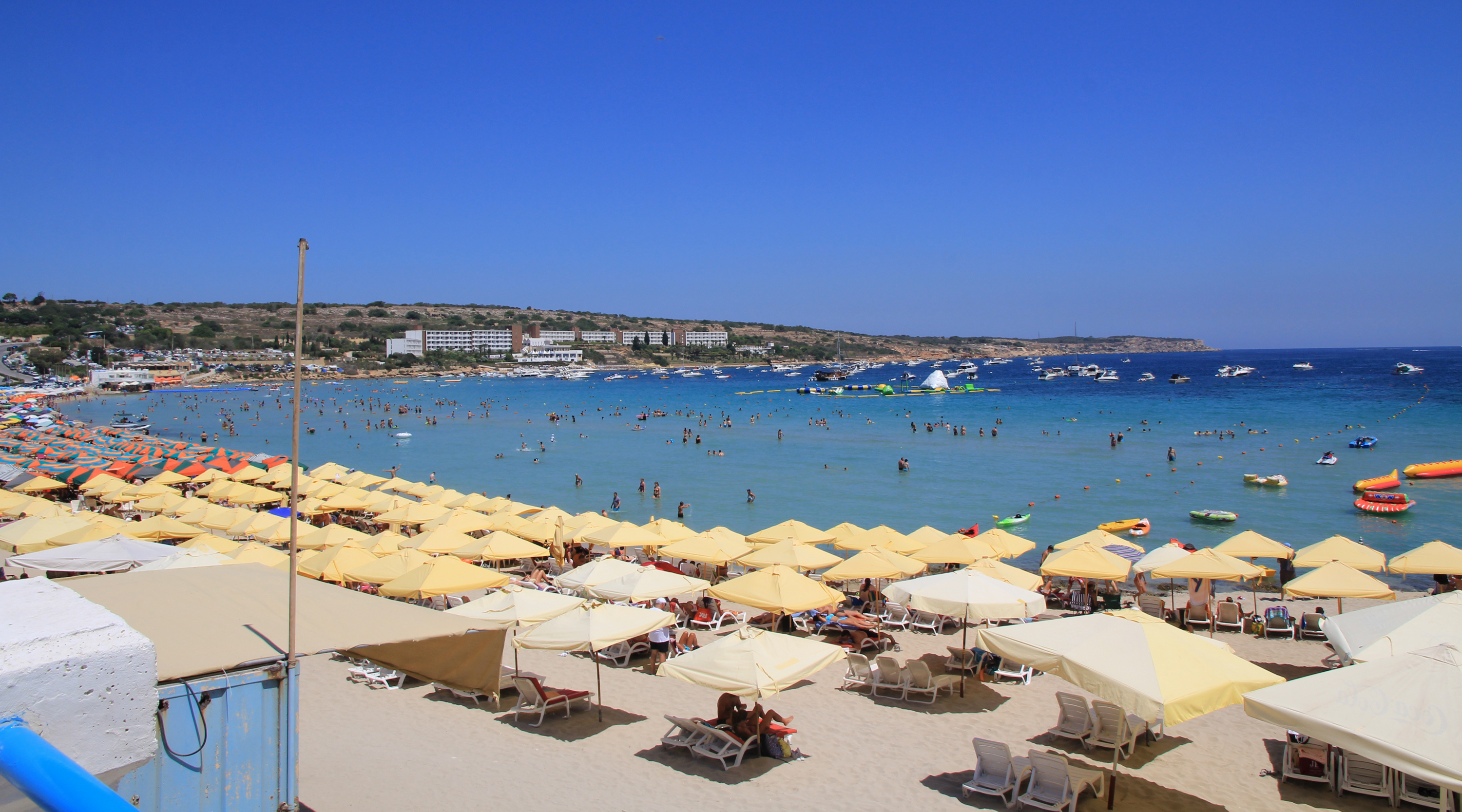 Malta is a popular tourist destination, with 1.6 million tourists per year. Three times more tourists visit than there are residents. Tourism infrastructure has increased dramatically over the years and a number of hotels are present on the island, although overdevelopment and the destruction of traditional housing is of growing concern. An increasing number of Maltese now travel abroad on holiday. In 2019, Malta had a record year in tourism, recording over 2.1 million tourists in one single year.
In recent years, Malta has advertised itself as a medical tourism destination, and a number of health tourism providers are developing the industry. However, no Maltese hospital has undergone independent international healthcare accreditation. Malta is popular with British medical tourists, pointing Maltese hospitals towards seeking UK-sourced accreditation, such as with the Trent Accreditation Scheme.
Additionally, Malta attracts a number of English Language Students from around the world.
Tourism in Malta contributes to around 11.6 percent of the country's Gross domestic product, Gross Domestic Product.
Malta is a popular tourist destination, with 1.6 million tourists per year. Three times more tourists visit than there are residents. Tourism infrastructure has increased dramatically over the years and a number of hotels are present on the island, although overdevelopment and the destruction of traditional housing is of growing concern. An increasing number of Maltese now travel abroad on holiday. In 2019, Malta had a record year in tourism, recording over 2.1 million tourists in one single year.
In recent years, Malta has advertised itself as a medical tourism destination, and a number of health tourism providers are developing the industry. However, no Maltese hospital has undergone independent international healthcare accreditation. Malta is popular with British medical tourists, pointing Maltese hospitals towards seeking UK-sourced accreditation, such as with the Trent Accreditation Scheme.
Additionally, Malta attracts a number of English Language Students from around the world.
Tourism in Malta contributes to around 11.6 percent of the country's Gross domestic product, Gross Domestic Product.
. Esa.int. Retrieved 7 June 2012. The Malta Council for Science and Technology (MCST) is the civil body responsible for the development of science and technology on an educational and social level. Most science students in Malta graduate from the University of Malta and are represented by S-Cubed (Science Student's Society), UESA (University Engineering Students Association) and ICTSA (University of Malta ICT Students' Association). Malta was ranked 21th in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, up from 27th in 2019, 2020 and 2021.
 A population and housing census is conducted every ten years in Malta. The November 2005 census counted an estimated 96 percent of the population. A preliminary report was issued in April 2006 and the results were weighted to estimate for 100 percent of the population.
Maltese natives make up the majority of the island. However, there are minorities, the largest of which are British people, Britons, many of whom are retirees.
The population of Malta was estimated at 408,000. , 17 percent were aged 14 and under, 68 percent were within the 15–64 age bracket whilst the remaining 13 percent were 65 years and over. Malta's population density of 1,282 per square km (3,322/sq mi) is by far the highest in the EU and one of the highest in the world. By comparison, the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, average population density for the World (land only, excluding Antarctica) was as of July 2014.
The only census year showing a fall in population was that of 1967, with a 1.7 per cent total decrease, attributable to a substantial number of Maltese residents who emigrated. The Maltese-resident population for 2004 was estimated to make up 97.0 per cent of the total resident population.
All censuses since 1842 have shown a slight excess of females over males. The 1901 and 1911 censuses came closest to recording a balance. The highest female-to-male ratio was reached in 1957 (1088:1000) but since then the ratio has dropped continuously. The 2005 census showed a 1013:1000 female-to-male ratio.
Population growth has slowed down, from +9.5 per cent between the 1985 and 1995 censuses, to +6.9 per cent between the 1995 and 2005 censuses (a yearly average of +0.7 per cent). The birth rate stood at 3860 (a decrease of 21.8 per cent from the 1995 census) and the death rate stood at 3025. Thus, there was a natural population increase of 835 (compared to +888 for 2004, of which over a hundred were foreign residents).
The population's age composition is similar to the age structure prevalent in the EU. Since 1967 there was observed a trend indicating an ageing population, and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Malta's Dependency ratio, old-age-dependency-ratio rose from 17.2 percent in 1995 to 19.8 percent in 2005, reasonably lower than the EU's 24.9 percent average; 31.5 percent of the Maltese population is aged under 25 (compared to the EU's 29.1 percent); but the 50–64 age group constitutes 20.3 percent of the population, significantly higher than the EU's 17.9 percent. Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio is expected to continue rising steadily in the coming years.
Maltese legislation recognises both civil and canonical (ecclesiastical) marriages. Annulments by the ecclesiastical and civil courts are unrelated and are not necessarily mutually endorsed. Malta voted in favour of divorce legislation in 2011 Maltese divorce referendum, a referendum held on 28 May 2011.
Abortion in Malta is illegal. It's the only European Union member state with a total ban on the procedure. There are no exceptions, including in cases of rape or incest. On 21 November 2022, the government led by the Labour Party proposed a bill that "introduces a new clause into the country’s criminal code allowing for the termination of a pregnancy if the mother’s life is at risk or if her health is in serious jeopardy".
A person must be 16 to marry. The number of brides aged under 25 decreased from 1471 in 1997 to 766 in 2005; while the number of grooms under 25 decreased from 823 to 311. There is a constant trend that females are more likely than males to marry young. In 2005 there were 51 brides aged between 16 and 19, compared to 8 grooms.
In 2021, the population of the Maltese Islands stood at 516,100.
The total fertility rate (TFR) was estimated at 1.45 children born/woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. In 2012, 25.8 per cent of births were to unmarried women. The life expectancy in 2018 was estimated at 83.
A population and housing census is conducted every ten years in Malta. The November 2005 census counted an estimated 96 percent of the population. A preliminary report was issued in April 2006 and the results were weighted to estimate for 100 percent of the population.
Maltese natives make up the majority of the island. However, there are minorities, the largest of which are British people, Britons, many of whom are retirees.
The population of Malta was estimated at 408,000. , 17 percent were aged 14 and under, 68 percent were within the 15–64 age bracket whilst the remaining 13 percent were 65 years and over. Malta's population density of 1,282 per square km (3,322/sq mi) is by far the highest in the EU and one of the highest in the world. By comparison, the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, average population density for the World (land only, excluding Antarctica) was as of July 2014.
The only census year showing a fall in population was that of 1967, with a 1.7 per cent total decrease, attributable to a substantial number of Maltese residents who emigrated. The Maltese-resident population for 2004 was estimated to make up 97.0 per cent of the total resident population.
All censuses since 1842 have shown a slight excess of females over males. The 1901 and 1911 censuses came closest to recording a balance. The highest female-to-male ratio was reached in 1957 (1088:1000) but since then the ratio has dropped continuously. The 2005 census showed a 1013:1000 female-to-male ratio.
Population growth has slowed down, from +9.5 per cent between the 1985 and 1995 censuses, to +6.9 per cent between the 1995 and 2005 censuses (a yearly average of +0.7 per cent). The birth rate stood at 3860 (a decrease of 21.8 per cent from the 1995 census) and the death rate stood at 3025. Thus, there was a natural population increase of 835 (compared to +888 for 2004, of which over a hundred were foreign residents).
The population's age composition is similar to the age structure prevalent in the EU. Since 1967 there was observed a trend indicating an ageing population, and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Malta's Dependency ratio, old-age-dependency-ratio rose from 17.2 percent in 1995 to 19.8 percent in 2005, reasonably lower than the EU's 24.9 percent average; 31.5 percent of the Maltese population is aged under 25 (compared to the EU's 29.1 percent); but the 50–64 age group constitutes 20.3 percent of the population, significantly higher than the EU's 17.9 percent. Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio is expected to continue rising steadily in the coming years.
Maltese legislation recognises both civil and canonical (ecclesiastical) marriages. Annulments by the ecclesiastical and civil courts are unrelated and are not necessarily mutually endorsed. Malta voted in favour of divorce legislation in 2011 Maltese divorce referendum, a referendum held on 28 May 2011.
Abortion in Malta is illegal. It's the only European Union member state with a total ban on the procedure. There are no exceptions, including in cases of rape or incest. On 21 November 2022, the government led by the Labour Party proposed a bill that "introduces a new clause into the country’s criminal code allowing for the termination of a pregnancy if the mother’s life is at risk or if her health is in serious jeopardy".
A person must be 16 to marry. The number of brides aged under 25 decreased from 1471 in 1997 to 766 in 2005; while the number of grooms under 25 decreased from 823 to 311. There is a constant trend that females are more likely than males to marry young. In 2005 there were 51 brides aged between 16 and 19, compared to 8 grooms.
In 2021, the population of the Maltese Islands stood at 516,100.
The total fertility rate (TFR) was estimated at 1.45 children born/woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. In 2012, 25.8 per cent of births were to unmarried women. The life expectancy in 2018 was estimated at 83.
 The
The
Maltese – an unusual formula
, MED Magazine (February 2005) The Maltese alphabet consists of 30 letters based on the Latin alphabet, including the diacritically altered letters ''ż'', ''ċ'' and ''ġ'', as well as the letters ''għ'', ''ħ'', and ''Ie (digraph), ie''. Maltese is the only
A view of the linguistic situation in Malta
NovesSl. Retrieved 24 February 2008 Maltese Sign Language is used by signers in Malta.
 The predominant religion in Malta is
The predominant religion in Malta is  For centuries, the Church in Malta was subordinate to the Diocese of Palermo, except when it was under Charles of Anjou, who appointed bishops for Malta, as did – on rare occasions – the Spanish and later, the Knights. Since 1808 all bishops of Malta have been Maltese. As a result of the History of Malta#Norman Kingdom of Sicily rule, Norman and Spanish periods, and the rule of the Knights, Malta became the devout Catholic nation that it is today. It is worth noting that the Office of the Roman Inquisition, Inquisitor of Malta had a very long tenure on the island following its establishment in 1530: the last Inquisitor departed from the Islands in 1798 after the Knights capitulated to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte. During the period of the Republic of Venice, several Maltese families emigrated to Corfu. Their descendants account for about two-thirds of the community of some 4,000 Catholics that now live on that island.
For centuries, the Church in Malta was subordinate to the Diocese of Palermo, except when it was under Charles of Anjou, who appointed bishops for Malta, as did – on rare occasions – the Spanish and later, the Knights. Since 1808 all bishops of Malta have been Maltese. As a result of the History of Malta#Norman Kingdom of Sicily rule, Norman and Spanish periods, and the rule of the Knights, Malta became the devout Catholic nation that it is today. It is worth noting that the Office of the Roman Inquisition, Inquisitor of Malta had a very long tenure on the island following its establishment in 1530: the last Inquisitor departed from the Islands in 1798 after the Knights capitulated to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte. During the period of the Republic of Venice, several Maltese families emigrated to Corfu. Their descendants account for about two-thirds of the community of some 4,000 Catholics that now live on that island.
 The patron saints of Malta are Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul, Saint Publius, and Agatha of Sicily, Saint Agatha. Although not a patron saint, George Preca, St George Preca (San Ġorġ Preca) is greatly revered as the second canonised Maltese saint after St. Publius. Pope Benedict XVI canonised Preca on 3 June 2007. A number of Maltese individuals are recognised as Beatification, Blessed, including Maria Adeodata Pisani and Nazju Falzon, with Pope John Paul II having beatified them in 2001.
Various Catholic religious orders are present in Malta, including the Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominican Order, Dominicans, Carmelites and Little Sisters of the Poor.
Most congregants of the local Protestant churches are not Maltese; their congregations draw on the many British retirees living in the country and vacationers from many other nations. There include St. Andrew's Scots Church, Malta, St. Andrew's Scots Church in Valletta (a joint Presbyterian and Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist congregation) and St Paul's Anglican Cathedral. There are several Charismatic, Pentecostal, and Baptist churches, including the Bible Baptist Church, Knisja Evanġelika Battista, an
The patron saints of Malta are Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul, Saint Publius, and Agatha of Sicily, Saint Agatha. Although not a patron saint, George Preca, St George Preca (San Ġorġ Preca) is greatly revered as the second canonised Maltese saint after St. Publius. Pope Benedict XVI canonised Preca on 3 June 2007. A number of Maltese individuals are recognised as Beatification, Blessed, including Maria Adeodata Pisani and Nazju Falzon, with Pope John Paul II having beatified them in 2001.
Various Catholic religious orders are present in Malta, including the Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominican Order, Dominicans, Carmelites and Little Sisters of the Poor.
Most congregants of the local Protestant churches are not Maltese; their congregations draw on the many British retirees living in the country and vacationers from many other nations. There include St. Andrew's Scots Church, Malta, St. Andrew's Scots Church in Valletta (a joint Presbyterian and Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist congregation) and St Paul's Anglican Cathedral. There are several Charismatic, Pentecostal, and Baptist churches, including the Bible Baptist Church, Knisja Evanġelika Battista, an
Trinity Evangelical Church
– a Reformed Baptist Church. The members of these churches are mainly Maltese. There are also a Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventist church in Birkirkara, and a New Apostolic Church congregation founded in 1983 in Gwardamangia.Vassallo, Harry (8 April 2009
A map of faith in Malta
. ''MaltaToday'' (8 April 2009). Retrieved 1 May 2017. There are approximately 600 Jehovah's Witnesses. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) is also represented. The Jewish population of Malta reached its peak in the Middle Ages under Norman rule. In 1479, Malta and
 In the 19th century, most emigration from Malta was to North Africa and the Middle East, although rates of Repatriation, return migration to Malta were high. Nonetheless, Maltese communities formed in these regions. By 1900, for example, British consular estimates suggest that there were 15,326 Maltese in
In the 19th century, most emigration from Malta was to North Africa and the Middle East, although rates of Repatriation, return migration to Malta were high. Nonetheless, Maltese communities formed in these regions. By 1900, for example, British consular estimates suggest that there were 15,326 Maltese in
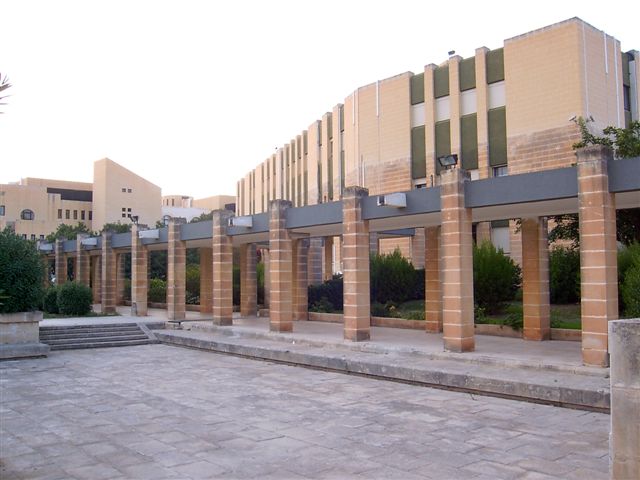
 Primary schooling has been compulsory since 1946; secondary education up to the age of sixteen was made compulsory in 1971. The state and the Catholic Church, Church provide education free of charge, both running a number of schools in Malta and Gozo, including De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College in Cospicua, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College in Birkirkara, St. Paul's Missionary College in Rabat, Malta, St. Joseph's School in Blata l-Bajda and List of schools in Malta, Saint Monica Girls' School in Mosta and St. Augustine's College (Malta), Saint Augustine College, with its primary sector in Marsa, Malta, Marsa and its secondary in Pietà, Malta, Pieta. , state schools are organised into networks known as Colleges and incorporate kindergarten schools, primary and secondary schools. A number of private schools are run in Malta, including San Andrea School and San Anton School in the valley of L-Imselliet (l/o Mġarr), St. Martin's College in Swatar and St. Michael School (Malta), St. Michael's School in Santa Venera. St. Catherine's High School, Pembroke offers an International Foundation Course for students wishing to learn English before entering mainstream education. , there are two international schools, Verdala International School and QSI Malta. The state pays a portion of the teachers' salary in Church schools.
Education in Malta is based on the Education in the United Kingdom, British model. Primary school lasts six years. Pupils sit for SEC O-level examinations at the age of 16, with passes obligatory in certain subjects such as Mathematics, a minimum of one science subject (Physics, Biology or Chemistry), English and Maltese. Upon obtaining these subjects, Pupils may opt to continue studying at a sixth form college such as Gan Frangisk Abela Junior College, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College, Giovanni Curmi Higher Secondary, De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College, St Edward's College, or else at another post-secondary institution such as MCAST. The sixth form course lasts for two years, at the end of which students sit for the matriculation examination. Subject to their performance, students may then apply for an undergraduate academic degree, degree or diploma.
The adult literacy rate is 99.5 per cent.
Maltese and English are both used to teach pupils at the primary and secondary school level, and both languages are also compulsory subjects. State school, Public schools tend to use both Maltese and English in a balanced manner. Private schools prefer to use English for teaching, as is also the case with most departments of the University of Malta; this has a limiting effect on the capacity and development of the Maltese language. Most university courses are in English. The College of Remote and Offshore Medicine based in Malta teaches exclusively in english, awarding undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
Of the total number of pupils studying a first foreign language at secondary level, 51 per cent take Italian whilst 38 per cent take French. Other choices include German, Russian, Spanish, Latin, Chinese and Arabic.
Malta is also a popular destination to study the English language, attracting over 83,000 students in 2019.
Primary schooling has been compulsory since 1946; secondary education up to the age of sixteen was made compulsory in 1971. The state and the Catholic Church, Church provide education free of charge, both running a number of schools in Malta and Gozo, including De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College in Cospicua, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College in Birkirkara, St. Paul's Missionary College in Rabat, Malta, St. Joseph's School in Blata l-Bajda and List of schools in Malta, Saint Monica Girls' School in Mosta and St. Augustine's College (Malta), Saint Augustine College, with its primary sector in Marsa, Malta, Marsa and its secondary in Pietà, Malta, Pieta. , state schools are organised into networks known as Colleges and incorporate kindergarten schools, primary and secondary schools. A number of private schools are run in Malta, including San Andrea School and San Anton School in the valley of L-Imselliet (l/o Mġarr), St. Martin's College in Swatar and St. Michael School (Malta), St. Michael's School in Santa Venera. St. Catherine's High School, Pembroke offers an International Foundation Course for students wishing to learn English before entering mainstream education. , there are two international schools, Verdala International School and QSI Malta. The state pays a portion of the teachers' salary in Church schools.
Education in Malta is based on the Education in the United Kingdom, British model. Primary school lasts six years. Pupils sit for SEC O-level examinations at the age of 16, with passes obligatory in certain subjects such as Mathematics, a minimum of one science subject (Physics, Biology or Chemistry), English and Maltese. Upon obtaining these subjects, Pupils may opt to continue studying at a sixth form college such as Gan Frangisk Abela Junior College, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College, Giovanni Curmi Higher Secondary, De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College, St Edward's College, or else at another post-secondary institution such as MCAST. The sixth form course lasts for two years, at the end of which students sit for the matriculation examination. Subject to their performance, students may then apply for an undergraduate academic degree, degree or diploma.
The adult literacy rate is 99.5 per cent.
Maltese and English are both used to teach pupils at the primary and secondary school level, and both languages are also compulsory subjects. State school, Public schools tend to use both Maltese and English in a balanced manner. Private schools prefer to use English for teaching, as is also the case with most departments of the University of Malta; this has a limiting effect on the capacity and development of the Maltese language. Most university courses are in English. The College of Remote and Offshore Medicine based in Malta teaches exclusively in english, awarding undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
Of the total number of pupils studying a first foreign language at secondary level, 51 per cent take Italian whilst 38 per cent take French. Other choices include German, Russian, Spanish, Latin, Chinese and Arabic.
Malta is also a popular destination to study the English language, attracting over 83,000 students in 2019.
 Malta has a long history of providing publicly funded health care. The first hospital recorded in the country was already functioning by 1372. The first hospital exclusively for women was opened in 1625 by Caterina Scappi, known as "La Senese".
Today, Malta has both a public healthcare system, known as the government healthcare service, where healthcare is free at the point of delivery, and a private healthcare system. Malta has a strong general practitioner-delivered primary care base and the public hospitals provide secondary and tertiary care. The Maltese Ministry of Health advises foreign residents to take out private medical insurance.
.
Malta has a long history of providing publicly funded health care. The first hospital recorded in the country was already functioning by 1372. The first hospital exclusively for women was opened in 1625 by Caterina Scappi, known as "La Senese".
Today, Malta has both a public healthcare system, known as the government healthcare service, where healthcare is free at the point of delivery, and a private healthcare system. Malta has a strong general practitioner-delivered primary care base and the public hospitals provide secondary and tertiary care. The Maltese Ministry of Health advises foreign residents to take out private medical insurance.
. Malta also boasts voluntary organisations such as Alpha Medical (Advanced Care), the Emergency Fire & Rescue Unit (E.F.R.U.), St John Ambulance and Red Cross Malta who provide first aid/nursing services during events involving crowds, Malta's primary hospital, opened in 2007. It has one of the largest medical buildings in Europe
The University of Malta has a medical school and a Faculty of Health Sciences, the latter offering diploma, degree (BSc) and postgraduate degree courses in a number of health care disciplines.
The Medical Association of Malta represents practitioners of the medical profession. The Malta Medical Students' Association (MMSA) is a separate body representing Maltese medical students, and is a member of European Medical Students' Association, EMSA and International Federation of Medical Students' Associations, IFMSA. MIME, the Maltese Institute for Medical Education, is an institute set up recently to provide CME to physicians in Malta as well as medical students. The Foundation Program followed in the UK has been introduced in Malta to stem the 'brain drain' of newly graduated physicians to the British Isles. The Malta Association of Dental Students (MADS) is a student association set up to promote the rights of Dental Surgery Students studying within the faculty of Dental Surgery of the University of Malta. It is affiliated with IADS, the International Association of Dental Students.
Malta also boasts voluntary organisations such as Alpha Medical (Advanced Care), the Emergency Fire & Rescue Unit (E.F.R.U.), St John Ambulance and Red Cross Malta who provide first aid/nursing services during events involving crowds, Malta's primary hospital, opened in 2007. It has one of the largest medical buildings in Europe
The University of Malta has a medical school and a Faculty of Health Sciences, the latter offering diploma, degree (BSc) and postgraduate degree courses in a number of health care disciplines.
The Medical Association of Malta represents practitioners of the medical profession. The Malta Medical Students' Association (MMSA) is a separate body representing Maltese medical students, and is a member of European Medical Students' Association, EMSA and International Federation of Medical Students' Associations, IFMSA. MIME, the Maltese Institute for Medical Education, is an institute set up recently to provide CME to physicians in Malta as well as medical students. The Foundation Program followed in the UK has been introduced in Malta to stem the 'brain drain' of newly graduated physicians to the British Isles. The Malta Association of Dental Students (MADS) is a student association set up to promote the rights of Dental Surgery Students studying within the faculty of Dental Surgery of the University of Malta. It is affiliated with IADS, the International Association of Dental Students.
 While Maltese music today is largely Western, traditional Maltese music includes what is known as ''Għana (folk music), għana''. This consists of background folk guitar music, while a few people, generally men, take it in turns to argue a point in a sing-song voice. The aim of the lyrics, which are improvised, is to create a friendly yet challenging atmosphere, and it takes a number of years of practice to be able to combine the required artistic qualities with the ability to debate effectively. Music plays an important part in Maltese culture as each locality parades its own band club, on various occasions these being multiple per locality, and function to establish the thematic musical background to the various Public holidays in Malta, village feasts that dot the Maltese islands throughout the year. Additionally, the Malta Philharmonic Orchestra is recognized as Malta’s foremost musical institution and is notable for being called to participate in important state events.
Contemporary music in Malta spans a variety of styles and sports international classical talents such as Miriam Gauci and Joseph Calleja, as well as non-classical music bands such as Winter Moods, and Red Electric (band), Red Electric, and singers like Ira Losco, Fabrizio Faniello, Glen Vella, Kevin Borg, Kurt Calleja, Chiara Siracusa, and Thea Garrett.
While Maltese music today is largely Western, traditional Maltese music includes what is known as ''Għana (folk music), għana''. This consists of background folk guitar music, while a few people, generally men, take it in turns to argue a point in a sing-song voice. The aim of the lyrics, which are improvised, is to create a friendly yet challenging atmosphere, and it takes a number of years of practice to be able to combine the required artistic qualities with the ability to debate effectively. Music plays an important part in Maltese culture as each locality parades its own band club, on various occasions these being multiple per locality, and function to establish the thematic musical background to the various Public holidays in Malta, village feasts that dot the Maltese islands throughout the year. Additionally, the Malta Philharmonic Orchestra is recognized as Malta’s foremost musical institution and is notable for being called to participate in important state events.
Contemporary music in Malta spans a variety of styles and sports international classical talents such as Miriam Gauci and Joseph Calleja, as well as non-classical music bands such as Winter Moods, and Red Electric (band), Red Electric, and singers like Ira Losco, Fabrizio Faniello, Glen Vella, Kevin Borg, Kurt Calleja, Chiara Siracusa, and Thea Garrett.
 Maltese architecture has been influenced by many different Mediterranean cultures and British architecture over its history. The first settlers on the island constructed
Maltese architecture has been influenced by many different Mediterranean cultures and British architecture over its history. The first settlers on the island constructed
 The arrival in Malta of Caravaggio, who painted at least seven works during his 15-month stay on these islands, further revolutionised local art. Two of Caravaggio's most notable works, ''The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist (Caravaggio), The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist'' and ''Saint Jerome Writing (Valletta), Saint Jerome Writing'', are on display in the Oratory (worship), Oratory of the Conventual Church of St. John. His legacy is evident in the works of local artists Giulio Cassarino (1582–1637) and Stefano Erardi (1630–1716). However, the Baroque movement that followed was destined to have the most enduring impact on Maltese art and architecture. The glorious vault paintings of the celebrated Calabrese artist, Mattia Preti transformed the severe, Mannerist interior of the Conventual Church St. John into a Baroque masterpiece. Preti spent the last 40 years of his life in Malta, where he created many of his finest works, now on display in the Museum of Fine Arts in Valletta. During this period, local sculptor Melchiorre Cafà, Melchior Gafà (1639–1667) emerged as one of the top Baroque sculptors of the Roman School.
The arrival in Malta of Caravaggio, who painted at least seven works during his 15-month stay on these islands, further revolutionised local art. Two of Caravaggio's most notable works, ''The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist (Caravaggio), The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist'' and ''Saint Jerome Writing (Valletta), Saint Jerome Writing'', are on display in the Oratory (worship), Oratory of the Conventual Church of St. John. His legacy is evident in the works of local artists Giulio Cassarino (1582–1637) and Stefano Erardi (1630–1716). However, the Baroque movement that followed was destined to have the most enduring impact on Maltese art and architecture. The glorious vault paintings of the celebrated Calabrese artist, Mattia Preti transformed the severe, Mannerist interior of the Conventual Church St. John into a Baroque masterpiece. Preti spent the last 40 years of his life in Malta, where he created many of his finest works, now on display in the Museum of Fine Arts in Valletta. During this period, local sculptor Melchiorre Cafà, Melchior Gafà (1639–1667) emerged as one of the top Baroque sculptors of the Roman School.
 During the 17th and 18th century, Naples, Neapolitan and Rococo influences emerged in the works of the Italian painters Luca Giordano (1632–1705) and Francesco Solimena (1657–1747), and these developments can be seen in the work of their Maltese contemporaries such as Gio Nicola Buhagiar (1698–1752) and Francesco Zahra (1710–1773). The Rococo movement was greatly enhanced by the relocation to Malta of Antoine de Favray (1706–1798), who assumed the position of court painter to Grand Master Pinto in 1744.
Neo-classicism made some inroads among local Maltese artists in the late-18th century, but this trend was reversed in the early 19th century, as the local Church authorities – perhaps in an effort to strengthen Catholic resolve against the perceived threat of Protestantism during the early days of British rule in Malta – favoured and avidly promoted the religious themes embraced by the Nazarene movement of artists. Romanticism, tempered by the naturalism introduced to Malta by Giuseppe Calì, informed the "salon" artists of the early 20th century, including Edward and Robert Caruana Dingli.
Parliament established the National School of Art in the 1920s. During the reconstruction period that followed the Second World War, the emergence of the "Modern Art Group", whose members included Josef Kalleya (1898–1998), George Preca (1909–1984), Anton Inglott (1915–1945), Emvin Cremona (1919–1987), Frank Portelli (artist), Frank Portelli (1922–2004), Antoine Camilleri (artist), Antoine Camilleri (1922–2005), Gabriel Caruana (1929–2018) and Esprit Barthet (1919–1999) greatly enhanced the local art scene. This group of forward-looking artists came together forming an influential pressure group known as the Modern Art Group. Together they forced the Maltese public to take seriously modern aesthetics and succeeded in playing a leading role in the renewal of Maltese art. Most of Malta's modern artists have in fact studied in Art institutions in England, or on the continent, leading to the explosive development of a wide spectrum of views and to a diversity of artistic expression that has remained characteristic of contemporary Maltese art. In Valletta, the National Museum of Fine Arts, Malta, National Museum of Fine Arts featured work from artists such as H. Craig Hanna."Right Outside my Window"
During the 17th and 18th century, Naples, Neapolitan and Rococo influences emerged in the works of the Italian painters Luca Giordano (1632–1705) and Francesco Solimena (1657–1747), and these developments can be seen in the work of their Maltese contemporaries such as Gio Nicola Buhagiar (1698–1752) and Francesco Zahra (1710–1773). The Rococo movement was greatly enhanced by the relocation to Malta of Antoine de Favray (1706–1798), who assumed the position of court painter to Grand Master Pinto in 1744.
Neo-classicism made some inroads among local Maltese artists in the late-18th century, but this trend was reversed in the early 19th century, as the local Church authorities – perhaps in an effort to strengthen Catholic resolve against the perceived threat of Protestantism during the early days of British rule in Malta – favoured and avidly promoted the religious themes embraced by the Nazarene movement of artists. Romanticism, tempered by the naturalism introduced to Malta by Giuseppe Calì, informed the "salon" artists of the early 20th century, including Edward and Robert Caruana Dingli.
Parliament established the National School of Art in the 1920s. During the reconstruction period that followed the Second World War, the emergence of the "Modern Art Group", whose members included Josef Kalleya (1898–1998), George Preca (1909–1984), Anton Inglott (1915–1945), Emvin Cremona (1919–1987), Frank Portelli (artist), Frank Portelli (1922–2004), Antoine Camilleri (artist), Antoine Camilleri (1922–2005), Gabriel Caruana (1929–2018) and Esprit Barthet (1919–1999) greatly enhanced the local art scene. This group of forward-looking artists came together forming an influential pressure group known as the Modern Art Group. Together they forced the Maltese public to take seriously modern aesthetics and succeeded in playing a leading role in the renewal of Maltese art. Most of Malta's modern artists have in fact studied in Art institutions in England, or on the continent, leading to the explosive development of a wide spectrum of views and to a diversity of artistic expression that has remained characteristic of contemporary Maltese art. In Valletta, the National Museum of Fine Arts, Malta, National Museum of Fine Arts featured work from artists such as H. Craig Hanna."Right Outside my Window"
, ''The Malta Independent'', 23 April 2006. Retrieved 11 June 2014 In 2018 the national collection of fine arts was moved and put on display in the new National Museum of Art, MUŻA, located at Auberge d'Italie, Auberge d’Italie in Valletta.
 Maltese cuisine shows strong Sicilian cuisine, Sicilian and Italian cuisine, Italian influences as well as influences of English cuisine, English, Spanish cuisine, Spanish, Maghreb cuisine, Maghrebin and Provençal cuisine, Provençal cuisines. A number of regional variations, particularly with regards to Gozo, can be noted as well as seasonal variations associated with the seasonal availability of produce and Christian feasts (such as Lent, Easter and Christmas). Food has been important historically in the development of a national identity in particular the traditional ''fenkata'' (i.e., the eating of stewed or fried rabbit). Potatoes are a staple of the Maltese diet as well.
A number of grapes are endemic to Malta, including Girgentina and Ġellewża. There is a strong Maltese wine, wine industry in Malta, with significant production of wines using these native grapes, as well as locally grown grapes of other more common varietals, such as Chardonnay and Syrah. A number of wines have achieved Protected Designation of Origin, with wines produced from grapes cultivated in Malta and Gozo designated as "DOK" wines, that is ''Denominazzjoni ta’ l-Oriġini Kontrollata''.
Maltese cuisine shows strong Sicilian cuisine, Sicilian and Italian cuisine, Italian influences as well as influences of English cuisine, English, Spanish cuisine, Spanish, Maghreb cuisine, Maghrebin and Provençal cuisine, Provençal cuisines. A number of regional variations, particularly with regards to Gozo, can be noted as well as seasonal variations associated with the seasonal availability of produce and Christian feasts (such as Lent, Easter and Christmas). Food has been important historically in the development of a national identity in particular the traditional ''fenkata'' (i.e., the eating of stewed or fried rabbit). Potatoes are a staple of the Maltese diet as well.
A number of grapes are endemic to Malta, including Girgentina and Ġellewża. There is a strong Maltese wine, wine industry in Malta, with significant production of wines using these native grapes, as well as locally grown grapes of other more common varietals, such as Chardonnay and Syrah. A number of wines have achieved Protected Designation of Origin, with wines produced from grapes cultivated in Malta and Gozo designated as "DOK" wines, that is ''Denominazzjoni ta’ l-Oriġini Kontrollata''.
 Local festivals, similar to those in Southern Italy, are commonplace in Malta and Gozo, celebrating weddings, Baptism, christenings and, most prominently, saints' days, honouring the patron saint of the local parish. On saints' days, in the morning, the ''festa'' reaches its apex with a Mass (liturgy), High Mass featuring a sermon on the life and achievements of the patron saint. In the evening, then, a statue of the religious patron is taken around the local streets in solemn procession, with the faithful following in respectful prayer. The atmosphere of religious devotion is preceded by several days of celebration and revelry: band marches, fireworks, and late-night parties.
Maltese Carnival, Carnival (Maltese: ''il-karnival ta' Malta'') has had an important place on the cultural calendar after Grand Master (order), Grand Master Piero de Ponte introduced it to the islands in 1535. It is held during the week leading up to Ash Wednesday, and typically includes masked balls, fancy dress and grotesque mask competitions, lavish late-night parties, a colourful, ticker-tape parade of allegorical float (parade), floats presided over by King Carnival (Maltese: ''ir-Re tal-Karnival''), marching bands and costumed revellers.
Local festivals, similar to those in Southern Italy, are commonplace in Malta and Gozo, celebrating weddings, Baptism, christenings and, most prominently, saints' days, honouring the patron saint of the local parish. On saints' days, in the morning, the ''festa'' reaches its apex with a Mass (liturgy), High Mass featuring a sermon on the life and achievements of the patron saint. In the evening, then, a statue of the religious patron is taken around the local streets in solemn procession, with the faithful following in respectful prayer. The atmosphere of religious devotion is preceded by several days of celebration and revelry: band marches, fireworks, and late-night parties.
Maltese Carnival, Carnival (Maltese: ''il-karnival ta' Malta'') has had an important place on the cultural calendar after Grand Master (order), Grand Master Piero de Ponte introduced it to the islands in 1535. It is held during the week leading up to Ash Wednesday, and typically includes masked balls, fancy dress and grotesque mask competitions, lavish late-night parties, a colourful, ticker-tape parade of allegorical float (parade), floats presided over by King Carnival (Maltese: ''ir-Re tal-Karnival''), marching bands and costumed revellers.
 Holy Week in Malta, Holy Week (Maltese: ''il-Ġimgħa Mqaddsa'') starts on Palm Sunday (''Ħadd il-Palm'') and ends on Easter, Easter Sunday (''Ħadd il-Għid''). Numerous religious traditions, most of them inherited from one generation to the next, are part of the Easter celebrations in the Maltese Islands, honouring the death and resurrection of Jesus.
Maltese folklore#Mnarja, Mnarja, or l-Imnarja (pronounced ''lim-nar-ya'') is one of the most important dates on the Maltese cultural calendar. Officially, it is a national festival dedicated to the feast of Saints Saint Peter, Peter and Paul the Apostle, Paul. Its roots can be traced back to the pagan Roman Republic, Roman feast of ''Luminaria'' (literally, "the illumination"), when torches and bonfires lit up the early summer night of 29 June.
A national feast since the rule of the Knights Hospitaller, Knights, Mnarja is a traditional Maltese festival of food, religion and music. The festivities still commence today with the reading of the ''"bandu"'', an official governmental announcement, which has been read on this day in Malta since the 16th century. Originally, Mnarja was celebrated outside St. Paul's Grotto, in the north of Malta. However, by 1613 the focus of the festivities had shifted to St Paul's Cathedral, Mdina, St Paul's Cathedral in Mdina and featured torchlight processions, the firing of 100 petards, horseraces, and races for men, boys, and slaves. Modern Mnarja festivals take place in and around the woodlands of Buskett Gardens, Buskett, just outside the town of Rabat.
It is said that under the Knights, this was the one day in the year when the Maltese were allowed to hunt and eat hare, wild rabbit, which was otherwise reserved for the hunting pleasures of the Knights. The close connection between Mnarja and rabbit stew (Maltese: ''"fenkata"'') remains strong today.
In 1854 British governor William Reid (British Army officer), William Reid launched an agricultural show at Buskett which is still being held today. The farmers' exhibition is still a seminal part of the Mnarja festivities today.
Mnarja today is one of the few occasions when participants may hear traditional Maltese ''Għana (folk music), għana''. Traditionally, grooms would promise to take their brides to Mnarja during the first year of marriage. For luck, many of the brides would attend in their wedding gown and veil, although this custom has long since disappeared from the islands.
Isle of MTV is a one-day music festival produced and broadcast on an annual basis by MTV. The festival has been arranged annually in Malta since 2007, with major pop artists performing each year. 2012 saw the performances of worldwide acclaimed artists Flo Rida, Nelly Furtado and Will.i.am at Fosos Square in Floriana. Over 50,000 people attended, which marked the biggest attendance so far.
In 2009 the first New Year's Eve street party was organised in Malta, parallel to what major countries in the world organise. Although the event was not highly advertised, and was controversial due to the closing of an arterial street on the day, it is deemed to have been successful and will most likely be organised every year.
The Malta International Fireworks Festival is an annual festival that has been arranged in the
Holy Week in Malta, Holy Week (Maltese: ''il-Ġimgħa Mqaddsa'') starts on Palm Sunday (''Ħadd il-Palm'') and ends on Easter, Easter Sunday (''Ħadd il-Għid''). Numerous religious traditions, most of them inherited from one generation to the next, are part of the Easter celebrations in the Maltese Islands, honouring the death and resurrection of Jesus.
Maltese folklore#Mnarja, Mnarja, or l-Imnarja (pronounced ''lim-nar-ya'') is one of the most important dates on the Maltese cultural calendar. Officially, it is a national festival dedicated to the feast of Saints Saint Peter, Peter and Paul the Apostle, Paul. Its roots can be traced back to the pagan Roman Republic, Roman feast of ''Luminaria'' (literally, "the illumination"), when torches and bonfires lit up the early summer night of 29 June.
A national feast since the rule of the Knights Hospitaller, Knights, Mnarja is a traditional Maltese festival of food, religion and music. The festivities still commence today with the reading of the ''"bandu"'', an official governmental announcement, which has been read on this day in Malta since the 16th century. Originally, Mnarja was celebrated outside St. Paul's Grotto, in the north of Malta. However, by 1613 the focus of the festivities had shifted to St Paul's Cathedral, Mdina, St Paul's Cathedral in Mdina and featured torchlight processions, the firing of 100 petards, horseraces, and races for men, boys, and slaves. Modern Mnarja festivals take place in and around the woodlands of Buskett Gardens, Buskett, just outside the town of Rabat.
It is said that under the Knights, this was the one day in the year when the Maltese were allowed to hunt and eat hare, wild rabbit, which was otherwise reserved for the hunting pleasures of the Knights. The close connection between Mnarja and rabbit stew (Maltese: ''"fenkata"'') remains strong today.
In 1854 British governor William Reid (British Army officer), William Reid launched an agricultural show at Buskett which is still being held today. The farmers' exhibition is still a seminal part of the Mnarja festivities today.
Mnarja today is one of the few occasions when participants may hear traditional Maltese ''Għana (folk music), għana''. Traditionally, grooms would promise to take their brides to Mnarja during the first year of marriage. For luck, many of the brides would attend in their wedding gown and veil, although this custom has long since disappeared from the islands.
Isle of MTV is a one-day music festival produced and broadcast on an annual basis by MTV. The festival has been arranged annually in Malta since 2007, with major pop artists performing each year. 2012 saw the performances of worldwide acclaimed artists Flo Rida, Nelly Furtado and Will.i.am at Fosos Square in Floriana. Over 50,000 people attended, which marked the biggest attendance so far.
In 2009 the first New Year's Eve street party was organised in Malta, parallel to what major countries in the world organise. Although the event was not highly advertised, and was controversial due to the closing of an arterial street on the day, it is deemed to have been successful and will most likely be organised every year.
The Malta International Fireworks Festival is an annual festival that has been arranged in the
Omertaa, Journal for Applied Anthropology
olume 2007/1, Thematic Issue on Malta
Antonio Lafreri map of Malta, 1565
. Eran Laor Cartographic Collection. The National Library of Israel
''Eight Thousand Years of Maltese Maritime History: Trade, Piracy, and Naval Warfare in the Central Mediterranean''
Gainesville : University Press of Florida.
Gov.mt
altese Government official site
Malta Environment and Planning Authority's
Geographic information system, GIS
Visit Malta
– Maltese tourism official site ; General information
Malta
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Malta
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * * * {{Authority control Malta, Collective recipients of the George Cross Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations English-speaking countries and territories Island countries Italian-speaking countries and territories Mediterranean islands Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union Pauline churches Phoenician colonies in Malta Southern European countries States and territories established in 1964 1964 establishments in Malta Countries in Europe Christian states Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. It consists of an archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
, between Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
. It lies south of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
(Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
), east of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, and north of Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
. The official languages are Maltese and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, and 66% of the current Maltese population is at least conversational in the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
language.
Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC. Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns and Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, Romans, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British, amongst others.
With a population of about 516,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country in area and fourth most densely populated sovereign country. Its capital is Valletta
Valletta (, mt, il-Belt Valletta, ) is an administrative unit and capital of Malta. Located on the main island, between Marsamxett Harbour to the west and the Grand Harbour to the east, its population within administrative limits in 2014 wa ...
, which is the smallest national capital in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
by area and population. According to the data from 2020 by Eurostat, the Functional Urban Area and metropolitan region covered the whole island and has a population of 480,134, and according to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, ESPON
Interreg is a series of programmes to stimulate cooperation between regions in and out of the European Union (EU), funded by the European Regional Development Fund. The first Interreg started in 1989. Interreg IV covered the period 2007–2013. I ...
and EU Commission, "the whole territory of Malta constitutes a single urban region". Malta increasingly is referred to as a city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, and also listed in rankings concerning cities"The Global Financial Centres"– Qatar Financial Centre, 2015. or metropolitan areas. Malta became a British colony in 1813, serving as a way station for ships and the headquarters for the British Mediterranean Fleet. It was besieged by the Axis powers during World War II and was an important Allied base for operations in North Africa and the Mediterranean. The
British parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
passed the Malta Independence Act in 1964, giving Malta independence from the United Kingdom as the State of Malta, with Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
as its queen. The country became a republic in 1974. It has been a member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
since independence, and joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
in 2004; it became part of the eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polici ...
monetary union in 2008.
Malta has had Christians since the time of Early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewis ...
, though was predominantly Muslim while under Arab rule, at which time Christians were tolerated. Muslim rule ended with the Norman invasion of Malta
The Norman invasion of Malta was an attack on the island of Malta, then inhabited predominantly by Muslims, by forces of the Norman County of Sicily
The County of Sicily, also known as County of Sicily and Calabria, was a Norman state compri ...
by Roger I Roger I may refer to:
:''In chronological order''
* Roger I of Carcassonne (died 1012), Count of Carcassonne
* Roger I of Tosny (), Norman noble
* Roger I "de Berkeley" (died 1093), Norman noble, possibly the son of Roger I of Tosny - see Baron ...
in 1091. Today, Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
is the state religion, but the Constitution of Malta guarantees freedom of conscience and religious worship. – Article 40: "all persons in Malta shall have full freedom of conscience and enjoy the free exercise of their respective mode of religious worship." The economy of Malta
The economy of Malta is a highly industrialised, service-based economy. It is classified as an advanced economy by the International Monetary Fund and is considered a high-income country by the World Bank and an innovation-driven economy by t ...
is heavily reliant on tourism, and the country promotes itself as a Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
tourist destination with its warmer climate compared to the rest of Europe, numerous recreational areas, and architectural and historical monuments, including three UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Sites: Ħal Saflieni Hypogeum
The Hypogeum of Ħal Saflieni is a Neolithic subterranean structure dating to the Saflieni phase (3300 – 3000 BC) in Maltese prehistory, located in Paola, Malta. It is often simply referred to as the Hypogeum ( mt, Ipoġew), literally meaning " ...
, Valletta, and seven megalithic temples which are some of the oldest free-standing structures in the world.
Etymology
The origin of the name ''Malta'' is uncertain, and the modern-day variation is derived from the Maltese language. The most common etymology is that the word ''Malta'' is derived from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word , ''meli'', "honey". The ancient Greeks called the island (''Melitē'') meaning "honey-sweet", possibly for Malta's unique production of honey; an endemic subspecies of bees live on the island. The Romans called the island ''Melita'', which can be considered either a Latinisation of the Greek or the adaptation of the Doric Greek pronunciation of the same word . In 1525 William Tyndale used the transliteration "Melite" in Acts 28:1 for ("After we were brought safely through, we then learned that the island was called Melita") as found in his translation of The New Testament that relied on Greek texts instead of Latin. "Melita" is the spelling used in the Authorized (King James) Version of 1611 and the American Standard Version of 1901. "Malta" is widely used in more recent versions, such as The Revised Standard Version of 1946 and The New International Version of 1973.
Another conjecture suggests that the word ''Malta'' comes from the Phoenician word ''Maleth'', "a haven", or 'port' in reference to Malta's many bays and coves. Few other etymological mentions appear in classical literature, with the term ''Malta'' appearing in its present form in the '' Antonine Itinerary'' (Itin. Marit. p. 518; Sil. Ital. xiv. 251).
History
Malta has been inhabited from around 5900 BC, since the arrival of settlers originating from European Neolithic agriculturalists. A significant prehistoricNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
culture marked by Megalithic structures, which date back to c. 3600 BC, existed on the islands, as evidenced by the temples of Bugibba, Mnajdra
Mnajdra ( mt, L-Imnajdra) is a megalithic temple complex found on the southern coast of the Mediterranean island of Malta. Mnajdra is approximately from the Ħaġar Qim megalithic complex. Mnajdra was built around the fourth millennium BCE; th ...
, Ggantija and others. The Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
colonised Malta between 800 and 700 BC, bringing their Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
and culture. They used the islands as an outpost from which they expanded sea explorations and trade in the Mediterranean until their successors, the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, were ousted by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
in 216 BC with the help of the Maltese inhabitants, under whom Malta became a municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (pl. ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ("duty holders"), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the priv ...
.
 After a probable sack by the
After a probable sack by the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
, Malta fell under Byzantine rule (4th to 9th century) and the islands were then invaded by the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a c ...
in AD 870. The fate of the population after the Arab invasion is unclear but it seems the islands may have been repopulated at the beginning of the second millennium by settlers from Arab-ruled Sicily who spoke Siculo-Arabic
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, الْلهجَة الْعَرَبِيَة الْصَقلِيَة), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century ...
.
The Muslim rule was ended by the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
who conquered the island in 1091. The islands were completely re-Christianised by 1249. The islands were part of the Kingdom of Sicily until 1530 and were briefly controlled by the Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou or House of Anjou-Sicily, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct French House of Capet, part of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" ...
. In 1530, Charles V of Spain gave the Maltese islands to the Order of Knights of the Hospital of St John of Jerusalem in perpetual lease.
The French under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
took hold of the Maltese islands in 1798, although with the aid of the British the Maltese were able to oust French control two years later. The inhabitants subsequently asked Britain to assume sovereignty over the islands under the conditions laid out in a Declaration of Rights, stating that "his Majesty has no right to cede these Islands to any power...if he chooses to withdraw his protection, and abandon his sovereignty, the right of electing another sovereign, or of the governing of these Islands, belongs to us, the inhabitants and aborigines alone, and without control." As part of the Treaty of Paris in 1814, Malta became a British colony. It ultimately rejected an attempted integration with the United Kingdom in 1956 after the British proved reluctant to integrate.
Malta became independent on 21 September 1964 ( Independence Day). Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
as queen
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother ...
, with a governor-general exercising authority on her behalf. On 13 December 1974 (Republic Day
Republic Day is the name of a holiday in several countries to commemorate the day when they became republics.
List
January 1 January in Slovak Republic
The day of creation of Slovak republic. A national holiday since 1993. Officially cal ...
), it became a republic within the Commonwealth, with the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
as head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
. On 31 March 1979, Malta saw the withdrawal of the last British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
troops and the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
from Malta. This day is known as Freedom Day, and Malta declared itself as a neutral and non-aligned state. Malta joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
on 1 May 2004, and joined the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polici ...
on 1 January 2008.
Prehistory
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
found by archaeologists at the Skorba Temples
The Skorba temples are megalithic remains on the northern edge of Żebbiegħ, in Malta, which have provided detailed and informative insight into the earliest periods of Malta's neolithic culture. The site was only excavated in the early 1960s, ...
resembles that found in Italy, and suggests that the Maltese islands were first settled in 5200 BC mainly by Stone Age hunters or farmers who had arrived from the Italian island of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, possibly the Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ...
. The extinction of the dwarf hippos, giant swans and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on Malta. Prehistoric farming settlements dating to the Early Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period were discovered in open areas and also in caves, such as Għar Dalam.
The Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ...
were the only tribe known to have inhabited the island at this time and are generally regarded as being closely related to the Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
. The population on Malta grew cereals
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food ...
, raised livestock and, in common with other ancient Mediterranean cultures, worshiped a fertility figure represented in Maltese prehistoric artifacts exhibiting the proportions seen in similar statuettes, including the Venus of Willendorf
The Venus of Willendorf is an Venus figurine estimated to have been made around 25,000-30,000 years ago. It was found on August 7, 1908, by a workman named Johann Veran or Josef Veram during excavations conducted by archaeologists Josef Szombat ...
.

 Pottery from the Għar Dalam phase is similar to pottery found in
Pottery from the Għar Dalam phase is similar to pottery found in Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one o ...
, Sicily. A culture of megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
ic temple builders then either supplanted or arose from this early period. Around the time of 3500 BC, these people built some of the oldest existing free-standing structures in the world in the form of the megalithic Ġgantija
Ġgantija (, "Giantess") is a megalithic temple complex from the Neolithic on the Mediterranean island of Gozo. The Ġgantija temples are the earliest of the Megalithic Temples of Malta and are older than the pyramids of Egypt. Their makers er ...
temples on Gozo; other early temples include those at Ħaġar Qim
Ħaġar Qim (; "Standing/Worshipping Stones") is a megalithic temple complex found on the Mediterranean island of Malta, dating from the Ġgantija phase (3600-3200 BC). The Megalithic Temples of Malta are among the most ancient religious ...
and Mnajdra
Mnajdra ( mt, L-Imnajdra) is a megalithic temple complex found on the southern coast of the Mediterranean island of Malta. Mnajdra is approximately from the Ħaġar Qim megalithic complex. Mnajdra was built around the fourth millennium BCE; th ...
.Daniel Cilia, ''Malta Before History'' (2004: Miranda Publishers)
The temples have distinctive architecture, typically a complex trefoil
A trefoil () is a graphic form composed of the outline of three overlapping rings, used in architecture and Christian symbolism, among other areas. The term is also applied to other symbols with a threefold shape. A similar shape with four ring ...
design, and were used from 4000 to 2500 BC. Animal bones and a knife found behind a removable altar stone suggest that temple rituals included animal sacrifice. Tentative information suggests that the sacrifices were made to the goddess of fertility, whose statue is now in the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta. The culture apparently disappeared from the Maltese Islands around 2500 BC. Archaeologists speculate that the temple builders fell victim to famine or disease, but this is not certain.
Another archaeological feature of the Maltese Islands often attributed to these ancient builders is equidistant uniform grooves dubbed "cart tracks" or "cart ruts" which can be found in several locations throughout the islands, with the most prominent being those found in Misraħ Għar il-Kbir, which is informally known as "Clapham Junction". These may have been caused by wooden-wheeled carts eroding soft limestone.
After 2500 BC, the Maltese Islands were depopulated for several decades until the arrival of a new influx of Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
immigrants, a culture that cremated
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre i ...
its dead and introduced smaller megalithic structures called dolmens to Malta. In most cases, there are small chambers here, with the cover made of a large slab placed on upright stones. They are claimed to belong to a population certainly different from that which built the previous megalithic temples. It is presumed the population arrived from Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
because of the similarity of Maltese dolmens to some small constructions found on the largest island of the Mediterranean sea.
Phoenicians, Carthaginians and Romans
 Phoenician traders colonised the islands sometime after 1000 BC as a stop on their trade routes from the eastern
Phoenician traders colonised the islands sometime after 1000 BC as a stop on their trade routes from the eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
to Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, joining the natives on the island. The Phoenicians inhabited the area now known as Mdina, and its surrounding town of Rabat, which they called '' Maleth''. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, who also much later inhabited Mdina, referred to it (and the island) as ''Melita''.
 After the fall of Phoenicia in 332 BC, the area came under the control of
After the fall of Phoenicia in 332 BC, the area came under the control of Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
, a former Phoenician colony. During this time the people on Malta mainly cultivated olives and carob
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and lands ...
and produced textiles.
During the First Punic War, the island was conquered after harsh fighting by Marcus Atilius Regulus
Marcus Atilius Regulus () was a Roman statesman and general who was a consul of the Roman Republic in 267 BC and 256 BC. Much of his career was spent fighting the Carthaginians during the first Punic War. In 256 BC, he and Luciu ...
. After the failure of his expedition, the island fell back in the hands of Carthage, only to be conquered again in 218 BC, during the Second Punic War, by Roman Consul Tiberius Sempronius Longus. After that, Malta became '' Foederata Civitas'', a designation that meant it was exempt from paying tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
or the rule of Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Ju ...
, and fell within the jurisdiction of the province of Sicily. Punic influence, however, remained vibrant on the islands with the famous Cippi of Melqart
The Cippi of Melqart are a pair of Phoenician marble cippi that were unearthed in Malta under undocumented circumstances and dated to the 2nd century BC. These are votive offerings to the god Melqart, and are inscribed in two languages, Ancie ...
, pivotal in deciphering the Punic language
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, is an extinct variety of the Phoenician language, a Canaanite language of the Northwest Semitic branch of the Semitic languages. An offshoot of the Phoenician language of coastal W ...
, dedicated in the 2nd century BC. Also the local Roman coinage, which ceased in the 1st century BC, indicates the slow pace of the island's Romanization, since the last locally minted coins still bear inscriptions in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
on the obverse (like "ΜΕΛΙΤΑΙΩ", meaning "of the Maltese") and Punic motifs, showing the resistance of the Greek and Punic cultures.
In the 1st century BC, Roman Senator and orator Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
commented on the importance of the Temple of Juno, and on the extravagant behaviour of the Roman governor of Sicily, Verres
Gaius Verres (c. 120–43 BC) was a Roman magistrate, notorious for his misgovernment of Sicily. His extortion of local farmers and plundering of temples led to his prosecution by Cicero, whose accusations were so devastating that his defence adv ...
. During the 1st century BC the island was mentioned by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
and Diodorus Siculus: the latter praised its harbours, the wealth of its inhabitants, its lavishly decorated houses and the quality of its textile products. In the 2nd century, Emperor Hadrian (r. 117–38) upgraded the status of Malta to ''municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (pl. ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ("duty holders"), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the priv ...
'' or free town: the island local affairs were administered by four '' quattuorviri iuri dicundo'' and a municipal senate, while a Roman procurator
Procurator (with procuracy or procuratorate referring to the office itself) may refer to:
* Procurator, one engaged in procuration, the action of taking care of, hence management, stewardship, agency
* ''Procurator'' (Ancient Rome), the title o ...
, living in Mdina, represented the proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military command, or ...
of Sicily. In 58 AD, Paul the Apostle was washed up on the islands together with Luke the Evangelist
Luke the Evangelist (Latin: '' Lucas''; grc, Λουκᾶς, '' Loukâs''; he, לוקאס, ''Lūqās''; arc, /ܠܘܩܐ לוקא, ''Lūqā’; Ge'ez: ሉቃስ'') is one of the Four Evangelists—the four traditionally ascribed authors of t ...
after their ship was wrecked on the islands. Paul the Apostle remained on the islands for three months, preaching the Christian faith. The island is mentioned at the Acts of the Apostles as Melitene ( el, Μελιτήνη).
In 395, when the Roman Empire was divided for the last time at the death of Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
, Malta, following Sicily, fell under the control of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
. During the Migration Period as the Western Roman Empire declined, Malta came under attack and was conquered or occupied a number of times. From 454 to 464 the islands were subdued by the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
, and after 464 by the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
. In 533 Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terr ...
, on his way to conquer the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa, reunited the islands under Imperial (Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
) rule. Little is known about the Byzantine rule in Malta: the island depended on the theme of Sicily and had Greek Governors and a small Greek garrison. While the bulk of population continued to be constituted by the old, Latinized dwellers, during this period its religious allegiance oscillated between the Pope and the Patriarch of Constantinople. The Byzantine rule introduced Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
families to the Maltese collective. Malta remained under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
until 870, when it fell to the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
.
Arab period and the Middle Ages
Malta became involved in the Arab–Byzantine wars, and the conquest of Malta is closely linked with that of Sicily that began in 827 after Admiral Euphemius' betrayal of his fellow Byzantines, requesting that theAghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a c ...
invade the island.
The Muslim chronicler and geographer al-Himyari recounts that in 870, following a violent struggle against the defending Byzantines, the Arab invaders, first led by Halaf al-Hadim, and later by Sawada ibn Muhammad, looted and pillaged the island, destroying the most important buildings, and leaving it practically uninhabited until it was recolonised by the Arabs from Sicily in 1048–1049. It is uncertain whether this new settlement took place as a consequence of demographic expansion in Sicily, as a result of a higher standard of living in Sicily (in which case the recolonisation may have taken place a few decades earlier), or as a result of civil war which broke out among the Arab rulers of Sicily in 1038.
The Arab Agricultural Revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution was the transformation in agriculture from the 8th to the 13th century in the Islamic region of the Old World. The agronomic literature of the time, with major books by Ibn Bassal and Abū l-Khayr al-Ishbīlī, d ...
introduced new irrigation, some fruits and cotton, and the Siculo-Arabic
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, الْلهجَة الْعَرَبِيَة الْصَقلِيَة), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century ...
language was adopted on the island from Sicily; it would eventually evolve into the Maltese language
Maltese ( mt, Malti, links=no, also ''L-Ilsien Malti'' or '), is a Semitic language derived from late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance superstrata spoken by the Maltese people. It is the national language of Malta and the only offic ...
.
Norman conquest
 The
The Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
attacked Malta in 1091, as part of their conquest of Sicily. The Norman leader, Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Roger Bosso and The Great, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101. He was a member of the ...
, was welcomed by Christian captives. The notion that Count Roger I reportedly tore off a portion of his checkered red-and-white banner and presented it to the Maltese in gratitude for having fought on his behalf, forming the basis of the modern flag of Malta
The flag of Malta ( mt, Bandiera ta' Malta) is a bicolour, with white in the hoist and red in the fly. A representation of the George Cross, awarded to Malta by George VI in 1942, is carried, edged with red, in the canton of the white stripe. T ...
, is founded in myth.
Malta became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Sicily, which also covered the island of Sicily and the southern half of the Italian Peninsula. The Catholic Church was reinstated as the state religion, with Malta under the See of Palermo, and some Norman architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used f ...
sprang up around Malta, especially in its ancient capital Mdina. King Tancred made Malta a fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
of the kingdom and installed a count of Malta The County of Malta was a feudal lordship of the Kingdom of Sicily, relating to the islands of Malta and Gozo. Malta was essentially a fief within the kingdom, with the title given by Tancred of Sicily the Norman king of Sicily to Margaritus of Bri ...
in 1192. As the islands were much desired due to their strategic importance, it was during this time that the men of Malta were militarised to fend off attempted conquest; early Counts were skilled Genoese privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s.
The kingdom passed on to the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
dynasty from 1194 until 1266. During this period, when Emperor Frederick II began to reorganise his Sicilian kingdom, Western culture and religion began to exert their influence more intensely. Malta was declared a county and a marquisate
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman w ...
, but its trade was totally ruined. For a long time it remained solely a fortified garrison.
A mass expulsion of Arabs occurred in 1224, and the entire Christian male population of Celano in Abruzzo was deported to Malta in the same year. In 1249 Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, decreed that all remaining Muslims be expelled from Malta or compelled to convert.
For a brief period, the kingdom passed to the Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou or House of Anjou-Sicily, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct French House of Capet, part of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" ...
, but high taxes made the dynasty unpopular in Malta, due in part to Charles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) ...
's war against the Republic of Genoa, and the island of Gozo was sacked in 1275.
Crown of Aragon rule and the Knights of Malta
House of Barcelona
The House of Barcelona was a medieval dynasty that ruled the County of Barcelona continuously from 878 and the Crown of Aragon from 1137 (as kings from 1162) until 1410. They descend from the Bellonids, the descendants of Wifred the Hairy. Th ...
, the ruling dynasty of the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
, from 1282 to 1409, with the Aragonese aiding the Maltese insurgents in the Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of ...
in the naval battle in Grand Harbour
The Grand Harbour ( mt, il-Port il-Kbir; it, Porto Grande), also known as the Port of Valletta, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It has been substantially modified over the years with extensive docks ( Malta Dockyard), wharves, a ...
in 1283.
Relatives of the Kings of Aragon ruled the island until 1409 when it formally passed to the Crown of Aragon. Early on in the Aragonese ascendancy, the sons of the monarchs received the title Count of Malta The County of Malta was a feudal lordship of the Kingdom of Sicily, relating to the islands of Malta and Gozo. Malta was essentially a fief within the kingdom, with the title given by Tancred of Sicily the Norman king of Sicily to Margaritus of Bri ...
. During this time much of the local nobility was created. By 1397, however, the bearing of the comital title reverted to a feudal basis, with two families fighting over the distinction, which caused some conflict. This led King Martin I of Sicily
Martin I of Sicily (c. 1374/1376 – 25 July 1409), called "The Younger", was King of Sicily from his marriage to Queen Maria in 1390 until his death.
Martin's father was the future King Martin I of Aragon, and his grandparents were King Pet ...
to abolish the title. The dispute over the title returned when the title was reinstated a few years later and the Maltese, led by the local nobility, rose up against Count Gonsalvo Monroy. Although they opposed the Count, the Maltese voiced their loyalty to the Sicilian Crown
The monarchs of Sicily ruled from the establishment of the County of Sicily in 1071 until the "perfect fusion" in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816.
The origins of the Sicilian monarchy lie in the Norman conquest of southern Italy which occ ...
, which so impressed King Alfonso
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen regnant, queen, which title is also given to the queen consort, consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contempora ...
that he did not punish the people for their rebellion. Instead, he promised never to grant the title to a third party and incorporated it back into the crown. The city of Mdina was given the title of ''Città Notabile'' as a result of this sequence of events.
On 23 March 1530, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, gave the islands to the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
under the leadership of Frenchman Philippe Villiers de L'Isle-Adam
Fra' Philippe de Villiers de L'Isle-Adam (1464 – 21 August 1534) was a prominent member of the Knights Hospitaller at Rhodes and later Malta. Having risen to the position of Prior of the ''Langue of Auvergne'', he was elected 44th Grand ...
, Grand Master of the Order, in perpetual lease for which they had to pay an annual tribute of a single Maltese Falcon.El halcón maltés regresará a España dos siglos después. ''El Pais'' (14 August 2005). Retrieved 1 May 2017. These knights, a military religious order also known as the Order of St John and later as the Knights of Malta, had been driven out of
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in 1522.
The Knights Hospitaller were the rulers of Malta and Gozo between 1530 and 1798. During this period, the strategic and military importance of the island grew greatly as the small yet efficient fleet of the Order of Saint John launched their attacks from this new base targeting the shipping lanes of the Ottoman territories around the Mediterranean Sea.
In 1551, the population of the island of Gozo (around 5,000 people) were enslaved by Barbary pirates and taken to the Barbary Coast in North Africa.
 The knights, led by Frenchman
The knights, led by Frenchman Jean Parisot de Valette
Fra' Jean "Parisot" de la Valette (4 February 1495 – 21 August 1568) was a French nobleman and 49th Grand Master of the Order of Malta, from 21 August 1557 to his death in 1568. As a Knight Hospitaller, joining the order in the ''Langue de Pr ...
, Grand Master of the Order, withstood the Great Siege of Malta by the Ottomans in 1565. The knights, with the help of Spanish and Maltese forces, were victorious and repelled the attack. Speaking of the battle Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his ''nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—es ...
said, "Nothing is better known than the siege of Malta." After the siege they decided to increase Malta's fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
s, particularly in the inner-harbour area, where the new city of Valletta
Valletta (, mt, il-Belt Valletta, ) is an administrative unit and capital of Malta. Located on the main island, between Marsamxett Harbour to the west and the Grand Harbour to the east, its population within administrative limits in 2014 wa ...
, named in honour of Valette, was built. They also established watchtower
A watchtower or watch tower is a type of fortification used in many parts of the world. It differs from a regular tower in that its primary use is military and from a turret in that it is usually a freestanding structure. Its main purpose is to ...
s along the coasts – the Wignacourt, Lascaris and De Redin towers
The De Redin Towers ( mt, Torrijiet ta' De Redin) are a series of small coastal watchtowers built in Malta by the Order of Saint John between 1658 and 1659. Thirteen towers were built around the coast of mainland Malta, eight of which still surv ...
– named after the Grand Masters who ordered the work. The Knights' presence on the island saw the completion of many architectural and cultural projects, including the embellishment of Città Vittoriosa (modern Birgu
Birgu ( mt, Il-Birgu , it, Vittoriosa), also known by its title Città Vittoriosa ("''Victorious City''"), is an old fortified city on the south side of the Grand Harbour in the South Eastern Region of Malta. The city occupies a promontory of ...
), the construction of new cities including Città Rohan (modern Ħaż-Żebbuġ) . Ħaż-Żebbuġ is one of the oldest cities of Malta, it also has one of the largest squares of Malta.
French period and British conquest
The Knights' reign ended whenNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
captured Malta on his way to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
during the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia ...
in 1798. Over the years preceding Napoleon's capture of the islands, the power of the Knights had declined and the Order had become unpopular. Napoleon's fleet arrived in 1798, en route to his expedition of Egypt. As a ruse towards the Knights, Napoleon asked for a safe harbour to resupply his ships, and then turned his guns against his hosts once safely inside Valletta. Grand Master Hompesch capitulated, and Napoleon entered Malta.
 During 12–18 June 1798, Napoleon resided at the Palazzo Parisio in Valletta. He reformed national administration with the creation of a Government Commission, twelve municipalities, a public finance administration, the abolition of all feudal rights and privileges, the
During 12–18 June 1798, Napoleon resided at the Palazzo Parisio in Valletta. He reformed national administration with the creation of a Government Commission, twelve municipalities, a public finance administration, the abolition of all feudal rights and privileges, the abolition of slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
and the granting of freedom to all Turkish and Jewish slaves. On the judicial level, a family code was framed and twelve judges were nominated. Public education was organised along principles laid down by Bonaparte himself, providing for primary and secondary education. He then sailed for Egypt leaving a substantial garrison in Malta.
The French forces left behind became unpopular with the Maltese, due particularly to the French forces' hostility towards Catholicism and pillaging of local churches to fund Napoleon's war efforts. French financial and religious policies so angered the Maltese that they rebelled, forcing the French to depart. Great Britain, along with the Kingdom of Naples and the Kingdom of Sicily, sent ammunition and aid to the Maltese, and Britain also sent its navy, which blockaded the islands.
On 28 October 1798, Captain Sir Alexander Ball
Sir Alexander John Ball, 1st Baronet ( it, Alessandro Giovanni Ball, 22 July 1757 – 25 October 1809) was a Rear-Admiral and Civil Commissioner of Malta. He was born in Ebworth Park, Sheepscombe, Gloucestershire. He was the fourth son of Rober ...
successfully completed negotiations with the French garrison on Gozo, the 217 French soldiers there agreeing to surrender without a fight and transferring the island to the British. The British transferred the island to the locals that day, and it was administered by Archpriest Saverio Cassar
Saverio Cassar (29 December 1746 – 16 December 1805) was a Gozitan priest and patriot, who was Governor-general of an independent Gozo from 1798 to 1801.
Cassar was born in Għajnsielem, in Nadur parish, Gozo on 29 December 1746. He studied i ...
on behalf of Ferdinand III of Sicily
Ferdinand I (12 January 1751 – 4 January 1825) was the King of the Two Sicilies from 1816, after his restoration following victory in the Napoleonic Wars. Before that he had been, since 1759, Ferdinand IV of the Kingdom of Naples and Ferdinand I ...
. Gozo remained independent until Cassar was removed from power by the British in 1801.
General Claude-Henri Belgrand de Vaubois
Claude-Henri Belgrand de Vaubois (1 October 1748 in Ville-sous-la-Ferté, Aube – 5 November 1839) was a French general during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He is best known for the surrender of Malta to the British in 1 ...
surrendered his French forces in 1800. Maltese leaders presented the main island to Sir Alexander Ball, asking that the island become a British Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
. The Maltese people created a Declaration of Rights in which they agreed to come "under the protection and sovereignty of the King of the free people, His Majesty the King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland". The Declaration also stated that "his Majesty has no right to cede these Islands to any power...if he chooses to withdraw his protection, and abandon his sovereignty, the right of electing another sovereign, or of the governing of these Islands, belongs to us, the inhabitants and aborigines alone, and without control."
British Empire and the Second World War
 In 1814, as part of the
In 1814, as part of the Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
, Malta officially became a part of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
and was used as a shipping way-station and fleet headquarters. After the Suez Canal opened in 1869, Malta's position halfway between the Strait of Gibraltar and Egypt proved to be its main asset, and it was considered an important stop on the way to India, a central trade route for the British.
A Turkish Military Cemetery was commissioned by Sultan Abdul Aziz and built between 1873 and 1874 for the fallen Ottoman soldiers of the Great Siege of Malta.
Between 1915 and 1918, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Malta became known as ''the Nurse of the Mediterranean'' due to the large number of wounded soldiers who were accommodated in Malta. In 1919, British troops fired into a crowd protesting against new taxes, killing four. The event, known as Sette Giugno
Sette Giugno (from Italian for "Seventh of June") is a Maltese national holiday celebrated annually on 7 June. It commemorates events which occurred on that day in 1919 when, following a series of riots by the Maltese population, British troops ...
(Italian for ''7 June''), is commemorated every year and is one of five National Days.
Before the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Valletta was the location of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
's British Mediterranean Fleet, Mediterranean Fleet's headquarters; however, despite Winston Churchill's objections, the command was moved to Alexandria, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, in April 1937 out of fear that it was too susceptible to air attacks from Europe.
During the Second World War, Malta played an important role for the Allies of World War II, Allies; being a British colony, situated close to Sicily and the Axis Powers, Axis shipping lanes, Malta was bombarded by the Italian and German air forces. Malta was used by the British to launch attacks on the Italian navy and had a submarine base. It was also used as a listening post, intercepting German radio messages including Enigma (machine), Enigma traffic. The bravery of the Maltese people during the second Siege of Malta (World War II), Siege of Malta moved King George VI to Award of the George Cross to Malta, award the George Cross to Malta on a collective basis on 15 April 1942 "to bear witness to a heroism and devotion that will long be famous in history". Some historians argue that the award caused Britain to incur disproportionate losses in defending Malta, as British credibility would have suffered if Malta had surrendered, Battle of Singapore, as British forces in Singapore had done. A depiction of the George Cross now appears in the upper hoist corner of the Flag of Malta and on the country's Coat of arms of Malta, arms. The collective award remained unique until April 1999, when the Royal Ulster Constabulary became the second recipient of a collective George Cross.
Independence and Republic

 Malta achieved its independence as the State of Malta on 21 September 1964 ( Independence Day) after intense negotiations with the United Kingdom, led by Maltese Prime Minister George Borġ Olivier. Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Elizabeth II as Queen of Malta and thus
Malta achieved its independence as the State of Malta on 21 September 1964 ( Independence Day) after intense negotiations with the United Kingdom, led by Maltese Prime Minister George Borġ Olivier. Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Elizabeth II as Queen of Malta and thus head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
, with a governor-general exercising executive authority on her behalf. In 1971, the Malta Labour Party led by Dom Mintoff won the general elections, resulting in Malta declaring itself a republic on 13 December 1974 (Republic Day
Republic Day is the name of a holiday in several countries to commemorate the day when they became republics.
List
January 1 January in Slovak Republic
The day of creation of Slovak republic. A national holiday since 1993. Officially cal ...
) within the Commonwealth, with a President of Malta, president as head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
. A defence agreement was signed soon after independence, and after being re-negotiated in 1972, expired on 31 March 1979 ( Freedom Day). Upon its expiry, the British base closed down and all lands formerly controlled by the British on the island were given up to the Maltese government. In the aftermath of the departure of the remaining British troops from the island in 1979 the country intensified Malta and the Non-Aligned Movement, its participation in the Non-Aligned Movement.
Malta adopted a policy of Neutral country, neutrality in 1980. In 1989, Malta was the venue of a Malta Summit, summit between US President George H. W. Bush and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, their first face-to-face encounter, which signalled the end of the Cold War.
On 16 July 1990, Malta, through its foreign minister, Guido de Marco, applied to join the European Union. After tough negotiations, a referendum was held on 8 March 2003, which resulted in a favourable vote. General Elections held on 12 April 2003, gave a clear mandate to the Prime Minister, Eddie Fenech Adami, to sign the treaty of accession to the European Union on 16 April 2003 in Athens, Greece.
Malta joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
on 1 May 2004. Following the European Council of 21–22 June 2007, Malta joined the eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polici ...
on 1 January 2008.
Politics
National
Malta is a republic whose parliamentary system and public administration are closely modelled on the Westminster system. Malta had the second-highest voter turnout in the world (and the highest for nations without mandatory voting), based on election turnout in national lower house elections from 1960 to 1995. The unicameral Parliament is made up of the President of Malta and the House of Representatives of Malta, House of Representatives ( mt, Kamra tad-Deputati). The President of Malta, a largely ceremonial position, is appointed for a five-year term by a resolution of the House of Representatives carried by a simple majority. The House of Representatives has 65 members, elected for a five-year term in 13 five-seat electoral divisions, called ''distretti elettorali'', with constitutional amendments that allow for mechanisms to establish strict proportionality amongst seats and votes of political parliamentary groups.
Members of the House of Representatives are elected by direct universal suffrage through single transferable vote every five years, unless the House is dissolved earlier by the president either on the advice of the Prime Minister of Malta, prime minister or through the adoption of a motion of no confidence carried within the House of Representatives and not overturned within three days. In either of these cases, the president may alternatively choose to invite another Member of Parliament who invariably should command the majority of the House of Representatives to form an alternative government for the remainder of the legislature.
The House of Representatives is nominally made up of 65 members of parliament whereby 5 members of parliament are elected from each of the thirteen electoral districts. However, where a party wins an absolute majority of votes but does not have a majority of seats, that party is given additional seats to ensure a parliamentary majority. The 80th article of the Constitution of Malta provides that the president appoint as prime minister "... the member of the House of Representatives who, in his judgment, is best able to command the support of a majority of the members of that House".
The House of Representatives has 65 members, elected for a five-year term in 13 five-seat electoral divisions, called ''distretti elettorali'', with constitutional amendments that allow for mechanisms to establish strict proportionality amongst seats and votes of political parliamentary groups.
Members of the House of Representatives are elected by direct universal suffrage through single transferable vote every five years, unless the House is dissolved earlier by the president either on the advice of the Prime Minister of Malta, prime minister or through the adoption of a motion of no confidence carried within the House of Representatives and not overturned within three days. In either of these cases, the president may alternatively choose to invite another Member of Parliament who invariably should command the majority of the House of Representatives to form an alternative government for the remainder of the legislature.
The House of Representatives is nominally made up of 65 members of parliament whereby 5 members of parliament are elected from each of the thirteen electoral districts. However, where a party wins an absolute majority of votes but does not have a majority of seats, that party is given additional seats to ensure a parliamentary majority. The 80th article of the Constitution of Malta provides that the president appoint as prime minister "... the member of the House of Representatives who, in his judgment, is best able to command the support of a majority of the members of that House".
 Maltese politics is a two-party system dominated by the Labour Party (Malta), Labour Party ( mt, Partit Laburista), a centre-left social democracy, social democratic party, and the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist Party ( mt, Partit Nazzjonalista), a centre-right Christian democracy, Christian democratic party. The Labour Party has been the governing party since 2013 and is currently led by Prime Minister Robert Abela, who has been in office since 13 January 2020. The Nationalist Party, with Bernard Grech as its leader, is currently in opposition. There are a number of small political parties in Malta which have no parliamentary representation.
Until the
Maltese politics is a two-party system dominated by the Labour Party (Malta), Labour Party ( mt, Partit Laburista), a centre-left social democracy, social democratic party, and the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist Party ( mt, Partit Nazzjonalista), a centre-right Christian democracy, Christian democratic party. The Labour Party has been the governing party since 2013 and is currently led by Prime Minister Robert Abela, who has been in office since 13 January 2020. The Nationalist Party, with Bernard Grech as its leader, is currently in opposition. There are a number of small political parties in Malta which have no parliamentary representation.
Until the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Maltese politics was dominated by the Language Question (Malta), Language Question fought out by Italophone and Anglophone parties. Post-war politics dealt with constitutional questions on the relations with Britain (first with Maltese integration into the United Kingdom referendum, 1956, integration then Independence Day (Malta), independence) and, eventually, History of Malta#The accession process to the European Union (1987–2004), relations with the European Union.
Since Malta is a republic, the head of state in Malta is the President of Malta, President of the Republic. The current President of the Republic is George Vella, who was appointed in 2019 after being nominated both by the Labour Party (Malta), Labour Party and the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist Party as opposition. He is the tenth president to be appointed.
Administrative divisions
Military
The objectives of the Armed Forces of Malta (AFM) are to maintain a military organisation with the primary aim of defending the islands' integrity according to the defence roles as set by the government in an efficient and cost-effective manner. This is achieved by emphasising the maintenance of Malta's territorial waters and airspace integrity. The AFM also engages in combating terrorism, fighting against illicit drug trafficking, conducting anti-illegal immigrant operations and patrols, and anti-illegal fishing operations, operating search and rescue (SAR) services, and physical or electronic security and surveillance of sensitive locations. Malta's search-and-rescue area extends from east ofTunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
to west of Crete, covering an area of around .
As a military organisation, the AFM provides backup support to the Malta Police Force (MPF) and other government departments/agencies in situations as required in an organised, disciplined manner in the event of national emergencies (such as natural disasters) or internal security and bomb disposal.
In 2020, Malta signed and ratified the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Geography
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
in the central Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
(in its Eastern Mediterranean, eastern basin), some from southern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
across the Malta Channel. Only the three largest islands—Malta Island, Malta (Malta), Gozo (Għawdex), and Comino (Kemmuna)—are inhabited. The islands of the archipelago lie on the Malta plateau, a shallow shelf formed from the high points of a land bridge between Sicily and North Africa that became isolated as sea levels rose after the Last Glacial Period, last ice age. The archipelago is located on the African plate, African tectonic plate.
Malta was considered an island of North Africa for centuries.
Numerous bays along the indented coastline of the islands provide good harbours. The landscape consists of low hills with terraced fields. The highest point in Malta is Ta' Dmejrek, at , near Dingli. Although there are some small rivers at times of high rainfall, there are no permanent rivers or lakes on Malta. However, some watercourses have fresh water running all year round at Baħrija near Ras ir-Raħeb, at l-Imtaħleb and San Martin, and at Lunzjata Valley in Gozo.
Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Malta belongs to the Liguro-Tyrrhenian province of the Mediterranean Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF, the territory of Malta belongs to the terrestrial ecoregion of Tyrrhenian-Adriatic sclerophyllous and mixed forests.
 The following uninhabited minor islands are part of the archipelago:
* Barbaġanni Rock ( Gozo)
* Cominotto (''Kemmunett'')
* Dellimara Island (Marsaxlokk)
* Filfla (Żurrieq)/(Siġġiewi)
* Fessej Rock
* Fungus Rock (''Il-Ġebla tal-Ġeneral''), ( Gozo)
* Għallis Rock (Naxxar)
* Ħalfa Rock ( Gozo)
* Large Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Islands of St. Paul/Selmunett Island (Mellieħa)
* Manoel Island, which connects to the town of Gżira, on the mainland via a bridge
* Mistra Rocks (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Taċ-Ċawl Rock ( Gozo)
* Qawra Point/Ta' Fraben Island (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Small Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Sala Rock (Żabbar)
* Xrobb l-Għaġin Rock (Marsaxlokk)
* Ta' taħt il-Mazz Rock
The following uninhabited minor islands are part of the archipelago:
* Barbaġanni Rock ( Gozo)
* Cominotto (''Kemmunett'')
* Dellimara Island (Marsaxlokk)
* Filfla (Żurrieq)/(Siġġiewi)
* Fessej Rock
* Fungus Rock (''Il-Ġebla tal-Ġeneral''), ( Gozo)
* Għallis Rock (Naxxar)
* Ħalfa Rock ( Gozo)
* Large Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Islands of St. Paul/Selmunett Island (Mellieħa)
* Manoel Island, which connects to the town of Gżira, on the mainland via a bridge
* Mistra Rocks (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Taċ-Ċawl Rock ( Gozo)
* Qawra Point/Ta' Fraben Island (San Pawl il-Baħar)
* Small Blue Lagoon Rocks (Comino)
* Sala Rock (Żabbar)
* Xrobb l-Għaġin Rock (Marsaxlokk)
* Ta' taħt il-Mazz Rock
Climate
Malta has a Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification ''Csa''), with mild winters and hot summers, hotter in the inland areas. Rain occurs mainly in autumn and winter, with summer being generally dry. The average yearly temperature is around during the day and at night. In the coldest month – January – the typical maximum temperature ranges from during the day and minimum at night. In the warmest month – August – the typical maximum temperature ranges from during the day and minimum at night. Amongst all capitals in the continent of Europe, Valletta – the capital of Malta has the warmest winters, with average temperatures of around during the day and at night in the period January–February. In March and December average temperatures are around during the day and at night.Weather of Malta– MET Office in Malta International Airport Large fluctuations in temperature are rare. Snow is very rare on the island, although various snowfalls have been recorded in the last century, the last one reported in various locations across Malta in 2014. The average annual sea temperature is , from in February to in August. In the 6 months – from June to November – the average sea temperature exceeds . The annual average relative humidity is high, averaging 75%, ranging from 65% in July (morning: 78% evening: 53%) to 80% in December (morning: 83% evening: 73%). Sunshine duration hours total around 3,000 per year, from an average 5.2 hours of sunshine duration per day in December to an average above 12 hours in July. This is about double that of cities in the northern half of Europe, for comparison: London – 1,461; however, in winter it has up to four times more sunshine; for comparison: in December, London has 37 hours of sunshine whereas Malta has above 160.
Urbanisation
Eurostat, 2015. According to the data from 2020 by Eurostat, the Functional Urban Area and metropolitan region covered the whole island and has a population of 480 134. According to the United Nations, about 95 percent of the area of Malta is urban and the number grows every year."World Urbanization Prospects"
– Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division, United Nations (Table A.2; page 79) Also, according to the results of ESPON and EU Commission studies, "''the whole territory of Malta constitutes a single urban region''"."Interim Territorial Cohesion Report"
– Preliminary results of ESPON and EU Commission studies Occasionally in books, government publications and documents, and in some international institutions, Malta is referred to as a
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
. Sometimes Malta is listed in rankings concerning cities or metropolitan areas.Metropolitan areas in Europe– Federal Institute for Research on Building, Urban Affairs and Spatial Development, 2011. Also, the Maltese coat-of-arms bears a mural crown described as "representing the fortifications of Malta and denoting a City State". Malta, with area of and population of over 0.5 million, is one of the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, most densely populated countries worldwide. World Health Organization, WHO reassigned the Islands and Small States Institute in Malta on 29 April 2022 as a collaborating center that included heavy work on topics like the development of policy recommendations on building health-system resilience in small states, the interrelationship between tourism, health systems and sustainability, with a focus on islands and small countries, through a planetary health and equity approach and the development of a toolkit on health information, digital health and evidence generation in small states.
Flora
The Maltese islands are home to a wide diversity of indigenous, sub-endemic and endemic plants. They feature many traits typical of a Mediterranean climate, such as drought resistance. The most common indigenous trees on the islands are olive (Olive, ''Olea europaea''), carob (''Ceratonia siliqua''), fig (Common fig, ''ficus carica''), holm oak (''Quercus ilex, Quericus ilex'') and Aleppo pine (''Pinus halepensis''), while the most common non-native trees are eucalyptus, acacia and Opuntia ficus-indica, opuntia. Endemic plants include the national flower ''widnet il-baħar'' (''Cheirolophus crassifolius), sempreviva ta' Malta (Helichrysum melitense),'' ''żigland t' Għawdex (Hyoseris frutescens'') and ''ġiżi ta' Malta'' (''Matthiola incana, Matthiola incana subsp. melitensis'') while sub-endemics include ''kromb il-baħar'' (''Jacobaea maritima, Jacobaea maritima subsp. sicula'') and ''xkattapietra'' (''Micromeria microphylla''). The flora and biodiversity of Malta is severely endangered by habitat loss, invasive species and human intervention.Economy
General
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
, especially during the Crimean War of 1854. The military base benefited craftsmen and all those who served the military.
In 1869, the opening of the Suez Canal gave Malta's economy a great boost, as there was a massive increase in the shipping which entered the port. Ships stopping at Malta's docks for refuelling helped the Entrepôt trade, which brought additional benefits to the island. However, towards the end of the 19th century, the economy began declining, and by the 1940s Malta's economy was in serious crisis. One factor was the longer range of newer merchant ships that required fewer refuelling stops.
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, which it joined on 1 May 2004, it Privatization, privatised some state-controlled firms and liberalised markets. For example, the government announced on 8 January 2007 that it was selling its 40 per cent stake in MaltaPost, to complete a privatisation process which had been ongoing for the previous five years. From 2000 to 2010, Malta privatised telecommunications, postal services, shipyards and Malta International Airport.
Malta has a financial regulator, the Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA), with a strong business development mindset, and the country has been successful in attracting gaming businesses, aircraft and ship registration, credit-card issuing banking licences and also fund administration. Service providers to these industries, including fiduciary and trustee business, are a core part of the growth strategy of the island. Malta has made strong headway in implementing EU Financial Services Directives including UCITs IV and Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFMs). As a base for alternative asset managers who must comply with new directives, Malta has attracted a number of key players including IDS, Iconic Funds, Apex Fund Services and TMF/Customs House.
Malta and Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
in 2006 discussed the commercial exploitation of the continental shelf between their countries, particularly for petroleum exploration. These discussions are also undergoing between Malta and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
for similar arrangements.
As of 2015, Malta did not have a property tax. Its property market, especially around the harbour area, was booming, with the prices of apartments in some towns like St Julian's, Sliema and Gzira skyrocketing.
According to Eurostat data, Maltese GDP per capita stood at Economy of the European Union#Richest and poorest NUTS regions (GDP PPP 2010), 88 per cent of the EU average in 2015 with €21,000.
The National Development and Social Fund from the Individual Investor Programme, a Immigrant investor programs, citizenship by investment programme also known as the "citizenship scheme", has become a significant income source for the government of Malta, adding 432,000,000 euro to the budget in 2018. This 'scheme' has very low due diligence and many doubtful Russian, Middle-eastern and Chinese have obtained a Maltese passport, which is also a European Union passport. In July 2020, the Labour government admitted this and has opted to stop it as of September 2020.
Banking and finance
 The two largest commercial banks are Bank of Valletta and HSBC Bank Malta, both of which can trace their origins back to the 19th century. As of recently, Digital banking, digital banks such as Revolut have also increased in popularity.
The Central Bank of Malta (Bank Ċentrali ta' Malta) has two key areas of responsibility: the formulation and implementation of monetary policy and the promotion of a sound and efficient financial system. It was established by the Central Bank of Malta Act on 17 April 1968. The Maltese government entered ERM II on 4 May 2005, and adopted the euro as the country's currency on 1 January 2008.
FinanceMalta is the quasi-governmental organisation tasked with marketing and educating business leaders coming to Malta and runs seminars and events around the world highlighting the emerging strength of Malta as a jurisdiction for banking and finance and insurance.
The two largest commercial banks are Bank of Valletta and HSBC Bank Malta, both of which can trace their origins back to the 19th century. As of recently, Digital banking, digital banks such as Revolut have also increased in popularity.
The Central Bank of Malta (Bank Ċentrali ta' Malta) has two key areas of responsibility: the formulation and implementation of monetary policy and the promotion of a sound and efficient financial system. It was established by the Central Bank of Malta Act on 17 April 1968. The Maltese government entered ERM II on 4 May 2005, and adopted the euro as the country's currency on 1 January 2008.
FinanceMalta is the quasi-governmental organisation tasked with marketing and educating business leaders coming to Malta and runs seminars and events around the world highlighting the emerging strength of Malta as a jurisdiction for banking and finance and insurance.
Transport
 Being a former British Colony, traffic in Malta Driving on the left or drives on the left. Car ownership in Malta is exceedingly high, considering the very small size of the islands; it is the fourth-highest in the European Union. The number of registered cars in 1990 amounted to 182,254, giving an automobile density of .
Malta has of road, (87.5 per cent) of which are paved and are unpaved (as of December 2003).
The main roads of Malta from the southernmost point to the northernmost point are these: Triq Birżebbuġa in Birżebbuġa, Għar Dalam Road and Tal-Barrani Road in Żejtun, Santa Luċija Avenue in Paola, Malta, Paola, Aldo Moro Street (Trunk Road), 13 December Street and Ħamrun-Marsa Bypass in Marsa, Malta, Marsa, Regional Road in Santa Venera/Msida/Gżira/San Ġwann, St Andrew's Road in Swieqi/Pembroke, Malta, Coast Road in Baħar iċ-Ċagħaq, Salina Road, Kennedy Drive, St. Paul's Bypass and Xemxija Hill in San Pawl il-Baħar, Mistra Hill, Wettinger Street (Mellieħa Bypass) and Marfa Road in Mellieħa.
Being a former British Colony, traffic in Malta Driving on the left or drives on the left. Car ownership in Malta is exceedingly high, considering the very small size of the islands; it is the fourth-highest in the European Union. The number of registered cars in 1990 amounted to 182,254, giving an automobile density of .
Malta has of road, (87.5 per cent) of which are paved and are unpaved (as of December 2003).
The main roads of Malta from the southernmost point to the northernmost point are these: Triq Birżebbuġa in Birżebbuġa, Għar Dalam Road and Tal-Barrani Road in Żejtun, Santa Luċija Avenue in Paola, Malta, Paola, Aldo Moro Street (Trunk Road), 13 December Street and Ħamrun-Marsa Bypass in Marsa, Malta, Marsa, Regional Road in Santa Venera/Msida/Gżira/San Ġwann, St Andrew's Road in Swieqi/Pembroke, Malta, Coast Road in Baħar iċ-Ċagħaq, Salina Road, Kennedy Drive, St. Paul's Bypass and Xemxija Hill in San Pawl il-Baħar, Mistra Hill, Wettinger Street (Mellieħa Bypass) and Marfa Road in Mellieħa.
 Malta bus, Buses (''xarabank'' or ''karozza tal-linja'') are the primary method of public transport, established in 1905. Malta's vintage buses operated in the Maltese islands up to 2011 and became popular tourist attractions in their own right. To this day they are depicted on many Maltese advertisements to promote tourism as well as on gifts and merchandise for tourists.
The bus service underwent extensive reform in July 2011. The management structure changed from having self-employed drivers driving their own vehicles to a service being offered by a single company through a public tender (in Gozo, being considered a small network, the service was given through direct order). The public tender was won by Arriva Malta, a member of the Arriva group, which introduced a fleet of brand new buses, built by King Long especially for service by Arriva Malta and including a smaller fleet of articulated buses brought in from Arriva London. It also operated two smaller buses for an intra-Valletta route only and 61 nine-metre buses, which were used to ease congestion on high-density routes. Overall Arriva Malta operated 264 buses. On 1 January 2014 Arriva ceased operations in Malta due to financial difficulties, having been nationalised as ''Malta Public Transport'' by the Maltese government, with a new bus operator planned to take over their operations. The government chose Autobuses Urbanos de León (ALSA (bus company), ALSA subsidiary) as its preferred bus operator for the country in October 2014. The company took over the bus service on 8 January 2015, while retaining the name ''Malta Public Transport''. It introduced the pre-pay 'tallinja card'. With lower fares than the walk-on rate, it can be topped up online. The card was initially not well received, as reported by several local news sites. During the first week of August 2015, another 40 buses of the Turkish make ''Otokar'' arrived and were put into service.
From October 2022 the bus system will be free of charge for residents of Malta.
From 1883 to 1931 Malta had a Malta Railway, railway line that connected Valletta to the army barracks at Mtarfa via Mdina and a number of towns and villages. The railway fell into disuse and eventually closed altogether, following the introduction of electric trams and buses. At the height of the bombing of Malta during the Second World War, Benito Mussolini, Mussolini announced that his forces had destroyed the railway system, but by the time war broke out, the railway had been mothballed for more than nine years.
As of 2021, an underground Malta Metro is being planned, with a projected total cost of €6.2 billion.
Malta bus, Buses (''xarabank'' or ''karozza tal-linja'') are the primary method of public transport, established in 1905. Malta's vintage buses operated in the Maltese islands up to 2011 and became popular tourist attractions in their own right. To this day they are depicted on many Maltese advertisements to promote tourism as well as on gifts and merchandise for tourists.
The bus service underwent extensive reform in July 2011. The management structure changed from having self-employed drivers driving their own vehicles to a service being offered by a single company through a public tender (in Gozo, being considered a small network, the service was given through direct order). The public tender was won by Arriva Malta, a member of the Arriva group, which introduced a fleet of brand new buses, built by King Long especially for service by Arriva Malta and including a smaller fleet of articulated buses brought in from Arriva London. It also operated two smaller buses for an intra-Valletta route only and 61 nine-metre buses, which were used to ease congestion on high-density routes. Overall Arriva Malta operated 264 buses. On 1 January 2014 Arriva ceased operations in Malta due to financial difficulties, having been nationalised as ''Malta Public Transport'' by the Maltese government, with a new bus operator planned to take over their operations. The government chose Autobuses Urbanos de León (ALSA (bus company), ALSA subsidiary) as its preferred bus operator for the country in October 2014. The company took over the bus service on 8 January 2015, while retaining the name ''Malta Public Transport''. It introduced the pre-pay 'tallinja card'. With lower fares than the walk-on rate, it can be topped up online. The card was initially not well received, as reported by several local news sites. During the first week of August 2015, another 40 buses of the Turkish make ''Otokar'' arrived and were put into service.
From October 2022 the bus system will be free of charge for residents of Malta.
From 1883 to 1931 Malta had a Malta Railway, railway line that connected Valletta to the army barracks at Mtarfa via Mdina and a number of towns and villages. The railway fell into disuse and eventually closed altogether, following the introduction of electric trams and buses. At the height of the bombing of Malta during the Second World War, Benito Mussolini, Mussolini announced that his forces had destroyed the railway system, but by the time war broke out, the railway had been mothballed for more than nine years.
As of 2021, an underground Malta Metro is being planned, with a projected total cost of €6.2 billion.

 Malta has three large natural harbours on its main island:
* The
Malta has three large natural harbours on its main island:
* The Grand Harbour
The Grand Harbour ( mt, il-Port il-Kbir; it, Porto Grande), also known as the Port of Valletta, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It has been substantially modified over the years with extensive docks ( Malta Dockyard), wharves, a ...
(or Port il-Kbir), located at the eastern side of the capital city of Valletta, has been a harbour since Roman Empire, Roman times. It has several extensive Dock (maritime), docks and Wharf, wharves, as well as a cruise liner terminal. A terminal at the Grand Harbour serves ferries that connect Malta to Pozzallo & Catania in Sicily.
* Marsamxett Harbour, located on the western side of Valletta, accommodates a number of yacht marinas.
* Marsaxlokk Harbour (Malta Freeport), at Birżebbuġa on the south-eastern side of Malta, is the islands' main cargo terminal. Malta Freeport is the List of world's busiest container ports, 11th busiest container ports in continent of Europe and 46th in the World with a trade volume of 2.3 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU's in 2008.
There are also two man-made harbours that serve a passenger and car ferry service that connects Ċirkewwa Harbour on Malta and Mġarr (Gozo), Mġarr Harbour on Gozo. The ferry makes numerous runs each day.
Malta International Airport (Ajruport Internazzjonali ta' Malta) is the only airport serving the Maltese islands. It is built on the land formerly occupied by the RAF Luqa air base. A heliport is also located there, but the scheduled service to Gozo ceased in 2006. The heliport in Gozo is at Xewkija.
Two further airfields at Ta' Qali and Ħal Far operated during the Second World War and into the 1960s but are now closed. Today, Ta' Qali houses a national park, Ta' Qali Stadium, stadium, the Crafts Village visitor attraction and the Malta Aviation Museum. This museum preserves several aircraft, including Hawker Hurricane, Hurricane and Spitfire fighters that defended the island in the Second World War.
 The national airline is Air Malta, which is based at Malta International Airport and operates services to 36 destinations in Europe and North Africa. The owners of Air Malta are the Government of Malta (98 percent) and private investors (2 percent). Air Malta employs 1,547 staff along with having a 25 percent share in Medavia.
Air Malta has concluded over 191 interline ticketing agreements with other International Air Transport Association, IATA airlines. It also has a codeshare agreement with Qantas covering three routes. In September 2007, Air Malta made two agreements with Abu Dhabi-based Etihad Airways by which Air Malta wet-leased two Airbus aircraft to Etihad Airways for the winter period starting 1 September 2007, and provided operational support on another Airbus A320 aircraft which it leased to Etihad Airways.
In June 2019, Ryanair has invested into a fully-fledged airline subsidiary, called Malta Air, operating a low-cost model. The Government of Malta holds one share in the airline whereby it holds rights to the brand name.
The national airline is Air Malta, which is based at Malta International Airport and operates services to 36 destinations in Europe and North Africa. The owners of Air Malta are the Government of Malta (98 percent) and private investors (2 percent). Air Malta employs 1,547 staff along with having a 25 percent share in Medavia.
Air Malta has concluded over 191 interline ticketing agreements with other International Air Transport Association, IATA airlines. It also has a codeshare agreement with Qantas covering three routes. In September 2007, Air Malta made two agreements with Abu Dhabi-based Etihad Airways by which Air Malta wet-leased two Airbus aircraft to Etihad Airways for the winter period starting 1 September 2007, and provided operational support on another Airbus A320 aircraft which it leased to Etihad Airways.
In June 2019, Ryanair has invested into a fully-fledged airline subsidiary, called Malta Air, operating a low-cost model. The Government of Malta holds one share in the airline whereby it holds rights to the brand name.
Communications
The mobile penetration rate in Malta exceeded 100% by the end of 2009. Malta uses the GSM900, UMTS(3G) and LTE(4G) mobile phone systems, which are compatible with the rest of the European countries, Australia and New Zealand. Telephone and cellular subscriber numbers have eight digits. There are no area codes in Malta, but after inception, the original first two numbers, and currently the 3rd and 4th digit, were assigned according to the locality. Fixed line telephone numbers have the prefix 21 and 27, although businesses may have numbers starting 22 or 23. An example would be 2*80**** if from Żabbar, and 2*23**** if from Marsa, Malta, Marsa. Gozitan landline numbers generally are assigned 2*56****. Mobile telephone numbers have the prefix 77, 79, 98 or 99. Malta's international calling code is +356. The number of pay-TV subscribers fell as customers switched to IPTV, Internet Protocol television (IPTV): the number of IPTV subscribers doubled in the six months to June 2012. In early 2012, the government called for a national Fibre to the Home (FttH) network to be built, with a minimum broadband service being upgraded from 4Mbit/s to 100Mbit/s.Currency
Maltese euro coins feature the Maltese cross on €2 and €1 coins, the coat of arms of Malta on the €0.50, €0.20 and €0.10 coins, and theMnajdra
Mnajdra ( mt, L-Imnajdra) is a megalithic temple complex found on the southern coast of the Mediterranean island of Malta. Mnajdra is approximately from the Ħaġar Qim megalithic complex. Mnajdra was built around the fourth millennium BCE; th ...
Temples on the €0.05, €0.02 and €0.01 coins.
Malta has produced collectors' coins with face value ranging from 10 to 50 euros. These coins continue an existing national practice of minting of silver and gold commemorative coins. Unlike normal issues, these coins are not accepted in all the eurozone. For instance, a €10 Maltese commemorative coin cannot be used in any other country.
From its introduction in 1972 until the introduction of the Euro in 2008, the currency was the Maltese lira, which had replaced the Maltese pound. The pound replaced the Maltese scudo in 1825.
Tourism
 Malta is a popular tourist destination, with 1.6 million tourists per year. Three times more tourists visit than there are residents. Tourism infrastructure has increased dramatically over the years and a number of hotels are present on the island, although overdevelopment and the destruction of traditional housing is of growing concern. An increasing number of Maltese now travel abroad on holiday. In 2019, Malta had a record year in tourism, recording over 2.1 million tourists in one single year.
In recent years, Malta has advertised itself as a medical tourism destination, and a number of health tourism providers are developing the industry. However, no Maltese hospital has undergone independent international healthcare accreditation. Malta is popular with British medical tourists, pointing Maltese hospitals towards seeking UK-sourced accreditation, such as with the Trent Accreditation Scheme.
Additionally, Malta attracts a number of English Language Students from around the world.
Tourism in Malta contributes to around 11.6 percent of the country's Gross domestic product, Gross Domestic Product.
Malta is a popular tourist destination, with 1.6 million tourists per year. Three times more tourists visit than there are residents. Tourism infrastructure has increased dramatically over the years and a number of hotels are present on the island, although overdevelopment and the destruction of traditional housing is of growing concern. An increasing number of Maltese now travel abroad on holiday. In 2019, Malta had a record year in tourism, recording over 2.1 million tourists in one single year.
In recent years, Malta has advertised itself as a medical tourism destination, and a number of health tourism providers are developing the industry. However, no Maltese hospital has undergone independent international healthcare accreditation. Malta is popular with British medical tourists, pointing Maltese hospitals towards seeking UK-sourced accreditation, such as with the Trent Accreditation Scheme.
Additionally, Malta attracts a number of English Language Students from around the world.
Tourism in Malta contributes to around 11.6 percent of the country's Gross domestic product, Gross Domestic Product.
Science and technology
Malta signed a co-operation agreement with the European Space Agency (ESA) for more-intensive co-operation in ESA projects.Malta signs Cooperation Agreement with ESA. Esa.int. Retrieved 7 June 2012. The Malta Council for Science and Technology (MCST) is the civil body responsible for the development of science and technology on an educational and social level. Most science students in Malta graduate from the University of Malta and are represented by S-Cubed (Science Student's Society), UESA (University Engineering Students Association) and ICTSA (University of Malta ICT Students' Association). Malta was ranked 21th in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, up from 27th in 2019, 2020 and 2021.
Demographics
 A population and housing census is conducted every ten years in Malta. The November 2005 census counted an estimated 96 percent of the population. A preliminary report was issued in April 2006 and the results were weighted to estimate for 100 percent of the population.
Maltese natives make up the majority of the island. However, there are minorities, the largest of which are British people, Britons, many of whom are retirees.
The population of Malta was estimated at 408,000. , 17 percent were aged 14 and under, 68 percent were within the 15–64 age bracket whilst the remaining 13 percent were 65 years and over. Malta's population density of 1,282 per square km (3,322/sq mi) is by far the highest in the EU and one of the highest in the world. By comparison, the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, average population density for the World (land only, excluding Antarctica) was as of July 2014.
The only census year showing a fall in population was that of 1967, with a 1.7 per cent total decrease, attributable to a substantial number of Maltese residents who emigrated. The Maltese-resident population for 2004 was estimated to make up 97.0 per cent of the total resident population.
All censuses since 1842 have shown a slight excess of females over males. The 1901 and 1911 censuses came closest to recording a balance. The highest female-to-male ratio was reached in 1957 (1088:1000) but since then the ratio has dropped continuously. The 2005 census showed a 1013:1000 female-to-male ratio.
Population growth has slowed down, from +9.5 per cent between the 1985 and 1995 censuses, to +6.9 per cent between the 1995 and 2005 censuses (a yearly average of +0.7 per cent). The birth rate stood at 3860 (a decrease of 21.8 per cent from the 1995 census) and the death rate stood at 3025. Thus, there was a natural population increase of 835 (compared to +888 for 2004, of which over a hundred were foreign residents).
The population's age composition is similar to the age structure prevalent in the EU. Since 1967 there was observed a trend indicating an ageing population, and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Malta's Dependency ratio, old-age-dependency-ratio rose from 17.2 percent in 1995 to 19.8 percent in 2005, reasonably lower than the EU's 24.9 percent average; 31.5 percent of the Maltese population is aged under 25 (compared to the EU's 29.1 percent); but the 50–64 age group constitutes 20.3 percent of the population, significantly higher than the EU's 17.9 percent. Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio is expected to continue rising steadily in the coming years.
Maltese legislation recognises both civil and canonical (ecclesiastical) marriages. Annulments by the ecclesiastical and civil courts are unrelated and are not necessarily mutually endorsed. Malta voted in favour of divorce legislation in 2011 Maltese divorce referendum, a referendum held on 28 May 2011.
Abortion in Malta is illegal. It's the only European Union member state with a total ban on the procedure. There are no exceptions, including in cases of rape or incest. On 21 November 2022, the government led by the Labour Party proposed a bill that "introduces a new clause into the country’s criminal code allowing for the termination of a pregnancy if the mother’s life is at risk or if her health is in serious jeopardy".
A person must be 16 to marry. The number of brides aged under 25 decreased from 1471 in 1997 to 766 in 2005; while the number of grooms under 25 decreased from 823 to 311. There is a constant trend that females are more likely than males to marry young. In 2005 there were 51 brides aged between 16 and 19, compared to 8 grooms.
In 2021, the population of the Maltese Islands stood at 516,100.
The total fertility rate (TFR) was estimated at 1.45 children born/woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. In 2012, 25.8 per cent of births were to unmarried women. The life expectancy in 2018 was estimated at 83.
A population and housing census is conducted every ten years in Malta. The November 2005 census counted an estimated 96 percent of the population. A preliminary report was issued in April 2006 and the results were weighted to estimate for 100 percent of the population.
Maltese natives make up the majority of the island. However, there are minorities, the largest of which are British people, Britons, many of whom are retirees.
The population of Malta was estimated at 408,000. , 17 percent were aged 14 and under, 68 percent were within the 15–64 age bracket whilst the remaining 13 percent were 65 years and over. Malta's population density of 1,282 per square km (3,322/sq mi) is by far the highest in the EU and one of the highest in the world. By comparison, the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, average population density for the World (land only, excluding Antarctica) was as of July 2014.
The only census year showing a fall in population was that of 1967, with a 1.7 per cent total decrease, attributable to a substantial number of Maltese residents who emigrated. The Maltese-resident population for 2004 was estimated to make up 97.0 per cent of the total resident population.
All censuses since 1842 have shown a slight excess of females over males. The 1901 and 1911 censuses came closest to recording a balance. The highest female-to-male ratio was reached in 1957 (1088:1000) but since then the ratio has dropped continuously. The 2005 census showed a 1013:1000 female-to-male ratio.
Population growth has slowed down, from +9.5 per cent between the 1985 and 1995 censuses, to +6.9 per cent between the 1995 and 2005 censuses (a yearly average of +0.7 per cent). The birth rate stood at 3860 (a decrease of 21.8 per cent from the 1995 census) and the death rate stood at 3025. Thus, there was a natural population increase of 835 (compared to +888 for 2004, of which over a hundred were foreign residents).
The population's age composition is similar to the age structure prevalent in the EU. Since 1967 there was observed a trend indicating an ageing population, and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Malta's Dependency ratio, old-age-dependency-ratio rose from 17.2 percent in 1995 to 19.8 percent in 2005, reasonably lower than the EU's 24.9 percent average; 31.5 percent of the Maltese population is aged under 25 (compared to the EU's 29.1 percent); but the 50–64 age group constitutes 20.3 percent of the population, significantly higher than the EU's 17.9 percent. Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio is expected to continue rising steadily in the coming years.
Maltese legislation recognises both civil and canonical (ecclesiastical) marriages. Annulments by the ecclesiastical and civil courts are unrelated and are not necessarily mutually endorsed. Malta voted in favour of divorce legislation in 2011 Maltese divorce referendum, a referendum held on 28 May 2011.
Abortion in Malta is illegal. It's the only European Union member state with a total ban on the procedure. There are no exceptions, including in cases of rape or incest. On 21 November 2022, the government led by the Labour Party proposed a bill that "introduces a new clause into the country’s criminal code allowing for the termination of a pregnancy if the mother’s life is at risk or if her health is in serious jeopardy".
A person must be 16 to marry. The number of brides aged under 25 decreased from 1471 in 1997 to 766 in 2005; while the number of grooms under 25 decreased from 823 to 311. There is a constant trend that females are more likely than males to marry young. In 2005 there were 51 brides aged between 16 and 19, compared to 8 grooms.
In 2021, the population of the Maltese Islands stood at 516,100.
The total fertility rate (TFR) was estimated at 1.45 children born/woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. In 2012, 25.8 per cent of births were to unmarried women. The life expectancy in 2018 was estimated at 83.
Languages
 The
The Maltese language
Maltese ( mt, Malti, links=no, also ''L-Ilsien Malti'' or '), is a Semitic language derived from late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance superstrata spoken by the Maltese people. It is the national language of Malta and the only offic ...
( mt, Malti) is one of the two constitutional languages of Malta, having become official, however, only in 1934, and being considered as the national language. Previously, Sicilian language, Sicilian was the official and cultural language of Malta from the 12th century, and the Tuscan dialect of Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
from the 16th century. Alongside Maltese, English is also an official language of the country and hence the laws of the land are enacted both in Maltese and English. However, article 74 of the Constitution states that "... if there is any conflict between the Maltese and the English texts of any law, the Maltese text shall prevail."
Maltese is a Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
descended from the now extinct Sicilian-Arabic (Siculo-Arabic
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, الْلهجَة الْعَرَبِيَة الْصَقلِيَة), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century ...
) dialect (from southern Italy) that developed during the Emirate of Sicily.Joseph M. BrincaMaltese – an unusual formula
, MED Magazine (February 2005) The Maltese alphabet consists of 30 letters based on the Latin alphabet, including the diacritically altered letters ''ż'', ''ċ'' and ''ġ'', as well as the letters ''għ'', ''ħ'', and ''Ie (digraph), ie''. Maltese is the only
Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
with official status in the European Union. Maltese has a Semitic base with substantial borrowing from Sicilian language, Sicilian, Italian, a little French, and more recently and increasingly, English. The hybrid character of Maltese was established by a long period of Maltese-Sicilian urban bilingualism gradually transforming rural speech and which ended in the early 19th century with Maltese emerging as the vernacular of the entire native population. The language includes different dialects that can vary greatly from one town to another or from one island to another.
In 2012, the Eurobarometer states that 97 percent of the Maltese population consider Maltese as mother tongue. Also, 89 percent of the population speak English, 66 percent speak Italian, and 17 percent speak French. This widespread knowledge of second languages makes Malta one of the most multilingual countries in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
. A study collecting public opinion on what language was "preferred" discovered that 86 percent of the population express a preference for Maltese, 12 percent for English, and 2 percent for Italian. Still, Italian television channels from Italy-based broadcasters, such as Mediaset and RAI, reach Malta and remain popular.Ignasi Badia i Capdevila (2004A view of the linguistic situation in Malta
NovesSl. Retrieved 24 February 2008 Maltese Sign Language is used by signers in Malta.
Religion
 The predominant religion in Malta is
The predominant religion in Malta is Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The second article of the Constitution of Malta establishes Catholicism as the state religion and it is also reflected in various elements of Culture of Malta, Maltese culture, although Entrenched clause, entrenched provisions for the freedom of religion are made.
There are more than 360 churches in Malta, Gozo, and Comino, or one church for every 1,000 residents. The parish church (Maltese: ''"il-parroċċa"'', or ''"il-knisja parrokkjali"'') is the architectural and geographic focal point of every Maltese town and village, and its main source of civic pride. This civic pride manifests itself in spectacular fashion during the local village ''festas'', which mark the day of the patron saint of each parish with marching bands, religious processions, special Holy Mass, Masses, fireworks (especially petards) and other festivities.
Malta is an Apostolic See; the Acts of the Apostles tells of how Paul of Tarsus, St. Paul, on his way from Jerusalem to Rome to face trial, was shipwrecked on the island of "Melite", which many Bible scholars identify with Malta, an episode dated around AD 60. As recorded in the Acts of the Apostles, St. Paul spent three months on the island on his way to Rome, curing the sick including the father of Publius, the "chief man of the island". Various traditions are associated with this account. The shipwreck is said to have occurred in the place today known as St Paul's Bay. The Maltese saint, Saint Publius is said to have been made Malta's first bishop and a grotto in Rabat, now known as "St Paul's Grotto" (and in the vicinity of which evidence of Christian burials and rituals from the 3rd century AD has been found), is among the earliest known places of Christian worship on the island.
Further evidence of Christian practices and beliefs during the period of Roman persecution appears in catacombs that lie beneath various sites around Malta, including St. Paul's Catacombs and St. Agatha's Catacombs in Rabat, just outside the walls of Mdina. The latter, in particular, were frescoed between 1200 and 1480, although invading Ottoman Empire, Turks defaced many of them in the 1550s. There are also a number of cave churches, including the grotto at Sanctuary of Our Lady of Mellieħa, Mellieħa, which is a Shrine of the Nativity of Our Lady where, according to legend, St. Luke painted a picture of the The Madonna, Madonna. It has been a place of pilgrimage since the medieval period.
The Acts of the Council of Chalcedon record that in 451 AD a certain Acacius was Bishop of Malta (''Melitenus Episcopus''). It is also known that in 501 AD, a certain Constantinus, ''Episcopus Melitenensis'', was present at the Second Council of Constantinople, Fifth Ecumenical Council. In 588 AD, Pope Gregory I deposed Tucillus, ''Miletinae civitatis episcopus'' and the clergy and people of Malta elected his successor Trajan in 599 AD. The last recorded Bishop of Malta before the invasion of the islands was a Greek named Manas, who was subsequently incarcerated at Palermo.
Maltese historian Giovanni Francesco Abela states that following their conversion to Christianity at the hand of Saul of Tarsus, St. Paul, the Maltese retained their Christian religion, despite the Fatimid invasion. Abela's writings describe Malta as a divinely ordained "bulwark of Christian, European civilization against the spread of Mediterranean Islam". The native Christian community that welcomed Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Roger Bosso and The Great, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101. He was a member of the ...
was further bolstered by immigration to Malta from Italy, in the 12th and 13th centuries.
 For centuries, the Church in Malta was subordinate to the Diocese of Palermo, except when it was under Charles of Anjou, who appointed bishops for Malta, as did – on rare occasions – the Spanish and later, the Knights. Since 1808 all bishops of Malta have been Maltese. As a result of the History of Malta#Norman Kingdom of Sicily rule, Norman and Spanish periods, and the rule of the Knights, Malta became the devout Catholic nation that it is today. It is worth noting that the Office of the Roman Inquisition, Inquisitor of Malta had a very long tenure on the island following its establishment in 1530: the last Inquisitor departed from the Islands in 1798 after the Knights capitulated to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte. During the period of the Republic of Venice, several Maltese families emigrated to Corfu. Their descendants account for about two-thirds of the community of some 4,000 Catholics that now live on that island.
For centuries, the Church in Malta was subordinate to the Diocese of Palermo, except when it was under Charles of Anjou, who appointed bishops for Malta, as did – on rare occasions – the Spanish and later, the Knights. Since 1808 all bishops of Malta have been Maltese. As a result of the History of Malta#Norman Kingdom of Sicily rule, Norman and Spanish periods, and the rule of the Knights, Malta became the devout Catholic nation that it is today. It is worth noting that the Office of the Roman Inquisition, Inquisitor of Malta had a very long tenure on the island following its establishment in 1530: the last Inquisitor departed from the Islands in 1798 after the Knights capitulated to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte. During the period of the Republic of Venice, several Maltese families emigrated to Corfu. Their descendants account for about two-thirds of the community of some 4,000 Catholics that now live on that island.
 The patron saints of Malta are Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul, Saint Publius, and Agatha of Sicily, Saint Agatha. Although not a patron saint, George Preca, St George Preca (San Ġorġ Preca) is greatly revered as the second canonised Maltese saint after St. Publius. Pope Benedict XVI canonised Preca on 3 June 2007. A number of Maltese individuals are recognised as Beatification, Blessed, including Maria Adeodata Pisani and Nazju Falzon, with Pope John Paul II having beatified them in 2001.
Various Catholic religious orders are present in Malta, including the Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominican Order, Dominicans, Carmelites and Little Sisters of the Poor.
Most congregants of the local Protestant churches are not Maltese; their congregations draw on the many British retirees living in the country and vacationers from many other nations. There include St. Andrew's Scots Church, Malta, St. Andrew's Scots Church in Valletta (a joint Presbyterian and Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist congregation) and St Paul's Anglican Cathedral. There are several Charismatic, Pentecostal, and Baptist churches, including the Bible Baptist Church, Knisja Evanġelika Battista, an
The patron saints of Malta are Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul, Saint Publius, and Agatha of Sicily, Saint Agatha. Although not a patron saint, George Preca, St George Preca (San Ġorġ Preca) is greatly revered as the second canonised Maltese saint after St. Publius. Pope Benedict XVI canonised Preca on 3 June 2007. A number of Maltese individuals are recognised as Beatification, Blessed, including Maria Adeodata Pisani and Nazju Falzon, with Pope John Paul II having beatified them in 2001.
Various Catholic religious orders are present in Malta, including the Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominican Order, Dominicans, Carmelites and Little Sisters of the Poor.
Most congregants of the local Protestant churches are not Maltese; their congregations draw on the many British retirees living in the country and vacationers from many other nations. There include St. Andrew's Scots Church, Malta, St. Andrew's Scots Church in Valletta (a joint Presbyterian and Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist congregation) and St Paul's Anglican Cathedral. There are several Charismatic, Pentecostal, and Baptist churches, including the Bible Baptist Church, Knisja Evanġelika Battista, anTrinity Evangelical Church
– a Reformed Baptist Church. The members of these churches are mainly Maltese. There are also a Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-day Adventist church in Birkirkara, and a New Apostolic Church congregation founded in 1983 in Gwardamangia.Vassallo, Harry (8 April 2009
A map of faith in Malta
. ''MaltaToday'' (8 April 2009). Retrieved 1 May 2017. There are approximately 600 Jehovah's Witnesses. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) is also represented. The Jewish population of Malta reached its peak in the Middle Ages under Norman rule. In 1479, Malta and
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
came under Kingdom of Aragon, Aragonese rule and the Alhambra Decree of 1492 forced all Jews to leave the country, permitting them to take with them only a few of their belongings. Several dozen Maltese Jews may have Religious conversion, converted to Christianity at the time to remain in the country. Today, there are two Jewish congregations.In 2019 the Jewish community in Malta gathered around 150 persons, slightly more than the 120 (of which 80 were active) estimated in 2003, and mostly elderly. Many among the newer generations decided to settle abroad, including in England and Israel. Most contemporary Maltese Jews are Sephardi, however, an Ashkenazi prayer book is used. In 2013 the Chabad Jewish Center in Malta was founded by Rabbi Haim Shalom Segal and his wife, Haya Moshka Segal.
The Maltese Jews found themselves without a synagogue when the building on Spur Street was demolished in 1979. In 1984, a new synagogue was opened at 182 Strada San Orsola, but it had to close down in 1995 as the building was collapsing.[14] In 2000, a new synagogue was built in Ta' Xbiex with donations from the United States and the UK. The Jewish Foundation of Malta now manages it along with a Jewish Center.
There is one Muslim mosque, the Mariam Al-Batool Mosque. A Muslim primary school recently opened. Of the estimated 3,000 Islam in Malta, Muslims in Malta, approximately 2,250 are foreigners, approximately 600 are naturalised citizens, and approximately 150 are native-born Maltese.
Zen Buddhism and the Baháʼí Faith claim some 40 members.
In a survey held by the Malta Today, the overwhelming majority of the Maltese population adheres to Christianity (95.2%) with Catholicism as the main denomination (93.9%).
According to the same report, 4.5% of the population declared themselves as either atheist or agnostic, one of the lowest figures in Europe. According to a Eurobarometer survey conducted in 2019, 83% of the population identified as Catholic Church, Catholic. The number of atheists has doubled from 2014 to 2018. Non-religious people have a higher risk of suffering from discrimination, such as lack of trust by society and unequal treatment by institutions. In the 2015 edition of the annual International Humanist and Ethical Union#The Freedom of Thought Report, Freedom of Thought Report from the International Humanist and Ethical Union, Malta was in the category of "severe discrimination". In 2016, following the Blasphemy law#Malta, abolishment of blasphemy law, Malta was shifted to the category of "systematic discrimination" (which is the same category as most EU countries).
Migration
Inbound migration
Historically a land of emigration, since the early 21st century Malta has seen a significant increase in net migration; the foreign-born population has grown nearly eightfold between 2005 and 2020. Most of the foreign community in Malta consists of active or retired British nationals and their dependents, centred on Sliema and surrounding suburbs. Other smaller foreign groups include Italians, Libyans, and Serbians, many of whom have assimilated into the Maltese people, Maltese nation over the decades. Malta is also home to a large number of foreign workers who migrated to the island for economic opportunity. This migration was driven predominantly in the early 21st century, when the Maltese economy was steadily booming yet the cost and quality of living on the island remained relatively stable. In recent years however the local Maltese housing index has doubled pushing property and rental prices to very high and almost unaffordable levels throughout the country, with the slight exception of Gozo. Salaries in Malta have risen very slowly and very marginally over the years, making life on the island much harder than it was a few years ago. Consequently, some expats in Malta have seen their relative financial fortunes decline, with others relocating to other European countries altogether. Since the late 20th century, Malta has become a transit country for migration routes from Africa towards Europe. As a member of theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and the Schengen Agreement, Malta is bound by the Dublin Regulation to process all claims for asylum by those asylum seekers that enter EU territory for the first time in Malta. However, irregular migrants who land in Malta are subject to a immigration detention, compulsory detention policy, being held in several camps organised by the Armed Forces of Malta (AFM), including those near Ħal Far and Safi, Malta, Ħal Safi. The compulsory detention policy has been denounced by several NGOs, and in July 2010, the European Court of Human Rights found that Malta's detention of migrants was arbitrary, lacking in adequate procedures to challenge detention, and in breach of its obligations under the European Convention on Human Rights. On 8 September 2020, Amnesty International criticized Malta for "illegal tactics" in the Mediterranean, against immigrants who were attempting to cross from North Africa. The reports claimed that the government's approach might have led to avoidable deaths.
In January 2014, Malta started granting citizenship for a €650,000 contribution plus investments, contingent on residence and criminal background checks. This "Immigrant investor programs, golden passport" citizenship scheme has been criticized as a fraudulent act by the Maltese Government, since it has come under scrutiny for selling citizenship to several dubious and criminal individuals from non-European countries. Concerns as to whether the Maltese citizenship scheme is allowing an influx of such individuals into the greater European Union have been raised by both the public as well as the European Council on multiple occasions.
Outbound migration
 In the 19th century, most emigration from Malta was to North Africa and the Middle East, although rates of Repatriation, return migration to Malta were high. Nonetheless, Maltese communities formed in these regions. By 1900, for example, British consular estimates suggest that there were 15,326 Maltese in
In the 19th century, most emigration from Malta was to North Africa and the Middle East, although rates of Repatriation, return migration to Malta were high. Nonetheless, Maltese communities formed in these regions. By 1900, for example, British consular estimates suggest that there were 15,326 Maltese in Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, and in 1903 it was claimed that 15,000 people of Maltese origin were living in Algeria.
Malta experienced significant emigration as a result of the collapse of a construction boom in 1907 and immediately after the Second World War, when the birth rate increased significantly. In the 20th century, most emigrants went to destinations in the New World, particularly to Australia, Canada, and the United States. Post Second World War, Malta's Emigration Department would assist emigrants with the cost of their travel. Between 1948 and 1967, 30 percent of the population emigrated. Between 1946 and the late-1970s, over 140,000 people left Malta on the assisted passage scheme, with 57.6% migrating to Australia, 22% to the United Kingdom, UK, 13% to Canada and 7% to the United States.
Emigration dropped dramatically after the mid-1970s and has since ceased to be a social phenomenon of significance. However, since Malta joined the EU in 2004 expatriate communities emerged in a number of European countries, particularly in Belgium and Luxembourg.
Education

 Primary schooling has been compulsory since 1946; secondary education up to the age of sixteen was made compulsory in 1971. The state and the Catholic Church, Church provide education free of charge, both running a number of schools in Malta and Gozo, including De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College in Cospicua, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College in Birkirkara, St. Paul's Missionary College in Rabat, Malta, St. Joseph's School in Blata l-Bajda and List of schools in Malta, Saint Monica Girls' School in Mosta and St. Augustine's College (Malta), Saint Augustine College, with its primary sector in Marsa, Malta, Marsa and its secondary in Pietà, Malta, Pieta. , state schools are organised into networks known as Colleges and incorporate kindergarten schools, primary and secondary schools. A number of private schools are run in Malta, including San Andrea School and San Anton School in the valley of L-Imselliet (l/o Mġarr), St. Martin's College in Swatar and St. Michael School (Malta), St. Michael's School in Santa Venera. St. Catherine's High School, Pembroke offers an International Foundation Course for students wishing to learn English before entering mainstream education. , there are two international schools, Verdala International School and QSI Malta. The state pays a portion of the teachers' salary in Church schools.
Education in Malta is based on the Education in the United Kingdom, British model. Primary school lasts six years. Pupils sit for SEC O-level examinations at the age of 16, with passes obligatory in certain subjects such as Mathematics, a minimum of one science subject (Physics, Biology or Chemistry), English and Maltese. Upon obtaining these subjects, Pupils may opt to continue studying at a sixth form college such as Gan Frangisk Abela Junior College, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College, Giovanni Curmi Higher Secondary, De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College, St Edward's College, or else at another post-secondary institution such as MCAST. The sixth form course lasts for two years, at the end of which students sit for the matriculation examination. Subject to their performance, students may then apply for an undergraduate academic degree, degree or diploma.
The adult literacy rate is 99.5 per cent.
Maltese and English are both used to teach pupils at the primary and secondary school level, and both languages are also compulsory subjects. State school, Public schools tend to use both Maltese and English in a balanced manner. Private schools prefer to use English for teaching, as is also the case with most departments of the University of Malta; this has a limiting effect on the capacity and development of the Maltese language. Most university courses are in English. The College of Remote and Offshore Medicine based in Malta teaches exclusively in english, awarding undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
Of the total number of pupils studying a first foreign language at secondary level, 51 per cent take Italian whilst 38 per cent take French. Other choices include German, Russian, Spanish, Latin, Chinese and Arabic.
Malta is also a popular destination to study the English language, attracting over 83,000 students in 2019.
Primary schooling has been compulsory since 1946; secondary education up to the age of sixteen was made compulsory in 1971. The state and the Catholic Church, Church provide education free of charge, both running a number of schools in Malta and Gozo, including De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College in Cospicua, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College in Birkirkara, St. Paul's Missionary College in Rabat, Malta, St. Joseph's School in Blata l-Bajda and List of schools in Malta, Saint Monica Girls' School in Mosta and St. Augustine's College (Malta), Saint Augustine College, with its primary sector in Marsa, Malta, Marsa and its secondary in Pietà, Malta, Pieta. , state schools are organised into networks known as Colleges and incorporate kindergarten schools, primary and secondary schools. A number of private schools are run in Malta, including San Andrea School and San Anton School in the valley of L-Imselliet (l/o Mġarr), St. Martin's College in Swatar and St. Michael School (Malta), St. Michael's School in Santa Venera. St. Catherine's High School, Pembroke offers an International Foundation Course for students wishing to learn English before entering mainstream education. , there are two international schools, Verdala International School and QSI Malta. The state pays a portion of the teachers' salary in Church schools.
Education in Malta is based on the Education in the United Kingdom, British model. Primary school lasts six years. Pupils sit for SEC O-level examinations at the age of 16, with passes obligatory in certain subjects such as Mathematics, a minimum of one science subject (Physics, Biology or Chemistry), English and Maltese. Upon obtaining these subjects, Pupils may opt to continue studying at a sixth form college such as Gan Frangisk Abela Junior College, St Aloysius' College (Malta), St. Aloysius' College, Giovanni Curmi Higher Secondary, De La Salle College (Malta), De La Salle College, St Edward's College, or else at another post-secondary institution such as MCAST. The sixth form course lasts for two years, at the end of which students sit for the matriculation examination. Subject to their performance, students may then apply for an undergraduate academic degree, degree or diploma.
The adult literacy rate is 99.5 per cent.
Maltese and English are both used to teach pupils at the primary and secondary school level, and both languages are also compulsory subjects. State school, Public schools tend to use both Maltese and English in a balanced manner. Private schools prefer to use English for teaching, as is also the case with most departments of the University of Malta; this has a limiting effect on the capacity and development of the Maltese language. Most university courses are in English. The College of Remote and Offshore Medicine based in Malta teaches exclusively in english, awarding undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
Of the total number of pupils studying a first foreign language at secondary level, 51 per cent take Italian whilst 38 per cent take French. Other choices include German, Russian, Spanish, Latin, Chinese and Arabic.
Malta is also a popular destination to study the English language, attracting over 83,000 students in 2019.
Healthcare
 Malta has a long history of providing publicly funded health care. The first hospital recorded in the country was already functioning by 1372. The first hospital exclusively for women was opened in 1625 by Caterina Scappi, known as "La Senese".
Today, Malta has both a public healthcare system, known as the government healthcare service, where healthcare is free at the point of delivery, and a private healthcare system. Malta has a strong general practitioner-delivered primary care base and the public hospitals provide secondary and tertiary care. The Maltese Ministry of Health advises foreign residents to take out private medical insurance.
.
Malta has a long history of providing publicly funded health care. The first hospital recorded in the country was already functioning by 1372. The first hospital exclusively for women was opened in 1625 by Caterina Scappi, known as "La Senese".
Today, Malta has both a public healthcare system, known as the government healthcare service, where healthcare is free at the point of delivery, and a private healthcare system. Malta has a strong general practitioner-delivered primary care base and the public hospitals provide secondary and tertiary care. The Maltese Ministry of Health advises foreign residents to take out private medical insurance.
. Malta also boasts voluntary organisations such as Alpha Medical (Advanced Care), the Emergency Fire & Rescue Unit (E.F.R.U.), St John Ambulance and Red Cross Malta who provide first aid/nursing services during events involving crowds, Malta's primary hospital, opened in 2007. It has one of the largest medical buildings in Europe
The University of Malta has a medical school and a Faculty of Health Sciences, the latter offering diploma, degree (BSc) and postgraduate degree courses in a number of health care disciplines.
The Medical Association of Malta represents practitioners of the medical profession. The Malta Medical Students' Association (MMSA) is a separate body representing Maltese medical students, and is a member of European Medical Students' Association, EMSA and International Federation of Medical Students' Associations, IFMSA. MIME, the Maltese Institute for Medical Education, is an institute set up recently to provide CME to physicians in Malta as well as medical students. The Foundation Program followed in the UK has been introduced in Malta to stem the 'brain drain' of newly graduated physicians to the British Isles. The Malta Association of Dental Students (MADS) is a student association set up to promote the rights of Dental Surgery Students studying within the faculty of Dental Surgery of the University of Malta. It is affiliated with IADS, the International Association of Dental Students.
Malta also boasts voluntary organisations such as Alpha Medical (Advanced Care), the Emergency Fire & Rescue Unit (E.F.R.U.), St John Ambulance and Red Cross Malta who provide first aid/nursing services during events involving crowds, Malta's primary hospital, opened in 2007. It has one of the largest medical buildings in Europe
The University of Malta has a medical school and a Faculty of Health Sciences, the latter offering diploma, degree (BSc) and postgraduate degree courses in a number of health care disciplines.
The Medical Association of Malta represents practitioners of the medical profession. The Malta Medical Students' Association (MMSA) is a separate body representing Maltese medical students, and is a member of European Medical Students' Association, EMSA and International Federation of Medical Students' Associations, IFMSA. MIME, the Maltese Institute for Medical Education, is an institute set up recently to provide CME to physicians in Malta as well as medical students. The Foundation Program followed in the UK has been introduced in Malta to stem the 'brain drain' of newly graduated physicians to the British Isles. The Malta Association of Dental Students (MADS) is a student association set up to promote the rights of Dental Surgery Students studying within the faculty of Dental Surgery of the University of Malta. It is affiliated with IADS, the International Association of Dental Students.
Culture
The culture of Malta reflects the various cultures, from the Phoenicians to the British, that have come into contact with the Maltese Islands throughout the centuries, including neighbouring Mediterranean cultures, and the cultures of the nations that ruled Malta for long periods of time prior to its Independence Day (Malta), independence in 1964.Music
 While Maltese music today is largely Western, traditional Maltese music includes what is known as ''Għana (folk music), għana''. This consists of background folk guitar music, while a few people, generally men, take it in turns to argue a point in a sing-song voice. The aim of the lyrics, which are improvised, is to create a friendly yet challenging atmosphere, and it takes a number of years of practice to be able to combine the required artistic qualities with the ability to debate effectively. Music plays an important part in Maltese culture as each locality parades its own band club, on various occasions these being multiple per locality, and function to establish the thematic musical background to the various Public holidays in Malta, village feasts that dot the Maltese islands throughout the year. Additionally, the Malta Philharmonic Orchestra is recognized as Malta’s foremost musical institution and is notable for being called to participate in important state events.
Contemporary music in Malta spans a variety of styles and sports international classical talents such as Miriam Gauci and Joseph Calleja, as well as non-classical music bands such as Winter Moods, and Red Electric (band), Red Electric, and singers like Ira Losco, Fabrizio Faniello, Glen Vella, Kevin Borg, Kurt Calleja, Chiara Siracusa, and Thea Garrett.
While Maltese music today is largely Western, traditional Maltese music includes what is known as ''Għana (folk music), għana''. This consists of background folk guitar music, while a few people, generally men, take it in turns to argue a point in a sing-song voice. The aim of the lyrics, which are improvised, is to create a friendly yet challenging atmosphere, and it takes a number of years of practice to be able to combine the required artistic qualities with the ability to debate effectively. Music plays an important part in Maltese culture as each locality parades its own band club, on various occasions these being multiple per locality, and function to establish the thematic musical background to the various Public holidays in Malta, village feasts that dot the Maltese islands throughout the year. Additionally, the Malta Philharmonic Orchestra is recognized as Malta’s foremost musical institution and is notable for being called to participate in important state events.
Contemporary music in Malta spans a variety of styles and sports international classical talents such as Miriam Gauci and Joseph Calleja, as well as non-classical music bands such as Winter Moods, and Red Electric (band), Red Electric, and singers like Ira Losco, Fabrizio Faniello, Glen Vella, Kevin Borg, Kurt Calleja, Chiara Siracusa, and Thea Garrett.
Literature
Documented Maltese literature is over 200 years old. However, a recently unearthed love ballad testifies to literary activity in the local tongue from the Medieval period. Malta followed a Romantic literary tradition, culminating in the works of Dun Karm Psaila, Malta's national poet. Subsequent writers like Ruzar Briffa and Karmenu Vassallo tried to estrange themselves from the rigidity of formal themes and versification. The next generation of writers, including Karl Schembri and Immanuel Mifsud, widened the tracks further, especially in prose and poetry.Architecture
 Maltese architecture has been influenced by many different Mediterranean cultures and British architecture over its history. The first settlers on the island constructed
Maltese architecture has been influenced by many different Mediterranean cultures and British architecture over its history. The first settlers on the island constructed Ġgantija
Ġgantija (, "Giantess") is a megalithic temple complex from the Neolithic on the Mediterranean island of Gozo. The Ġgantija temples are the earliest of the Megalithic Temples of Malta and are older than the pyramids of Egypt. Their makers er ...
, one of the oldest manmade freestanding structures in the world. The Neolithic temple builders (3800–2500 BC) endowed the numerous temples of Malta and Gozo with intricate bas-relief designs, including spirals evocative of the tree of life and animal portraits, designs painted in red ochre, ceramics, and a vast collection of human form sculptures, particularly the Venus of Malta. These can be viewed at the temples themselves (most notably, the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni, Hypogeum and Tarxien Temples), and at the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta. Malta's temples such as Imnajdra are full of history and have a story behind them. Malta is currently undergoing several large-scale building projects, while areas such as the Valletta Waterfront and Tigné Point have been or are being renovated.
The Roman period introduced highly decorative mosaic floors, marble colonnades, and classical statuary, remnants of which are beautifully preserved and presented in the Roman Domus, a country villa just outside the walls of Mdina. The early Christian frescoes that decorate the catacombs beneath Malta reveal a propensity for eastern, Byzantine tastes. These tastes continued to inform the endeavours of medieval Maltese artists, but they were increasingly influenced by the Romanesque art, Romanesque and Southern Gothic movements.
Art
Towards the end of the 15th century, Maltese artists, like their counterparts in neighbouring Sicily, came under the influence of the School of Antonello da Messina, which introduced Renaissance ideals and concepts to the decorative arts in Malta. The artistic heritage of Malta blossomed under the Knights of St. John, who brought Italian and Flemish Mannerist painters to decorate their palaces and the churches of these islands, most notably, Matteo Perez d'Aleccio, whose works appear in the Grandmaster's Palace in Valletta, Magisterial Palace and in the St. John's Co-Cathedral, Conventual Church of St. John in Valletta, and Filippo Paladini, who was active in Malta from 1590 to 1595. For many years, Mannerism continued to inform the tastes and ideals of local Maltese artists. The arrival in Malta of Caravaggio, who painted at least seven works during his 15-month stay on these islands, further revolutionised local art. Two of Caravaggio's most notable works, ''The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist (Caravaggio), The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist'' and ''Saint Jerome Writing (Valletta), Saint Jerome Writing'', are on display in the Oratory (worship), Oratory of the Conventual Church of St. John. His legacy is evident in the works of local artists Giulio Cassarino (1582–1637) and Stefano Erardi (1630–1716). However, the Baroque movement that followed was destined to have the most enduring impact on Maltese art and architecture. The glorious vault paintings of the celebrated Calabrese artist, Mattia Preti transformed the severe, Mannerist interior of the Conventual Church St. John into a Baroque masterpiece. Preti spent the last 40 years of his life in Malta, where he created many of his finest works, now on display in the Museum of Fine Arts in Valletta. During this period, local sculptor Melchiorre Cafà, Melchior Gafà (1639–1667) emerged as one of the top Baroque sculptors of the Roman School.
The arrival in Malta of Caravaggio, who painted at least seven works during his 15-month stay on these islands, further revolutionised local art. Two of Caravaggio's most notable works, ''The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist (Caravaggio), The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist'' and ''Saint Jerome Writing (Valletta), Saint Jerome Writing'', are on display in the Oratory (worship), Oratory of the Conventual Church of St. John. His legacy is evident in the works of local artists Giulio Cassarino (1582–1637) and Stefano Erardi (1630–1716). However, the Baroque movement that followed was destined to have the most enduring impact on Maltese art and architecture. The glorious vault paintings of the celebrated Calabrese artist, Mattia Preti transformed the severe, Mannerist interior of the Conventual Church St. John into a Baroque masterpiece. Preti spent the last 40 years of his life in Malta, where he created many of his finest works, now on display in the Museum of Fine Arts in Valletta. During this period, local sculptor Melchiorre Cafà, Melchior Gafà (1639–1667) emerged as one of the top Baroque sculptors of the Roman School.
 During the 17th and 18th century, Naples, Neapolitan and Rococo influences emerged in the works of the Italian painters Luca Giordano (1632–1705) and Francesco Solimena (1657–1747), and these developments can be seen in the work of their Maltese contemporaries such as Gio Nicola Buhagiar (1698–1752) and Francesco Zahra (1710–1773). The Rococo movement was greatly enhanced by the relocation to Malta of Antoine de Favray (1706–1798), who assumed the position of court painter to Grand Master Pinto in 1744.
Neo-classicism made some inroads among local Maltese artists in the late-18th century, but this trend was reversed in the early 19th century, as the local Church authorities – perhaps in an effort to strengthen Catholic resolve against the perceived threat of Protestantism during the early days of British rule in Malta – favoured and avidly promoted the religious themes embraced by the Nazarene movement of artists. Romanticism, tempered by the naturalism introduced to Malta by Giuseppe Calì, informed the "salon" artists of the early 20th century, including Edward and Robert Caruana Dingli.
Parliament established the National School of Art in the 1920s. During the reconstruction period that followed the Second World War, the emergence of the "Modern Art Group", whose members included Josef Kalleya (1898–1998), George Preca (1909–1984), Anton Inglott (1915–1945), Emvin Cremona (1919–1987), Frank Portelli (artist), Frank Portelli (1922–2004), Antoine Camilleri (artist), Antoine Camilleri (1922–2005), Gabriel Caruana (1929–2018) and Esprit Barthet (1919–1999) greatly enhanced the local art scene. This group of forward-looking artists came together forming an influential pressure group known as the Modern Art Group. Together they forced the Maltese public to take seriously modern aesthetics and succeeded in playing a leading role in the renewal of Maltese art. Most of Malta's modern artists have in fact studied in Art institutions in England, or on the continent, leading to the explosive development of a wide spectrum of views and to a diversity of artistic expression that has remained characteristic of contemporary Maltese art. In Valletta, the National Museum of Fine Arts, Malta, National Museum of Fine Arts featured work from artists such as H. Craig Hanna."Right Outside my Window"
During the 17th and 18th century, Naples, Neapolitan and Rococo influences emerged in the works of the Italian painters Luca Giordano (1632–1705) and Francesco Solimena (1657–1747), and these developments can be seen in the work of their Maltese contemporaries such as Gio Nicola Buhagiar (1698–1752) and Francesco Zahra (1710–1773). The Rococo movement was greatly enhanced by the relocation to Malta of Antoine de Favray (1706–1798), who assumed the position of court painter to Grand Master Pinto in 1744.
Neo-classicism made some inroads among local Maltese artists in the late-18th century, but this trend was reversed in the early 19th century, as the local Church authorities – perhaps in an effort to strengthen Catholic resolve against the perceived threat of Protestantism during the early days of British rule in Malta – favoured and avidly promoted the religious themes embraced by the Nazarene movement of artists. Romanticism, tempered by the naturalism introduced to Malta by Giuseppe Calì, informed the "salon" artists of the early 20th century, including Edward and Robert Caruana Dingli.
Parliament established the National School of Art in the 1920s. During the reconstruction period that followed the Second World War, the emergence of the "Modern Art Group", whose members included Josef Kalleya (1898–1998), George Preca (1909–1984), Anton Inglott (1915–1945), Emvin Cremona (1919–1987), Frank Portelli (artist), Frank Portelli (1922–2004), Antoine Camilleri (artist), Antoine Camilleri (1922–2005), Gabriel Caruana (1929–2018) and Esprit Barthet (1919–1999) greatly enhanced the local art scene. This group of forward-looking artists came together forming an influential pressure group known as the Modern Art Group. Together they forced the Maltese public to take seriously modern aesthetics and succeeded in playing a leading role in the renewal of Maltese art. Most of Malta's modern artists have in fact studied in Art institutions in England, or on the continent, leading to the explosive development of a wide spectrum of views and to a diversity of artistic expression that has remained characteristic of contemporary Maltese art. In Valletta, the National Museum of Fine Arts, Malta, National Museum of Fine Arts featured work from artists such as H. Craig Hanna."Right Outside my Window", ''The Malta Independent'', 23 April 2006. Retrieved 11 June 2014 In 2018 the national collection of fine arts was moved and put on display in the new National Museum of Art, MUŻA, located at Auberge d'Italie, Auberge d’Italie in Valletta.
Cuisine
Customs
A 2010 Charities Aid Foundation study found that the Maltese were the most generous people in the world, with 83% contributing to charity. Maltese folktales include various stories about mysterious creatures and supernatural events. These were most comprehensively compiled by the scholar (and pioneer in Maltese archaeology) Manuel Magri, Manwel Magri in his core criticism "''Ħrejjef Missirijietna''" ("Fables from our Forefathers"). This collection of material inspired subsequent researchers and academics to gather traditional Folklore, tales, fables and legends from all over the Archipelago. Magri's work also inspired a series of comic books (released by Klabb Kotba Maltin in 1984): the titles included ''Bin is-Sultan Jiźźewweġ x-Xebba tat-Tronġiet Mewwija'' and ''Ir-Rjieħ''. Many of these stories have been popularly re-written as Children's literature by authors writing in Maltese, such as Trevor Żahra. While giants, witches, and dragons feature in many of the stories, some contain entirely Maltese creatures like the Kaw kaw, Il-Belliegħa and L-Imħalla among others. The traditional Maltese obsession with maintaining spiritual (or ritual) purity means that many of these creatures have the role of guarding forbidden or restricted areas and attacking individuals who broke the strict codes of conduct that characterised the island's pre-industrial society.Traditions
Traditional Maltese proverbs reveal cultural importance of childbearing and fertility: "''iż-żwieġ mingħajr tarbija ma fihx tgawdija''" (a childless marriage cannot be a happy one). This is a belief that Malta shares with many other Mediterranean cultures. In Maltese folktales the local variant of the classic closing formula, "and they all lived happily ever after" is "''u għammru u tgħammru, u spiċċat''" (and they lived together, and they had children together, and the tale is finished). Rural Malta shares in common with the Mediterranean society a number of superstitions regarding fertility, menstruation, and pregnancy, including the avoidance of cemeteries during the months leading up to childbirth, and avoiding the preparation of certain foods during menses. Pregnant women are encouraged to satisfy their food craving, cravings for specific foods, out of fear that their unborn child will bear a representational birth mark (Maltese: ''xewqa'', literally "desire" or "craving"). Maltese and Sicilian women also share certain traditions that are believed to predict the sex of an unborn child, such as the cycle of the moon on the anticipated date of birth, whether the baby is carried "high" or "low" during pregnancy, and the movement of a wedding ring, dangled on a string above the abdomen (sideways denoting a girl, back and forth denoting a boy). Traditionally, Maltese newborns were baptised as promptly as possible, should the child die in infancy without receiving this vital Sacrament; and partly because according to Maltese (and Sicilian) folklore an unbaptised child is not yet a Christian, but "still a Turk". Traditional Maltese delicacies served at a baptismal feast include ''biskuttini tal-magħmudija'' (almond macaroons covered in white or pink icing), ''it-torta tal-marmorata'' (a spicy, heart-shaped tart of chocolate-flavoured almond paste), and a liqueur known as ''rożolin'', made with rose petals, violets, and almonds. On a child's first birthday, in a tradition that still survives today, Maltese parents would organise a game known as ''il-quċċija'', where a variety of symbolic objects would be randomly placed around the seated child. These may include a hard-boiled egg, a Bible, crucifix or Rosary#Rosary beads, rosary beads, a book, and so on. Whichever object the child shows the most interest in is said to reveal the child's path and fortunes in adulthood. Money refers to a rich future while a book expresses intelligence and a possible career as a teacher. Infants who select a pencil or pen will be writers. Choosing Bibles or rosary beads refers to a clerical or monastic life. If the child chooses a hard-boiled egg, it will have a long life and many children. More recent additions include calculators (refers to accounting), thread (fashion) and wooden spoons (cooking and a great appetite). Traditional Maltese weddings featured the bridal party walking in procession beneath an ornate canopy, from the home of the bride's family to the parish church, with singers trailing behind serenading the bride and groom. The Maltese word for this custom is ''il-ġilwa''. This custom along with many others has long since disappeared from the islands, in the face of modern practices. New wives would wear the għonnella, a traditional item of Maltese clothing. However, it is no longer worn in modern Malta. Today's couples are married in churches or chapels in the village or town of their choice. The nuptials are usually followed by a lavish and joyous wedding reception, often including several hundred guests. Occasionally, couples will try to incorporate elements of the traditional Maltese wedding in their celebration. A resurgent interest in the traditional wedding was evident in May 2007, when thousands of Maltese and tourists attended a traditional Maltese wedding in the style of the 16th century, in the village of Żurrieq. This included ''il-ġilwa'', which led the bride and groom to a wedding ceremony that took place on the parvis of St. Andrew's Chapel. The reception that followed featured folklore music (''Għana (folk music), għana'') and dancing.Festivals and events
 Local festivals, similar to those in Southern Italy, are commonplace in Malta and Gozo, celebrating weddings, Baptism, christenings and, most prominently, saints' days, honouring the patron saint of the local parish. On saints' days, in the morning, the ''festa'' reaches its apex with a Mass (liturgy), High Mass featuring a sermon on the life and achievements of the patron saint. In the evening, then, a statue of the religious patron is taken around the local streets in solemn procession, with the faithful following in respectful prayer. The atmosphere of religious devotion is preceded by several days of celebration and revelry: band marches, fireworks, and late-night parties.
Maltese Carnival, Carnival (Maltese: ''il-karnival ta' Malta'') has had an important place on the cultural calendar after Grand Master (order), Grand Master Piero de Ponte introduced it to the islands in 1535. It is held during the week leading up to Ash Wednesday, and typically includes masked balls, fancy dress and grotesque mask competitions, lavish late-night parties, a colourful, ticker-tape parade of allegorical float (parade), floats presided over by King Carnival (Maltese: ''ir-Re tal-Karnival''), marching bands and costumed revellers.
Local festivals, similar to those in Southern Italy, are commonplace in Malta and Gozo, celebrating weddings, Baptism, christenings and, most prominently, saints' days, honouring the patron saint of the local parish. On saints' days, in the morning, the ''festa'' reaches its apex with a Mass (liturgy), High Mass featuring a sermon on the life and achievements of the patron saint. In the evening, then, a statue of the religious patron is taken around the local streets in solemn procession, with the faithful following in respectful prayer. The atmosphere of religious devotion is preceded by several days of celebration and revelry: band marches, fireworks, and late-night parties.
Maltese Carnival, Carnival (Maltese: ''il-karnival ta' Malta'') has had an important place on the cultural calendar after Grand Master (order), Grand Master Piero de Ponte introduced it to the islands in 1535. It is held during the week leading up to Ash Wednesday, and typically includes masked balls, fancy dress and grotesque mask competitions, lavish late-night parties, a colourful, ticker-tape parade of allegorical float (parade), floats presided over by King Carnival (Maltese: ''ir-Re tal-Karnival''), marching bands and costumed revellers.
 Holy Week in Malta, Holy Week (Maltese: ''il-Ġimgħa Mqaddsa'') starts on Palm Sunday (''Ħadd il-Palm'') and ends on Easter, Easter Sunday (''Ħadd il-Għid''). Numerous religious traditions, most of them inherited from one generation to the next, are part of the Easter celebrations in the Maltese Islands, honouring the death and resurrection of Jesus.
Maltese folklore#Mnarja, Mnarja, or l-Imnarja (pronounced ''lim-nar-ya'') is one of the most important dates on the Maltese cultural calendar. Officially, it is a national festival dedicated to the feast of Saints Saint Peter, Peter and Paul the Apostle, Paul. Its roots can be traced back to the pagan Roman Republic, Roman feast of ''Luminaria'' (literally, "the illumination"), when torches and bonfires lit up the early summer night of 29 June.
A national feast since the rule of the Knights Hospitaller, Knights, Mnarja is a traditional Maltese festival of food, religion and music. The festivities still commence today with the reading of the ''"bandu"'', an official governmental announcement, which has been read on this day in Malta since the 16th century. Originally, Mnarja was celebrated outside St. Paul's Grotto, in the north of Malta. However, by 1613 the focus of the festivities had shifted to St Paul's Cathedral, Mdina, St Paul's Cathedral in Mdina and featured torchlight processions, the firing of 100 petards, horseraces, and races for men, boys, and slaves. Modern Mnarja festivals take place in and around the woodlands of Buskett Gardens, Buskett, just outside the town of Rabat.
It is said that under the Knights, this was the one day in the year when the Maltese were allowed to hunt and eat hare, wild rabbit, which was otherwise reserved for the hunting pleasures of the Knights. The close connection between Mnarja and rabbit stew (Maltese: ''"fenkata"'') remains strong today.
In 1854 British governor William Reid (British Army officer), William Reid launched an agricultural show at Buskett which is still being held today. The farmers' exhibition is still a seminal part of the Mnarja festivities today.
Mnarja today is one of the few occasions when participants may hear traditional Maltese ''Għana (folk music), għana''. Traditionally, grooms would promise to take their brides to Mnarja during the first year of marriage. For luck, many of the brides would attend in their wedding gown and veil, although this custom has long since disappeared from the islands.
Isle of MTV is a one-day music festival produced and broadcast on an annual basis by MTV. The festival has been arranged annually in Malta since 2007, with major pop artists performing each year. 2012 saw the performances of worldwide acclaimed artists Flo Rida, Nelly Furtado and Will.i.am at Fosos Square in Floriana. Over 50,000 people attended, which marked the biggest attendance so far.
In 2009 the first New Year's Eve street party was organised in Malta, parallel to what major countries in the world organise. Although the event was not highly advertised, and was controversial due to the closing of an arterial street on the day, it is deemed to have been successful and will most likely be organised every year.
The Malta International Fireworks Festival is an annual festival that has been arranged in the
Holy Week in Malta, Holy Week (Maltese: ''il-Ġimgħa Mqaddsa'') starts on Palm Sunday (''Ħadd il-Palm'') and ends on Easter, Easter Sunday (''Ħadd il-Għid''). Numerous religious traditions, most of them inherited from one generation to the next, are part of the Easter celebrations in the Maltese Islands, honouring the death and resurrection of Jesus.
Maltese folklore#Mnarja, Mnarja, or l-Imnarja (pronounced ''lim-nar-ya'') is one of the most important dates on the Maltese cultural calendar. Officially, it is a national festival dedicated to the feast of Saints Saint Peter, Peter and Paul the Apostle, Paul. Its roots can be traced back to the pagan Roman Republic, Roman feast of ''Luminaria'' (literally, "the illumination"), when torches and bonfires lit up the early summer night of 29 June.
A national feast since the rule of the Knights Hospitaller, Knights, Mnarja is a traditional Maltese festival of food, religion and music. The festivities still commence today with the reading of the ''"bandu"'', an official governmental announcement, which has been read on this day in Malta since the 16th century. Originally, Mnarja was celebrated outside St. Paul's Grotto, in the north of Malta. However, by 1613 the focus of the festivities had shifted to St Paul's Cathedral, Mdina, St Paul's Cathedral in Mdina and featured torchlight processions, the firing of 100 petards, horseraces, and races for men, boys, and slaves. Modern Mnarja festivals take place in and around the woodlands of Buskett Gardens, Buskett, just outside the town of Rabat.
It is said that under the Knights, this was the one day in the year when the Maltese were allowed to hunt and eat hare, wild rabbit, which was otherwise reserved for the hunting pleasures of the Knights. The close connection between Mnarja and rabbit stew (Maltese: ''"fenkata"'') remains strong today.
In 1854 British governor William Reid (British Army officer), William Reid launched an agricultural show at Buskett which is still being held today. The farmers' exhibition is still a seminal part of the Mnarja festivities today.
Mnarja today is one of the few occasions when participants may hear traditional Maltese ''Għana (folk music), għana''. Traditionally, grooms would promise to take their brides to Mnarja during the first year of marriage. For luck, many of the brides would attend in their wedding gown and veil, although this custom has long since disappeared from the islands.
Isle of MTV is a one-day music festival produced and broadcast on an annual basis by MTV. The festival has been arranged annually in Malta since 2007, with major pop artists performing each year. 2012 saw the performances of worldwide acclaimed artists Flo Rida, Nelly Furtado and Will.i.am at Fosos Square in Floriana. Over 50,000 people attended, which marked the biggest attendance so far.
In 2009 the first New Year's Eve street party was organised in Malta, parallel to what major countries in the world organise. Although the event was not highly advertised, and was controversial due to the closing of an arterial street on the day, it is deemed to have been successful and will most likely be organised every year.
The Malta International Fireworks Festival is an annual festival that has been arranged in the Grand Harbour
The Grand Harbour ( mt, il-Port il-Kbir; it, Porto Grande), also known as the Port of Valletta, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It has been substantially modified over the years with extensive docks ( Malta Dockyard), wharves, a ...
of Valletta since 2003. The festival offers fireworks displays of a number of Maltese as well as foreign fireworks factories. The festival is usually held in the last week of April every year.
Media
The most widely read and financially the strongest newspapers are published by Allied Newspapers Ltd., mainly ''The Times of Malta'' (27 percent) and its Sunday edition ''The Sunday Times of Malta'' (51.6 percent). Due to Multilingualism, bilingualism half of the newspapers are published in English and the other half in Maltese. The Sunday newspaper ''It-Torċa'' ("The Torch") published by the Union Press, a subsidiary of the General Workers' Union (Malta), General Workers' Union, is the widest Maltese language paper. Its sister paper, ''L-Orizzont'' ("The Horizon"), is the Maltese daily with the biggest circulation. There is a high number of daily or weekly newspapers; there is one paper for every 28,000 people. Advertising, sales, and Subsidy, subsidies are the three main methods of financing newspapers and magazines. However, most of the papers and magazines tied to institutions are subsidised by the same institutions, they depend on advertising or subsidies from their owners. There are eight terrestrial television channels in Malta: TVM (Malta), TVM, TVMNews+, Parliament TV (Malta), Parliament TV, One (Maltese TV channel), One, NET Television (Malta), NET Television, Smash Television, F Living and Xejk. These channels are transmitted by digital terrestrial, free-to-air signals on Ultra high frequency, UHF channel 66. The state and List of political parties in Malta, political parties subsidise most of the funding of these television stations. TVM, TVMNews+, and Parliament TV are operated by Public Broadcasting Services, the public broadcasting, national broadcaster, and members of the European Broadcasting Union, EBU. Media.link Communications Ltd., the owner of NET Television, and One Productions Ltd., the owner of One, are affiliated with the Nationalist Party (Malta), Nationalist and Labour Party (Malta), Labour parties, respectively. The rest are privately owned. The Malta Broadcasting Authority supervises all local broadcasting stations and ensures their compliance with legal and licence obligations as well as the preservation of due impartiality; in respect of matters of political or industrial controversy or relating to current public policy; while fairly apportioning broadcasting facilities and time between persons belong to different political parties. The Broadcasting Authority ensures that local broadcasting services consist of public, private and community broadcasts that offer varied and comprehensive programming to cater for all interests and tastes. The Malta Communications Authority reported that there were 147,896 pay TV subscriptions active at the end of 2012, which includes analogue and digital cable, pay digital terrestrial TV and IPTV. For reference the latest census counts 139,583 households in Malta. Satellite reception is available to receive other European television networks such as the BBC from Great Britain and RAI and Mediaset from Italy.Sport
In 2018 Malta hosted its first Esports tournament, 'Supernova CS:GO Malta', a Counter-Strike: Global Offensive tournament with a $150,000 prize pool.See also
* Outline of Malta * Index of Malta-related articlesReferences
Notes
Sources
* * * * * *Omertaa, Journal for Applied Anthropology
olume 2007/1, Thematic Issue on Malta
Antonio Lafreri map of Malta, 1565
. Eran Laor Cartographic Collection. The National Library of Israel
Attribution
*Bibliography
* * * * * * * Charles Mifsud, The Climatological History of The Maltese Islands, Minerva 1984 * * * *Atauz, Ayse Devrim (2008)''Eight Thousand Years of Maltese Maritime History: Trade, Piracy, and Naval Warfare in the Central Mediterranean''
Gainesville : University Press of Florida.
Further reading
* Hastings, M. 2021. ''Operation Pedestral The Fleet that Battled to Malta 1942'', William Collins ISBN 978-0-00-836494-6External links
; GovernmentGov.mt
altese Government official site
Malta Environment and Planning Authority's
Geographic information system, GIS
Visit Malta
– Maltese tourism official site ; General information
Malta
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Malta
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * * * {{Authority control Malta, Collective recipients of the George Cross Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations English-speaking countries and territories Island countries Italian-speaking countries and territories Mediterranean islands Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union Pauline churches Phoenician colonies in Malta Southern European countries States and territories established in 1964 1964 establishments in Malta Countries in Europe Christian states Countries of Europe with multiple official languages