|
Ion Suppression In Liquid Chromatography–mass Spectrometry
Ion suppression in LC-MS and LC-MS/MS refers to reduced detector response, or signal:noise as a manifested effect of competition for ionisation efficiency in the ionisation source, between the analyte(s) of interest and other endogenous or exogenous (e.g. plasticisers extracted from plastic tubes, mobile phase additives) species which have not been removed from the sample matrix during sample preparation. Ion suppression is not strictly a problem unless interfering compounds elute at the same time as the analyte of interest. In cases where ion suppressing species do co-elute with an analyte, the effects on the important analytical parameters including precision, accuracy and limit of detection (analytical sensitivity) can be extensive, severely limiting the validity of an assay's results. History Since its inception as a tool of analytical chemistry, LC-MS/MS spread rapidly and indeed continues to do so in (amongst others) bioanalytical fields. One of the advantages of the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
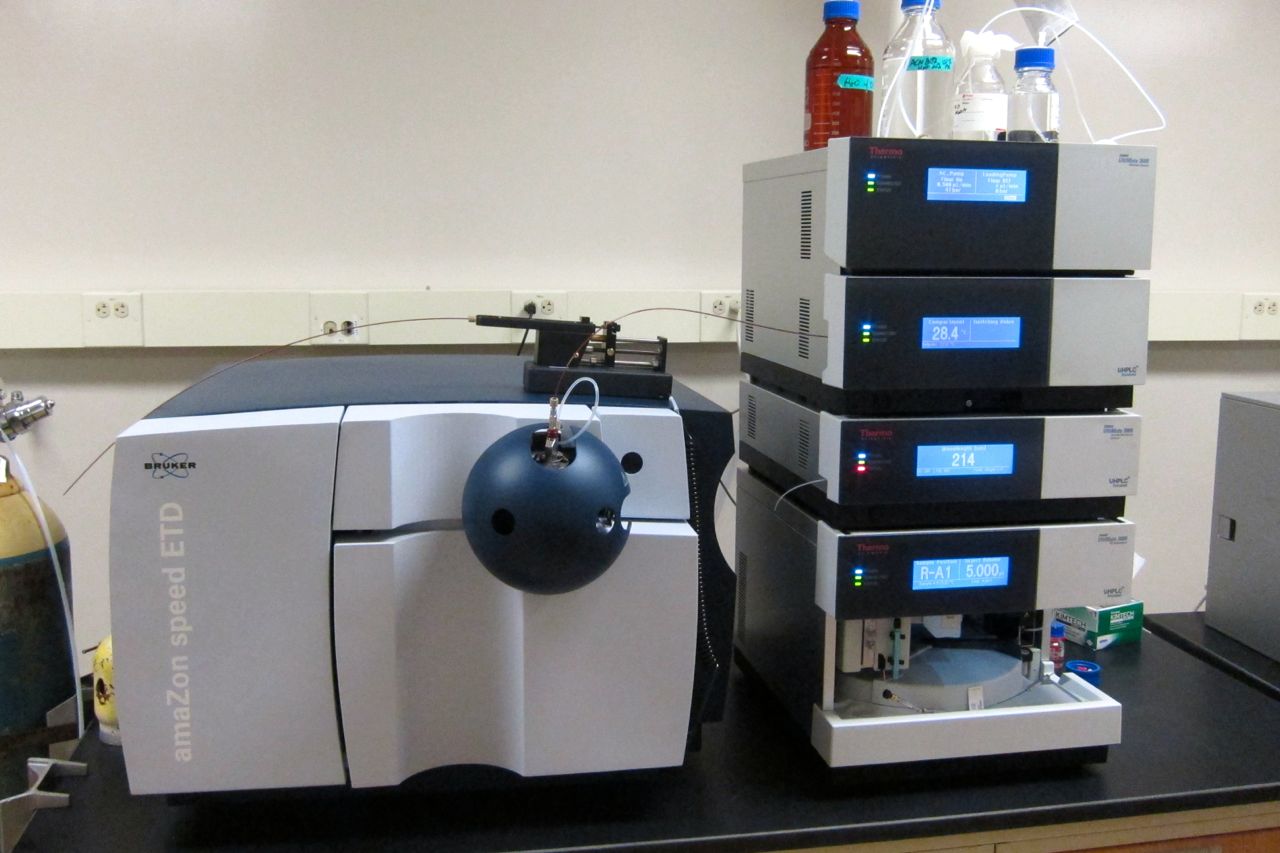
Liquid Chromatography–mass Spectrometry
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography (or HPLC) with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). Coupled chromatography - MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of each technique are enhanced synergistically. While liquid chromatography separates mixtures with multiple components, mass spectrometry provides spectral information that may help to identify (or confirm the suspected identity of) each separated component. MS is not only sensitive, but provides selective detection, relieving the need for complete chromatographic separation. LC-MS is also appropriate for metabolomics because of its good coverage of a wide range of chemicals. This tandem technique can be used to analyze biochemical, organic, and inorganic compounds commonly found in complex samples of environmental and biological origin. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is an ionization method used in mass spectrometry which utilizes gas-phase ion-molecule reactions at atmospheric pressure (105 Pa), commonly coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). APCI is a soft ionization method similar to chemical ionization where primary ions are produced on a solvent spray. The main usage of APCI is for polar and relatively less polar thermally stable compounds with molecular weight less than 1500 Da. The application of APCI with HPLC has gained a large popularity in trace analysis detection such as steroids, pesticides and also in pharmacology for drug metabolites. Instrument structure A typical APCI source usually consists of three main parts: a sample inlet, a corona discharge needle, and an ion transfer region under intermediate pressure. In the case of the heated nebulizer inlet from an LC, as shown in the figure, the eluate flows at 0.2 to 2.0 mL/min into a pneumatic nebulizer which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Dilution
Isotope dilution analysis is a method of determining the quantity of chemical substances. In its most simple conception, the method of isotope dilution comprises the addition of known amounts of isotopically enriched substance to the analyzed sample. Mixing of the isotopic standard with the sample effectively "dilutes" the isotopic enrichment of the standard and this forms the basis for the isotope dilution method. Isotope dilution is classified as a method of internal standardisation, because the standard (isotopically enriched form of analyte) is added directly to the sample. In addition, unlike traditional analytical methods which rely on signal intensity, isotope dilution employs signal ratios. Owing to both of these advantages, the method of isotope dilution is regarded among chemistry measurement methods of the highest metrological standing. Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number. All isotopes of a given element have the same num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Isotope
