MALDI imaging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 MALDI mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is the use of
MALDI mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is the use of
 Sample preparation is a critical step in imaging spectroscopy. Scientists take thin tissue slices mounted on conductive microscope slides and apply a suitable MALDI matrix to the tissue, either manually or automatically. Next, the microscope slide is inserted into a MALDI mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer records the spatial distribution of molecular species such as peptides, proteins or small molecules. Suitable image processing software can be used to import data from the mass spectrometer to allow visualization and comparison with the optical image of the sample. Recent work has also demonstrated the capacity to create three-dimensional molecular images using MALDI imaging technology and comparison of these image volumes to other imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (
Sample preparation is a critical step in imaging spectroscopy. Scientists take thin tissue slices mounted on conductive microscope slides and apply a suitable MALDI matrix to the tissue, either manually or automatically. Next, the microscope slide is inserted into a MALDI mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer records the spatial distribution of molecular species such as peptides, proteins or small molecules. Suitable image processing software can be used to import data from the mass spectrometer to allow visualization and comparison with the optical image of the sample. Recent work has also demonstrated the capacity to create three-dimensional molecular images using MALDI imaging technology and comparison of these image volumes to other imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (
MALDI MS-imaging interest group
Imaging MS interest group
DFG (German Research Foundation) National Core Facility for MALDI MS-imaging
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maldi Imaging Mass spectrometry
 MALDI mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is the use of
MALDI mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is the use of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization
In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of b ...
as a mass spectrometry imaging
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to visualize the spatial distribution of molecules, as biomarkers, metabolites, peptides or proteins by their molecular masses. After collecting a mass spectrum at one spot, ...
technique in which the sample, often a thin tissue section, is moved in two dimensions while the mass spectrum
A mass spectrum is a histogram plot of intensity vs. ''mass-to-charge ratio'' (''m/z'') in a chemical sample, usually acquired using an instrument called a ''mass spectrometer''. Not all mass spectra of a given substance are the same; for example ...
is recorded. Advantages, like measuring the distribution of a large amount of analytes at one time without destroying the sample, make it a useful method in tissue-based study.
Sample preparation
 Sample preparation is a critical step in imaging spectroscopy. Scientists take thin tissue slices mounted on conductive microscope slides and apply a suitable MALDI matrix to the tissue, either manually or automatically. Next, the microscope slide is inserted into a MALDI mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer records the spatial distribution of molecular species such as peptides, proteins or small molecules. Suitable image processing software can be used to import data from the mass spectrometer to allow visualization and comparison with the optical image of the sample. Recent work has also demonstrated the capacity to create three-dimensional molecular images using MALDI imaging technology and comparison of these image volumes to other imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (
Sample preparation is a critical step in imaging spectroscopy. Scientists take thin tissue slices mounted on conductive microscope slides and apply a suitable MALDI matrix to the tissue, either manually or automatically. Next, the microscope slide is inserted into a MALDI mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer records the spatial distribution of molecular species such as peptides, proteins or small molecules. Suitable image processing software can be used to import data from the mass spectrometer to allow visualization and comparison with the optical image of the sample. Recent work has also demonstrated the capacity to create three-dimensional molecular images using MALDI imaging technology and comparison of these image volumes to other imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
).
Tissue preparation
The tissue samples must be preserved quickly in order to reduce molecular degradation. The first step is to freeze the sample by wrapping the sample then submerging it in a cryogenic solution. Once frozen, the samples can be stored below -80 °C for up to a year. When ready to be analyzed, the tissue is embedded in a gelatin media which supports the tissue while it is being cut, while reducing contamination that is seen inoptimal cutting temperature compound
Optimal cutting temperature compound (OCT compound) is used to embed tissue samples prior to frozen sectioning on a microtome-cryostat. This process is undertaken so as to mount slices (sections) of a sample onto slides for analysis.
Components ...
(OCT) techniques. The mounted tissue section thickness varies depending on the tissue.
Tissue sections can then be thaw-mounted by placing the sample on the surface of a conductive slide that is of the same temperature, and then slowly warmed from below. The section can also be adhered to the surface of a warm slide by slowly lowering the slide over the cold sample until the sample sticks to the surface.
The sample can then be stained in order to easily target areas of interest, and pretreated with washing in order to remove species that suppress molecules of interest. Washing with varying grades of ethanol removes lipids in tissues that have a high lipid concentration with little delocalization and maintains the integrity of the peptide spatial arrangement within the sample.

Matrix application
The matrix must absorb at the laser wavelength and ionize the analyte. Matrix selection and solvent system relies heavily upon the analyte class desired in imaging. The analyte must be soluble in the solvent in order to mix and recrystallize the matrix. The matrix must have a homogeneous coating in order to increase sensitivity, intensity, and shot-to-shot reproducibility. Minimal solvent is used when applying the matrix in order to avoid delocalization. One technique is spraying. The matrix is sprayed, as very small droplets, onto the surface of the sample, allowed to dry, and re-coated until there is enough matrix to analyze the sample. The size of the crystals depend on the solvent system used. Sublimation can also be used to make uniform matrix coatings with very small crystals. The matrix is placed in a sublimation chamber with the mounted tissue sample inverted above it. Heat is applied to the matrix, causing it to sublime and condense onto the surface of the sample. Controlling the heating time controls the thickness of the matrix on the sample and the size of the crystals formed. Automated spotters are also used by regularly spacing droplets throughout the tissue sample. The image resolution relies on the spacing of the droplets.Image production
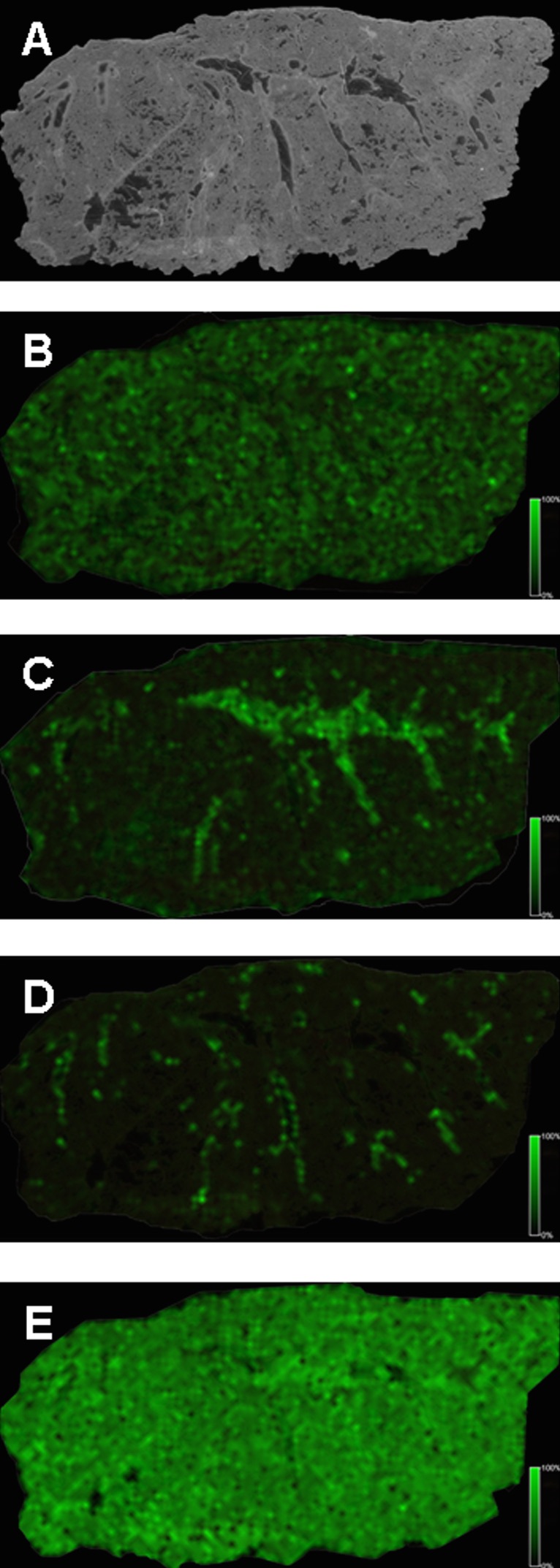
Images are constructed by plotting ion intensity versus relative position of the data from the sample. Spatial resolution highly impacts the molecular information gained from analysis.Applications
MALDI-MSI involves the visualization of the spatial distribution of proteins, peptides, lipids, and other small molecules within thin slices of tissue, such as animal or plant. The application of this technique to biological studies has increased significantly since its introduction. MALDI-MSI is providing major contributions to the understanding of diseases, improving diagnostics, and drug delivery. Significant studies are of the eye, cancer research, drug distribution, and neuroscience. MALDI-MSI has been able to differentiate between drugs and metabolites and provide histological information in cancer research, which makes it a promising tool for finding new protein biomarkers. However, this can be challenging because of ion suppression, poor ionization, and low molecular weight matrix fragmentation effects. To combat this, chemical derivatization is used to improve detection.See also
*Histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vi ...
*Tissue microarray
Tissue microarrays (also TMAs) consist of paraffin blocks in which up to 1000 separate tissue cores are assembled in array fashion to allow multiplex histological analysis.
History
The major limitations in molecular clinical analysis of tiss ...
*Laser capture microdissection
Laser capture microdissection (LCM), also called microdissection, laser microdissection (LMD), or laser-assisted microdissection (LMD or LAM), is a method for isolating specific cells of interest from microscopic regions of tissue/cells/organisms ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
MALDI MS-imaging interest group
Imaging MS interest group
DFG (German Research Foundation) National Core Facility for MALDI MS-imaging
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maldi Imaging Mass spectrometry