Malayta Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Malaita is the primary island of 
 Malaita's climate is extremely wet. It is located in the Intertropical Convergence Zone ("Doldrums"), with its fickle weather patterns. The sun is at zenith over Malaita, and thus the effect is most pronounced, in November and February.
Malaita's climate is extremely wet. It is located in the Intertropical Convergence Zone ("Doldrums"), with its fickle weather patterns. The sun is at zenith over Malaita, and thus the effect is most pronounced, in November and February.  Malaitan hydrology includes thousands of small springs, rivulets, and streams, characteristic of a young drainage pattern. At higher altitudes
Malaitan hydrology includes thousands of small springs, rivulets, and streams, characteristic of a young drainage pattern. At higher altitudes
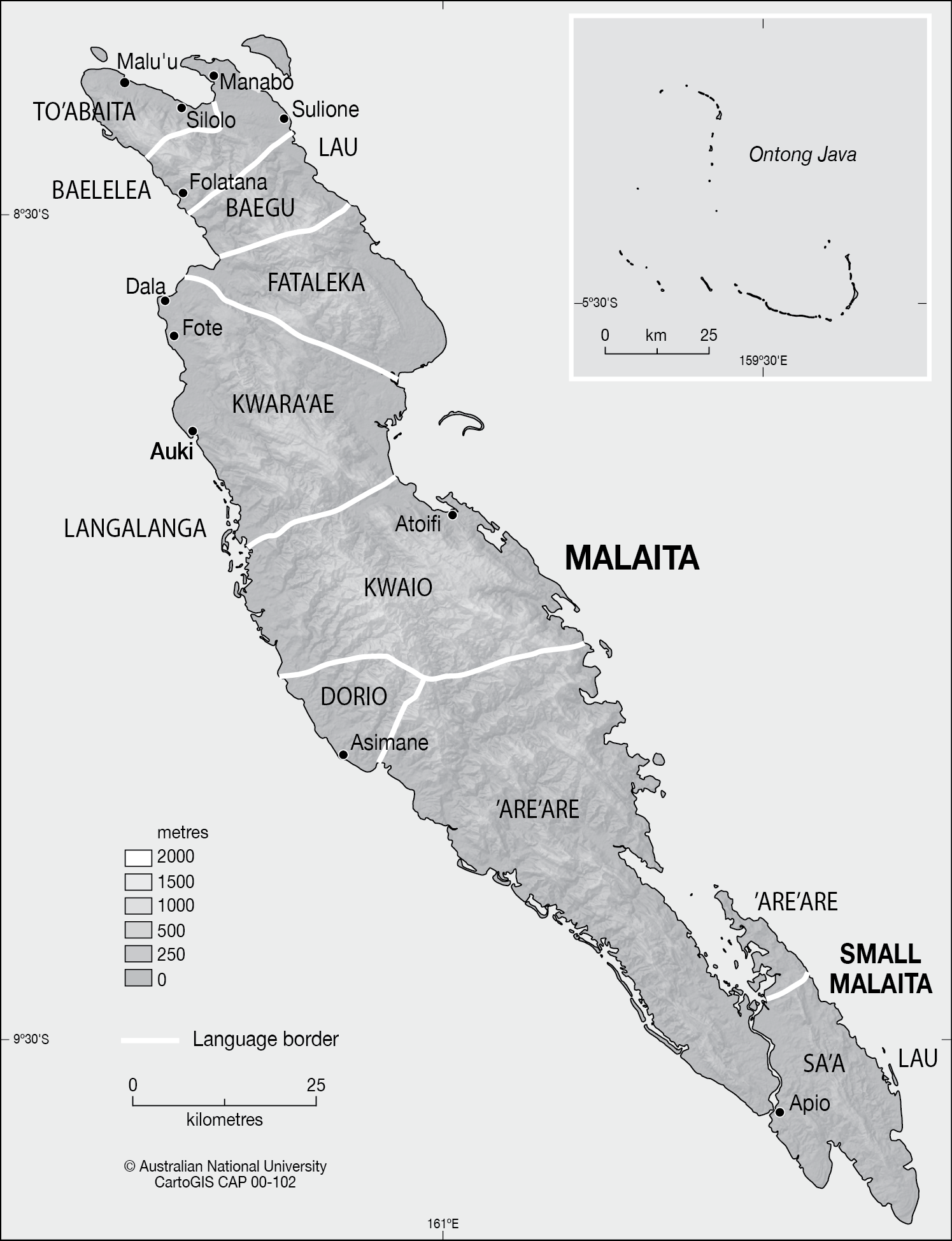 Malaitans speak a variety of languages within the Malaitan language family, a subbranch of the
Malaitans speak a variety of languages within the Malaitan language family, a subbranch of the
Malaita Province
Malaita Province is the most populous and one of the largest of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. It is named after its largest island, Malaita (also known as "Big Malaita" or "Maramapaina"). Other islands include South Malaita Island (a ...
in Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
. Malaita is the most populous island of the Solomon Islands, with a population of 161,832 as of 2021, or more than a third of the entire national population. It is also the second largest island in the country by area, after Guadalcanal. A tropical and mountainous island, Malaita's river systems and tropical forests are being exploited for ecosystem stability by keeping them pristine.
The largest city and provincial capital is Auki
Auki is the provincial capital of Malaita Province, Solomon Islands. It is situated on the northern end of Langa Langa Lagoon on the north-west coast of Malaita Island. It is one of the largest provincial towns in Solomon Islands. It was establi ...
, on the northwest coast and is on the northern shore of the Langa Langa Lagoon
Langa Langa Lagoon or ''Akwalaafu'' is a natural lagoon on the West coast of Malaita near the provincial capital Auki within the Solomon Islands. The lagoon is 21 km in length and just under 1 km wide. The "lagoon people" or "salt wa ...
. The people of the Langa Langa Lagoon and the Lau Lagoon
Lau Lagoon is a part of the Solomon Islands. It is located on the northeast coast of Malaita Island. The lagoon is more than 35 kilometers long and contains about 60 artificial islands built on the reef.
The Lau lagoon is home to a number ...
on the northeast coast of Malaita call themselves ''wane i asi'' ‘salt-water people’ as distinct from ''wane i tolo'' ‘bush people’ who live in the interior of the island.

South Malaita Island
South Malaita Island is the island at the southern tip of the larger island of Malaita in the eastern part of the Solomon Islands. It is also known as Small Malaita and Maramasike for Areare speakers and Malamweimwei for more than 80% of the isla ...
, also known as ''Small Malaita'' and ''Maramasike'' for Areare speakers and Malamweimwei known to more than 80% of the islanders, is the island at the southern tip of the larger island of Malaita.
Name
Most local names for the island are Mala, or its dialect variants Mara or Mwala. The name Malaita or Malayta appears in the logbook of the Spanish explorers who in the 16th century visited the islands, and claimed that to be the actual name. They first saw the island from Santa Isabel, where it is called Mala. One theory is that "ita" was added on, as the Bughotu word for up or east, or in this context "there." BishopGeorge Augustus Selwyn
George Augustus Selwyn (5 April 1809 – 11 April 1878) was the first Anglican Bishop of New Zealand. He was Bishop of New Zealand (which included Melanesia) from 1841 to 1869. His diocese was then subdivided and Selwyn was Metropolitan (later ...
referred to it as Malanta in 1850. Mala was the name used under British control; now Malaita is used for official purposes. The name Big Malaita is also used to distinguish it from the smaller South Malaita Island
South Malaita Island is the island at the southern tip of the larger island of Malaita in the eastern part of the Solomon Islands. It is also known as Small Malaita and Maramasike for Areare speakers and Malamweimwei for more than 80% of the isla ...
.
History
Early settlement and European discovery
Malaita was, along with the other Solomon Islands, settled by Austronesian speakers between 5000 and 3500 years ago; the earlier Papuan speakers are thought to have only reached the western Solomon Islands. However, Malaita has not been archaeologically examined, and a chronology of its prehistory is difficult to establish. In the traditional account of theKwara'ae
The Kwara'ae language (previously called Fiu after the location of many of its speakers) is spoken in the north of Malaita Island in the Solomon Islands. In 1999, there were 32,400 people known to speak the language. It is the largest indigenous ...
, their founding ancestor arrived about twenty generations ago, landed first on Guadalcanal, but followed a magical staff which led him on to the middle of Malaita, where he established their cultural norms. His descendants then dispersed to the lowland areas on the edges of the island.
First recorded sighting by Europeans of Malaita was by the Spaniard Álvaro de Mendaña on 11 April 1568. More precisely the sighting was due to a local voyage done by a small boat, in the accounts the brigantine Santiago, commanded by Maestre de Campo Pedro Ortega Valencia
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish, Portuguese, and Galician name for ''Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter.
The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning " ...
and having Hernán Gallego Hernán is a Spanish masculine given name, originating from Germanic Hernan in the Visigoth culture in Spain. It is the Latinized version of the compound name ''Fard-nanth'', which seems to mean "gentle traveler" or "spiritual traveler". The House ...
as pilot. In his account, Gallego chief pilot of Mendaña's expedition, establishes that they called the island Malaita after its native name and explored much of the coast, though not the north side. The Maramasiki Passage was thought to be a river. At one point they were greeted with war canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
s and fired at with arrows; they retaliated with shots and killed and wounded some. However, after this discovery, the entire Solomon Islands chain was not found, and even its existence doubted, for two hundred years.
Labour trade and missions
After it was re-discovered in the late 18th century, Malaitans were subjected to harsh treatment fromwhaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
boat crews and blackbirders (labour recruiters). Contact with outsiders also brought new opportunities for education. The first Malaitans to learn to read and write were Joseph Wate and Watehou, who accompanied Bishop John Coleridge Patteson
John Coleridge Patteson (1 April 1827 – 20 September 1871) was an English Anglican bishop, missionary to the South Sea Islands, and an accomplished linguist, learning 23 of the islands' more than 1,000 languages.
In 1861, Patteson was s ...
to St John's College, Auckland.
From the 1870s to 1903 Malaitan men (and some women) comprised the largest number of Solomon Islander Kanaka workers in the indentured labour trade to Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
, Australia and to Fiji. The 1870s were a time of illegal recruiting practices known as blackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people in ...
. Malaitans are known to have volunteered as indentured labourers with some making their second trip to work on plantations, although the labour system remained exploitative. In 1901 the Commonwealth of Australia enacted the Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901
The Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901 was an Act of the Parliament of Australia which was designed to facilitate the mass deportation of nearly all the Pacific Islanders (called "Kanakas") working in Australia, especially in the Queensland sugar ...
which facilitated the deportation of Pacific Islanders that was the precursor to the White Australia policy
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin, especially Asians (primarily Chinese) and Pacific Islanders, from immigrating to Australia, starting i ...
. However, many islanders remained and formed the South Sea Islander
South Sea Islanders are the Australian descendants of Pacific Islanders from more than 80 islandsincluding the Oceanian archipelagoes of the Solomon Islands, New Caledonia, Vanuatu, Fiji, the Gilbert Islands and New Irelandwho were kidnappe ...
community of Australia. Many labourers that returned to Malaita had learnt to read and had become Christian. The skills of literacy and protest letters as to being deported from Australia was a precedent for the later Maasina Ruru
Maasina Ruru was an emancipation movement for self-government and self-determination in the British Solomon Islands during and after World War II, 1945–1950, credited with creating the movement towards independence for the Solomon Islands. The ...
movement.
Many of the earliest missionaries, both Catholic and Protestant, were killed, and this violent reputation survives in the geographic name of Cape Arsacides, the eastward bulge of the northern part of the island, meaning Cape of the Assassins. The cape was even mentioned in Herman Melville
Herman Melville ( born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); ''Typee'' (1846), a rom ...
's epic novel ''Moby Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is the sailor Ishmael's narrative of the obsessive quest of Ahab, captain of the whaling ship ''Pequod'', for revenge against Moby Dick, the giant whi ...
'' by Ishmael, the novel's narrator. Ishmael talks of his friendship with the fictional Tranquo, King of Tranque. However, some of the earliest missionaries were Malaitans who had worked abroad, such as Peter Ambuofa Peter Ambuofa was an early convert to Christianity among Solomon Islanders who established a Christian community on Malaita, and a key figure in the history of the South Seas Evangelical Mission (now South Seas Evangelical Church, SSEC).
Peter Amb ...
, who was baptised at Bundaberg, Queensland
Bundaberg is a city in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia, and is the tenth largest city in the state. Bundaberg's regional area has a population of 70,921, and is a major centre of the Wide Bay–Burnett geographical region. The Bun ...
in 1892, and gathered a Christian community around him when he returned in 1894. In response to his appeals, Florence Young
Florence Selina Harriet Young (10 October 1856 – 28 May 1940) was a New Zealand-born missionary who established the Queensland Kanaka Mission in order to convert Kanaka (Pacific Island worker), Kanaka labourers in Queensland, Australia. In addit ...
led the first party of the Queensland Kanaka Mission (the ancestor of the SSEC) to the Solomons in 1904. Anglican and Catholic churches also missionized at this point, and set up schools in areas such as Malu'u
Malu'u is a village on the north coast of Malaita island in the Solomon Islands. The seat of the sub provincial area, it lies on Suafa Bay, within Malaita Province, along the road between Auki and Lau Lagoon.
History
The Anglican missionaries Ho ...
.
As the international labour trade slowed, an internal labour trade within the archipelago developed, and by the 1920s thousands of Malaitans worked on plantations on other islands.
Establishment of colonial power
At this time, there was no central power among the groups on Malaita, and there were numerousblood feud
A feud , referred to in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, or private war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially families or clans. Feuds begin because one pa ...
s, exacerbated by the introduction of Western guns, and steel tools which meant less time constraints for gardening. Around 1880, Kwaisulia, one of the chiefs, negotiated with labour recruiters to receive a supply of weapons in exchange of workers, based on a similar negotiation made by a chief on the Shortland Islands
The Shortland Islands is an archipelago of Western Province, Solomon Islands, at . The island group lies in the extreme north-west of the country's territory, close to the south-east edge of Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea.
The largest isl ...
; this weapon supply gave the chiefs considerable power. However, labour recruitment was not always smooth. In 1886, the vessel ''Young Dick'' was attacked at Sinerango, Malaita, and most of its crew murdered.Kent, 102. In 1886, Britain defined its area of interest in the Solomons, including Malaita, and central government control of Malaita began in 1893, when Captain Gibson R.N., of , declared the southern Solomon Islands as a British Protectorate with the proclamation of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate
The British Solomon Islands Protectorate was first declared over the southern Solomons in 1893, when Captain Gibson, R.N., of , declared the southern islands a British protectorate. Other islands were subsequently declared to form part o ...
, claiming to regulate the local warfare and unfair labour trade, although it coincided with the German acquisition of territories to the west and French interest in those to the east.
Auki
Auki is the provincial capital of Malaita Province, Solomon Islands. It is situated on the northern end of Langa Langa Lagoon on the north-west coast of Malaita Island. It is one of the largest provincial towns in Solomon Islands. It was establi ...
was established as a government station in 1909, as headquarters of the administrative district of Malaita. The government began to pacify the island, registering or confiscating firearms, collecting a head tax, and breaking the power of unscrupulous war leaders. One important figure in the process was District Commissioner William R. Bell, who was killed in 1927 by a Kwaio, along with a cadet named Lillies and 13 Solomon Islanders in his charge. A massive punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beh ...
, known as the Malaita massacre
The Malaita massacre inflicted a large number of deaths on the island of Malaita in the Solomon Islands in late 1927. William R. Bell, the District Officer of Malaita in the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, and many of his deputies were ki ...
, ensued; at least 60 Kwaio were killed, nearly 200 detained in Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island——in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1 ...
(the protectorate capital), and many sacred sites and objects were destroyed or desecrated. Resentment about this incident continues, and in 1983 leaders from the Kwaio area council requested that the national government demand from the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
about $100 million in compensation for the incident. When the central government did not act on this request, the council encouraged a boycott of the 1986 national elections.
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, which played a major role in Solomons history, did not have a major impact upon Malaita. Auki became the temporary capital when Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island——in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1 ...
was seized by the Japanese, and it too was briefly raided by Japan, but little fighting happened on the island. Malaitans who fought in battalions, however, brought a new movement for self-determination known as Maasina Ruru
Maasina Ruru was an emancipation movement for self-government and self-determination in the British Solomon Islands during and after World War II, 1945–1950, credited with creating the movement towards independence for the Solomon Islands. The ...
(or "Marching Rule"), which spread quickly across the island. Participants united across traditional religious, ethnic, and clan lines, lived in fortified nontraditional villages, and refused to cooperate with the British.Ross, 58-59. The organization of the movement on Malaita was considerable. The island was divided into nine districts, roughly along the lines of the government administrative districts, and leaders were selected for each district. Courts were set up, each led by a custom chief (''alaha'ohu''), who became powerful figures.Kent, 146. The British initially treated the movement cautiously, even praised aspects of it, but when they found there could be no common ground between the government and the movement, retaliated firmly, with armed police patrols, insisting that the chiefs recant or be arrested. Some did recant, but in September 1947 most were tried in Honiara, charged with terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
or robbery, and convicted to years of hard labour.
However, the movement continued underground, and new leaders renamed the organization the Federal Council. The High Commissioner visited Malaita to negotiate a settlement, and proposed the formation of the Malaita Council, which would have a president elected by members, though they would have to recognize the government's authority and agree to cooperate with their administrators.Kent, 149. The council became the first installment of local government in the Solomon Islands, and its first president was Salana Ga'a. The establishment of the council reduced the tension on Malaita, although Maasina Rule elements did continue until at least 1955. The council was shown not to be simply a means of appeasement, but submitted nearly seventy resolutions and recommendations to the High Commissioner in its first two years of existence.
Post-independence
The Solomon Islands were granted independence in July 1978. The first prime minister wasPeter Kenilorea
Sir Peter Kenilorea KBE (23 May 1943 – 24 February 2016) was a Solomon Islander politician, officially styled The Rt Hon. Sir Peter Kenilorea as a member of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. He was the first Prime Minister of an indepe ...
from 'Are'are (Malaita). The provinces were re-organized in 1981, and Malaita became the main island of Malaita Province. Malaita remains the most populous island in the country, and continues to be a source for migrants, a role it played since the days of the labour trade. There are villages of Malaitans in many provinces, including eight " squatter" settlements that make up about 15 percent of the population of Honiara, on Guadalcanal.
Malaitans who had emigrated to Guadalcanal became a focus of the civil war which broke out in 1999, and the Malaita Eagle Force
The Malaita Eagle Force was a militant organisation, originating in the island of Malaita, in the Solomon Islands. It was formed in the early 2000s and soon crossed over to Honiara, the capital of Solomon Islands.
It was set up during 'The Ten ...
(MEF) was formed to protect their interest, both on Guadalcanal and on their home island. The organization of Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands
The Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI), also known as Operation Helpem Fren, Operation Anode and Operation Rata (by New Zealand), was created in 2003 in response to a request for international aid by the Governor-General of ...
(RAMSI) has contributed to the infrastructure development of the island.
After the Solomon Islands switched diplomatic recognition to China from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
in 2019, with a delegation led by prime minister Manasseh Sogavare
Manasseh Damukana Sogavare (born 17 January 1955) is the sixth and current Prime Minister of the Solomon Islands, serving since 24 April 2019. He previously held the office in 2000–2001, 2006—2007 and 2014–2017; in all he has served over ni ...
being received with great hostility and the provincial government refusing to discuss the topics Sogavare had originally arrived to discuss, instead airing concerns over the diplomatic switch. Mass pro-Taiwan protests broke out throughout Malaita, and some protesters even demanded independence from the Solomon Islands, sparking concerns over the fragility of the government.
Geography
Malaita is a thin island, about long and wide at its widest point. Its length is in a north-northwest-to-south-southeast direction, but local custom and official use generally rotate it to straight north-south orientation, and generally refer to the "east coast" or "northern end," when northeast or northwest would be more accurate. To the southwest is the Indispensable Strait, which separates it from Guadalcanal and the Florida Islands. To the northeast and east is openPacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
, except for the small Sikaiana
Sikaiana (formerly called the Stewart Islands) is a small atoll NE of Malaita in Solomon Islands in the south Pacific Ocean. It is almost in length and its lagoon, known as Te Moana, is totally enclosed by the coral reef. Its total land s ...
, part of the province northeast. To the northwest of the island is Santa Isabel Island
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province.
Location and geographic data
Choiseul lies t ...
. To the immediate southwest is South Malaita Island (also called Small Malaita or Maramasike), separated by the narrow Maramasike Passage. Beyond that is Makira
The island of Makira (also known as San Cristobal and San Cristóbal) is the largest island of Makira-Ulawa Province in the Solomon Islands. It is third most populous island after Malaita and Guadalcanal, with a population of 55,126 as of 2020. ...
, the southernmost large island in the Solomon archipelago.
 Malaita's climate is extremely wet. It is located in the Intertropical Convergence Zone ("Doldrums"), with its fickle weather patterns. The sun is at zenith over Malaita, and thus the effect is most pronounced, in November and February.
Malaita's climate is extremely wet. It is located in the Intertropical Convergence Zone ("Doldrums"), with its fickle weather patterns. The sun is at zenith over Malaita, and thus the effect is most pronounced, in November and February. Trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
come during the Southern Hemisphere's winter, and from about April to August they blow from the southeast fairly steadily. During the summer, fringes of monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
blow over the island. Because of the surrounding sea, air temperatures are fairly consistent, with a difference between daily highs and lows averaging to . However, across the year, the difference is much less; the mean daily temperature in the warmest month is only warmer than that of the coolest. Rainfall is heavy and there is constant high humidity. The most common daily pattern follows an adiabatic process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: ''adiábatos'', "impassable") is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. Unlike an isothermal proces ...
, with a calm, clear morning, followed by a breeze blowing in from higher pressures over the sea, culminating in a cloudy and drizzly afternoon. At night, the weather pattern reverses, and drizzle and heavy dew dissipate the cloud cover for the morning. Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depen ...
s are the only violent weather, but they can be destructive.
Like the other islands in the archipelago, Malaita is near the Andesite line and thus forms part of the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring o ...
. Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s are common on the island, but there is little evidence of current volcanic activity. The main structural feature of Malaita is the central ridge which runs along the length of the island, with flanking ridges and a few outlying hills. There is a central hilly country, between Auki and the Kwai Harbour, which separates the central ridge into northern and southern halves, the latter being somewhat longer. The northern ridge reaches a height of about , while the southern goes up to . Geologically, Malaita has a basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic intrusive core, covered in most places by strata of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
, especially limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
and chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a ...
, and littered with fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s. The limestone provides numerous sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s and cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
rns.
 Malaitan hydrology includes thousands of small springs, rivulets, and streams, characteristic of a young drainage pattern. At higher altitudes
Malaitan hydrology includes thousands of small springs, rivulets, and streams, characteristic of a young drainage pattern. At higher altitudes waterfall
A waterfall is a point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in severa ...
s are common, and in some places canyons have been cut through the limestone. Nearer the coasts, rivers are slower and deeper, and form mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
swamps of brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
, along with alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. All ...
deposits of gravel, sand, or mud. The coastal plain is very narrow. Inland soils are of three types, wet black, dry black, and red. The wet black soil, too poorly drained for most horticulture except taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
, is found in valleys or at the foot of slopes. Dry black makes the best gardening sites. The red soil, probably laterite, does not absorb runoff and forms a hard crust, and is preferred for settlement sites.
Environment
There are several vegetation zones based on altitude. Along the coast is either a rocky or sandy beach, where pandanus, coconuts, and vines predominate, or a swamp, supporting mangrove andsago
Sago () is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of ''Metroxylon sagu''. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is c ...
palms. ''Terminalia
Terminalia may refer to:
* Terminalia (festival), a Roman festival to the god of boundaries Terminus
* ''Terminalia'' (plant), a tree genus
* Terminalia (insect anatomy), the terminal region of the abdomen in insects
* ''Polyscias terminalia'', a ...
'' grows in some drier areas. The lower slopes, up to about , have a hardwood forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
These fo ...
of banyan
A banyan, also spelled "banian", is a fig that develops accessory trunks from adventitious prop roots, allowing the tree to spread outwards indefinitely. This distinguishes banyans from other trees with a strangler habit that begin life as a ...
s, '' Canarium'', Indo-Malayan hardwoods, and, at higher altitudes, bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
. In forested groves, there is relatively little undergrowth. In this zone is also the most intense human cultivation, which, when abandoned, a dense secondary forest grows, which is nearly impassably thick with shrubs and softwoods. Above about is a cloud forest, with a dense carpeting of mosses, lichens, and liverwort
The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of ...
s, with cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male o ...
s as the dominant tall plant.
Like most Pacific islands, there are not large numbers of mammals. Apart from several species of bats, there are introduced species of pigs, cuscuses and rodents. There are also dugongs
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest m ...
in the mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
swamps, and sometimes dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s in the lagoon.
Reptiles and amphibians are common as well, especially skinks and geckos. Crocodiles were once common, but have been so frequently hunted for their hides that they are nearly extinct. There are several venomous sea snakes and two species of venomous land snakes, in the elapid family. There are also numerous species of frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s of various sizes.
Fish and aquatic invertebrates are typical of the Indo-Pacific region. There are a few species of freshwater fish (including mudskippers and several other species of teleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tele ...
fish), mangrove crab
Mangrove crabs are crabs that live among mangroves, and may belong to many different species and even families. They have been shown to be ecologically significant in many ways. They keep much of the energy within the forest by burying and cons ...
s and coconut crab
The coconut crab (''Birgus latro'') is a species of terrestrial hermit crab, also known as the robber crab or palm thief. It is the largest terrestrial arthropod in the world, with a weight of up to . It can grow to up to in width from the tip ...
s. On land, centipedes, scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always en ...
s, spider
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species ...
s, and especially insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s are very common. All common orders of insects are represented, including some spectacular butterflies. The common Anopheles
''Anopheles'' () is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus ''Plasmodium'', which ...
mosquito ensures that vivax malaria is endemic.
Malaitans once believed in anthropoid apes that lived in the centre of the island, which are said to be tall and come in troops to raid banana plantations.
There are a great number and variety of birds. Almost every family of avifauna were found in Ernst Mayr's 1931 survey. Several species of parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
s, cockatoo
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea (true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the orde ...
s, and owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
s are kept as pets. Some bird species are endemic to Malaita.
Important Bird Area
The Malaita Highlands form a site that has been identified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area (IBA) because it supports populations ofthreatened
Threatened species are any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which are vulnerable to endangerment in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensa ...
or endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
bird species. At 58,379 ha, it encompasses the highest peak of the island and the surrounding montane and lowland forest. Significant birds for which the site was identified include metallic pigeons, chestnut-bellied imperial pigeons, pale mountain pigeons, duchess lorikeet
The duchess lorikeet (''Charmosynoides margarethae'') is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It is the only species placed in the genus ''Charmosynoides''. It is found throughout the Solomon Islands archipelago. Its natural habitats ...
s and the endemic red-vested myzomelas, Malaita fantails and Malaita white-eyes. Potential threats to the site include logging and human population growth.
Dolphin hunting
According to Malaitian oral history, a Polynesian woman named Barafaifu introduceddolphin drive hunting
Dolphin drive hunting, also called dolphin drive fishing, is a method of hunting dolphins and occasionally other small cetaceans by driving them together with boats and then usually into a bay or onto a beach. Their escape is prevented by closing ...
from Ontong Java Atoll
Ontong Java Atoll or Luangiua, (formerly ''Lord Howe Atoll'', not to be confused with Lord Howe Island) is one of the largest atolls on earth.
Geographically it belongs to a scattered group of three atolls which includes nearby Nukumanu Atol ...
; she settled in Fanalei village in South Malaita as it was the place for hunting. Dolphin hunting ceased in the mid-19th century, possibly because of the influence of Christian missionaries. However, in 1948 it was revived at settlements on several islands, including Fanalei, Walande (10 km to the north), Ata'a, Felasubua, Sulufou (in the Lau Lagoon
Lau Lagoon is a part of the Solomon Islands. It is located on the northeast coast of Malaita Island. The lagoon is more than 35 kilometers long and contains about 60 artificial islands built on the reef.
The Lau lagoon is home to a number ...
) and at Mbita'ama harbour. In most of these communities, the hunt had ceased again by 2004. However, Fanalei in South Malaita remained the preeminent dolphin hunting village.
The dolphins are hunted as food, for their teeth, and for live export. The teeth of certain species have a value for trade, brideprice ceremonial traditions, funeral feasts, and compensation. The teeth of melon-headed whale
The melon-headed whale (''Peponocephala electra''), also known less commonly as the electra dolphin, little killer whale, or many-toothed blackfish, is a toothed whale of the oceanic dolphin family (Delphinidae). The common name is derived fro ...
were traditionally the most desirable; however, they were over-hunted and became locally rare. The other species hunted are spinner dolphin
The spinner dolphin (''Stenella longirostris'') is a small dolphin found in off-shore tropical waters around the world. It is famous for its acrobatic displays in which it rotates around its longitudinal axis as it leaps through the air. It is a ...
and the pantropical spotted dolphin
The pantropical spotted dolphin (''Stenella attenuata'') is a species of dolphin found in all the world's temperate and tropical oceans. The species was beginning to come under threat due to the killing of millions of individuals in tuna purse s ...
. While Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin
The Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops aduncus'') is a species of bottlenose dolphin. This dolphin grows to long, and weighs up to . It lives in the waters around India, northern Australia, South China, the Red Sea, and the eastern ...
(''Tursiops aduncus'') have been captured for live export, the bottlenose dolphin is not hunted as the teeth are not considered to have any value.
In recent years only villages on South Malaita Island
South Malaita Island is the island at the southern tip of the larger island of Malaita in the eastern part of the Solomon Islands. It is also known as Small Malaita and Maramasike for Areare speakers and Malamweimwei for more than 80% of the isla ...
have continued to hunt dolphin. In 2010, the villages of Fanalei, Walende, and Bitamae signed a memorandum of agreement with the non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from g ...
, Earth Island Institute
The Earth Island Institute is a non-profit environmental group founded in 1982 by David Brower. Located in Berkeley, California, it supports activism around environmental issues through fiscal sponsorship that provides the administrative and org ...
, to stop hunting dolphin. However, in early 2013 the agreement broke down and some men in Fanalei resumed hunting. The hunting of dolphin continued in early 2014. Researchers from the South Pacific Whale Research Consortium, the Solomon Islands Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources, and Oregon State University
Oregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant, research university in Corvallis, Oregon. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. It has the 10th largest engineering c ...
’s Marine Mammal Institute have concluded that hunters from the village of Fanalei in the Solomon Islands have killed more than 1,600 dolphins in 2013, included at least 1,500 pantropical spotted dolphins, 159 spinner dolphins and 15 bottlenose dolphins
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the comm ...
. The total number killed during the period 1976-2013 was more than 15,400.
The price at which dolphin teeth are traded in Malaita rose from the equivalent of 18c in 2004 to about 90c in 2013.
Demographics and culture
Malaitans are of a varyingphenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
. The skin varies from rich chocolate to tawny, most clearly darker than Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
ns, but not generally as dark as the peoples of Bougainville or the western Solomons, whom Malaitans refer to as "black men". Most have dark brown or black bushy hair, but it varies in colour from reddish blond, yellow to whitish blond, to ebony black, and in texture from frizzled to merely wavy. Tourists often mistakenly believe the blond hair of Malaitans is bleached by peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where R = any element. The group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable.
The most common peroxide is hydrogen ...
, but this is not so; the blond or reddish hair colour is quite natural. Male-pattern baldness is widespread, but not as common as among Europeans. Most have smooth skin, but some grow hair on their arms, legs, and chest, and have beards. Most Malaitans are shorter than average Europeans, though not as short as Negrito
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the O ...
s. Relatively robust physiques are more common among coastal populations, while people from higher altitudes tend to be leaner.
Languages and ethnic groups
 Malaitans speak a variety of languages within the Malaitan language family, a subbranch of the
Malaitans speak a variety of languages within the Malaitan language family, a subbranch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
. The diversity is not as great as once thought, and some of the groups are mutually intelligible. Some of the exaggeration in the number of languages may be due to the inappropriateness of lexicostatistical techniques and glottochronological analysis, given the widespread use of word taboo
Word taboo, also called taboo language, language taboo or linguistic taboo is a kind of taboo that involves restricting the use of words or other parts of language due to social constraints. This may be due to a taboo on specific parts of the langu ...
and metathesis as word play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, pho ...
. According to Harold M. Ross, from north to south along the island's axis, the linguistic groups are roughly the Northern Malaita languages (more properly a collection of dialects without a standard name, generally To'abaita, Baelelea, Baegu, Fataleka, and Lau
Lau or LAU may refer to:
People
* Lau (surname)
* Liu (劉/刘), a common Chinese family name transliterated Lau in Cantonese and Hokkien
* Lau clan, one of the Saraswat Brahmin clans of Punjab
* LAU (musician): Laura Fares
Places
* Lebane ...
), Kwara'e in the hilly area between the ridges, Kwaio
Kwaio is an ethnic group found in central Malaita, in the Solomon Islands. According to Ethnologue, they numbered 13,249 in 1999. Much of what is known about the Kwaio is due to the work of the anthropologist Roger M. Keesing, who lived among t ...
in about the geographic centre of the island, and 'Are'are to the south. Each of these spreads across the width of the island. In addition, there is the Langalanga in a lagoon on the west coast between the Kwara'ae and Kwaio regions, and Kwarekwareo on the western coast between the Kwaio and 'Are'are regions, which may be a dialect of Kwaio. Sa'a, spoken on South Malaita, is also a member of the family. Mutual intelligibility is also aided by the large degree of trade and intermarriage among the groups.
The peoples of Malaita share many aspects of their culture, although they are generally divided into ethnic groups along linguistic lines. In pre-colonial times, settlements were small and moved frequently. Both agnatic descent (patrilineal lines from a founding ancestor) and cognatic descent (through links of outmarrying women) are important. These lineages determine rights of residence and land use in a complex way. In the northern area, local descent groups, united in ritual hierarchies, are largely autonomous, but conceptualize their relationship as a phratry
In ancient Greece, a phratry ( grc, φρᾱτρῐ́ᾱ, phrātríā, brotherhood, kinfolk, derived from grc, φρᾱ́τηρ, phrā́tēr, brother, links=no) was a group containing citizens in some city-states. Their existence is known in most I ...
in a manner similar to certain groups in highland New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
. In the central area, local descent groups are fully autonomous, though still linked by ritual. In the south, the 'Are'are people Areare or Are'are may refer to:
*ꞌAreꞌare people, an ethnic group in the Solomon Islands
*ꞌAreꞌare language
The Areare language is spoken by the ꞌAreꞌare people of the southern part of Malaita island, as well as nearby South Malaita ...
developed a more hierarchical organization and more outward orientation, a cultural tradition that reaches its peak on the hereditary chiefs and rituals of Small Malaita to the south. One exception to these generalizations are cultures which have migrated in more recent times, such as the northern Lau
Lau or LAU may refer to:
People
* Lau (surname)
* Liu (劉/刘), a common Chinese family name transliterated Lau in Cantonese and Hokkien
* Lau clan, one of the Saraswat Brahmin clans of Punjab
* LAU (musician): Laura Fares
Places
* Lebane ...
, who settled in several seaside areas (and offshore islands) in southern Malaita about 200 years ago, and with whom there has been little cultural exchange.
Religion
The traditional religion of the island isancestor worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of t ...
. In one oral tradition, the earliest residents knew the name of the creator, but thought his name was so holy that they did not want to tell their children. Instead, they instructed their children to address their requests to their ancestors, who would be their mediators.Leslie Fugui and Simeon Butu, "Religion," in ''Ples Blong Iumi'', 76. In some parts of Malaita the high god responsible for creation, who has now retired from active work, is known as ''Agalimae'' ("the god of the universe"). Congregations of local descent groups propitiate their ancestors at shrine
A shrine ( la, scrinium "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred or holy space dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, daemon, or similar figure of respect, wherein they ...
s, led by ritual officiants (''fataabu'' in northern Malaita). On Malaita, many shrines have been preserved, not only for their sanctity but also because they serve as territorial markers that can resolve land disputes.
With European contact, Catholics and Anglicans
Anglicanism is a Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia ...
spread their gospels, and many missionaries were killed. The Protestant South Seas Evangelical Mission
The South Sea Evangelical Church (SSEC) is an evangelical, Pentecostal church in Solomon Islands. In total, 17% of the population of Solomon Islands adheres to the church, making it the third most common religious affiliation in the country behind ...
(SSEM, now known as the South Seas Evangelical Church, SSEC), originally based in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
, made considerable inroads by following the imported workers home to their native islands. More recently, Jehovah's Witnesses and the Seventh-day Adventist Church have converted many. Many Malaitans have been active in the Solomon Islands Christian Association
The Solomon Islands Christian Association (SICA) is an ecumenical Christian non-governmental organisation in the Solomon Islands. The association comprises the five largest Christian churches in the country, the Anglican Church of Melanesia, the Ro ...
, a national inter-denominational organization that set a precedent for cooperation during the period of independence. The Kwaio
Kwaio is an ethnic group found in central Malaita, in the Solomon Islands. According to Ethnologue, they numbered 13,249 in 1999. Much of what is known about the Kwaio is due to the work of the anthropologist Roger M. Keesing, who lived among t ...
people have been the most resistant to Christianity.
Economy
For the most part, the Malaitans survive by subsistence agriculture, withtaro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
and sweet potatoes as the most important crops. After the establishment of government control, a plantation was established on the west coast, near Baunani. However, many Malaitans work on plantations on other islands in the archipelago, for most the only way to buy prestigious Western goods. Retail trade was largely conducted by Chinese merchants, with headquarters in Honiara, and dispatching goods to remote locations on the island, where they are sometimes purchased by middlemen who keep "stores" (usually of suitcase side) in remote places.
Arts
The Malaitans are famous for their music and dance, which are sometimes associated with rituals. Several of the groups, including the 'Are'are, famous for theirpanpipe
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth). Multiple varieties of pan flutes have bee ...
ensembles, are among SSEC members whose traditional music is no longer performed for religious reasons.Zemp, Hugo. Liner notes to ''Solomon Islands: 'Are'are Panpipe Ensembles.'' Le Chant du Monde LDX 274961.62, 1994. Page 58-59. Secular dancing is similar to widespread patterns in the Solomons, following patterns learned from plantation labour gangs or moves learned at the cinema in Honiara. Sacred dances follow strict formal patterns, and incorporate panpipers in the group. Some dances represent traditional activities, such as the ''tue tue'' dance, about fishing, which depict movements of the boat and fish, and the birds overhead.
Malaitan shell-money, manufactured in the Langalanga lagoon, is the traditional currency, and was used throughout the Solomon Islands, as far as Bougainville. The money consists of small polished shell disks which are drilled and placed on strings. It can be used as payment for brideprice, funeral feasts and compensation, as well ordinary purposes as a cash
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-im ...
equivalent. It is also worn as an adornment and status symbol. The standard unit, known as the ''tafuliae'', is several strands 1.5 m in length. Previously the money was also manufactured on Makira
The island of Makira (also known as San Cristobal and San Cristóbal) is the largest island of Makira-Ulawa Province in the Solomon Islands. It is third most populous island after Malaita and Guadalcanal, with a population of 55,126 as of 2020. ...
and Guadalcanal.Romano Kokonge, 63. It is still produced on Malaita, but much is inherited, from father to son, and the old traditional strings are now rare.Kent, 44. Porpoise teeth are also used as money, often woven into belts.
Notes
References
*Roger Keesing
Roger Martin Keesing (16 May 1935 – 7 May 1993) was an American linguist and anthropologist, most notable for his fieldwork on the Kwaio people of Malaita in the Solomon Islands, and his writings on a wide range of topics including kinship, reli ...
, ''Kwaio Religion: The Living and the Dead in a Solomon Island Society''. New York: Columbia University Press, 1982.
* Roger M. Keesing and Peter Corris. ''Lightning Meets the West Wind: The Malaita Massacre''. Melbourne: Oxford University Press, 1980.
* Janet Kent. ''The Solomon Islands''. Harrisburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 1972.
* James Page, 'Education and Acculturation on Malaita: An Ethnography of Intraethnic and Interethnic Affinities'.''The Journal of Intercultural Studies.'' 1988. #15/16:74-81; available on-line at http://eprints.qut.edu.au/archive/00003566/.
* ''Ples Blong Iumi: Solomon Islands: The Past Four Thousand Years''. Honiara: University of the South Pacific, 1989.
* Harold M. Ross. ''Baegu: Social and Ecological Organization in Malaita, Solomon Islands''. Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 1973.
Further reading
*Guppy, Henry B. (1887) ''The Solomon Islands and Their Natives''. London: Swan Sonnenschein, Lowrey & Co {{authority control Islands of the Solomon Islands Important Bird Areas of the Solomon Islands