The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abundance of such stable isotopes can be measured experimentally (isotope analysis), yielding an isotope ratio that can be used as a research tool. Theoretically, such stable isotopes could include the radiogenic daughter products of radioactive decay, used in radiometric dating. However, the expression stable-isotope ratio is preferably used to refer to isotopes whose relative abundances are affected by isotope fractionation in nature. This field is termed stable isotope geochemistry. Stable-isotope ratios Measurement of the ratios of naturally occurring stable isotopes (isotope analysis) plays an important role in isotope geochemistry, but stable isotopes (mostly hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur) are also finding uses in ecological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Standard
An internal standard in analytical chemistry is a chemical substance that is added in a constant amount to samples, the blank and calibration standards in a chemical analysis. This substance can then be used for calibration by plotting the ratio of the analyte signal to the internal standard signal as a function of the analyte concentration of the standards. This is done to correct for the loss of analyte during sample preparation or sample inlet. The internal standard is a compound that is very similar, but not identical to the chemical species of interest in the samples, as the effects of sample preparation should, relative to the amount of each species, be the same for the signal from the internal standard as for the signal(s) from the species of interest in the ideal case. Adding known quantities of analyte(s) of interest is a distinct technique called standard addition, which is performed to correct for matrix effects. This ratio for the samples is then used to obtain their anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Precipitation
Protein precipitation is widely used in downstream processing of biological products in order to concentrate proteins and purify them from various contaminants. For example, in the biotechnology industry protein precipitation is used to eliminate contaminants commonly contained in blood. The underlying mechanism of precipitation is to alter the solvation potential of the solvent, more specifically, by lowering the solubility of the solute by addition of a reagent. General principles The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein's surface. Hydrophobic residues predominantly occur in the globular protein core, but some exist in patches on the surface. Proteins that have high hydrophobic amino acid content on the surface have low solubility in an aqueous solvent. Charged and polar surface residues interact with ionic groups in the solvent and increase the solubility of a protein. Knowledge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivatization
Derivatization is a technique used in chemistry which converts a chemical compound into a product (the reaction's derivate) of similar chemical structure, called a derivative. Generally, a specific functional group of the compound participates in the derivatization reaction and transforms the educt to a derivate of deviating reactivity, solubility, boiling point, melting point, aggregate state, or chemical composition. Resulting new chemical properties can be used for quantification or separation of the educt. Derivatization techniques are frequently employed in chemical analysis of mixtures and in surface analysis, e.g. in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy where newly incorporated atoms label characteristic groups. Derivatization reactions Several characteristics are desirable for a derivatization reaction: # The reaction is reliable and proceeds to completion. Less unreacted starting material will simplify analysis. Also, this allows a small amount of analyte to be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Phase Extraction
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is an extractive technique by which compounds that are dissolved or suspended in a liquid mixture are separated from other compounds in the mixture according to their physical and chemical properties. Analytical laboratories use solid phase extraction to concentrate and purify samples for analysis. Solid phase extraction can be used to isolate analytes of interest from a wide variety of matrices, including urine, blood, water, beverages, soil, and animal tissue. SPE uses the affinity of solutes dissolved or suspended in a liquid (known as the mobile phase) for a solid through which the sample is passed (known as the stationary phase) to separate a mixture into desired and undesired components. The result is that either the desired analytes of interest or undesired impurities in the sample are retained on the stationary phase. The portion that passes through the stationary phase is collected or discarded, depending on whether it contains the desired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Source
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic molecules. The gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molecule by attachment of an electron to create an ion of the form A−•. The reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
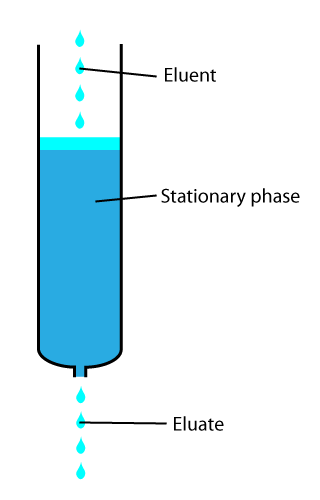
Elution
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions. In a liquid chromatography experiment, for example, an analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column. The adsorbent, a solid phase (stationary phase), is a powder which is coated onto a solid support. Based on an adsorbent's composition, it can have varying affinities to "hold" onto other molecules—forming a thin film on the surface of its particles. Elution then is the process of removing analytes from the adsorbent by running a solvent, called an "eluent", past the adsorbent/analyte complex. As the solvent molecules "elute", or travel down through the chromatography column, they can either pass by the adsorbent/analyte complex or they can displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its place. After the solvent molecules displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material. Each component in the sample interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent material, causing different flow rates for the different components and leading to the separation of the components as they flow out of the column. HPLC has been used for manufacturing (''e.g.'', during the production process of pharmaceutical and biological products), legal (''e.g.'', detecting performance enhancement drugs in urine), research (''e.g.'', separating the components of a complex biological sample, or of similar synthetic chemicals from each other), and medical (''e.g.'', detecting vitamin D levels in blood serum) purposes. Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |